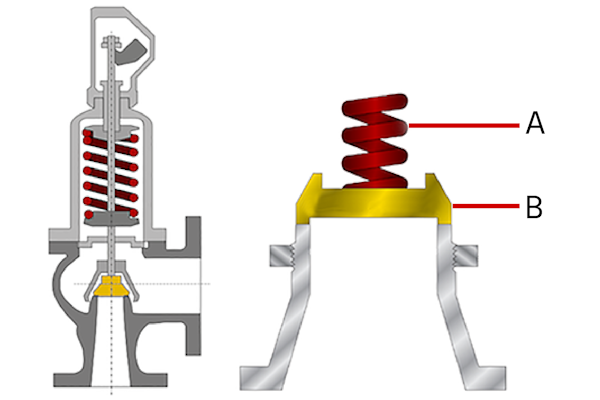
the safety valve discharges automatically at the pressure of in stock

Finding a quality driving school in can be a difficult and time consuming task. driving-schools.com comprehensive database of driving schools helps you pick one that’s right for you.

With a basically fully-charged air system (within the effective operating range for the compressor), turn off the engine, release all brakes, and let the system settle (air gauge needle stops moving). Time for 1 minute. The air pressure should not drop more than:

There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
In addition to reducing the effects of backpressure, the bellows also serve to isolate the spindle guide and the spring from the process fluid, this is important when the fluid is corrosive.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
For process applications, austenitic stainless steel is commonly used for seats and discs; sometimes they are ‘stellite faced’ for increased durability. For extremely corrosive fluids, nozzles, discs and seats are made from special alloys such as ‘monel’ or ‘hastelloy’.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
A key option is the type of seating material used. Metal-to-metal seats, commonly made from stainless steel, are normally used for high temperature applications such as steam. Alternatively, resilient discs can be fixed to either or both of the seating surfaces where tighter shut-off is required, typically for gas or liquid applications. These inserts can be made from a number of different materials, but Viton, nitrile or EPDM are the most common. Soft seal inserts are not generally recommended for steam use.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A standard or open lever is the simplest type of lever available. It is typically used on applications where a small amount of leakage of the fluid to the atmosphere is acceptable, such as on steam and air systems, (see Figure 9.2.5 (a)).
Where it is not acceptable for the media to escape, a packed lever must be used. This uses a packed gland seal to ensure that the fluid is contained within the cap, (see Figure 9.2.5 (b)).
For service where a lever is not required, a cap can be used to simply protect the adjustment screw. If used in conjunction with a gasket, it can be used to prevent emissions to the atmosphere, (see Figure 9.2.6).
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).
An elastomer bellows or diaphragm is commonly used in hot water or heating applications, whereas a stainless steel one would be used on process applications employing hazardous fluids.
As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.

As well, the compressor in the system is capable of pumping air pressure to 500 psi (3450kPa), which poses danger to both the driver and others around the vehicle.
The driver of a commercial vehicle must know that the safety valve makes the sound of a machine gun when it releases excess air pressure from the system.

A series of anomalies occurred in the boiler room that evening. The steel compression tank for the hydronic loop flooded, leaving no room for expansion. Water will expand at 3% of its volume when heated from room temperature to 180° F. When the burner fired, the expansion of the water increased the system pressure within the boiler. The malfunctioning operating control did not shut off the burner at the set point which caused the relief valve to open.
The brass relief valve discharge was installed with copper tubing piped solid to a 90° ell on the floor and the tubing further extended to the floor drain. The combination of hot water and steam from the boiler caused the discharge copper tubing to expand, using the relief valve as a fulcrum. The expansion of the copper discharge tubing pressing against the floor was enough to crack the brass relief valve, flooding the boiler room. The damage was not discovered until the next morning, several hours after the leak occurred. Thousands of dollars in damage was sustained and luckily no one was injured.
Each boiler requires some sort of pressure relieving device. They are referred to as either a safety, relief or safety relief valve. While these names are often thought of as interchangeable, there are subtle differences between them. According to the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors, the following are the definitions of each:
• Safety valve— This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard.
• Relief valve— This device is used for liquid service. It operates automatically by opening farther as the pressure increases beyond the initial opening pressure and recloses when the pressure drops below the opening pressure.
• Safety relief valve— This device includes the operating characteristics of both a safety valve and a relief valve and may be used in either application.
• Temperature and pressure safety relief valve— This device is typically used on potable water heaters. In addition to its pressure-relief function, it also includes a temperature-sensing element which causes the device to open at a predetermined temperature regardless of pressure. The set temperature on these devices is usually 210°.
• Relief valve piping— The boiler contractor installed a bushing on the outlet of the safety relief valve. Instead of 1 1/2-in. pipe, the installer used 3/4-in. pipe. When asked about it, he answered that he did not have any 1 1/2-in. pipe but had plenty of 3/4-in. pipe. I explained and then had to show the disbelieving contractor the code that states that the relief valve discharge piping has to be the same diameter as the relief valve outlet (see 2012 International Mechanical Code, 1006.6). By reducing the discharge pipe size, the relieving capacity of the safety valve may not be adequate to properly relieve the pressure inside the boiler, causing a dangerous situation.
The code also states that the discharge material shall be of rigid pipe that is approved for the temperature of the system. The inlet pipe size shall be full diameter of the pipe inlet for the relief valve. Some manufacturers suggest using black iron pipe rather than copper tubing. If using copper, it should have an air space that allows expansion should the relief valve open to avoid the accident that I referenced above. The discharge piping has to be supported and the weight of the piping should not be on the safety relief valve. Valves are not permitted in the inlet piping to or discharge piping from the relief valve. If you are using copper tubing on discharge piping, verify that there is room for expansion.
• Installation— Read the manufacturer’s installation manual as each may have different requirements. For instance, Conbraco requires that the discharge piping must terminate with a plain end and use a material that can handle temperatures of 375° or greater. This will preclude PVC or CPVC pipe for the discharge piping. The instruction manual for its model 12-14 steam relief valve stipulates that you cannot use a pipe wrench to install it. That would be good to know.
I once visited Boiler Utopia as the floor was clean and waxed. All the pipes were covered and exposed pipes were painted. There were large stickers detailing what was inside each pipe as well as directional arrows. Nothing was stacked next to the boilers. Yellow caution lines were painted on the floor around each boiler. I was in heaven. As I walked around the rear of the boiler, something clicked and triggered a warning bell. The discharge of the relief valve piping was about 6 in. from the floor but instead of a plain or angled cut end, the pipe had a threaded pipe cap on the termination. I asked the maintenance person about it and he said that the valve was leaking all over his newly waxed floor and this was the only way he could stop it. When I said that the discharge pipe should not have been threaded, he explained that it was not threaded and he had to take it to the local hardware store to thread it. I informed him that the cap had to be removed. We cut the pipe on an angle to prevent this.
• Steam boiler— Most manufacturers recommend a drip pan ell on the discharge of the steam boiler relief valve to eliminate the weight of the discharge piping on the relief valve. Some codes require the discharge to be vented outdoors.
• Testing— I will ask the attendees in my classes, “How often do you test the relief valves?” Most do not make eye contact and when I follow up with, “Why are they not tested?” I often hear that opening the relief valve will cause it to leak. I suggest that you refer to each manufacturer’s directions for testing. For instance, one will recommend once a year while another recommends twice a year. One manufacturer says, “Safety/relief valves should be operated only often enough to assure they are in good working order.” I am not sure what that even means. You want to also verify the proper test procedure as some will only want the relief valve tested when the boiler is at 75% of the rated pressure or higher of the relief valve.
Safety valve is a type of valve that automatically actuates when the pressure of inlet side of the valve increases to a predetermined pressure, to open the valve disc and discharge the fluid and when the pressure decreases to the prescribed value, to close the valve disc again. It is called a safety valve as a final safety device which control the pressure and discharges.

(a) The tank must be provided with pressure relief devices for the protection of the tank assembly and piping system. The discharge from these devices must be directed away from operating personnel, principal load bearing members of the outer jacket, car structure, trucks and safety appliances. Vent or weep holes in pressure relief devices are prohibited. All main pressure relief devices must discharge to the outside of the protective housings in which they are located, except that this requirement does not apply to pressure relief valves installed to protect isolated sections of lines between the final valve and end closure.
(b) Materials. Materials used in pressure relief devices must be suitable for use at the temperature of the lading and otherwise compatible with the lading in both the liquid and vapor phases.
(c) Inner tank. Pressure relief devices for the inner tank must be attached to vapor phase piping and mounted so as to remain at ambient temperature prior to operation. The inner tank must be equipped with one or more pressure relief valves and one or more safety vents (except as noted in paragraph (c)(3)(iv) of this section), and installed without an intervening shut-off valve (except as noted in paragraph (c)(3)(iii) of this section). Additional requirements are as follows:
(1) Safety vent. The safety vent shall function at the pressure specified in § 179.401-1. The safety vent must be flow rated in accordance with the applicable provisions of AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A (IBR, see § 171.7 of this subchapter), and provide sufficient capacity to meet the requirements of AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A, A8.07(a).
(A) The opening through all piping and fittings between the inner tank and its pressure relief devices must have a cross-sectional area at least equal to that of the pressure relief device inlet, and the flow characteristics of this upstream system must be such that the pressure drop will not adversely affect the relieving capacity or the proper operation of the pressure relief device.
(B) When the required relief capacity is met by the use of multiple pressure relief device placed on one connection, the inlet internal cross-sectional area of this connection must be sufficient to provide the required flow capacity for the proper operation of the pressure relief device system.
(A) The opening through the discharge lines must have a cross-sectional area at least equal to that of the pressure relief device outlet and may not reduce the relieving capacity below that required to properly protect the inner tank.
(B) When the required relieving capacity is met by use of multiple pressure relief devices placed on a common discharge manifold, the manifold outlet internal cross-sectional area must be at least equal to the combined outlet areas of the pressure relief devices.
(iii) Duplicate pressure relief devices may be used when an approved 3-way selector valve is installed to provide for relief through either duplicate pressure relief device. The 3-way valve must be included in the mounting prescribed by AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A, A6.02(g), when conducting the flow capacity test on the safety vent prescribed by AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A, A6.01. Flow capacity tests must be performed with the 3-way valve at both of the extreme positions as well as at the mid-position and the flow capacity must be in accordance with AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A, A8.07(a).
(iv) An alternate pressure relief valve, set as required in § 179.401-1, may be used in lieu of the safety vent, provided it meets the flow capacity prescribed in AAR Specifications for Tank Cars, appendix A at a flow rating pressure of 110 percent of its start-to-discharge pressure. Installation must -
(4) Evaporation control. The routine release of vaporized lading may be controlled with a pressure controlling and mixing device, except that a pressure controlling and mixing device is required on each DOT-113A60W car. Any pressure controlling and mixing device must -
(ii) Have sufficient capacity to limit the pressure within the inner tank to that pressure specified in § 179.401-1, when the discharge is equal to twice the normal venting rate during transportation, with normal vacuum and the outer shell at 130 °F; and
(iii) Prevent the discharge of a gas mixture exceeding 50% of the lower flammability limit to the atmosphere under normal conditions of storage or transportation.
(5) Safety interlock. If a safety interlock is provided for the purpose of allowing transfer of lading at a pressure higher than the pressure control valve setting but less than the pressure relief valve setting, the design must be such that the safety interlock will not affect the discharge path of the pressure relief value or safety vent at any time. The safety interlock must automatically provide an unrestricted discharge path for the pressure control device at all times when the tank car is in transport service.
(d) Outer jacket. The outer jacket must be provided with a suitable system to prevent buildup of annular space pressure in excess of 16 psig or the external pressure for which the inner tank was designed, whichever is less. The total relief area provided by the system must be a minimum of 25 square inches, and means must be provided to prevent clogging of any system opening, as well as to ensure adequate communication to all areas of the insulation space. If a safety vent is a part of the system, it must be designed to prevent distortion of the rupture disc when the annular space is evacuated.

Pressure relief valve outlets, position of(1) The discharge point of the cylinder or tank safety valve must be positioned so that any gas discharged through the valve would be directed away from any building, structure, caravan, towing vehicle, marine craft or gas installation.(2) A pressure relief valve outlet must not be located in any building, structure, caravan, or marine craft (except as permitted by clause 301) unless it is located within a housing specifically provided for that purpose.
Pressure relief valve shall be manufactured in accordance with a national or international standard and be certified for capacity or flow resistance by the National Board.

The termination must be at a point where readily visible to the building occupants and shall serve only that one relief valve. The termination point must not be more than 6 inches above the floor or flood level rim of the receptor, and one must be careful to maintain the required air gap when discharging to a receptor. Air gap requirements will be discussed in Chapter 9.

Disclaimer: This Code of Ordinances and/or any other documents that appear on this site may not reflect the most current legislation adopted by the Municipality. American Legal Publishing Corporation provides these documents for informational purposes only. These documents should not be relied upon as the definitive authority for local legislation. Additionally, the formatting and pagination of the posted documents varies from the formatting and pagination of the official copy. The official printed copy of a Code of Ordinances should be consulted prior to any action being taken.
For further information regarding the official version of any of this Code of Ordinances or other documents posted on this site, please contact the Municipality directly or contact American Legal Publishing toll-free at 800-445-5588.
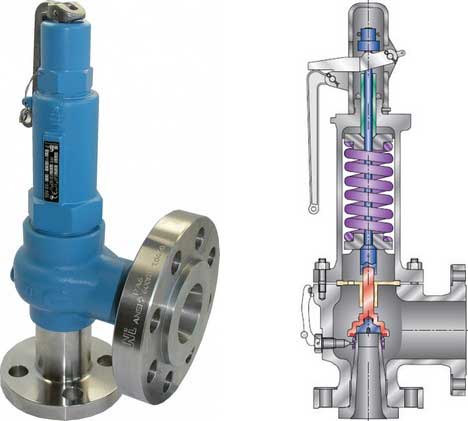

Curtiss-Wright"s selection of Pressure Relief Valves comes from its outstanding product brands Farris and Target Rock. We endeavor to support the whole life cycle of a facility and continuously provide custom products and technologies. Boasting a reputation for producing high quality, durable products, our collection of Pressure Relief Valves is guaranteed to provide effective and reliable pressure relief.
While some basic components and activations in relieving pressure may differ between the specific types of relief valves, each aims to be 100% effective in keeping your equipment running safely. Our current range includes numerous valve types, from flanged to spring-loaded, threaded to wireless, pilot operated, and much more.
A pressure relief valve is a type of safety valve designed to control the pressure in a vessel. It protects the system and keeps the people operating the device safely in an overpressure event or equipment failure.
A pressure relief valve is designed to withstand a maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). Once an overpressure event occurs in the system, the pressure relief valve detects pressure beyond its design"s specified capability. The pressure relief valve would then discharge the pressurized fluid or gas to flow from an auxiliary passage out of the system.
Below is an example of one of our pilot operated pressure relief valves in action; the cutaway demonstrates when high pressure is released from the system.
Air pressure relief valves can be applied to a variety of environments and equipment. Pressure relief valves are a safety valve used to keep equipment and the operators safe too. They"re instrumental in applications where proper pressure levels are vital for correct and safe operation. Such as oil and gas, power generation like central heating systems, and multi-phase applications in refining and chemical processing.
At Curtiss-Wright, we provide a range of different pressure relief valves based on two primary operations – spring-loaded and pilot operated. Spring-loaded valves can either be conventional spring-loaded or balanced spring-loaded.
Spring-loaded valves are programmed to open and close via a spring mechanism. They open when the pressure reaches an unacceptable level to release the material inside the vessel. It closes automatically when the pressure is released, and it returns to an average operating level. Spring-loaded safety valves rely on the closing force applied by a spring onto the main seating area. They can also be controlled in numerous ways, such as a remote, control panel, and computer program.
Pilot-operated relief valves operate by combining the primary relieving device (main valve) with self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief valves, also known as the pilot control. This pilot control dictates the opening and closing of the main valve and responds to system pressure. System pressure is fed from the inlet into and through the pilot control and ultimately into the main valve"s dome. In normal operating conditions, system pressure will prevent the main valve from opening.
The valves allow media to flow from an auxiliary passage and out of the system once absolute pressure is reached, whether it is a maximum or minimum level.
When the pressure is below the maximum amount, the pressure differential is slightly positive on the piston"s dome size, which keeps the main valve in the closed position. When system pressure rises and reaches the set point, the pilot will cut off flow to the dome, causing depressurization in the piston"s dome side. The pressure differential has reversed, and the piston will rise, opening the main valve, relieving pressure.
When the process pressure decreases to a specific pressure, the pilot closes, the dome is repressurized, and the main valve closes. The main difference between spring-loaded PRVs and pilot-operated is that a pilot-operated safety valve uses pressure to keep the valve closed.
Pilot-operated relief valves are controlled by hand and are typically opened often through a wheel or similar component. The user opens the valve when the gauge signifies that the system pressure is at an unsafe level; once the valve has opened and the pressure has been released, the operator can shut it by hand again.
Increasing pressure helps to maintain the pilot"s seal. Once the setpoint has been reached, the valve opens. This reduces leakage and fugitive emissions.
At set pressure the valve snaps to full lift. This can be quite violent on large pipes with significant pressure. The pressure has to drop below the set pressure in order for the piston to reseat.
The pilot is designed to open gradually, so that less of the system fluid is lost during each relief event. The piston lifts in proportion to the overpressure.
At Curtiss-Wright we also provide solutions for pressure relief valve monitoring. Historically, pressure relief valves have been difficult or impossible to monitor. Our SmartPRV features a 2600 Series pressure relief valve accessorized with a wireless position monitor that alerts plant operators during an overpressure event, including the time and duration.
There are many causes of overpressure, but the most common ones are typically blocked discharge in the system, gas blowby, and fire. Even proper inspection and maintenance will not eliminate the occurrence of leakages. An air pressure relief valve is the only way to ensure a safe environment for the device, its surroundings, and operators.
A PRV and PSV are interchangeable, but there is a difference between the two valves. A pressure release valve gradually opens when experiencing pressure, whereas a pressure safety valve opens suddenly when the pressure hits a certain level of over pressurization. Safety valves can be used manually and are typically used for a permanent shutdown. Air pressure relief valves are used for operational requirements, and they gently release the pressure before it hits the maximum high-pressure point and circulates it back into the system.
Pressure relief valves should be subject to an annual test, one per year. The operator is responsible for carrying out the test, which should be done using an air compressor. It’s imperative to ensure pressure relief valves maintain their effectiveness over time and are checked for signs of corrosion and loss of functionality. Air pressure relief valves should also be checked before their installation, after each fire event, and regularly as decided by the operators.
Direct-acting solenoid valves have a direct connection with the opening and closing armature, whereas pilot-operated valves use of the process fluid to assist in piloting the operation of the valve.
A control valve works by varying the rate of fluid passing through the valve itself. As the valve stem moves, it alters the size of the passage and increases, decreases or holds steady the flow. The opening and closing of the valve is altered whenever the controlled process parameter does not reach the set point.
Control valves are usually at floor level or easily accessible via platforms. They are also located on the same equipment or pipeline as the measurement and downstream or flow measurements.
An industrial relief valve is designed to control or limit surges of pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air system valves. It does so as a form of protection for the system and defending against instrument or equipment failure. They are usually present in clean water industries.
A PRV is often referred to as a pressure relief valve, which is also known as a PSV or pressure safety valve. They are used interchangeably throughout the industry depending on company standards.

The effects of exceeding safe pressure levels in an unprotected pressure vessel or system, can have catastrophic effects on both plant and personnel. Safety relief valves should be used to protect any pressurised system from the effects of exceeding its design pressure limit.
A safety relief valve is designed to automatically discharge gas, vapour or liquid from any pressure containing system, preventing a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and protecting plant and personnel.
A valve which automatically discharges gases and vapours so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded. It is characterised by a rapid full opening action and is used for steam, gases or vapour service.
A valve which automatically discharges fluid, usually liquid, when a predetermined upstream pressure is exceeded. The term is commonly used for pressure relieving valves in which the lift is proportional to the increase in pressure above the set pressure.
A valve which will automatically discharge gases, vapours or liquids, to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded. It is characterised by a rapid opening action.
The Bailey 707 Safety Relief Valve encompasses a top guided design, combining an unobstructed seat bore with high lift capability. This bronze bodied valve can be supplied with a resilient or metal trim with a choice of screwed and flanged connections.
The Bailey 707 is certified to BS EN 4126 Part 1 (BS6759 pt 1:2:3) and is suitable for duty on air/gas, steam/hot water (above 100ºC) and process liquid.
Test levers are available for inline safety checking, alternatively a sealed dome can be supplied for service conditions requiring a pressure tight seal on the discharge side, eg. liquid service with enclosed discharge.
Positive reseating is achieved with freely pivoting EPDM discs for gas, hot water and other liquid duties up to 150°C. Optional Aflas soft seats increase the range to 200°C. Precision lapped stainless steel trim gives positive re-seating for steam duty at higher temperatures. Fitted with a test lever for inline safety checking, or alternatively with a sealed dome for service conditions requiring a pressure tight seal on the discharge side, eg. liquid service.
The 716T is the ultimate solution to hot water system protection, it protects unvented hot water systems, against both excess pressure and excess temperature. Increasing pressure is sensed by the spring, which automatically opens the relief valve at the pre-set pressure and the integral probe independently monitors increases in temperature, safely opening the relief valve between 90°C and 95°C.
The temperature probes are designed to have a smooth surface free from crevices, to reduce mineral build-up, and are white powder coated to minimise galvanic action within the heater.
The 716T has a bronze body, Dzr brass internals and silicone seat in accordance with potable water code requirements. A soft seat provides leak tight operation. The spring and spring chamber are protected from the hot water by the EPDM diaphragm, reducing corrosion and increasing life in service.
The 746 Safety Relief Valve incorporates a freely pivoting disc, which ensures correct alignment with the nozzle. The combination of top guiding,unobstructed seat bore and full lift capability ensures the highest possible discharge rate thus maximum plant protection.
The 746 safety relief valve is available in both conventional and balanced bellows types, and features a special disc style for liquid application, which enhances valve performance.
The ‘conventional’ arrangement is suitable for applications where the built up pressure will not exceed 5%. The conventional valve can also be used in systems where the superimposed backpressure is at a constant level (up to 80%).
The ‘balanced bellows’ arrangement is for applications where several safety relief valves discharge into a common discharge manifold, or in any circumstances where a variable back pressure can occur, up to a maximum of 40%.
The 756 Safety Valve combines a top piston guided valve and an unobstructed seat bore with a full lift capability, giving maximum discharge capacity. The design incorporates an adjustable blowdown ring and meets all the requirements of BS6759 Part 1.
A freely pivoting disc and precision lapped stainless steel trim gives positive re-seating for steam duty. As standard the 756 is fitted with a test lever for inline testing. Ideally suited to applications on steam boilers and pipelines where blowdown tolerances are critical.
The 766 Safety Valve is a double spring high lift valve with high discharge capacity. The top guided piston design incorporates an adjustable blowdown ring and meets all the requirements of BS6759 Part 1.
A freely pivoting disc and precision lapped stainless steel trim gives positive re-seating for steam duty. Fitted as standard with test lever for inline testing.Ideally suited to applications on steam boilers and pipelines where blowdown tolerances are critical.
The 776 Safety Relief Valve is designed for cryogenic duty down to -196°C. The valve combines a full lift design and top guided construction with an unobstructed seat bore to provide maximum discharge capacity. Positive sealing is achieved through a freely pivoted disc with Kel F (PCTFE) soft seat technology.
This spring operated liquid relief valve has a cartridge type assembly which can be withdrawn from the body without disturbing the spring setting and hence relieving pressure. This allows the seating surfaces to be cleaned without the need to reset the valve. The 480 is a bronze relief valve, the 485 is also bronze with a renewable stainless steel seat and disc, while the 490 is all stainless steel.
Typically for use on positive displacement pumps, for relief or bypass duties. The spring cartridge assembly can be supplied separately for use as an integral pump bypass relief valve.
The type 616D is a spring operated high capacity safety valve for low-pressure air applications. It is designed to deliver precise relieving and re-seating pressures while the protected open discharge gives downward flow. The non-stick seating surfaces give positive shut-off and freedom from sticking, whilst the mixture of aluminium and gunmetal make it light but

Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This should only be necessary once for each IP address you access the site from.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.




 8613371530291
8613371530291