overshot dog price

An overbite might not seem like a serious condition for your dog, but severely misaligned teeth can lead to difficulty eating, gum injuries and bruising, bad breath and different types of dental problems, including tooth decay and gingivitis. Fortunately, there are ways to help fix the problem before it becomes irreversible.
An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
This problem is especially common in breeds with narrow, pointed muzzles, such as collies, shelties, dachshunds, German shepherds, Russian wolfhounds and any crossbred dogs that include these ancestries.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If an overbite is more severe, dental intervention may be necessary to correct the misalignment. While this is not necessary for cosmetic reasons – a small overbite may look unsightly, but does not affect the dog and invasive corrective procedures would be more stressful than beneficial – in severe cases, a veterinarian may recommend intervention. There are spacers, braces and other orthodontic accessories that can be applied to a dog"s teeth to help correct an overbite. Because dogs" mouths grow more quickly than humans, these accessories may only be needed for a few weeks or months, though in extreme cases they may be necessary for up to two years.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.
An overbite might be disconcerting for both you and your dog, but with proper care and treatment, it can be minimized or completely corrected and your dog"s dental health will be preserved.

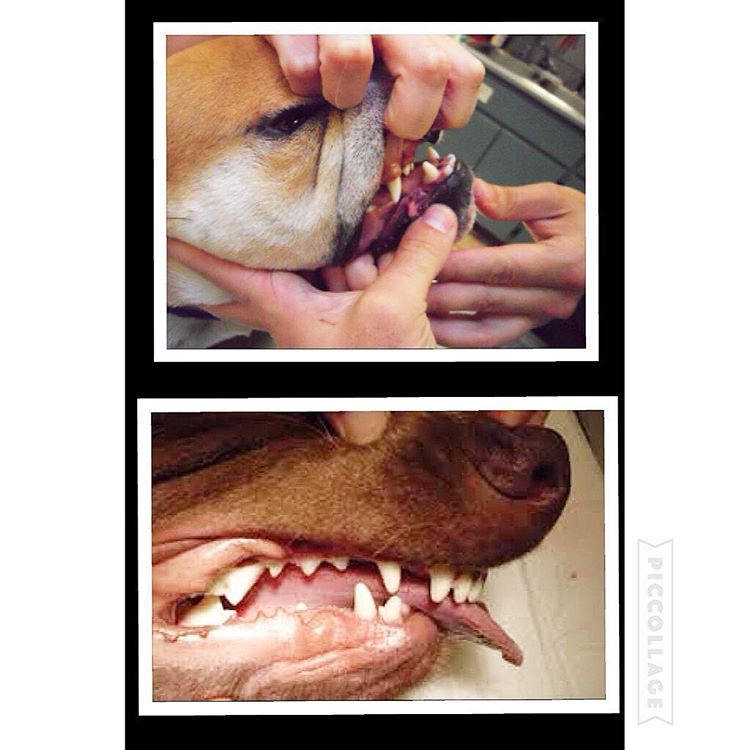
Enzo is a short-haired Havanese and he was born with his lower jaw shorter than the upper jaw. This is called an Overbite, also referred to as an Overshot Jaw, a Parrot Mouth or Mandibular Brachygnathism. This malocclusion is a genetic change and can be seen in a number of breeds, oftentimes collie related breeds and dachshunds. Occasionally this change happens because of differences in the growth of the upper and lower jaws, and in many cases it doesn’t cause any significant problems other than cosmetically.
Once extracted, each deciduous canine tooth was about 2 centimeters long; the roots were about 1.5 centimeters. Many people are surprised to learn that the root of a dog’s tooth is so large – 2/3 to 3/4 of the tooth is below the gumline. This is one reason why it is so important to use radiographs to evaluate teeth on a regular basis, not just in a growing puppy. Adult teeth can, and frequently do, have problems that are only visible with a radiograph.

A dog underbite is a dental or skeletal condition characterized by lower teeth that extend outward farther than the upper front teeth. This condition is also called a Class-3 malocclusion.
Malocclusion in dogs causes an abnormal alignment of the teeth, which results in an abnormal bite. A dog whose lower jaw is protruding and with the bottom teeth sticking out when at rest is known as an underbite dog.
Dental is probably the number one cause of malocclusion in dogs. Dental underbites occur when one or a couple of teeth are abnormally positioned within a normal facial skeletal structure, says Dr. Santiago Peralta, assistant professor of veterinary dentistry and oral surgery at Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine (CUCVM).1
Dental underbite commonly happens when a baby tooth fails to fall out and is still present when a permanent tooth erupts. This causes crowding among teeth. Thus the abnormal position and underbite look in your dog.
This cause of underbite on dogs is the easiest to correct. According to Sacramento Veterinary Dental Services, the extraction of the primary teeth (interceptive orthodontics) should be performed as soon as possible to correct the problem.2
Dr. Nadine Fiani, assistant clinical professor of dentistry and oral surgery at CUCVM, says the skeletal type of malocclusion is where the dog’s facial structure is abnormal, causing the teeth not to fit together correctly.
Skeletal underbite in dogs may be more problematic than dental.An abnormal mouth bone structure may cause the canine teeth or maxillary incisors to make abnormal contact with the gums causing severe distress and damage to your pup’s teeth and gums. This could fasten the rapid onset of periodontal disease.
“[A dog underbite] will be acquired, whether because something happened during gestation or something happened during growth and development. The condition can develop due to an infection, trauma, or any other event that may alter maxillofacial [face and jaw] growth.”
A dog underbite may also be caused by jaw fractures that don’t heal properly. Trauma to the face and jaw caused by bites, accidents, or getting hit by a car can cause your dog to develop an underbite.
Fortunately, most dog underbites do not require any treatment. If the underbite is not causing damage to a dog’s mouth (i.e., preventing chewing or swallowing), there may be no need for treatment.
Any dog breed can develop an underbite. However, Class 3 malocclusions (dog underbite) are more common in brachiocephalic dog breeds, like Pugs and Bulldogs. However, an underbite can appear in any dog breed.
Most malocclusions are genetic. It’s important to have your dog’s bite evaluated for non-symmetrical jaw growth by a professional, especially if your dog is brachycephalic.
Upon examination, your vet should recommend treatment if necessary. In some cases, underbites don’t cause any irritation and are nothing to worry about. Be sure to request a dental radiograph (X-rays) for your pet. This will help identify most oral diseases in dogs.
Orthodontic treatments for dogs with underbites vary in price depending on the condition, the number of teeth involved, rounds of anesthesia, among other factors. The treatment cost of malocclusion in dogs usually fluctuates between $1,500 and $4,000, according to PetMD.
Just like adult dogs, puppies with underbites are prone to health issues. If your dog has an underbite, seek medical attention to determine if your puppy’s underbite is detrimental to his health.
An underbite is permanent and generally does not get worse with age. Dogs with underbites do not have many problems. However, the main issue you may encounter is that the teeth align and rub against each other and create a wound within the gums or hard palate.
Switching from hard to soft dog food is advised when living with a dog with an underbite. Some dogs with underbites tend to have trouble chewing their food. Nom Nom fresh dog food is a great alternative to aid when this happens and to put less stress on your dog’s teeth when eating his food.
When it comes to dog treats for dogs with underbites, consider these soft-baked dog treats by Merrick or American Journey’s soft chewy dog treat. You also want to provide a soft chewing dog toy like Chuckit! Roller Dog Toy. Its textured chenille fabric is gentle on dogs’ mouths.
Dogs whose teeth have been extracted or re-shaped must maintain a strict recovery period by only eating soft foods. Regular cleaning is needed to make sure the dog’s teeth continue to be healthy. Be sure to brush your dog’s teeth regularly.
This helps promote fresher breath and cleaner mouth reducing the chances of periodontal disease, which is more common in dogs with underbites and present in 80% of dogs have by age 3. No toothbrush required.
Finally, dogs with underbites often develop excessive tartar and calculus build-up. Hence, it’s also a good idea to target the build-up of plaque and tartar with a Dental Formula Water to leave your dog’s teeth and gums in tip-top condition.
A dog’s bite typically sets at ten months old. It is unlikely that an underbite will improve on its own at this point. However, there is a chance that your dog’s underbite can worsen due to poor oral hygiene and neglecting the condition.
Most dogs that show underbite symptoms as a young puppy will likely have a dog underbite for the rest of their lives. This misalignment can sometimes self-correct as your dog develops, but if your dog is genetically predisposed, it is highly unlikely for this to happen. Dog underbite can be corrected through surgery and braces in some cases.
Genetics, accidents, dental or skeletal problems can lead to underbites in dogs. In some breeds, underbites are the result of intentional breeding practices. Breeders breed underbite dogs specifically to engineer the type of jaw structure of a bulldog or a boxer.
An underbite malocclusion can be considered normal and healthy as long as the dog can chew and eat solid food comfortably and their bite is functional. Some breeds of dogs, usually flat-faced or brachycephalic, are naturally born with underbites. These breeds have been genetically bred to have a lower jaw that is slightly longer than the upper.
Bulldogs have brachycephalic skulls, which means their faces are pushed inward. As a result, the upper jaw is usually shorter than the lower — underbite. In some bulldogs, the underbite is minor, while in others, it is extreme that they find eating difficult.
As a responsible underbite dog parent, you need to be proactive in checking your dog regularly for any developments that could cause substantive health and dental issues so they can live a long and healthy life by your side.
If you plan to adopt or buy a genetically predisposed underbite dog, you need to understand and meet the special care and potential treatment requirements of such a sog.
Granted, a perfectly aligned set of pearl whites is sought-after for a million-dollar smile in the human world. However, in the doggy world, having a canine malocclusion or underbite (misaligned teeth) is the least of their worries.
Nonetheless, knowledge is power! In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of a dog underbite, including the causes, cost, and treatment. Knowing this can aid in the minimization of problems and curb the reoccurrence of irregular bites in bloodlines.
It describes a skeletal or dental condition characterized by the lower teeth protruding farther than the upper front teeth. A dog underbite is also known as a Class-3 malocclusion. In addition to creating an appearance in the face and mouth that closely resembles a bulldog, malocclusion triggers abnormal teeth alignment, which causes an irregular bite.
A pooch with a protruding lower jaw and bottom teeth sticking out when at rest is referred to as an underbite dog. Before we delve into whether or not underbite on pooches can be rectified, it’s essential to understand what causes it and its variations.
Nonetheless, the dental cause of a dog underbite is the easiest to rectify, provided that interceptive orthodontics (the extraction of primary teeth) is performed as soon as possible.
In some dog breeds, an underbite is a cherished quality that is part of the norm. For instance, pugs, boxers, Pekingese, and bulldogs are renowned for their brachycephalic features. In this scenario, an abnormal mouth bone structure may result in the maxillary incisors or teeth making irregular contact with the gums. Consequentially, this leads to adverse distress and damage to your canine’s gums and teeth.
Typically, a dog’s lower and upper teeth intersect in a ‘scissor bite’ when the jaw is closed. However, some scenarios arise whereby the lower teeth stick out in front of the upper ones causing a reverse scissor bite. Genetic causes of a dog underbite are seen in long and medium-muzzled pooches.
At times, the case of a dog underbite is acquired from the inappropriate tugging and chewing during the delicate stage of teething. Puppies then develop bite issues whereby their growing teeth shift from their initial position.
To avoid this predicament, refrain from playing tug-of-war and other aggressive games with your dog. Using ropes or towels to delight in these games can result in your pet’s teeth shifting into an unusual position, which results in their misalignment.
Dogs with adverse undershot bites may experience challenges in chewing. Furthermore, their soft tissues get damaged. At times, the undershot bite is adverse enough to require tooth extraction or orthodontic treatment.
However, it’s more prevalent in certain breeds than others. Although small dog breeds with underbite are the most common, boxers and other larger breeds are also susceptible. Here are a few examples:
If your dog has an underbite and you’re scratching your head wondering whether it can be rectified, fret not, as the answer is yes! The good news is most dog types of underbite don’t call for any treatment if it’s not interfering with the chewing and swallowing process.
It’s a procedure that encompasses the extraction, shifting, and shortening of teeth to ensure they perfectly fit like a puzzle and no longer hurt a dog.
Untreated underbite causes more than off-kilter smiles. As you may have guessed, dogs with malocclusion are susceptible to a wealth of health risks, as outlined below. It ushers in a life of discomfort for your beloved canine companion.
Upon examination, the vet will recommend treatment if need be. At times, an underbite doesn’t cause irritation, which should put you at ease. Nonetheless, ensure you request a type of X-ray known as a dental radiograph for your pet. It will easily pinpoint most oral ailments in dogs.
Underbite in young dogs can be rectified using braces. Nonetheless, filling and extraction can also be applied. The treatment alternatives for a puppy with an underbite vary based on the type of malocclusion involved, their health status, and age.
As is the case with adult dogs, a puppy with an underbite is susceptible to health problems. If you notice an underbite, we recommend seeking medical attention to determine if it’s detrimental to their health. If you’re wondering whether your puppy will grow out of the underbite, the truth is, although it’s possible, the chances are slim to none if it’s genetic.
Symptomatic dog underbite can gain from early treatment and care to prevent eating challenges and pain, among other complications. With that being said, here’s a breakdown of a few ways to care for a pooch with an underbite.
We recommend switching from hard to soft food when residing with a pup with an underbite. After all, it’s a no-brainer that a dog underbite causes chewing problems.
Wet dog food is an excellent option as it puts minimal stress on your pooch’s teeth when eating. You can also consider soft, chewy, or baked dog treats.
Frequent cleaning is necessary to ensure a pup’s teeth remain in tip-top health. Therefore, brush your dog’s teeth with a vet-recommended toothpaste and toothbrush every two days.
A dog with an underbite typically develops excessive calculus and tartar. As such, targeting this build-up with dental formula water will keep your pooch’s gums and teeth in excellent condition.
While a dog underbite isn’t necessarily a problem, it’s undoubtedly a cause for concern. Turning a blind eye can usher in a boatload of health adversities for your pup, and that’s the last thing you need.
Therefore, as a responsible dog owner, you should be proactive in taking the steps we’ve discussed to pinpoint and treat an underbite for your pet to live a long, healthy, and happy life right by your side. Moreover, you need to exercise vigilance when it comes to planning regular checkups to monitor your pup’s health.
Lastly, without a shadow of a doubt, all pooches are worthy of equal care and love. However, we don’t recommend seeking out dog breeds that are susceptible to an underbite (regardless of how adorable they are) unless you can provide the much-needed care that includes hefty vet bills if complications crop up.

Undershot is a class III malocclusion that is also referred to as mandibular prognathism, maxillary brachygnathism, mandibular mesioclusion, or an underbite. This malocclusion is characterized by a shorter upper jaw and a longer lower jaw, resulting in lower teeth that are in front of the upper teeth. While this condition is normal for some breeds, such as Bulldogs, in many breeds it is unusual. An undershot jaw occurs when the lower jaw grows faster than normal and becomes longer than the upper jaw, and is usually evident around 8 weeks of age in puppies. This misalignment can cause soft tissue trauma, such as to the lips. When the incisors meet instead of fitting next to each other, it is called a level bite. When the malocclusion causes the lower incisors to be placed in front of the upper incisors, it is called a reverse scissors bite.
The cause of overshot and undershot jaws in dogs relate to the increased or decreased rate of growth of the upper and lower jaws in relation to one another. This can occur due to a: Genetic disorder Trauma; Systemic infection ;Nutritional disorder; Endocrine disorder; Abnormal setting of puppy teeth; Early or late loss of puppy teeth.
After a quick physical exam, your vet may have to sedate your dog in order to perform a thorough oral exam. This will assess your dog’s skull type and teeth location in relation to the teeth on the opposite jaw. Often, the placement of the upper and lower incisors in relation to one another can determine what type of malocclusion your dog has. Your vet will note any areas of trauma due to teeth striking those areas, and any cysts, tumors, abscesses, or remaining puppy teeth that may be present. A dental X-ray can also help to assess the health of the jaws and teeth. These diagnostic methods will lead to a diagnosis of an overshot or undershot jaw in your dog.
Treatment of a jaw misalignment will depend on the severity of the condition. If your dog has a misalignment, but can still bite and chew food without problems, no treatment may be needed. If the misalignment is caught early in a puppy’s life, it may only be temporary and may correct itself over time. However, there are times when intervention may be needed. If your puppy’s teeth are stopping the normal growth of his jaws, then surgery to remove those puppy teeth may be performed. This may allow the jaws to continue to grow, but will not make them grow. For older dogs who are experiencing pain and trauma due to misaligned jaws and teeth, oral surgery is generally performed to extract teeth that are causing trauma, to move teeth so that they fit, or to create space for a misaligned tooth to occupy. Other therapies include crown reductions or braces.
If your dog is genetically programmed to have an overshot or undershot jaw, intervention can help, but will not slow or stop the abnormal growth of either jaw. Prevent jaw misalignments in puppies by not breeding dogs who have overshot or undershot jaws.

You can download this article on puppy teeth problems as an ebook free of charge (and no email required) through the link below. This comprehensive article covers such topics as malocclusions, overbites, underbites and base narrow canines in dogs. Special emphasis is placed on early intervention – a simple procedure such as removing retained puppy teeth can save many problems later on.
One of the biggest misconceptions is that dental problems don’t need the same treatment in animals as they do in humans. Nothing could be further from the truth! Dogs’ teeth have the same type of nerve supply in their teeth as we do, so anything that hurts us will hurt them as well.
All dogs, whether they are performance dogs or pets, deserve to have a healthy, pain-free mouth. Oral and dental issues frequently go undiagnosed in dogs, partly because the disease is hidden deep inside the mouth, and partly because dogs are so adept at hiding any signs of pain. As a pack animal, they don’t want to let the rest of the pack (including us!) know they have a problem, as anything that limits their usefulness to the pack may be grounds for exclusion. This is a survival instinct. Dogs will suffer in silence for as long as they can, and they only stop eating when they cannot bear the pain any longer.
This article has been written to help you understand how oral and dental problems develop in puppies, what the implications of these issues are, and what options are available to you and your pup to achieve the best outcomes in terms of overall health, comfort and performance. You don’t need to read it from top to bottom, as your dog would need to be pretty unlucky to need all the advice included here!
If you would like to speak to me for advice on your dog, please feel very welcome to call me on 1300 838 336, or you can email me on support@ sydneypetdentistry.com.au.
baby) teeth which erupt between 3-8 weeks of age. These are replaced by the adult (permanent) teeth between 4-7 months of age. Adult dogs should have a total of 42 teeth. The difference in the number of deciduous and adult teeth arises because some adult teeth (the molars and first premolars) don’t have a deciduous version.
The bulk of the tooth is made up of dentine (or dentin), a hard bony-like material with tiny dentinal tubules (pores) running from the inside to the outside. In puppies, the dentine is relatively thin, making the tooth more fragile than in an older dog. The dentine thickens as the tooth matures throughout life.
Crowded upper incisor teeth in an English Bulldog, with trapping of food and debris. There is an extra incisor present which is exacerbating the problem.
‘Base narrow’ canines (Linguoverted or ‘inverted’ canines) are a relatively common and painful problem in Australian dogs. The lower canines erupt more vertically or ‘straight’ than normal (instead of being tilted outwards), and strike the roof of the mouth. This causes pain whenever the dog chews or closes its mouth, and can result in deep punctures through the palatal tissues (sometimes the teeth even penetrate into the nasal cavity!). In our practice in Sydney, we see this most commonly in Staffordshire Bull Terriers and Labrador Retrievers.
Lance’ canines (Mesioverted, hard or ‘spear’ canines) occur when an upper canine erupts so it is pointing forward, like a tusk. This is seen most commonly in Shetland Sheepdogs, and can lead to lip trauma and displacement of the lower canine tooth (which cannot erupt to sit in its normal position in front of the upper canine).
Class II malocclusions (‘overshot’) arise when the lower jaw is relatively short compared with the upper jaw. This type of occlusion is NEVER considered normal and can result in significant and painful trauma to the upper gums, hard palate and teeth from the lower canines and incisors.
When the upper and lower teeth are locked against each other, the independent growth of either jaw is severely limited. This can occasionally work in the dog’s favour, for example if the lower jaw is slightly long compared with the upper jaw, the corner incisors may lock the lower canines in position behind them, limiting any further growth spurts of the lower jaw.
Retained or persistent deciduous (puppy) teeth can also cause malocclusions by forcing the erupting adult teeth into an abnormal position. As previously mentioned, this may be a genetic trait, but can also occur sporadically in any breed of dog.
The basic rule is that every dog deserves a pain-free, functional mouth. If there is damage occurring to teeth, or oral tissues, we need to alleviate this, to allow the dog to live happily and healthily. If there is no functional problem and no trauma occurring, then treatment is simply not required.
Sometimes the hardest part is determining whether the problem is in fact causing pain. As we know, dogs are very adept at masking signs of oral pain, and will and will continue to eat despite real pain. Puppies, in particular, don’t know any better if they have had pain since their teeth first erupted very early in life.
The overriding aim is always to give the dog a healthy, pain-free and functional mouth. Sometimes this will result in a ‘normal’ mouth, whereas in other cases, this might not be realistically achievable.
While some basic advantages and disadvantages of the different treatment options are outlined here, it is very important to seek specific advice for your individual dog, as no two mouths are exactly the same, and an individual bite assessment will help us determine the best course of action together. You can contact us anytime.
Extraction of lower canine teeth – the roots of these teeth make up about 70% of the front of the jaw, and so there is a potential risk of jaw fracture associated with their removal. Some dogs also use these teeth to keep the tongue in position, so the tongue may hang out after extraction.
Crown reduction is commonly performed to treat base narrow canines, or class II malocclusions, where the lower canines are puncturing the hard palate. Part of the tooth is surgically amputated, a dressing inside the tooth to promote healing and the tooth is sealed with a white filling (just like the ones human dentists use). This procedure MUST be performed under controlled conditions as it exposes the highly sensitive pulp tissue. If performed incorrectly, the pulp will become infected and extremely painful for the rest of the dog’s life.
While the dog may lose some function, this is far preferable to doing nothing (this condemns the dog to a life of pain). Indeed, unless released into the wild, dogs do well even if we need to extract major teeth (canines and carnassials), as they have the humans in their pack to do all the hunting and protecting for them.
The aim of any veterinary procedure should always be to improve the welfare of the patient, so the invasiveness of any treatment needs to be weighed up against the likely benefits to the dog. Every animal deserves a functional, comfortable bite, but not necessarily a perfect one. Indeed, some malocclusions (particularly those involving skeletal abnormalities) can be difficult to correct entirely.
In addition to the welfare of the individual dog, both veterinarians and breeders need to consider the overall genetic health of the breed. Both the Australian National Kennel Club and (in New South Wales where our practice is situated) the Veterinary Practitioners’ Board stress that alteration of animals to conceal genetic defects for the purpose of improving their value for showing (and breeding) is not ethical.
The bottom line is that, while all dogs will have multiple treatment options available, and in some cases the occlusion can be corrected to the point of being ‘good for show’, advice should definitely be sought about the likelihood of a genetic component prior to embarking upon this, as the consequences for the breed can be devastating if such animals (or their close relatives) become popular sires or dams.
Sometimes a tooth is congenitally missing, that is it has never developed. While dogs can physically cope well with missing teeth, in some breeds this is considered a serious fault, and will severely affect the chances of the dog being successful in the show ring.
We cannot rely on dogs to tell us when they have oral pain. It is up to us to be vigilant and watch for signs of developing problems. Train your pup to allow handling and examination of the mouth from an early age. We will be posting some videos of oral examination tips shortly, watch out in your email inbox for this. Things can change quickly – check their teeth and bite formation frequently as they grow.
Remember, early recognition and treatment is crucial if we want to keep your dog happy and healthy in and out of the show ring. The sooner we treat dental problems, the higher the chance of getting the best possible results with the least invasive treatment.
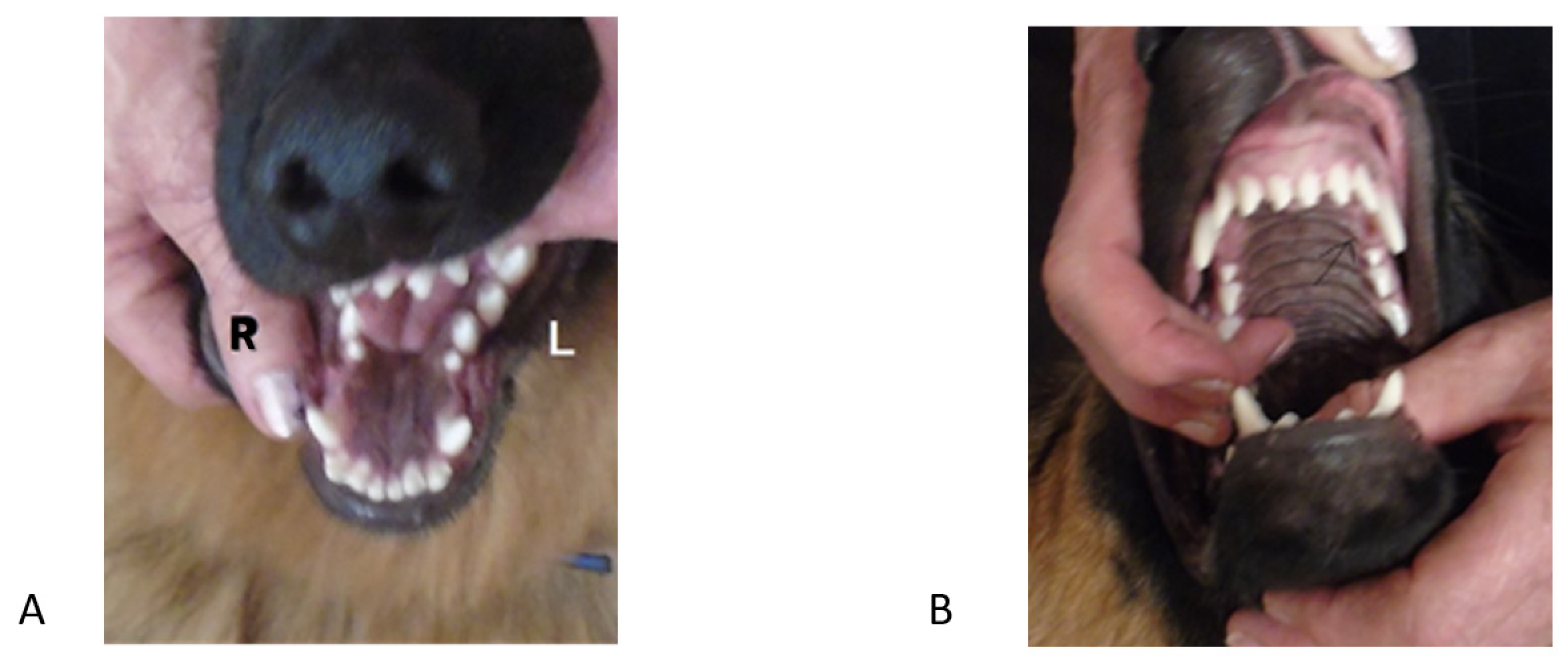
Yes, dogs can have underbites just like people can have them, but the snaggletoothed gaze of a dog with an underbite can certainly be endearing. Treating an underbite in a dog, though, can be vastly different than treating one in a person.
An underbite is a type of malocclusion. The prefix, "mal," comes from Latin and literally means "bad," so a malocclusion is a bad occlusion. In underbites, the lower jaw juts out too far, leading to misalignment of the bottom and top teeth when the mouth is closed. Dogs with an underbite may have a snaggletoothed appearance, with one or both lower canines visibly sticking out of their mouth. Underbites are also sometimes termed Type 3 Malocclusion in dogs because, unfortunately, it"s not the only type of malocclusion dogs can have. They can also have overbites (aka Type 2 Malocclusion) and cross-bites, just like people.
Underbites are almost always congenital in nature. This means that it"s present from birth. They are most commonly seen in brachycephalic breeds, such as Boxers, Boston terriers, Brussels Griffons, Bulldogs, Lhasa Apso, Shih Tzu, Pugs, etc. In fact, underbites are so commonly seen in these breeds that they are considered to be their normal dentition In rare instances, facial trauma can also cause an underbite.
Regardless of whyyour dog has an underbite, it"s important to understand the repercussions a dog with an underbite may face. An underbite (or any dental malocclusion) can make a dog more prone to dental disease. If the upper teeth and lower teeth don"t line up like they"re supposed to, that can make some teeth more prone to tartar build up. It can also lead to more tooth-on-tooth wear and can also damage or irritate the gums, lips, or hard palate.
In people, an underbite is fixed by orthodontics and braces. Believe it or not, they make braces for dogs, too! However, they are used primarily under the supervision of a board certified veterinary dentist, not a general practitioner. Additionally, they aren"t used for cosmetic purposes as in people. Braces are used in dogs only when there is a medical problem warranting their use. Application of the braces and subsequent adjustment of the brackets will require general anesthesia and dental radiography. A more common approach is to remove teeth that are badly affected by the malocclusion or are causing pain due to digging into the gums or lips.
For most dogs with underbites, management of problems created by the malocclusion is the treatment of choice. Dogs that have underbites may require more at-home, preventative dental care. Chews and oral rinses certainly don"t hurt, but they are also not nearly as effective as brushing the teeth. If you have a dog with an underbite, training them to accept daily tooth brushing can be helpful. It"s important that you use veterinary specific toothpaste as human toothpaste usually contains fluoride, which can be harmful if swallowed. Additionally, most dogs don"t prefer the minty flavors of human toothpaste. Veterinary toothpaste comes in more dog-friendly flavors such as poultry and beef.
Eventually, though, even daily brushing may not be enough to stave off dental disease. If your dog has gingivitis, heavy tartar, and/or bad breath, your dog may need a dental cleaning. This is similar to when humans routine dental cleanings with ultrasonic scaling, followed by polishing the enamel smooth. The major difference being that dogs need to be put under anesthesia for safe, effective dental cleanings and in order to safely take dental radiographs.
If your dog has an infected or abscessed tooth, the most common treatment is to simply take out the tooth in question. Most dogs can do just fine without the infected tooth. However, those same veterinary dentists that can place braces when needed can also perform root canals to save infected and/or fractured teeth. The cost of this may be prohibitive in some cases, but it is a good option to look into to help maintain a healthy mouth.
Unfortunately, because the most common reason for an underbite to happen is congenital, it can be difficult to prevent one if you are looking for a breed of dog that is prone to them. As mentioned, this abnormality is considered to part of the breed standard for these snub nosed breeds because it"s a result of their signature "pushed-in" faces. A pug or bulldog isn"t a pug or bulldog without a smushed-looking face, and breeding its snout to be so short predisposes it to problems.
Underbites in dogs can put them at risk for future dental disease and may cause chronic pain or difficulty chewing. If your dog has an underbite and you"re worried about the health of its teeth, speak to your veterinarian.

While there are a number of reasons why you may be thinking of offering your dog at stud, the most important goal, above all else, should be to improve the breed.
We do not currently keep a register of stud dogs. If you wish to use your dog at stud, please contact your local breed club for more information and advice.
If you have not mated your dog before, you may want to seek advice from experienced stud dog owners to find out what to expect before, during and after the mating has taken place. When first using your dog at stud, it can be advantageous to try and mate him with an experienced bitch.
Before breeding from a dog or bitch, we advise that breeders investigate whether there are any possible inherited conditions that may affect the breed. A stud dog can father many puppies and so it is essential that they are healthy and fully health tested to reduce the risk of passing on any health issues on to future generations. Stud dog owners can check which health tests are applicable to their breed by referring to our Breeds A to Z, or by checking with their local breed club. It is advisable to speak to your dog’s breeder prior to mating to see if there are any health concerns in your dog’s pedigree.
There are several health schemes currently in operation to assist in the prevention or control of some diseases. These tests include DNA tests which give a definitive answer on the status of each dog. Where these schemes exist, we strongly recommend that both sire and dam are tested. In the case of a DNA test, we recommend that at least one parent should have tested clear for the particular condition. Read further breeding advice on mating DNA tested dogs.
If you are considering purchasing a stud dog, then our Health Test Results Finder allows you to search for any health results for a dog which is registered on The Kennel Club’s Breed Register, either by its registered name or registration number (or stud book number).
Inbreeding, put simply, is the mating of related individuals – those individuals with common ancestors. High levels of inbreeding can impact the health of individual dogs, as it increases the chances of a dog being at risk for both known and unknown inherited disorders. It could also have an impact on the breed as a whole, e.g. a reduction in litter size and fertility.
Popular sires, or male dogs, that are used to produce large numbers of puppies, are one of the biggest contributors to a reduction in genetic diversity, an increase in inbreeding and elevated levels of genetic diseases within a breed.
These dogs are often chosen because they have good characteristics, such as traits associated with good health.Breeders will use these dogs because they wish to improve the breed, but excessive use of any males can be detrimental to the overall population. Learn more about the impact of your dog becoming a popular sire.
Dogs have different dispositions and personalities and when choosing two dogs to mate together, both should both have a good temperament. The temperament of the potential parents will be a good guide to predicting the temperament of any potential puppies. If a dog shows any suspect temperament, such as aggression, then it should not be bred from.
Before the mating occurs, it is important that a detailed written stud dog contract is agreed upon and signed to prevent any future confusion. Ensure that a copy of your signed contracts are filed away in a safe place.
The terms and conditions of a mating do not fall within the jurisdiction of The Kennel Club. It is therefore advisable that any breeding terms or stud fees should be arranged by mutual agreement in writing between the owner of the dog and the owner of the bitch before the mating takes place.
As a general point, if a dog has not previously been used at stud, the owner might charge a nominal fee covering expenses at the very least. Once the dog has been proven (i.e. has produced puppies), the stud fee may be reviewed for any future matings according to the value of the dog as a proven sire and the quality of his progeny.
A guide to an appropriate stud fee may be obtained from studying online advertisements, as breeders may advertise their dogs for stud. Alternatively you can contact your nearest breed club, who may be able to give you advice on this and any other matters relating to your breed.
You will also need to ensure that your dog’s Kennel Club registration does not carry any breeding restrictions or endorsements. If there are any, before any mating occurs, you will need to discuss this further with the person from whom you obtained the dog, as any breeding restrictions or endorsements will need to be removed before the registration of a litter can take place. In most cases it will be the breeder who has placed the restriction, and they will therefore be the person empowered to remove it.
Although the main responsibilities of theAssured Breeders scheme relate to the dam owner, there are responsibilities such as permanent identification required for the stud dog. Assured breeders are given a high profile through The Kennel Club and advertised on our website all year round. There are a variety ofdiscounts and rewardsavailable for members of the scheme.
Using your dog on a bitch that is not well matched may have an impact on the puppies produced and your dog’s reputation. It is your responsibility to ensure that a mating between the two dogs is justified and that a mating will be beneficial to the breed.

Underbites may not be the first thing you think of when it comes to dogs, however, there are several breeds sporting this toothy grin. Find out which dogs have underbites and why dogs have underbites in the first place.
Like humans, an underbite in a dog refers to the lower teeth projecting beyond the upper teeth. Veterinarians will refer to this issue as malocclusion. While an underbite can happen in various breeds, it’s commonly seen in brachycephalic breeds.
Besides short-skull breeds, underbites are also common in small dogs. Dogs that belong to the toy breed classification also typically suffer from other dental issues such as overcrowding or protruding teeth.
Shih Tzus are a beloved companion animal commonly found in homes worldwide. These friendly little creatures have a long history of being lap dogs for noble women in China.
Perhaps the dog most commonly associated with an underbite is the English Bulldog. This breed’s predisposal for malocclusion completes the Bulldog’s look. It’s fair to assume if you are purchasing a bulldog, you will have to deal with an underbite.
This is why it’s important to only purchase your English Bulldog from a responsible, ethical, and reputable breeder. A Bulldog with an excessive underbite will not only require expensive dental visits but may experience discomfort while eating.
These lap dogs were bred as companions to royal figures in the Chinese city of Peking. Today, these toy-sized dogs are loved by many. They are regarded as friendly, intelligent, and full of personality.
Pekingese dogs are distinguished by their “lion mane” coat. It’s also not uncommon for these small dogs to present an underbite. Like other brachycephalic breeds, they are prone to having underbites.
It’s not hard to spot a Pug! Their black masked, squished face and fawn shorthair coat set them apart from other dogs. There’s nothing like those little curled tails wagging to greet you!
Like other dogs on this list, Pugs are considered a short skull or brachycephalic breed. With this comes your typical dental problems, including an underbite.
This attribute sets it apart from other short-skulled breeds that often prefer a more sedentary lifestyle. These dogs weigh no more than 25 pounds yet love to run, hike, or explore the park. This feature makes them ideal for city dwellers with an active lifestyle.
While most of the breeds on this list are small dogs, larger breeds such as Boxers also suffer from underbites. Boxers can weigh up to 80 lbs and belong to the working group classification. These dogs are known to be highly intelligent and easily trainable.
These tiny dogs come from Mexico. They are known for having a huge personality trapped in a tiny body! While they may not have a squished face like other breeds on this list, they are a small breed and only reach about 6 lbs on average.
These fluffy little dogs share the homes of millions of people around the world. These dogs originated in Poland and were bred to pull carts, guard livestock, and do other physical jobs. However, they were eventually bred to be smaller to be companion animals.
These long-haired, white, small dogs are very popular. You will typically find Maltese dogs living in urban areas. Their small size has made them ideal city dogs.
The first Spaniel to make it on our list, King Charles Spaniels, are a very popular family dog. They rank consistently in the top 20 most popular breeds in the U.S. While most commonly sporting a red and white coat, you can also find King Charles Spaniels to be black and tan and tri-colored.
While known for being friendly and intelligent, King Charles Spaniels are prone to various health issues. The most common health issues are ear infections and dental problems. While these little dogs make fantastic pets, don’t be surprised to find yourself in the veterinarian’s office!
Like the English Bulldog, French Bulldogs are short-skulled dogs with squished faces. What sets them apart from other bulldogs? They have pointed, bat-like ears that stick up.
They are sometimes mistaken for a Boston Terrier. While French Bulldogs have been rising in popularity over the past decade, it’s important to understand these dogs commonly exhibit various health problems.
It’s not uncommon for French Bulldogs to have severe underbites. It’s essential to only purchase puppies from reputable breeders that understand genetics.
Usually, treatment is not necessary. However, there are treatment options if you suspect your dog is experiencing discomfort or pain related to their underbite. Typically, these include extractions, physical therapies, and root canal treatments.
Your local vet is a good place to start! If your dog’s underbite is severe, they will be able to connect you with specialists in your area. Veterinary dentists are specialists that receive extra training to treat oral and dental issues in your pet.
For most dogs, it is simply the result of genetics. This is especially true if you have a short-skull or small breed. In rarer cases, malocclusion may be the result of trauma. This trauma may have occurred in the womb or early in a dog’s life.
Sometimes, a young dog’s underbite may correct itself. However, it’s most likely that if your puppy is exhibiting an underbite, it will have it throughout its life. This is especially true if you have a brachycephalic or small breed.
If you have a pup with an underbite or are looking at possibly getting one, it’s essential to understand the risk associated with dogs with underbites. While underbites are typically not a problem for most dogs, consult your veterinarian if you’re worried about your dog’s teeth or bite.

We advise you email us images of the teeth (mouth closed, lips up and side on for both left and right) just a few days before you travel. Things change quickly in growing dogs and it might save you a wasted journey.
These permanent teeth can theoretically be treated by three options. Not all options are available to all cases. These options are described below and are either surgical removal of the lower canines teeth (and possibly incisors also), crown amputation and partial pulpectomy or orthodontics via an inclined bite plane bonded to the upper canines and incisors. The latter option may not be available to all dogs if the diastema (space) between the upper third incisor and canine is too small for the lower canines to move into or if the lower canines are located behind (palatal) to the upper canines.
This is a very delicate procedure and carries very high success rate (in our hands) since the availability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA). We have used it as the material of choice since 2005. The previous agent (calcium hydroxide) was much more caustic and tended to "burn" the pulp. The success rate of MTA treated cases is quoted as 92% in a seminal ten year study based in vet dental clinics in Finland. This compares with 67% when caclium hydroxide was previously the agent. Luotonen N et al, JAVMA, Vol 244, No. 4, February 15, 2014 Vital pulp therapy in dogs: 190 cases (2001–2011).
In some mild cases of lingual displacement we may be able to use crown extensions for a few weeks. For this treatment we bond composite resin extensions on the lower canines to increase the crown length by around 30%. This allows the lower canines to occupy the correct position and also provides more leverage to tip the crown tips buccally. The crown extensions remain in place for around 2 months and are then removed and the tooth surface smoothed and treated. The major downside is that if the dog damages or breaks them off, you need to return here for repairs. Sticks and other hard objects can easily cause damage and some toys also have to be withdrawn for the treatment period.
Not all dogs or owners are suited to this. Bite planes can become dislodged if the dog bites a stick or other hard object. Bite planes also need cleaned and adjusted from time to time under sedation or anaesthesia. All of this means more travel and expense for you and more anaesthesia for your pet. It is our view that if a treatment has uncertain outcomes built in it should probably not be used.




 8613371530291
8613371530291