give the difference between safety valve and relief valve quotation

As you already know, there are a multitude of pressure relief valves out there. In the industry, we tend to use terms like safety valve and relief valve interchangeably. And for the most part, this makes sense. Most pressure relief valves are designed to do the same thing — release pressure in a system.
But is there a difference between some of these commonly used terms, and if so, what does it mean for you? Here’s a quick breakdown of two popular terms: safety valve vs. relief valve.
While both terms refer to valves used to release pressure from a pressurized system, their technical definitions are a bit different. In general, the term relief valve refers to a valve within a pressurized system that is used to control pressure for the optimal functionality of the system. Relief valves are designed to help your facility avoid system failures, and protect equipment from overpressurized conditions.
The term safety valve, on the other hand, refers to pressure valves that are designed to protect people, property, and processes. In other words, the term safety valve refers to a failsafe, last resort valve that will release pressure to prevent a catastrophe, usually in the event that all other relief valves have failed to adequately control pressure within a system.
The general purpose of both safety valves and relief valves are the same. Both are pressure relief valves, and they are designed to let off pressure in any situation where a system becomes overpressurized. That said, relief valves and safety valves do function slightly differently:
Relief Valves are designed to control pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air systems. These valves open in proportion to the increase in system pressure. This means they don’t fly all the way open when the system is slightly overpressure. Instead, they open gradually, allowing the system to return to the preset pressure level. When that level is reached, the valve shuts again.
Safety Valves are used for one reason — safety. Instead of controlling the pressure in a system, they’re designed to immediately release pressure in the event of an emergency or system failure. Unlike relief valves, safety valves open immediately and completely to avoid a disaster, rather than to control the pressure of a system.
While both safety valves and relief valves work to release excess pressure, the way they go about it is a little different. Check out this table, courtesy of Difference Between, for a little more information about the differences between the two valves:
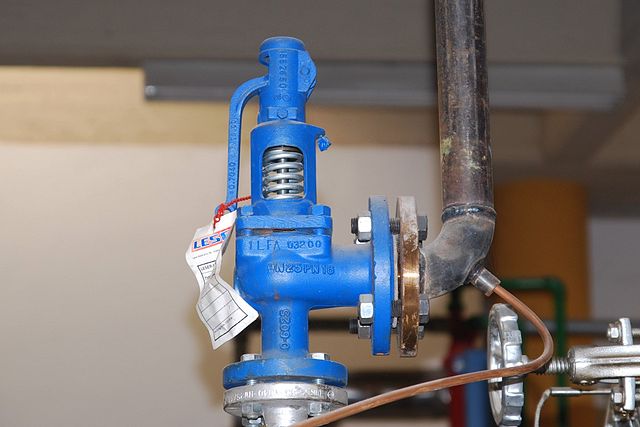

Industrial equipment often uses either safety or relief valves to prevent damaging pressure levels from building up. Though they perform similar functions, there are some critical differences between safety and relief valves. Understanding these two valves’ differences is essential for proper pressure system operation. So here we discuss the pressure safety valve vs pressure relief valve.
A pressure relief valve is a device that releases pressure from a system. The relief valve is generally immune to the effects of back pressure and must be periodically stripped down. Pressure relief valves are one the essential parts of a pressure system to prevent system failures. They are set to open at a predetermined pressure level. Each pressure system has a setpoint that is a predetermined limit. The setpoint determines when the valve will open and prevents overpressure.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in gas or liquid systems where there is a need to prevent excessive pressure from building up. When the pressure in the system reaches a certain level, the valve will open and release the pressure. Pressure relief valves are an essential safety feature in many designs and can help to prevent damage to the system or components.
PRVs are generally considered to be safe and reliable devices. However, before installing a PRV in a system, some potential disadvantages should be considered. Here are five pros and cons of pressure relief valves:
Pros: Pressure relief valves are anessential safety feature in many systems. They protect against over-pressurization by relieving excess pressure from the system. This can help to prevent severe damage or even explosions.
Pressure relief valves can help to improve the efficiency of a system. The system can operate at lower overall pressure by relieving excess pressure and saving energy.
Pressure relief valves can be used as a safety device in systems that are susceptible to overpressurization. By relieving pressure before it builds up to a dangerous level, they can help to prevent accidents and injuries.
Cons: Pressure relief valves can be a potential source of leaks. If not properly maintained, the valve may not seat properly and can allow fluids or gasses to escape.
Pressure relief valves can sometimes cause problems if they do not open or close properly. This can lead to process disruptions and may cause safety issues.
A pressure safety valve is a device used to release pressure from a system that has exceeded its design limit. This safety valve is a fail-safe device. This type of valve is typically used in systems that contain fluids or gasses under high pressure. Pressure safety valves are designed to open and release pressure when the system has exceeded its maximum pressure limit. This helps to prevent the system from rupturing or exploding.
Pressure safety valves are an essential part of many different types of systems and can help keep both people and property safe. If anyone is ever in a situation where they need to release pressure from a system, it is essential to know how to use a pressure safety valve correctly.
A pressure safety valve (PSV) is a type used to relieve a system’s pressure. PSVs are commonly used in chemical and process industries, as well as in some kinds of pressure vessels. There are both advantages and disadvantages to using a PSV. Some of the pros of using a PSV include: PSVs can help to prevent overpressurization, which can be dangerous.
A safety valve is a pressure relief device used to prevent the over-pressurization of a system. On the other hand, a relief valve is a device used to relieve pressure from a system that is already overpressurized. Function Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Valve
The function of a pressure relief valve is to protect a system or component from excess pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, is designed to protect from overpressurization. Both types of valves are used in various industries, but each has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in systems where a small amount of overpressure can cause damage. On the other hand, safety valves are designed for systems where overpressurization could be catastrophic. Both valves have advantages and disadvantages, so choosing the right type of valve for the specific application is essential.
Relief valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure and will close once the pressure has been relieved. Safety valves are similar in that they are also used to protect equipment from excessive pressure. However, safety valves are designed to stay open until they are manually closed. This is because safety valves are typically used in applications where it is not safe to have a closed valve, such as in a gas line. Operation Of Safety Relief Valve Vs Pressure Relief Valve
Two types of valves are commonly used in industrial settings: relief valves and safety valves. Both of these valves serve essential functions, but they operate in different ways.
Relief valves are designed to relieve pressure build-up in a system. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released. On the other hand, safety valves are designed to prevent accidents by preventing system pressure from getting too high. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released before an accident can occur.
So, which valve is better? That depends on the situation. A relief valve is the better option to protect the system from pressure build-up. If anyone need to protect the system from accidents, then a safety valve is the better option Setpoint Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Relief Valve
The relief valve is made to open when it reaches a specific pressure, commonly described as a “setpoint”. Setpoints shouldn’t be misinterpreted as the pressure set. A setpoint on a relief valve is set to the lowest possible pressure rating, which means it is set to the lowest system pressure before an overpressure situation is observed. The valve will open as the pressure increases to a point higher than the setpoint. The setting point is determined as pounds per square inch (PSIG) and should be within the maximum allowed operating pressure (MAWP) limits. In safety valves, the setpoint is typically placed at about 3 percent over the working pressure level, whereas relief valves are determined at 10 percent.
No, the safety valve and relief valve can not be used interchangeably. Though both valves are seal butterfly valve and used for safety purposes, they serve different functions. A safety valve relieves excess pressure that builds up in a system, while a relief valve regulates the pressure in a system.
Knowing the difference between these two types of valves is essential, as using the wrong valve for the intended purpose can potentially be dangerous. If unsure which type of valve to use, it is always best to consult with a professional.
A few key points help us understand the safety valve vs pressure relief valve. Safety valves are designed to relieve pressure in a system when it gets too high, while relief valves are designed to relieve pressure when it gets too low. Safety valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure, while relief valves are generally open at a particular vacuum. Safety valves are typically intended for one-time use, while relief valves can be used multiple times. Choose the trusted valve manufactureraccording to the specific business needs.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Whenever a gas or liquid is used as a working fluid for a machine, it is transported under pressure, regardless of its size. Sometimes the pressure in these systems and interconnecting pipes can be so large that a rupture can cause catastrophic damage or even death. This was the main cause of the failure of steam operating systems (such as large boilers) in the 19th century. In order to regulate the pressure in the system and in the pipe, equipment must be introduced to automatically reduce the pressure by allowing the working fluid in the system to escape when the system reaches its critical limit.
The safety valve and the relief valve are two types of equipment that fall into the pressure relief valve (PRV) category and are operated on the basis of the use of static inlet pressure to drive the equipment.
When the critical pressure is reached, the pressure relief valve, which is controlled by the inlet static pressure, opens completely. This is what we called “THE SAFETY VALVE”. The opening of the valve is accompanied by a popping sound caused by a sudden opening, which is a feature of this type of valve.
Safety Valves are commonly used in systems that use compressible gases, such as steam and air, as working fluids. When connected to a pressurized system (such as a boiler), static pressure within the system presses the valve against the spring-loaded mechanism. When internal pressure exceeds the critical value, the disc is separated from the seat, exposing the pressure to a larger surface area of the disc. This larger area results in a larger force applied to the spring mechanism, and as a result, the valve is fully open.
The pressure relief valve used in a liquid system with the same function as the safety valve is called the RELIEF VALVE. Its primary function is to control or limit the internal pressure of the system or container and prevent the system from reaching the critical limit due to abnormal process, instrument or equipment failure or fire. In contrast to the Safety Valve, the relief valve opens gradually.

In the process industry, both terms refer to safety devices, which generally come in the form of valves, cylinders, and other cylinders that protect people, property, and the environment. Safety valves and relief valves are integral components of process safety. However, they are used for almost identical purposes. Their main difference lies in their operating mechanisms.
In the event of an overpressure, a safety valve or pressure relief valve (PRV) protects pressure-sensitive equipment. It is recommended to strip down relief valves regularly and prevent serious damage due to backpressure. Pressure relief valves are a crucial part of any pressurized system. In order to prevent system failures, you can set the pressure to open at predetermined levels. A setpoint, also known as a predetermined design limit, is set for all pressure systems. When the setpoint is exceeded, an overpressure valve opens.
There are various types of safety valves used in several types of industries, including power plants, petrochemical plants, boilers, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and more. Using safety valves helps to prevent accidents and injuries that can harm people, property, and processes. Pressure builds up in vessels and systems automatically when the device is activated above a preset level. Safety valves must be configured so that their prescribed pressure is exceeded in order for them to function (i.e., relieve pressure). Ideally, excess pressure should be released either to the atmosphere or back into the pneumatic system to prevent damage to the vessel. In addition, excess pressure should be released to keep pressure within a certain range. As soon as a slight increase in pressure above the desired limit has lifted the safety valve, it opens.
Valve relief removes excessive pressure from a system by limiting its pressure level to a safe level. Often referred to as pressure relief valves (PRVs) or safety relief valves, these valves provide relief from pressure. The purpose of a relief valve is, for example, to adjust the pressure within a vessel or a system so that a specific level is maintained. The goal of a relief valve, unlike a safety valve, is not to prevent damage to the vessel; rather, it is to control the pressure limit of a system dynamically depending on the requirements. Conversely, safety valves have a maximum allowable pressure set at a certain level, which allows escaping liquid or gas whenever the pressure exceeds it, eliminating damage to the system. It is imperative that safety valves are installed in a control system to prevent the development of pressure fluctuations that can cause property damage, life loss, and environmental pollution.
The hydraulic system relies on a pressure relief system in order to regulate the running pressure. By allowing excess pressure to escape from the pressurized zone, pressure relief valves and safety valves prevent overpressure when the pressure in the system reaches a predefined limit. By venting excess pressure through a relief port, or returning it through a return line, a pneumatic system can enable the excess pressure to escape into the atmosphere. Pump-driven pressure generators and control media that cannot be vented into the atmosphere are typical examples of this type of application.
Excess pressure may be relieved from the system using relief valves and safety valves. The valve opening increases proportionally as the vessel pressure increases with the relief valve. Gradually opening the valve rather than abruptly releases only a prescribed amount of fluid. As pressure is reduced, the release proceeds at this rate until the pressure drops. By contrast, an emergency safety valve operates automatically when a predetermined pressure is reached in the system, preventing a catastrophic system failure. When the system is under excessive stress, the safety valve regulates the pressure within the system and prevents overpressure.
Defining a “setpoint” is the process of defining a pressure level which triggers the device to vent excess pressure. Setpoint is different from pressure. Overpressure is prevented by setting these devices lower than the highest pressure the system can handle before overpressure occurs. Setting the device below this pressure prevents overpressure. The valve opens when pressure rises above the setpoint. A setpoint also known as the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) cannot be exceeded when deciding the pressure in pounds per square inch (PSIG). The adjustment points for safety valves are generally 3 percent above working pressures, while adjustment points for relief valves are 10% above working pressures.
Pressure in an auxiliary passage can be controlled by a safety valve as well as a relief valve by releasing excess pressure. Safety valves of this type are pressure-sensitive and reliable. Safety valves can be categorized according to their capacity and setpoint, although both terms often refer to safety valves. Self-opening devices open automatically when maximum allowable pressure has been reached rather than being manually activated to prevent over-pressurizing. Contrary to relief valves, safety valves are typically used for venting steam or vapor into the atmosphere. Relief valves regulate fluid flow and compressed air pressure and gases, whereas safety valves typically regulate steam and vapor venting. Put simply, relief valves are used for more gradual pressure control requiring accurate, dynamic systems, whereas safety valves are used for one set to prevent damage to a system.
For pressure control applications that require dynamic setpoints and therefore varying pressure limits, our Electronic Relief Valve is the appropriate solution. This device accepts a control voltage to dynamically set the relief pressure setpoint. Traditional relief valves are set manually, so that a technician must adjust the relief valve and have a pressure gauge to find the accurate setpoint. The Kelly Pneumatic Electronic Relief Valve allows an electronic control system to quickly and safely command a dynamic maximum pressure based on feedback from current system specifications. The Kelly Electronic Relief Valve also has an optional feedback signal representing the current pressure in the system. This allows the control system to dynamically respond to changing conditions.
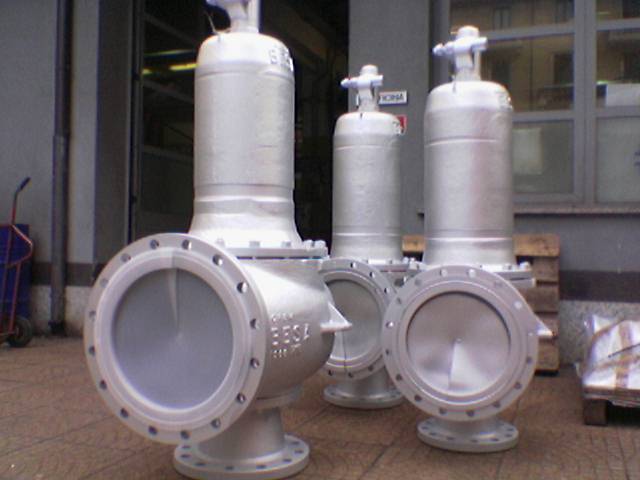

Both the terms are used interchangeably in the process industry as every pressurized system requires safety devices to protect life, property, and environment. Relief valves and safety valves are the two principle safety devices designed to prevent overpressure conditions in process industries. Although, both the devices are used almost for the same purpose, the difference lies mainly in how they operate.
Relief valves, or commonly known as pressure relief valves (PRVs), belong to the family of protective devices specifically designed to protect pressure-sensitive systems and equipment from the damaging effects of overpressure conditions. A relief valve device is basically immune to the back pressure effects of a system and is subject to periodic stripdown. Pressure relief valves are one of the most critical parts of a pressure system that are set to open at a preset pressure level in order to avoid system failures. Every pressure system is set with a predetermined design limit called a setpoint, above which the valve begins to open to prevent overpressure conditions.
A safety valve is the last resort of people, property, and processes in the process industry comprising of power plants, petrochemicals, boilers, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and many more. It’s kind of a fail-safe device that actuates automatically in order to prevent the accumulation of pressure in a vessel or system beyond a preset limit. The device is so designed so that the safety valve trips automatically when the given pressure is attained. It simply allows the excess pressure to escape in order to prevent any damage to the vessel. Additionally, it also makes sure the pressure remains within the limits in the future. Even a slight increment in pressure lifts the safety valve and it closes as soon as the pressure is reduced to the prescribed limit.
A relief valve, also known as pressure relief valve (PRV) or safety relief valve, is type of a safety valve device used to limit or control the pressure level in a system within a safe threshold limit to avoid an overpressure condition. In simple terms, a relief valve is a device designed to control the pressure in a vessel or system to a specific set level. A safety valve, on the other hand, is a device used to let go excess pressure from a vessel or equipment when the pressure crosses a certain predetermined limit. It simply allows liquids or gases to escape if the pressure gets too high to prevent any damage.
Pressure relief valves are mainly used in hydraulic systems to limit the pressure in the system to a specific preset level and when the pressure reaches the safety design limit, the relief valve responds by releasing the excess flow from an auxiliary passage from the system back to the tank in order to prevent equipment failure. The main purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property, and environment against failure in the control system pressure. Simply put, a safety valve opens when the pressure exceeds the designed set pressure limit.
For a safety relief valve, the opening is directly proportional to the increase in the vessel pressure. This means the opening of the valve is rather gradual than sudden, allowing it to open only at a preset pressure level and release fluids until the pressure drops to the desired set pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, will open immediately when the system pressure reaches the set pressure level in order to system failure. It is safety device capable of operating at all times and is the last resort to prevent catastrophic failure in systems under overpressure conditions.
A pressure relief valve is designed to open at a certain pressure level which is generally called as a “setpoint”. A setpoint should not be confused with the set pressure. In fact, a setpoint of a relief valves is adjusted to the lowest maximum pressure rating meaning it is set below the maximum system pressure allowed before the overpressure condition occurs. The valve begins to open when the pressure reaches up to some level above the setpoint. The setpoint is measured in pounds per square inch (PSIG) and must not exceed the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). In safety valves, the setpoint is usually set at 3 percent above the working pressure level whereas in relief valves, it is set at 10 percent.
Both relief valves and safety valves are high-performance pressure-sensitive safety devices so designed to control or limit the pressure inside the system or vessel by releasing the excessive pressure from the auxiliary passage out of the system. Although both are common terms used for safety valves, the difference lies mainly in the capacity and setpoint. While the former is operator-assisted and is designed to relieve pressure in order to avoid overpressure condition, the latter is a self-operated device which opens automatically when the maximum allowable pressure is reached. Relief valves are mostly used in fluid or compressed air systems, whereas safety valves are mainly used to release vapor or steam into the atmosphere.
Sagar Khillar is a prolific content/article/blog writer working as a Senior Content Developer/Writer in a reputed client services firm based in India. He has that urge to research on versatile topics and develop high-quality content to make it the best read. Thanks to his passion for writing, he has over 7 years of professional experience in writing and editing services across a wide variety of print and electronic platforms.
Outside his professional life, Sagar loves to connect with people from different cultures and origin. You can say he is curious by nature. He believes everyone is a learning experience and it brings a certain excitement, kind of a curiosity to keep going. It may feel silly at first, but it loosens you up after a while and makes it easier for you to start conversations with total strangers – that’s what he said."

Pressure relief valves are a type of safety valve that are commonly used to protect a system and the people operating it. Whereas pressure regulators take incoming line pressure and regulates it down to the pressure that is required by the downstream system. Pressure Regulators can be used for reasons of safety and/or cost. Both of these valves are very important to its specific application. In this article, we will discuss the difference between a pressure relief valve and regulator.
Pressure Regulators take an incoming line pressure and regulate it down to the pressure that is required by the downstream system. This may be for other instrumentation to operate effectively or simply to control the output flow of a pipe. Lower system pressures mean less risk and lower running costs and a reduced risk of air loss through a system. Pressure regulators can be used in many applications including pneumatics, compressed air and water.
There are various kinds of pressure regulators available within MGA Controls range – from general purpose units covering everyday industrial applications to more specialised precision pressure regulators, manifold regulators, pilot operated regulators and large capacity pilot operated versions. View our full range of pressure regulators in our store.
Pressure relief valves are used to control or limit pressure spikes in a compressed air system. When the system pressure increases beyond a predetermined set point, the valve opens and relieves that pressure, bringing it back in line with normal operating parameters. The main function of a Pressure relief valve is to vent excess pressure and protect other system components, all the while maintaining optimum performance.
Air systems benefit highly from pressure relief valves, however different types of pressure relief valves can be used in a wide range of industries. For example, the water industry utilises the valve to make sure water pressure doesn’t reach such a level that it will burst pipes.
The IMI Norgren Olympian Plus pressure relief valve is designed to protect compressed air systems against over-pressurisation. It has high relief capacity while being sensitive and accurate. As part of the Olympian Plus range of products, it is suitable for in-line or modular installation and is compatible with other products in the Olympian Plus range, such as the B64G Filter/Regulator and the L64 Series Lubricator. Some of the key pressure relief valve features include:
Choosing a pressure relief valve isn’t always easy, but here at MGA Controls, we specialise in helping you choose the correct valve for your application. There are six basic factors to consider before choosing your pressure relief valve:
You must also consider the physical dimensions of the application and the plant, as well as factors related to the environment in which the valve will operate.
Here at MGA Controls, pressure relief valves can be fitted to an existing system and can be specified in sizes ranging from 1/4″ to 1.1/2″. We carry a wide range of stock that is available for quick delivery in your time of need.
To speak to a member of our technical team about choosing a pressure relief valve or the difference between a pressure relief valve and regulator contact us today on 01704 898980 or email sales@mgacontrols.co.uk. To request a free quote or view our general range of products contact our team.

Relief valves and back pressure regulators are two types of pressure regulators used to control pressure levels in gas applications. However, although they do a similar job, back pressure regulators and relief valves are very different. In this article, we will give you more information about these two types of gas regulators to help you better understand their differences.
In any system, the pressure relief valve is designed to open at a predetermined set pressure. The diaphragm expands and pushes on the valve seat if the gas pressure exceeds the preset limit. That provides an escape route for the gas, reducing pressure in the system. When pressure levels return to normal, the valve closes.
Direct Acting Pressure Relief Valve: It is a basic pressure control containing one poppet and one spring. The direct-acting pressure relief valve can limit the highest of pressures as it handles abrupt, transitory pressure increases brilliantly. They are also great as pilot control for other valves.
Pilot-operated Pressure Relief Valve: Works well as emergency relief in high-flow or high-pressure feed overpressure situations. Unlike the direct relief valve, an operator opens this valve when the pressure reading hits unsafe levels.
Petrochemical industries: Control the flow of dye, detergents, plastics, and other additives at set quantities and pressure to produce various commodities.
Pressure relief valves are vital for regulating the flow rate, and fluid movement path, and keeping the system functioning optimally. Similarly, pressure relief valves prevent the collapse of the hydraulic system if the pressure rises above the designed capacity, so it protects life, environment, and property.
A back pressure regulator contains a pilot, diaphragm, and valve. Gas from the upstream push on the diaphragm when the pilot plug lets it through. As the flow pushes up on the plunger, the gas pushes down on the diaphragm, keeping the valve closed since the diaphragm has a larger surface area than the plunger.
However, upstream pressure forces the diaphragm up when the pressure exceeds the set pressure, which closes the pilot plug. That vents gas from the top of the diaphragm, regulating the upstream pressure.
A BPR emphasizes a steady state of pressure; it’s not a case of on or off. It will keep adjusting its position to keep the inlet pressure at optimum levels, only opening the diaphragm to release excess pressure.
Poppet-type: Instead of a spring or piston, it uses a small metal ball called a poppet. As the gas flows into the regulator, the poppet moves towards the center of the regulator until it reaches the end of its travel. Once it comes to the end of its stroke, it seals off the opening in the regulator.
Back pressure regulators are crucial for preventing over-pressurization of downstream pneumatic and hydraulic equipment. They also have the sensitivity to respond to the slightest upstream changes and are the go-to solution for keeping flow rate constant, perfect for accurately measuring the quantity of gas
The pressure relief valve is a safety feature that opens or closes whenever too much pressure needs releasing. On the other hand, the back pressure regulator is not a safety measure—it is an intrinsic part of the system meant to keep it at a steady pressure.
In short, a back pressure regulator keeps the pressure at a level that will enable the downstream system to work as required. It keeps adjusting according to information received from pressure sensors to keep the pressure at functional levels.
As gas regulators, the relief valve and the back pressure regulator are crucial in relieving pressure from a gas supply system. The only difference is the pressure relief valve acts as a safety feature to release pressure buildup. Conversely, the back pressure regulator is a part of the system to maintain a predetermined pressure.
Norgas Controls provides gas regulators, gas valves, and gas meters for natural, propane, compressed, and sour gases across Canada. Our experts can help you choose the right product for your application. Feel free to contact us for more information or to tell us about your needs by completing a quote request.

Thus, its operation is automatic; it will open only to release the pressure and not exceed the liquid force; therefore, its use is more common with fluids (although, they can also be used with vapours or moderate gases). In terms of capacity, they can withstand low pressures and their processes are continuous.

Both pressure relief valves (PRV) and pressure safety valves (PSV) are used for process safety to relieve excess pressure. Although they’re often used interchangeably, they do have different functions and it’s important to know the difference.
If the PRV fails to maintain optimal pressure, the PSV kicks in. This valve opens quickly to avoid overpressurization when a set pressure is reached, preventing a potential safety incident.
Industrial Valve offers new PSVs and PRVs from Farris. Our Farris Authorized Service Team (FAST) can conduct pre-installation testing, install your valve, and perform regularly scheduled maintenance to keep your workflow operating at peak efficiency. Should you ever need an emergency repair, just call us – our technicians are available 24 hours a day!

Relief valves are designed to open at a preset pressure (or temperature) level and relieve the system when it has exceeded the desired level. The valve"s relief of elevated liquid, gas, or steam pressures prevents damage to the system. We offer a wide selection of relief valves for any application.
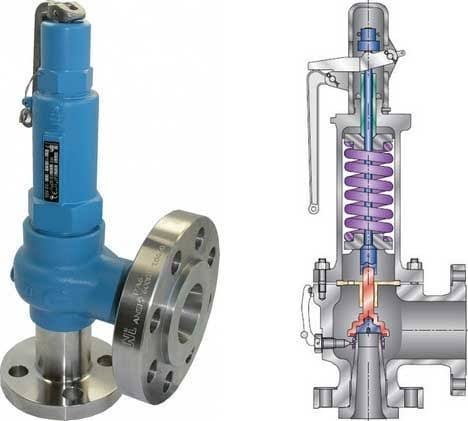

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The documents are meant to be used as a guide for developing local laws and regulations and also may be used to update a jurisdiction’s existing requirements. As such, they’re intended to be modifiable to meet any jurisdiction’s local conditions.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
General guidance on proper installation may seem like common sense to experienced installers and inspectors. A few of the most important guidelines and best practices include:
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

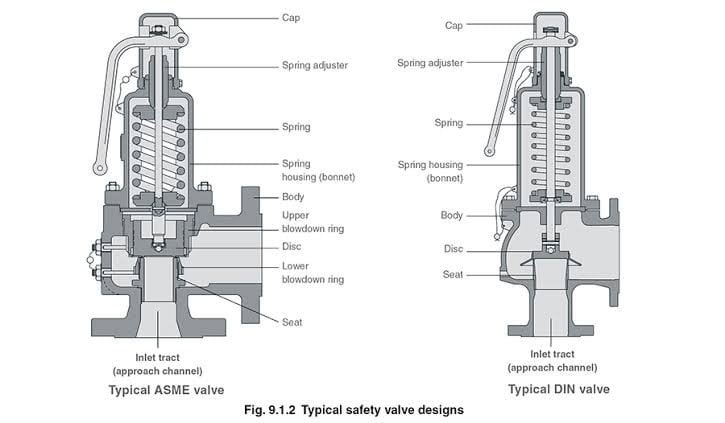
2.2.1.1.2 Spring-loaded pressure relief valves are referred to by a variety of terms, such as safety valves, relief valves and safety relief valves. These terms have been traditionally applied to valves for gas/vapor service, liquid service, or multi-service applications, respectively. The more generic term, pressure relief valve, is used in the text and is applicable to all three.
Recently, I happened to be looking at a copy of API RP-576, Inspection of Pressure-Relieving Devices, Dec-2000, and found they have a broader discussion about the different designs and actually list limitations to their use. Among the limitations listed: Safety valves should not be used in liquid service, Relief valves should not be used in vapor service.
Seems that it would have been more appropriate to include the API RP-576 discussions in API RP-520 but I guess it is fairly obvious, don"t expect a valve designed for liquid service only to perform equally well in vapor service.
Anyway, the bottom line is you need to identify all requirements for your relief system design whether a case controls for relief area sizing or not. Then select the appropriate relief valve for all possible cases you identified. If you do have a situation that requires a relief valve to relieve a vapor for some cases or a liquid for others, be sure the valve you select has certified capacities for both vapor and liquid service or gives at least orifice area/nozzle discharge coefficient for both vapors and liquids.
Dante Valve is a full-service manufacturer, distributor and VR™ certified repair facility of valves and related products for the industrial and military markets.
We manufacture military specification Danco pressure relief valves; we distribute Kunkle relief valves and TRAC regulating, reducing, and temperature regulating valves, fittings and flanges; we also provide CNC machining services.

“Directive 94/9/EC, better known by the acronym ATEX, was implemented in Italy by Presidential Decree 126 of 23 March 1998 and applies to products intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. With the entry into force of the ATEX Directive, the standards previously in force were repealed and from 1 July 2003 it is prohibited to market products that do not comply with the new provisions.
Directive 94/9/EC is a ‘new approach’ directive which aims to allow the free movement of goods within the Community. This is achieved by harmonising legal safety requirements, following a risk-based approach. It also aims to eliminate or, at least, minimise the risks arising from the use of certain products in or in relation to a potentially explosive atmosphere. This
means that the likelihood of an explosive atmosphere arising must be considered not only on a “one-off” basis and from a static point of view, but all the operating conditions that may arise from the process must also be taken into account.
The Directive covers equipment, whether alone or combined, intended for installation in “zones” classified as hazardous; protective systems serving to stop or contain explosions; components and parts essential to the functioning of equipment or protective systems; and control and adjustment safety devices useful or necessary for the safe and reliable functioning of equipment or protective systems.
Among the innovative aspects of the Directive, which covers all explosion hazards of any kind (electrical and non-electrical), the following should be highlighted:
The classification of the installation zone of the equipment will be the responsibility of the end user; therefore according to the risk area of the customer (e.g. zone 21 or zone 1) the manufacturer will have to supply equipment suitable for that zone.

WITT is a manufacturer of Pressure relief valvesor Safety relief valves for technical gases. They are designed to protect against overpressure by discharging pressurized gases and vapors from pipelines, pressure vessels and plant components. Safety relief valves (SRV) are often the last line of defense against explosion – and such an explosion could be fatal. Other common names for safety relief valves are pressure relief valve (PRV), safety valve, pressure safety valve, overpressure valve, relief valve or blow-off valve.
WITT safety valves are very precise. They are individually preset to open at a predetermined pressure within the range 0.07 to 652 Psi. Their small size and orientation-independent installation allow a wide range of connection options. WITT relief valves also stand out due to their high blow-off flow rates of up to 970m³/h. They can be used within a temperature range of -76° F to +518°F and even with very low pressures.
For maximum safety, WITT undertakes 100 % testing of each safety relief valve before it is delivered. In addition, WITT offers individual testing of eachsafety valveby the TÜV, with their certificate as proof of the correct set pressure.
WITTsafety relief valvesare direct-acting, spring-loaded valves. When the preset opening pressure is reached, a spring-loaded element in the valve gives way and opens, and the pressure is relieved. Once the pressures are equalized, the valve closes automatically and can be reactivated any time the pressure rises again. Depending on the application and the nature of the gas, the safety relief valvescan either discharge to atmosphere, or via a connected blow-off line. The opening pressure of the safety valves is preset by WITT at the factory according to the customer’s requirements.
Safety relief valvesare used in numerous industries and industrial applications where, for example, gases pass through pipelines or where special process vessels have to be filled with gas at a certain pressure.
These include, among other things:Pipeline, plant and container constructionIndustrial furnace constructionInsulators and reactors (e.g. “glovebox” systems)hydrogen-powered vehiclesAdditive manufacturing (3D printer)
For most industrial applications using technical gases, brass is usually the standard material of construction of thesafety relief valvebody/housing. For the use of pressure relief valves with aggressive and corrosive gases, the housings are made of high-quality stainless steel (1.4541/AISI 321, 1.4404/AISI 316L, 1.4305/AISI 303 or 1.4571/AISI 316Ti). The use of aluminium as a housing material is also possible.
Depending on the type of gas used and individual customer requirements, various sealing materials and elastomers are available to ensure the safety of your systems under even the most difficult conditions.
WITT pressure relief valves are available with different connections. In addition to the standard versions with the usual internal or external threads, special versions with KF or CF flanges, VCR or UNF threads can also be ordered. Special adapters for connecting the safety relief valve to a blow-off line are also available.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.




 8613371530291
8613371530291