safety valve plans free sample

Avoid the headache, hassle and costly repair bills caused by a water or sewer emergency on your property, or an in-home plumbing problem. A single call to Safety Valve takes care of it all.
New to Safety Valve? Enter your address below to check eligibility. Already a customer? Log in to manage your account. You must register first if you haven"t done so.

Pressure relief valve is related to Microchek.com. We offer competitive pricing and reliability because we are the manufacture. Parts are molded and assembled in the U.S. The Microchek system incorporates this cartridge and a wide selection of end pieces to accommodate most connection requirements. The Microchek valve is a cartridge check valve incorporating an innovative guided poppet design. Relief valves are used to hold a fluid circuit or reservoir at a positive or negative pressure. We can select valves that fall into a specific cracking pressure range if needed. The Microchek valve has a low pressure drop and can be specified with a wide variety of cracking pressures.
The Microchek valve is a cartridge check valve incorporating an innovative guided poppet design. Relief valves are used to hold a fluid circuit or reservoir at a positive or negative pressure. We want the opportunity to help you solve your flow control applications and we can build special configurations.
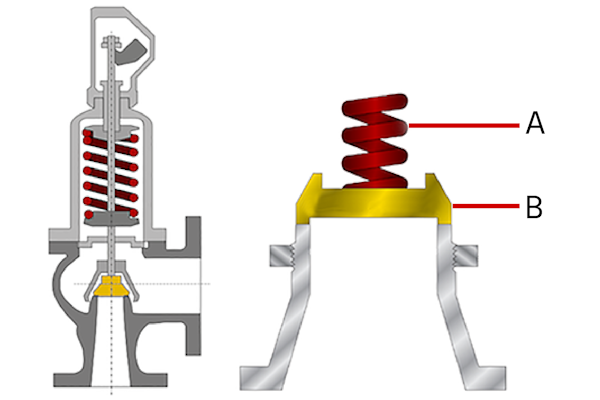
A safety valve must always be sized and able to vent any source of steam so that the pressure within the protected apparatus cannot exceed the maximum allowable accumulated pressure (MAAP). This not only means that the valve has to be positioned correctly, but that it is also correctly set. The safety valve must then also be sized correctly, enabling it to pass the required amount of steam at the required pressure under all possible fault conditions.
Once the type of safety valve has been established, along with its set pressure and its position in the system, it is necessary to calculate the required discharge capacity of the valve. Once this is known, the required orifice area and nominal size can be determined using the manufacturer’s specifications.
In order to establish the maximum capacity required, the potential flow through all the relevant branches, upstream of the valve, need to be considered.
In applications where there is more than one possible flow path, the sizing of the safety valve becomes more complicated, as there may be a number of alternative methods of determining its size. Where more than one potential flow path exists, the following alternatives should be considered:
This choice is determined by the risk of two or more devices failing simultaneously. If there is the slightest chance that this may occur, the valve must be sized to allow the combined flows of the failed devices to be discharged. However, where the risk is negligible, cost advantages may dictate that the valve should only be sized on the highest fault flow. The choice of method ultimately lies with the company responsible for insuring the plant.
For example, consider the pressure vessel and automatic pump-trap (APT) system as shown in Figure 9.4.1. The unlikely situation is that both the APT and pressure reducing valve (PRV ‘A’) could fail simultaneously. The discharge capacity of safety valve ‘A’ would either be the fault load of the largest PRV, or alternatively, the combined fault load of both the APT and PRV ‘A’.
This document recommends that where multiple flow paths exist, any relevant safety valve should, at all times, be sized on the possibility that relevant upstream pressure control valves may fail simultaneously.
The supply pressure of this system (Figure 9.4.2) is limited by an upstream safety valve with a set pressure of 11.6 bar g. The fault flow through the PRV can be determined using the steam mass flow equation (Equation 3.21.2):
Once the fault load has been determined, it is usually sufficient to size the safety valve using the manufacturer’s capacity charts. A typical example of a capacity chart is shown in Figure 9.4.3. By knowing the required set pressure and discharge capacity, it is possible to select a suitable nominal size. In this example, the set pressure is 4 bar g and the fault flow is 953 kg/h. A DN32/50 safety valve is required with a capacity of 1 284 kg/h.
Coefficients of discharge are specific to any particular safety valve range and will be approved by the manufacturer. If the valve is independently approved, it is given a ‘certified coefficient of discharge’.
This figure is often derated by further multiplying it by a safety factor 0.9, to give a derated coefficient of discharge. Derated coefficient of discharge is termed Kdr= Kd x 0.9
Critical and sub-critical flow - the flow of gas or vapour through an orifice, such as the flow area of a safety valve, increases as the downstream pressure is decreased. This holds true until the critical pressure is reached, and critical flow is achieved. At this point, any further decrease in the downstream pressure will not result in any further increase in flow.
A relationship (called the critical pressure ratio) exists between the critical pressure and the actual relieving pressure, and, for gases flowing through safety valves, is shown by Equation 9.4.2.
Overpressure - Before sizing, the design overpressure of the valve must be established. It is not permitted to calculate the capacity of the valve at a lower overpressure than that at which the coefficient of discharge was established. It is however, permitted to use a higher overpressure (see Table 9.2.1, Module 9.2, for typical overpressure values). For DIN type full lift (Vollhub) valves, the design lift must be achieved at 5% overpressure, but for sizing purposes, an overpressure value of 10% may be used.
For liquid applications, the overpressure is 10% according to AD-Merkblatt A2, DIN 3320, TRD 421 and ASME, but for non-certified ASME valves, it is quite common for a figure of 25% to be used.
Two-phase flow - When sizing safety valves for boiling liquids (e.g. hot water) consideration must be given to vaporisation (flashing) during discharge. It is assumed that the medium is in liquid state when the safety valve is closed and that, when the safety valve opens, part of the liquid vaporises due to the drop in pressure through the safety valve. The resulting flow is referred to as two-phase flow.
The required flow area has to be calculated for the liquid and vapour components of the discharged fluid. The sum of these two areas is then used to select the appropriate orifice size from the chosen valve range. (see Example 9.4.3)

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).

The primary purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property and the environment. Safety valves are designed to open and release excess pressure from vessels or equipment and then close again.
The function of safety valves differs depending on the load or main type of the valve. The main types of safety valves are spring-loaded, weight-loaded and controlled safety valves.
Regardless of the type or load, safety valves are set to a specific set pressure at which the medium is discharged in a controlled manner, thus preventing overpressure of the equipment. In dependence of several parameters such as the contained medium, the set pressure is individual for each safety application.

Surface-controlled subsurface safety valves (SCSSVs) are critical components of well completions, preventing uncontrolled flow in the case of catastrophic damage to wellhead equipment. Fail-safe closure must be certain to ensure proper security of the well. However, this is not the only function in which it must be reliable—the valve must remain open to produce the well. Schlumberger surface controlled subsurface safety valves exceed all ISO 10432 and API Spec 14A requirements for pressure integrity, leakage acceptance criteria, and slam closure.
Through decades of innovation and experience, Schlumberger safety valve flapper systems are proven robust and reliable. The multizone dynamic seal technology for hydraulic actuation of subsurface safety valves is a further improvement in reliability performance when compared with traditional seal systems in the industry.
The multizone seal technology is currently available in the GeoGuard high-performance deepwater safety valves, which is validated to API Spec 14A V1 and V1-H.
Safety anti-water backflow function to guarantee the proper working of the water heating tank; High-quality stainless steel spring ensures better working performance and also the long using life;
Safety relief valves are safety devices used to automatically release pressure from a system. A valve is installed at the end of a pipe, and it opens when the pressure in the pipe gets too high. The function of this device is to protect both people and equipment from potential damage that an overpressurized system can cause. 12 types of safety relief valves, so you will know what kind you need for your business or home!
Each type of valve has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks, so choosing the right one for your specific needs is important. For example, a thermal expansion valve is perfect for systems subject to wide fluctuations in temperature. At the same time, a spring-loaded safety relief valve is ideal for systems that have a low-pressure ceiling. Make sure you consult with a professional before making your final decision!
-Pressure reducing and regulating stations pressure-sensitive discs. Each type of valve has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks, so choosing the right one for your specific needs is essential. For example, a thermal expansion valve is perfect for systems subject to wide fluctuations in temperature. At the same time, a spring-loaded safety relief valve is ideal for systems that have a low-pressure ceiling.
The Non-Return Safety Relief Valve is a safety device that prevents the backflow of water into the water tank. Its primary function is to prevent the backflow of water from the tank. Its secondary position is to relieve excess pressure in the system by allowing some flow out of the relief valve when needed.
The Non-Return Safety Relief Valve is designed to work in a water tank. The valve has a float inside it, rising and falling as the water level changes. When the float reaches a certain point, it closes off the pipe leading from the tank to your house so that no more water can get out of the tank than you have already used. This prevents any overflow or leakage from occurring.

— Pressure safety relief valves are typically used to control pressure on boilers in heating systems, on stored hot water cylinders in domestic hot water systems, and generally in water systems. T&P relief Valve Function:
This is caused by water expanding during the heating cycle. The T/P valve will then relieve pressure by releasing hot water drips to the drain line. It is recommended that an expansion control valve be fitted to the cold water supply line to reduce cold water(not hot water) during the heating cycle expansion, thereby saving energy and increasing the life of the T&P relief valve. Local regulations may require installing an expansion control valve in the cold water supply line.
With so many brass pressure relief valves to choose from, it can be challenging to find the right one. Whether you are looking for a valve that has a higher flow rate or is more durable, here are some essential things to consider when choosing your next brass pressure relief valve:
Once you have answered these questions, you can narrow your search for the perfect brass pressure relief valve. For example, if you have a system that operates at a high PSI, you will need a valve to withstand higher pressures. Conversely, if you have a minor piping system, you may consider a valve with a lower flow rate.
Always read the manufacturer’s instructions carefully before installing, no matter what type of valve you choose. By following these simple guidelines, you can be confident that your new brass pressure relief valve will provide years of reliable service.
Answering these questions will make it easier to narrow your search for the perfect brass pressure relief valve. For example: if you have a more extensive piping system with high operating pressures, you may want to consider one that can handle higher flow rates and has extra features (such as a pilot light). Conversely, if you choose between two valves that can withstand up to 150 PSI but only differ by 0.25 GPM in their flow rate, then maybe select based on price alone. The key here is knowing what factors matter most when purchasing something like this, so don’t be afraid to ask for help from a qualified technician.
Like anything else, it’s essential to read the manufacturer’s instructions carefully before installation. Following these guidelines ensures that your new brass pressure relief valve will provide years of quality service!
Once you have chosen the perfect brass pressure relief valve for your system, it is essential to install it properly. These instructions are based on a typical installation with similar-sized piping and valves. The first step in choosing an appropriate location for installing your new valve will be finding out what type of piping system you currently have.
Once you have determined the pipe size in PSI, it is time to find what pressure relief valve will work with your system. Now that you know the piping system and pipe size, finding a brass pressure relief valve should be as easy as pie!
As one of the leading manufacturers of cavity free plug valves and special valves, AZ supplies to production plants in the chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, paper, food industries as well as for nuclear power plants and many other areas. Special valves for highest demands in areas with high operating pressures and aggressive, toxic or abrasive media are designed and developed together with our customers. In the 50 years of the company’s existence, AZ has continuously developed to meet the increasing requirements of customers active around the world and today AZ manufactures internationally on four continents.
Besides the P/T value of the sleeve the limitations of the valve bodies also have to be considered. Please refer to the EN 12516-1 resp. ASME B16.34 in order to choose a proper pressure rating (PN/class). The shown values refer to austenitic stainless steel 1.4408 (A351 Gr. CF8M).

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
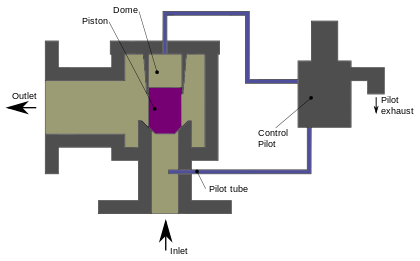
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

Like a seat belt, the free-look provision is a safety valve you probably won’t ever need, but it’s good to know it’s there, at least in the vast majority of states—just in case.




 8613371530291
8613371530291