gwr safety valve quotation

A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.
Safety valves were first developed for use on steam boilers during the Industrial Revolution. Early boilers operating without them were prone to explosion unless carefully operated.
Vacuum safety valves (or combined pressure/vacuum safety valves) are used to prevent a tank from collapsing while it is being emptied, or when cold rinse water is used after hot CIP (clean-in-place) or SIP (sterilization-in-place) procedures. When sizing a vacuum safety valve, the calculation method is not defined in any norm, particularly in the hot CIP / cold water scenario, but some manufacturers
The earliest and simplest safety valve was used on a 1679 steam digester and utilized a weight to retain the steam pressure (this design is still commonly used on pressure cookers); however, these were easily tampered with or accidentally released. On the Stockton and Darlington Railway, the safety valve tended to go off when the engine hit a bump in the track. A valve less sensitive to sudden accelerations used a spring to contain the steam pressure, but these (based on a Salter spring balance) could still be screwed down to increase the pressure beyond design limits. This dangerous practice was sometimes used to marginally increase the performance of a steam engine. In 1856, John Ramsbottom invented a tamper-proof spring safety valve that became universal on railways. The Ramsbottom valve consisted of two plug-type valves connected to each other by a spring-laden pivoting arm, with one valve element on either side of the pivot. Any adjustment made to one of valves in an attempt to increase its operating pressure would cause the other valve to be lifted off its seat, regardless of how the adjustment was attempted. The pivot point on the arm was not symmetrically between the valves, so any tightening of the spring would cause one of the valves to lift. Only by removing and disassembling the entire valve assembly could its operating pressure be adjusted, making impromptu "tying down" of the valve by locomotive crews in search of more power impossible. The pivoting arm was commonly extended into a handle shape and fed back into the locomotive cab, allowing crews to "rock" both valves off their seats to confirm they were set and operating correctly.
Safety valves also evolved to protect equipment such as pressure vessels (fired or not) and heat exchangers. The term safety valve should be limited to compressible fluid applications (gas, vapour, or steam).
For liquid-packed vessels, thermal relief valves are generally characterized by the relatively small size of the valve necessary to provide protection from excess pressure caused by thermal expansion. In this case a small valve is adequate because most liquids are nearly incompressible, and so a relatively small amount of fluid discharged through the relief valve will produce a substantial reduction in pressure.
Flow protection is characterized by safety valves that are considerably larger than those mounted for thermal protection. They are generally sized for use in situations where significant quantities of gas or high volumes of liquid must be quickly discharged in order to protect the integrity of the vessel or pipeline. This protection can alternatively be achieved by installing a high integrity pressure protection system (HIPPS).
In the petroleum refining, petrochemical, chemical manufacturing, natural gas processing, power generation, food, drinks, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industries, the term safety valve is associated with the terms pressure relief valve (PRV), pressure safety valve (PSV) and relief valve.
The generic term is Pressure relief valve (PRV) or pressure safety valve (PSV). PRVs and PSVs are not the same thing, despite what many people think; the difference is that PSVs have a manual lever to open the valve in case of emergency.
Relief valve (RV): an automatic system that is actuated by the static pressure in a liquid-filled vessel. It specifically opens proportionally with increasing pressure
Pilot-operated safety relief valve (POSRV): an automatic system that relieves on remote command from a pilot, to which the static pressure (from equipment to protect) is connected
Low pressure safety valve (LPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the difference between the vessel pressure and the ambient atmospheric pressure is small.
Vacuum pressure safety valve (VPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the pressure difference between the vessel pressure and the ambient pressure is small, negative and near to atmospheric pressure.
Low and vacuum pressure safety valve (LVPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the pressure difference is small, negative or positive and near to atmospheric pressure.
In most countries, industries are legally required to protect pressure vessels and other equipment by using relief valves. Also, in most countries, equipment design codes such as those provided by the ASME, API and other organizations like ISO (ISO 4126) must be complied with. These codes include design standards for relief valves and schedules for periodic inspection and testing after valves have been removed by the company engineer.
Today, the food, drinks, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals industries call for hygienic safety valves, fully drainable and Cleanable-In-Place. Most are made of stainless steel; the hygienic norms are mainly 3A in the USA and EHEDG in Europe.
The first safety valve was invented by Denis Papin for his steam digester, an early pressure cooker rather than an engine.steelyard" lever a smaller weight was required, also the pressure could easily be regulated by sliding the same weight back and forth along the lever arm. Papin retained the same design for his 1707 steam pump.Greenwich in 1803, one of Trevithick"s high-pressure stationary engines exploded when the boy trained to operate the engine left it to catch eels in the river, without first releasing the safety valve from its working load.
Although the lever safety valve was convenient, it was too sensitive to the motion of a steam locomotive. Early steam locomotives therefore used a simpler arrangement of weights stacked directly upon the valve. This required a smaller valve area, so as to keep the weight manageable, which sometimes proved inadequate to vent the pressure of an unattended boiler, leading to explosions. An even greater hazard was the ease with which such a valve could be tied down, so as to increase the pressure and thus power of the engine, at further risk of explosion.
Although deadweight safety valves had a short lifetime on steam locomotives, they remained in use on stationary boilers for as long as steam power remained.
Weighted valves were sensitive to bouncing from the rough riding of early locomotives. One solution was to use a lightweight spring rather than a weight. This was the invention of Timothy Hackworth on his leaf springs.
These direct-acting spring valves could be adjusted by tightening the nuts retaining the spring. To avoid tampering, they were often shrouded in tall brass casings which also vented the steam away from the locomotive crew.
The Salter coil spring spring balance for weighing, was first made in Britain by around 1770.spring steels to make a powerful but compact spring in one piece. Once again by using the lever mechanism, such a spring balance could be applied to the considerable force of a boiler safety valve.
The spring balance valve also acted as a pressure gauge. This was useful as previous pressure gauges were unwieldy mercury manometers and the Bourdon gauge had yet to be invented.
Paired valves were often adjusted to slightly different pressures too, a small valve as a control measure and the lockable valve made larger and permanently set to a higher pressure, as a safeguard.Sinclair for the Eastern Counties Railway in 1859, had the valve spring with pressure scale behind the dome, facing the cab, and the locked valve ahead of the dome, out of reach of interference.
In 1855, John Ramsbottom, later locomotive superintendent of the LNWR, described a new form of safety valve intended to improve reliability and especially to be tamper-resistant. A pair of plug valves were used, held down by a common spring-loaded lever between them with a single central spring. This lever was characteristically extended rearwards, often reaching into the cab on early locomotives. Rather than discouraging the use of the spring lever by the fireman, Ramsbottom"s valve encouraged this. Rocking the lever freed up the valves alternately and checked that neither was sticking in its seat.
A drawback to the Ramsbottom type was its complexity. Poor maintenance or mis-assembly of the linkage between the spring and the valves could lead to a valve that no longer opened correctly under pressure. The valves could be held against their seats and fail to open or, even worse, to allow the valve to open but insufficiently to vent steam at an adequate rate and so not being an obvious and noticeable fault.Rhymney Railway, even though the boiler was almost new, at only eight months old.
Naylor valves were introduced around 1866. A bellcrank arrangement reduced the strain (percentage extension) of the spring, thus maintaining a more constant force.L&Y & NER.
All of the preceding safety valve designs opened gradually and had a tendency to leak a "feather" of steam as they approached "blowing-off", even though this was below the pressure. When they opened they also did so partially at first and didn"t vent steam quickly until the boiler was well over pressure.
The quick-opening "pop" valve was a solution to this. Their construction was simple: the existing circular plug valve was changed to an inverted "top hat" shape, with an enlarged upper diameter. They fitted into a stepped seat of two matching diameters. When closed, the steam pressure acted only on the crown of the top hat, and was balanced by the spring force. Once the valve opened a little, steam could pass the lower seat and began to act on the larger brim. This greater area overwhelmed the spring force and the valve flew completely open with a "pop". Escaping steam on this larger diameter also held the valve open until pressure had dropped below that at which it originally opened, providing hysteresis.
These valves coincided with a change in firing behaviour. Rather than demonstrating their virility by always showing a feather at the valve, firemen now tried to avoid noisy blowing off, especially around stations or under the large roof of a major station. This was mostly at the behest of stationmasters, but firemen also realised that any blowing off through a pop valve wasted several pounds of boiler pressure; estimated at 20 psi lost and 16 lbs or more of shovelled coal.
Pop valves derived from Adams"s patent design of 1873, with an extended lip. R. L. Ross"s valves were patented in 1902 and 1904. They were more popular in America at first, but widespread from the 1920s on.
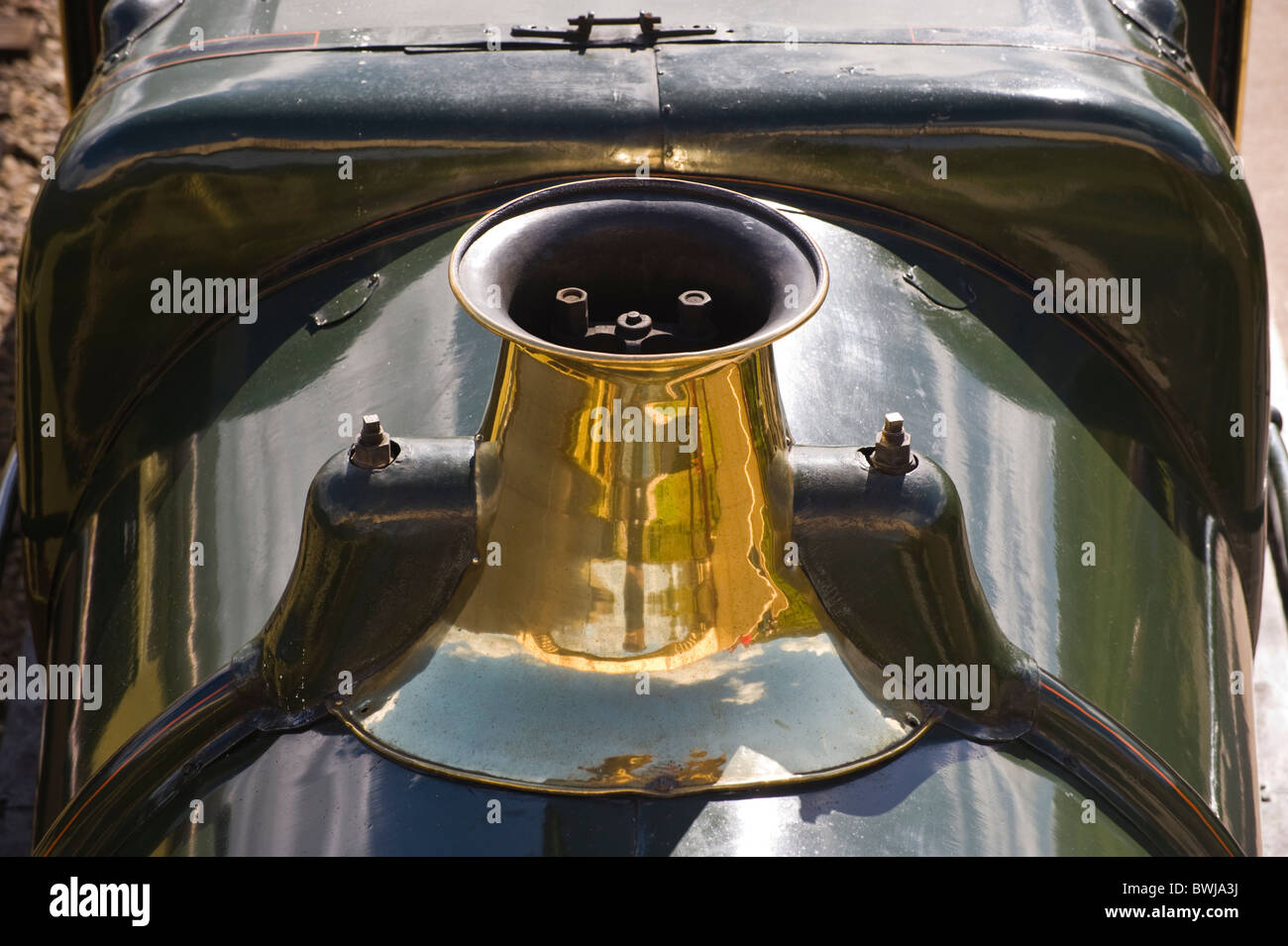
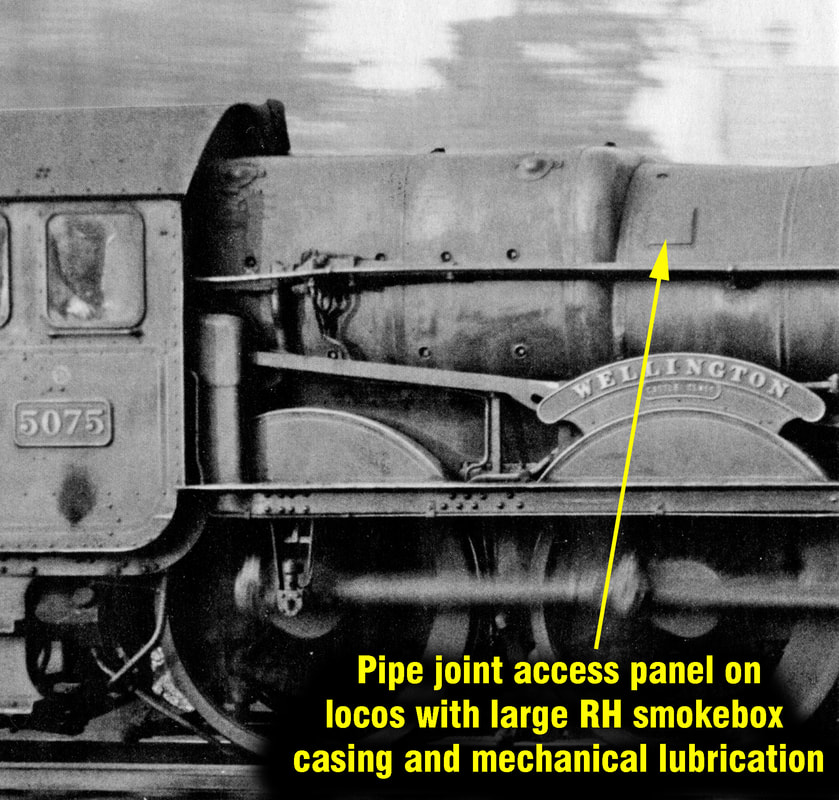
Although showy polished brass covers over safety valves had been a feature of steam locomotives since Stephenson"s day, the only railway to maintain this tradition into the era of pop valves was the GWR, with their distinctive tapered brass safety valve bonnets and copper-capped chimneys.
Developments in high-pressure water-tube boilers for marine use placed more demands on safety valves. Valves of greater capacity were required, to vent safely the high steam-generating capacity of these large boilers.Naylor valve) became more critical.distilled feedwater and also a scouring of the valve seats, leading to wear.
High-lift safety valves are direct-loaded spring types, although the spring does not bear directly on the valve, but on a guide-rod valve stem. The valve is beneath the base of the stem, the spring rests on a flange some height above this. The increased space between the valve itself and the spring seat allows the valve to lift higher, further clear of the seat. This gives a steam flow through the valve equivalent to a valve one and a half or twice as large (depending on detail design).
The Cockburn Improved High Lift design has similar features to the Ross pop type. The exhaust steam is partially trapped on its way out and acts on the base of the spring seat, increasing the lift force on the valve and holding the valve further open.
To optimise the flow through a given diameter of valve, the full-bore design is used. This has a servo action, where steam through a narrow control passage is allowed through if it passes a small control valve. This steam is then not exhausted, but is passed to a piston that is used to open the main valve.
There are safety valves known as PSV"s and can be connected to pressure gauges (usually with a 1/2" BSP fitting). These allow a resistance of pressure to be applied to limit the pressure forced on the gauge tube, resulting in prevention of over pressurisation. the matter that has been injected into the gauge, if over pressurised, will be diverted through a pipe in the safety valve, and shall be driven away from the gauge.
There is a wide range of safety valves having many different applications and performance criteria in different areas. In addition, national standards are set for many kinds of safety valves.
Safety valves are required on water heaters, where they prevent disaster in certain configurations in the event that a thermostat should fail. Such a valve is sometimes referred to as a "T&P valve" (Temperature and Pressure valve). There are still occasional, spectacular failures of older water heaters that lack this equipment. Houses can be leveled by the force of the blast.
Pressure cookers usually have two safety valves to prevent explosions. On older designs, one is a nozzle upon which a weight sits. The other is a sealed rubber grommet which is ejected in a controlled explosion if the first valve gets blocked. On newer generation pressure cookers, if the steam vent gets blocked, a safety spring will eject excess pressure and if that fails, the gasket will expand and release excess pressure downwards between the lid and the pan. Also, newer generation pressure cookers have a safety interlock which locks the lid when internal pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure, to prevent accidents from a sudden release of very hot steam, food and liquid, which would happen if the lid were to be removed when the pan is still slightly pressurised inside (however, the lid will be very hard or impossible to open when the pot is still pressurised).

RM2CPW1YB–. Locomotive engineering : a practical journal of railway motive power and rolling stock . electric headlight. Safety Car Heating &Lighting Companys steam-heat equip-ment, including Mason reducing valve. 39 whistle and to be about one thousand timesmore ear-torturing. We think if the peo-ple who complain about the Englishwhistle only went through the agony ofhearing the whistle of an American loco-motive screaming through the country inthe middle of the night, they would bethankful that the English whistle was noworse than it is. The Whistle Nuisance in England. Americans who have heard the wh

7. Electrical goods. These are sold as ‘antiques’ only and if bought for use must be checked over for compliance with safety regulations by a qualified electrician before use.
10. Electrical items. These are subject to detailed statutory safety controls. Where such items are accepted for sale you accept responsibility for the cost of testing by external contractors. Goods not certified as safe by an electrician (unless antiques) will not be accepted for sale. They must be removed at your expense on your being notified. We reserve the right to dispose of unsafe goods as refuse, at your expense.
11. Soft furnishings. The sale of soft furnishings is strictly regulated by statute law in the interests of fire safety. Goods found to infringe safety regulations will not be offered and must be removed at your expense. We reserve the right to dispose of unsafe goods as refuse, at your expense. The rights of disposal referred to in clause 10 and 11 are subject to the provisions of The Torts (Interference with Goods) Act 1977.
9. Third party liability.All bidders, buyers and other members of the public on our premises are there at their own risk and must note the lay-out of the accommodation and security arrangements. Accordingly neither the auctioneer nor our employees or agents shall incur liability for death or personal injury or for the safety of the property of persons visiting prior to or at a sale (except in each case as may be required by law by reason of our negligence)

Of all the challenges you face keeping your customers’ plants operating at full capacity, safety and relief valves shouldn’t be one of them. NASVI’s job is to give you the confidence that your valve supply chain is rock solid regardless the pressure it’s under.

Safety Valve Steam Pressure Relief Valve Train Steam Engine Ship DN15 1/2". A28H-16 Safety Relief Valve spring-loaded full-open safety valve. 1 Piece Safety Relief Valve. Pressure Range: 1.0-1.3MPa. Store Home |Sporting Goods |Home, Furniture & DIY |Health & Beauty |Jewellery & Watches |Clothes, Shoes & Accessories |Vehicle Parts & Accessories |Crafts |Business, Office & Industrial |Garden & Patio |Computers/Tablets & Networking |Pet Supplies |Mobile Phones & Communication |Baby |Sound & Vision |Collectables |Toys & Games |Video Games & Consoles |Cameras & Photography |Art |Dolls & Bears |Musical Instruments |Books, Comics & Magazines |Wholesale & Job Lots Safety Valve Steam Pressure Relief Valve Train Steam Engine Ship DN15 1/2" Description: --A28H-16 Safety Relief Valve spring-loaded full-open safety valve --Diameter DN15, pressure range 1.0-1.3MPa. --Suitable for overpressure protection devices on equipment or pipelines with water air and steam with working temperature ≤250°C. --When the pressure in the equipment or pipeline exceeds the allowable value, the valve will automatically open and then discharge completely. --When the pressure is low, the valve will automatically close to ensure the safe operation of the equipment. Specification: Model: A28H-16 Diameter: DN15 Material: Steel Pressure Range: 1.0-1.3MPa Operating Temperature: ≤250℃ Package Includes: 1 Piece Safety Relief Valve 1 Piece Product Certificate 1 Piece User Manual Shipping And Handling Policy The buyer is responsible for any applicable import duties and local taxes. Please verify with your customs before making your purchase. Please verify your address during checkout. We are not responsible for any wrong or undeliverable addresses. People always bought together with

Some people have proposed a “safety valve” to control the costs of a cap-and-trade policy to fight global warming. This post explains what a safety valve is, and why it provides only an illusion of cost management.
The “safety valve” or “escape hatch” is meant to address this. It specifies that when prices reach a predetermined dollar value, businesses no longer have to rely on the established supply of allowances available in the market. Instead, the federal government makes new allowances available for sale at a specified price – potentially in an unlimited quantity.
There are two problems with this approach:A safety valve destroys the cap. The hard limit on emissions is the cornerstone of a cap-and-trade policy. Without a solid cap, we can’t be sure our emissions will go down enough to avoid the worst consequences of global warming. A safety valve gives the illusion that we are controlling emissions while allowing more greenhouse gas pollution into the atmosphere.
A safety valve limits the economic opportunity of those who develop cleaner technology. Higher permit prices signal the market to invest more in innovative low-carbon technologies – happy news if you’re in the business of inventing and selling ways to cut pollution. A safety valve would sharply curtail incentive for innovation. This drives up costs in the long run, and discourages the development of the clean technology we need.
A safety valve seriously undermines the main advantages of a cap. Its ability to control costs is an illusion, it lets more pollution into the atmosphere, and discourages entrepreneurs from investing in pollution-cutting technology.
The original copper chimney cap and brass safety valve cover are now glued in place. The safety valve lever is a thin piece of plastic which slots into the saw-kerf cut into the cab front before. The roof covers-up the rest of the slot. A thin piece of metal would have been better, but I didn’t think about it till after.
Now I have to do No.2764. The plan is too keep the panniers, but backdate the bunker, paint the steam dome and safety valve cover brass, and apply lining, as they probably did in 1910.




 8613371530291
8613371530291