boiler safety valve discharge piping brands

The S100 Safety Shut Off valve is mainly used to avoid any damage to components as well as to avoid too high or too low pressure in the gas train. This could cause high financial losses and/or injured ...
130 Series Safety valves are also available as Relief valves. Relief valves, identified by the letter R after the type number, are devices with an operational function, ...
Parker"s cartridge safety relief valves (CSRV) are designed to offer the highest level of protection while maintaining easy serviceability. The CSRV was designed from the existing Parker ...

There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).

Pressure relief devices are used to provide a means of venting excess pressure which could rupture a boiler or pressure vessel. A pressure relief device is the last line of defense for safety. If all other safety devices or operating controls fail, the pressure relief device must be capable of venting excess pressure.
There are many types of pressure relief devices available for use in the boiler and pressure vessel industry. This inspector guide will address the most common devices found on boilers and pressure vessels. Virtually all jurisdictions require a pressure relief device to be manufactured and certified in accordance with the ASME BPV Code in addition to being capacity-certified by the National Board.
Safety Valve – This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard.
Relief Valve – This device is typically used for liquid service. It operates automatically by opening farther as the pressure increases beyond the initial opening pressure and recloses when the pressure drops below the opening pressure.
Safety Relief Valve – This device includes the operating characteristics of both a safety valve and a relief valve and may be used in either application.
Temperature and Pressure Safety Relief Valve – This device is typically used on potable water heaters. In addition to its pressure-relief function, it also includes a temperature-sensing element which causes the device to open at a predetermined temperature regardless of pressure. The set temperature on these devices is usually 210°F.
The inlet piping connected to the device must not be smaller in diameter than the inlet opening of the device. An inlet pipe that is smaller than the device inlet opening could alter the operating characteristics for which the device was designed.
The discharge piping connected to the device must be no smaller than the discharge opening of the device. A discharge pipe that is smaller than the device discharge opening could cause pressure to develop on the discharge side of the device while operating.
Multiple devices discharging into a discharge manifold or header is a common practice. The discharge manifold or header must be sized so the cross-sectional area is equal to or greater than the sum of the discharge cross-sectional areas of all the devices connected to the discharge manifold or header. Failing this requirement, the devices would be subjected to pressure on the discharge side of the device while operating. Even a small amount of pressure here could adversely affect the operation of the device.
Constant leakage of the device can cause a build-up of scale or other solids around the discharge opening. This build-up can prevent the device from operating as designed.
Discharge piping connected to the device must be supported so as not to impart any loadings on the body of the device. These loadings could affect or prevent the proper operation of the device including proper reclosure after operating.
Some devices, especially on larger boilers, may have a discharge pipe arrangement which incorporates provisions for expansion as the boiler heats up or cools down. These expansion provisions must allow the full range of movement required to prevent loads being applied to the device body.
Drain holes in the device body and discharge piping, when applicable, must be open to allow drainage of liquids from over the device disk on spring loaded valves. Any liquid allowed to remain on top of the device disk can adversely affect the operating characteristics of the device.
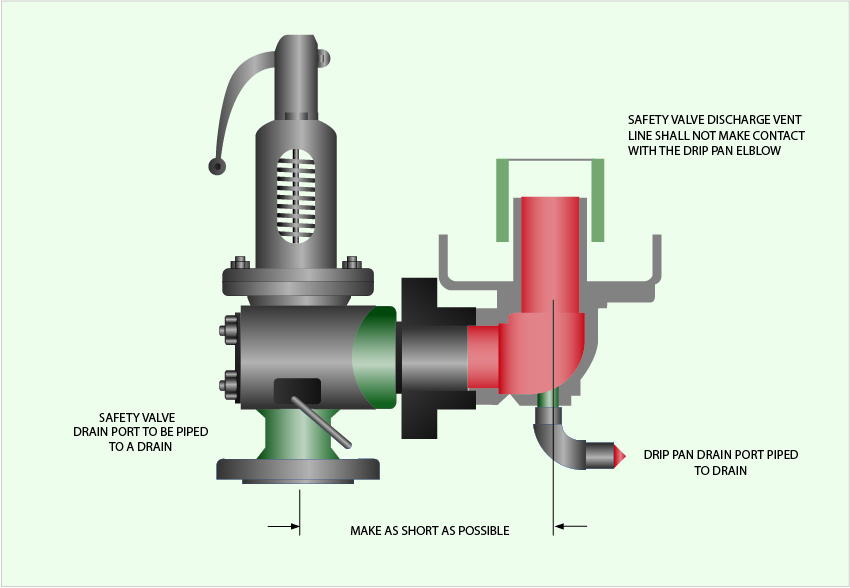
Most jurisdictional requirements state the device must be "piped to a point of safe discharge." This must be accomplished while keeping the run of discharge piping as short as possible. Most jurisdictions also limit the number of 90 degree elbows that may be installed in the discharge piping. Too long of a run and multiple elbows can adversely affect the operation of the device.
While inspecting a boiler or pressure vessel, the inspector will also be evaluating the pressure relief device(s) installed on, or associated with, the equipment. The inspector should:
Compare the device nameplate set pressure with the boiler or pressure vessel maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and ensure the device set pressure does not exceed the MAWP. A device with a set pressure less than MAWP is acceptable. If multiple devices are used, at least one must have a set pressure equal to or less than the MAWP. The ASME Code should be reviewed for other conditions relating to the use of multiple devices.
Instruct the owner or owner"s representative to lift the test lever, if so equipped, on spring-loaded devices. ASME BPV Code Section IV devices can have the test levers lifted without pressure in the boiler. All other devices must have at least 75% of the device set pressure under the device disk prior to lifting the test lever. If the device is found to be stuck in a closed position, the equipment should be immediately removed from service until such time the device can be replaced or repaired.
The small pressure relief devices found on many air compressor vessels have a ring inserted through a drilled hole on the end of the device stem. These are tested by pulling the stem straight out and then releasing. The discharge openings in this type of device are holes drilled around the periphery of the device. These holes often get filled with oily dust and grit which can cause eye damage when the device is tested. A rag, loosely wrapped around the device when testing, can help prevent personal injury from the dust and grit.

Relief valves are designed to open at a preset pressure (or temperature) level and relieve the system when it has exceeded the desired level. The valve"s relief of elevated liquid, gas, or steam pressures prevents damage to the system. We offer a wide selection of relief valves for any application.

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

A series of anomalies occurred in the boiler room that evening. The steel compression tank for the hydronic loop flooded, leaving no room for expansion. Water will expand at 3% of its volume when heated from room temperature to 180° F. When the burner fired, the expansion of the water increased the system pressure within the boiler. The malfunctioning operating control did not shut off the burner at the set point which caused the relief valve to open.
The brass relief valve discharge was installed with copper tubing piped solid to a 90° ell on the floor and the tubing further extended to the floor drain. The combination of hot water and steam from the boiler caused the discharge copper tubing to expand, using the relief valve as a fulcrum. The expansion of the copper discharge tubing pressing against the floor was enough to crack the brass relief valve, flooding the boiler room. The damage was not discovered until the next morning, several hours after the leak occurred. Thousands of dollars in damage was sustained and luckily no one was injured.
Each boiler requires some sort of pressure relieving device. They are referred to as either a safety, relief or safety relief valve. While these names are often thought of as interchangeable, there are subtle differences between them. According to the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors, the following are the definitions of each:
• Safety valve— This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard.
• Relief valve— This device is used for liquid service. It operates automatically by opening farther as the pressure increases beyond the initial opening pressure and recloses when the pressure drops below the opening pressure.
• Safety relief valve— This device includes the operating characteristics of both a safety valve and a relief valve and may be used in either application.
• Temperature and pressure safety relief valve— This device is typically used on potable water heaters. In addition to its pressure-relief function, it also includes a temperature-sensing element which causes the device to open at a predetermined temperature regardless of pressure. The set temperature on these devices is usually 210°.
• Relief valve piping— The boiler contractor installed a bushing on the outlet of the safety relief valve. Instead of 1 1/2-in. pipe, the installer used 3/4-in. pipe. When asked about it, he answered that he did not have any 1 1/2-in. pipe but had plenty of 3/4-in. pipe. I explained and then had to show the disbelieving contractor the code that states that the relief valve discharge piping has to be the same diameter as the relief valve outlet (see 2012 International Mechanical Code, 1006.6). By reducing the discharge pipe size, the relieving capacity of the safety valve may not be adequate to properly relieve the pressure inside the boiler, causing a dangerous situation.
The code also states that the discharge material shall be of rigid pipe that is approved for the temperature of the system. The inlet pipe size shall be full diameter of the pipe inlet for the relief valve. Some manufacturers suggest using black iron pipe rather than copper tubing. If using copper, it should have an air space that allows expansion should the relief valve open to avoid the accident that I referenced above. The discharge piping has to be supported and the weight of the piping should not be on the safety relief valve. Valves are not permitted in the inlet piping to or discharge piping from the relief valve. If you are using copper tubing on discharge piping, verify that there is room for expansion.
• Installation— Read the manufacturer’s installation manual as each may have different requirements. For instance, Conbraco requires that the discharge piping must terminate with a plain end and use a material that can handle temperatures of 375° or greater. This will preclude PVC or CPVC pipe for the discharge piping. The instruction manual for its model 12-14 steam relief valve stipulates that you cannot use a pipe wrench to install it. That would be good to know.
I once visited Boiler Utopia as the floor was clean and waxed. All the pipes were covered and exposed pipes were painted. There were large stickers detailing what was inside each pipe as well as directional arrows. Nothing was stacked next to the boilers. Yellow caution lines were painted on the floor around each boiler. I was in heaven. As I walked around the rear of the boiler, something clicked and triggered a warning bell. The discharge of the relief valve piping was about 6 in. from the floor but instead of a plain or angled cut end, the pipe had a threaded pipe cap on the termination. I asked the maintenance person about it and he said that the valve was leaking all over his newly waxed floor and this was the only way he could stop it. When I said that the discharge pipe should not have been threaded, he explained that it was not threaded and he had to take it to the local hardware store to thread it. I informed him that the cap had to be removed. We cut the pipe on an angle to prevent this.
• Steam boiler— Most manufacturers recommend a drip pan ell on the discharge of the steam boiler relief valve to eliminate the weight of the discharge piping on the relief valve. Some codes require the discharge to be vented outdoors.
• Testing— I will ask the attendees in my classes, “How often do you test the relief valves?” Most do not make eye contact and when I follow up with, “Why are they not tested?” I often hear that opening the relief valve will cause it to leak. I suggest that you refer to each manufacturer’s directions for testing. For instance, one will recommend once a year while another recommends twice a year. One manufacturer says, “Safety/relief valves should be operated only often enough to assure they are in good working order.” I am not sure what that even means. You want to also verify the proper test procedure as some will only want the relief valve tested when the boiler is at 75% of the rated pressure or higher of the relief valve.
Temperature/pressure-relief or TPR valves are safety devices installed on water heating appliances, such as boilers and domestic water supply heaters. TPRs are designed to automatically release water in the event that pressure or temperature in the water tank exceeds safe levels.
If temperature sensors and safety devices such as TPRs malfunction, water in the system may become superheated (exceed the boiling point). Once the tank ruptures and water is exposed to the atmosphere, it will expand into steam almost instantly and occupy approximately 1,600 times its original volume. This process can propel a heating tank like a rocket through multiple floors, causing personal injury and extensive property damage.
Water-heating appliance explosions are rare due to the fact that they require a simultaneous combination of unusual conditions and failure of redundant safety components. These conditions only result from extreme negligence and the use of outdated or malfunctioning equipment.
The TPR valve will activate if either water temperature (measured in degrees Fahrenheit) or pressure (measured in pounds per square inch [PSI]) exceed safe levels. The valve should be connected to a discharge pipe (also called a drain line) that runs down the length of the water heater tank. This pipe is responsible for routing hot water released from the TPR to a proper discharge location.
It is critical that discharge pipes meet the following requirements, which can be found in InterNACHI’s Water Heater Discharge Piping mini-course, at www.nachi.org/education. A discharge pipe should:
discharge to a termination point that is readily observable by occupants, because discharge indicates that something is wrong, and to prevent unobserved termination capping.
A properly functioning TPR valve will eject a powerful jet of hot water from the discharge pipe when fully activated, not a gentle leak. A leaky TPR valve is an indication that it needs to be replaced. In the rare case that the TPR valve does activate, the homeowner should immediately shut off the water and contact a qualified plumber for assistance and repair.
Inspectors should recommend that homeowners test TPR valves monthly, although inspectors should never do this themselves. The inspector should demonstrate to the homeowner how the main water supply can be shut off, and explain that it can be located at the home"s main water supply valve, or at the water supply shut-off for the appliance on which the TPR is mounted.
The pressure at which a TPR valve will activate is printed on a data plate located beneath the test lever. This amount should not exceed the working pressure limit marked on the data plate of the water-heating appliance it serves.
TPR valves with missing data plates should be replaced.Although a TPR valve might never become activated, it is an essential safety component on boilers and domestic water heaters. Guidelines concerning these valves and their discharge pipes reflect real hazards that every homeowner and home inspector should take seriously. More information about this subject can be found in InterNACHI"s Water Heater Discharge Piping mini-course, InterNACHI"s Plumbing Inspection course or by contacting a qualified plumber.

Many electronic, pneumatic and hydraulic systems exist today to control fluid system variables, such as pressure, temperature and flow. Each of these systems requires a power source of some type, such as electricity or compressed air in order to operate. A pressure Relief Valve must be capable of operating at all times, especially during a period of power failure when system controls are nonfunctional. The sole source of power for the pressure Relief Valve, therefore, is the process fluid.
Once a condition occurs that causes the pressure in a system or vessel to increase to a dangerous level, the pressure Relief Valve may be the only device remaining to prevent a catastrophic failure. Since reliability is directly related to the complexity of the device, it is important that the design of the pressure Relief Valve be as simple as possible.
The pressure Relief Valve must open at a predetermined set pressure, flow a rated capacity at a specified overpressure, and close when the system pressure has returned to a safe level. Pressure Relief Valves must be designed with materials compatible with many process fluids from simple air and water to the most corrosive media. They must also be designed to operate in a consistently smooth and stable manner on a variety of fluids and fluid phases.
The basic spring loaded pressure Relief Valve has been developed to meet the need for a simple, reliable, system actuated device to provide overpressure protection.
The Valve consists of a Valve inlet or nozzle mounted on the pressurized system, a disc held against the nozzle to prevent flow under normal system operating conditions, a spring to hold the disc closed, and a body/Bonnet to contain the operating elements. The spring load is adjustable to vary the pressure at which the Valve will open.
When a pressure Relief Valve begins to lift, the spring force increases. Thus system pressure must increase if lift is to continue. For this reason pressure Relief Valves are allowed an overpressure allowance to reach full lift. This allowable overpressure is generally 10% for Valves on unfired systems. This margin is relatively small and some means must be provided to assist in the lift effort.
Most pressure Relief Valves, therefore, have a secondary control chamber or huddling chamber to enhance lift. As the disc begins to lift, fluid enters the control chamber exposing a larger area of the disc to system pressure.
This causes an incremental change in force which overcompensates for the increase in spring force and causes the Valve to open at a rapid rate. At the same time, the direction of the fluid flow is reversed and the momentum effect resulting from the change in flow direction further enhances lift. These effects combine to allow the Valve to achieve maximum lift and maximum flow within the allowable overpressure limits. Because of the larger disc area exposed to system pressure after the Valve achieves lift, the Valve will not close until system pressure has been reduced to some level below the set pressure. The design of the control chamber determines where the closing point will occur.
A safety Valve is a pressure Relief Valve actuated by inlet static pressure and characterized by rapid opening or pop action. (It is normally used for steam and air services.)
A low-lift safety Valve is a safety Valve in which the disc lifts automatically such that the actual discharge area is determined by the position of the disc.
A full-lift safety Valve is a safety Valve in which the disc lifts automatically such that the actual discharge area is not determined by the position of the disc.
A Relief Valve is a pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure. It may be provided with an enclosed spring housing suitable for closed discharge system application and is primarily used for liquid service.
A safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve characterized by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application and may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
A conventional safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which has its spring housing vented to the discharge side of the Valve. The operational characteristics (opening pressure, closing pressure, and relieving capacity) are directly affected by changes of the back pressure on the Valve.
A balanced safety Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which incorporates means of minimizing the effect of back pressure on the operational characteristics (opening pressure, closing pressure, and relieving capacity).
A pilotoperated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve in which the major relieving device is combined with and is controlled by a self-actuated auxiliary pressure Relief Valve.
A poweractuated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve in which the major relieving device is combined with and controlled by a device requiring an external source of energy.
A temperature-actuated pressure Relief Valve is a pressure Relief Valve which may be actuated by external or internal temperature or by pressure on the inlet side.
A vacuum Relief Valve is a pressure relief device designed to admit fluid to prevent an excessive internal vacuum; it is designed to reclose and prevent further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored.
Many Codes and Standards are published throughout the world which address the design and application of pressure Relief Valves. The most widely used and recognized of these is the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, commonly called the ASME Code.
is the gauge pressure at which the lift is sufficient to discharge the predetermined flowing capacity. It is equal to the set pressure plus opening pressure difference.
is the calculated mass flow from an orifice having a cross sectional area equal to the flow area of the safety Valve without regard to flow losses of the Valve.
the pressure at which a Valve is set on a test rig using a test fluid at ambient temperature. This test pressure includes corrections for service conditions e.g. backpressure or high temperatures.
is the value of increasing static inlet pressure of a pressure Relief Valve at which there is a measurable lift, or at which the discharge becomes continuous as determined by seeing, feeling or hearing.
Because cleanliness is essential to the satisfactory operation and tightness of a safety Valve, precautions should be taken during storage to keep out all foreign materials. Inlet and outlet protectors should remain in place until the Valve is ready to be installed in the system. Take care to keep the Valve inlet absolutely clean. It is recommended that the Valve be stored indoors in the original shipping container away from dirt and other forms of contamination.
Safety Valves must be handled carefully and never subjected to shocks. Rough handling may alter the pressure setting, deform Valve parts and adversely affect seat tightness and Valve performance.
When it is necessary to use a hoist, the chain or sling should be placed around the Valve body and Bonnet in a manner that will insure that the Valve is in a vertical position to facilitate installation.
Many Valves are damaged when first placed in service because of failure to clean the connection properly when installed. Before installation, flange faces or threaded connections on both the Valve inlet and the vessel and/or line on which the Valve is mounted must be thoroughly cleaned of all dirt and foreign material.
Because foreign materials that pass into and through safety Valves can damage the Valve, the systems on which the Valves are tested and finally installed must also be inspected and cleaned. New systems in particular are prone to contain foreign objects that inadvertently get trapped during construction and will destroy the seating surface when the Valve opens. The system should be thoroughly cleaned before the safety Valve is installed.
The gaskets used must be dimensionally correct for the specific flanges. The inside diameters must fully clear the safety Valve inlet and outlet openings so that the gasket does not restrict flow.
For flanged Valves, draw down all connection studs or bolts evenly to avoid possible distortion of the Valve body. For threaded Valves, do not apply a wrench to the Valve body. Use the hex flats provided on the inlet bushing.
Safety Valves are intended to open and close within a narrow pressure range. Valve installations require accurate design both as to inlet and discharge piping. Refer to International, National and Industry Standards for guidelines.
The Valve should be mounted vertically in an upright position either directly on a nozzle from the pressure vessel or on a short connection fitting that provides a direct, unobstructed flow between the vessel and the Valve. Installing a safety Valve in other than this recommended position will adversely affect its operation.
Discharge piping should be simple and direct. A "broken" connection near the Valve outlet is preferred wherever possible. All discharge piping should be run as direct as is practicable to the point of final release for disposal. The Valve must discharge to a safe disposal area. Discharge piping must be drained properly to prevent the accumulation of liquids on the downstream side of the safety Valve.
The weight of the discharge piping should be carried by a separate support and be properly braced to withstand reactive thrust forces when the Valve relieves. The Valve should also be supported to withstand any swaying or system vibrations.
If the Valve is discharging into a pressurized system be sure the Valve is a "balanced" design. Pressure on the discharge of an "unbalanced" design will adversely affect the Valve performance and set pressure.
The Bonnets of balanced bellows safety Valves must always be vented to ensure proper functioning of the Valve and to provide a telltale in the event of a bellows failure. Do not plug these open vents. When the fluid is flammable, toxic or corrosive, the Bonnet vent should be piped to a safe location.
It is important to remember that a pressure Relief Valve is a safety device employed to protect pressure vessels or systems from catastrophic failure. With this in mind, the application of pressure Relief Valves should be assigned only to fully trained personnel and be in strict compliance with rules provided by the governing codes and standards.

Tired of keeping track of your valve inventory’s annual certification records? We offer complete management of your safety relief valves. With an inventory of repair parts and in stock relief valves of all sizes, we can respond to any customer emergency. We offer annual certification services as well as repair of all major brands, including Kunkle, Conbraco, Consolidated, Dresser, Apollo and more.

This article describes the requirements for a discharge tube or drain line on temperature & pressure relief valves used on any appliance that heats water. These include hydronic heating boilers (hot water boilers), steam boilers, and all types of water heaters, both those that use a water storage tank or cylinder and those that heat water on demand such as tankless water heaters.
Here we describe the installation specifications for TPR valve drain line piping and we include an extensive list of discharge tube installation or condition defects, most of which are unsafe. All of them are improper.
The Temperature & Pressure Relief Valve or TPR Valve on any heated appliance that contains water, such as a heating boiler, hot water tank, water heater, water cylinder, must have a drain line or discharge tube properly installed, routed, and made of proper materials. The purpose of this drain line is to discharge potentially hot scalding water to a safe location so that a bystander is not scalded.
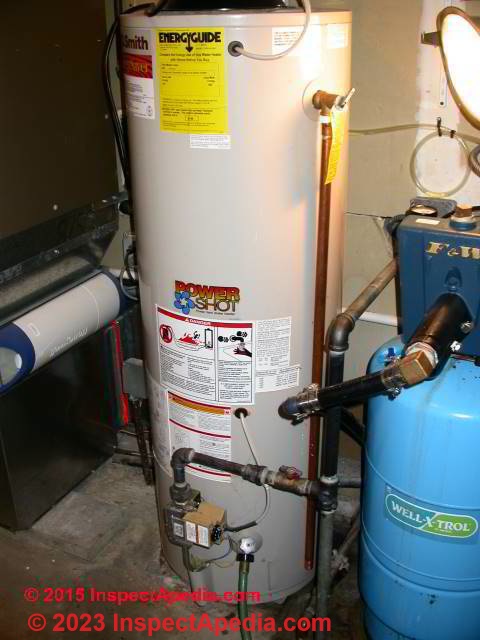
At left we see a typical TPR valve installation (by the author) including the vertical 3/4" copper drain piping that will discharge any T&P valve spillage to the floor.
An unsafe TPR drain line installation is shown at the top of this page. Only a complete fool would do what we found on this boiler. To "stop" an annoying boiler drip at the pressure temperature relief valve, the mechanic installed a short length of pipe capped by a drain valve which he could simply shut. This might have been installed on a system for other reasons, such as connecting a hose to permit easy draining of pressure off of the boiler through the TP valve.
But it is in all events dangerous, illegal, and plain stupid to ever install a shutoff valve or any other sort of "cap" on a pressure/temperature relief valve.
But how dangerous is it to omit a discharge drain tube on a TPR valve? The possibility of a scalding burn is obvious but do these accidents actually happen?
Noticing that a TPR discharge tube was missing on a heating boiler during a home inspection I [DF] pointed out this safety hazard to my client while the real estate agent nearby frowned at my "old maid" trouble-making personality.
My client burst into tears. Sobbing she told me that she was grateful that inspectors would routinely point-out this hazard. Her son, playing with friends in the basement, lost an eye when he and a pal opened the discharge lever on a heating boiler, scalding his face and ruining his left eye forever.
Less dramatic but scary, at a different inspection I found that a string tied through a small hole in the end of the TPR valve"s test lever. The string was routed up towards the ceiling, over a horizontal plumbing line and back down to a termination in a nice knot a few feet above the floor.
This interesting TPR test lever addition was explained by the building owner. His son and friends liked to play steam boat. It was fun to pull the string, pretending it was a steam boat whistle, and to see the burst of steamy hot water emerge from the end of the discharge line.
TPR Valve Discharge tube is installed: Check that the Temperature/Pressure relief valve has a discharge tube properly installed. The drain line must be connected to the discharge outlet of the T&P valve to "avoid water damage and scalding injury." (Watts 2011)
Our photo (left) shows an oil fired water heater with a T&P valve that has no discharge tube installed. There are of course other operating problems with this water heater as the photo makes clear.
TPR Valve Discharge tube blocked: Check that the discharge is not blocked by anything whatsoever. Our page top photo shows a shutoff drain valve installed at the end of a short T&P valve discharge line.
The risk is that the valve is no longer leaking not because a proper repair has been made, but because the valve has become clogged and blocked by mineral salts left behind by the evaporating hot water - leaving the installation dangerous and risking a BLEVE - explosion.
This is an unsafe condition as the operation of the temperature or pressure relief valve may be interfered with by the insulation and also because the valve cannot be inspected for evidence of leaks or failure.
Similarly, discharging a relief valve leakage or drip to a location where the leak or drip cannot be observed is a dangerous practice because the leak can go unnoticed, causing failure to recognize an unsafe condition.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Piped "UP": the drain line must never be piped upwards in any of its course. The hazard is that the drain can become blocked or that a small drip, representing an unsafe condition at the T&P valve, may be hidden as the water simply accumulates in the bend of the trap or upwards piped section.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Crimped, Plugged, or Reduced: the drain line may not be bent, crimped, nor plugged by any material. The diameter of the drain line may not be reduced to a size smaller than the opening of the T&P valve that it serves. Some jurisdictions may limit the number of elbows or bends permitted in the piping.
The photos above illustrates this unsafe installation practice: a 1/2" copper tube has been installed through a reducing fitting into the mouth or piping of a 3/4" diameter TPR valve.
Below the reducer from 3/4" to 1/2" was installed at the TPR valve opening. At above right a reducing elbow was used to shrink the 3/4" horizontal T&P drain line (from the TPR valve mouth) to 1/2" for the vertical run to the floor. Both of these installations are improper and unsafe.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Active Leaking: above we show a wet floor area as well as the corroded end of the T&P discharge tube in our first photo: this relief valve is actively leaking. In this case investigation showed that the valve itself had failed - we replaced it.
TPR Valve Drain line Drip Marks: any drip stains on the floor below the valve discharge tube (second photo above ) also indicate a history of leaks at the T&P valve. Without further investigation we don"t know if this problem has been repaired or if it is simply intermittent.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Opening is Wet: If there is corrosion on the end of the discharge tube or if you see drip stains on the floor below the drain pipe, even if the floor is dry you should always test for active or recent spillage at the relief valve. It"s possible that water on the floor has dried (on its own or with some help before a building inspection).
But if there has been recent spillage at the TPR valve the interior of the end of the discharge tube can confirm that. Using your finger, feel the inside of the tip of the discharge tube and check for water - it should be dry.
As the two photos show below, even though the floor was dry below this T&P drain line, the interior of the drain was wet - there was active leaking (or someone had recently opened the valve).
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Materials: the drain line material requirements vary by jurisdiction; some areas permit both plastic as well as copper or galvanized steel piping. But where plastic drain line materials are used, the temperature rating of the plastic must be above the highest temperature that might be produced by the heating appliance to which the T&P valve is connected.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Termination Fittings: the end of the discharge or drain line tube should not be threaded nor fitted with any device that would permit attachment of a cap, plug, or valve that could close off the line.
TPR Valve Discharge Tube Termination Location: The water that may be discharged from a T&P valve must be conducted to a safe place of disposal. This may be a floor drain (recommended by Watts) or in some jurisdictions another location may be permitted.
Some jurisdictions do not permit the discharge drain destination to be hidden from view, on the theory that you won"t see a drip or leak and won"t thus detect an unsafe condition.
Other jurisdictions, such as in the U.K., permit the TPR valve drain line to be piped to a hidden location but require the installation of a tundish in the drain line at a suitable visible location.
The Tundish will allow the occupants to see that the TPR valve is leaking, and its air gap provides other plumbing sanitation and blockage protection features.
Outdoor terminations of a T&P valve drain line may be permitted in some jurisdictions, even required, to avoid water damage inside the building. However unless a tundish device is properly included such installations are unsafe. And piping a T&P drain line outside in freezing climates is unsafe because a dripping line may freeze and become blocked.
TPR Valve Mounting Leaks: Check for leaks around the valve where it is mounted on the boiler or boiler piping. This is a TPR valve defect, not a TPR discharge tube defect, but depending on the valve position and location, a leak around the TRP valve mount may send water (or corrosion or mineral salts) down the outside of the discharge tube, offering a valuable visual clue and possibly being mistaken for a defect in the tube itself
I am ... in the process of selling a condo I own. I got this request for repairs for the hot water heater with a picture of the heater. On the picture it shows the that the discharge line is above the TPR valve, and that this is a problem (see description on attachment). This doesn"t make any sense to me. Can you help me decide what the best action would be? thanks. - R.N. 7/11/2013
The photo is a bit difficult to read but if you look closely where the two flexible copper lines enter the wall behind the water heater, you"ll see that the smaller leftmost flexible tube, connected back to the water heater TP valve, enters the wall at a height above the valve outlet opening. What the home inspector said was perfectly correct and represents a safety hazard.
The temperature/pressure relief valve on a water heater is connected to a drain line so that if the valve opens someone nearby is not shot in the face with hot water. The discharge drain extension is typically taken to just a few inches above the floor or in some jurisdictions it may be directed outdoors - a solution that I think is risky because IF the valve should be leaking, dripping, etc., one wants to notice that and fix it to keep the system safe.
The inspector"s report makes a valid point: we should never route the discharge tube "up" from the actual outlet opening of the TP valve. That"s because if the valve should develop a small leak or be discharged on occasion, the up-routed discharge tube will keep water and debris remaining in the tube at the valve outlet where debris or mineral accumulation clog the valve or interfere with its operating spring.
The result over time could be that the valve becomes clogged and would then fail to open in a true emergency - risking, ultimately a dangerous BLEVE or water heater explosion.
Watch out: ALSO, I suspect from the photo that your water heater has a discharge tube that directs the valve outlet into a wall and going to who knows where. If the other end of that line is not already readily visible and in a location where it would be noticed, that too would be unsafe and improper.
The FIX for this unsafe condition is usually trivial: the discharge tube must be routed only "downwards" from the TP valve outlet opening, and the end of the discharge tube must be in a readily accessible, visible, and safe location. You"d probably find these same instructions in the installation manual for the water heater.
The COST for this repair should be no more than a simple plumbing service call and perhaps a few piping connections. What would make sense to me and what would be most economical would be to combine this repair with any other plumbing repairs that are needed at the home.
10. Terminate not more than 6 inches (152 mm) and not less than two times the discharge pipe diameter above the floor or waste receptor flood level rim.
14. Be one nominal size larger than the size of the relief-valve outlet, where the relief-valve discharge piping is constructed of PEX or PE-RT tubing. The outlet end of such tubing shall be fastened in place.
10. Terminate not more than 6 inches (152 mm) above and not less than two times the discharge pipe diameter above the floor or flood level rim of the waste receptor.
Some model and adopted building and plumbing codes expressly prohibit discharging the TPR valve out of the room containing the heating appliance that it is intended to protect.
1. All pressurized storage-type water heaters and unfired hot water storage tanks shall be equipped with one or more combination temperature and pressure relief valves. The temperature steam rating of a combination temperature and pressure relief valve or valves shall equal or exceed the energy input rating in BTU per hour of the water heater. No shut off valve or other restricting device may be installed between the water heater or storage tank and the combination temperature and pressure relief valve.
2. All pressurized non-storage type water heaters shall be provided with a pressure relief valve installed at the hot water outlet with no shut off valve between the heater and the relief valve.
3. Temperature a




 8613371530291
8613371530291