wire rope failure osha brands

A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
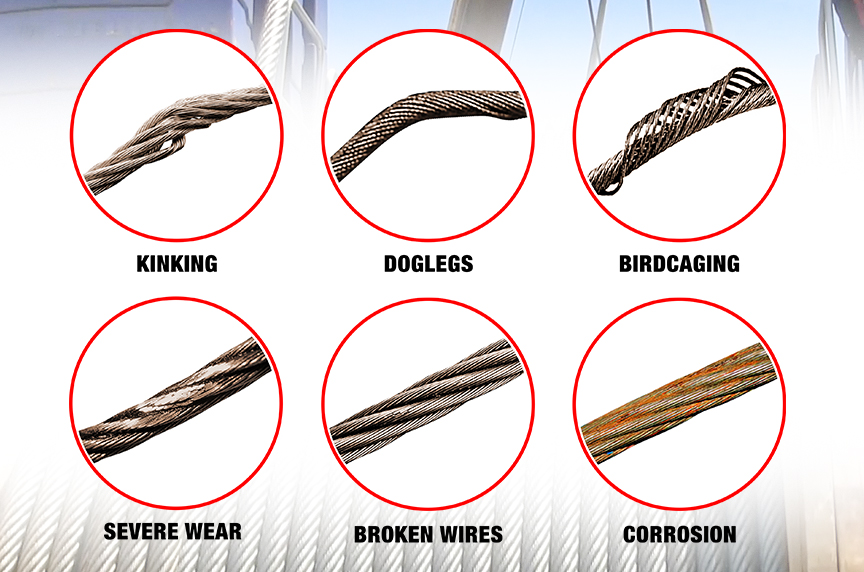
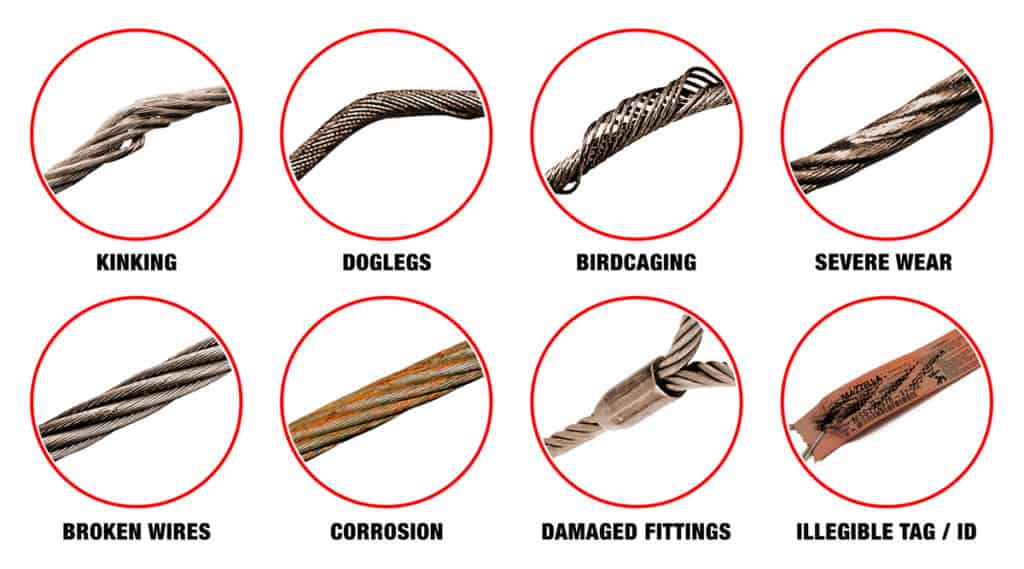
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
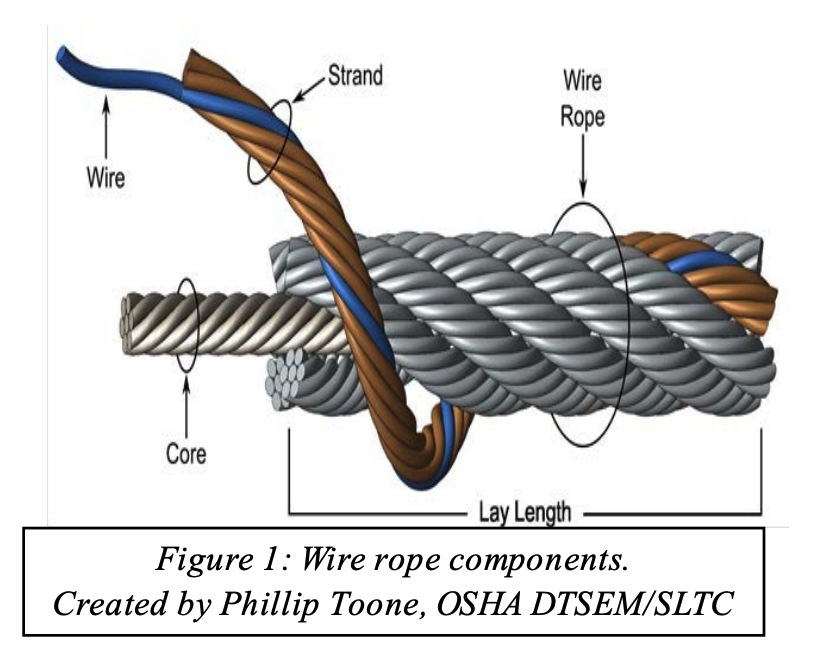
Original equipment wire rope and replacement wire rope must be selected and installed in accordance with the requirements of this section. Selection of replacement wire rope must be in accordance with the recommendations of the wire rope manufacturer, the equipment manufacturer, or a qualified person.
Wire rope design criteria: Wire rope (other than rotation resistant rope) must comply with either Option (1) or Option (2) of this section, as follows:
Option (1). Wire rope must comply with section 5-1.7.1 of ASME B30.5-2004 (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that section"s paragraph (c) must not apply.
Option (2). Wire rope must be designed to have, in relation to the equipment"s rated capacity, a sufficient minimum breaking force and design factor so that compliance with the applicable inspection provisions in § 1926.1413 will be an effective means of preventing sudden rope failure.
Type I rotation resistant wire rope ("Type I"). Type I rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have little or no tendency to rotate or, if guided, transmits little or no torque. It has at least 15 outer strands and comprises an assembly of at least three layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type II rotation resistant wire rope ("Type II"). Type II rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have significant resistance to rotation. It has at least 10 outer strands and comprises an assembly of two or more layers of strands laid helically over a center in two or three operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type III rotation resistant wire rope ("Type III"). Type III rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have limited resistance to rotation. It has no more than nine outer strands, and comprises an assembly of two layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type I must have an operating design factor of no less than 5, except where the wire rope manufacturer and the equipment manufacturer approves the design factor, in writing.
A qualified person must inspect the rope in accordance with § 1926.1413(a). The rope must be used only if the qualified person determines that there are no deficiencies constituting a hazard. In making this determination, more than one broken wire in any one rope lay must be considered a hazard.
Each lift made under § 1926.1414(e)(3) must be recorded in the monthly and annual inspection documents. Such prior uses must be considered by the qualified person in determining whether to use the rope again.
Rotation resistant ropes may be used as boom hoist reeving when load hoists are used as boom hoists for attachments such as luffing attachments or boom and mast attachment systems. Under these conditions, all of the following requirements must be met:
The requirements in ASME B30.5-2004 sections 5-1.3.2(a), (a)(2) through (a)(4), (b) and (d) (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that the minimum pitch diameter for sheaves used in multiple rope reeving is 18 times the nominal diameter of the rope used (instead of the value of 16 specified in section 5-1.3.2(d)).
The operating design factor for these ropes must be the total minimum breaking force of all parts of rope in the system divided by the load imposed on the rope system when supporting the static weights of the structure and the load within the equipment"s rated capacity.
Wire rope clips used in conjunction with wedge sockets must be attached to the unloaded dead end of the rope only, except that the use of devices specifically designed for dead-ending rope in a wedge socket is permitted.
Prior to cutting a wire rope, seizings must be placed on each side of the point to be cut. The length and number of seizings must be in accordance with the wire rope manufacturer"s instructions.

Mishandling of workplace materials is the single largest cause of accidents in the workplace. Fortunately, most of these accidents are avoidable. With wire rope slings playing an important role with cranes, derricks, and hoists, it’s important to understand how to make a proper selection.
A wire rope sling is made of wire rope. It is composed of single wires that have been twisted into strands. These strands are then twisted to form a wire rope.
The strength of a wire rope sling is a function of size, grade, and construction. It needs to accommodate the applied maximum load. The more a sling is used, both the design and the sling’s strength are reduced. A sling loaded beyond it strength will fail. For older slings it’s important to inspect often.
Wire rope slings must be able to take repeated bending without wires failing due to fatigue, sometimes called bending without failure. The best way to preventing fatigue failure is to use blocking or padding to increase the radius of bend.
The ability of wire rope to withstand abrasion. It’s determined by size, number of wires, and construction of the rope. Remember that smaller wires bend easier and offer greater flexibility, which also means they are more susceptible to abrasion.
The misuse of a wire rope will cause the sling to be unsafe well before any other reason. Kinking or bird caging will reduce the strength of a wire rope. Bird caging is forcibly untwisting the wire rope strands and they become spread outward. Be sure to keep up proper use per the manufacturer specifications.
These are just four factors to consider when determining the best wire rope slings for your application. Keep in mind that weight, size, flexibility, and shape of the loads being handled will also affect the life of a wire rope sling.

Maintain a record for each rope that includes the date of inspection, type of inspection, the name of the person who performed the inspection, and inspection results.
Use the "rag-and-visual" method to check for external damage. Grab the rope lightly and with a rag or cotton cloth, move the rag slowly along the wire. Broken wires will often "porcupine" (stick out) and these broken wires will snag on the rag. If the cloth catches, stop and visually assess the rope. It is also important to visually inspect the wire (without a rag). Some wire breaks will not porcupine.
Measure the rope diameter. Compare the rope diameter measurements with the original diameter. If the measurements are different, this change indicates external and/or internal rope damage.
Visually check for abrasions, corrosion, pitting, and lubrication inside the rope. Insert a marlin spike beneath two strands and rotate to lift strands and open rope.
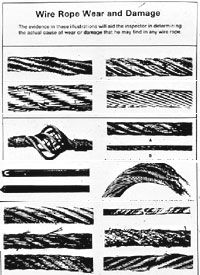
Assess the condition of the rope at the section showing the most wear. Discard a wire rope if you find any of the following conditions:In running ropes (wound on drums or passed over sheaves), 6 or more broken wires in one rope lay length; 3 or more broken wires in one strand in one rope lay. (One rope lay is the distance necessary to complete one turn of the strand around the diameter of the rope.)
Corrosion from lack of lubrication and exposure to heat or moisture (e.g., wire rope shows signs of pitting). A fibre core rope will dry out and break at temperatures above 120°C (250°F).
Kinks from the improper installation of new rope, the sudden release of a load or knots made to shorten a rope. A kink cannot be removed without creating a weak section. Discarding kinked rope is best.

The following is a fairly comprehensive listing of critical inspection factors. It is not, however, presented as a substitute for an experienced inspector. It is rather a user’s guide to the accepted standards by which wire ropes must be judged. Use the outline to skip to specific sections:
Rope abrades when it moves through an abrasive medium or over drums and sheaves. Most standards require that rope is to be removed if the outer wire wear exceeds 1/3 of the original outer wire diameter. This is not easy to determine, and discovery relies upon the experience gained by the inspector in measuring wire diameters of discarded ropes.
All ropes will stretch when loads are initially applied. As a rope degrades from wear, fatigue, etc. (excluding accidental damage), continued application of a load of constant magnitude will produce incorrect varying amounts of rope stretch.
Initial stretch, during the early (beginning) period of rope service, caused by the rope adjustments to operating conditions (constructional stretch).
Following break-in, there is a long period—the greatest part of the rope’s service life—during which a slight increase in stretch takes place over an extended time. This results from normal wear, fatigue, etc.
Thereafter, the stretch occurs at a quicker rate. This means that the rope has reached the point of rapid degradation: a result of prolonged subjection to abrasive wear, fatigue, etc. This second upturn of the curve is a warning indicating that the rope should soon be removed.
In the past, whether or not a rope was allowed to remain in service depended to a great extent on the rope’s diameter at the time of inspection. Currently, this practice has undergone significant modification.
Previously, a decrease in the rope’s diameter was compared with published standards of minimum diameters. The amount of change in diameter is, of course, useful in assessing a rope’s condition. But, comparing this figure with a fixed set of values can be misleading.
As a matter of fact, all ropes will show a significant reduction in diameter when a load is applied. Therefore, a rope manufactured close to its nominal size may, when it is subjected to loading, be reduced to a smaller diameter than that stipulated in the minimum diameter table. Yet under these circumstances, the rope would be declared unsafe although it may, in actuality, be safe.
As an example of the possible error at the other extreme, we can take the case of a rope manufactured near the upper limits of allowable size. If the diameter has reached a reduction to nominal or slightly below that, the tables would show this rope to be safe. But it should, perhaps, be removed.
Today, evaluations of the rope diameter are first predicated on a comparison of the original diameter—when new and subjected to a known load—with the current reading under like circumstances. Periodically, throughout the life of the rope, the actual diameter should be recorded when the rope is under equivalent loading and in the same operating section. This procedure, if followed carefully, reveals a common rope characteristic: after an initial reduction, the diameter soon stabilizes. Later, there will be a continuous, albeit small, decrease in diameter throughout its life.
Deciding whether or not a rope is safe is not always a simple matter. A number of different but interrelated conditions must be evaluated. It would be dangerously unwise for an inspector to declare a rope safe for continued service simply because its diameter had not reached the minimum arbitrarily established in a table if, at the same time, other observations lead to an opposite conclusion.
Corrosion, while difficult to evaluate, is a more serious cause of degradation than abrasion. Usually, it signifies a lack of lubrication. Corrosion will often occur internally before there is any visible external evidence on the rope surface.
Pitting of wires is a cause for immediate rope removal. Not only does it attack the metal wires, but it also prevents the rope’s component parts from moving smoothly as it is flexed. Usually, a slight discoloration because of rusting merely indicates a need for lubrication.
Severe rusting, on the other hand, leads to premature fatigue failures in the wires necessitating the rope’s immediate removal from service. When a rope shows more than one wire failure adjacent to a terminal fitting, it should be removed immediately. To retard corrosive deterioration, the rope should be kept well lubricated with a clear wire rope lube that can penetrate between strands. In situations where extreme corrosive action can occur, it may be necessary to use galvanized wire rope.
Kinks are tightened loops with permanent strand distortion that result from improper handling when a rope is being installed or while in service. A kink happens when a loop is permitted to form and then is pulled down tight, causing permanent distortion of the strands. The damage is irreparable and the sling must be taken out of service.
Doglegs are permanent bends caused by improper use or handling. If the dogleg is severe, the sling must be removed from service. If the dogleg is minor, exhibiting no strand distortion and cannot be observed when the sling is under tension, the area of the minor dogleg should be marked for observation and the sling can remain in service.
Bird caging results from torsional imbalance that comes about because of mistreatment, such as sudden stops, the rope being pulled through tight sheaves, or wound on too small a drum. This is cause for rope replacement unless the affected section can be removed.
Particular attention must be paid to wear at the equalizing sheaves. During normal operations, this wear is not visible. Excessive vibration or whip can cause abrasion and/or fatigue. Drum cross-over and flange point areas must be carefully evaluated. All end fittings, including splices, should be examined for worn or broken wires, loose or damaged strands, cracked fittings, worn or distorted thimbles and tucks of strands.
After a fire or the presence of elevated temperatures, there may be metal discoloration or an apparent loss of internal lubrication. Fiber core ropes are particularly vulnerable. Under these circumstances the rope should be replaced.
Continuous pounding is one of the causes of peening. This can happen when the rope strikes against an object, such as some structural part of the machine, or it beats against a roller or it hits itself. Often, this can be avoided by placing protectors between the rope and the object it is striking.
Another common cause of peening is continuous working-under high loads—over a sheave or drum. Where peening action cannot be controlled, it is necessary to have more frequent inspections and to be ready for earlier rope replacement.
Below are plain views and cross-sections show effects of abrasion and peening on wire rope. Note that a crack has formed as a result of heavy peening.
Scrubbing refers to the displacement of wires and strands as a result of rubbing against itself or another object. This, in turn, causes wear and displacement of wires and strands along one side of the rope. Corrective measures should be taken as soon as this condition is observed.
Wires that break with square ends and show little surface wear have usually failed as a result of fatigue. Such fractures can occur on the crown of the strands or in the valleys between the strands where adjacent strand contact exists. In almost all cases, these failures are related to bending stresses or vibration.
If diameter of the sheaves, rollers or drum cannot be increased, a more flexible rope should be used. But, if the rope in use is already of maximum flexibility, the only remaining course that will help prolong its service life is to move the rope through the system by cutting off the dead end. By moving the rope through the system, the fatigued sections are moved to less fatiguing areas of the reeving.
The number of broken wires on the outside of a wire rope are an index of its general condition, and whether or not it must be considered for replacement. Frequent inspection will help determine the elapsed time between breaks. Ropes should be replaced as soon as the wire breakage reaches the numbers given in the chart below. Such action must be taken without regard to the type of fracture.
* All ropes in the above applications—one outer wire broken at the point of contact with the core that has worked its way out of the rope structure and protrudes or loops out of the rope structure. Additional inspection of this section is required.
Rope that has either been in contact with a live power line or been used as “ground” in an electric welding circuit, will have wires that are fused, discolored and/or annealed and must be removed.
On occasion, a single wire will break shortly after installation. However, if no other wires break at that time, there is no need for concern. On the other hand, should more wires break, the cause should be carefully investigated.
On any application, valley breaks—where the wire fractures between strands—should be given serious attention. When two or more such fractures are found, the rope should be replaced immediately. (Note, however, that no valley breaks are permitted in elevator ropes.)
It is good to remember that once broken wires appear—in a rope operating under normal conditions—a good many more will show up within a relatively short period. Attempting to squeeze the last measure of service from a rope beyond the allowable number of broken wires (refer to table on the next page) will create an intolerably hazardous situation.
Recommended retirement criteria for all Rotation Resistant Ropes are 2 broken wires in 6 rope diameters or 4 broken wires in 30 rope diameters (i.e. 6 rope diameters for a 1″ diameter rope = 6″).
Distortion of Rotation Resistant Ropes, as shown below, can be caused by shock load / sudden load release and/or induced torque, and is the reason for immediate removal from service.

In 1998, a crane load line broke while lifting the south topside module of the Petronius platform, dropping the module into the Gulf of Mexico. The cost was estimated to be around 116 million US dollars. Since 1999 more than 60 people have been killed as a result of wire ropes breaking and more than 65 associated injuries.
Not many people appreciate that there are literally thousands of wire rope designs, most of which can be put into a specific category. According to BS ISO 4309 2010 there are currently more than 25 categories of crane wire rope, each with differing characteristics and also different discard criteria. Deterioration can be measured, counted or calculated and the wire rope eventually taken out of service based on sophisticated discard criteria published in chosen standards, codes of practice or users handbooks.
Unfortunately there is no simple answer to either of these questions. All wire ropes will eventually break due to corrosion, wear or fatigue even if they are maintained and used properly. Unpredictable wire rope failures will inevitably occur, quite often when you least expect it if the discard criteria is ignored, or those using the equipment are ignorant of it.
James Dawes of Topeka, Illinois, was killed in 2008 after being struck by the boom of a Link-Belt crane; the accident was caused by the boom hoist wire rope breaking. The crane rope had been inspected, but a report said that the inspector failed to reject the rope showing a high number of visible wire breaks. Premature or unexpected wire rope failures can also be attributed to poor manufacture, incorrect handling and storage, poor installation technique, poor selection or fitting of its termination, infrequent or inadequate inspection and poor maintenance. Of course there is always the possibility that mechanical damage can occur and this is usually attributed to human error.
It is necessary, particularly during offshore operations that frequent inspections are carried out over the whole length of the working part of all steel wire ropes. The frequency of inspections should be based on the severity of use and risk assessment and particular attention should be paid to the critical areas of the wire rope; areas that are frequently running over sheaves, compensating sheaves and the rope termination to name a few.
If a wire rope has not been subjected to an abnormal environmental condition such as excessive heat, chemical attack or any corrosive solution and it has not been the victim of any form of mechanical damage, then trained operatives and inspectors can reasonably predict the length of time the steel wire rope is likely to last. That prediction, of course, will be dependent on the knowledge and experience of those making it coupled with known facts about the rope, its current condition and the application it is running on. The Inspector should be aware of the previous rope’s history, capacities of loads and the reeving systems employed together with the frequency of use etc.
Various standards and codes of practice have been written by recognized bodies and institutes based on the experience of experts or representatives of corporate organizations who have a vested interest. These standards do offer guidance on when a wire rope should be removed from service based on wear, abrasion and fatigue amongst others things, but none of these standards have any legal status except when they are called up by contract. Indeed they can all be supported or overturned in a court of law by an expert.
The users handbook, or more importantly the safe use instructions do have legal status. In many parts of the world these days, suppliers of cranes or any machinery for that matter, issue safe use instructions with new equipment. Modern applications employ modern wire rope and, in some cases, sheaves and pulleys that are made with materials other than steel. Original equipment manufacturers of such applications may impose discard criteria for the wire rope that is stricter than those in chosen standards. By law the user must follow manufacturers’ instructions.
Wire ropes will deteriorate much more quickly if they go dry and are allowed to remain in that condition. Tests have proven that a dry rope will lose up to 60 % of its expected life if it is not re-lubricated. There are differing schools of thought as to how wire rope should be lubricated. Some believe that a thin lubricant should be applied using a paintbrush. It is thought that this method allows the lubricant to penetrate. Experience has proven however, that thin penetrative lubricants will easily drain away or fly off in hot climates.
Another school of thought, and the one I stand on, is that grease should be pressure lubricated into the rope. This method, if applied properly, will ensure that the grease penetrates the rope pushing out the old lubricant with it and any possible corrosive agents such as salt water and sand. Any lubricant that is used must be compatible with the type that was applied previously and it is a good idea to consider the environment as well.
In any event, wire ropes usually announce that they are about to break. A series of individual wire breaks can be heard. These are likely to go on over several seconds and continuing for up to ten minutes before ultimate failure. Therefore, if operatives understand the warning signals, expensive incidents could be avoided.
Figure 2 shows two pieces of the same rope, the bottom portion quite clearly shows a progression of wire breaks. The operator was able to put the load down before disaster struck. The root cause of this fault was core deterioration brought about by internal corrosion.
To answer the other question on accountability, the list is extensive. Usually the first suspect is the wire rope manufacturer and that may be where the problem lies, but very often that is not the case. What if you were supplied the wrong rope for the application? Maybe you ordered the wrong rope or your buyer bought it from a cheap unapproved manufacturing source.
Perhaps your supplier is responsible, maybe he provided you with a rope that was produced to the wrong specifications. Would you know the difference? Perhaps you were sold a rope that had been stored in the suppliers or manufactures stock for a number of years and, whilst it was there, it hadn’t been properly maintained. Maybe the rope had been badly handled or installed incorrectly. The list of possibilities is endless.
In 1999 a ropeway in the French Alps snapped causing 21 deaths. In 2003, a ropeway wire rope snapped and 7 people died and a further 42 were injured. In 2007 a crane wire rope snapped at New Delhi’s metro, the entire structure tumbled down crushing workers underneath, six people were killed and 13 more were injured. In 2009 26 people were killed and 5 people were injured when a rope failed in a mine and a further 6 people were injured when a lift rope broke inside London’s Tower Bridge.
If you find yourself in the unfortunate situation after the unthinkable premature failure of a wire rope, then you might like to know that there are independent analytical services capable of determining probable cause. One of these is Doncaster Analytical Services Ltd (DAS), they have an independent metallurgical laboratory providing factual analysis and testing of wire rope for any reason (contact Mr Shui Lee, Technical Director, Tel +44(0)1302 556063, email: shui.lee@doncasteranalyticalservices. com).
You do not need a wire rope to fail in order to learn. Careful analysis of discarded ropes can also give you valuable information about your application, the way it operates, and the rope you have been using.
Based on this information, a trained, skilled and experienced inspector will be able to advise on a better crane or wire rope design, or to an improvement in maintenance procedures and safety.
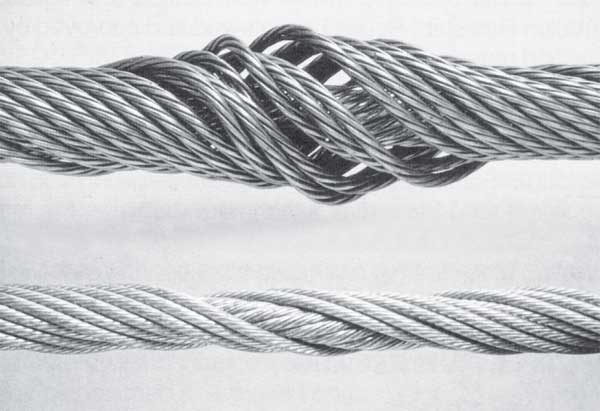
Any wire rope in use should be inspected on a regular basis. You have too much at stake in lives and equipment to ignore thorough examination of the rope at prescribed intervals.
The purpose of inspection is to accurately estimate the service life and strength remaining in a rope so that maximum service can be had within the limits of safety. Results of the inspection should be recorded to provide a history of rope performance on a particular job.
On most jobs wire rope must be replaced before there is any risk of failure. A rope broken in service can destroy machinery and curtail production. It can also kill.
Because of the great responsibility involved in ensuring safe rigging on equipment, the person assigned to inspect should know wire rope and its operation thoroughly. Inspections should be made periodically and before each use, and the results recorded.
When inspecting the rope, the condition of the drum, sheaves, guards, cable clamps and other end fittings should be noted. The condition of these parts affects rope wear: any defects detected should be repaired.
To ensure rope soundness between inspections, all workers should participate. The operator can be most helpful by watching the ropes under his control. If any accident involving the ropes occurs, the operator should immediately shut down his equipment and report the accident to his supervisor. The equipment should be inspected before resuming operation.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act has made periodic inspection mandatory for most wire rope applications. If you need help locating the regulations that apply to your application, please give our rigging experts a call.

Hoisting loads with a wire rope is a simple operation. Hook it up; lift it. Turns out, it’s more complicated than it appears. The details of setting up, inspecting, and maintaining lifts with wire ropes are not complicated, but are critical. A lift that goes awry is dangerous. A bad lift puts workers at risk. In this article, we discuss the causes of wire rope failure and how to avoid them.
Abrasion breaks are caused by external factors such as coming into contact with improperly grooved sheaves and drums. Or just hitting against some object during operation. Worn, broken wire ends is the result of an abrasion break. Common causes of abrasion breaks include:
Core slippage or protrusion is caused by shock load or improper installation of the wire rope. Excessive torque can cause core slippage that forces the outer strands to shorten. The core will then protrude from the rope. Wire ropes designed to be rotation-resistant should be handled carefully so as not to disturb its lay length.
Corrosion breaks cause pitting on the individual wires that comprise the rope. This type of damage is caused by poor lubrication. However, corrosion breaks are also caused by the wire rope coming into contact with corrosive chemicals, such as acid.
There are many ways the strands of a rope can be crushed or flattened. Improper installation is a common cause. To avoid crushing, you’ll want the first layer of the wire rope to be very tight. You’ll also need to properly break-in a new wire rope. Other causes of crushing include cross winding, using a rope of the wrong diameter, or one that it too long.
Cracks to individual wires are caused by fatigue breaks. Fatigue breaks happen because the wire rope is being bent over the sheave over and over again. In time, the constant rubbing of the wire rope against the sheave or drum causes these breaks. Sheaves that are too small will accelerate fatigue breaks because they require more bending. Worn bearings and misaligned sheaves can also cause fatigue. A certain number of broken wires is acceptable. The worker responsible for equipment inspection prior to use should know the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard for wire ropes. The ASME standard determines whether the wire rope must be replaced. (https://www.asme.org/)
Selecting the right wire rope for the job is critical. There is never a perfect rope. For example, you will need to make a tradeoff between fatigue resistance and abrasion resistance. There are several aspects to wire rope design to consider, including:
In general, the proper wire rope will have a strength rating high enough to handle the load. (Strength is rated in tons.) It can handle the stress of repeated bending as it passes over sheaves or around drums. How you attach the rope in preparation for the lift matters and should only be handled by properly trained workers.
The wire rope (and all the equipment involved in a lift) should be fully inspected prior to the lift. The worker performing the inspection should be well-versed in the types of damage that can cause a wire rope to fail. Using a checklist is highly recommended. This will ensure that the inspection is complete. Worker and supervisor signoff will increase accountability. Of course, the wire rope must be maintained according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
How a wire rope is stored, the weather conditions in which it is used, and how they are cleaned all affect its useful life. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides these recommendations: (Source: https://www.osha.gov/dsg/guidance/slings/wire.html)
Preventing wire rope failures starts with selecting the right one for the job. When in doubt, talk with your local equipment dealer. Be prepared to discuss your specific job requirements. A thorough inspection of the wire rope prior to using it is critical. Finally, properly store your wire rope. The selection, inspection, and care of wire rope is key to job safety.

One piece of equipment most often used in the steel erection industry is the wire rope sling. It is also one of the most abused pieces of equipment. There are many ways wire rope slings are abused, including being laid in the dirt; pulled out from under a load by the crane; used without softeners when lifting heavy loads; or being straightened by an old-school choker straightener. Straightening your slings over and over weakens the wires and you lose the strength of your sling. These are all unacceptable practices. Wire rope slings must be visually inspected before each day’s use. During inspection, you must know and understand what to look for to determine whether you should continue to use or discard the sling.
The ASME volume B30.9-2018: Slings revises the 2014 edition, and contains changes pertaining to wire-rope slings, starting with a new section on “Rigger Responsibilities.” Those changes include: Clarified that a qualified person should, if necessary, determine additional steps that need to be taken after identifying a hazard during inspection.
Early signs of wire rope sling failure can actually provide the user with a margin of safety. A wire sling needs to be discarded when it shows signs of:Severe corrosion,
The goal of a sling inspection is to evaluate remaining strength in a previously used sling to determine its suitability for continued use. Daily visual inspections, designed to detect serious damage or deterioration that would weaken the sling, are usually performed by the person using the sling daily. Obvious issues, such as broken wires, kinks, crushing, broken attachments, and severe corrosion, should be looked for. Any deterioration that could result in appreciable loss of original strength should be noted to determine if further use would result in a safety hazard.
Train all employees in the safe use of rigging and proper rigging gear inspect inspection before each use. No more than three broken wires in a rope lay are allowed. Wire rope slings, like chain slings, must be cleaned prior to each inspection because they are subject to damage hidden by dirt or oil. In addition, they must be lubricated according to manufacturer"s instructions. Lubrication prevents or reduces corrosion and wear due to friction and abrasion. Before applying any lubricant, however, the sling user should make certain that the sling is dry. Applying lubricant to a wet or damp sling traps moisture against the metal and hastens corrosion. Corrosion deteriorates wire rope. It may be indicated by pitting, but it is sometimes hard to detect. If a wire rope sling shows any sign of significant deterioration, that sling must be removed until it can be examined by a person who is qualified to determine the extent of the damage. Using rigging racks or storing slings in a Conex storage container is always a best practice. Using with the correct size of shackle while choking slings will prolong the life of the sling. Finally, a monthly inspection color code program will assure inspections are being performed.
Three industry standards provide the end-user with guidelines for inspection and criteria that warrants removal from service: OSHA 1926.251(c)(4)(iv) for Construction), OSHA 1910.184 for General Industry) and ASME B30.9.
This detailed blog post from Mazzella Companies outlines the specifics on how to inspect wire rope slings, when to discard slings, and how often to inspect them.
As a result of the heavy responsibilities placed on wire rope, it is no wonder why a cable suffers from wear and tear. The most common problem that occurs when using wire rope, is block twisting or cabling. This is especially the case for companies using wire rope within the construction industry. When this happens, it is easy to blame the rope, but normally there are other issues that need to be addressed.
Each time a load is applied to a wire rope, it will slightly twist or unlay. With time, the wire rope will eventually suffer from block twisting or rope distortion. When the problem gets too big (roughly 180 degrees of twisting), it is best to no longer use the rope. Using a rope that has been cabled is dangerous and unsafe for workers.

Wire rope and cranes are joined at the hip when endeavoring to lift, move or transport materials. For centuries the combination of rope (sisal, manila, vegetable, steel, synthetic…) and a winching system have stirred the imagination of engineers and other interested persons in aiding the lifting and handling of heavy objects.
Giant strides in the development of the “crane and rope” system have led to unimaginable progress in leaps and bounds in today’s world. One thing that has remained constant over many decades is the fact that all types of rope used on cranes do eventually wear our and must be replaced.
This article focuses on actual wire rope failures, or near failures, that have occurred. The fact that all wire ropes on a crane will deteriorate over periods of operation is a universal truth, but the useful service life of wire rope will vary according to applications, operating conditions, working environment, type of crane, crane operator and other factors. Therefore, it is a necessity that proper inspection, maintenance and retirement criteria be firmly established to achieve safe and efficient working conditions.
The industry accepted sources for inspection and retirement procedures are listed in the ASME B 30.5 Safety Standard for Mobile Cranes & Locomotive (Photograph #1), and the OSHA Regulation CFR 29 1926 .552 OSHA Regulations on Cranes & Derricks.
When a wire rope on a crane fails, traumatic consequences will likely follow. At the very least, equipment damage and downtime will ensue, but more importantly lives many times are lost. These wire rope failures are mostly, not because of structural causes, but from human error, neglect, lack of training or not following known instructions. In my experience, the three main reasons for wire rope failures on cranes are misuse, abuse and overuse.
Lift-All operating procedures require that you always inspect slings before each use. OSHA states that the sling and all fastening and attachments shall be inspected for damage or defects by a competent person designated by the employer. Damaged or defective slings shall be immediately removed from service.
In addition to these requirements, OSHA and ASME specify that chain slings receive a thorough inspection at least once per year, and that the employer maintain a record of the most recent inspection.
The three basic types of steel slings are: chain, wire mesh, and wire rope. Per OSHA and/or ASME instructions, wire rope slings with the following conditions must be removed from service immediately: kinking, crushing, bird-caging, wear, corrosion, damaged sleeves or end fittings, missing or illegible identification, or heat damage. Wire rope slings damaged by heat can be difficult to recognize. A good indication of damage is absence of lubrication or discoloration. Another common cause for wire rope sling rejection is broken wires. Ten broken wires in one rope lay, or five broken wires in one strand in one rope lay is cause for rejection.
The following conditions on wire mesh slings indicate they must be removed from service immediately: broken welds or wires, abrasion, corrosion or heat damage, missing or illegible identification, reduced flexibility, or field repairs.
The safety inspection must include end fittings and attachments in both the synthetic and steel sling categories. According to OSHA regulations, end fittings and attachments must be replaced when they show any of these problems: cracks, distortion, or wear.
If a hook latch is present, it must be in good working condition, or it could prevent the sling from working properly. Slings and their end fittings that do not pass safety inspections should either be destroyed or sent back to the manfacturer for further evaluation and possible repair. Never attempt to do the repairs yourself. Damaged slings and their fittings should never be used in any lifting situation. Web slings, toughflex roundslings, and wire rope slings cannot be repaired. However, undamaged end fittings and attachments can be returned to the manufacturer for possible reuse. Chain and wire mesh slings can be repaired by the manufacturer. We recommend that any reused parts or end fittings be proof tested and certified.

A customer recently contacted us to reorder the wire rope component of their Electrolifttwin hook monorail hoist. While the hoist was only a year old, they had replaced the wire rope twice within six months. They sent a picture of the damaged rope and asked for reasons why the wire rope was failing.What’s killing my wire rope?
It’s important to note that the wire rope used for hoists and overhead cranes is specially made of extra flexible Improved Plow Steel (IPS). It’s considered superior in durability and tensile strength (bending) to standard, everyday wire rope.
When properly sized and lubricated, a wire rope should last for years, even with frequent use. Wire rope hoists are recommended for heavy duty applications, high frequency usage and where long lifts are needed.
The Answer:Most likely, there’s a problem with how the hoist is operated. Wire rope failure is almost always due to operator error. By design, hoist hook blocks must be raised and lowered straight up and straight down, and the wire rope cable wraps around the drum, within the grooving, in one layer. In the course of picking up a load, if the operator side pulls the rope by more than about three degrees from vertical, the wire rope will jump the drum’s grooves.
Once the grooves are jumped, the operator must realize the error and stop using the hoist immediately. To correct the issue, the load must be lowered and the wire rope must be allowed to return it to the correct drum grooves. If the operator continues to use the hoist with the wire rope piled up at one end of the drum, the rope gets pinched and the cable can become damaged. Also in the course of usage, if the cable goes slack and the wire rope jumps over the drum guard, it could get caught between the drum and the shaft, and the wire rope could fail.
To prevent this problem, we recommend operator training classesand regular inspection of the unit. Every shift should start with an examination of the rope by lowering the hook all the way down. If the rope is damaged, including even one strand broken, stop the process and get the rope replaced. We recommend keeping spare ropes in stock to avoid downtime and




 8613371530291
8613371530291