mud pump suction stabilizer made in china

Buy high-capacity pump suction stabilizer that are guaranteed to keep your appliances up and running in perfect condition from Alibaba.com. These pump suction stabilizer are offered from the best and most energy-efficient brands and provides users with an elevated experience. These pump suction stabilizer are designed to ensure safety and stability and are available in a number of variants.
pump suction stabilizer offered on Alibaba.com have many necessary and interesting features such as fail-safe circuit protection and cut-off points. These pump suction stabilizer have a high range and are likely to fit most home and commercial purposes. These pump suction stabilizer have finely crafted exteriors to ensure that there is no risk of shock or accidents. Some of these items even have LED displays for a smoother experience and greater transparency.
pump suction stabilizer are suitable for all sorts of large appliances and do not malfunction easily. They require very limited maintenance and not much has to be spent on their upkeep. pump suction stabilizer ensure that your expensive appliances and machines do not get damaged due to fluctuations and are inevitable for any home or commercial enterprise that engages multiple electronic items. pump suction stabilizer on the site offer optimal performance at economical prices.
Choose the pump suction stabilizer that best suit your needs, whether for home, office or industry. pump suction stabilizer suppliers are sure to want to snap up this attractive chance to buy quality items at discounted prices. Grab these amazing deals today.

Buy high-capacity pump suction stabilizers that are guaranteed to keep your appliances up and running in perfect condition from Alibaba.com. These pump suction stabilizers are offered from the best and most energy-efficient brands and provides users with an elevated experience. These pump suction stabilizers are designed to ensure safety and stability and are available in a number of variants.
pump suction stabilizers offered on Alibaba.com have many necessary and interesting features such as fail-safe circuit protection and cut-off points. These pump suction stabilizers have a high range and are likely to fit most home and commercial purposes. These pump suction stabilizers have finely crafted exteriors to ensure that there is no risk of shock or accidents. Some of these items even have LED displays for a smoother experience and greater transparency.
pump suction stabilizers are suitable for all sorts of large appliances and do not malfunction easily. They require very limited maintenance and not much has to be spent on their upkeep. pump suction stabilizers ensure that your expensive appliances and machines do not get damaged due to fluctuations and are inevitable for any home or commercial enterprise that engages multiple electronic items. pump suction stabilizers on the site offer optimal performance at economical prices.
Choose the pump suction stabilizers that best suit your needs, whether for home, office or industry. pump suction stabilizers suppliers are sure to want to snap up this attractive chance to buy quality items at discounted prices. Grab these amazing deals today.

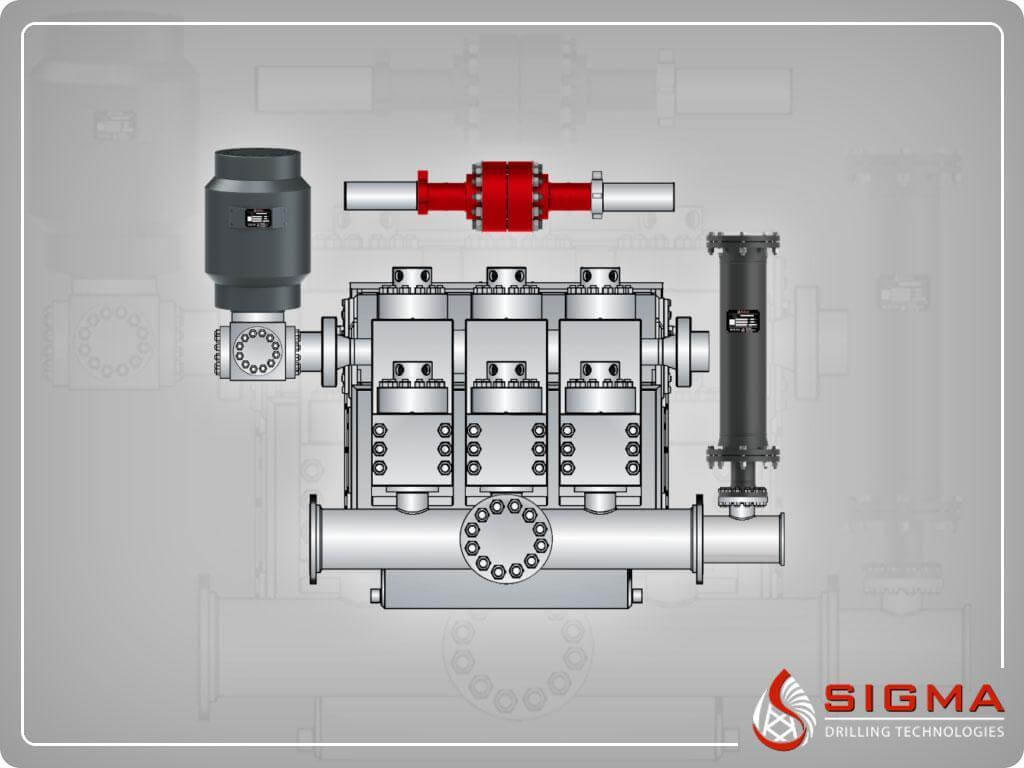
The structural features and properties of F series mud pumps are more advanced. Wearing parts of fluid end can be universally used with those of API standards.
F series mud pumps are firm and compact in structure and small in size, with good functional performances, which can adapt to drilling technological requirements such as oilfield high pump pressure and large displacement etc. The F series mud pumps can be maintained at lower stroke rate for their long stroke, which effectively improves the feeding water performance of mud pumps and prolongs the service life of the fluid end. The suction stabilizer, with advanced structure and reliable service, can achieve the best buffering effect. Power ends of the F series mud pumps adopt the reliable combination of forced lubrication and splash lubrication to increase the service life of power ends.
This series of pumps is manufactured strictly in accordance with API Spec 7K Drilling and Workover Equipment Specifications and carried out delivery test in accordance with the standard.

Invented to address the pitfalls standpipes have, cartridge vessels made it possible for gas to be contained by separating gases from drilling fluids with a rubber membrane. Unfortunately, your problem with cartridge vessels is they will eventually fail. When they do, compressibility is lost, rendering the suction stabilizer incapable of absorbing any energy and leaving the vessel utterly ineffective. Every time a cartridge vessel fails, it leaves the reciprocating pump less efficient, which ultimately costs time, money, and human resources, commodities that are precious on a drilling rig.
Even though the cartridge vessel is an improvement above the standpipe, the misinformation or assumptions that people make regarding the stabilizers still render it pretty ineffective. One common mistake is installing a stabilizer in place of a standpipe, resulting in an improper location. A stabilizer’s intended design and purpose are installed directly off the suction manifold between the reciprocating pump and the charge pump.

What if you could improve the efficiency of your mud pump, add protection for your charge pump, and extend the life of your pumps’ expendables? Would you like to gain performance, versatility, and savings?
Sigma Drilling Technologies has once again pioneered an advancement with it’s Charge Free Stabilizer™, or CFS. This patent-pending design utilizes a multi-phase mitigation method allowing for both compression and kinetic exchange without any gas charging or unreliable cartridges. The CFS was designed to maximize the performance of Sigma’s Charge Free Conversion Kit®. The CFC Kit has revolutionized pulsation control, and the CFS takes absolute advantage. The Charge Free Stabilizer™ supersedes all other stabilizer options available, and its list of benefits far exceeds that of any other.
The Charge Free Stabilizer™ by Sigma is the only stabilizer on the market of its kind. Now your new suction stabilizer will outperform your expectations, all without the regular maintenance and without any expensive re-designs.
Performance Pulsation Control is meeting the suction stabilizer needs of clients across the country. We can tailor a suction stabilizer and suction pulsation dampener to fit the specific output requirements of any commercial industry that relies on consistent and precise pump solutions. Some of the customization possibilities you’ll find for your business applications include:

This series includes any of our end-suction centrifugal pumps combined with our high capacity, vacuum-assist,dry-priming system, capable of rapid, unattended priming and continuous repriming.Units are available for Solids Handling or Clear Liquid Service. Enclosed Silent Packages are available with DBA Ratings under 70 DBA@ 7 meters. Pumps are also available in a variety of different metallurgies.

F 1300 mud pump for oil drilling have features of solid and compact structure, small volume, good and reliable performance. It can meet the drilling requirements such as high pressure and big displacements whether in land drilling or off-shore drilling.
F 1300 mud pumps have a longer stroke and can be operated at a lower stroke, thus improved the water supplying performance effectively and extended the lifetime of mud pump fluid end parts greatly.

Emsco、Gardner-Denver, National oilwell, Ideco, Brewster, Drillmec, Wirth, Ellis, Williams, OPI, Mud King, LEWCO, Halliburton, SPM, Schlumberger, Weatherford

2011 TRAILER MOUNTED LOADMASTER 1000 HP ELECTRIC DRILLING RIG – 13000’ w/ 4-1/2” DP HRI 1000-E SINGLE DRUM WITH WICHITA 3-25 KKB DISK BRAKE POWERED BY TWO (2) GE 761 TRACTION MOTORS AMERICAN BLOCK ROTARY TABLE 27-1/2” WITH 53-1/4” CENTER POWERED BY GE 752, (3) CAT 3512A DIESEL ENGINES WITH (3) CAT1100 KW AC GENERATORS. ROUGHLY +/- 35,000 HRS EACH (ASSET # 19134, 19136 and 19135) DSI 118’ WITH 425,000# SHL-MTD. ON A HEAVY-DUTY TRI-AXLE TRAILER DSI 17’ TELESCOPING WITH 425,000 ROTARY CAPACITY WITH A SETBACK CAPACITY OF 300,000# 15’ CLEAR HEIGHT FROM BOTTOM OF ROTARY TO GROUND, TWO (2) F-1600 TRIPLEX MUD PUMPS (ASSET # 1000050 and ASSET# 19131) (MASTER SKIDED WITH (2) GE752 TRACTION MOTORS ON EACH PUMP, 5000PSI Fluid Ends, PD-K20). MOTORS INCLUDED-NOT SHOWN IN PICTURE. (1) Shaker Tank ASSET # 120013(H-96″ W 116″ L-513″), (1) Suction Tank ASSET#120014 (W-116″, H-96″, L-513″). REBUILT 3 1/8″ 5000K CHOKE MANIFOLD. ANNULAR BOP TOWNSEND TYPE 84 11” 5000 PSI WP DBL RAM BOP. NOV TOP DRIVE SYSTEM – TDS10SA, 250 TON (COMES WITH VFD, TRACK, TORQUE BUSHING, DRILLERS PANEL). 250 TON AMERICAN HOOK / BLOCK COMBO. ST80C IRON ROUGHNECK. Steel Toolpusher House w/Office, Kitchen, Bedroom, Bathroom, Laundry Room & Parts Room, 3 Beam Skid Dims 46′ x 12′ x10’6″ . ONE (1) 300 BBL WATER TANK / (1) 200 BBL FUEL TANK. Meyer 6 Station REBUILT Accumulator 20 BOTTLE, 300Gallon 480 Volt 21’ L x 9’ W x 9.6’ H IEC SCR I DRIVE, 3 GENERATOR X 4 SCR BAYS ,TOP DRIVE BREAKER
NATIONAL OILWELL A1700 TRIPLEX MUD PUMP W/FORGED STEEL FLUID ENDS, PULSATION DAMPENER, BELT DRIVE, P/B (2) 1,000HP ELECTRIC MOTORS, SKIDDED (NOTE:LESS 1 MOTOR)(ASSET# 17050)
NATIONAL OILWELL A1700 TRIPLEX MUD PUMP W/FORGED STEEL FLUID ENDS, PULSATION DAMPENER, BELT DRIVE, P/B (2) 1,000HP ELECTRIC MOTORS, SKIDDED(ASSET# 19087)
KOOMEY 10-STATION CLOSING UNIT W/ (2) AIR ACTUATORS, TRIPLEX CHARGE PUMP P/B 60HP ELECTRIC MOTOR, (24) 10-GAL ACCUMULATOR BOTTLES, MTD ON A COVERED SKID 20’L X 8’W X 10’H(ASSET# 19102)
CCUMULATOR TYPE 80 STYLE BPMF MODEL FKQ 720-6 6-STATION CLOSING UNIT W/ (3) AIR ACTUATORS, TRIPLEX CHARGE PUMP P/B 60HP ELECTRIC MOTOR, (12) 10-GAL ACCUMULATOR BOTTLES MTD ON A 20’L X 8’W X 10’H SKID(ASSET# 19101)
KOOMEY TYPE 80 6-STATION CLOSING UNIT W (1) AIR ACUATOR, (CHARGE PUMP MISSING), P/B 15HP ELECTRIC MOTOR, (12) 10-GAL ACCUMULATOR BOTTLES, MTD ON A 12 ½’L X 6’W SKID(ASSET# 100134)
KOOMEY T201603S 7-STATION CLOSING UNIT W/ (2) AIR ACTUATORS, TRIPLEX CHARGE PUMP P/B 20HP ELECTRIC MOTOR, (16) 10-GAL ACCUMULATOR BOTTLES, MTD ON A 12 ½’L X 6’W SKID(ASSET# 19139)
LUBESTER SKID W/ (4) 350 GAL TOTES. HOSES & REELS, PRESSURE WASHER W/GP SERIES 47 PUMP P/B 7.5 HP ELECTRIC MOTOR. MASTER SKIDDED W/ROOF(ASSET# 100122)

Since the NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump was built approximately 60 years ago, the industry has widely accepted the three cylinder or triplex style pump. Triplex mud pumps are manufactured worldwide, and many companies have emulated the original design and developed an improved form of the triplex pump in the past decade.
NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pumps have many advantages they weight 30% less than a duplex of equal horsepower or kilowatts. The lighter weight parts are easier to handle and therefore easier to maintain. The other advantages include;They cost less to operate
One of the more important advantages of triplex over duplex pumps, is that they can move large volumes of mud at the higher pressure is required for modern deep hole drilling.
NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump is gradually phasing out duplex units. In a triplex pump, the pistons discharge mud only when they move forward in the liner. Then, when they moved back they draw in mud on the same side of the piston. Because of this, they are also called “single acting.” Single acting triplex pumps, pump mud at a relatively high speeds. NOV A1700-PT Triplex Mud Pump has three pistons each moving in its own liner. It also has three intake valves and three discharge valves. It also has a pulsation dampener in the discharge line.

● The power end of F series mud pump adapts combined lubricating system of forced and splash lubrication, Reliable to lubricate and increased the service life of power end.
F04B15/02—Pumps adapted to handle specific fluids, e.g. by selection of specific materials for pumps or pump parts the fluids being viscous or non-homogeneous
A quintuplex mud pump has a crankshaft supported in the pump by external main bearings. The crankshaft has five eccentric sheaves, two internal main bearing sheaves, and two bull gears. Each of the main bearing sheaves supports the crankshaft by a main bearing. One main bearing sheave is disposed between second and third eccentric sheaves, while the other main bearing sheave is disposed between third and fourth eccentric sheaves. One bull gear is disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, while the second bull gear is disposed between fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves. A pinion shaft has pinion gears interfacing with the crankshaft"s bull gears. Connecting rods on the eccentric sheaves use roller bearings and transfer rotational movement of the crankshaft to pistons of the pump"s fluid assembly.
Triplex mud pumps pump drilling mud during well operations. An example of a typical triplex mud pump 10 shown in FIG. 1A has a power assembly 12, a crosshead assembly 14, and a fluid assembly 16. Electric motors (not shown) connect to a pinion shaft 30 that drives the power assembly 12. The crosshead assembly 14 converts the rotational movement of the power assembly 12 into reciprocating movement to actuate internal pistons or plungers of the fluid assembly 16. Being triplex, the pump"s fluid assembly 16 has three internal pistons to pump the mud.
As shown in FIG. 1B, the pump"s power assembly 14 has a crankshaft 20 supported at its ends by double roller bearings 22. Positioned along its intermediate extent, the crankshaft 20 has three eccentric sheaves 24-1 . . . 24-3, and three connecting rods 40 mount onto these sheaves 24 with cylindrical roller bearings 26. These connecting rods 40 connect by extension rods (not shown) and the crosshead assembly (14) to the pistons of the pump"s fluid assembly 16.
In addition to the sheaves, the crankshaft 20 also has a bull gear 28 positioned between the second and third sheaves 24-2 and 24-3. The bull gear 28 interfaces with the pinion shaft (30) and drives the crankshaft 20"s rotation. As shown particularly in FIG. 1C, the pinion shaft 30 also mounts in the power assembly 14 with roller bearings 32 supporting its ends. When electric motors couple to the pinion shaft"s ends 34 and rotate the pinion shaft 30, a pinion gear 38 interfacing with the crankshaft"s bull gear 28 drives the crankshaft (20), thereby operating the pistons of the pump"s fluid assembly 16.
When used to pump mud, the triplex mud pump 10 produces flow that varies by approximately 23%. For example, the pump 10 produces a maximum flow level of about 106% during certain crankshaft angles and produces a minimum flow level of 83% during other crankshaft angles, resulting in a total flow variation of 23% as the pump"s pistons are moved in differing exhaust strokes during the crankshaft"s rotation. Because the total flow varies, the pump 10 tends to produce undesirable pressure changes or “noise” in the pumped mud. In turn, this noise interferes with downhole telemetry and other techniques used during measurement-while-drilling (MWD) and logging-while-drilling (LWD) operations.
In contrast to mud pumps, well-service pumps (WSP) are also used during well operations. A well service pump is used to pump fluid at higher pressures than those used to pump mud. Therefore, the well service pumps are typically used to pump high pressure fluid into a well during frac operations or the like. An example of a well-service pump 50 is shown in FIG. 2. Here, the well service pump 50 is a quintuplex well service pump, although triplex well service pumps are also used. The pump 50 has a power assembly 52, a crosshead assembly 54, and a fluid assembly 56. A gear reducer 53 on one side of the pump 50 connects a drive (not shown) to the power assembly 52 to drive the pump 50.
As shown in FIG. 3, the pump"s power assembly 52 has a crankshaft 60 with five crankpins 62 and an internal main bearing sheave 64. The crankpins 62 are offset from the crankshaft 60"s axis of rotation and convert the rotation of the crankshaft 60 in to a reciprocating motion for operating pistons (not shown) in the pump"s fluid assembly 56. Double roller bearings 66 support the crankshaft 60 at both ends of the power assembly 52, and an internal double roller bearing 68 supports the crankshaft 60 at its main bearing sheave 64. One end 61 of the crankshaft 60 extends outside the power assembly 52 for coupling to the gear reducer (53; FIG. 2) and other drive components.
As shown in FIG. 4A, connecting rods 70 connect from the crankpins 62 to pistons or plungers 80 via the crosshead assembly 54. FIG. 4B shows a typical connection of a connecting rod 70 to a crankpin 62 in the well service pump 50. As shown, a bearing cap 74 fits on one side of the crankpin 62 and couples to the profiled end of the connecting rod 70. To reduce friction, the connection uses a sleeve bearing 76 between the rod 70, bearing cap 74, and crankpin 62. From the crankpin 62, the connecting rod 70 connects to a crosshead 55 using a wrist pin 72 as shown in FIG. 4A. The wrist pin 72 allows the connecting rod 70 to pivot with respect to the crosshead 55, which in turn is connected to the plunger 80.
In use, an electric motor or an internal combustion engine (such as a diesel engine) drives the pump 50 by the gear reducer 53. As the crankshaft 60 turns, the crankpins 62 reciprocate the connecting rods 70. Moved by the rods 70, the crossheads 55 reciprocate inside fixed cylinders. In turn, the plunger 80 coupled to the crosshead 55 also reciprocates between suction and power strokes in the fluid assembly 56. Withdrawal of a plunger 80 during a suction stroke pulls fluid into the assembly 56 through the input valve 82 connected to an inlet hose or pipe (not shown). Subsequently pushed during the power stroke, the plunger 80 then forces the fluid under pressure out through the output valve 84 connected to an outlet hose or pipe (not shown).
In contrast to using a crankshaft for a quintuplex well-service pump that has crankpins 62 as discussed above, another type of quintuplex well-service pump uses eccentric sheaves on a direct drive crankshaft. FIG. 4C is an isolated view of such a crankshaft 90 having eccentric sheaves 92-1 . . . 92-5 for use in a quintuplex well-service pump. External main bearings (not shown) support the crankshaft 90 at its ends 96 in the well-service pumps housing (not shown). To drive the crankshaft 90, one end 91 extends beyond the pumps housing for coupling to drive components, such as a gear box. The crankshaft 90 has five eccentric sheaves 92-1 . . . 92-5 for coupling to connecting rods (not shown) with roller bearings. The crankshaft 90 also has two internal main bearing sheaves 94-1, 94-2 for internal main bearings used to support the crankshaft 90 in the pump"s housing.
In the past, quintuplex well-service pumps used for pumping frac fluid or the like have been substituted for mud pumps during drilling operations to pump mud. Unfortunately, the well-service pump has a shorter service life compared to the conventional triplex mud pumps, making use of the well-service pump as a mud pump less desirable in most situations. In addition, a quintuplex well-service pump produces a great deal of white noise that interferes with MWD and LWD operations, further making the pump"s use to pump mud less desirable in most situations. Furthermore, the well-service pump is configured for direct drive by a motor and gear box directly coupling on one end of the crankshaft. This direct coupling limits what drives can be used with the pump. Moreover, the direct drive to the crankshaft can produce various issues with noise, balance, wear, and other associated problems that make use of the well-service pump to pump mud less desirable.
One might expect to provide a quintuplex mud pump by extending the conventional arrangement of a triplex mud pump (e.g., as shown in FIG. 1B) to include components for two additional pistons or plungers. However, the actual design for a quintuplex mud pump is not as easy as extending the conventional arrangement, especially in light of the requirements for a mud pump"s operation such as service life, noise levels, crankshaft deflection, balance, and other considerations. As a result, acceptable implementation of a quintuplex mud pump has not been achieved in the art during the long history of mud pump design.
What is needed is an efficient mud pump that has a long service life and that produces low levels of white noise during operation so as not to interfere with MWD and LWD operations while pumping mud in a well.
A quintuplex mud pump is a continuous duty, reciprocating plunger/piston pump. The mud pump has a crankshaft supported in the pump by external main bearings and uses internal gearing and a pinion shaft to drive the crankshaft. Five eccentric sheaves and two internal main bearing sheaves are provided on the crankshaft. Each of the main bearing sheaves supports the intermediate extent of crankshaft using bearings. One main bearing sheave is disposed between the second and third eccentric sheaves, while the other main bearing sheave is disposed between the third and fourth eccentric sheaves.
One or more bull gears are also provided on the crankshaft, and the pump"s pinion shaft has one or more pinion gears that interface with the one or more bull gears. If one bull gear is used, the interface between the bull and pinion gears can use herringbone or double helical gearing of opposite hand to avoid axial thrust. If two bull gears are used, the interface between the bull and pinion gears can use helical gearing with each having opposite hand to avoid axial thrust. For example, one of two bull gears can be disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, while the second bull gear can be disposed between fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves. These bull gears can have opposite hand. The pump"s internal gearing allows the pump to be driven conventionally and packaged in any standard mud pump packaging arrangement. Electric motors (for example, twin motors made by GE) may be used to drive the pump, although the pump"s rated input horsepower may be a factor used to determine the type of motor.
Connecting rods connect to the eccentric sheaves and use roller bearings. During rotation of the crankshaft, these connecting rods transfer the crankshaft"s rotational movement to reciprocating motion of the pistons or plungers in the pump"s fluid assembly. As such, the quintuplex mud pump uses all roller bearings to support its crankshaft and to transfer crankshaft motion to the connecting rods. In this way, the quintuplex mud pump can reduce the white noise typically produced by conventional triplex mud pumps and well service pumps that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations.
Turning to the drawings, a quintuplex mud pump 100 shown in FIGS. 5 and 6A-6B has a power assembly 110, a crosshead assembly 150, and a fluid assembly 170. Twin drives (e.g., electric motors, etc.) couple to ends of the power assembly"s pinion shaft 130 to drive the pump"s power assembly 110. As shown in FIGS. 6A-6B, internal gearing within the power assembly 110 converts the rotation of the pinion shaft 130 to rotation of a crankshaft 120. The gearing uses pinion gears 138 on the pinion shaft 130 that couple to bull gears 128 on the crankshaft 120 and transfer rotation of the pinion shaft 130 to the crankshaft 120.
For support, the crankshaft 120 has external main bearings 122 supporting its ends and two internal main bearings 127 supporting its intermediate extent in the assembly 110. As best shown in FIG. 6A, rotation of the crankshaft 120 reciprocates five independent connecting rods 140. Each of the connecting rods 140 couples to a crosshead 160 of the crosshead assembly 150. In turn, each of the crossheads 160 converts the connecting rod 40"s movement into a reciprocating movement of an intermediate pony rod 166. As it reciprocates, the pony rod 166 drives a coupled piston or plunger (not shown) in the fluid assembly 170 that pumps mud from an intake manifold 192 to an output manifold 198. Being quintuplex, the mud pump 100 has five such pistons movable in the fluid assembly 170 for pumping the mud.
The cross-section in FIG. 10A shows a crosshead 160 for the quintuplex mud pump. The end of the connecting rod 140 couples by a wrist pin 142 and bearing 144 to a crosshead body 162 that is movable in a crosshead guide 164. A pony rod 166 coupled to the crosshead body 162 extends through a stuffing box gasket 168 on a diaphragm plate 169. An end of this pony rod 166 in turn couples to additional components of the fluid assembly (170) as discussed below.
The cross-section in FIG. 10B shows portion of the fluid assembly 170 for the quintuplex mud pump. An intermediate rod 172 has a clamp 174 that couples to the pony rod (166; FIG. 10A) from the crosshead assembly 160 of FIG. 10A. The opposite end of the rod 172 couples by another clamp to a piston rod 180 having a piston head 182 on its end. Although a piston arrangement is shown, the fluid assembly 170 can use a plunger or any other equivalent arrangement so that the terms piston and plunger can be used interchangeably herein. Moved by the pony rod (166), the piston head 182 moves in a liner 184 communicating with a fluid passage 190. As the piston 182 moves, it pulls mud from a suction manifold 192 through a suction valve 194 into the passage 190 and pushes the mud in the passage 190 to a discharge manifold 198 through a discharge valve 196.
As noted previously, a triplex mud pump produces a total flow variation of about 23%. Because the present mud pump 100 is quintuplex, the pump 100 offers a lower variation in total flow, making the pump 100 better suited for pumping mud and producing less noise that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations. In particular, the quintuplex mud pump 100 can produce a total flow variation as low as about 7%. For example, the quintuplex mud pump 100 can produce a maximum flow level of about 102% during certain crankshaft angles and can produce a minimum flow level of 95% during other crankshaft angles as the pump"s five pistons move in their differing strokes during the crankshaft"s rotation. Being smoother and closer to ideal, the lower total flow variation of 7% produces less pressure changes or “noise” in the pumped mud that can interfere with MWD and LWD operations.
Although a quintuplex mud pump is described above, it will be appreciated that the teachings of the present disclosure can be applied to multiplex mud pumps having at least more than three eccentric sheaves, connecting rods, and fluid assembly pistons. Preferably, the arrangement involves an odd number of these components so such mud pumps may be septuplex, nonuplex, etc. For example, a septuplex mud pump according to the present disclosure may have seven eccentric sheaves, connecting rods, and fluid assembly pistons with at least two bull gears and at least two bearing sheaves on the crankshaft. The bull gears can be arranged between first and second eccentric sheaves and sixth and seventh eccentric sheaves on the crankshaft. The internal main bearings supporting the crankshaft can be positioned between third and fourth eccentric sheaves and the fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves on the crankshaft.
a crankshaft rotatably supported in the pump by a plurality of main bearings, the crankshaft having five eccentric sheaves and a first bull gear disposed thereon, the main bearings including a first internal main bearing sheave disposed between the second and third eccentric sheaves and including a second internal main bearing sheave disposed between the third and fourth eccentric sheaves;
a pinion shaft for driving the crankshaft, the pinion shaft rotatably supported in the pump and having a first pinion gear interfacing with the first bull gear on the crankshaft; and
6. A pump of claim 1, wherein the crankshaft comprises a second bull gear disposed thereon, and wherein the pinion shaft comprises a second pinion gear disposed thereon and interfacing with the second bull gear.
7. A pump of claim 6, wherein the first bull gear is disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, and wherein the second bull gear is disposed between the fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves.
8. A pump of claim 6, wherein the five eccentric sheaves, the first and second internal main bearing sheaves, and the first and second bull gears are equidistantly spaced from one another on the crankshaft.
9. A pump of claim 6, wherein the first and second pinion gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand, and wherein the first and second bull gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand complementary to the pinion gears.
a crankshaft rotatably supported in the pump by two external main bearings and two internal main bearings, the crankshaft having five eccentric sheaves, two internal main bearing sheaves for the internal main bearings, and at least one bull gear disposed thereon;
13. A pump of claim 11, wherein a first of the main bearing sheaves is disposed between the second and third eccentric sheaves, and wherein a second of the main bearing sheaves is disposed between the third and fourth eccentric sheaves.
16. A pump of claim 11, wherein the at least one bull gear comprises first and second bull gears disposed on the crankshaft, and wherein the at least one pinion gear comprises first and second pinion gears disposed on the crankshaft.
17. A pump of claim 16, wherein the first bull gear is disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, and wherein the second bull gear is disposed between the fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves.
18. A pump of claim 16, wherein the five eccentric sheaves, the two internal main bearing sheaves, and the first and second bull gears are equidistantly spaced from one another on the crankshaft.
19. A pump of claim 16, wherein the first and second pinion gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand, and wherein the first and second bull gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand complementary to the pinion gears.
a crankshaft rotatably supported in the pump by a plurality of main bearings, the crankshaft having five eccentric sheaves and first and second bull gears disposed thereon, the first bull gear disposed between the first and second eccentric sheaves, the second bull gear disposed between the fourth and fifth eccentric sheaves;
a pinion shaft for driving the crankshaft, the pinion shaft rotatably supported in the pump, the pinion shaft having a first pinion gear interfacing with the first bull gear on the crankshaft and having a second pinion gear interfacing with the second bull gear on the crankshaft; and
26. A pump of claim 21, wherein the main bearings include first and second internal main gearing sheaves disposed on the crankshaft, and wherein the five eccentric sheaves, the two internal main bearing sheaves, and the first and second bull gears are equidistantly spaced from one another on the crankshaft.
27. A pump of claim 21, wherein the first and second pinion gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand, and wherein the first and second bull gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand complementary to the pinion gears.
a crankshaft rotatably supported in the pump by a plurality of main bearings, the crankshaft having five eccentric sheaves and first and second bull gears disposed thereon, the main bearings including two internal main bearing sheaves disposed on the crankshaft, wherein the five eccentric sheaves, the two internal main bearing sheaves, and the first and second bull gears are equidistantly spaced from one another on the crankshaft;
a pinion shaft for driving the crankshaft, the pinion shaft rotatably supported in the pump, the pinion shaft having a first pinion gear interfacing with the first bull gear on the crankshaft and having a second pinion gear interfacing with the second bull gear on the crankshaft; and
34. A pump of claim 29, wherein the first and second pinion gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand, and wherein the first and second bull gears comprise helical gearing of opposite hand complementary to the pinion gears.
"Triplex Mud Pump Parts and Accessories;" Product Information Brochure; copyright 2007 Sunnda LLC; downloaded from http://www.triplexmudpump.com/triplex-mud-pump-parts.php on Sep. 5, 2008.
"Triplex Mud Pumps Triplex Mud Pump Parts for Sale;" copyright 2007 Sunnda LLC; Product Information Brochure located at http://www.triplexmudpump.com/.
"Triplex Mud Pumps Triplex Mud Pump Parts;" copyright 2007 Sunnda LLC; downloaded from http://www.triplexmudpump.com/F-series-triplex-mud-pumps-power-end.php on Sep. 5, 2008.
China Petrochemical International Co., Ltd.; "Quintuplex Mud Pump;" Product Information Brochure downloaded from http://www.intl.sinopec.com.cn/emExp/upstream/Quituplex-Mud-Pump.htm downloaded on Oct. 2, 2008.
FMC Technologies; "Fluid Control: Well Service Pump;" Product Information Brochure; downloaded from http://www.fmctechnologies.com/-FluidControl-old/WellServicePump.aspx on Sep. 5, 2008.
National Oilwell; "Triplex Mud Pumps;" Product Information Brochure; downloaded from http://nql.com/Archives/2000%20Composite%20Catalog/pg-32.html downloaded on Sep. 5, 2008.




 8613371530291
8613371530291