asme safety valve testing requirements supplier
The ASME Pressure Relief Device (PRD) Testing Laboratory Accreditation Program accredits manufacturers of pressure relief devices and assemblers of pressure relief valves. It is a hybrid program in that it accredits both the manufacturer and specific personnel within the manufacturing organization (the authorized observer). It is operated in conjunction with The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors. Therefore, a manufacturer seeking this accreditation submits an application directly to ASME, but details about the program and review process can be found on The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspector"s website.
Companies that have been accredited through the PRD Accreditation Program are operating in accordance with the applicable rules of the associated ASME BPVC, the ASME PTC-25 standard, "Pressure Relief Devices," as well as one of the standards of construction accepted by The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors.

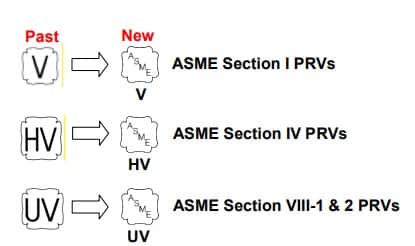
The National Board’s goal is to maintain the integrity of the National Board marks and symbols (NB,VR, andT/O) and the ASME Certification mark with V ,UV, UD, HV, and NV designators. By doing so, we make it possible for National Board members to rely on the presence of these marks in their efforts to protect the general public.
The National Board offers the Certificate of Authorization and VR Stamp for the repair of pressure relief valves. Requirements are included in the current mandatory edition of the National Board Inspection Code(NBIC), Part 4, and NB-514, Accreditation of VR Repair Organizations.
The National Board offers the Certificate of Authorization for use of the T/O mark which indicates accreditation as a pressure relief valve Testing Organization. The program includes provisions for minor adjustments to restore valve performance. Requirements are based upon the current mandatory edition of the National Board Inspection Code(NBIC), Part 2, Part 4, and NB-528, Accreditation of T/O Test Only Organizations.
Representatives from the National Board are assigned to visit company sites to select production sample valves for testing at National Board- and ASME- accepted labs.
Many processes involve the use of high pressure steam, water or air. Piping systems carrying these fluids must be protected from over-pressures that could cause damage or injury. A pressure relief valve is a device that opens to vent any pressure higher than the relief valve’s operating set point. The water heater in your house, for example, has a pressure relief valve set to open at a pressure that is lower than the burst pressure of the heater tank. That way if pressure inside the tank exceeds the relief valve’s set point pressure, the valve will open and vent the pressure before the tank is damaged – you get a wet floor but you don’t have to replace the heater tank.
Pressure relief valves come in all sizes and pressures and these are critical parts of a high pressure piping system carrying steam in an industrial plants, refineries, power plants, etc. The ASME has established criteria for the size and set point pressures for relief valves operating in industrial systems. Additionally, these valve are tested on a regular basis to insure that they open at the correct pressure and do not impede the flow of fluid as the pressure is vented. The vales are tested at their operating pressures and temperatures, and the opening pressure and pressure drop through the valve as it vents must be measured.
There are testing laboratories that are used to test industrial pressure relief valves by simulating the operating conditions for water, air and steam. One customer of Validyne has a test lab capable of generating up to 10,000 lbs. per hour of steam at 300 psig, air flows to 3500 SCFM at 500 psig and water flow rates of 500 gpm at 300 psig. Pressure relief valves are tested depending on their operating conditions, and the valves are instrumented to verify correct operation at their set point pressure.
The Validyne product used to make relief valve measurements is the DP15 pressure transducers. One transducer is used to measure the pressure upstream of the relief valve, a second DP15 measures the downstream pressure. These transducers are 300 or 500 psi, depending on the test. A third DP15 measures the pressure drop across the relief valve when it is flowing and this transducer is typically 100 In H2O full scale. The DP15s are used because they can be mounted remotely from the control station. A large steam relief valve, for example, is connected to piping with runs of 25 and 30 feet. The DP15 can be mounted at the measurement point and the cable to the demodulator can be up to 50 feet with no compromise in calibration.
The pressure transducers are connected to Validyne CD23 demodulator with digital display. The CD23 features large LED displays that are helpful for the operator to see while opening and closing large control valves during the test. The display can be given directly in PSIG and the CD23 provides an analog output proportional to pressure that can be connected to a LabVIEW computer to record the pressures during the test. Alternatively the pressure sensors can also be connected to the USB2250 DAQ.
The Validyne CD23s and DP15s have given many years of service in this difficult environment and this reliability, plus the ability to interface to a data acquisition system make it a great solution for relief valve testing.
The Pressure Safety Valve Inspection article provides you information about inspection of pressure safety valve and pressure safety valve test in manufacturing shop as well as in operational plants.
Your pressure safety valve is a direct spring-loaded pressure-relief valve that is opened by the static pressure upstream of the valve and characterized by rapid opening or pop action.
Your construction code for pressure safety valve is API Standard 526 and covers the minimum requirements for design, materials, fabrication, inspection, testing, and commissioning.
These are:API Recommended Practice 520 for Sizing and SelectionAPI Recommended practice 521 Guideline for Pressure Relieving and Depressing SystemsAPI Recommended Practice 527 Seat Tightness of Pressure Relief Valves
For example in the state of Minnesota the ASME Code application and stamping for pressure vessel and boiler is mandatory which “U” and “S” symbols are designated for stamping on the nameplate.
For example if there is pressure vessel need to be installed in the state of Minnesota then the pressure vessel nameplate shall be U stamped and pressure vessel safety valve shall be UV stamped.
National Board Inspection Code (NBIC) have own certification scheme for pressure safety valves and using NB symbol. The NBIC code book for this certification is NB 18.
National Board Inspection Code is assisting ASME organization for ASME UV symbol certification by providing ASME designee in manufactures auditing program.
There are some other standards and codes which are used in pressure safety valve such as:ASME PTC 25 for pressure relief devices which majorly is used for assessment of testing facility and apparatus for safety valvesBS EN ISO 4126-1, 4126-2 and 4126-3 which is construction standard similar to API STD 526.
This API RP 527 might be used in conjunction of API RP 576 as testing procedure for seat tightness testing of pressure safety valve for periodical servicing and inspection.
These are only important points or summery of points for pressure safety valve in-service inspection and should not be assumed as pressure safety valve inspection procedure.
Pressure safety valve inspection procedure is comprehensive document which need to cover inspection methods to be employed, equipment and material to be used, qualification of inspection personnel involved and the sequence of the inspection activities as minimum.
You may use following content as summery of points for Pressure Safety Valve Inspection in operational plantDetermination pressure safety valve inspection interval based API STD 510 and API RP 576 requirementsInspection of inlet and outlet piping after pressure safety valve removal for any foulingInspection of pressure safety valve charge and discharge nozzles for possible deposit and corrosion productsTaking care for proper handling of pressure safety valves from unit to the valve shop. The detail of handling and transportation instruction is provided in API RP 576.Controlling of seals for being intact when the valves arrived to the valve shop.Making as received POP test and recording the relieving pressure.
If the POP pressure is higher than the set pressure the test need to be repeated and if in the second effort it was near to the set pressure it is because of deposit.If in the second effort it was not opened near to the set pressure either it was set wrongly or it was changed during the operationIf the pressure safety valve was not opened in 150% of set pressure it should be considered as stuck shut.If the pressure safety valve was opened below the set pressure the spring is weakenedMaking external visual inspection on pressure safety valve after POP test. The test need contain following item as minimum;the flanges for pitting and roughness
Making body wall thickness measurementDismantling of pressure safety valve if the result of as received POP test was not satisfactoryMaking detail and comprehensive visual and dimensional inspection on the dismantled valve parts (after cleaning)Making special attention to the dismantled valves seating surfaces inspection e.g. disk and seat for roughness, wear and damage which might cause valve leakage in serviceReplacing the damaged parts in dismantled valves based manufacture recommendation and API RP 576 requirementsMaking precise setting of the pressure safety valve after reassembly based manufacture recommendation or NB-18 requirements
Making at least two POP test after setting and making sure the deviation from set pressure is not more than 2 psi for valves with set pressure equal or less than 70 psi or 3% for valves with set pressure higher than 70 psiMaking valve tightness test for leakage purpose after approval of the setting pressure and POP tests. The test method and acceptance criteria must be according to the API RP 576.The API RP 527 also can be used for pressure safety valve tightness test.Recording and maintaining the inspection and testing results.

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The documents are meant to be used as a guide for developing local laws and regulations and also may be used to update a jurisdiction’s existing requirements. As such, they’re intended to be modifiable to meet any jurisdiction’s local conditions.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

Pressure Safety and Relief Valves (PSV) are totally directed by codes and regulations. The four most important codes and standards for PSVs (safety valve standards) are ASME (USA), API (USA),ISO (international) and PED (Europe).
ISO 4126-6.Safety devices for protection against excessive pressure — Part 6: Application, selection and installation of bursting disc safety devices.
ISO 4126-9.Safety devices for protection against excessive pressure — Part 9: Application and installation of safety devices excluding stand-alone bursting disc safety devices.
ISO 4126-10.Safety devices for protection against excessive pressure — Part 10: Sizing of safety valves for gas/liquid two-phase flow.ISO Pressure relief code
Austria.SAA AS 1271.Safety valves, other valves, liquid level gauges and other fittings for boilers and unfired pressure vessels.Other Countries Pressure Relief International ISO Codes

Testing the safety relief valve is extremely important to the overall safety of your boiler system. In this post, we’ll be talking about what goes into testing a steam relief valve, but safety valve repairs should only be performed by a company holding a current Certificate of Authorization (VR) from the National Board of Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
Using certified and calibrated gauges is essential to accurate testing. WARE’s own Rick Walker recommends using two gauges, for maximum accuracy and in case one isn’t properly functioning.
Relief valves need to open and close at very specific pressures, and also need to open smoothly. A smooth opening contains a clean “pop” sound, and not a simmering or chattering sound. Responding to the appropriate pressures and opening and closing cleanly are both important signs a professional maintenance provider will look for in a safety valve.
Safety valves contain a compression screw, which puts pressure on a spring and causes the valve to function. The compression screw is where a maintenance provider will try to dial in your valve’s functionality and make set-pressure adjustments. It’s important to note if a valve is cold it might test higher, but as the valve gets hotter its metal will expand and its innerspring will slightly decompress.
Once the valve is warm and has stabilized, it’s best to give it more than one test (Rick does three) to make sure the valve is consistent and within ASME code.
ASME defines a safety valve as properly functioning at 150 psi if it tests within 3% of the set pressure. If your valve tests within 3% of the set pressure three times in a row on properly calibrated gauges, you’re likely good to go.

(1) Boiler safety valves and safety relief valves must be as indicated in PG-67 through PG-73 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (incorporated by reference; see 46 CFR 52.01-1) except as noted otherwise in this section.
(3) On river steam vessels whose boilers are connected in batteries without means of isolating one boiler from another, each battery of boilers shall be treated as a single boiler and equipped with not less than two safety valves of equal size.
(4) (Modifies PG-70.) The total rated relieving capacity of drum and superheater safety valves as certified by the valve manufacturer shall not be less than the maximum generating capacity of the boiler which shall be determined and certified by the boiler manufacturer. This capacity shall be in compliance with PG-70 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
(5) In the event the maximum steam generating capacity of the boiler is increased by any means, the relieving capacity of the safety valves shall be checked by an inspector, and, if determined to be necessary, valves of increased relieving capacity shall be installed.
(6) (Modifies PG-67.) Drum safety valves shall be set to relieve at a pressure not in excess of that allowed by the Certificate of Inspection. Where for any reason this is lower than the pressure for which the boiler was originally designed and the revised safety valve capacity cannot be recomputed and certified by the valve manufacturer, one of the tests described in PG-70(3) of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be conducted in the presence of the Inspector to insure that the relieving capacity is sufficient at the lower pressure.
(8) Lever or weighted safety valves now installed may be continued in use and may be repaired, but when renewals are necessary, lever or weighted safety valves shall not be used. All such replacements shall conform to the requirements of this section.
(1) (Modifies PG-68.) Superheater safety valves shall be as indicated in PG-68 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted otherwise in this paragraph.
(2) The setting of the superheater safety valve shall not exceed the design pressure of the superheater outlet flange or the main steam piping beyond the superheater. To prevent damage to the superheater, the drum safety valve shall be set at a pressure not less than that of the superheater safety valve setting plus 5 pounds minimum plus approximately the normal load pressure drop through the superheater and associated piping, including the controlled desuperheater if fitted. See also § 52.01-95(b) (1).
(3) Drum pilot actuated superheater safety valves are permitted provided the setting of the pilot valve and superheater safety valve is such that the superheater safety valve will open before the drum safety valve.
(1) (Modifies PG-71.) Safety valves shall be installed as indicated in PG-71 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted otherwise in this paragraph.
(2) The final setting of boiler safety valves shall be checked and adjusted under steam pressure and, if possible, while the boiler is on the line and the steam is at operating temperatures, in the presence of and to the satisfaction of a marine inspector who, upon acceptance, shall seal the valves. This regulation applies to both drum and superheater safety valves of all boilers.
(3) The safety valve body drains required by PG-71 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be run as directly as possible from the body of each boiler safety valve, or the drain from each boiler safety valve may be led to an independent header common only to boiler safety valve drains. No valves of any type shall be installed in the leakoff from drains or drain headers and they shall be led to suitable locations to avoid hazard to personnel.
(1) (Modifies PG-72.) The operation of safety valves shall be as indicated in PG-72 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code except as noted in paragraph (d)(2) of this section.
(2) (Modifies PG-73.) The lifting device required by PG-73.1.3 of section I of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code shall be fitted with suitable relieving gear so arranged that the controls may be operated from the fireroom or engineroom floor.

Your pressure relief valves (PRVs) are some of the most important pieces of equipment in your plant. They are what protects your systems from overpressure events that can damage your systems and, in some cases, have catastrophic consequences.
One of the most common questions we get is about relief valve testing frequency. There is no single answer that’s right for every valve or application. It depends on the service conditions, valve condition, and level of performance desired.
Effort should be made to conduct inspections and testing of pressure relieving devices at the time they become due in accordance with the schedule previously established, assuming that the equipment has been in continuous operation, interrupted only by the normal shutdown.
The required testing frequency depends on the service. For example, a valve used in a corrosive or fouling service needs to be tested more often than the same valve used in a noncorrosive, nonfouling service. Other conditions that call for shorter testing intervals include:
It’s also important to look at the valve testing history over time. If the valve consistently passes the test, then it can be tested less often. If the results are inconsistent, then the valve should be tested more often. For new processes, especially those where the service conditions (corrosion, fouling, etc.) can’t be accurately predicted, the initial inspection should be performed “as soon as practical after operations begin to establish a safe and suitable testing interval.”
Our valve technicians are factory-trained and ASME and National Board certified to test PRVs from all valve manufacturers.Contact us to learn how we can help you keep your plant up and running.
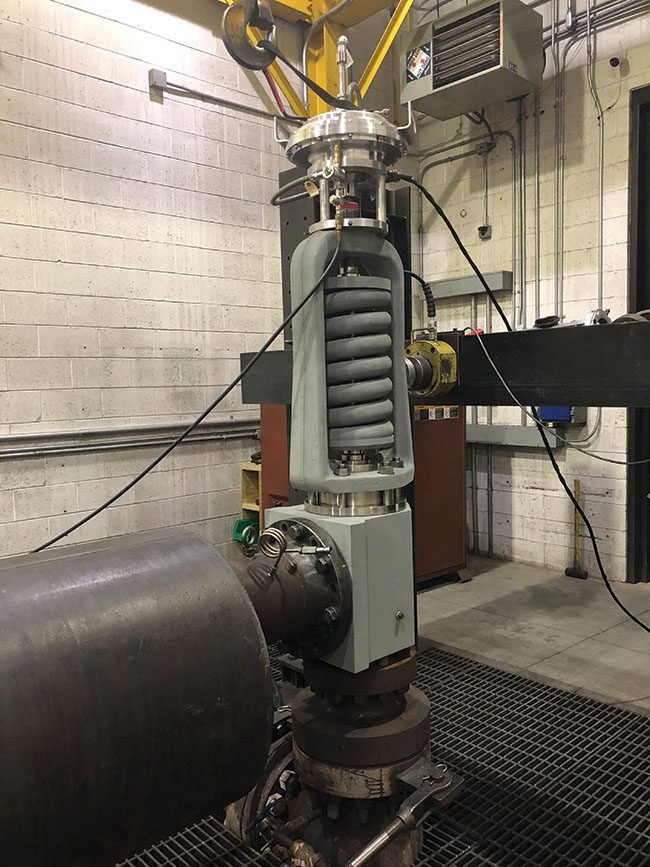

The primary role of a safety relief valve is to prevent over-pressure situations in pressurized vessels or systems. If the tank’s relief valve fails, it can lead to an accident that destroys property, life, or landscape.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors is one of the governing bodies for the testing and/or repair of ASME Safety Relief Valves.
You, as the owner of the valve, can test it, but it must be done in accordance with the National Board Inspection Code and your state’s and/or local regulations.
Based on the National Board Code, which bases their inspection intervals on what type of service the valve is used for, the following intervals are suggested:
Also, keep in mind that this piping should be oriented so that no liquid relieved through this piping can flow back and rest on the ASME safety relief valve’s outlet port.
The ASME relief valves are set to fully open at its “set” pressure but will begin to partially open before then – normally at 10% below its set pressure.
If your valve is allowed to do this, trash and/or corrosion can set in over time which could prevent the valve from either closing completely or from fully opening, either of which is not a favorable solution.

A relief valve is one of the most crucial pressured system components and often the last device to prevent catastrophic failures in high-pressured systems. That is why it is essential that relief valves are always certified and should work at all times.
Relief valves are pressure valves that are designed to open at a preset pressure and discharge fluid until the pressure drops to a safe and acceptable level. This means the relief valve is the last resort that releases pressure when other components in the system have failed to control the pressure.
Safety is of paramount importance when it comes to dealing with relief valves. So, it’s critical for industries to make sure the valves are working as designed.
The only way to do that is through periodic inspection and standardized testing. The standards about relief valves and associated assemblies like boilers and pressured vessels are regulated by ASME, API, OSHA, National Board, and individual State codes.
Standard requirements include periodic inspection, testing, and recertification. Certification assures that a valve’s condition and performance are essentially equal to that of a new valve.
Though ASME is the leading organization governing pressured systems’ standards and codes, the body itself does not certify the valves. Certification and recertification of relief valves are done by the National Board (NB).
Performing periodic testing on relief valves is the best practice to ensure that the valves are in good working condition and the employees and work environment is safe.
The above recommendations constitute correct inspecting and testing practices for efficient Relief Valve operations and, ultimately, a safe working environment. However, one crucial safety measure is to use a pressure indicator with a full-scale range higher than the valve’s relief pressure.
In fact, we believe proper valve inspection, testing, and maintenance is the best investment you make in the safety and security of your company and employees.
Our valve experts focus on getting your old valves tested and recertified for safe use. On top of that, we evaluate the repair condition of every valve and recommend the right solution to manage your equipment better.

Industry leading pressure and safety relief valve designs with over 140 years of technical and application expertise providing custom engineered solutions for O&G, Refining, Chemical, Petrochemical, Process and Power applications. Our designs meet global and local codes and standards (API 526; ASME Section I, IV & VIII; EN ISO 4126; PED & more). Gain insight into the performance of your pressure relief valves with wireless monitoring.




 8613371530291
8613371530291