rongsheng refinery capacity price

BEIJING, Aug 14 (Reuters) - Rongsheng Petrochemical , the listed arm of a major shareholder in one of China’s biggest private oil refineries, expects demand for energy and chemical products to return to normal in the country in the second half of this year.
Rongsheng expects to start trial operations of the second phase of the refining project, adding another 400,000 bpd of refining capacity and 1.4 million tonnes of ethylene production capacity in the fourth quarter of 2020.
“We expect the effects of the coronavirus pandemic on energy and chemicals to have basically faded in spite of the possibility of new waves of outbreak,” said Quan Weiying, board secretary of Rongsheng, in response to Reuters questions in an online briefing.
But Li Shuirong, president of Rongsheng, told the briefing that it was still in the process of applying for an export quota and would adjust production based on market demand. (Reporting by Muyu Xu and Chen Aizhu; Editing by Jacqueline Wong)

China"s private refiner Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical is set to start trial runs at its second 200,000 b/d crude distillation unit at the 400,000 b/d phase 2 refinery by the end of March, a source with close knowledge about the matter told S&P Global Platts March 9.
"The company targets to commence the phase II project this year, and run both the two phases at above 100% of their capacity, which will lift crude demand in 2021," the source said.
ZPC cracked 23 million mt of crude in 2020, according the the source. Platts data showed that the utilization rate of its phase 1 refinery hit as high as 130% in a few months last year.
Started construction in the second half of 2019, units of the Yuan 82.9 billion ($12.74 billion) phase 2 refinery almost mirror those in phase 1, which has two CDUs of 200,000 b/d each. But phase 1 has one 1.4 million mt/year ethylene unit while phase 2 plans to double the capacity with two ethylene units.
ZPC currently holds about 6 million cu m (37.74 million barrels) in crude storage tanks, equivalent to 47 days of the two plants" consumption if they run at 100% capacity.
With the entire phase 2 project online, ZPC expects to lift its combined petrochemicals product yield to 71% from 65% for the phase 1 refinery, according to the source.
Zhejiang Petroleum, a joint venture between ZPC"s parent company Rongsheng Petrochemical and Zhejiang Energy Group, planned to build 700 gas stations in Zhejiang province by end-2022 as domestic retail outlets of ZPC.
Established in 2015, ZPC is a JV between textile companies Rongsheng Petrochemical, which owns 51%, Tongkun Group, at 20%, as well as chemicals company Juhua Group, also 20%. The rest 9% stake was reported to have transferred to Saudi Aramco from the Zhejiang provincial government. But there has been no update since the agreement was signed in October 2018.

The higher throughput in 2021 was attributed to refining capacity expansion, and as refineries produced more oil products to compensate for the reduction in imports of blending materials for gasoline and gasoil, analysts said.
The integrated Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical refinery continued to raise its crude throughput to around 2.84 million mt in December, up 7.2% from 1.72 million mt in November, which was up 54% from October, according to JLC data. The refinery ramped up throughput after it was allocated more quotas in late October.
The Hengli Petrochemical (Dalian) Refinery in Liaoning province also raised its throughput by 3.6% month on month to 1.7 million mt in December. This comes after the completion of the maintenance at its secondary units, according to refinery sources.
However, Shandong independent refineries have gradually started to cut crude throughput from around Jan. 22 in response to a directive to cap utilization below 70% during the Winter Olympics, as Beijing aims to ensure that emissions remain under control, refinery sources told S&P Global Platts. But some refinery sources believe the overall impact will not be much more than what occurs every year since the Winter Olympics will be held around the Lunar New Year holidays, when independent refineries are forced to cut crude throughput due to logistics and manpower constraints.
In other news, Sinopec"s Hainan Petrochemical refinery in southern China is expected to export about 50,000 mt of refined oil products in January 2022, according to a refinery source. This was down 55% from 110,000 mt planned for export in December 2021.
PetroChina"s West Pacific Petrochemical Corp. refinery will skip gasoil exports in January after skipping them in December and November due to good demand in the domestic market.
PetroChina"s flagship refinery Dalian Petrochemical in northeastern Liaoning province will raise its gasoline exports to 160,000 mt in January, according to sources with knowledge of the matter. This will be about 357% higher than its planned exports in December. Dalian will double jet fuel exports to 80,000 mt in January, from 40,000 mt last month. Dalian plans to process around 1.3 million mt of crudes in January, translating to 75% of its nameplate capacity, stable on the month.
** Sinochem has been in the process of starting up its 12 million mt/year CDU and related refining units at its Quanzhou Petrochemical facility in southern Fujian province, according to a source with knowledge of the matter Jan. 19. The refining and petrochemical units were shut at around Dec. 1, 2021 for maintenance, which lasted for about 40-50 days, according to the maintenance schedule. The refinery will likely process about 450,000 mt to 500,000 mt of crudes for the remainder of February, compared with around 1.2 million mt during normal months.
** Sinopec"s Fujian Refining and Chemical Co. refinery in southeastern Fujian province has been in the process of restarting from a scheduled maintenance this week, according to a source with knowledge of the matter Jan. 19. The refinery was expected to return to normal operations around Jan. 20, about nine days behind schedule, mainly due to the slow progress in procuring some parts, the source added. The 4 million mt/year crude distillation unit, as well as some secondary units, including the aromatics units, were to be restarted along the way. Following the restart of the CDU, the crude throughput at the refinery will likely increase to around 750,000 mt in January, or 63% of its nameplate capacity. This compares with a run rate of 56%, or 660,000 mt, in December 2021.
** Japan"s ENEOS said Dec. 28 it plans to shut the sole crude distillation unit at its Marifu refinery in the west in late January for scheduled maintenance until early March 2022.
** Idemitsu Kosan restarted the sole 160,000 b/d crude distillation unit at its Aichi refinery in central Japan on Dec. 5 after completing planned maintenance, a spokesperson said Dec. 20.
** PetroChina"s Yunnan Petrochemical refinery in southwestern Yunnan province, has shut its 4 million mt/year residual hydrogenation unit and some of its relative downstream facilities due to a blast. The blast hit the residual hydrogenation unit Dec. 13 morning, according to a press release issued by the Anning city local government in Yuannan. A refining engineer said the closure of residual hydrogenation unit would cut about 30% of the refinery"s daily production.
** Sinopec"s Hainan Petrochemical refinery in southern China plans to completely shut for scheduled maintenance over March-April 2022, a source with the refinery said. This is a routine maintenance that is normally carried out by Chinese refineries every three to four years, according to the source. Sinopec Hainan refinery last carried out complete maintenance over November 2017-January 2018.
** Japan"s ENEOS said it will decommission the 120,000 b/d No. 1 CDU at its 270,000 b/d Negishi refinery in Tokyo Bay in October 2022. It will also decommission secondary units attached to the No. 1 CDU, including a vacuum distillation unit and fluid catalytic cracker. ENEOS will also decommission a 270,000 mt/year lubricant output unit at the Negishi refinery.
** Sinopec is looking to launch its 2 million mt/year crude distillation unit expansion at Luoyang Petrochemical in central China in January, with a new crude pipeline able to supply sufficient feedstock, a refinery source said late December. "We have reconfigured an existing crude pre-treater into a 2 million mt/year CDU to increase the primary capacity to 10 million mt/year. The start-up will be in the next month with the crude pipeline having been put into use in November," the refinery source said. The expansion was initially set to be put into use in H2 2020, but was delayed to H1 2021 due to construction of the 10 million mt/year Rizhao-Puyang-Luoyang crude pipeline and weak demand in oil product market, Platts reported. The source said the expansion needs more crude supplies discharged from Rizhao port in Shandong province and transmitted through the Rizhao-Puyang-Luoyang crude pipeline.
** Chinese Sinopec"s refinery Zhenhai Refining and Chemical currently has a 27 million mt/year refining capacity and a 2.2 million mt/year ethylene plant, after its phase 1 expansion project of 4 million mt/year crude distillation unit and a 1.2 million mt/year ethylene unit was delivered end-June.
** PetroChina"s Guangxi Petrochemical in southern Guangxi province plans to start construction at its upgrading projects at the end of 2021, with the works set to take 36 months. The projects include upgrading the existing refining units as well as setting up new petrochemical facilities, which will turn the refinery into a refining and petrochemical complex. The project will focus on upgrading two existing units: the 2.2 million mt/year wax oil hydrocracker and the 2.4 million mt/year gasoil hydrogenation refining unit. For the petrochemicals part, around 11 main units will be constructed, which include a 1.2 million mt/year ethylene cracker.
** Axens said its Paramax technology has been selected by state-owned China National Offshore Oil Corp. for the petrochemical expansion at the plant. The project aims at increasing the high-purity aromatics production capacity to 3 million mt/year. The new aromatics complex will produce 1.5 million mt/year of paraxylene in a single train.
** China"s privately held refining complex, Shenghong Petrochemical, is likely to start feeding crudes into its newly built 16 million mt/year crude distillation unit, according to a company source in early January. The refinery initially planned to start up at the end of August, but this was postponed to the end of December due to slower-than-expected construction work, and then again to around the Lunar New Year. The construction of the complex started in December 2018. Located in the coastal city of Lianyungang in Jiangsu province, the company"s 16 million mt/year CDU is the country"s single biggest by capacity.
** Chinese privately owned refining and petrochemical complex Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical has fully started up commercial operation at it 400,000 b/d Phase 2 refining and petrochemical project, parent company Rongsheng Petrochemical said in a document Jan. 12. There are two crude distillation units in the Phase 2 project, each with a capacity of 200,000 b/d. ZPC started trial run at one of the CDUs in November 2020. Due to tight feedstock supplies, the refiner could not feed the other CDU until the end of November 2021, when it gained crude import quota for the project. The nameplate capacity of the company doubled to 800,000 b/d in Phase 2. It will run four CDUs at about 82% of nameplate capacity in January. Rongsheng said Phase 2 adds 6.6 million mt/year aromatics and 1.4 million mt/year ethylene production capacity.
** Saudi Aramco continues to pursue and develop the integrated refining and petrochemical complex in China with Norinco Group and Panjin Sinchen. The joint venture plans to build an integrated refining and petrochemical complex in northeast China"s Liaoning province Panjin city with a 300,000 b/d refinery, 1.5 million mt/year ethylene cracker and a 1.3 million mt/year PX unit.
Construction work is expected to be completed in 24 months. The complex has been set up with the aim of consolidating the outdated capacities in Shandong province. A total of 10 independent refineries, with a total capacity of 27.5 million mt/year, will be mothballed over the next three years. Jinshi Petrochemical, Yuhuang Petrochemical and Zhonghai Fine Chemical, Yuhuang Petrochemical and Zhonghai Fine Chemical will be dismantled, while Jinshi Asphalt has already finished dismantling.
** PetroChina officially started construction works at its greenfield 20 million mt/year Guangdong petrochemical refinery in the southern Guangdong province on Dec. 5, 2018.
In Asia and the Middle East, at least nine refinery projects are beginning operations or are scheduled to come online before the end of 2023. At their current planned capacities, they will add 2.9 million barrels per day (b/d) of global refinery capacity once fully operational.
In the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) June 2022 Oil Market Report, the IEA expects net global refining capacity to expand by 1.0 million b/d in 2022 and by an additional 1.6 million b/d in 2023. Net capacity additions reflect total new capacity minus capacity that has closed.
The scheduled expansions follow a period of reduced global refining capacity. Net global capacity declined in 2021 for the first time in 30 years, according to the IEA. The new refinery projects would increase production of refined products, such as gasoline and diesel, and in turn, they might reduce the current high prices for these products.
China’s refinery capacity is scheduled to increase significantly this year. The Shenghong Petrochemical facility in Lianyungang has an estimated capacity of 320,000 b/d, and they report that trial crude oil-processing operations began in May 2022. In addition, PetroChina’s 400,000 b/d Jieyang refinery is expected to come online in the third quarter of 2022. A planned 400,000 b/d Phase II capacity expansion also began operations earlier this year at Zhejiang Petrochemical Corporation’s (ZPC) Rongsheng facility. More information on these expansions is available in our Country Analysis Executive Summary: China.
Outside of China, the 300,000 b/d Malaysian Pengerang refinery (also known as the RAPID refinery) restarted in May 2022 after a fire forced the refinery to shut down in March 2020. In India, the Visakha Refinery is undergoing a major expansion, scheduled to add 135,000 b/d by 2023.
New projects in the Middle East are also likely to be an important source of new refining capacity. The 400,000 b/d Jizan refinery in Saudi Arabia reportedly came online in late 2021 and began exporting petroleum products earlier this year. More recently, the 615,000 b/d Al Zour refinery in Kuwait—the largest in the country when it becomes fully operational—began initial operations earlier this year. A new 140,000 b/d refinery is scheduled to come online in Karbala, Iraq, this September, targeting fully operational status by 2023. A new 230,000 b/d refinery is set to come online in Duqm, Oman, likely in early 2023.
These estimates do not necessarily include all ongoing refinery capacity expansions. Moreover, many of these projects have already been subject to major delays, and the possibility of partial starts or continued delays related to logistics, construction, labor, finances, political complications, or other factors may cause these projects to come online later than estimated. Although the potential for project complications and cancellations is always a significant risk, these projects could otherwise account for an increase of nearly 3.0 million b/d of new refining capacity by the end of 2023.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that global refining capacity decreased by 730,000 barrels per day (b/d) in 2021—the first decline in global refining capacity in 30 years.
In the United States, refining capacity has decreased by about 1.1 million b/d since the start of 2020, contributing 184,000 b/d to the global decline in 2021. Global demand for refined products dropped substantially in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Less petroleum demand and the associated lower petroleum product prices encouraged refinery closures, reducing global refining capacity, particularly in the United States, Europe, and Japan. However, the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) notes that a number of new refinery projects are set to come online during 2022 and 2023, increasing capacity.
As global demand for petroleum products returned closer to pre-pandemic levels through 2021 and early 2022, the loss of refinery capacity contributed to higher crack spreads—the difference between the price of a barrel of crude oil and the wholesale price of petroleum products—which serve as one indicator of the profitability of refining.
Associated sanctions on Russia—with more than 5 million b/d in crude oil processing capacity—disrupted exports of Russia’s refined products into the global market, and will likely continue to do so as import bans in the European Union and United Kingdom come into full force.
Constraints on global refinery capacity have been contributing to higher crack spreads in the first half of 2022, and they are likely to continue contributing to high crack spreads through at least the end of this year.
In its June 2022 Oil Market Report, the IEA expects net global refining capacity to expand by 1.0 million b/d in 2022 and by an additional 1.6 million b/d in 2023. New refining capacity growth includes several high-profile, high-capacity refinery projects underway, particularly in China and the Middle East, which could add more than 4.0 million b/d of new capacity over the next two years.
High-capacity refineries require access to reliable sources of crude oil inputs to maintain higher utilization and to a sufficiently large pool of potential customers to supply. Many of these new refineries are located in coastal areas and have easy access to export refined products that are not consumed domestically.
The most global refining capacity under development is in China. Chinese capacity is scheduled to increase significantly this year because of the start of at least two new refinery projects and a major refinery expansion.
The first new refinery is the private Shenghong Petrochemical facility in Lianyungang, which has an estimated capacity of 320,000 b/d and reported trial crude oil-processing operations beginning in May 2022.
The second new refinery is PetroChina’s 400,000 b/d Jieyang refinery, in the southern Guangdong province, which is expected to come online in the third quarter of 2022 (3Q22). A planned 400,000 b/d Phase II capacity expansion also began operations earlier in 2022 at Zhejiang Petrochemical Corporation’s (ZPC) Rongsheng facility.
Although these projects are the most imminent new capacity expansions in China, the country is expected to continue increasing its refining and petrochemical processing capacity through a number of additional projects expected to come online by 2030.
Most noteworthy among these additional expansions are the 300,000 b/d Huajin and the 400,000 b/d Yulong refinery projects, which both have target start dates in 2024.
Outside of China, the 300,000 b/d Malaysian Pengerang refinery restarted in May 2022 after a fire forced the refinery to shut down in March 2020. The refinery’s return is likely to decrease petroleum product prices and increase supply, particularly in south and southeast Asian markets.
Substantial refinery capacity was also added in the Middle East during the past year. The 400,000 b/d Jizan refinery in Saudi Arabia reportedly came online in late 2021 and began exporting petroleum products earlier this year.
More recently, the 615,000 b/d Al Zour refinery in Kuwait—the largest in the country when it becomes fully operational—began initial operations earlier this year and the facility’s operators expect to increase production through the end of 2022.
A new 140,000 b/d refinery is scheduled to come online in Karbala, Iraq, this September, targeting to be fully operational by 2023. A new 230,000 b/d refinery operated by a joint venture between state-owned-firms OQ (of Oman) and Kuwait Petroleum International is set to come online in Duqm, Oman, likely in early 2023.
More than 2 million b/d of new refining capacity construction is expected to come online to support markets in the Indian Ocean basin in 2022. At the same time, a handful of major projects are also planned in the Atlantic basin.
The 650,000 b/d Dangote Industries refinery in Lagos, Nigeria, set to be the largest in the country when completed, may come online in late 2022 or 2023. The refinery would most likely meet Nigeria’s domestic petroleum product demand as well as demand in nearby African countries, and it would also reduce demand for gasoline and diesel imports into the region from Europe or the United States.
In Mexico, state-owned refiner Pemex has been building a 340,000 b/d refinery in Dos Bocas, which hosted an inauguration ceremony on 1 July, even though the refinery is still under construction and is unlikely to begin producing fuels until at least 2023.
TotalEnergies is planning to restart its 222,000 b/d Donges refinery along the Atlantic Coast of France in May 2022, after closing the facility in late 2020, and some reports indicate the facility has begun importing crude oil for processing.
In addition to major new refinery projects, other facilities are also moving forward with capacity expansions at existing refineries—particularly in India. HPCL’s Visakha Refinery is undergoing a major expansion, estimated at 135,000 b/d, which is scheduled to come online by 2023. A number of other similar expansions are underway in India that may come into effect in 2024 or later.
Although no projects to build new refineries in the United States are currently planned, major refinery expansions are underway at a handful of Gulf Coast refineries, most notably ExxonMobil’s Beaumont, Texas refinery, which plans to increase its capacity by 250,000 b/d by 2023.
Facilities along the Gulf Coast currently account for 54% of all US domestic refining capacity. They supply fuels for US domestic petroleum consumption, but they are also substantial exporters into the Atlantic basin market, particularly into Central and South America and also into Europe.
If the projects mentioned above were to come online according to their present timelines, global refinery capacity would increase by 2.3 million b/d in 2022 and by 2.1 million b/d in 2023.
EIA cautions that the estimate is not necessarily a complete list of ongoing refinery capacity expansions. Moreover, many of these projects have also already been subject to major delays, and the possibility of partial starts or continued delays related to logistics, construction, labor, finances, political complications, or other factors may cause these projects to come online later than currently estimated.
With the new issue, ZPC, China"s largest refiner with 800,000 barrels per day crude processing capacity, has obtained 40 million tonnes of quotas for the year, fully matching its refining capacity.
In a move to encourage higher refinery production to help a struggling economy, authorities earlier this month issued a small portion of the first-batch crude oil import quotas for 2023, months ahead of the usual timeline.

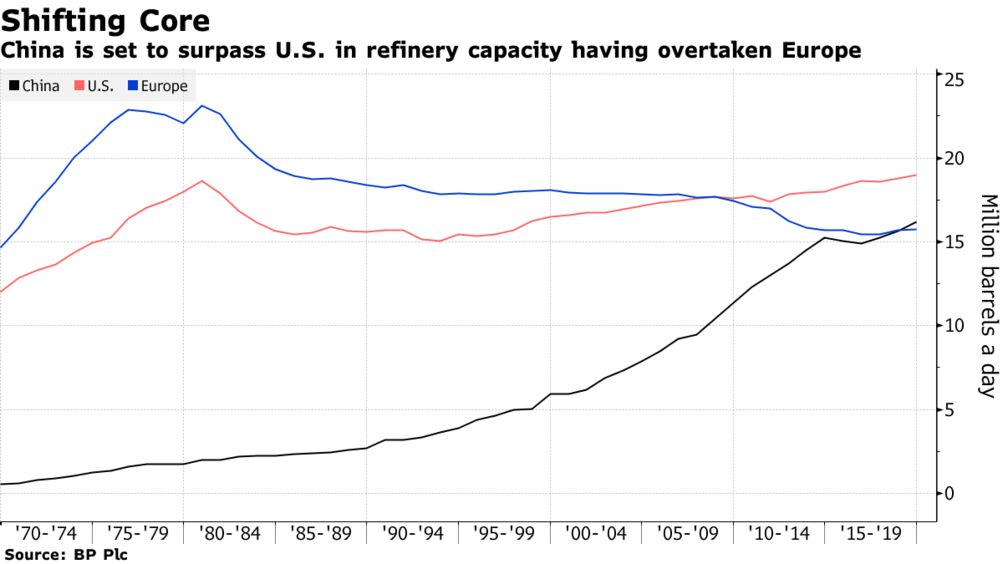
This year, China is expected to overtake the United States as the world’s largest oil refining country.[1] Although China’s bloated and fragmented crude oil refining sector has undergone major changes over the past decade, it remains saddled with overcapacity.[2]
Privately owned unaffiliated refineries, known as “teapots,”[3] mainly clustered in Shandong province, have been at the center of Beijing’s longtime struggle to rein in surplus refining capacity and, more recently, to cut carbon emissions. A year ago, Beijing launched its latest attempt to shutter outdated and inefficient teapots — an effort that coincides with the emergence of a new generation of independent players that are building and operating fully integrated mega-petrochemical complexes.[4]
China’s “teapot” refineries[5] play a significant role in refining oil and account for a fifth of Chinese crude imports.[6] Historically, teapots conducted most of their business with China’s major state-owned companies, buying crude oil from and selling much of their output to them after processing it into gasoline and diesel. Though operating in the shadows of China’s giant national oil companies (NOCs),[7] teapots served as valuable swing producers — their surplus capacity called on in times of tight markets.
Four years later, the NDRC adopted a different approach, awarding licenses and quotas to teapot refiners to import crude oil and granting approval to export refined products in exchange for reducing excess capacity, either upgrading or removing outdated facilities, and building oil storage facilities.[10] But this partial liberalization of the refining sector did not go exactly according to plan. Swelling with new sources of feedstock that catapulted China into the position of the world’s largest oil importer, teapots increased their production of refined fuels and, benefiting from greater processing flexibility and low labor costs undercut larger state rivals and doubled their market share.[11]
Meanwhile, as teapots expanded their operations, they took on massive debt, flouted environmental rules, and exploited taxation loopholes.[12] Of the refineries that managed to meet targets to cut capacity, some did so by double counting or reporting reductions in units that had been idled.[13] And when, reversing course, Beijing revoked the export quotas allotted to teapots and mandated that products be sold via state-owned companies, it trapped their output in China, contributing to the domestic fuel glut.
2021 marked the start of the central government’s latest effort to consolidate and tighten supervision over the refining sector and to cap China’s overall refining capacity.[14] Besides imposing a hefty tax on imports of blending fuels, Beijing has instituted stricter tax and environmental enforcement[15] measures including: performing refinery audits and inspections;[16] conducting investigations of alleged irregular activities such as tax evasion and illegal resale of crude oil imports;[17] and imposing tighter quotas for oil product exports as China’s decarbonization efforts advance.[18]
The politics surrounding this new class of greenfield mega-refineries is important, as is their geographical distribution. Beijing’s reform strategy is focused on reducing the country’s petrochemical imports and growing its high value-added chemical business while capping crude processing capacity. The push by Beijing in this direction has been conducive to the development of privately-led mega refining and petrochemical projects, which local officials have welcomed and staunchly supported.[20]
Yet, of the three most recent major additions to China’s greenfield refinery landscape, none are in Shandong province, home to a little over half the country’s independent refining capacity. Hengli’s Changxing integrated petrochemical complex is situated in Liaoning, Zhejiang’s (ZPC) Zhoushan facility in Zhejiang, and Shenghong’s Lianyungang plant in Jiangsu.[21]
As China’s independent oil refining hub, Shandong is the bellwether for the rationalization of the country’s refinery sector. Over the years, Shandong’s teapots benefited from favorable policies such as access to cheap land and support from a local government that grew reliant on the industry for jobs and contributions to economic growth.[22] For this reason, Shandong officials had resisted strictly implementing Beijing’s directives to cull teapot refiners and turned a blind eye to practices that ensured their survival.
But with the start-up of advanced liquids-to-chemicals complexes in neighboring provinces, Shandong’s competitiveness has diminished.[23] And with pressure mounting to find new drivers for the provincial economy, Shandong officials have put in play a plan aimed at shuttering smaller capacity plants and thus clearing the way for a large-scale private sector-led refining and petrochemical complex on Yulong Island, whose construction is well underway.[24] They have also been developing compensation and worker relocation packages to cushion the impact of planned plant closures, while obtaining letters of guarantee from independent refiners pledging that they will neither resell their crude import quotas nor try to purchase such allocations.[25]
To be sure, the number of Shandong’s independent refiners is shrinking and their composition within the province and across the country is changing — with some smaller-scale units facing closure and others (e.g., Shandong Haike Group, Shandong Shouguang Luqing Petrochemical Corp, and Shandong Chambroad Group) pursuing efforts to diversify their sources of revenue by moving up the value chain. But make no mistake: China’s teapots still account for a third of China’s total refining capacity and a fifth of the country’s crude oil imports. They continue to employ creative defensive measures in the face of government and market pressures, have partnered with state-owned companies, and are deeply integrated with crucial industries downstream.[26] They are consummate survivors in a key sector that continues to evolve — and they remain too important to be driven out of the domestic market or allowed to fail.
In 2016, during the period of frenzied post-licensing crude oil importing by Chinese independents, Saudi Arabia began targeting teapots on the spot market, as did Kuwait. Iran also joined the fray, with the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) operating through an independent trader Trafigura to sell cargoes to Chinese independents.[27] Since then, the coming online of major new greenfield refineries such as Rongsheng ZPC and Hengli Changxing, and Shenghong, which are designed to operate using medium-sour crude, have led Middle East producers to pursue long-term supply contracts with private Chinese refiners. In 2021, the combined share of crude shipments from Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, and Kuwait to China’s independent refiners accounted for 32.5%, an increase of more than 8% over the previous year.[28] This is a trend that Beijing seems intent on supporting, as some bigger, more sophisticated private refiners whose business strategy aligns with President Xi’s vision have started to receive tax benefits or permissions to import larger volumes of crude directly from major producers such as Saudi Arabia.[29]
The shift in Saudi Aramco’s market strategy to focus on customer diversification has paid off in the form of valuable supply relationships with Chinese independents. And Aramco’s efforts to expand its presence in the Chinese refining market and lock in demand have dovetailed neatly with the development of China’s new greenfield refineries.[30] Over the past several years, Aramco has collaborated with both state-owned and independent refiners to develop integrated liquids-to-chemicals complexes in China. In 2018, following on the heels of an oil supply agreement, Aramco purchased a 9% stake in ZPC’s Zhoushan integrated refinery. In March of this year, Saudi Aramco and its joint venture partners, NORINCO Group and Panjin Sincen, made a final investment decision (FID) to develop a major liquids-to-chemicals facility in northeast China.[31] Also in March, Aramco and state-owned Sinopec agreed to conduct a feasibility study aimed at assessing capacity expansion of the Fujian Refining and Petrochemical Co. Ltd.’s integrated refining and chemical production complex.[32]

As the shift in oil demand from Covid-19 turned the tables of regional levels of fuel production and exports, China succeeded in overtaking the USA as the world’s biggest oil refiner in 2020. As China began to ramp up its refining capacity throughout the pandemic, the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) published data showing thatChina processed more crude oil than the U.S.for much of 2020.
Oil refineries across the U.S. have been losing momentum in response to the Covid-19 pandemic. At the end of last year, Royal Dutch Shell Plc ground production at its Convent refinery in Louisiana to a halt. This same facility had 35 times the refining capacity of China when it opened in 1967, showing how dramatically the tables have turned over the past couple of decades.
Oil refineries have also been impeded this year by the severe storm that hit the state of Texas in February. During the storm, oil refining fell to its lowest levels since 2008. This was largely due to frozen pipelines which forced producers to halt activities.Refinery crude runs fell by 2.6 million bpdthroughout the week to 12.2 million bpd.
Meanwhile, in November, China was processing around1.2 million bpd of crude oil. Much of this new refining work was taking place in the new unit at Rongsheng Petrochemical’s giant Zhejiang facility in northeast China.
China is not the only Asian giant to invest in refining over the next decade. Just a few weeks ago,India announced plan to invest $4.5 billion in a Panipat refinery expansionby September 2024. This would increase Panipat’s capacity by two-thirds to 500,000 bpd.
Only slightly behind China, as the world’s third largest oil importer and consumer, India is striving to increase its oil refining capacity by 60 percent to meet the country’s increasing oil demand. This comes as Prime Minister Narendra Modi has pledged to improve India’s manufacturing sector.
State-owned Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) has also announced plans to build a new refinery at Nagapattinam in the southern state of Tamil Naduat a cost of $4.01 billion. The IOC subsidiary Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited is expected to develop the refinery. The project is aimed at meeting the demand of petroleum products across southern India.
While U.S. refining activities are expected to pick up before the end of the year, a dramatically increased oil refining capacity in China, as well as new projects in India, suggest that the face of the industry could change over the next decade. As oil demand wanes in the U.S. and continues to increase across Asia, many Asian countries will be seeking out refined products from closer to home to meet their needs.

The United States has the most complex and efficient refining industry in the world, but we also have less refining capacity than we used to. After more than two decades of growth in which the United States became the world’s largest refiner by volume, our industry has contracted. We’ve lost 1.1 million barrels of daily refining capacity over the course of the global pandemic with at least seven facilities shuttering, closing units or beginning the transition away from petroleum processing.
With a global energy crunch underway, much focus has been placed on crude oil supply and demand. And while this is the primary driver of our current price challenges, it’s not the only factor. Refining matters too. Crude oil has no utilitarian value until it runs through a refinery and gets processed into fuels like wholesale gasoline, diesel and jet fuel. Because of this, it’s not an overstatement to say that energy security requires a strong refining sector.
Where the issue of refining capacity is concerned, it’s important to understand what refining capacity is, why we’ve lost capacity in the United States and how policies can advance the competitiveness of our refineries in the global market. Let’s take a look:
How much refining capacity does the United States have?At the start of 2020, the United States had the largest refining industry in the world by a stretch, with 135 operable petroleum refineries and total refining capacity of 19 million barrels per day. Today, we have 128 operable refineries with total crude distillation capacity of 17.9 million barrels per day—a loss of 1.1 million barrels.
In this same period of time, the world lost a total of 3.3 million barrels of daily refining capacity. Roughly 1/3 of these losses occurred in the United States. With this realignment, and planned refinery openings and capacity expansions in Asia, trade press reports suggest China will overtake the United States as the country with the most refining capacity by year’s end.
Is COVID the only reason why the U.S. is losing refining capacity?No. A combination of factors is responsible for the United States’ loss of refining capacity. Choices to convert or shutter refineries are made very carefully—factoring in present and projected future fuel demand, the political environment as well as facility locations and their individual market access. Political and financial pressure to move away from petroleum derived fuels, costs associated with federal and state regulatory compliance and facilities’ singular economic performance all inform these decisions. The sharp drop in fuel demand over the course of the pandemic certainly sped up the timeframe for refining contractions, closures and transitions, but many of these moves were already planned or underway, something Chevron CEO Mike Wirth acknowledged in a recent interview.
Even if that wasn’t the case, reopening a refinery is a major effort. It would require significant lead time to inspect machinery and attain necessary operating permits. Staff would need to be reassembled and/or recruited and trained. And the facilities themselves would need to be reintegrated with supply chains. A hypothetical restart is not a quick-turn project, and the investment cannot be based on short-term data.
How is lost refining capacity affecting fuel prices and production?Less refining capacity means less maximum fuel production globally. As a result of tighter supply, fuel purchasers are willing to pay more for refined products. They have increased bids to buy and secure finished fuel which has pushed prices up throughout the global market.
In regions that have been most affected by refining capacity losses—such as the U.S. West Coast and Mid-Atlantic—the loss of local petroleum fuel production is contributing to higher prices and affecting regional demand for imports of gasoline, diesel and jet fuel from the global market. Because of infrastructure limitations and an uncompetitive shipping environment, economic access to domestic crude oil and refined products is limited.
Even with less capacity, United States refiners are working around the clock to produce fuel for consumers. Our refining sector is unmatched in terms of utilization. Nationally, and even with some regions undergoing planned facility maintenance, American refiners are running at 93% capacity. Along the Gulf Coast, utilization is 95%, and on the East Coast, 98%.
What does lost capacity say about the future of liquid fuels?In much of the world, demand for liquid fuels is almost back to pre-pandemic levels. Refining capacity is not. This mismatch has created a shortfall in refined product that has been exacerbated by the sudden decrease in oil and refined product from Russia and China’s decision to stop contributing fuel to the global market. New capacity is coming, though it is intended to satisfy demand growth in Asia, the Middle East and Africa, rather than replace what’s recently been lost. In these markets, roughly three million barrels of new daily capacity will come online by the end of 2022, with an additional 1.3 million barrels per day to follow in 2023.
Capacity expansions at existing refineries—rather than new facility construction—are underway in the United States as well, primarily aimed at increasing refinery throughput of U.S. light sweet crude oil.
The U.S. refining sector has experienced significant capacity losses over the last few years for reasons beyond COVID, though the pandemic certainly did fast-track decisions to repurpose or shutter facilities. Restarting those facilities is not an option in most cases as they have already been dismantled, converted or are in the conversion process. In other cases, returning idled capacity to safe operation would be so labor intensive and time consuming that any market impact would be years out.
Refiners remain focused on maximizing the production of fuelsfrom our operable facilities, ensuring that the capacity we do have isrunning efficiently and cost effectively to supply U.S. consumersand meet global energy demand.

As MRC informed before, TotalEnergies has recently inaugurated the extension of Synova in Normandy, the French leader in recycled polypropylene production. TotalEnergies is therefore doubling its mechanical recycling production capacity for recycled polymers, to meet growing demand for sustainable polymers from customers, such as Automotive Manufacturer (Auto OEM) and the construction industry.

The newly-built highly-integrated mega Chinese refinery-cum-petrochemical complexes are immensely more efficient than the 50-60 year-old clunkers that they are replacing across the globe spanning from the U.S. west coast to the Philippines, bringing a new paradigm to the oil market, they said.
“We have these new refineries coming up in China that were planned 3-5 years ago but China does not need the extra capacity right now, the world also does not need it. We are going to see margins getting worse for refiners in the region and more capacity will be shut,” said one trading source.
The U.S. has an operable refining capacity of about 18.62 million b/d, which shrank to as low as 13.32 million b/d in April 2020 before rebounding to 14.68 million b/d, according to data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA). About 1 million b/d are likely to be permanently shuttered because of poor refining margins due in part to the demand erosion wreaked by COVID-19.
On the other hand, China’s refining capacity is forecast to climb to 20 million b/d by 2025 from 17.5 million b/d at the end of this year, according to the Economics & Technology Research Institute (ETRI) of the China National Petroleum Corp.
The volumes suggest that the Chinese government for now is comfortable for its refiners, both state and privately-owned, to have a bigger share of the overseas market which traders said would extend deeper into Australia, New Zealand and the west coast of the Americas where refining capacity is shrinking.
So far in Asia, Royal Dutch Shell announced the closure of its 60-year-old 110,000 b/d Tabangao refinery in the Philippines and plans to cut capacity by half at its biggest 500,000 b/d facility in Singapore. Shell said it aims to have just six integrated refineries by 2025.
BP Australia earlier said it would convert its 152,000 b/d Kwinana refinery in Western Australia into an import terminal. Ampol said Oct. 8 it is studying a similar conversion of its 109,000 b/d Lytton site, echoing a statement by Refining NZ, the sole operator in New Zealand. The Australian government last month announced plans to subsidize refiners as long as they maintain operations in Australia, days after Viva said it may shut the 120,000 b/d Geelong site.
One of the export quota recipient, Zhejiang Petrochemical Corp. (ZPC) was given 1 million mt. The company, which is majority owned by Rongsheng Petrochemical Co., is in the final stages of getting the second phase of its 800,000 b/d refinery up and running.
Mobility curbs delayed the commissioning of new plants while supply of propylene from refinery sources was curtailed as refiners cut runs, according to Asia Light Olefins World Analysis - Propylene.
A bumper 10 million-barrel spot crude oil purchase by Rongsheng Petrochemical suggests it is keen to get the second phase of its massive 40 million mt/yr, or 800,000 b/d, refinery and chemical project at subsidiary Zhejiang Petrochemical Co. Ltd (ZPC) running in the coming months, trading sources said.
Rongsheng announced in August plans to begin trial runs at the second 400,000 b/d tranche of the project in the fourth quarter of 2020 and looks set to achieve this aim despite COVID-19-related construction delays due to social distancing restrictions earlier in the year.
Market participants said Rongsheng was absent from the spot market for a couple of months and returned this week to buy the medium-sour Middle East cargoes, which led some to believe it was restocking but added that the scale of the purchase does point to some use in the new facility.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Continuing low refinery runs coupled with the autumnal turnaround season has tightened supplies from across the European barrel since September, creating backwardation in naphtha and gasoline and causing middle distillate differentials to strengthen versus distillate futures, according to OPIS and Intercontinental Exchange pricing.
Refinery runs at the world"s third largest crude oil importer are forecast to increase to 90% in November from around 80-85% in October with further hikes anticipated in December, with one source adding that it could reach 100% due to the combination of renewed diesel and strong gasoline demand.
India reduced refinery throughput in August to 16.1 million mt, or 3.82 million b/d, down a hefty 26.4% from a year ago, according to data from the Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC). This works out to 76% of the country"s nameplate 5.02 million b/d capacity and 73.6% of the 5.19 million b/d processed a year ago, the data showed.
There are no major refinery turnarounds planned in the fourth quarter aside from the month-long shutdown of the 400,000 b/d Vadinar facility in October.
Egypt"s Middle East Oil Refinery (MIDOR) company, located in Alexandria, has issued a tender to buy 90,000 metric tons of gasoil for October and November delivered into El Dekheila Port, according to a document seen by OPIS amid better-than-expected recovery in the region.
MIDOR delivers refined products to the national oil company, EGPC, and the local market. Its refinery has a crude distillation capacity of 100,000 b/d and is one of the newest and most sophisticated of Egypt"s nine operating refineries, according to IHS Markit data. Egypt has a total atmospheric distillation capacity of 737,000 b/d.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Turnarounds at the nearby 210,000-b/d Petronineos-operated refinery and the petchem plant were originally scheduled for April this year, but the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic scotched those plans.
One source told OPIS that a short period of maintenance work on a 110,000-b/d crude distillation unit at the refinery was about to end, and so many workers engaged in that project will be redeployed to work on the forthcoming petchems plant shutdown.
India, the second-largest crude oil importer in Asia, reduced refinery throughput in August to 16.1 million mt, or 3.82 million b/d, down a hefty 26.4% from a year ago, according to data from the Petroleum Planning & Analysis Cell (PPAC). This works out to 76% of the country"s nameplate 5.02 million b/d capacity and 73.6% of the 5.19 b/d processed a year ago, the data showed.
"We expect the demand recovery to continue and that would support higher refinery runs in October/November. However, from a year-on-year point of view, there is still a long a way to go to reach the 2019 level," said Premasish Das, IHS Markit research and analysis director.
IHS Markit estimates September refinery runs at 4.1 million b/d, rising to 4.4 million b/d in October/November, Das said, adding that the forecast may be slightly on the optimistic side.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Large oil companies with a strong trading team, such as Glencore, Vitol, Trafigura, Gunvor, bp, Total and so forth, holding deep pockets and capacity to execute such costly contango plays typically reap rewards in the billions.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Demand in India will increase as two massive crude units, the Indian Oil Corp. 300,000 b/d Paradip refinery and a 380,000 b/d unit at the mega Reliance Industries Jamnagar site begin operations after around a three-week maintenance.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with the OPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Asia naphtha demand as a petrochemical feedstock will continue to grow as new crackers begin operations even as below-capacity refinery utilization rates in some countries squeeze supply further, they said.
PTT Global Chemical, Thailand"s biggest ethylene maker, will add a new 500,000 mt/year naphtha cracker by December while in South Korea, YNCC is set to complete an expansion by early 2021, boosting the capacity of one of its three plants by 60% to 930,000 mt/year, according to the Monthly Analysis.
Refinery run rates in Asia and the Middle East are expected to improve to 74% this month and reach 82% by January 2021, from below 70% in April during the depth of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) lockdowns, said April Tan, IHS Markit associate director in Singapore.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
A Royal Dutch Shell refinery in the Philippines became the first Asian casualty of the fuel demand destroying coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic as other sites in the region brace themselves for similar fallouts in the face of new virus outbreaks and poor refining margins while more sites come onstream in China.
Pilipinas Shell Petroleum Corp said on Thursday that its near 60-year-old 110,000 b/d Tabangao refinery in Batangas province was no longer economically viable and would be turned into an import terminal.
“Due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global, regional and local economies, and the oil supply-demand imbalance in the region, it is no longer economically viable for us to run the refinery,” Pilipinas Shell President and CEO Cesar Romero said in the statement.
Refining margins in Asia are under tremendous pressure due to the sharp drop in fuel demand with the benchmark Singapore complex gross margin dropping to minus $3.78/bbl in May/June, according to an update by Refining NZ, which is studying the possibility of converting its refinery in New Zealand to an import terminal.
“This is not a surprise. We are working on a list of refineries in Asia that are vulnerable because of COVID-19 and this refinery keeps coming up in many of the criteria,”said Premasish Das, IHS Markit downstream research and analysis director, adding that there are sites in Japan, Australia, New Zealand and even in Singapore that face uncertain futures.
The Philippines closure will be a boon to the overall Shell system, given its mega refining complex in Singapore with a 500,000 b/d processing capacity, which will now have a new captive outlet as the unit in Tabangao was operating at around 80-85% of capacity prior to its temporary closure in May due to COVID-19, trading sources said.
RIL brought forward the turnaround of a 380,000 b/d CDU at the export-oriented 705,200 b/d Jamnagar refinery to this week from the initial schedule of Oct. 15, according to sources. The works were expected to finish in three to four weeks.
U.S. refined product output capacity that has been chasing significantly weaker demand since April due to the economic fallout of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is about to lose another refinery to temporary shutdown, market sources report.
When operating at or near full capacity, the Calcasieu refinery supplies a considerable amount of heavy naphtha and low-sulfur vacuum gasoil (LSVGO) into the U.S. Gulf Coast spot market. Figures from the U.S. Energy Information Administration show the refinery as having 36,000 b/d of vacuum distillation capacity (hence the VGO output) but nothing in the way of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) capacity or catalytic reforming capacity.
A testament to the Calcasieu refinery"s length on intermediate feedstocks is the fact that Calcasieu-quality LSVGO and Calcasieu-quality heavy naphtha were both seen on offer in the U.S. Gulf Coast spot market last week.
Other U.S. refineries shelved during the pandemic are Marathon Petroleum"s 166,000-b/d plant in Martinez, Calif., and its 28,000-b/d refinery in Gallup, N.M. (both in April). As reported by OPIS on June 16, restart of at least the Martinez refinery is not likely in 2020, according to some large unbranded wholesale customers who were privately informed by company sales executives.
Another U.S. refinery -- HollyFrontier"s 52,000-b/d refinery in Cheyenne, Wyo. -- is also soon to exit the petroleum-processing business. As previously reported, the refinery is expected to halt refining operations by Aug. 1 in order to begin the process of converting the facility to renewable diesel production by the first quarter of 2022.
Lower refinery utilization and the COVID-inspired drop in U.S. demand have also dismissed octane worries for the moment. The best means of addressing tough Tier 3 sulfur standards this year would have required running catalytic reformers at very high rates, and that might have limited output of high- octane components. But the lowest refinery runs of the 21st century have left plenty of spare capacity in refining complexes and kept octane spreads in check.
If that consensus is accurate, refiners could well run at about 75% of capacity through year"s end, with plenty of additional capacity for crude units, reformers and cat crackers.
U.S. refinery utilization has averaged less than 83% of capacity for 15 weeks, including a number of plants at minimum rates or idled (Marathon Petroleum"s refineries in Martinez, Calif., and Gallup, N.M).
Flaring occurred Tuesday at the Shell-operated 404,000-b/d Pernis refinery near Rotterdam in the Netherlands, according to eyewitnesses, with market sources saying Europe"s largest plant is becoming fully operational after a turnaround.
The trader had previously suggested that some units at Pernis, including those maximising the refinery"s middle distillates production, would not be operational until the middle of July, even though other units came back online last month.
The purchases well exceed Chinese refinery runs, especially in the second quarter when the nation was in the grip of COVID-19, leading most participants to agree that a lot of the oil has gone into storage, the capacity of which many had underestimated, according to Feng.
"China will have to de-stock in one way or another as it simply cannot have unlimited storage capacity to hold that much crude," Feng, who was also one of the authors of the analysis, said at that time.
However, shipments have picked in July as seen in recent shipping fixture reports but are still well short of typical levels due to COVID-19, which may lead to reduced refinery runs resulting in a longer period of lower imports, trading sources said.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Supply of all naphtha grades tightened as refiners worldwide operated at below capacity to counter the loss in fuel demand stemming from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mobility restrictions. At the same time, resilient petrochemical demand kept Asia cracker run rates at more than 85%, widening the supply shortfall, they said.
The freeing up of tankers from earlier use as floating storage at the start of COVID-19 lockdowns, along with below-capacity refinery utilization, curtailed liquidity in oil product trades and led to the slump in freight, he added.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Ethane prices will be driven higher by increasing outright natural gas prices due to the loss of associated gas production and the need to drill for gas from drier fields. Demand will be flattish in 2020 before recovering through to 2025 on growing US petrochemical consumption and boosted by new export capacity to start up at the end of the year.
Energy Transfer"s Orbit ethane export facility in the US Gulf Coast, the group"s joint venture with China"s Satellite Petrochemicals, will be in service in the fourth quarter. The export terminal will have the capacity to export 180,000 b/d alongside 800,000 bbl of refrigerated ethane storage, the group said at the conference.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
CPC Corp. is seeking gasoline in a surprise move following the closure of a 50,000 b/d residue fluid catalytic cracker (RFCC) at its Taoyuan refinery in Taiwan for turnaround amid growing demand as governments relax lockdown measures to curb the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
The tender came as CPC Corp. shut the RFCC at its 200,000 b/d Taoyuan refinery on May 7 for maintenance works that are expected to last until around Aug. 20, as reported earlier.
"We may see some demand from countries where refinery runs were slashed. They have not raised runs fast enough yet to meet demand recovery," the trader said.
Supply of all naphtha grades tightened because of lower global refinery runs due to fuel demand loss stemming from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mobility restrictions. At the same time, resilient petrochemical demand has kept Asia cracker run rates at more than 85% in recent months, widening the supply shortfall, they said.
"Asia was awash with arbitrage barrels in May and June because there was no gasoline blending demand. Now gasoline demand has returned, cracker demand is still there, but refinery runs are recovering at a slow pace because middle distillate margins remain weak," said a northeast Asian buyer.
Gain greater transparency into Asia-Pacific markets for more strategic buy and sell decisions on refinery feedstocks, LPG and gasoline with theOPIS Asia Naphtha & LPG Report.
Global commodities trader Gunvor is mothballing its 107,500-b/d Antwerp refinery in Belgium following the cratering of European refining margins during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the company"s CEO Torbjorn Tornqvist has announced.
Gunvor"s Antwerp refinery has a much lower potential output than several other refineries in Europe"s key Amsterdam-Rotterdam-Antwerp refining hub, and its size is one of several factors adversely affecting its strength, IHS Markit refining and marketing consulting director Hedi Grati told OPIS.
"Gunvor"s refinery in Antwerp is smaller and less complex than its peers in the port and across the border in nearby Rotterdam. Additionally, there is less integration with marketing activities such as fuels retail, which would otherwise provide some more security of demand," said Grati.
"The continued strength of Urals crude, at a premium to dated Brent, must have seriously weighed on the refinery"s bottom line," Grati added. The refinery was designed to process medium-sulfur crude oil, such as the Urals grade.
The refinery, in the southern Malaysian Johor state, was shut after a massive fire and explosion on March 15 that killed five people. The incident, the second in a year, occurred at a Diesel Hydro Treating Unit (DHT), the company said in a March 16 statement.
The refinery was saddled with issues since it began production last year. In April 2019, another massive fire and explosion almost completely destroyed an atmospheric residue desulphurizer (ARDS), crippling operations as the site was no longer able to process intended sour crudes.
Consequently, the refinery as a whole, and the RFCC in particular, was running at very low rates, market sources said. The fire-hit ARDS was due to restart in the middle of this year, Petronas said in a quarterly report.
The refinery is designed to produce 98,000 b/d of gasoline, 28,000 b/d of jet fuel, 88,000 b/d of diesel, 5,000 b/d of fuel oil and 458,000 mt/year of slurry sulfur. Its gasoline and diesel meet Euro 5 specifications.
The refinery also provides feedstock to an integrated petrochemical complex with a nameplate capacity of 3.3 million mt/year. The cracker has a capacity to produce 1.26 million mt/year of ethylene, 600,000 mt/year of propylene and 180,000 mt/year of butadiene, according to IHS Markit data.
California refined products margins are better than they were when Marathon temporarily idled its 161,000-b/d Martinez refinery in April, but fuel demand has not improved to where a restart of the complex is likely in 2020, sources said.
Some large unbranded wholesale customers told OPIS that they have been privately informed by Martinez sales executives that a restart in 2020 appears out of the question. But the




 8613371530291
8613371530291