wire rope failure osha price

A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
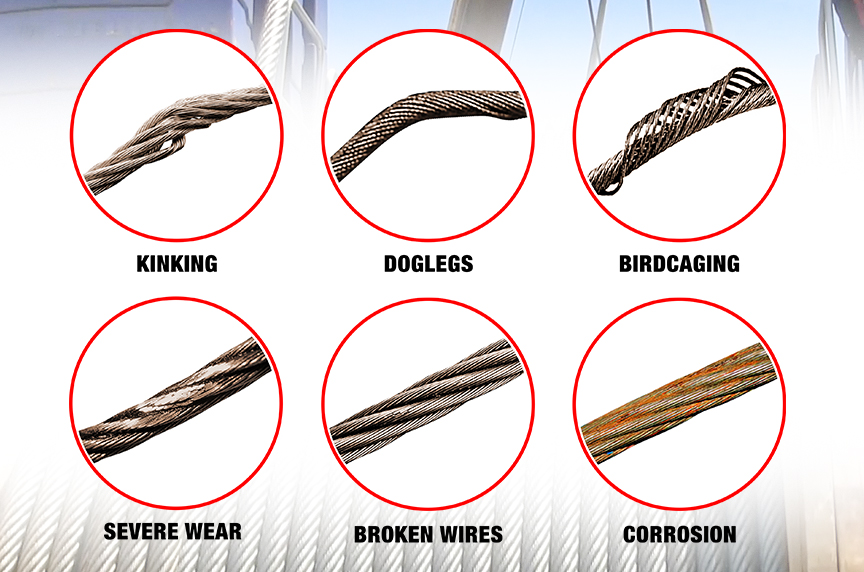
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
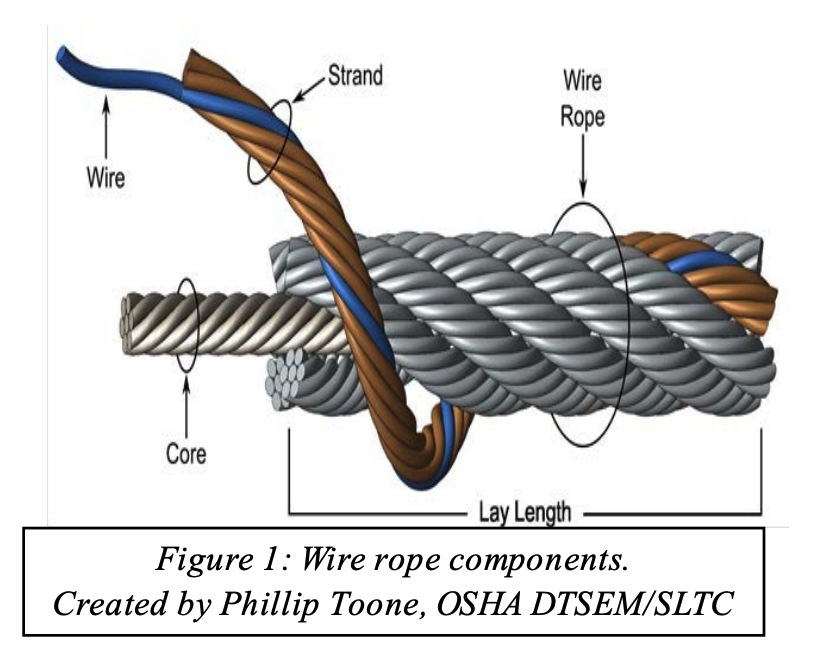
Scope. This section applies to slings used in conjunction with other material handling equipment for the movement of material by hoisting, in employments covered by this part. The types of slings covered are those made from alloy steel chain, wire rope, metal mesh, natural or synthetic fiber rope (conventional three strand construction), and synthetic web (nylon, polyester, and polypropylene).
Cable laid endless sling-mechanical joint is a wire rope sling made endless by joining the ends of a single length of cable laid rope with one or more metallic fittings.
Cable laid grommet-hand tucked is an endless wire rope sling made from one length of rope wrapped six times around a core formed by hand tucking the ends of the rope inside the six wraps.
Cable laid rope sling-mechanical joint is a wire rope sling made from a cable laid rope with eyes fabricated by pressing or swaging one or more metal sleeves over the rope junction.
Master link or gathering ring is a forged or welded steel link used to support all members (legs) of an alloy steel chain sling or wire rope sling. (See Fig. N-184-3.)
Diagram indicates Forms of Hitch and Kind of Sling. Eye&Eye Vertical Hitch. Eye&Eye Choker Hitch. Eye&Eye Basket Hitch (Alterates have identical load rations). Endless Vertical Hitch. Endless Choker Hitch. Endless Basket Hitch (Alternateve have identical load ratings). Notes: Angles 5 deg or less from the veritcal may be considered vertical angles. For slings with legs more than 5 deg off vertical, the actual angle as shown in Figure N-184-5 must be considered. Explanation of Symbols: Minimum Diameter of Curvature. Represents a contact surface which shall have a diameter of curvature at least double the diameter of the rope from which the sling is made. Represents a contact surface which shall have a diameter of curvature at least 8 times the diameter of the rope. Represents a load in a choker hitch and illustrates the rotary force on the load and/or the slippage of the rope in contact with the load. Diameter of curvature of load surface shall be at least double the diameter of the rope.
Strand laid endless sling-mechanical joint is a wire rope sling made endless from one length of rope with the ends joined by one or more metallic fittings.
Strand laid grommet-hand tucked is an endless wire rope sling made from one length of strand wrapped six times around a core formed by hand tucking the ends of the strand inside the six wraps.
Strand laid rope is a wire rope made with strands (usually six or eight) wrapped around a fiber core, wire strand core, or independent wire rope core (IWRC).
Sling use. Employers must use only wire-rope slings that have permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer, and that indicate the recommended safe working load for the type(s) of hitch(es) used, the angle upon which it is based, and the number of legs if more than one.
Cable laid and 6 × 19 and 6 × 37 slings shall have a minimum clear length of wire rope 10 times the component rope diameter between splices, sleeves or end fittings.
Safe operating temperatures. Fiber core wire rope slings of all grades shall be permanently removed from service if they are exposed to temperatures in excess of 200 °F. When nonfiber core wire rope slings of any grade are used at temperatures above 400 °F or below minus 60 °F, recommendations of the sling manufacturer regarding use at that temperature shall be followed.
Sling use. Employers must use natural and synthetic fiber-rope slings that have permanently affixed and legible identification markings stating the rated capacity for the type(s) of hitch(es) used and the angle upon which it is based, type of fiber material, and the number of legs if more than one.
Safe operating temperatures. Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings, except for wet frozen slings, may be used in a temperature range from minus 20 °F to plus 180 °F without decreasing the working load limit. For operations outside this temperature range and for wet frozen slings, the sling manufacturer"s recommendations shall be followed.
Splicing. Spliced fiber rope slings shall not be used unless they have been spliced in accordance with the following minimum requirements and in accordance with any additional recommendations of the manufacturer:
In manila rope, eye splices shall consist of at least three full tucks, and short splices shall consist of at least six full tucks, three on each side of the splice center line.
In synthetic fiber rope, eye splices shall consist of at least four full tucks, and short splices shall consist of at least eight full tucks, four on each side of the center line.
Strand end tails shall not be trimmed flush with the surface of the rope immediately adjacent to the full tucks. This applies to all types of fiber rope and both eye and short splices. For fiber rope under one inch in diameter, the tail shall project at least six rope diameters beyond the last full tuck. For fiber rope one inch in diameter and larger, the tail shall project at least six inches beyond the last full tuck. Where a projecting tail interferes with the use of the sling, the tail shall be tapered and spliced into the body of the rope using at least two additional tucks (which will require a tail length of approximately six rope diameters beyond the last full tuck).
Removal from service. Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings shall be immediately removed from service if any of the following conditions are present:

On December 23, 2003, Employee #1 was working as contracted maintenance craftsman performing a scheduled wash-up of a Tri-Nip paper press. Employee #1 secured the blind drill roll to the underside of the press roll loading arm. The roll, weighing 23,000 lbs, was suspended from a 15-ton Acco Louden bridge crane, using a 0.625-inch wire rope that was attached to a 20.50-foot spanner bar. The spanner bar weighed 2,000 lbs and supported each end of the blind drill roll. With the roll partially secured, the shank ball end of the 0.625-inch wire rope failed and the spanner bar fell forward. Employee #1 attempted to avoid the spanner bar by jumping backwards. He fell to the platform below injuring his back. Employee #1 was hospitalized at Saint Francis Hospital in Lynwood, where he was treated for a fracture to his lower vertebrae and a head laceration. He was released seven days later. A detailed investigation determined that despite the crane having been inspected by CranePro less than two months before and a new cable installed, the fractured shank ball was undersized, measuring 16 inches less in diameter than required. Additionally, the wire of the failed shank did not run all the way through the shank ball assembly. .

On April 12, 2005, an employee and two coworkers were waiting on the seventh floor for the bucket elevator to arrive. One employee bent over the top rail (wire rope) of the guardrail system to look to see where the elevator was. When the employee put his hands on the top rail and leaned against the wire rope, it loosened from its end connections, and the employee fell approximately 61 ft to his death. Employees from another company (Roy Anderson Corp.) had incorrectly secured the ends of the wire rope rails to their anchor points. The wire rope rail was not capable of withstanding the force of a man (weighing approximately 200 lbs) leaning against it. The employees who erected the wire rope guardrail system were not experienced in erecting it.
Original equipment wire rope and replacement wire rope must be selected and installed in accordance with the requirements of this section. Selection of replacement wire rope must be in accordance with the recommendations of the wire rope manufacturer, the equipment manufacturer, or a qualified person.
Wire rope design criteria: Wire rope (other than rotation resistant rope) must comply with either Option (1) or Option (2) of this section, as follows:
Option (1). Wire rope must comply with section 5-1.7.1 of ASME B30.5-2004 (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that section"s paragraph (c) must not apply.
Option (2). Wire rope must be designed to have, in relation to the equipment"s rated capacity, a sufficient minimum breaking force and design factor so that compliance with the applicable inspection provisions in § 1926.1413 will be an effective means of preventing sudden rope failure.
Type I rotation resistant wire rope ("Type I"). Type I rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have little or no tendency to rotate or, if guided, transmits little or no torque. It has at least 15 outer strands and comprises an assembly of at least three layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type II rotation resistant wire rope ("Type II"). Type II rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have significant resistance to rotation. It has at least 10 outer strands and comprises an assembly of two or more layers of strands laid helically over a center in two or three operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type III rotation resistant wire rope ("Type III"). Type III rotation resistant rope is stranded rope constructed to have limited resistance to rotation. It has no more than nine outer strands, and comprises an assembly of two layers of strands laid helically over a center in two operations. The direction of lay of the outer strands is opposite to that of the underlying layer.
Type I must have an operating design factor of no less than 5, except where the wire rope manufacturer and the equipment manufacturer approves the design factor, in writing.
A qualified person must inspect the rope in accordance with § 1926.1413(a). The rope must be used only if the qualified person determines that there are no deficiencies constituting a hazard. In making this determination, more than one broken wire in any one rope lay must be considered a hazard.
Each lift made under § 1926.1414(e)(3) must be recorded in the monthly and annual inspection documents. Such prior uses must be considered by the qualified person in determining whether to use the rope again.
Rotation resistant ropes may be used as boom hoist reeving when load hoists are used as boom hoists for attachments such as luffing attachments or boom and mast attachment systems. Under these conditions, all of the following requirements must be met:
The requirements in ASME B30.5-2004 sections 5-1.3.2(a), (a)(2) through (a)(4), (b) and (d) (incorporated by reference, see § 1926.6) except that the minimum pitch diameter for sheaves used in multiple rope reeving is 18 times the nominal diameter of the rope used (instead of the value of 16 specified in section 5-1.3.2(d)).
The operating design factor for these ropes must be the total minimum breaking force of all parts of rope in the system divided by the load imposed on the rope system when supporting the static weights of the structure and the load within the equipment"s rated capacity.
Wire rope clips used in conjunction with wedge sockets must be attached to the unloaded dead end of the rope only, except that the use of devices specifically designed for dead-ending rope in a wedge socket is permitted.
Prior to cutting a wire rope, seizings must be placed on each side of the point to be cut. The length and number of seizings must be in accordance with the wire rope manufacturer"s instructions.

In 1998, a crane load line broke while lifting the south topside module of the Petronius platform, dropping the module into the Gulf of Mexico. The cost was estimated to be around 116 million US dollars. Since 1999 more than 60 people have been killed as a result of wire ropes breaking and more than 65 associated injuries.
Not many people appreciate that there are literally thousands of wire rope designs, most of which can be put into a specific category. According to BS ISO 4309 2010 there are currently more than 25 categories of crane wire rope, each with differing characteristics and also different discard criteria. Deterioration can be measured, counted or calculated and the wire rope eventually taken out of service based on sophisticated discard criteria published in chosen standards, codes of practice or users handbooks.
Unfortunately there is no simple answer to either of these questions. All wire ropes will eventually break due to corrosion, wear or fatigue even if they are maintained and used properly. Unpredictable wire rope failures will inevitably occur, quite often when you least expect it if the discard criteria is ignored, or those using the equipment are ignorant of it.
James Dawes of Topeka, Illinois, was killed in 2008 after being struck by the boom of a Link-Belt crane; the accident was caused by the boom hoist wire rope breaking. The crane rope had been inspected, but a report said that the inspector failed to reject the rope showing a high number of visible wire breaks. Premature or unexpected wire rope failures can also be attributed to poor manufacture, incorrect handling and storage, poor installation technique, poor selection or fitting of its termination, infrequent or inadequate inspection and poor maintenance. Of course there is always the possibility that mechanical damage can occur and this is usually attributed to human error.
It is necessary, particularly during offshore operations that frequent inspections are carried out over the whole length of the working part of all steel wire ropes. The frequency of inspections should be based on the severity of use and risk assessment and particular attention should be paid to the critical areas of the wire rope; areas that are frequently running over sheaves, compensating sheaves and the rope termination to name a few.
If a wire rope has not been subjected to an abnormal environmental condition such as excessive heat, chemical attack or any corrosive solution and it has not been the victim of any form of mechanical damage, then trained operatives and inspectors can reasonably predict the length of time the steel wire rope is likely to last. That prediction, of course, will be dependent on the knowledge and experience of those making it coupled with known facts about the rope, its current condition and the application it is running on. The Inspector should be aware of the previous rope’s history, capacities of loads and the reeving systems employed together with the frequency of use etc.
Various standards and codes of practice have been written by recognized bodies and institutes based on the experience of experts or representatives of corporate organizations who have a vested interest. These standards do offer guidance on when a wire rope should be removed from service based on wear, abrasion and fatigue amongst others things, but none of these standards have any legal status except when they are called up by contract. Indeed they can all be supported or overturned in a court of law by an expert.
The users handbook, or more importantly the safe use instructions do have legal status. In many parts of the world these days, suppliers of cranes or any machinery for that matter, issue safe use instructions with new equipment. Modern applications employ modern wire rope and, in some cases, sheaves and pulleys that are made with materials other than steel. Original equipment manufacturers of such applications may impose discard criteria for the wire rope that is stricter than those in chosen standards. By law the user must follow manufacturers’ instructions.
Wire ropes will deteriorate much more quickly if they go dry and are allowed to remain in that condition. Tests have proven that a dry rope will lose up to 60 % of its expected life if it is not re-lubricated. There are differing schools of thought as to how wire rope should be lubricated. Some believe that a thin lubricant should be applied using a paintbrush. It is thought that this method allows the lubricant to penetrate. Experience has proven however, that thin penetrative lubricants will easily drain away or fly off in hot climates.
Another school of thought, and the one I stand on, is that grease should be pressure lubricated into the rope. This method, if applied properly, will ensure that the grease penetrates the rope pushing out the old lubricant with it and any possible corrosive agents such as salt water and sand. Any lubricant that is used must be compatible with the type that was applied previously and it is a good idea to consider the environment as well.
In any event, wire ropes usually announce that they are about to break. A series of individual wire breaks can be heard. These are likely to go on over several seconds and continuing for up to ten minutes before ultimate failure. Therefore, if operatives understand the warning signals, expensive incidents could be avoided.
Figure 2 shows two pieces of the same rope, the bottom portion quite clearly shows a progression of wire breaks. The operator was able to put the load down before disaster struck. The root cause of this fault was core deterioration brought about by internal corrosion.
To answer the other question on accountability, the list is extensive. Usually the first suspect is the wire rope manufacturer and that may be where the problem lies, but very often that is not the case. What if you were supplied the wrong rope for the application? Maybe you ordered the wrong rope or your buyer bought it from a cheap unapproved manufacturing source.
Perhaps your supplier is responsible, maybe he provided you with a rope that was produced to the wrong specifications. Would you know the difference? Perhaps you were sold a rope that had been stored in the suppliers or manufactures stock for a number of years and, whilst it was there, it hadn’t been properly maintained. Maybe the rope had been badly handled or installed incorrectly. The list of possibilities is endless.
In 1999 a ropeway in the French Alps snapped causing 21 deaths. In 2003, a ropeway wire rope snapped and 7 people died and a further 42 were injured. In 2007 a crane wire rope snapped at New Delhi’s metro, the entire structure tumbled down crushing workers underneath, six people were killed and 13 more were injured. In 2009 26 people were killed and 5 people were injured when a rope failed in a mine and a further 6 people were injured when a lift rope broke inside London’s Tower Bridge.
If you find yourself in the unfortunate situation after the unthinkable premature failure of a wire rope, then you might like to know that there are independent analytical services capable of determining probable cause. One of these is Doncaster Analytical Services Ltd (DAS), they have an independent metallurgical laboratory providing factual analysis and testing of wire rope for any reason (contact Mr Shui Lee, Technical Director, Tel +44(0)1302 556063, email: shui.lee@doncasteranalyticalservices. com).
You do not need a wire rope to fail in order to learn. Careful analysis of discarded ropes can also give you valuable information about your application, the way it operates, and the rope you have been using.
Based on this information, a trained, skilled and experienced inspector will be able to advise on a better crane or wire rope design, or to an improvement in maintenance procedures and safety.

Any wire rope in use should be inspected on a regular basis. You have too much at stake in lives and equipment to ignore thorough examination of the rope at prescribed intervals.
The purpose of inspection is to accurately estimate the service life and strength remaining in a rope so that maximum service can be had within the limits of safety. Results of the inspection should be recorded to provide a history of rope performance on a particular job.
On most jobs wire rope must be replaced before there is any risk of failure. A rope broken in service can destroy machinery and curtail production. It can also kill.
Because of the great responsibility involved in ensuring safe rigging on equipment, the person assigned to inspect should know wire rope and its operation thoroughly. Inspections should be made periodically and before each use, and the results recorded.
When inspecting the rope, the condition of the drum, sheaves, guards, cable clamps and other end fittings should be noted. The condition of these parts affects rope wear: any defects detected should be repaired.
To ensure rope soundness between inspections, all workers should participate. The operator can be most helpful by watching the ropes under his control. If any accident involving the ropes occurs, the operator should immediately shut down his equipment and report the accident to his supervisor. The equipment should be inspected before resuming operation.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act has made periodic inspection mandatory for most wire rope applications. If you need help locating the regulations that apply to your application, please give our rigging experts a call.

Do you know who is supposed to be inspecting your lifting slings? More importantly, do you know how often they’re inspecting them? OSHA and ASME have different inspection requirements, frequencies, and removal criteria for each type of sling—including alloy chain slings, synthetic slings, metal mesh slings, and wire rope slings.
In this article, our goal is to help you understand what is required to inspect wire rope slings to meet ASME standards, which in turn, will help to ensure the safety of the users,help extend the service life of the slings, and help reduce unnecessary equipment repair costs and loss of production due to equipment downtime.
As a starting point, the same work practices which apply to all “working” wire rope apply to wire rope which has been fabricated into a sling. Therefore, a good working knowledge of wire rope design and construction will not only be useful, but essential in conducting a wire rope sling inspection.
There are two industry standards that exist to provide the end-user with guidelines for inspection and criteria that warrants removal from service: OSHA 1910.184 and ASME B30.9.
Initial Inspection (prior to initial use): Best practice is to inspect the wire rope sling upon receiving it from the manufacturer. Double-check the sling tag to make sure it’s what you ordered and that the rated capacity meets all of your project specifications and lifting requirements.
Frequent (daily or prior to use): Designate a Competent Person to perform a daily visual inspection of slings and all fastenings and attachments for damage, defects, or deformities. The inspector should also make sure that the wire rope sling that was selected meets the specific job requirements it’s being used for.
Users can’t rely on a once-a-day inspection if the wire rope sling is used multiple times throughout the day. Damage to wire rope can occur on one lift and best practice is to perform a visual inspection before any shift change or changes in lifting application. Because shock loads, severe angles, sharp edges, and excessive heat can quickly cause damage to a lifting sling, the user should inspect the sling prior to each lift.
Depending on the severity of the operating environment and frequency of use, your business may decide to inspect wire rope slings more often than the minimum yearly requirement.
Per ASME B30.9, the wire rope sling tag on all new slings shall be marked by the manufacturer to include:Rated load for the types of hitches (single-leg vertical, choker, and basket) and the angle upon which they are based
The goal of a sling inspection is to evaluate remaining strength in a sling which has been used previously to determine if it is suitable for continued use. When inspecting wire rope slings, daily visual inspections are intended to detect serious damage or deterioration which would weaken the sling.
This inspection is usually performed by the person using the sling in a day-to-day job. The user should look for obvious things, such as broken wires, kinks, crushing, broken attachments, severe corrosion, etc. Any deterioration of the sling which could result in appreciable loss of original strength should be carefully noted and determination made on whether further use would constitute a safety hazard.
2. Broken Wires: For strand-laid grommets and single-part slings, ten randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay, or five broken wires in one strand in one rope lay. For cable laid, cable laid grommets and multi-part slings, use the following:
3. Distortion: Kinking, crushing, birdcaging or other damage which distorts the rope structure. The main thing to look for is wires or strands that are pushed out of their original positions in the rope.
7. Corrosion: Severe corrosion of the rope or end attachments which has caused pitting or binding of wires should be cause for replacing the sling. Light surface rust does not substantially affect strength of a sling.
9. Unbalance:A very common cause of damage is the kink which results from pulling through a loop while using a sling, thus causing wires and strands to be deformed and pushed out of their original position. This unbalances the sling, reducing its strength.
10. Kinks: Are tightened loops with permanent strand distortion that result from improper handling when a rope is being installed or while in service. A kink happens when a loop is permitted to form and then is pulled down tight, causing permanent distortion of the strands. The damage is irreparable and the sling must be taken out of service.
11. Doglegs: Are permanent bends caused by improper use or handling. If the dogleg is severe, the sling must be removed from service. If the dogleg is minor, (exhibiting no strand distortion) and cannot be observed when the sling is under tension, the area of the minor dogleg should be marked for observation and the sling can remain in service.
The best lifting and rigging inspection program is of no value if slings, which are worn out and have been retired, are not properly disposed of. When it is determined by the inspector that a sling is worn out or damaged beyond use, it should be tagged immediately DO NOT USE.
If it’s determined that the wire rope will be removed from service, we suggest cutting it down into more manageable sizes before discarding. This extra effort will help to accommodate the needs of most recycling facilities that will accept the damaged wire rope and also help to make sure that it cannot be used any further. Keep the following in mind when disposing of wire rope slings and wire rope cable:Cut into approximately 3’ to 4’ sections
OSHA does not provide clear guidelines on how to properly and adequately inspect wire rope slings. It is up to the designated inspection personnel to know the requirements of the sling inspection standards, and to develop a comprehensive inspection protocol. Wire rope inspection should follow a systematic procedure:First, it is necessary that all parts of the sling are readily visible. The sling should be laid out so every part is accessible.
Next, the sling should be sufficiently cleaned of dirt and grease so wires and fittings are easily seen. This can usually be accomplished with a wire brush or rags.
The best way to help extend the life of a wire rope sling, and help to ensure that it stays in service, is to properly maintain it during and in-between each use. Inspections are easier to perform—and probably more thorough—when slings are easily accessible and organized, kept off of the ground, and stored in a cool and dry environment.Hang slings in a designated area where they are off of the ground and will not be subjected to mechanical damage, corrosive action, moisture, extreme temperatures, or to kinking.
Like any other machine, wire rope is thoroughly lubricated at time of manufacture. Normally, for sling use under ordinary conditions, no additional lubrication is required. However, if a sling is stored outside or in an environment which would cause corrosion, lubrication should be applied during the service life to prevent rusting or corroding.
If lubrication is indicated, the same type of lubrication applied during the manufacturing process should be used. Your sling manufacturer can provide information on the type of lubricant to be used and provide the best method of application. We recommend a wire rope lubricant that is designed to penetrate and adhere to the wire rope core.
Proper inspection of your wire rope slings for damage or irregularities, prior to each use, is the best way to help keep everybody on the job site safe. Keep in mind that you’re planning to lift valuable and expensive equipment, and if a failure were to occur, it would not only cause unnecessary equipment repair costs and costly downtime, but also potentially jeopardize the lives of workers on site.
At Mazzella, we offer a variety of services including site assessments, rigging and crane operator training, sling inspection and repairs, overhead crane inspections and so much more. Our rigging inspection program is its own dedicated business unit with a team of inspectors that are certified through Industrial Training International to meet OSHA 1910.184 and ASME B30.9 requirements for sling inspection.

Before the beginning of each shift, check for hooks that are bent, permanently stretched, twisted, or otherwise damaged. This type of damage to a hook can lead to an improperly balanced load and, eventually, the beginning of a crack or break. And that isn’t the only reason why damaged hooks are dangerous. For example, in the case of sling hooks, a stretched hook can cause the hook to be separated from the latch, and it won’t be able to balance and hold load or keep it secure. Any time that a load isn’t properly balanced on a hook it can lead to further problems.
If your wire rope is frayed, it needs to be replaced. According to OSHA, damage to just one strand in a rope can lead to breakage and then cascade failure of other strands. And degradation can be caused by various things, including load cycles, lubrication, chemical exposure, and weather exposure. Wire ropes also fail from the inside, so the rope could be seriously compromised by the time you see the damage.
And don’t forget that wire rope needs to be lubricated. Lubrication performs two essential tasks: it enables the individual wires to move smoothly over each other and protect the wires from corrosion (which we just discussed as a potential issue with frayed ropes). And while lubricant is applied when the rope is manufactured, it must be reapplied because bending, stretching, and loading will cause it to dissipate.
Let’s face it: rust can be very damaging. It will cause steel to deteriorate, which can eventually affect the load capacity of your crane. And when that happens, just a small, corroded bolt could lead to serious injury for someone in your facility. Even a small area of rust can lead to a significant failure and may indicate that other crane parts are also corroding.
And don’t forget that the inside of your wire ropes could be corroded — which is why signs of corrosion can point to other hazardous issues. You might not see the corrosion within the wire rope, but you might see it on nearby parts. So, make sure to check joints, bearings, wires, and any moving parts for signs of rust.
Let’s discuss why you should be proactive about your crane. Let’s start with the ability to prevent catastrophic failures: by spotting a bent hook you can prevent a dropped load which could damage the cargo and nearby equipment and put your employees at risk. And preventing these kinds of failures can lead to less downtime and higher productivity, both of which translate into lost profit.
Addressing smaller issues before they become catastrophic failures contributes to productivity and reduced repair costs while minimizing the downtime of your crane. And this also contributes to better maintenance of your equipment which in turn leads to better performance.
Hi-Speed Industrial Service provides the inspection, maintenance, and repair services you need. Our inspection services are performed in accordance with OSHA 1910.179 and ASME/ANSI B30.2 — and we can even train your staff to perform them. We also offer predictive maintenance programs for cranes and can customize these programs to meet the needs of your facility. Finally, we offer 24/7 emergency repair services performed by highly trained, extensively experienced technicians. Contact us today to learn more.

Removal criteria for wire rope, wire rope slings, synthetic web/round slings, chain slings, rigging hardware, and below-the-hook lifting devices is the focus here. Personnel qualification is available.




 8613371530291
8613371530291