ndt wire rope inspection price

This is because the end ofuser rope must be stronger than lead insurers, so they can lessstand the test of time and even if the end of a rope. It are also used in manufacturing areas, construction, and many other areas of construction.
Stainless steel wire rope is one of the most convenient materials and can be bought in bulk for the long time. even if steel wire is high, it is important to know the shape and size of the wire rope.
One of the most important things to wire in places is your customers ’ work. Before buying wire rope at Alibaba.com, it is important to know what type of customers is wire rope inspectors and whether they ’ re going to work or any other place where your customers work, wire rope inspectors should be able to provide wire rope inspections to any customers, so they can check whether the quality is a quality or a indicator. wire rope inspectors should be able to check the quality of materials used when wire rope is used, and even if it is at the same time as your customers, wire should check at any end of the day.
One of the main purposes of wire rope inspections is to identify the condition that the wire rope is ised and, according to the quality of the attached, and the wire itself. One of the most important types of wire rope inspections is to make the that, or the other, a welded steel design needs to be checked before, and any wire rope is applied. Hence, wire rope inspectors should be able to check the quality of the wire rope used by installing wire ropepes.
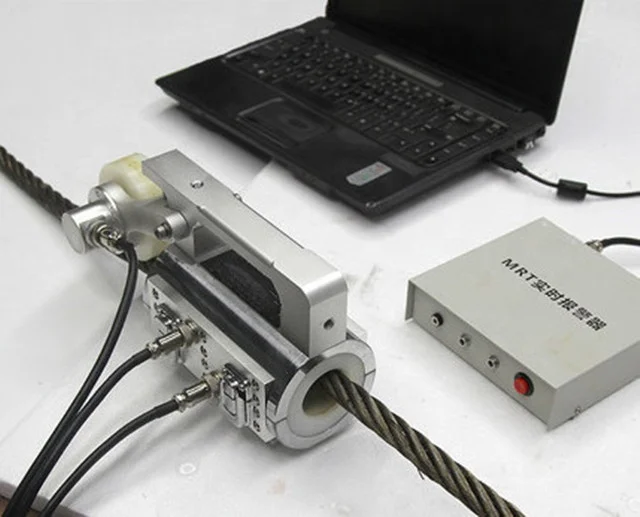

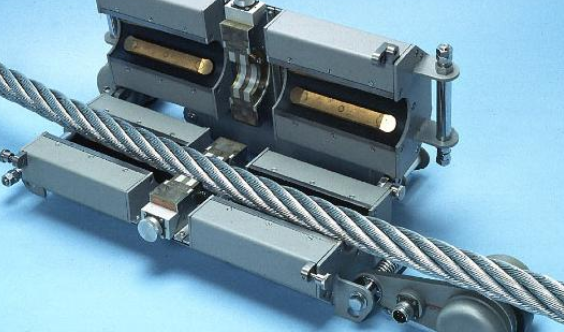
lAdopts electromagnetic qualitative, quantitative and orientation methods to do online overall NDT of broken wires, corrosion, wear, metal, loose strands, jump wire cross-sectional area, deformation and material anomalies of wire rope.

The Magnograph® series of wire rope NDT testers are the leading non-destructive instrument to test the condition of steel rope sections. Detecting corrosion and broken wires, this is simply not possible with visual inspections.
This state-of-the-art NDT testing of wire rope quickly and efficiently identifies defects through the entire cross section of rope. Even non-skilled personnel can operate the Magnograph. View real-time data and perform post-test data analysis easier than ever before.
Magnograph® MAG II is designed to test ropes from 12-64mm (1/2 to 2-1/2 inch) diameters. It utilizes 5 different sizes of interchangeable rope guides in the sensor head.
Depend on the Magnograph® for professional wire rope inspection you can trust. By using Magnograph® and its computerized systems, you will benefit from many outstanding advantages:

we provide quality products and customer service that our customers are accustomed to. Herb has invested time, over the past five years, with a transition team lead by Ori and Joe Shtekler to ensure a smooth transition. To NDT Technology LLC.
NDT Technology, LLC. is a developer and manufacturer of nondestructive test instrumentation for the in-service inspection of wire ropes and cables. Our company is the world’s premier maker of wire rope inspection instrumentation. Our success in this niche business can be attributed to the superior performance of our products and our never-ending pursuit of innovation.
Our wire rope NDE equipment is especially suited for the inspection of so-called high-value wire ropes (i.e., large diameter (>100mm) subsea construction ropes with lengths in excess of 2000m). Our rope testers also show great promise for the inspection of spiral strand.

The ROPE device family consists of a wide range of detectors, suitable for the test of ropes employed in different areas, such as goods lifting and ropeways.
The ROPE device allows a safe, reliable and objective control of the rope integrity, by highlighting the presence of internal and external broken wires, wear and corrosion, in according to the UNI ISO 4309 standard.
The detector is wired connected to a recording unit (IASH) that allows to acquire, show and store the data in order to give to the operator complete management of the signals.

Non-destructive wire rope inspection involves determining the condition of wire rope still in service to ensure that it is safe for use. Every steel wire rope, which is subject to corrosion, abrasion, and fatigue, will fail one day if it is not discarded in time. Steel wire rope flaw detectors enable accurate measurement of loss of metallic area (LMA) and detection of outer and inner localized flaws (LF), such as broken wires, strands, pitting corrosion. Our wire rope test and inspection equipment is suitable for underground and surface mining, cranes and heavy lifting onshore and offshore, cable ways, cable bridges, elevators, guy ropes of flare stacks and masts, overhead transmission lines, etc.

With over 100 years of combined experience in the wire rope industry, our professionally qualified and skilled team of technicians offer efficient, safe, and cost-effective wire rope testing and visual inspections.
Testing can be done on a wide variety of wire ropes including aerial passenger lifts, surface lifts, material tramways, automated people movers (APM), cable belts, shaft elevators, winch cables, zip lines etc. For zip lines we use our mechanical trolley to inspect all types of zip line cables. The MRT System is fully computerized and provides an electromagnetic evaluation of any ferrous rope up to 70mm (2 ¾ inches) in diameter. We use the newest technology for Magnetic rope Testing (MRT) equipment developed at the INSTITUTE OF MECHANICAL HANDLING AND LOGISTGICS (IFT) at the UNIVERSITY OF STUGGART.
Two fully computerized magnets as well as measurement and evaluation software precisely detect anomalies throughout the profile of the entire rope length. The fully automated process is computer accurate and inspects up to 5 meters of rope per second (980 fpm). When testing track ropes, the magnet lifts automatically at the towers and the slack carriers.

We Are Providing Ndt Inspection Services By Using Wire Rope Testing Equipment For All Steel Wire Rope Applications Like Bridge Incpection,Mining Industry,Cableway Inspection,Crane Inspection,Oil And Gas Industry, Shipping And Many More.
Laboratory LRM-NDE Perform The MRT ExaminationIn All Kinds Of Industries And All Available Diameters, Construction Of Wire Ropes With The Use Of LRM XXI Diagnostic System.

Extend the life of your crane’s wire ropes with our tensioning and electromagnetic inspection solution.Investing in new wire ropes can be a costly and time consuming exercise. Our ndt wire rope inspection services provides our clients with a service that allows them to confidently extend the life of their ropes and by in-situ condition based inspection.
By using this technique for wire rope inspection, clients gain real information about the condition of their ropes which leads to the potential of their life span being extended and in return reduces replacement costs.
Abstract: Non-destructive inspection of steel wire ropes becomes quite common for onshore and offshore operations, and relevant equipment is now available on the market. The reason for growing interest to this inspection is increasing in prices for wire ropes, especially for ropes of large diameter, which may not considered as consumable product anymore, but as assets, and thus should be discarded for reason, i.e. according to discard criteria and their actual technical condition. The key issues for wire rope non-destructive inspection are prompt equipment and correct data interpretation. Rugged and reliable equipment capable to make data interpretation with computer without human intervention is of interest of many customers. INTRON PLUS LTD. has developed MFL instrument INTROS-AUTO, that is a successor of widely used wire rope tester INTROS. It is designed for non-destructive inspection of wire ropes with automatic data interpretation. Following criteria are used to discard rope – number of broken wires along lay length and loss of metallic cross section area in percentage. Discard criteria can be adjusted according to agreement with the customer. INTROS-AUTO stores detailed data, which can be downloaded and interpreted in regular manner. The instrument is ready for inspection of ropes as large as 135 mm in diameter and can be used for periodical or permanent wire rope monitoring onshore and offshore. Keywords: Wire ropes, MFL, automatic data interpretation, monitoring. ---------------------------Ropes produced from carbon steel wires are used in cranes, elevators, mining hoists, etc. to carry people and freight. The bigger and longer is rope, the more expensive it is. Degradation of ropes happens due to different reasons, e.g. friction between internal wires, friction between external wires and sheave surface, corrosion of wires, bending of the rope over the sheaves, and always leads to reduction in rope breaking strength. When the breaking strength is less tha ...

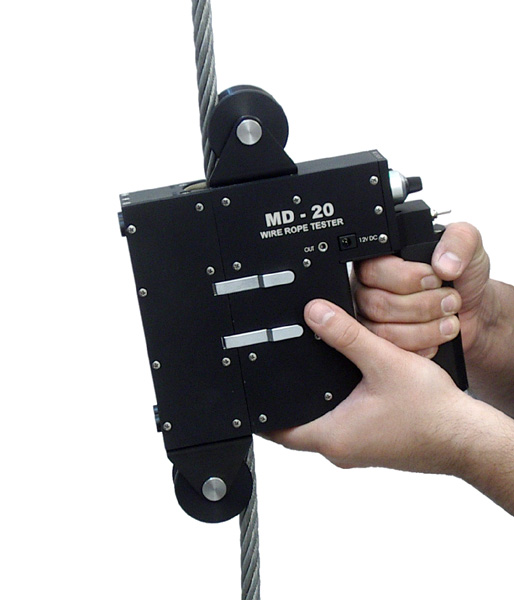
The first of the above categories is less expensive than the second category and the instruments are almost simple tools, mostly hand-held. This kind of instruments makes visual examination of the rope more convenient and reliable. Sometimes, like Meraster MD-20 Tester, they are equipped with a recording signal output, which allows their application as sensing head for detailed inspection of the rope.
The second category of instrumentation is intended to perform detailed tests. In conjunction with visual examination they may be applied to determine the moment when the rope should be discarded. Generally this instrumentation consists of two units: a sensing head; and a signal processing/recording instrument. Sometimes the signal processing part and a standard chart recorder are supplied as separate units. Now some suppliers offer portable computers and software for use instead of chart recording. Detectability of rope defects depends mainly on the sensing head employed but readability of its signals and ease of operation depend mainly on recording/processing instrument.
The sensing head brings the running sector of wire rope to the condition close to magnetic saturation and senses magnetic fields. All reputable manufacturers employ at least double-channel sensing system: one to detect localised losses (LF), and the other one to detect the distributed loss of metallic cross-sectional area (LMA or TCMA). Only some types of Polish-made and German heads are equipped with additional channels to estimate the depth inside the rope of a localised loss position.
Detecting capabilities of sensing heads vary between manufacturers and rope constructions. They depend on strong magnetisation capability, shape of magnetic concentrators in the sensor and operating principle of the sensor. In order to measure running rope length (and speed of relative movement), some manufacturers supply heads equipped with special transducer for indicating rope/head movement as an electric signal. Some manufacturers use it to synchronise the strip chart feed with the rope/head travel. This signal is also useful to compensate the speed influence on the inductive coil signal.
Processing electronics depends on the sensor types and equipment features. For example the Hall generator sensor requires supply control and compensation of DC component of its signal, and the inductive sensor signal needs rope speed compensation to achieve good performance of the instrumentation. Some instruments have additional circuits that make them more convenient in use, e.g. rope length/speed measuring circuits.
A strip chart recorder seems to be indispensable in each fully functional wire rope NDT instrument, as a third part of an instrumentation set, or integrated with the electronic processing part of the equipment. Mostly, manufacturers of these NDT instruments use standard, stand-alone or OEM unit recorders. Almost, it is a two-channel digital thermal array printer or sometime analogue pen recorder. A recorder appropriate for this sort of application must be equipped with drive control to achieve good correlation between the recording and the wire rope at any non-controlled rope speed, within test speed range. The recording should be performed at real time mode, instantly. Meraster MD120 Defectograph is an example of extremely task dedicated recording instrument.
In addition, specialised computer software is supplied as an extension of the equipment capabilities. However some manufacturers supply software and notebooks instead of chart recording instruments. This way seems to be easier today but mainly for suppliers. Actually, most of NDT users prefer instant ease readable strip chart recording then signal runs displayed on notebook screen.
Based on many years of previous experience, the first model of this instrument was introduced in 1994. Since this date MD120 series has been supplied to rope experts in Poland and around the world and it has been recognised as a valuable state-of-art instrument
Apart from the standard features of reliable instrumentation, mentioned above, the unique features of the MD120 Defectograph are: capability of determining the rope defect depth location inside the rope; running integral method for easy read out of high density of defects; zoom replay of recording; solid state memory (computer compatibility); automatic printing of annotations; automatic set up after entering the specific rope code ("settings + rope code" memory).
This last channel needs some explanation to understand its unique role. There are two advantages of this recording, particularly for mining hoist ropes, where broken wires are concentrated. First, more readable indication of a real damage resulting from broken wires, located close to each other, than in "localised losses" channel. Second, set-up of integration range in instrument according to rope discard criteria "number of broken wires in any x diameter length" allows indicating total losses in appropriate rope sectors lengths.
The instrument operates continuously, in the "running integration" mode, where integration is being performed on a length in the next rope sector. The instrument is recording current values of the integral (total of losses) of previous rope sector, last "x" metres length. If the length of integration range is set appropriate to discard criteria, it gives direct readable indications of rope sectors in which the number of broken wires probably exceeds value of the discard criteria.
During the rope NDT procedure performed in-situ, audio-alarm and "Zoom Replay" capabilities are useful. The Defectograph generates the audio-signal when the pulse value in the "localised losses" channel has exceeded pre-set alarm level. When a significant rope defect has been observed during recording, the user can stop the rope (or head) movement and recording of signalss, and then may replay a previous recording in the zoom mode. Defect position may be read out precisely and found in the rope. Visual examination of the rope sector in question should then be made, additionally.
Solid state memory is an option. This is a credit card size SRAM IC Memory Card conforming to the PCMCIA (PC Card) standard. PCMCIA cards are compatible with almost notebook computers. Also PCMCIA slots can be added to most of personal computer systems. In certain rope NDT conditions, for instance subject to magnetism, this method of data transfer has many advantages. With this option, the Defectograph may store additionally an all-rope test record in the memory card. Capacity of the recording depends on the card version, e.g. 1 MB card can storage test of a rope of 600 m in length and 4 MB - 2400 m. Then data may be sent easily and quickly to a computer via the PCMCIA slot. This way, the user can archive many test records for further comparative analysis and can employ software to help him in his work on rope test results. Also data from Memory Card may be replayed on a strip chart with an MD120 Defectograph, including old test records from computer storage memory.
The recorder prints automatically the number of annotations on strip chart, e.g. rope length in metres, a rope code set by the operator; recorder settings, direction of movement, date and time. Before a rope test, the user can enter into the instrument a specific identification code, which will be printed on the chart, and test settings like channel sensitivities will be stored with this identification code in non-volatile memory in the instrument. If the same codes are entered in future, the same settings may be applied automatically.
The recorder may operate in one of two main modes: chart feed synchronous to rope movement; or chart feed at constant selectable speed. Recording is done by means of a thermal array line printing on thermal paper. All of the instrument settings and measured values are displayed on a liquid crystal display. Any instrument setting may be changed with one only knob-push-button.
Field service and user-friendly oriented functionality of the MD120 in conjunction with its capability of computer aided post-testing analysis make this instrument useful as well as every-day tool for rope expert and as a source of data for researchers and developers of methods. Easy access to the test records with computer software tools seems to be a real aid to make faster progress in the development of rope evaluation methods.

With the aid of technologically advanced manufacturing unit, we are able to provideNDT Wire Rope Testing. This is demanded for indication of a rope weakening due to internal and external corrosion. The offeredNDT Wire Rope Testingis delivered to our customers only after its proper examination. Further, we are offering this testing device in different specifications at the economical prices.

Wire ropes are complex machines with a great many moving parts. They require attention, skilled operators, careful maintenance, inspection and lubrication.
In spite of their vital importance, wire ropes are frequently treated as and considered low-tech commodities. Failures are frequently accepted as “inevitable.”
With the appropriate inspections, wire rope failures can be predicted, and expenses and losses reduced. Consider that the price tag of rope failures can easily be in the seven or even eight digit range, and the cost of an inspection is marginal.
Much more dependable than visual inspections, magnetic rope testing (MRT) is a reliable non-destructive evaluation/examination (NDE) procedure used for the in-service inspection of wire ropes. NDE methods allow the detection and evaluation of external as well as internal rope deterioration. This allows the inspection of a rope’s entire cross-section to the core. MRT drastically increases wire rope safety. At the same time, it promises significant annual savings.
Ropes usually degrade internally with no visible indications. Internal deterioration modes include inter-strand nicking that will eventually develop into clusters of internal broken wires and corrosion including corrosion pitting.
External deterioration includes winding-on-drum damage. Urgently needed, suitable inspection equipment and procedures are now available – especially for the quantitative characterization of internal rope deterioration.

ice evaluation of amusement park rides, bridges, cranes, ship loaders and may other load bearing assets. This article briefly introduces the various wire rope testing methods and their respective advantages and disadvantages. The basic wire rope testing methods are visual wire rope testing, magnetic flux leakage (MFL) wire rope testing, long range ultrasonic testing (LRUT) and acoustic emission testing of steel cables.
Visual wire rope is a fast and economical non-destructive testing technique that detects wire breaks on the outside diameter of the wire rope. Wire rope testing is commonly performed using a cloth rag lightly wrapped the rope that catches on protruding wires. Visual wire rope testing is performed routinely across all industries. Visual inspection cannot determine condition under collars, seizing wires, separators, sockets and gatherers since due to accessibility. In addition to wire breaks, this method can detect reductions in diameter, corrosion, birdcage, waviness, kinks and deformations.
MFL testing of wire rope and steel cables introduces a magnetic field along the primary axis of the wire rope using magnetizing measurement head. Wire breaks cause a disruption in the magnetic field causing it to leak out from the rope. The magnetic flux leakage (MFL) is detected by a Hall sensor in the measuring head. The measuring head is generally equipped with an encoder wheel to accurately track wire break locations.
MFL wire rope testing is most practical and economical on moving ropes since a winching system is not required to pull the measuring head. Additionally, the maximum rope diameter that can be MFL tested is approximately 4”. Lastly, specialized measuring heads, at extra cost, may be required for groups of wire ropes with minimum clearance. Consider that each measuring head has certain size and must small enough to mount in the clearance area between the ropes. Example MFL wire rope testing data is shown in Figure 2. The wire rope testing data are presented as milli-voltage (mV) versus distance correlated to the encoder wheel. The measured mV on the vertical axis is proportional to the magnetic flux leakage caused by wire rope breaks. The upper data (OUT) reports on wire rope testing of the outer strands of the cable. The middle data (INN) reports on wire rope testing of the inner strands of the cable. The bottom (blue) wire rope testing data records loss of metallic area (LMA) during the wire rope inspection.
MFL wire rope testing is performed on ropes in the 0.50 to 4.00” diameter range. Moving rope like those used on amusement park rides, ski-lifts, elevators, and lifting devices are easily tested with and MFL measuring head and encoder wheel. MFL wire rope testing is often performed on standing ropes like those found on ship loaders and bridge stay cables, however, these applications are slightly more complicated, time consuming, and expensive due to a winching requirement.
TKS specializes in the monitoring of suspender cables and ropes in cable-stay and suspension bridges, using acoustic emission (AE) for wire breaks. This technology is recommended for larger diameter ropes and cables that may not be suitable for MFL wire rope testing or long-range ultrasound testing (LRUT), also known as guided wave ultrasonic testing (GWUT). Bridge cable inspection using acoustic emission technology has been utilized to provide risk-based inspection and maintenance for fracture critical members in infrastructure such as bridges and storage tanks. The technology provides real-time feedback on structural condition without the need for direct access to the area of interest.
Acoustic emission in bridge cable is produced by wire breaks, strand breaks, corrosion related events that may be correlated to individual strand deterioration, or group of strand deterioration, and other mechanisms. Bridge cable acoustic emission data is analyzed for both intensity and rate at which it is generated. Acoustic emission intensity is analyzed by considering acoustic emission amplitude, acoustic emission energy, and acoustic emission counts. The rate at which acoustic emission is emitted is analyzed to determine if deterioration is progressing. No acoustic emission activity implies that no active AE source was present during the duration of the test. Acoustic emission rates may also be categorized as stable, increasing linearly, and exponentially.
Follow-up visual inspections are recommended based on inspection results. Cable rubbing or fretting at gatherers, collars, separators and sockets generate acoustic emission which may be confused with acoustic emission generated from wire breaks. Broader disadvantages include that multiple sensors are require per cable with significant installation setup time. No defect sizing is possible.
Long range ultrasound (LRUT), or guided wave ultrasonic testing (GWUT), is used as a screening tool for oil and natural gas pipelines, bridge pile, and railroad track. The technology provides real-time feedback on structural condition without the need for direct access to the area of interest. Cable inspection typically takes about 20 minutes. The sensor is installed on bottom end of cable with a low frequency ultrasonic wave transmitted from the sensor to top end of cable – typically the main cable. Similarly a guided wave is transmitted downwards to the suspender rope socket. Ultrasound is reflected back from wire breaks and other cable defects and cable defects are identified by location and severity: minor, moderate and advanced. Follow-up visual inspections are recommended based on inspection results.
The technology deploys magnetostrictive sensors (MSS) which may be installed in 15-30 minutes depending on access and cable conditions. The MSS sensor consists of conductors wrapped around the cable and centered between two permanent magnets. Guided waves are generated in the cable through induction. The instrumentation is lap-top based and transports easily to the inspection site and in between inspection locations on-site. Example data is shown below in distance – amplitude response. Reflections from the cable socket and main cable are observable at 0 and 100 feet, respectively. Confirmed corrosion was detected at approximately 85 feet (X1).

At Premiere Scana Technology, we have make our clients contented by increasing safety and reducing cost through proper cost cutting by using our advanced technology we save wire rope wastage. Get that wire rope inspected ensure real safety know the exact condition of that crane wire rope before using that crane.
We have the expertise to advise on wire rope consumption without compromising on safety. Most recently, we began to introduce our services to the Offshore Supply Vessel and found that the old ways of cutting the winch wires and sending them for inspection is not a productive nor the best way to ensure wire rope is safe for service. We provide In-situ wire rope inspection without removing the wires on the winch, we can perform an inspection by spooling the entire wire rope and inspecting 99% of the full length on the vessel itself. This gives the best assurance for checking the entire wire rope integrity.
Wire Rope inspection using visual methods have proven to be unproductive and not quantitative in nature besides human fatigue can cause the inspection to be incomplete and have gaps that can cause dangerous mishaps.
We are able to detect wire rope defects without removing the ropes on the machinery and we can do an inspection for example on a Oil Rig pedestal crane within 16 hours for the 3 wire ropes, boom, whip and main Hoist line. We have also developed a comprehensive package that is most applicable and economical for Shipyards, Marine vessel, Offshore Support Vessel and all kinds of Winches and Cranes for heavy lifting or towing. Our device detects corrosion, abrasion, fatigue and broken wires internally and externally on the wire ropes. The difference between us and the competitor is that we have a factory that produces this device and we have constant upgrade program that enables us to produce the most current up to date devices that can inspect all types of wire rope construction.




 8613371530291
8613371530291