overshot jaw in puppies manufacturer

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
Enzo is the Hawthorne Hills Veterinary Hospital Pet of the Month for May. Everyone knows that puppies need vaccines to keep them healthy and protected from diseases. However, it can be easy to underestimate the benefits of thorough and regular examinations when puppies are growing into adulthood. Every breed has special characteristics that make them unique and add to their appeal and sometimes there are physical changes that need to be addressed quickly. For this reason our veterinarians believe in examinations with every vaccine, especially during a puppy’s formative months.
Enzo is a short-haired Havanese and he was born with his lower jaw shorter than the upper jaw. This is called an Overbite, also referred to as an Overshot Jaw, a Parrot Mouth or Mandibular Brachygnathism. This malocclusion is a genetic change and can be seen in a number of breeds, oftentimes collie related breeds and dachshunds. Occasionally this change happens because of differences in the growth of the upper and lower jaws, and in many cases it doesn’t cause any significant problems other than cosmetically.
Dr. Robin Riedinger evaluated Enzo at his first visit when he was just 11 weeks of age and while the lower jaw was too short, there was no evidence of damage and no indication that this was causing a problem for Enzo. When there is abnormal occlusion of the teeth, it is important to monitor closely for trouble caused by the teeth being aligned improperly. Malocclusions can lead to gum injuries, puncturing of the hard palate, abnormal positioning of adjacent teeth, abnormal wear and bruising of the teeth, permanent damage and subsequent death of one or more teeth, and in the long run, premature loss of teeth. Some malocclusions can be severe enough to interfere with normal eating and drinking.
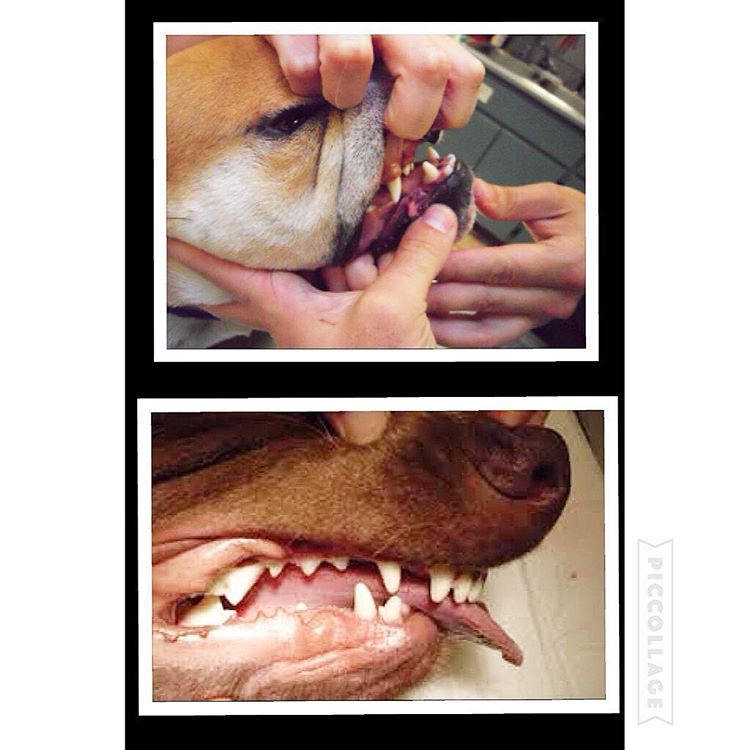
Within three weeks, when Enzo was only 3.5 months old, it was clear that our doctors would need to intervene. The left and right sides of Enzo’s upper jaw (maxilla) were growing at different rates because the lower canine teeth were being trapped by the upper canine teeth. This is called Dental Interlock. Because the teeth are ‘locked’ in place, the lower jaw cannot grow symmetrically and this creates a number of other problems. Early intervention is critical.
The solution for Dental Interlock is to extract the teeth from the shorter jaw; in this case, the lower ‘baby’ canines and thereby allow the lower jaw (mandible) to grow in the best way possible. This procedure is most effective when the Dental Interlock is discovered early and the extractions are performed quickly. In some cases, this can be as early as ten weeks of age. Dr. Riedinger consulted with a local veterinary dental specialist to confirm the treatment plan and to get advice on extracting the deciduous teeth without damaging the developing adult canines. Dental radiographs are essential to proper extraction technique and also to ensure that there are no other abnormalities below the gumline.
You can see how long the roots of the deciduous ‘baby’ teeth are. During normal growth, the body will begin to resorb the roots, making them loose, and allow them to fall out as the adult tooth begins to emerge. When we need to remove the deciduous teeth before they are loose, it can be quite tricky to remove the tooth carefully without breaking it and without injuring the adjacent teeth.
Once extracted, each deciduous canine tooth was about 2 centimeters long; the roots were about 1.5 centimeters. Many people are surprised to learn that the root of a dog’s tooth is so large – 2/3 to 3/4 of the tooth is below the gumline. This is one reason why it is so important to use radiographs to evaluate teeth on a regular basis, not just in a growing puppy. Adult teeth can, and frequently do, have problems that are only visible with a radiograph.
Enzo came through his procedure extremely well. He was given pain medications for comfort and had to eat canned foods and avoid chewing on his toys for the next two weeks to ensure that the gum tissue healed properly. As he continues to grow we will be monitoring how his jaw develops and Dr. Riedinger will also be watching the alignment of his adult canine teeth when they start to emerge around six months of age. Hopefully this early intervention will minimize problems for Enzo in the future.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This condition is most often spotted at either the first or second puppy checks or between 6 and 8 months of age as the permanent (adult) teeth erupt. Either the deciduous or permanent lower canines occlude into the soft tissues of the roof or the mouth causing severe discomfort and, possibly, oral nasal fistulae.
The fact sheet answers many questions you may have about the cause of this problem and the various treatments available. It is important not to delay treatment of deciduous lower canines as the window of opportunity is only a matter of a few weeks until the permanent canines erupt at 22 to 26 weeks of age. A new problem can then present with bigger teeth causing more damage.
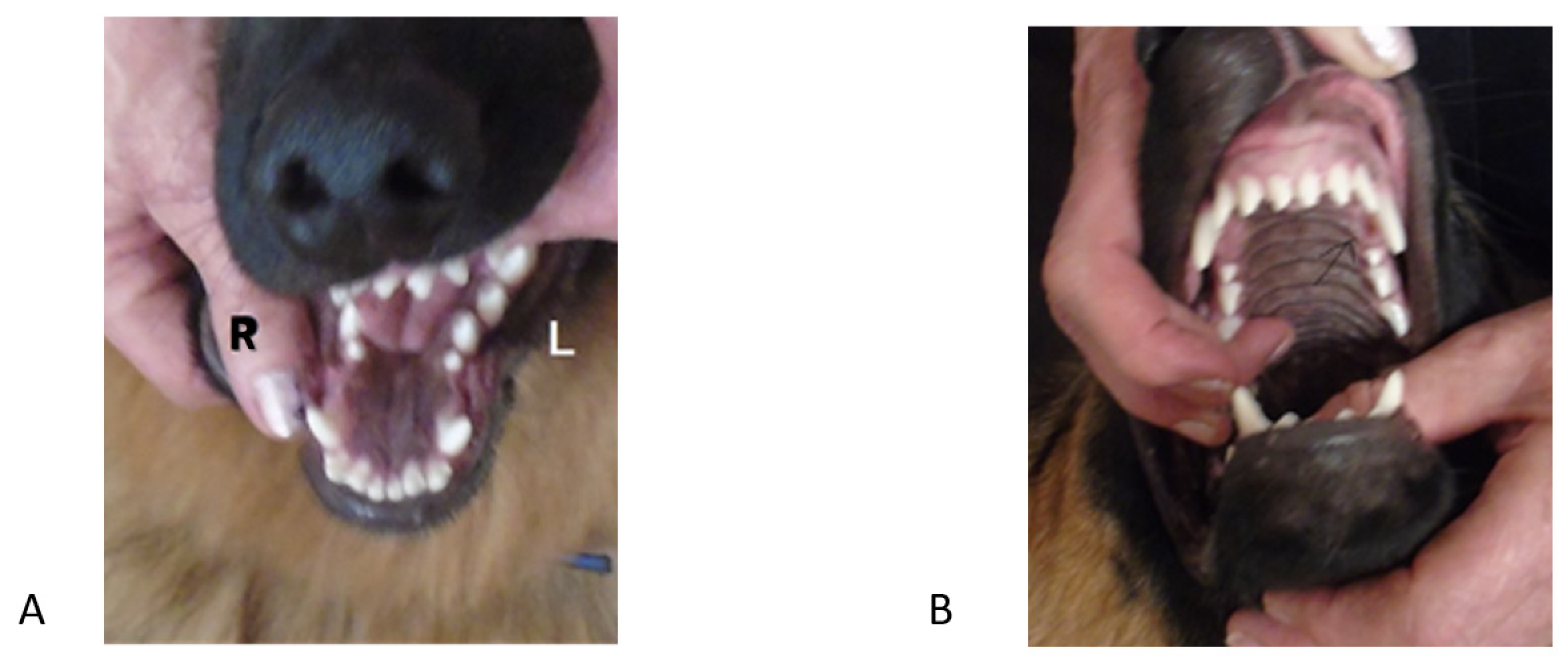
We advise you email us images of the teeth (mouth closed, lips up and side on for both left and right) just a few days before you travel. Things change quickly in growing dogs and it might save you a wasted journey.
This is an inherited condition - an autosomal recessive mutation. Both parents may look normal but carry recessive genes for the condition. When this genetic information is passed onto the litter, approximately one pup in four will be affected, appear abnormal and can pass the genetic information on if bred from. In addtion, two pups in four will carry an abnormal gene from one parent and a normal gene from the other. This pups will look normal but can pass the problem on if bred. Finally one pup in four will not be a carrier of abnormal genes, will be unaffected and cannot pass the trait on to future generations.
If this condition appears in the litter, the most responsible course of action is not to breed from the parents again - either as a pair or individually with others. As there is currently no test to identify this gene, selecting another mate may mean they too are recessive carriers. All the normal looking sibling pups are likely to also carry the recessive genes. It is wise that they too do not contribute to passing the problem back into the breed"s gene pool. In many affected breeds, the gene pool of breeding individuals to select from is very small. If recessive carriers are routinely mating then it is not long before increasing numbers of pups appear with this condition. Over four decades we have monitored the breeds treated here and it is disappointing to note that many previously unaffected breeds are now being seen on a regular basis.
When a pup is treated for this condition we routinely supply the Kennel Club with a Change of Conformation form so they can track the parental origin. We also ask for permssion to send a DNA swab to the Animal Health Trust. This is anonymously evaluated as part of a research programme to identify the exact genetic origin of the condition with the aim of a simple test becoming available to identify recessive carriers. In time this will allow owners of known recessive carriers to select a mate unaffected by the condition.
Owners with young puppies identified with this problem at first presentation are advised to have the deciduous lower canines removed as soon as possible. There are three reasons for this:
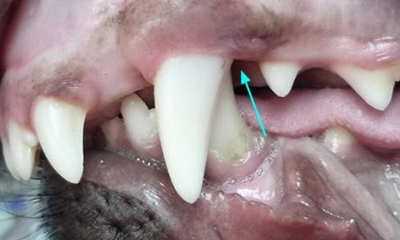
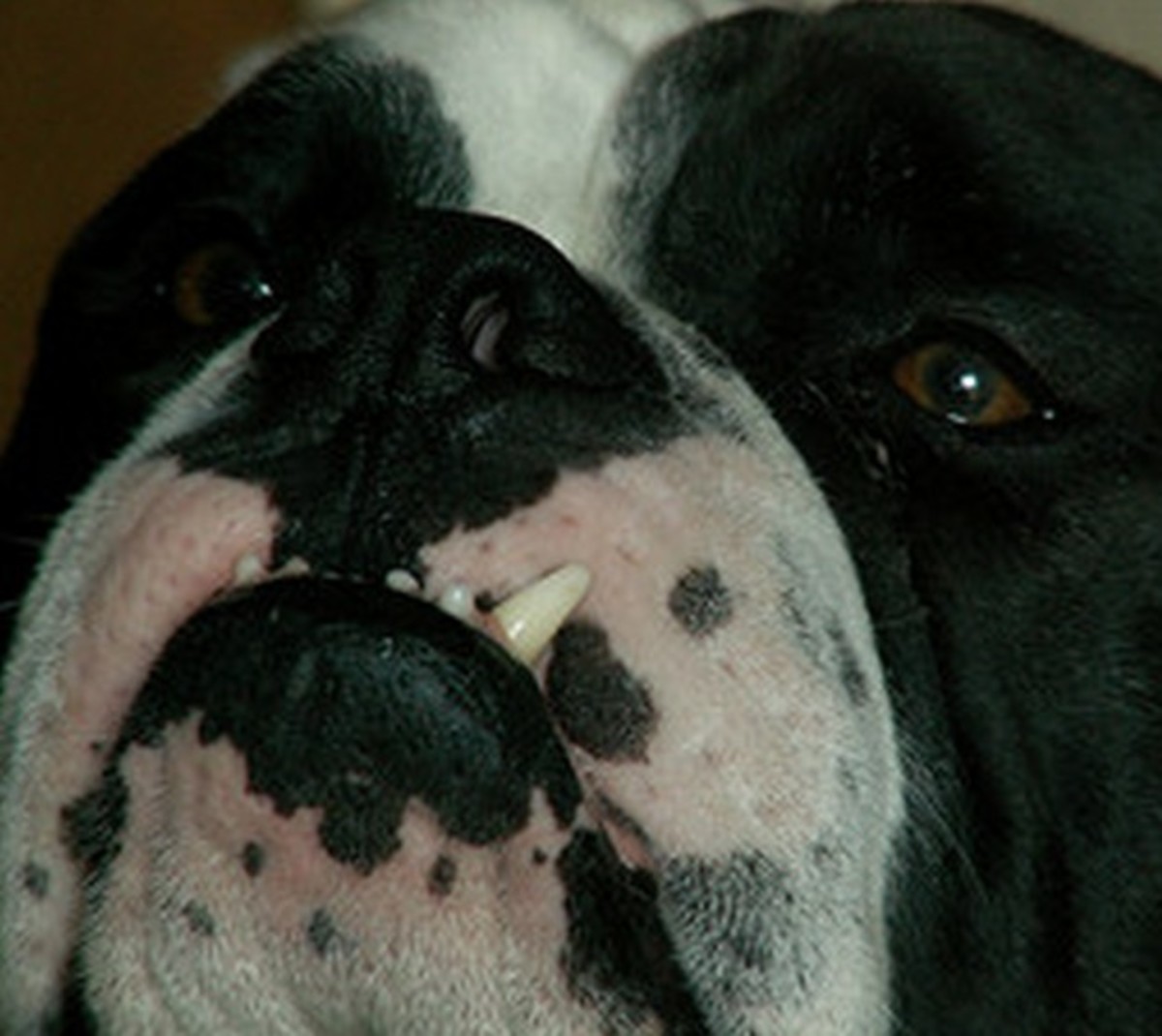
Firstly, and most importantly, these teeth are sharp and hitting the soft tissues of the palate. These pups cannot close their mouth without pain and often hold the mouth slightly open to avoid contact. This is not pleasant. See above for an example of the damage caused to the hard palate by this problem.
Secondly, the growth of the mandible is rostral from the junction of the vertical and horizontal ramus. If the lower canines are embedded in pits in the hard palate, the normal rostral growth of the mandible(s) cannot take place normally due to the dental interlock caused by the lower canines being embedded in hard palate pits. This can cause deviation of the skull laterally or ventral bowing of the mandibles (lower jaws).
Thirdly, the permanent lower canine is located lingual to the deciduous canine. This means that if the deciduous lower canines are in a poor position it is a certainty the permanent teeth will be worse. See the radiograph below. The deciduous canines are on the outside of the jaws and the developing permanent canines are seen in the jaw as small "hats". It is clear that the eruption path of the permanent canines will be directly dorsal and not buccally inclined as is normal.
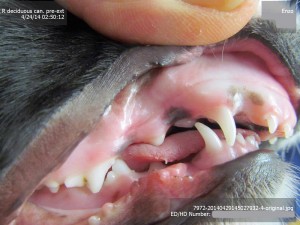
For these three reasons it is advisable to surgically remove the lower canine teeth as soon as possible to allow maximum time between the surgery and the time the permanent teeth erupt at between 22 and 24 weeks of age. See our file for illustration of removal of deciduous canines.
The deciduous tooth root is three to four times longer than the visible crown and curved - often 2.5cm in length and curved. The root apex is often located below the third lower premolar. See middle and right images below with extracted deciduous tooth laid over extraction site.
The roots are very fragile and will break easily if unduly stressed during removal. A broken root needs to be identified and removed otherwise it continues to form a barrier to the eruption path of the permanent canine and can cause local infection.
The permanent successor tooth is located lingual to the deciduous tooth and wholly within the jaw at this stage. Any use of luxators or elevators on the lingual half of the deciduous tooth will cause permanent damage to the developing enamel of the permanent tooth. See the images below showing canines (and also the third incisor) with extensive damage to the enamel. The radiograph also shows how much damage can occur to the teeth - see the top canine and adjacent incisor. Some severely damaged teeth need to be extracted while other can be repaired with a bonded composite. This damage is avoidable with careful technique using an open surgical approach.
Surgery to remove the deciduous canines may not prevent to need for surgery on the permanent canines but, without it, few cases will resolve if left to nature. Many owners are reluctant to have young pups undergo surgery. Our view is that surgical removal of the lower deciduous canines will not guarantee the problem does not happen again when the permanent teeth erupt but without surgery the chances are very slim.
In a few selected cases - usually only very mild lingual displacement - we can consider placing crown extensions on the lower canines to help guide them into a more natural position. It carries some uncertainly and will not be suited or work in all cases. The images below show crown extensions on a young Springer Spaniel.
Please note that the use of a rubber ball to assist tipping of the deciduous lower canines buccally is not appropriate at this age and will not work - see below.
If the permanent teeth are lingually displaced the pup is usually older than 24 weeks. The trauma caused by the teeth on the soft tissues can be considerable with pain as a consequence.
Do not try ball therapy with deciduous (puppy) teeth. There are two main reasons for this. Puppy teeth are fragile and can easily break. More importantly, the adult canine tooth bud is developing in the jaw medial to the deciduous canine tooth (see radiograph above in the puppy section). If the deciduous crown tips outwards the root will tip inwards. This will push the permanent tooth bud further medial than it already is.
Ball therapy will only work with adult teeth and only in some cases where the lower canines have a clear path to be tipped sideways - laterally - through the space between the upper third incisor and canine. The window of opportunity can be quite short, around 6 weeks, and starts when the lower canine teeth are almost making contact with the hard palate.
If you are considering ball therapy ask your vet their opinion and get them to send us images of each side of the closed mouth from the side with mouth closed and lips up.
The size and type of the ball or Kong is critical. The ball diameter should be the distance between the tips of the two lower canine teeth plus 50%. Therefore if this distance is 30mm the ball diameter is 45mm. If the ball is too small it will sit between the lower canines and produce no tipping force when the pup bites down. Too large a ball can intrude the lower canines back into their sockets.
The owner needs to encourage play with the ball several times a day (6 - 8) or as often as they will tolerate with a short attention span. The ball should be only at the front of the mouth to go any good. If there are no positive results in six weeks a further veterinary evaluation is advised.
These permanent teeth can theoretically be treated by three options. Not all options are available to all cases. These options are described below and are either surgical removal of the lower canines teeth (and possibly incisors also), crown amputation and partial pulpectomy or orthodontics via an inclined bite plane bonded to the upper canines and incisors. The latter option may not be available to all dogs if the diastema (space) between the upper third incisor and canine is too small for the lower canines to move into or if the lower canines are located behind (palatal) to the upper canines.
This is a sterile procedure to reduce the height of the lower canine crown that exposes the pulp. It requires a removal of some pulp (partial coronal pulpectomy) and placement of a direct pulp capping.
This is a very delicate procedure and carries very high success rate (in our hands) since the availability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA). We have used it as the material of choice since 2005. The previous agent (calcium hydroxide) was much more caustic and tended to "burn" the pulp. The success rate of MTA treated cases is quoted as 92% in a seminal ten year study based in vet dental clinics in Finland. This compares with 67% when caclium hydroxide was previously the agent. Luotonen N et al, JAVMA, Vol 244, No. 4, February 15, 2014 Vital pulp therapy in dogs: 190 cases (2001–2011).
The intention of the procedure is to keep the pulp alive and allow the shortened lower canines to develop normally and contribute to the strength of the lower jaws.
Radiograph left lower canine before (left) and immediately after (right) surgery. Note the immature morphology of the canine teeth - thin walls and open root apices.
In order to monitor this process of maturation we need to radiograph these teeth twice at 4-6 months post-op and again at 12 -16 weeks post-op. This is a mandatory check. The quoted success reate of 92% implies 8% failure. Half of those to fail in the Luotonen study happened over a year post-op. To ensure any failure of maturity is identified we will not perform this surgery unless the owner agrees to this.
The left radiograph shows the left lower canine immediately after crown amputation and partial pulpectomy. The right radiograph is same tooth 18 weeks post-op. Note the thicker dentine walls, development of an internal dentine bridge between pulp and direct pulp cap and the closed and matured root apex. These three criteria indicate a successful procedure at this stage.
The advantage of this procedure is that the whole of the root and the majority of the crown remain. The strength and integrity of the lower jaw is not weakened by the procedure and long term results are very good due to the use of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate as a direct pulp dressing.
Surgical extraction of the lower canine may seem attractive to clients as the problem is immediately dealt with without the uncertainties of orthodontics and the post-op check that is part of any crown amputation procedure.
However, many owners are concerned (rightly) about the loss of the tooth and the weakness it may cause to the lower jaw(s). It is not our preferred option. This is not an easy surgical extraction and the resulting loss of the root causes a weakness in the lower jaws. This is compounded if both lower canines are removed.
As this is an elective procedure (e.g. sterile) it is possible to use a bone allograft to fill the void created by the loss of the large canine tooth. The graft will promote new bone growth within a few weeks. Grafts can be very expensive as the void to be filled is large. This can increase the cost of the procedure markedly.
In some mild cases of lingual displacement we may be able to use crown extensions for a few weeks. For this treatment we bond composite resin extensions on the lower canines to increase the crown length by around 30%. This allows the lower canines to occupy the correct position and also provides more leverage to tip the crown tips buccally. The crown extensions remain in place for around 2 months and are then removed and the tooth surface smoothed and treated. The major downside is that if the dog damages or breaks them off, you need to return here for repairs. Sticks and other hard objects can easily cause damage and some toys also have to be withdrawn for the treatment period.
Orthodontic tipping as a treatment has the least certain outcome of all three option. It might seem less invasive than surgery but does require very careful case selection and management.
Normally a composite resin bite plane is bonded onto the upper teeth (see below) with an incline cut into the sides. The lower canine makes contact with the incline when the mouth closes and, over time, the force tips the tooth buccally. This takes around four to eight weeks. The lower canine will often migrate back into a lingually displaced position when the bite plane is removed. This can occur if the tooth height of the lower canine is too short (stunted). If the lower canine is not self-retained by the upper jaw when the mouth is shut further surgery may be required.
Orthodontic treatment will also conceal a defect and will not be performed unless the patient is neutered. In addition we have an ethical obligation to inform the Kennel Club of a change in conformation.
The images below show a lingually displaced left lower canine before treatment and after application of a bite plane. The bite plane remains in the mouth as long as it takes for the power of the bite to tip the lower canine into the normal position by pushing it up the incline.
Not all dogs or owners are suited to this. Bite planes can become dislodged if the dog bites a stick or other hard object. Bite planes also need cleaned and adjusted from time to time under sedation or anaesthesia. All of this means more travel and expense for you and more anaesthesia for your pet. It is our view that if a treatment has uncertain outcomes built in it should probably not be used.
If you’ve been to a dog show, you probably noticed the judges checking dogs’ teeth. Have you ever wondered what they’re looking for? Are they checking to see if the dogs flossed?
When judges look at a dog’s teeth, they are actually evaluating the dog’s occlusion, also known as their bite to make sure it meets the breed standard. Occlusion refers to the way the upper and lower teeth align, or more specifically, the way they fit together.
Types of malocclusionsClass 1 malocclusions occur when the upper and lower jaws are aligned (i.e. no underbite or overbite) but the teeth don’t come together properly because of crowding, misalignment, or rotation.
Class 2 malocclusionsare also known as an overbite. An overbite occurs when the maxillary (upper jaw) teeth are displaced forward relative to the mandibular (lower jaw) teeth.
Class 3 malocclusions are also known as an underbite. An underbite occurs when the mandibular (lower jaw) teeth protrude forward relative to the maxillary (upper jaw) teeth.
Malocclusion in dogs is usually hereditary, which means the condition is passed down to future generations. Malocclusions are common in certain breeds of dogs. For example, class 3 malocclusions (underbites) are commonly seen in brachycephalic breeds such as Boxers, Shih Tzus, Bulldogs, and Pugs.
During your dog’s annual exam, your veterinarian will check your dog’s teeth and bite (another reason why annual exams are so important). If your puppy is developing any alignment issues, your veterinarian may suggest dental radiographs and may even refer your puppy to a veterinary dentist to correct any serious malocclusions before they become a problem.
So what if your dog’s teeth aren’t perfect? After all, he isn’t a toothpaste model. Well, malocclusions aren’t just a cosmetic issue. Certain types of malocclusions can cause difficulty or discomfort when eating or chewing. Some malocclusions cause trauma to the gums, palate, cheeks, other teeth and lead to excessive tartar and calculus build up. In fact, in veterinary medicine, malocclusions are only treated if they are causing pain or problems with chewing — not for aesthetic reasons. Dogs with a crooked smile are still adorable!
Fortunately, not all malocclusions require treatment and some are even considered normal for particular breeds. Malocclusions that do not cause discomfort or trouble eating do not require any treatment. Symptomatic malocclusions benefit from early detection and treatment to prevent pain, difficulty eating, and other complications. Treatment depends on the type of malocclusion and may involve interceptive orthodontics to move teeth, shorten teeth or extract teeth. Be sure to take your dog to the veterinarian every year to have his teeth checked and ensure he’s not having problems with his teeth and bite.
If you have any questions or concerns, you should always visit or call your veterinarian -- they are your best resource to ensure the health and well-being of your pets.

Normally, a puppy will have 28 baby teeth once it is six months old. By the time it reaches adulthood, most dog breeds will have 42 teeth. A misalignment of a dog"s teeth, or malocclusion, occurs when their bite does not fit accordingly. This may begin as the puppy"s baby teeth come in and usually worsens as their adult teeth follow.
The smaller front teeth between the canines on the upper and lower jaws are called incisors. These are used to grasp food and to keep the tongue inside the mouth. Canines (also known as cuspids or fangs) are found behind the front teeth, which are also used to grasp. Behind the canines are the premolars (or bicuspids) and their function is to shear or cut food. Molars are the last teeth found at the back of the mouth and they are used for chewing.
If problems with the palate persist, a fistula may result and become infected. In cases of misaligned teeth (or malocclusion), the dog may have difficulty chewing, picking up food, and may be inclined to eat only larger pieces. They are also prone to tartar and plaque build-up.
The tips of the premolars (the teeth right behind the canines) should touch the spaces between the upper premolars, which is called the scissor bite. However, it is normal for flat-faced breeds (brachycephalic) such as Boxers, Shih Tzus, and Lhasa Apsos not to have scissor bites.
With an overbite, the upper jaw is longer than the lower one. When the mouth is closed, a gap between the upper and lower incisors occurs. Puppies born with an overbite will sometimes have the problem correct itself if the gap is not too large. However, a dog"s bite will usually set at ten months old. At this time improvement will not happen on its own. Your pet"s overbite may worsen as the permanent teeth come in because they are larger and can damage the soft parts of the mouth. Teeth extractions are sometimes necessary.
The way the upper teeth align with the lower teeth is called occlusion. It is normal for most breeds to have a slight overlap of the upper front teeth. When the jaw is closed, the lower canine (fang) should fit in front of the upper canine. Most cases of malocclusion have a hereditary link.
Most bite malocclusions do not require treatment. In some cases, extractions may be necessary. It’s a good idea to brush the teeth regularly to prevent abnormal build-up of tartar and plaque. Your veterinarian will sometimes recommend a dental specialist if you want to correct the teeth misalignment. In recent years, “braces” have been made for puppies to realign the teeth.

Photos of “dogs with underbites” have been the focus of many an adorable Internet slideshow. But while misaligned teeth in dogs, or canine malocclusion, may make our pets seem more endearing or “ugly-cute,” it can be a serious health issue.
To learn more about this condition, we spoke with two board-certified veterinary dentists from the Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine (CUCVM). Here is everything you need to know about canine malocclusion, including symptoms and causes, and when to seek treatment.
Canine malocclusion simply refers to when a dog’s teeth don’t fit together properly, whether it’s his baby teeth or adult teeth. Determining whether a dog suffers from malocclusion can be tricky because, unlike with humans, there’s no standard way a dog’s bite should look. “The dimensions and bite configuration of every dog are so different,” says Dr. Santiago Peralta, assistant professor of veterinary dentistry and oral surgery at CUCVM. “The big question is not whether it’s ‘normal,’ but more so: is it functionally comfortable for the animal?”
So, what makes for a comfortable bite? In general, “The lower canines should be sitting on the outside of the gum line and in front of the upper canines,” explains Dr. Nadine Fiani, assistant clinical professor of dentistry and oral surgery at CUCVM. “One of the most common abnormalities that we see is where the lower canine is so upright that it actually barges up into the hard palate.” Basically, if your dog has tooth-to-tooth contact or tooth-to-soft tissue contact that shouldn’t be there, that’s clinically relevant malocclusion, she says, and it is sometimes accompanied by erosion or trauma to teeth or tissue.
While clients and breeders may use descriptors like “underbite” or “overbite,” Peralta and Fiani don’t use these terms in their practice. “The meaning of each of those terms may vary depending on who you ask. And because it’s subjective lay-terminology, it potentially can be very confusing,” Peralta says. Veterinary dentists rely instead on technical nomenclature, like that preferred by the American Dental Veterinary College (ADVC), in making their diagnoses and considering treatment.
The big question on a dog owner’s mind when it comes to any health issue is, of course, how can I tell ifmydog is suffering? In the case of canine malocclusion, it won’t be obvious—just because your dog appears to have an underbite doesn’t mean he is experiencing pain or discomfort. Sometimes, a veterinarian may note a malocclusion in a puppy at the time of vaccination, Fiani says. But otherwise, you’ll need to observe your dog’s behavior and bite, and bring any issues to your vet’s attention. “The reality is, most dogs that have some kind of malocclusion will have had it for the vast majority of their life,” she says, “and so often, they will be in pain, but they may not necessarily overtly show that.”
If your dog is indeed in pain, he or she might engage in subtle behavior changes such as acting “head-shy” (recoiling when you pet her on the head or face), rubbing her head against the wall or with her paws, or demonstrating difficulty picking up or chewing food, Peralta explains. Physical symptoms of malocclusion may include unusually bad breath or bloody drool.
Any changes in behavior or physical health—even subtle ones—are worth checking out, since untreated malocclusion can have very painful consequences. Fiani cites oronasal fistula as one of the most severe side effects, which is when an abnormal communication (or hole) forms between mouth and nose as a result of a lower canine that is too vertically positioned. This can lead to not only great pain and discomfort, but also possible nasal disease. And if a malocclusion involves teeth that are crowded together, Fiani says, this can cause a buildup of plaque and, eventually, gingivitis or gum disease.
In broad terms, malocclusions are either skeletal or dental in origin, Fiani explains. A dental origin is when a dog may have “one or a couple of teeth that are abnormally positioned within a normal facial skeletal structure,” and are causing pain or discomfort.
The skeletal type of malocclusion, Fiani notes, is where the facial skeleton is abnormal, causing the teeth not to fit together properly. For example, the “underbite” affects short-faced breeds like Bulldogs and Boxers, which have malformed skulls because of breeding. (Long-faced breeds like Sighthounds are prone to similar issues.)
While breeding can have an impact, there is a range of potential causes for either type of malocclusion. “Malocclusions can have a genetic basis that will be likely transmitted from generation to generation,” Peralta says, “and some of them will be acquired, whether because something happened during gestation or something happened during growth and development, either an infection or trauma or any other event that may alter maxillofacial [face and jaw] growth.” He explains that trauma to the face and jaw can stem from events like being bitten by another animal or getting hit by a car. Fiani adds that jaw fractures that don’t heal properly can also result in malocclusion.
“It doesn’t always exactly matter why there’s a malocclusion, the question is: do you need to treat it?” Fiani says. “The bottom line is, if you have abnormal tooth-to-tooth contact or if you have abnormal tooth-to-soft tissue contact, then something has to be done about it.” If you notice any of the previously mentioned signs, it’s time to consult with your veterinarian, who will typically determine whether a referral to a dental specialist is warranted for further assessment. If you’ve got an image-obsessed hound, let’s be clear: veterinary dentists treat medical issues, not cosmetic ones. “We will not perform any sort of orthodontic treatment on an animal for aesthetic purposes,” Fiani emphasizes. “There has to be a clear-cut medical reason for preventing disease or prevention of discomfort or pain.”
Treatment options will vary depending on the specific issue facing your dog, his age, and other factors, but typically will fall into one of two categories: extraction or orthodontic treatment. Tooth extractions can be performed by your general practitioner or a dental specialist, depending, Fiani says, but orthodontics is always the purview of specialists. “That’s really when we’re using appliances to try and shift the teeth around so that they fit together in a way that no longer hurts the dog,” she explains.
So, if your dog is known for his quirky underbite, it’s probably a good idea to seek medical advice. It can be difficult to tell if malocclusion is causing issues, so don’t be afraid to ask your veterinarian questions, and pay close attention to your dog’s health and behavior. The bottom line is that, left untreated, malocclusion can lead to more than just an off-kilter smile—it can result in a painful life for your pooch.
An overbite might not seem like a serious condition for your dog, but severely misaligned teeth can lead to difficulty eating, gum injuries and bruising, bad breath and different types of dental problems, including tooth decay and gingivitis. Fortunately, there are ways to help fix the problem before it becomes irreversible.
An overbite is a genetic, hereditary condition where a dog"s lower jaw is significantly shorter than its upper jaw. This can also be called an overshot jaw, overjet, parrot mouth, class 2 malocclusion or mandibular brachynathism, but the result is the same – the dog"s teeth aren"t aligning properly. In time, the teeth can become improperly locked together as the dog bites, creating even more severe crookedness as the jaw cannot grow appropriately.
This problem is especially common in breeds with narrow, pointed muzzles, such as collies, shelties, dachshunds, German shepherds, Russian wolfhounds and any crossbred dogs that include these ancestries.
Dental examinations for puppies are the first step toward minimizing the discomfort and effects of an overbite. Puppies can begin to show signs of an overbite as early as 8-12 weeks old, and by the time a puppy is 10 months old, its jaw alignment will be permanently set and any overbite treatment will be much more challenging. This is a relatively narrow window to detect and correct overbites, but it is not impossible.
Small overbites often correct themselves as the puppy matures, and brushing the dog"s teeth regularly to prevent buildup can help keep the overbite from becoming more severe. If the dog is showing signs of an overbite, it is best to avoid any tug-of-war games that can put additional strain and stress on the jaw and could exacerbate the deformation.
If an overbite is more severe, dental intervention may be necessary to correct the misalignment. While this is not necessary for cosmetic reasons – a small overbite may look unsightly, but does not affect the dog and invasive corrective procedures would be more stressful than beneficial – in severe cases, a veterinarian may recommend intervention. There are spacers, braces and other orthodontic accessories that can be applied to a dog"s teeth to help correct an overbite. Because dogs" mouths grow more quickly than humans, these accessories may only be needed for a few weeks or months, though in extreme cases they may be necessary for up to two years.
If the dog is young enough, however, tooth extraction is generally preferred to correct an overbite. Puppies have baby teeth, and if those teeth are misaligned, removing them can loosen the jaw and provide space for it to grow properly and realign itself before the adult teeth come in. Proper extraction will not harm those adult teeth, but the puppy"s mouth will be tender after the procedure and because they will have fewer teeth for several weeks or months until their adult teeth have emerged, some dietary changes and softer foods may be necessary.
An overbite might be disconcerting for both you and your dog, but with proper care and treatment, it can be minimized or completely corrected and your dog"s dental health will be preserved.

Most people aren’t born with perfectly aligned teeth. Usually, slightly misaligned teeth don’t require any medical treatment. However, correcting an underbite, especially when it’s severe, can have big benefits.
Teeth will become easier to clean. Your risks for tooth decay and gum disease will decrease. You’ll also feel less strain on your teeth, jaws, and facial muscles.
This can reduce your risks of breaking a tooth and also painful symptoms of temporomandibular disorders, which are common with underbites. Some common treatments for underbite include:
Brushing and flossing your teeth regularly in addition to visiting a dentist for checkups and cleanings are important parts of treatment for healthy teeth. But those with an underbite or other dental issues must take special care of their teeth to prevent further damage and decay.
Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time with toothpaste containing fluoride. Pay attention to brushing along your gumline and on the inside, outside, and the back of your mouth. Be sure you floss in addition to brushing. See your dentist at least twice a year for checkups and cleanings.
In less severe cases of underbite, a dentist may be able to use wire or plastic braces or other dental appliances to move the teeth into their correct place.
Removal of one or more teeth on the lower jaw may also help improve the appearance of an underbite if overcrowding of the teeth is contributing to the issue. A dentist may also use a grinding device to shave down or smooth teeth that are large or stick out.
The earlier an underbite is addressed, the better. If a child’s underbite is less severe, parents should wait until at least age 7 to seek corrective treatment such as braces. That’s when permanent teeth begin to erupt.
Surgery has its risks and should only be used in children when underbite is interfering with their quality of life or ability to eat, breathe, or speak.

Undershot is a class III malocclusion that is also referred to as mandibular prognathism, maxillary brachygnathism, mandibular mesioclusion, or an underbite. This malocclusion is characterized by a shorter upper jaw and a longer lower jaw, resulting in lower teeth that are in front of the upper teeth. While this condition is normal for some breeds, such as Bulldogs, in many breeds it is unusual. An undershot jaw occurs when the lower jaw grows faster than normal and becomes longer than the upper jaw, and is usually evident around 8 weeks of age in puppies. This misalignment can cause soft tissue trauma, such as to the lips. When the incisors meet instead of fitting next to each other, it is called a level bite. When the malocclusion causes the lower incisors to be placed in front of the upper incisors, it is called a reverse scissors bite.
The cause of overshot and undershot jaws in dogs relate to the increased or decreased rate of growth of the upper and lower jaws in relation to one another. This can occur due to a: Genetic disorder Trauma; Systemic infection ;Nutritional disorder; Endocrine disorder; Abnormal setting of puppy teeth; Early or late loss of puppy teeth.
After a quick physical exam, your vet may have to sedate your dog in order to perform a thorough oral exam. This will assess your dog’s skull type and teeth location in relation to the teeth on the opposite jaw. Often, the placement of the upper and lower incisors in relation to one another can determine what type of malocclusion your dog has. Your vet will note any areas of trauma due to teeth striking those areas, and any cysts, tumors, abscesses, or remaining puppy teeth that may be present. A dental X-ray can also help to assess the health of the jaws and teeth. These diagnostic methods will lead to a diagnosis of an overshot or undershot jaw in your dog.
Treatment of a jaw misalignment will depend on the severity of the condition. If your dog has a misalignment, but can still bite and chew food without problems, no treatment may be needed. If the misalignment is caught early in a puppy’s life, it may only be temporary and may correct itself over time. However, there are times when intervention may be needed. If your puppy’s teeth are stopping the normal growth of his jaws, then surgery to remove those puppy teeth may be performed. This may allow the jaws to continue to grow, but will not make them grow. For older dogs who are experiencing pain and trauma due to misaligned jaws and teeth, oral surgery is generally performed to extract teeth that are causing trauma, to move teeth so that they fit, or to create space for a misaligned tooth to occupy. Other therapies include crown reductions or braces.
If your dog is genetically programmed to have an overshot or undershot jaw, intervention can help, but will not slow or stop the abnormal growth of either jaw. Prevent jaw misalignments in puppies by not breeding dogs who have overshot or undershot jaws.

Prognathism, also called Habsburg jaw or Habsburgs" jawHouse of Habsburg,mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull.general dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and orthodontics, this is assessed clinically or radiographically (cephalometrics). The word prognathism derives from Greek πρό (pro, meaning "forward") and γνάθος (gnáthos, "jaw"). One or more types of prognathism can result in the common condition of malocclusion, in which an individual"s top teeth and lower teeth do not align properly.
Mandibular prognathism, where teeth have almost reached their final, straight position by dental braces. This makes the prognathism more obvious, and it will take an operation, moving the jaw backwards, to give the ultimate result.
Prognathism in humans can occur due to normal variation among phenotypes. In human populations where prognathism is not the norm, it may be a malformation, the result of injury, a disease state, a hereditary condition,
Prognathism is considered a disorder only if it affects chewing, speech or social function as a byproduct of severely affected aesthetics of the face.
Clinical determinants include soft tissue analysis where the clinician assesses nasolabial angle, the relationship of the soft tissue portion of the chin to the nose, and the relationship between the upper and lower lips; also used is dental arch relationship assessment such as Angle"s classification.
Cephalometric analysis is the most accurate way of determining all types of prognathism, as it includes assessments of skeletal base, occlusal plane angulation, facial height, soft tissue assessment and anterior dental angulation. Various calculations and assessments of the information in a cephalometric radiograph allow the clinician to objectively determine dental and skeletal relationships and determine a treatment plan.
Prognathism should not be confused with micrognathism, although combinations of both are found. It affects the middle third of the face, causing it to jut out, thereby increasing the facial area, similar to the phenotype of archaic hominids and other apes. Mandibular prognathism is a protrusion of the mandible, affecting the lower third of the face. Alveolar prognathism is a protrusion of that portion of the maxilla where the teeth are located, in the dental lining of the upper jaw.
Prognathism can also be used to describe ways that the maxillary and mandibular dental arches relate to one another, including malocclusion (where the upper and lower teeth do not align). When there is maxillary or alveolar prognathism which causes an alignment of the maxillary incisors significantly anterior to the lower teeth, the condition is called an overjet. When the reverse is the case, and the lower jaw extends forward beyond the upper, the condition is referred to as retrognathia (reverse overjet).
Harmful habits such as thumb sucking or tongue thrusting can result in or exaggerate an alveolar prognathism, causing teeth to misalign. Functional appliances can be used in growing children to help modify bad habits and neuro-muscular function, with the aim of correcting this condition.
In disease states, maxillary prognathism is associated with Cornelia de Lange syndrome;retrognathism, where there is a lack of growth of the mandible, is by far a more common condition.
Prognathism, if not extremely severe, can be treated in growing patients with orthodontic functional or orthopaedic appliances. In adult patients this condition can be corrected by means of a combined surgical/orthodontic treatment, where most of the time a mandibular advancement is performed. The same can be said for mandibular prognathism.
Pedro II of Brazil, showing progenism. His mother was the Archduchess Maria Leopoldina of Austria, a member of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine by birth.
Pathologic mandibular prognathism is a potentially disfiguring genetic disorder where the lower jaw outgrows the upper, resulting in an extended chin and a crossbite. In both humans and animals, it can be the result of inbreeding.shih tzus and boxers, it can lead to problems such as underbite.
Although more common than appreciated, the best known historical example is Habsburg jaw, or Habsburg or Austrian lip, due to its prevalence in members of the House of Habsburg, which can be traced in their portraits.geneticists and pedigree analysis; most instances are considered polygenic,
Allegedly introduced into the family by a member of the Piast dynasty, it is clearly visible on family tomb sculptures in St. John"s Cathedral, Warsaw. A high propensity for politically motivated intermarriage among Habsburgs meant the dynasty was virtually unparalleled in the degree of its inbreeding. Charles II of Spain, who lived 1661 to 1700, is said to have had the most pronounced case of the Habsburg jaw on record,consanguineous marriages in the dynasty preceding his birth.
Prior to the development of modern dentistry, there was no treatment for this condition; those who had it simply endured it. Today, the most common treatment for mandibular prognathism is a combination of orthodontics and orthognathic surgery. The orthodontics can involve braces, removal of teeth, or a mouthguard.
Peacock, Zachary S.; Klein, Katherine P.; Mulliken, John B.; Kaban, Leonard B. (September 2014). "The Habsburg Jaw-re-examined". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A. 164A (9): 2263–2269. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.36639. PMID 24942320. S2CID 35651759.
Zamudio Martínez, Gabriela; Zamudio Martínez, Adriana (2020). "A Royal Family Heritage: The Habsburg Jaw". Facial Plastic Surgery & Aesthetic Medicine. 22 (2): 120–121. doi:10.1089/fpsam.2019.29017.mar. PMID 32083497. S2CID 211232475.
Though prognathism is not the norm among white Americans, white Americans can occasionally have non-pathological prognathism, similar to that of other populations around the world and clearly distinct from the examples of pathological prognathism shown in the pictures.
Безуглый, Т. А. (2020). "Влияние На Человека Признаков, Передаваемых По Аутосомно-Рецессивному Типу (на Примере Династии Габсбургов)" [Influence on the Human Traits Transmitted According to the Autosomal-Recessive Type (on the Example of the Habsburg Dynasty)] (in Russian).
Vilas, Román; Ceballos, Francisco C.; Al-Soufi, Laila; González-García, Raúl; Moreno, Carlos; Moreno, Manuel; Villanueva, Laura; Ruiz, Luis; Mateos, Jesús; González, David; Ruiz, Jennifer; Cinza, Aitor; Monje, Florencio; Álvarez, Gonzalo (17 November 2019). "Is the "Habsburg jaw" related to inbreeding?". Annals of Human Biology. 46 (7–8): 553–561. doi:10.1080/03014460.2019.1687752. PMID 31786955. S2CID 208536371.

Markings in the shape of a saddle over the back. Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
Used to describe several breeds, this color is a dull, yellowish gray of medium saturation. Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
Used to describe Boston Terriers, this color appears black except that it has a red cast when viewed in the sun or bright light. Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
A division of the regular or primary class. The division can be breed-specific, having to do with color, height, weight, or coat (e.g., Open-Fawn), or event-specific (e.g., Novice A or B in obedience events). Best of Breed or Best of Variety are not divided into secondary classes. Secondary classes are offered at the discretion of the Event Committee of the club holding the event.
Used to describe Chesapeake Bay Retrievers, this color is similar to deadgrass, but it is more accurately a lightening of the chocolate hue. Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
One color or whole color except for lighter shadings. Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
A suffix title conferred on dogs that have qualified the required number of times in Senior tests at hunting tests for pointing breeds, retrievers, and spaniels.
A prefix title conferred on dogs that have earned the Grand Nite Champion and have won the required number of first placements in AKC Coonhound night hunts.
All footprints falling on a single line of travel. When a dog breaks into a trot, his body is supported by only two legs at a time, which move as alternating diagonal pairs. To achieve balance, his legs angle inward toward a center line beneath his body, and the greater the speed, the closer they come to tracking on a single line.
A gait fault indicated by a quick outward snatching of the hock as it passes the supporting leg and twists the rear pastern far in beneath the body. The action causes noticeable rocking in the rear quarters.
The state of mental and physical health when all organs and faculties are complete and functioning normally, each in its rightful relation to the other.
A department that specializes in handling anything outside the normal domestic registration; e.g., Foreign Applications, Open Registry, and Special Litters.
Department formed at the AKC to handle questions and problems that come from the show group of customers of the AKC. Designed to offer a premium level of service to those significantly involved in the sport.
Deep red (almost brown) with intermingling of black hairs (Miniature Pinscher). Color definitions may vary by breed. Always check the breed standard for the definitive color description.
Person who is responsible for the smooth running of a specific ring; for example, assembling the classes, distributing armbands, etc., thereby enabling the judge to concentrate on judging the dogs.
Monthly publication of the AKC. A listing of dogs that have sired or produced a litter that has been registered with the AKC. With this information, a person can use Stud Book volumes to trace a dog’s lineage and to produce pedigrees.
Class where a stud dog is shown and judged with at least two of his offspring. Judging is based on the quality of the get, not the sire. (Club may permit more offspring to be shown. The upper limit must be stated in the Premium List.)
The form that must be completed by the current owner and the new owner when a registered or registerable dog changes hands more than once before being transferred or registered. This form is attached to the original registration certificate or application. Also called the gray form.
A non-regular competition offered in conjunction with regular classes at specialty shows for puppies or veterans. Class divisions, requirements, and conditions are established by the club. No championship points are awarded.

Isaac Schilling’s wish list is now complete, with yellow Labrador Winnie by his side to share in the festivities, continuing a nearly decade-old tradition of having a Canine Companions dog accompany him — not only to events such as special needs holiday parties – but throughout life itself.




 8613371530291
8613371530291