wire rope failure osha made in china
A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
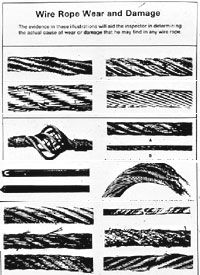
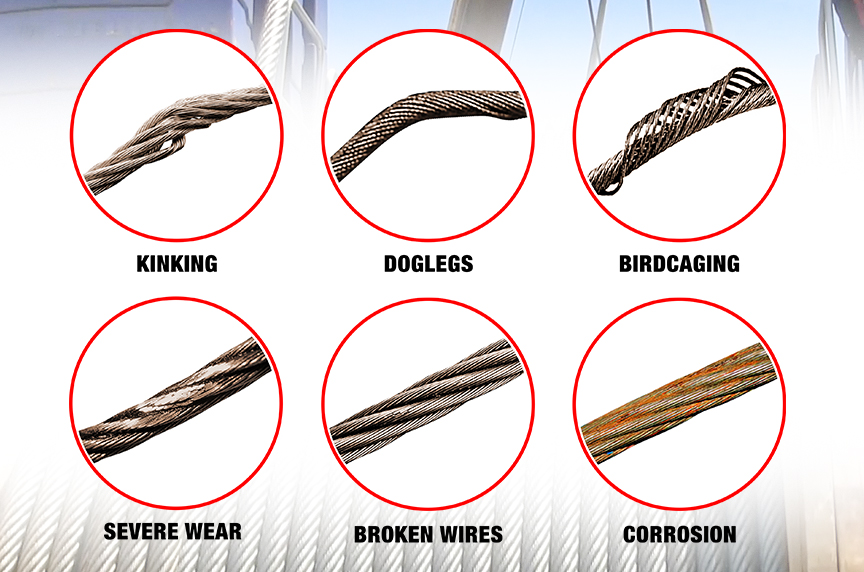
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Thank you for your inquiry of January 4, requesting clarification of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards at 29 CFR 1910.184(f)(5) which gives removal from service criteria for wire rope slings. We apologize for the delay in response.
The OSHA standards at 29 CFR 1910.184(f)(5)(i) and 29 CFR 1910.184(f)(5)(ii) require wire rope slings to be removed from service immediately when the following conditions are found:
The following method may be used to determine whether the wire rope sling must be removed from service as required by 29 CFR 1910.184(f)(5)(ii). The outside individual wires are not separated from the wire rope to make them available for measuring. To measure the wear or scraping of one-third the original diameter must be measured with a micrometer at the worn or scraped area and compared to the original diameter of whole wire rope. If the difference of this measurement is equal to, or more than, one-third the original diameter of an individual outside wire, the wire rope sling must be removed from service.
OSHA will allow a wire rope to be left in service with respect to a pass/fail gage measurement if the difference between the original diameter of the whole wire rope and a pass/fail gage OD failed measurement is less than one-third the original diameter of the outside individual wire.

Original equipment wire rope and replacement wire rope must be selected and installed in accordance with the requirements of this section. Selection of replacement wire rope must be in accordance with the recommendations of the wire rope manufacturer, the equipment manufacturer, or a qualified person.
Wire rope design criteria: Wire rope (other than rotation resistant rope) must comply with either Option (1) or Option (2) of this section, as follows:
Option (1). Wire rope must comply with section 5-1.7.1 of ASME B30.5-2004 (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that section"s paragraph (c) must not apply.
Option (2). Wire rope must be designed to have, in relation to the equipment"s rated capacity, a sufficient minimum breaking force and design factor so that compliance with the applicable inspection provisions in § 1926.1413 will be an effective means of preventing sudden rope failure.
Type I rotation resistant wire rope ("Type I"). Type I rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have little or no tendency to rotate or, if guided, transmits little or no torque. It has at least 15 outer strands and comprises an assembly of at least three layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type II rotation resistant wire rope ("Type II"). Type II rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have significant resistance to rotation. It has at least 10 outer strands and comprises an assembly of two or more layers of strands laid helically over a center in two or three operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type III rotation resistant wire rope ("Type III"). Type III rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have limited resistance to rotation. It has no more than nine outer strands, and comprises an assembly of two layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type I must have an operating design factor of no less than 5, except where the wire rope manufacturer and the equipment manufacturer approves the design factor, in writing.
A qualified person must inspect the rope in accordance with § 1926.1413(a). The rope must be used only if the qualified person determines that there are no deficiencies constituting a hazard. In making this determination, more than one broken wire in any one rope lay must be considered a hazard.
Each lift made under § 1926.1414(e)(3) must be recorded in the monthly and annual inspection documents. Such prior uses must be considered by the qualified person in determining whether to use the rope again.
Rotation resistant ropes may be used as boom hoist reeving when load hoists are used as boom hoists for attachments such as luffing attachments or boom and mast attachment systems. Under these conditions, all of the following requirements must be met:
The requirements in ASME B30.5-2004 sections 5-1.3.2(a), (a)(2) through (a)(4), (b) and (d) (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that the minimum pitch diameter for sheaves used in multiple rope reeving is 18 times the nominal diameter of the rope used (instead of the value of 16 specified in section 5-1.3.2(d)).
The operating design factor for these ropes must be the total minimum breaking force of all parts of rope in the system divided by the load imposed on the rope system when supporting the static weights of the structure and the load within the equipment"s rated capacity.
Wire rope clips used in conjunction with wedge sockets must be attached to the unloaded dead end of the rope only, except that the use of devices specifically designed for dead-ending rope in a wedge socket is permitted.
Prior to cutting a wire rope, seizings must be placed on each side of the point to be cut. The length and number of seizings must be in accordance with the wire rope manufacturer"s instructions.

Employee #1 was sandblasting and painting the interior of a surge water tank from a single point suspension scaffold. The scaffold was suspended from a 5/16 in. wire rope that failed approximately 20 in. below its attachment point. Employee #1"s fall was arrested by his fall protective equipment, and he sustained only a bruise on his arm. The wire rope used to suspend the scaffold was badly damaged, with numerous broken wires, worn and flattened strands, an area that was coiled, a kink with the core protruding, and a number of areas where the rope was bent. Despite its poor condition, the cable had not been removed from service.
WASHINGTON -- New guidance from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) will help employers select and use the appropriate slings when handling and moving materials. The document, Guidance on Safe Sling Use, was released today by the agency.
"OSHA"s current general industry standard is more than 30 years old," said Assistant Secretary of Labor for OSHA, Edwin G. Foulke, Jr. "This guidance document will aid users in the safe selection and use of slings, including synthetic round slings, which are not covered in OSHA"s standard, as well as the newer grades of materials being used in alloy steel chain and wire rope slings."
OSHA adopted its general industry sling standard on June 27, 1975, based on ANSI B30.9-1971 Slings standard. OSHA has since made only minor corrections. OSHA issued its construction industry sling standard on February 9, 1979, and its sling standard for shipyards on April 20, 1982.
Improper selection or use of slings can result in sling failure or load slippage, which in turn can lead to injuries or death. OSHA accident data for the years 1994 through 1996 show that there were four fatalities in general industry involving the misuse or failure of slings.
OSHA intends to format the final product for use on the Web. With the document in web format, a user can quickly get information on the type of sling he or she is using without having to look through material that is not relevant to the workplace.
Under the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970, employers are responsible for providing a safe and healthful workplace for their employees. OSHA"s role is to assure the safety and health of America"s working men and women by setting and enforcing standards; providing training, outreach, and education; establishing partnerships; and encouraging continual process improvement in workplace safety and health. For more information, visit www.osha.gov.

Failure of chains and chain slings are typically due to overloading, sharp edges, environmental deterioration, and exposure to heat (for example, from electrical arc, welding, and cutting torches). Use of damaged chains and chain slings may result in serious accidents.

OSHA standards often dictate that some rigging equipment needs to be made in the United States or Canada. These regulations are particularly stringent for shackles.

One topic that’s sure to spark a lively discussion among those who work in the lifting or material handling industries is, “Are import rigging products just as good as domestic products?” There’s a certain stigma attached to rigging products like hooks, wire rope, chain slings, and synthetic roundslings that are brought in to the U.S. from overseas.
25 or 30 years ago, if you asked an industry veteran if they trusted import products on the job site, the answer was clearly, “No.” Import products were viewed as inferior across the board—from shackles, sling hooks, wire rope, blocks, and wire rope clips. When import rigging products started hitting the market, there were horror stories of failed hooks, broken cables and slings, mislabeled and unmarked shackles—resulting in injuries to workers and expensive damage to equipment and materials.
Ultimately, the decision to choose a domestic or an imported wire rope, shackle, hook, sling or any other type of rigging product will come down to what best suits your company’s needs. There are obviously advantages and disadvantages to choosing either.
One thing to consider prior to purchasing an imported rigging product is to make sure that it meets federal specifications. For instance, if you’re considering using an imported wire rope, request a “certificate of conformance” from the distributor—this will at least give you documentation that the rope meets the RR-W-410 federal specifications required for domestic-made wire rope. It can also make certain that import rigging hardware items have the proper markings in accordance with federal standards.

Any wire rope in use should be inspected on a regular basis. You have too much at stake in lives and equipment to ignore thorough examination of the rope at prescribed intervals.
The purpose of inspection is to accurately estimate the service life and strength remaining in a rope so that maximum service can be had within the limits of safety. Results of the inspection should be recorded to provide a history of rope performance on a particular job.
On most jobs wire rope must be replaced before there is any risk of failure. A rope broken in service can destroy machinery and curtail production. It can also kill.
Because of the great responsibility involved in ensuring safe rigging on equipment, the person assigned to inspect should know wire rope and its operation thoroughly. Inspections should be made periodically and before each use, and the results recorded.
When inspecting the rope, the condition of the drum, sheaves, guards, cable clamps and other end fittings should be noted. The condition of these parts affects rope wear: any defects detected should be repaired.
To ensure rope soundness between inspections, all workers should participate. The operator can be most helpful by watching the ropes under his control. If any accident involving the ropes occurs, the operator should immediately shut down his equipment and report the accident to his supervisor. The equipment should be inspected before resuming operation.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act has made periodic inspection mandatory for most wire rope applications. If you need help locating the regulations that apply to your application, please give our rigging experts a call.

Effective July 8, 2011, OSHA has updated its regulations for slings for both general industry (1901.184) and construction (1926.251). According to a memo from the Association of Crane and Rigging Professionals, a summary of the key changes are as follows. The full regulation can be viewed at: http://www.osha.gov/FedReg_osha_pdf/FED20110608.pdf.
All load capacity tables for slings have been removed from the rule. Tables previously designated in OSHA were based on the 1971 ANSI B30.9 standard, which are now obsolete. The outdated tables are being replaced with a requirement that prohibits employers from loading slings in excess of the recommended safe working load as shown on permanently affixed identification markings.
Employers must now use only slings and shackles with permanently affixed identification markings showing the maximum load capacity. In the past, this was not required for wire rope slings.
Crane Hot Line asked Terry Driscoll of John Sakach Co., a specialty rigging supplier with locations in Illinois and Missouri, for his perspective on the new rule. “It is long overdue to bring wire rope slings on the same playing field as chain and synthetic slings,” he said. From a practical standpoint, Driscoll believes rigging shops may be struggling with finding the perfect wire rope sling tag to withstand the work environment. “Whether the tag is aluminum, stainless steel, Tyvek, RFID, or synthetic, it is very difficult to create a ‘permanent tag.’ Heavy duty, sure, but permanent?”
After the sling leaves the sling shop, it’s up to the end user to continue to stay in compliance. Driscoll advises that users establish a process for re-tagging slings after they have been inspected. “Inspecting the slings properly should be as much of a factor as looking for a tag on the sling,” he says. He also suggests educating riggers to avoid rigging with the tag end of the sling. But when tags inevitably become damaged or pulled off from normal wear and tear, end users should have additional tags as part of their tool box to prevent work stoppage or fines.

Rope diameter is specified by the user and is generally given in the equipment manufacturer’s instruction manual accompanying the machine on which the rope is to be used.
Rope diameters are determined by measuring the circle that just touches the extreme outer limits of the strands— that is, the greatest dimension that can be measured with a pair of parallel-jawed calipers or machinist’s caliper square. A mistake could be made by measuring the smaller dimension.
The right way to unreel.To unreel wire rope from a heavy reel, place a shaft through the center and jack up the reel far enough to clear the floor and revolve easily. One person holds the end of the rope and walks a straight line away from the reel, taking the wire rope off the top of the reel. A second person regulates the speed of the turning reel by holding a wood block against the flange as a brake, taking care to keep slack from developing on the reel, as this can easily cause a kink in the rope. Lightweight reels can be properly unreeled using a vertical shaft; the same care should be taken to keep the rope taut.
The wrong way to unreel.If a reel of wire rope is laid on its flange with its axis vertical to the floor and the rope unreeled by throwing off the turns, spirals will occur and kinks are likely to form in the rope. Wire rope always should be handled in a way that neither twists nor unlays it. If handled in a careless manner, reverse bends and kinks can easily occur.
The right way to uncoil.There is only one correct way to uncoil wire rope. One person must hold the end of the rope while a second person rolls the coil along the floor, backing away. The rope is allowed to uncoil naturally with the lay, without spiraling or twisting. Always uncoil wire rope as shown.
The wrong way to uncoil.If a coil of wire rope is laid flat on the floor and uncoiled by pulling it straight off, spirals will occur and kinking is likely. Torsions are put into the rope by every loop that is pulled off, and the rope becomes twisted and unmanageable. Also, wire rope cannot be uncoiled like hemp rope. Pulling one end through the middle of the coil will only result in kinking.
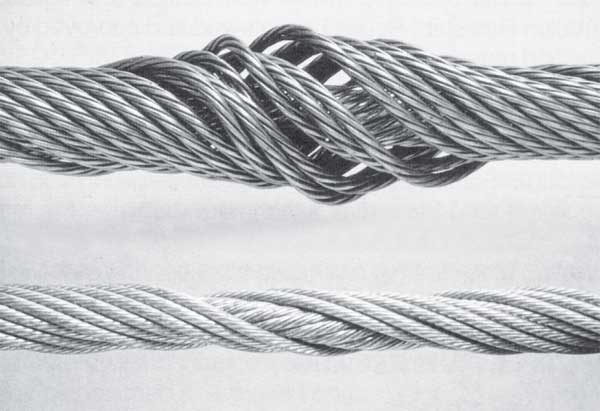
Great stress has been placed on the care that should be taken to avoid kinks in wire rope. Kinks are places where the rope has been unintentionally bent to a permanent set. This happens where loops are pulled through by tension on the rope until the diameter of the loop is only a few inches. They also are caused by bending a rope around a sheave having too severe a radius. Wires in the strands at the kink are permanently damagedand will not give normal service, even after apparent “re-straightening.”
When wire rope is wound onto a sheave or drum, it should bend in the manner in which it was originally wound. This will avoid causing a reverse bend in the rope. Always wind wire rope from the top of the one reel onto the top of the other.Also acceptable, but less so, is re-reeling from the bottom of one reel to the bottom of another. Re-reeling also may be done with reels having their shafts vertical, but extreme care must be taken to ensure that the rope always remains taut. It should never be allowed to drop below the lower flange of the reel. A reel resting on the floor with its axis horizontal may also be rolled along the floor to unreel the rope.
Wire rope should be attached at the correct location on a flat or smooth-faced drum, so that the rope will spool evenly, with the turns lying snugly against each other in even layers. If wire rope is wound on a smooth-face drum in the wrong direction, the turns in the first layer of rope will tend to spread apart on the drum. This results in the second layer of rope wedging between the open coils, crushing and flattening the rope as successive layers are spooled.
A simple method of determining how a wire rope should be started on a drum. The observer stands behind the drum, with the rope coming towards him. Using the right hand for right-lay wire rope, and the left hand for left lay wire rope, the clenched fist denotes the drum, the extended index finger the oncoming rope.
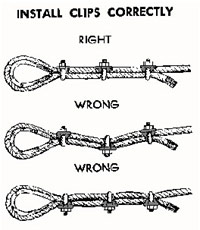
Clips are usually spaced about six wire rope diameters apart to give adequate holding power. They should be tightened before the rope is placed under tension. After the load is placed on the rope, tighten the clips again to take care of any lessening in rope diameter caused by tension of the load. A wire rope thimble should be used in the eye of the loop to prevent kinking.
U-bolt Clips.There is only one correct method for attaching U-bolt clips to wire rope ends, as shown in TheRightWayimage below. The base of the clip bears on the live end of the rope; the “U” of the bolt bears on the dead end.
Compare this with the incorrect methods. Five of the six clips shown are incorrectly attached—only the center clip in the top view is correct. When the “U” of the clip bears on the live end of the rope, there is a possibility of the rope being cut or kinked, with subsequent failure.
Proper seizing and cutting operations are not difficult to perform, and they ensure that the wire rope will meet the user’s performance expectations. Proper seizings must be applied on both sides of the place where the cut is to be made. In a wire rope, carelessly or inadequately seized ends may become distorted and flattened, and the strands may loosen. Subsequently, when the rope is operated, there may be an uneven distribution of loads to the strands; a condition that will significantly shorten the life of the rope.
Either of the following seizing methods is acceptable. Method No. 1 is usually used on wire ropes over one inch in diameter. Method No. 2 applies to ropes one inch and under.
Method No. 1: Place one end of the seizing wire in the valley between two strands. Then turn its long end at right angles to the rope and closely and tightly wind the wire back over itself and the rope until the proper length of seizing has been applied. Twist the two ends of the wire together, and by alternately pulling and twisting, draw the seizing tight.
The Seizing Wire. The seizing wire should be soft or annealed wire or strand. Seizing wire diameter and the length of the seize will depend on the diameter of the wire rope. The length of the seizing should never be less than the diameter of the rope being seized.
Proper end seizing while cutting and installing, particularly on rotation-resistant ropes, is critical. Failure to adhere to simple precautionary measures may cause core slippage and loose strands, resulting in serious rope damage. Refer to the table below ("Suggested Seizing Wire Diameters") for established guidelines. If core protrusion occurs beyond the outer strands, or core retraction within the outer strands, cut the rope flush to allow for proper seizing of both the core and outer strands.
The majority of wire rope problems occurring during operation actually begin during installation, when the rope is at its greatest risk of being damaged. Proper installation procedures are vital in the protection and performance of wire rope products.
Until the rope is installed it should be stored on a rack, pallet or reel stand in a dry, well-ventilated storage shed or building. Tightly sealed and unheated structures should be avoided as condensation between rope strands may occur and cause corrosion problems. If site conditions demand outside storage, cover the rope with waterproof material and place the reel or coil on a support platform to keep it from coming directly in contact with the ground.
While lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process, the wire rope must still be protected by additional lubrication once it is installed. Lubricants will dry out over a period of time and corrosion from the elements will occur unless measures are taken to prevent this from happening. When the machine becomes idle for a period of time, apply a protective coating of lubricant to the wire rope. Moisture (dew, rain, and snow) trapped between strands and wires will create corrosion if the rope is unprotected. Also apply lubricant to each layer of wire rope on a drum because moisture trapped between layers will increase the likelihood of corrosion.
Always use the nominal diameter as specified by the equipment manufacturer. Using a smaller diameter rope will cause increased stresses on the rope and the probability of a critical failure is increased if the rated breaking strength does not match that of the specified diameter. Using a larger diameter rope leads to shorter service life as the rope is pinched in the sheave and drum grooves which were originally designed for a smaller diameter rope. Just as using a different diameter rope can create performance problems, so can the use of an excessively undersized or oversized rope.
Measure the wire rope using a parallel-jawed caliper as discussed in Measuring Rope Diameter at the top of this page. If the rope is the wrong size or outside the recommended tolerance, return the rope to the wire rope supplier. It is never recommended nor permitted by federal standards to operate cranes with the incorrect rope diameter. Doing so will affect the safety factor or reduce service life and damage the sheaves and drum. Note that in a grooved drum application, the pitch of the groove may be designed for the rope’s nominal diameter and not the actual diameter as permitted by federal standards.
Wire rope can be permanently damaged by improper unreeling or uncoiling practices. The majority of wire rope performance problems start here.Improper unreeling practices lead to premature rope replacement, hoisting problems and rope failure.
Place the payout reel as far away from the boom tip as is practical, moving away from the crane chassis. Never place the payout reel closer to the crane chassis than the boom point sheave. Doing so may introduce a reverse bend into the rope and cause spooling problems. Follow the guidelines highlighted under Unreeling and Uncoiling and Drum Winding. Take care to determine whether the wire rope will wind over or under the drum before proceeding. If the wire rope supplier secured the end of the rope to the reel by driving a nail through the strands, ask that in the future a U-bolt or other nondestructive tie-down method be used; nails used in this manner damage the rope.
Take extra precaution when installing lang lay, rotation-resistant, flattened strand or compacted ropes. Loss of twist must be avoided to prevent the strands from becoming loosened, causing looped wire problems.
The end of the rope must be securely and evenly attached to the drum anchorage point by the method recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Depending on the crane’s regulatory requirements, at least two to three wraps must remain on the drum as dead wraps when the rope is unwound during normal operations. Locate the dead end rope anchorage point on the drum in relation to the direction of the lay of the rope. Do not use an anchorage point that does not correspond with the rope lay. Mismatching rope lay and anchorage point will cause the wraps to spread apart from each other and allow the rope to cross over on the drum. Very gappy winding will occur resulting in crushing damage in multilayer applications.
Back tension must be continually applied to the payout reel and the crewman installing the rope must proceed at a slow and steady pace whether the drum is smooth or grooved.Regardless of the benefits of a grooved drum, tension must be applied to ensure proper spooling. An improperly installed rope on a grooved drum will wear just as quickly as an improperly installed rope on a smooth drum. If a wire rope is poorly wound and as a result jumps the grooves, it will be crushed and cut under operating load conditions where it crosses the grooves.
Every wrap on the first or foundation layer must be installed very tightly and be without gaps. Careless winding results in poor spooling and will eventually lead to short service life. The following layers of rope must lay in the grooves formed between adjacent turns of the preceding layer of rope. If any type of overwind or cross-winding occurs at this stage of installation and is not corrected immediately, poor spooling and crushing damage will occur.
On a multilayer spooling drum be sure that the last layer remains at least two rope diameters below the drum flange top. Do not use a longer length than is required because the excess wire rope will cause unnecessary crushing and may jump the flange. Loose wraps that occur at any time must be corrected immediately to prevent catastrophic rope failure.
The use of a mallet is acceptable to ensure tight wraps, however a steel-faced mallet should be covered with plastic or rubber to prevent damage to the rope wires and strands.
Rotation-resistant ropes of all constructions require extra care in handling to prevent rope damage during installation. The lay length of a rotation-resistant rope must not be disturbed during the various stages of installation. By introducing twist or torque into the rope, core slippage may occur—the outer strands become shorter in length, the core slips and protrudes from the rope. In this condition the outer strands become over- loaded because the core is no longer taking its designed share of the load. Conversely, when torque is removed from a rotation-resistant rope core slippage can also occur. The outer strands become longer and the inner layers or core become overloaded, reducing service life and causing rope failure.
The plain end of a wire rope must be properly secured. If the entire cross section of the rope is not firmly secured, core slippage may occur, causing the core to pull inside the rope’s end and allowing it to protrude elsewhere, either through the outer strands (popped core) or out the other end of the line. The outer layer of the outside strands may also become overloaded as there is no complete core-to-strand support.
Secure the ends of the rope with either seizing or welding methods as recommended under Seizing Wire Rope. It is imperative that the ends be held together tightly and uniformly throughout the entire installation procedure, including attaching the end through the wedge socket and the drum dead end wedge
When installing a new line, connect the old line to the new line by using a swivel-equipped cable snake or Chinese finger securely attached to the rope ends. The connection between the ropes during change-out must be very strong and prevent torque from the old rope being transferred into the new rope.Welding ropes together or using a cable snake without the benefit of a swivel increases the likelihood of introducing torque into the new rope. A swivel-equipped cable snake is not as easy as welding the ropes, but this procedure can be mastered with a little patience and practice.

Sheaves facilitate the smooth and safe operation of overhead crane hoists. Damaged sheaves can wear ropes prematurely and cause other dangerous hazards, such as binding wire rope. Konecranes technicians are trained to identify and correct problems with sheaves and other parts of hoisting equipment.
Sheaves carrying ropes which can be momentarily unloaded shall be provided with close-fitting guards or other suitable devices to guide the rope back into the groove when the load is applied again.
The sheaves in the bottom block shall be equipped with close-fitting guards that will prevent ropes from becoming fouled when the block is lying on the ground with ropes loose.
In using hoisting ropes, the crane manufacturer"s recommendation shall be followed. The rated load divided by the number of parts of rope shall not exceed 20 percent of the nominal breaking strength of the rope.
Rope clips attached with U-bolts shall have the U-bolts on the dead or short end of the rope. Spacing and number of all types of clips shall be in accordance with the clip manufacturer"s recommendation. Clips shall be drop-forged steel in all sizes manufactured commercially. When a newly installed rope has been in operation for an hour, all nuts on the clip bolts shall be retightened.
Wherever exposed to temperatures, at which fiber cores would be damaged, rope having an independent wirerope or wire-strand core, or other temperature-damage resistant core shall be used.
Replacement rope shall be the same size, grade, and construction as the original rope furnished by the crane manufacturer, unless otherwise recommended by a wire rope manufacturer due to actual working condition requirements.
Konecranes wire rope inspections can help crane users extend the life of hoist ropes. Ropes, sheaves and other reeving system components are inspected for compliance with crane standards, and to determine if they have flaws that could hinder safe operation. Contact us today to schedule an assessment.
*The foregoing OSHA regulations are not intended to be a comprehensive overview of all applicable regulations pertaining to the designated topic. State laws may mandate different safety and maintenance standards. Accordingly, please consult applicable state laws as well as original equipment manufacturer specifications for further guidance. The statements and descriptions contained herein constitute the opinion/recommendation of the seller and are not intended to create any express warranties.
Wire rope slings can be used in many different industries such as general manufacturing, automotive, metals production and petroleum and gas. Wire rope slings are strong and flexible and can be resistant to abrasion and corrosion. Wire rope slings should be inspected by trained and qualified service personnel to minimize the risk or failure and to stay compliant with regulations.
Employers must use only wire-rope slings that have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer, and that indicate the recommended safe working load for the type(s) of hitch(es) used, the angle upon which it is based, and the number of legs if more than one.
Cable laid and 6 × 19 and 6 × 37 slings shall have a minimum clear length of wire rope 10 times the component rope diameter between splices, sleeves or end fittings.
Fiber core wire rope slings of all grades shall be permanently removed from service if they are exposed to temperatures in excess of 200 °F. When nonfiber core wire rope slings of any grade are used at temperatures above 400 °F or below minus 60 °F, recommendations of the sling manufacturer regarding use at that temperature shall be followed.
Konecranes inspectors and technicians can inspect the slings and other rigging equipment in your facility to determine if it meets OSHA standards. The Konecranes Slings and Accessories Inspection checks non-maintainable load lifting attachments and accessories to identify deficiencies and deviations from local statutory safety and health regulations. The inspection service utilizes radio frequency identification (RFID) tags to record load lifting attachment inspection data and a smartphone app to help quickly and reliably identify attachments.
*The foregoing OSHA regulations are not intended to be a comprehensive overview of all applicable regulations pertaining to the designated topic. State laws may mandate different safety and maintenance standards. Accordingly, please consult applicable state laws as well as original equipment manufacturer specifications for further guidance. The statements and descriptions contained herein constitute the opinion/recommendation of the seller and are not intended to create any express warranties.




 8613371530291
8613371530291