what is kelly bushing in stock
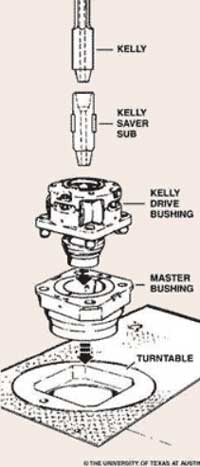
Kelly bushing is that elevated device positioned right on top of the rotary table and used to transmit torque from the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing is designed to be the connection between the rotary table and the kelly. The kelly is a 4 or 6 sided steel pipe.
The purpose of the rotary table is to generate the rotary action (torque) and power necessary to rotate the drillstring and drill a well. The torque generated by the rotary table is useless if it is not transferred to the kelly (the drillstring is connected to the kelly).
Hence, through the kelly bushing the torque generated at the rotary table is transferred to the kelly. To achieve this connection, the inside profile of the kelly bushing matches the outer profile of the kelly so that the kelly fits or “sits” comfortably in the kelly bushing.
There are various designs for the kelly bushing including the split type, the pin-drive type and the square-drive type. Each of these designs has different ways in which they are connected and disconnected from the rotary table.
The internal diameter of the kelly bushing can be cut into the shape of a square (4-sided) or a hexagon (6-sided) depending on the outer shape of the kelly that will be used. The internals of a Kelly bushing is designed to resemble the outer shape of a Kelly just like the insides of a key lock is cut to exactly match the outer shape of the key.
The kelly bushing is not designed to hold tightly onto the Kelly; the kelly is still permitted to move up and down through the kelly bushing. This requirement is a must since drilling cannot progress if the kelly remains on a fixed spot. As the well is drilled deeper, the kelly also moves downward through the Kelly bushing.
The kelly bushing is sometimes used as a reference point from which depth measurements can be taken. All depths must be recorded with respect to a reference point; the kelly bushing (KB) is one of the depth references used in the oil and gas industry.
The top of the kelly bushing is normally used as the depth reference.For example, 7500ft KB means 7500ft below the kelly bushing or 7500ft measured from the top of the kelly bushing down to that point in the well.
In some other cases, depths could be recorded as 7500ft MDBKB meaning 7500ft measured depth below the kelly bushing. This is mostly used when the measured depth is different from the true vertical depth of the well, common with deviated and horizontal wells.

An adapter that serves to connect the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing has an inside diameter profile that matches that of the kelly, usually square or hexagonal. It is connected to the rotary table by four large steel pins that fit into mating holes in the rotary table. The rotary motion from the rotary table is transmitted to the bushing through the pins, and then to the kelly itself through the square or hexagonal flat surfaces between the kelly and the kelly bushing. The kelly then turns the entire drillstring because it is screwed into the top of the drillstring itself. Depth measurements are commonly referenced to the KB, such as 8327 ft KB, meaning 8327 feet below the kelly bushing.

This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience.

This is the brief explanation of a Kelly rotating system on the rig. Kelly rig is on an old style rigs and nowadays it is mostly used on land operations. For offshore operation, a top drive system is used instead.
First of all, it is important for new people to look at these images before reading the information below because they show the equipment’s name and where they are on the rig.
The upper end of the drill pipe is screwed onto the saver sub. The saver sub is used to protect and minimize wearr and tear on the threads at the bottom of the Kelly. The Kelly is about 40 ft in length with a square or hexagonal shape and it is hollow throughout in order to transport the drilling mud. Kelly moves freely through a Kelly bushing even though the drill stem is rotated.
A Kelly cock valve is located at the top of a Kelly and it is a safety valve which can be closed to stop back pressure from coming back to damage other surface equipment.
A swivel attached to the hook does not rotate, but at the bottom part it supports the Kelly which is being rotated while drilling. Drilling mud is pumped from a mud pump to a stand pipe manifold, Kelly hose and then to a gooseneck connection at a swivel.
A rotary table rotates a Kelly bushing and it simultaneously rotates a Kelly and a drill string and a drill bit. A rotary table has two main functions. The first one is to provide rotation to a drill stem and a bit and the second function is to hold slip in order to support the weight of a drill stem when it is not connected to a Kelly.
Generally, a rotary drive consists of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket. A rotary-drive sprocket is a part of the draw-works. In other rig power systems, an independent electric motor or engine with a direct drive to a rotary table is utilized. For this case, the rotary is normally driven by a drive shaft instead of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket.
A master bushing severs its function as a rotary motion transmission from a rotary table to a Kelly. Additionally, it is a link between a slip and a rotary table.
A Kelly bushing (some people call “rotary Kelly bushing”) engages a master bushing via four pins and rollers inside a Kelly bushing to allow a Kelly to move up or down freely while it is rotated or in a static mode.

The kelly provides a connection between the rotary table, also called the kelly bushing, to the drill string that allows the drill string to turn around its longitudinal axis and move up and down along its length. The hole in the kelly is matched by a hole in the kelly bushing that allows for the passage of drilling fluid into the bore. A kelly is used in fluid or oil assisted bore projects.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Jiangsu Xinxiang share Co., Ltd was founded in 1994, its predecessor was established in 1955, it‘s located in high-tech industrial concentration zone of Nantong City, Jiangsu Province; near to a new developing international deep-water port Yangkou Port which commitment to ship 200,000 tons goods; world famous modern city Shanghai is only 2.5 hours away from it by car; company registered capital is 60,000,000 RMB, the total assets is 119.85 million RMB, it covers an area of 160,000 square meters and currently over 500 employees. Jiangsu Xinxiang Share Co., Ltd is "self-import and export enterprise", "private technology enterprises in Jiangsu Province", "high-tech enterprises in Jiangsu Province", it is top ten companies of the first national large and medium-sized industrial enterprises in independent innovation capacity of the industry; it accessed to API7, 7K, 8A, 8C, and has the right to use the logo, and also passed the ISO9001:2000 quality system certification in the earlier stage within the same industry.

In the oil and gas industry, depth in a well is the measurement, for any point in that well, of the distance between a reference point or elevation, and that point. It is the most common method of reference for locations in the well, and therefore, in oil industry speech, “depth” also refers to the location itself.
Because wells are not always drilled vertically, there may be two “depths” for every given point in a wellbore: the measured depth (MD) measured along the path of the borehole, and the true vertical depth (TVD), the absolute vertical distance between the datum and the point in the wellbore. In perfectly vertical wells, the TVD equals the MD; otherwise, the TVD is less than the MD measured from the same datum. Common datums used are ground level (GL), drilling rig floor (DF), rotary table (RT), kelly bushing (KB) and mean sea level (MSL). [1]
Kelly Bushing Height (KB):The height of the drilling floor above the ground level. Many wellbore depth measurements are taken from the Kelly Bushing. The Kelly bushing elevation is calculated by adding the ground level to the Kelly bushing height.
Driller’s Depth below rotary table (DDbrt): The depth of a well or features within the wellbore as measured while drilling. The measured length of each joint of drillpipe or tubing is added to provide a total depth or measurement to the point of interest. Drillers depth is the first depth measurement of a wellbore and is taken from the rotary table level on the rig floor. In most cases, subsequent depth measurements, such as those made during the well completion phase, are corrected to the wellhead datum that is based on drillers depth (reference: Schlumberger Oilfield Glossary).
Although depth calculation is an intuitive concept, it is the source of much confusion because it is frequently not specified correctly. Absolute depth should always be specified with three components:
True vertical depth is obtained from a record of the deviation survey report. These surveys are generally run on deviated wellbores. It records measured depth (MD), inclination (deviation angle), azimuth angle, true vertical depth, and dogleg severity at various increments. To obtain a TVD, simply obtain a measured depth, go to the survey, and read off the TVD. If the desired measured depth is not in the survey, then extrapolate between the two closest points.
NB: Inclination is taken to be the angle of the well course from the vertical. Azimuth is taken clockwise from geographic north. In other words, the inclination angle measures the vertical direction and the azimuthal angle examines the horizontal direction.

Bushing that rotationally connects the rotary table to the drill string kelly bar, the top of which is commonly used as vertical reference for the drill floor.
Source: API Specification 16Q, Design, Selection, Operation, and Maintenance of Marine Drilling Riser Systems, Second Edition, April 2017. Global Standards
Source: ISO 13624-1:2009, Petroleum and natural gas industries – Drilling and production equipment – Part 1:Design and operation of marine drilling riser equipment. Global Standards

The IADC Lexicon is © IADC. However, the documents from which the definitions were drawn may be copyrighted by the original sources, and may not be used without express permission of the copyright holders. IADC expressly recognizes the copyrights of contributors to this Lexicon, including API, OGP, ISO, NORSOK and DNV.

A large valve, usually installed above the ram preventers, that forms a seal in the annular space between the pipe and well bore. If no pipe is present, it forms a seal on the well bore itself. See blowout preventer.†
A blowout preventer that uses rams to seal off pressure on a hole that is with or without pipe. It is also called a ram preventer. Ram-type preventers have interchangeable ram blocks to accommodate different O.D. drill pipe, casing, or tubing.†
A pit in the ground to provide additional height between the rig floor and the well head to accommodate the installation of blowout preventers, ratholes, mouseholes, and so forth. It also collects drainage water and other fluids for disposal.†
The arrangement of piping and special valves, called chokes, through which drilling mud is circulated when the blowout preventers are closed to control the pressures encountered during a kick.†
A centrifugal device for removing sand from drilling fluid to prevent abrasion of the pumps. It may be operated mechanically or by a fast-moving stream of fluid inside a special cone-shaped vessel, in which case it is sometimes called a hydrocyclone.†
A centrifugal device, similar to a desander, used to remove very fine particles, or silt, from drilling fluid. This keeps the amount of solids in the fluid to the lowest possible level.†
The hoisting mechanism on a drilling rig. It is essentially a large winch that spools off or takes in the drilling line and thus raises or lowers the drill stem and bit.†
The cutting or boring element used in drilling oil and gas wells. Most bits used in rotary drilling are roller-cone bits. The bit consists of the cutting elements and the circulating element. The circulating element permits the passage of drilling fluid and uses the hydraulic force of the fluid stream to improve drilling rates.†
A heavy, thick-walled tube, usually steel, used between the drill pipe and the bit in the drill stem. It is used to put weight on the bit so that the bit can drill.†
A wire rope hoisting line, reeved on sheaves of the crown block and traveling block (in effect a block and tackle). Its primary purpose is to hoist or lower drill pipe or casing from or into a well. Also, a wire rope used to support the drilling tools.†
On diesel electric rigs, powerful diesel engines drive large electric generators. The generators produce electricity that flows through cables to electric switches and control equipment enclosed in a control cabinet or panel. Electricity is fed to electric motors via the panel.†
A large, hook-shaped device from which the elevator bails or the swivel is suspended. It is designed to carry maximum loads ranging from 100 to 650 tons and turns on bearings in its supporting housing.†
The heavy square or hexagonal steel member suspended from the swivel through the rotary table. It is connected to the topmost joint of drill pipe to turn the drill stem as the rotary table turns.†
A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
A portable derrick capable of being erected as a unit, as distinguished from a standard derrick, which cannot be raised to a working position as a unit.†
A series of open tanks, usually made of steel plates, through which the drilling mud is cycled to allow sand and sediments to settle out. Additives are mixed with the mud in the pit, and the fluid is temporarily stored there before being pumped back into the well. Mud pit compartments are also called shaker pits, settling pits, and suction pits, depending on their main purpose.†
A diesel, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), natural gas, or gasoline engine, along with a mechanical transmission and generator for producing power for the drilling rig. Newer rigs use electric generators to power electric motors on the other parts of the rig.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
A series of trays with sieves or screens that vibrate to remove cuttings from circulating fluid in rotary drilling operations. The size of the openings in the sieve is selected to match the size of the solids in the drilling fluid and the anticipated size of cuttings. Also called a shaker.†
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
A relatively short length of chain attached to the tong pull chain on the manual tongs used to make up drill pipe. The spinning chain is attached to the pull chain so that a crew member can wrap the spinning chain several times around the tool joint box of a joint of drill pipe suspended in the rotary table. After crew members stab the pin of another tool joint into the box end, one of them then grasps the end of the spinning chain and with a rapid upward motion of the wrist "throws the spinning chain"-that is, causes it to unwrap from the box and coil upward onto the body of the joint stabbed into the box. The driller then actuates the makeup cathead to pull the chain off of the pipe body, which causes the pipe to spin and thus the pin threads to spin into the box.†
A vertical pipe rising along the side of the derrick or mast. It joins the discharge line leading from the mud pump to the rotary hose and through which mud is pumped going into the hole.†
A rotary tool that is hung from the rotary hook and traveling block to suspend and permit free rotation of the drill stem. It also provides a connection for the rotary hose and a passageway for the flow of drilling fluid into the drill stem.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

Buyer acknowledges and agrees that all equipment / parts are sold as is / where is without guarantee or warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied.

Buyer acknowledges and agrees that all equipment / parts are sold as is / where is without guarantee or warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

A kelly drive is a type of well drilling device on an oil or gas drilling rig that employs a section of pipe with a polygonal (three-, four-, six-, or eight-sided) or splined outer surface, which passes through the matching polygonal or splined kelly (mating) bushing and rotary table. This bushing is rotated via the rotary table and thus the pipe and the attached drill string turn while the polygonal pipe is free to slide vertically in the bushing as the bit digs the well deeper. When drilling, the drill bit is attached at the end of the drill string and thus the kelly drive provides the means to turn the bit (assuming that a downhole motor is not being used).
The kelly is the polygonal tubing and the kelly bushing is the mechanical device that turns the kelly when rotated by the rotary table. Together they are referred to as a kelly drive. The upper end of the kelly is screwed into the swivel, using a left-hand thread to preclude loosening from the right-hand torque applied below. The kelly typically is about 10 ft (3 m) longer than the drill pipe segments, thus leaving a portion of newly drilled hole open below the bit after a new length of pipe has been added ("making a connection") and the drill string has been lowered until the kelly bushing engages again in the rotary table.
The kelly hose is the flexible, high-pressure hose connected from the standpipe to a gooseneck pipe on a swivel above the kelly and allows the free vertical movement of the kelly while facilitating the flow of the drilling fluid down the drill string. It generally is of steel-reinforced rubber construction but also assemblies of Chiksan steel pipe and swivels are used.
The kelly is below the swivel. It is a pipe with either four or six flat sides. A rotary bushing fits around the flat sides to provide the torque needed to turn the kelly and the drill string. Rollers in the bushing permit the kelly free movement vertically while rotating. Since kelly threads would be difficult to replace, normally the lower end of the kelly has saver sub — or a short piece of pipe — that can be refurbished more cheaply than the kelly. Usually, a ball valve, called the lower kelly cock, is positioned between the kelly and the kelly saver sub. This valve is used for well control if the surface pressure becomes too high for the rotary hose or surface conditions.
According to the ″Dictionary of Petroleum Exploration, Drilling and Production″, ″[The] kelly was named after Michael J. (King) Kelly, a Chicago baseball player (1880-1887) who was known for his base running and long slides.″

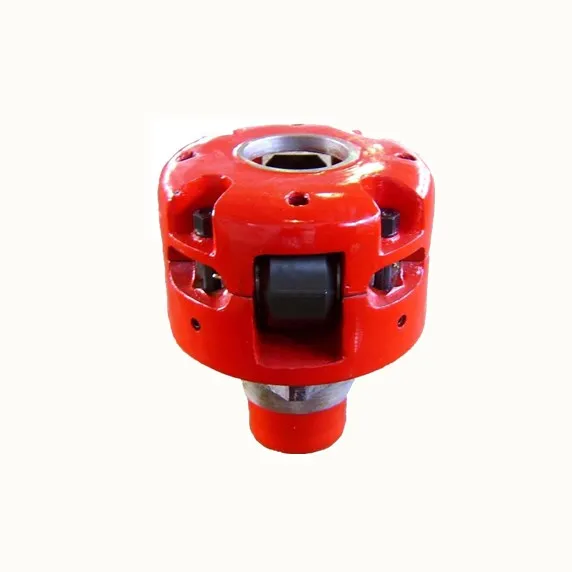
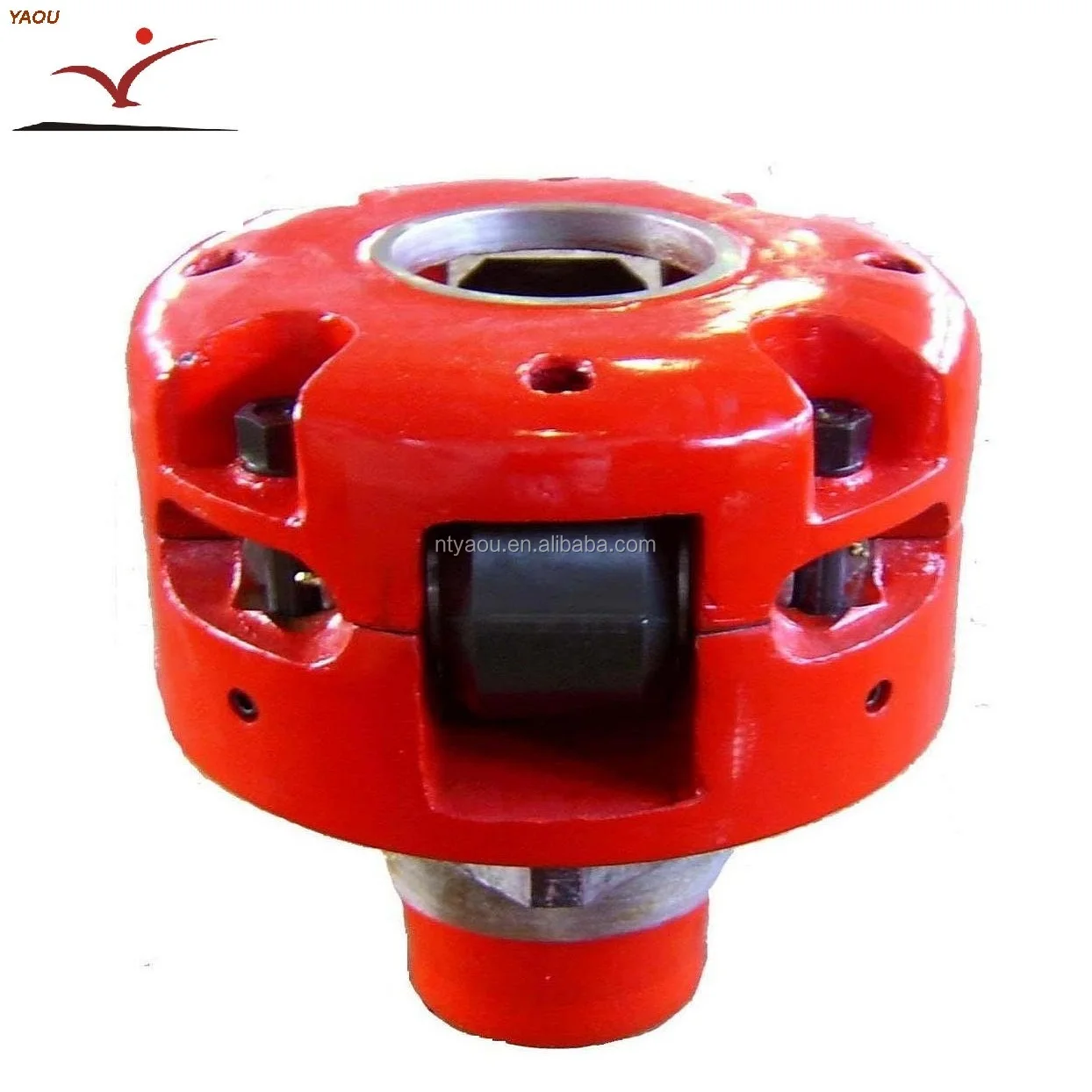
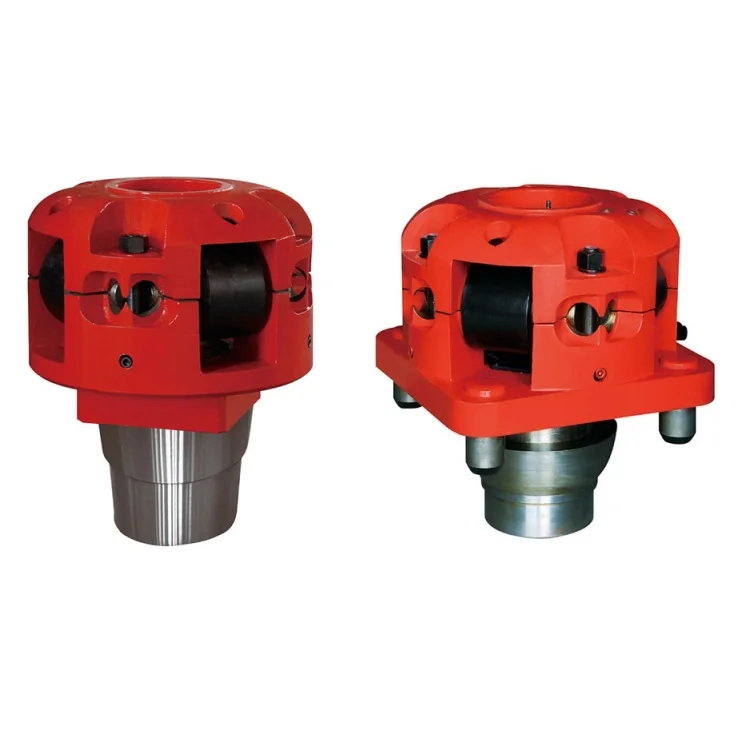
B.Roller Kelly bushing can be square drive or pin drive, and can be applicable for rotary table size from 17½ to 37½. By changing roller sizes, the bushing can accommodate square kellys from 2½ to 5¼ or hex kellys from 3 to 6. Roller Kelly bushing has three series: SD(light duty), MD(medium duty) and HD(heavy duty).
Square drive Roller Kelly bushing consists of lower body half, upper body half, roller, roller pin and etc. when the bushing is installed to square kelly or hex kelly, the square part of the lower body half can be fitted in the square of the master bushing. When operating, the rotary table drive master bushing and master bushing drive Roller Kelly bushing and Roller Kelly bushing drive square kelly or hex Kelly to rotate, such is the torque transporting. The lower body half is conically shaped to readily enter the bore of the master bushing and automatically center bushing and drill string within the bore of the master bushing. Inside rollers are journal bearings which are fitted to the roller pin, when kelly rotates and moves downward, the rollers rotates with Kelly, such change sliding friction to rolling friction and minimize the abrasion of the kelly. The bushing is equipped with mud-scrapper assembly to clean the mud.




 8613371530291
8613371530291