what is kelly bushing factory

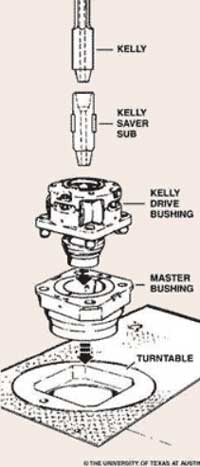
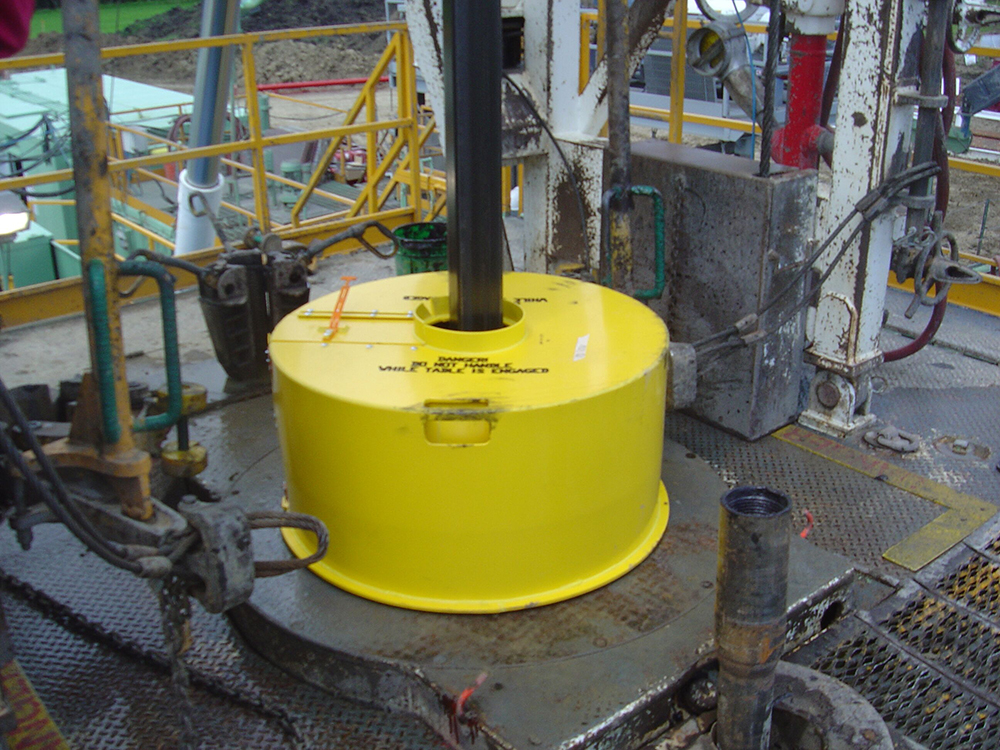
Kelly bushing is that elevated device positioned right on top of the rotary table and used to transmit torque from the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing is designed to be the connection between the rotary table and the kelly. The kelly is a 4 or 6 sided steel pipe.
The purpose of the rotary table is to generate the rotary action (torque) and power necessary to rotate the drillstring and drill a well. The torque generated by the rotary table is useless if it is not transferred to the kelly (the drillstring is connected to the kelly).
Hence, through the kelly bushing the torque generated at the rotary table is transferred to the kelly. To achieve this connection, the inside profile of the kelly bushing matches the outer profile of the kelly so that the kelly fits or “sits” comfortably in the kelly bushing.
There are various designs for the kelly bushing including the split type, the pin-drive type and the square-drive type. Each of these designs has different ways in which they are connected and disconnected from the rotary table.
The internal diameter of the kelly bushing can be cut into the shape of a square (4-sided) or a hexagon (6-sided) depending on the outer shape of the kelly that will be used. The internals of a Kelly bushing is designed to resemble the outer shape of a Kelly just like the insides of a key lock is cut to exactly match the outer shape of the key.
The kelly bushing is not designed to hold tightly onto the Kelly; the kelly is still permitted to move up and down through the kelly bushing. This requirement is a must since drilling cannot progress if the kelly remains on a fixed spot. As the well is drilled deeper, the kelly also moves downward through the Kelly bushing.
The kelly bushing is sometimes used as a reference point from which depth measurements can be taken. All depths must be recorded with respect to a reference point; the kelly bushing (KB) is one of the depth references used in the oil and gas industry.
The top of the kelly bushing is normally used as the depth reference.For example, 7500ft KB means 7500ft below the kelly bushing or 7500ft measured from the top of the kelly bushing down to that point in the well.
In some other cases, depths could be recorded as 7500ft MDBKB meaning 7500ft measured depth below the kelly bushing. This is mostly used when the measured depth is different from the true vertical depth of the well, common with deviated and horizontal wells.

An adapter that serves to connect the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing has an inside diameter profile that matches that of the kelly, usually square or hexagonal. It is connected to the rotary table by four large steel pins that fit into mating holes in the rotary table. The rotary motion from the rotary table is transmitted to the bushing through the pins, and then to the kelly itself through the square or hexagonal flat surfaces between the kelly and the kelly bushing. The kelly then turns the entire drillstring because it is screwed into the top of the drillstring itself. Depth measurements are commonly referenced to the KB, such as 8327 ft KB, meaning 8327 feet below the kelly bushing.
Please send us your inquiry with detail item description or with Model number. If there is no packing demand we take it as our regular exported standard packing. We will offer you an order form for filling. We will recommend you the most suitable model according to information you offered.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

The kelly is a primary link between the drilling rig’s surface equipment and the bit, and is therefore a critical component of the rotary system. Although top drive systems have replaced kelly/rotary table combinations on many rigs, some knowledge of their manufacture and operation is useful.
Their angled surfaces, or drive flats, are designed to fit into a drive roller assembly on the kelly bushing, so that as the rotary table turns to the right, the kelly turns with it. To allow for normal right-hand rotation of the drill string, kellys have right-hand threads on their bottom connections and left-hand threads on their top connections.
The American Petroleum Institute has established manufacturing and design standards for kellys, and has included them in the follwoing publications:API RP 7G, Recommended Practice for Drill Stem Design and Operating Limits.
For a kelly to be efficient in turning the drill string, the clearance between its drive flat surfaces and the rollers in the kelly bushing must be kept to a minimum. Kellys most often wear out due to a rounding-off of the drive corners, as shown in Figure 1 (new kelly with new drive assembly) and Figure 2 (worn kelly with worn drive assembly).
For minimal rounding, there must be a close fit between the kelly and the roller assembly, with the rollers fitting the largest spot on the kelly flats. Manufacturing techniques and rig operating practices play important roles in determining this fit.
Both square and hexagonal kellys are manufactured either from bars with an “as-forged” drive section, or from bars with fully-machined drive sections. Forged kellys are cheaper to manufacture. But machined kellys tend to last longer because:Unlike forged kellys, machined kellys are not subject to the metallurgical process of decarburization, which leaves a relatively soft layer of material on the drive surface that can accelerate the rounding process and increase the potential for fatigue cracks;
To minimize rounding, rig personnel should follow these guidelines (Brinegar, 1977):Always use new drive-bushing roller assemblies to break in a new kelly.
Frequently inspect and periodically replace drive assemblies to ensure that clearance and contact angle between the kelly and the rollers is held to a minimum;
Fatigue failures are seldom a problem with kellys because of the high-quality steels used in their manufacture. Nevertheless, kellys should be regularly inspected for cracks and other signs of wear, particularly within the threaded connections, in the areas where the flats join the upper and lower upsets and in the center of the drive section.
In general, the stress level for a given tensile load is less in the drive section of a hexagonal kelly than in the drive section of a square kelly of comparable size. Hexagonal kellys are thus likely to last longer than square kellys before failing under a given bending load.
Kellys can become crooked or bent due to improper handling. Examples of mishandling include dropping the kelly, misaligning it in the rathole and thereby exerting a side pull, using poor tie-down practices during rig moves, not using the kelly scabbard and improper loading or unloading techniques. Depending on where a bend is located, it may cause fatigue damage not only to the kelly but to the rest of the drill string, and can also result in uneven wear on the kelly bushing.
Unusual side motions or swaying of the swivel are good indicators of a crooked kelly. A good field service shop has equipment for straightening bent kellys, making this an easily-corrected problem.
A kelly saver subshould always be run between the kelly and the top joint of drill pipe. This protects the kelly’s lower connection threads from wear, as joints of drill pipe are continually made up and broken out. A saver sub is much less expensive and much easier to replace than the kelly itself, and it can also be equipped with a rubber protector to help keep the kelly centralized and to protect the top joint of casing against wear.
A kelly cock is a valve installed above or below the kelly, which prevents fluid from escaping through the drill string if the well should begin to flow or “kick.” As an extra well control precaution, an upper kelly cock (having left-hand threads) should be installed directly above the kelly, while a lower kelly cock (having right-hand threads) should be installed below the kelly. Installing two kelly cocks ensures that at least one of them is always accessible, regardless of the kelly’s position.
Automatic check valves, designed to close when the mud pumps are shut off, are also available, and can be installed below the kelly to prevent mud from spilling onto the rig floor during connections.

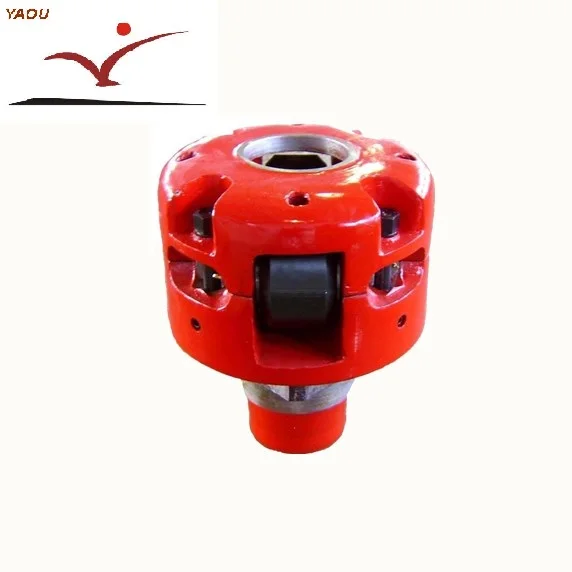
Roller Kelly Bushings can be classed as two types based on different ways of drive, square drive and pin drive. Also they can be classed as three types based on different style, heavy, medium and light-duty. They are used for 17.1/2 to 49.1/2inch rotary tables. They are designed and manufactured according to API Spec 7K.

MASTER BUSHING AS SEMBLY Original Filed Jan. 4, 1967 United States Patent Int. Cl. F16d 3/06 US. Cl. 6423.5 17 Claims ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE An improved master bushing assembly capable of selectively driving either a pin drive kelly bushing or a square drive kelly bushing.
Master bushings presently in use in the well drilling industry are of two general types, namely: those which function to drive a square drive kelly bushing; and those which function to drive a pin drive kelly bushing. Although it is desirable to have both the square and pin type master bushings vailalble to the same rig concurrently, some operators cannot hear the expense involved in equipping themselves so fully. Additionally, if an operator does have both type master bushings available and drilling conditions dictate a desired change from a pin to a square drive kelly bushing or conversely, this necessitates the removal of the existing master bushing, for example a pin type, and inserting a square type in place thereof within the rotary table, thereby resulting in increased operation costs.
The present invention comprises a master bushing which, when used in conjunction with adapter means and/ or spacer means, permits selective use of a pin drive or square drive kelly bushing without the need to change the master bushing as is required with conventional master bushings.
The objects and advantages of this invention will be more readily apparent from the following description and drawings of preferred embodiments of this invention in which:
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a master bushing as,- sembly embodying one form of the present invention showing elements disassembled from one another;
FIG. 2 is a front elevational view partly in section of the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 1 showing certain of the elements thereof operatively assembled together with ments" thereof operatively assembled together with a rotary table and a square drive kelly bushing.
type master bushing assembly 10 comprising a master bushing 11 used in conjunction with a polygonal drive adapter, shown as a square drive adapter, insert 12 and a; pin drive type master bushing assembly 10" comprising the master bushing 11 used in conjunction with a pin drive spacing adapter insert 113. FIG. 2 shows master bushing assembly 10 arranged to be rotatably driven in a well known manner in a suitably rotatably driven rotary table 13 which rotary table is suitably supported by a rotary table frame 14. A polygonal drive, shown as a Patented Sept. 8, 1970 square drive, kelly bushing 15 engaging a swivel supported kelly 16 for rotation about its longitudinal axis while at the same time permitting relative vertical movement of the kelly 16 to advance a connected drill string downwardly within a well, is suitably received in the square drive adapter insert 12. A familiar stabbing skirt 17 extends downwardly from a downwardly extending centrally disposed square drive 42 fixed to the under surface of the main body portion 43 of the kelly bushing 15. The master bushing assembly 10 coacts with the kelly bushing 15 "for rotatably driving the kelly bushing 15.
The rotary table 13 includes a rigid tubular body section 18 supported in rotary table frame 14 by bearings 19 for rotation about its vertically extending longitudinal axis. The body section 18 has a lower cylindrical opening 20 and a larger upper generally square shaped opening 21 which together with lower opening 20 defines a generally square horizontal annular shoulder 22. The upper opening 21 extends up to the horizontal upper surface 23 of the rotary table 13.
The master bushing 11 includes a rigid tubular cylindrically externally shaped main body portion 25 complementary in external shape with and snugly received by lower portion 20 of rotary table 13. The inner opening 26 of body portion 25 is generally cylindrically shaped. A generally square shaped bevelled-corner flange 27 is fixed to the upper end portion of main body portion 25 and extends outwardly therefrom. Flange 27 has a generally flat horizontal upper surface 28 which, when master bushing -11 is interfitted with rotary table 13, is coplanar with the horizontal upper surface 23 of rotary table 13. Flange 27 also has a centrally disposed generally polygonal, as shown square, shaped recess 29, extending therewithin, which recess 29 has its center point coincident with the longitudinal axis of main body portion 25 and is greater in its side dimension than the diameter of inner opening 26, so that an annular shoulder 30 is defined between recess 29 and inner opening 26. The outer shape of flange 27 is complementary in shape with and snugly and non-rotatably received by the upper opening 21 of rotary table 13 such that the undersurface of flange 27 and shoulder 22 abut. The flange 27 has four longitudinally extending identical cylindrical openings 31 uniformly spaced at the corner portions of the flange 27 which receive the pin drive means (not shown) therein, of a pin drive kelly bushing (not shown) of a well known construction.
The square drive adapter insert 12 has a dual function of accommodating slips together with serving as the drive adapter means of the present invention, and includes a tubular cylindrically externally shaped lower portion 34 comprised of two identical semi-cylindrical bodies 35. The outer surface of lower portion 34 is complementary in shape to the inner opening 26 of body portion 25 of master bushing 11 and is removably received therein. Lower portion 34 has a frusto-conical downwardly tapering inner opening 36 suitably shaped for receiving slips. A generally square shaped bevelled-corner flange 37 comprised of two identical halves 38 is fixed to and extends outwardly from the upper end of lower portion 34. The outer shape of the sides of flange 37 is generally complementary in shape with that of the sides of recess 29 of main body portion 25 of master bushing 11, such that flange 37 is snugly and non-rotatably received in recess 29 with the upper surface of flange 37 being coplanar with the upper surface 28 of flange 27 of master bushing 11. Flange 37 has a centrally disposed longitudinally extending generally polygonal, shown as square, shaped opening 40 therewithin, which opening 40 has a side dimension greater than the major diameter of inner opening 36 of lower portion 34 so that an annular shoulder 41 is defined between opening 40 and inner opening 36. Square opening 40 of flange 37 is suitably sized to snugly removably receive the square drive portion 42 of kelly bushing 15.
The pin drive spacing insert 113 is used in combination with bushing 11 when a pin drive kelly bushing (not shown) of a well known construction, is rotatably driven by having the pin drive means (not shown) thereof received in openings 31 of flange 27. Insert 113 is dimensionally identical to the drive adapter insert 12 hereinabove described, with the exception that insert 113 has a differently shaped interior opening than insert 12, namely a frusto-conical downwardly tapering inner opening 32, which is suitably shaped for receiving a pin drive kelly bushing tapered guide skirt (not shown) of a well known construction therein. The exterior contact surfaces of inserts 12 and 113 are identical, therefore, no further description of insert 113 is believed necessary and it will be received within master bushing 11 in exactly the manner insert 12 is received as hereinabove described.
In addition, the principles of this invention taught by the embodiment hereinabove described and shown in FIGS. 1 through 3 may be applied to a master bushing which can be classified as an adapter receiving chamber, that is it, in itself, will have no drive provisions on the flange thereof, but will provide support for a square drive adapter insert or a pin drive adapter insert. The square drive adapter will be identical to insert 12 hereinabove described, however, the pin drive adapter will differ from insert 113 hereinabove described in that it will have drive pin receiving openings within the upper outwardly extending flange thereof. In this case the master bushing need not have the large flange that is required if the drive pin receiving openings were to be located therein.
FIGS. 4 and 5 represent another embodiment of a polygonal, shown as square, drive master bushing assembly of the present invention generally indicated at 65, which comprises a pin drive master bushing 11, of a construction well known in the art, and a pin drive to polygonal, shown as square, drive adapter insert means, generally indicated at 52, which converts the pin drive master bushing 11 to the square drive master bushing assembly 65.
Since certain elements as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5 are identical to those of FIGS. 1 through 3, the same reference characters will be applied to corresponding elements. Master bushing 11 is dimensionally identical to the master bushing 11 hereinabove described and illustrated in FIGS. 1 through 3, with the exception that master bushing 11" has a differently shaped interior opening Within the flange 27, namely a cylindrical opening 50". Additionally, as shown in FIGS. 4 and 5 the master bushing 11" is suitably arranged to be rotatably driven by the rotary table 13 suitably supported by the rotary table frame 14. The exterior contact surfaces of master bushings 11" and 11 are identical, therefore, no further description of master bushing 11" is believed necessary and it will be received within the rotary table 13 in exactly the manner master bushing 11 is received therein as hereinbefore described with reference to the embodiment of this invention illustrated in FIGS. 1 through 3.
The drive adapter means 52 includes an upper rigid flat plate portion 54 and an insert bowl portion 60 extending downwardly from the underside of plate portion 54. The plate portion 54 has a centrally disposed generally polygonal shaped, shown as square shaped, opening 55 therewithin and has external dimensions substantially the same as the dimensions of flange 27 of main body portion of master bushing 11". Square opening 55 is suitably sized and shaped, and plate portion 54 has a suitable thickness such that the square drive portion 42 of the square drive kelly bushing 15 will be snugly and non-rotatably received in square opening 55 as will be shown hereinafter.
Four cylindrically shaped pins 56 extends downwardly from and are rigidly fixed to the corner regions of the undersurface of plate portion 54 with the respective longitudinal centerlines of such pins 56 being substantially parallel with the vertical centerline of plate portion 54. Pins 56 have outer diameters substantially the same as the inner diameters of openings 31 in flange 27 of main body portion 25 of master bushing 11, with pins 56 having a longitudinal length to be received in openings 31 such that the undersurface of plate member 54 is flush with the upper surface 28- of flange 27.
Insert bowl portion 60 comprises a rigid cylindrically externally shaped body 62 being externally complementary shaped with and snugly removably received within the inner opening 26 of the main body 25 of master bushing 11". An outwardly extending generally cylindrically shaped flange 63 comprises the upper portion of body 62, which flange 63 is integral with and extends downwardly from the underside of plate portion 54. The flange 63 has an external shape complementary with the shape of recess 50 of flange 27 of main body portion 25 of master bushing 11", such that flange 63 is snugly received in recess 50. The inner opening 64 of body 62 is shaped in a frustoconical downwardly tapering manner for accommodating slips.
With plate portion 54 being mated with the master bushing 11" by interfitting pins 56 in openings 31 and insert bowl portion 60 into opening 26 the lower surface of the main body portion 43 of kelly bushing 15 will abut the upper surface of plate portion 54 and the square drive portion 42 of kelly bushing 15 will be snugly received in opening 55 with the lower surface of square drive portion 42 being coplanar with the upper surface 28 of flange 27.
Other embodiments more clearly illustrating the application of the principles of this invention are to be seen on pages 344 and 345 of Tools for Drilling, Producing, Fishing (68-69 catalogue) published by Baash-Ross Division of Joy Manufacturing Company, Houston, Tex. or equivalent pages shown on the composite catalogue of Oil Well Field Equipment and Services, 28th revision, published by World Oil.
Having described embodiments of my present invention and in accordance with the patent statutes, it is to be realized that modifications may be made without departing from the broad scope of the present invention. Accordingly, it is requested that the scope of this invention be not restricted to the specific forms shown for the uses mentioned except to the extent indicated in the appended claims.
1. A master bushing comprising: a body member having an opening extending therethrough and an outer configuration of a form that said body member is closely and non-rotatively received within the central opening of a given rotary drilling table with the axes of said openings being coincident; said opening in said body member being of a form to non-rotatively receive an adapter insert completely therein; said body member being partially in the form of an outwardly extending flange portion at the end thereof last receivable within such a central opening; and said flange portion having a plurality of parallel externally accessible open bores of a size and orientation to receive the pins of a known pin drive kelly bushing therein.
2. A master bushing as specified in claim 1 having a spacing adapter inserted in said opening in said body member, said insert comprising: a member having an outwardly extending flange portion at the end thereof last receivable within said opening in said body member; said member having a downwardly depending bowl portion; and said member having a circular central opening extending therethrough for the guiding and centerin of a known pin drive kelly bushing.
4. A master bushing as specified in claim 1 having a driving adapter inserted in said opening in said body member, said insert comprising: a member having an outwardly extending flange portion at the end thereof last receivable within said opening in said body member; and said member having a central polygonal cross-sectional opening at the upper end thereof of a size and orientation to non-rotatively receive a drive portion of a known polygonal drive kelly bushing.
7. A master bushing assembly comprising: a body member having an opening extending therethrough and an outer configuration of a form that said body member is closely and non-rotatively received within the central opening of a given rotary drilling table with the axes of said openings being coincident; a driving adapter insert having an outer configuration of a form that said insert is non-rotatively received within said opening extending through said body member; and said insert having a central polygonal cross-sectional opening at the upper end thereof of a size and orientation to non-rotatively receive a drive portion of a known polygonal drive kelly bushing.
8. A drive adapter for downward insertion into a pin drive kelly bushing wherein said adapter comprises: a body member having an opening extending centrally therethrough, said body having a lower portion with an external configuration coaxial with said opening and complementary and slidably receivable in an insert bowl passageway of a known pin drive master bushing, said opening having a configuration at the upper end thereof for receiving the square drive portion of a square drive kelly bushing and a configuration extending downwardly from said upper end thereof for receiving slip member; and drive pins for drivingly cooperating with said known pin drive master bushing and said body member.
9. A master bushing assembly comprising a drive adapter as specified in claim 8 in combination with a pin drive master bushing wherein said main body upper end surface becomes coplanar with the upper surface of said master bushing upon being so inserted.
10. A master bushing assembly comprising: a master bushing having means for accommodating a selected one of a pin drive insert and a square drive insert therein in combination with said selected one of said inserts providing for driving connection to a kelly drive bushing.
11. A master bushing assembly as specified in claim 10 wherein said master bushing has an upwardly open through bore with a top portion of polygonal internal cross section.
12. A master bushing assembly as specified in claim 11 wherein said selected one of said inserts is a pin drive spacing insert having a top external profile of mating polygonal cross section with said through bore top portion.
13. A master bushing assembly as specified in claim 11 wherein said selected one of said inserts is a polygonal drive adapter insert having a top external profile of mating polygonal cross section with said through bore top portion and an upwardly open central recess of polygonal cross section mateable with a known polygonal drive kelly bushing.
15. An adapter insert for a pin drive master bushing, said adapter insert having drive pins thereon for drivingly mating with a known pin drive master bushing and said adapter having an internal upwardly open recess of polygonal cross section mateable with the polygonal drive portion of a known polygonal drive kelly bushing.
16. A master bushing assembly comprising: a pin drive master bushing in combination with an adapter insert as specified in claim 15 for prividing driving connection between rotary drilling table and a polygonal drive kelly bushing.
References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1,628,303 5/1927 Harris et al. 6423.5 X 1,864,952 6/1932 Smith 64-235 2,204,112 6/1940 Abegg 64-235 X 2,286,593 6/ 1942 Abegg 64-23.5 2,306,130 12/1942 Long 6423.7 2,904,311 9/1959 Spiri 6423.7

These 2 important is very important for drilling rig owner. After years when your machine needs maintenance you wont need our factory send you parts for maintenance. If you will have any trouble while drilling you will able to solve your problem easly finding spare parts at your local market and changing parts will be not complicated as Hydraulic system top drive drilling rigs.

Start shopping at Alibaba.com to discover wholesale rotary kelly bushing at incredible prices.Browse through rotary kelly bushing for any type of vehicle.Bearings can be produced from a broad variety of materials, such as different steel, rubber, plastic, brass, and ceramic. These materials, each having their own benefits that render them appropriate to specific operations, including noise level, mass, weight, capacity, and resistance, and a series of options to match your individual needs and requirements.
This particular type of rolling component has had a lengthy lifespan, originally made popular in bicycles then, automobiles. It decreases spinning rubbing while withstanding axial and radial loads and has the potential to be used across a broad spectrum of different industries, of which aerospace, agricultural and machinery, wagons and other automobiles, skateboards, and of course fidget spinners!
However, getting a bushing that is properly functioning is critical to a comfortable and smooth ride, as they maintain the car in good conditions. We have variously available bushings including, grounding bushing, polyurethane bushings, energy suspension bushings, brass bushings, and even drill bushings.Buy our selection of rotary kelly bushing now. For those of you who are looking for quality wholesale rotary kelly bushing at a bargain price, well then you should look no further! At Alibaba.com, you may find a great array of quality automotive accessories and everything at an awesome price.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Roller Kelly Bushings can be classed as two types based on different ways of drive, square drive and pin drive. Also they can be classed as three types based on different style, heavy, medium and light-duty. They are used for 17.1/2 to 49.1/2inch rotary tables. They are designed and manufactured according to API Spec 7K.

Roller Kelly Bushings can be classified as two types based on different ways of drive, square drive and pin drive. Also they can be classified as three types based on different style, heavy, medium and light-duty. They are used for 17 1/2 to 49 1/2inch rotary tables. They are designed and manufactured according to API Spec 7K.
2. It is to drive kelly spinner by matching with master bushing. Through rotating of four rollers, the friction between rollers and kelly pipe is reduced and service life is extended.
Topland is an integrated supplier established in 2008. We are a global group of oilfield supplies with excellent teams in more than 5 countries. such as UAE, Kuwait, Iran and Saudi Arabia. We cooperated with ADES, ECDE, EDC, SOCAR-AQS, PDL, SAKSON, ONGC etc.
Drilling rig equipment and the related spares for the oil and natural gas industries. Like Rig Components, Drawworks Spare parts and Mud Pump Spare parts, Hydraulic Disc Brake,Solids Control Equipment, Drilling and Fishing Tools,Wellhead Control Equipment,Drilling Accessories, Cementing Equipment and Tools etc.

This is the brief explanation of a Kelly rotating system on the rig. Kelly rig is on an old style rigs and nowadays it is mostly used on land operations. For offshore operation, a top drive system is used instead.
First of all, it is important for new people to look at these images before reading the information below because they show the equipment’s name and where they are on the rig.
The upper end of the drill pipe is screwed onto the saver sub. The saver sub is used to protect and minimize wearr and tear on the threads at the bottom of the Kelly. The Kelly is about 40 ft in length with a square or hexagonal shape and it is hollow throughout in order to transport the drilling mud. Kelly moves freely through a Kelly bushing even though the drill stem is rotated.
A Kelly cock valve is located at the top of a Kelly and it is a safety valve which can be closed to stop back pressure from coming back to damage other surface equipment.
A swivel attached to the hook does not rotate, but at the bottom part it supports the Kelly which is being rotated while drilling. Drilling mud is pumped from a mud pump to a stand pipe manifold, Kelly hose and then to a gooseneck connection at a swivel.
A rotary table rotates a Kelly bushing and it simultaneously rotates a Kelly and a drill string and a drill bit. A rotary table has two main functions. The first one is to provide rotation to a drill stem and a bit and the second function is to hold slip in order to support the weight of a drill stem when it is not connected to a Kelly.
Generally, a rotary drive consists of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket. A rotary-drive sprocket is a part of the draw-works. In other rig power systems, an independent electric motor or engine with a direct drive to a rotary table is utilized. For this case, the rotary is normally driven by a drive shaft instead of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket.
A master bushing severs its function as a rotary motion transmission from a rotary table to a Kelly. Additionally, it is a link between a slip and a rotary table.
A Kelly bushing (some people call “rotary Kelly bushing”) engages a master bushing via four pins and rollers inside a Kelly bushing to allow a Kelly to move up or down freely while it is rotated or in a static mode.




 8613371530291
8613371530291