single layer wire rope in stock

The use of wire rope, sometimes called steel cable, steel sling rope, or steel rigging wire, is extremely popular in the material handling industry. Wire ropes come in a huge variety of designs and constructions, all suited for different lifting applications. Each type of wire rope has benefits and drawbacks. What all wire ropes have in common however, is that they are made up of steel wires which form individual stands. These strands are laid in a helical pattern around a fiber or steel core to form the rope. Different wire configurations and strand structures offer specific benefits to fit virtually any rigging application. These benefits include:
Selecting the correct wire rope for your rigging application often requires the rigger to make a compromise between different steel cable properties. For example, a wire rope with a small number of large outer wires will be more resistant to crushing, but less resistant to bending fatigue. Conversely, a wire rope with a larger number of small outer wires will be more bending fatigue resistant but less crushing resistant. These differences not only change the way the wire rope is used but they also change the way the wire rope is to be properly cared for.
Here at Tri-State Rigging Equipment we pride ourselves on providing our customers with only the highest quality steel wire ropes, from only the most reputable manufacturers. We can provide you with any rigging product on the market so if you cannot find what you are looking for, or if you don’t know exactly what you need, call or email our sales team to speak with a rigging product specialist.
The wires of a cable rope are the smallest component and are twisted together to form individual strands. Wires can be constructed in a variety of materials and grades, all affecting the properties offered by the cable rope. These materials include:
These different materials and grades affect the cable rope’s strength, bending fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and curve of the wire rope.
The strands of the steel cable consist of two or more wires and are laid in a helical pattern around the core. The way strands of steel cable are laid affect the properties offered by the steel cable.
The job of the core inside a steel cable rope is to support the strands and keep them in place relative to each other when bending and when under load. Wire rope cores can be made of a variety of materials including natural fiber, synthetic fiber and steel.
The lubrication of a steel cable rope is extremely important and often overlooked. Wire rope lubricant is added during the manufacturing process and penetrates the wire rope throughout, core included. The purpose of wire rope lubrication is twofold. First, it reduces friction between wires and strands. Second, it provides corrosion resistance to wires, strands and the core. A lack of proper lubrication is very serious and is cause to remove any and all affected wire rope from service.
In a preformed steel wire rope, the wires and strands are manufactured into the helical shape they will take when the wire rope is constructed. Preformed wire rope offers more flexibility and fatigue resistance than non-preformed wire rope. This allows the rigging wire to be uniformly spooled on a drum.
When riggers talk about the lay of a rope, they are talking about two things. One, the way the wires are laid to form a strand (right or left), and two, the way the strands are laid around the wire rope core (regular, lang, or alternate).
Regular Lay: The wires are parallel with the core of the rope. The direction of the wires is opposite to the direction of the strands. Compared to lang laid wire rope, regular lay offers more crushing and rotation resistance, allowing it to spool better on a drum.
Lang Lay: The wires are laid at an angle to the wire rope core. The direction of the wires is the same as the direction of the strands. Compared to other wire rope lays, lang lay offers more bending fatigue and abrasion resistance.
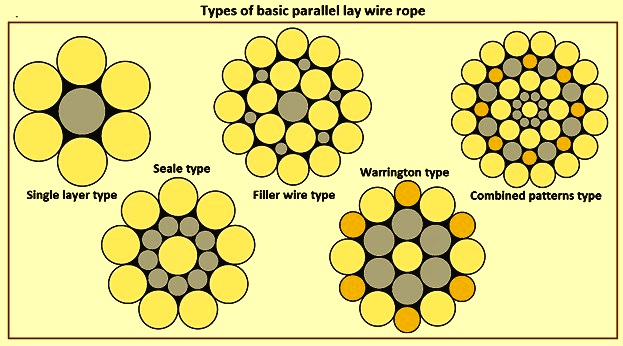
Wire ropes can be constructed using one of the five main strand patterns or a combination of two or more of the basic strand patterns. The wire rope strand pattern refers to the number of wires per layer, the number of layers, and the size of the wires. The strand pattern of a wire rope is a very important determining factor when it comes to choosing the correct wire rope for your specific rigging application. The five basic strand patterns are:
Filler Wire: This strand pattern is constructed by laying two layers of same sized wires around a center. The outer layer will have 2x the amount of wires than the inner layer. In the valleys of the inner wires are small filler wires to fill in the gaps between the inner and outer layers.
Seale: A layer of same sized wires smaller than the center wire is laid around the center. The outer layer consists of the same amount of wires as the inner layer but bigger in size. The outer wires lay in the valleys of the inner wires.
Warrington: This strand pattern consists of two wire layers. A layer of wires is laid around a same sized center wire to form the inner layer. The outer layer is formed by laying wires of alternating sizes, big and small, around the inner layer. The larger outer wires lay in the valleys of the inner wires and the smaller outer wires lay on the crowns of the inner wires.
Combination: A combination wire rope strand pattern is constructed by combining two or more of the strand patterns above to form a single unique strand pattern.
Fiber cores offer riggers more flexibility due to their natural or synthetic polypropylene fibers. This also means, however, that fiber core wire ropes are more susceptible to crushing and are not suitable for high heat environments.
In environments that exceed 180° F, a steel wire rope core should be used. Steel wire rope cores can be either an independent wire rope or an individual wire rope strand. Steel wire rope cores offer greater support for the strands and wires of the steel cable when compared to fiber cores.
The classification of a wire rope is based on the number of strands, as well as the number of wires in each strand. Below is a table of the most common wire rope configurations arranged in specific classifications.
In addition to the general classifications of steel wire rope, here at Tri-State Rigging Equipment, we also offer a wide range of specialty wire rope constructions. These include:
Rotation Resistant Wire Rope: This special construction of steel cable rope is designed to resist twisting and turning while under load. Rotation resistant wire rope must be specially cared for to prevent introducing twist into the rope.
Compacted Strand Wire Rope: This special type of wire rope is constructed using compacted outer strands. The outer strands are run through rollers or a die before the rope is closed. This increases the density of the outer stands and gives the steel cable rope a smoother outer surface. Compacted strand wire ropes offer greater strength and durability than standard round wire rope.
Swaged Wire Rope: Unlike a compacted wire rope, a swaged wire rope is compacted using a swaging machine after the wire rope had been closed. The outer wires of a swaged wire rope can be either compacted or round. Like compacted strand wire rope, swaged wire rope offers more strength and durability when compared to similar sized round wire ropes, however, it offers less bending fatigue resistance.
Plastic Coated Wire Rope: This type of wire rope is coated in a layer of plastic to protect the rope from abrasion, wear, and environmental factors. A drawback to plastic coated wire rope is that the plastic coating covers the strands and wires making it harder to inspect the wire rope.
Plastic Impregnated (PI) Wire Rope: A plastic impregnated wire rope is filled internally with a matrix of plastic that fills the gaps between wires and strands. This plastic filling reduces internal friction and improves bending fatigue resistance.
Plastic Coated or Plastic Filled IWRC Wire Rope: This type of wire rope features an independent wire rope core that is either filled or coated in plastic. This reduces internal friction in the wire rope and gives the wire rope greater bending fatigue resistance.
Tri-State Rigging Equipment is a service provider and distributor for all steel wire rope and steel cable for rigging and lifting, serving clients from coast to coast, Canada, Mexico and especially focused in the states of Missouri, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, Arkansas, Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, South Carolina, Florida, and Oklahoma.

Wire rope is technically defined as multi-wire strands laid geometrically around a core while also used more generally as a term to classify multiple product families including aircraft cable, coated aircraft cable, general purpose wire rope, strand, rotation resistant wire rope, compacted/swaged wire rope, and cable laid wire rope.
Aircraft cable does not fit the definition of wire rope in the strictest sense as it does not have an independent core, but rather a strand core, in which the center is one of the strands that is laid with the outside strand layers. Aircraft cable is available in diameters 3/8" or less with breaking strengths similar to that of equal diameter independent wire rope core (IWRC) and is available in stainless steel and galvanized steel.
Wire rope can be galvanized via three processes. Listed from least corrosion-resistant to the most corrosion-resistant, they are electro-galvanizing, hot-dip galvanizing, and drawn-galvanizing. In addition to being the most corrosion-resistant types of galvanized wire rope, drawn-galvanized has another added benefit which is a breaking strength that is the same as bright wire rope does. Electro-galvanized and hot-dip galvanized wire rope have breaking strengths that are approximately 10% lower.
Wire rope is specified by the number of strands in the rope, the number of wires in each strand, and a description of the core’s material of construction. For example, the notation “6x7 FC” means that the rope has six strands with seven wires in each strand and a fiber core. Commonly used core designations include FC (fiber core), independent wire rope core (IWRC), wire strand core (WSC), and poly core (PC).
There are two elements to wire rope lubrication, the core, and outer strands. IWRC wire rope always has a lubricated core (unless specially ordered as otherwise). Bright wire rope always has lubricated outer strands. Galvanized wire rope can be manufactured in either dry finish or lubricated with respect to the outer strands. Typically stainless steel wire rope is manufactured with a lubricated IWRC and dry finish outer strands.
Stainless Steel Wire Ropes are an important part of our core product range. We keep stock of AISI 316 Marine Grade Stainless Steel Wire Rope from 0.5mm up to 26mm in various constructions including: 1X19, 7X7, 7X19 and 6X36 wire core.
Providing high quality materials is an extremely important part of our ethos which is why our stainless steel wire ropes are produced in accordance with BSMA29 standards by one of the leading stainless steel wire rope manufacturers in the world.
Our ropes are used in demanding conditions and it is therefore vital that the tolerance and chemical composition of the material is as per the required AISI 316 requirements. Applications and markets include:structural and architectural, balustrade, yacht rigging and Stay Wire applications.
Steel Wire Rope Ltd have specialised in supplying multi stranded galvanised steel wire rope since 1989. We stock from 0.5mm up to 64mm in various constructions including 1X19, 7X7,6X19, 7X19, 6X36, 8X19, 8X36, 19X7 and 35X7 with both Fibre Core and Steel Cores. In addition to these conventional steel wire ropes we can offer special wire ropes from high quality manufacturers.
Most wire ropes operate in demanding conditions and must resist crushing, bending fatigue and abrasion. We recognise that it is vital that all of our wire ropes need to perform to the highest levels to maximise service life therefore increasing productivity for the end user. With our technical experience we have worked hard with our partners to ensure that all material is manufactured to the very best standards in the steel wire rope industry.
Each steel wire rope can be supplied fully assembled complete with end terminals such as a thimble eyes, swaged ends and wedge sockets as well as many other solutions. These cable assemblies are manufactured in house by our team of engineers complete to your specifications.

As specialist for manufacturing quality steel wire ropes over 20 years, our company can supply strong, durable and reliable ropes that capable to minimize your downtime and maximize cost effectiveness. Decades of experience we owned make us know clearly the work you do and capable to provide professional guidance.
We select the best steel or stainless steel as raw material for wire rope manufacturing. Our products are manufactured under strict quality managements and test before they leave the factory.
Our engineers can provide professional advice about picking up optimal steel wire ropes for their application, installation guidance to ensure maximum return in their wire rope system.
If you are going to pick up steel wire ropes that suit your project perfectly, you must have an ideal about the construction about them. Our company can supply bright wire rope, galvanized wire rope, stainless steel wire rope, compacted wire rope, rotation resistant wire ropes, mining wire rope, elevator wire rope, crane wire rope and gas & oilfield wire ropes. Here are some details to solve the problem that may puzzle you whether you are browsing the web or picking up steel wire ropes.
Bright steel wire ropes mean no surface treatment is applied to the rope. Therefore, they have the lower price among these three wire ropes. Generally, they are fully lubricated to protect the rope from rust and corrosion.
Galvanized steel wire ropes feature compressed zinc coating for providing excellent corrosion resistance. With higher break strength yet lower price than stainless steel, galvanized steel wire ropes are widely used in general engineering applications such as winches and security ropes.
Stainless steel wire ropes, made of quality 304, 305, 316 steels, are the most corrosive type for marine environments and other places subjected to salt water spray. Meanwhile, bright and shiny appearance can be maintained for years rather than dull as galvanized steel wire ropes.
Steel wire ropes are composed of multiple strands of individual wires that surrounding a wire or fiber center to form a combination with excellent fatigue and abrasion resistance. These wires and strands are wound in different directions to from different lay types as follows:
Beside above lay types, alternative lay ropes which combine regular lay and lang lay together and ideal for boom hoist and winch lines, can also be supplied as your request.
Two main methods about seizing steel wire ropes in conjunction with soft or annealing wire or strands to protect cut ends of the ropes form loosening.

Dy-pac® 18 The 18 series is a compacted rotation resistant rope construction consisting of a inner part with an outer layer of strands spun in the opposite direction.

Wire rope is a complex mechanical device that has many moving parts all working in tandem to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. This structure provides strength, flexibility, and the ability to handle bending stresses. Different configurations of the material, wire, and strand structure will provide different benefits for the specific lifting application, including:Strength
However, selecting the proper wire rope for your lifting application requires some careful thought. Our goal is to help you understand the components of a wire rope, the construction of wire rope, and the different types of wire rope and what they might be used for. This will allow you to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
A wire rope is, in reality, a very complicated machine. A typical 6 x 25 rope has 150 wires in its outer strands, all of which move independently and together in a very complicated pattern around the core as the rope bends. Clearances between wires and strands are balanced when a rope is designed so that proper bearing clearances will exist to permit internal movement and adjustment of wires and strands when the rope has to bend. These clearances will vary as bending occurs, but are of the same range as the clearances found in automobile engine bearings.
Understanding and accepting the “machine idea” gives a rope user a greater respect for rope, and enables them to obtain better performance and longer useful life from rope applications. Anyone who uses a rope can use it more efficiently and effectively when they fully understand the machine concept.
Wires are the smallest component of wire rope and they make up the individual strands in the rope. Wires can be made from a variety of metal materials including steel, iron, stainless steel, monel, and bronze. The wires can be manufactured in a variety of grades that relate to the strength, resistance to wear, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and curve of the wire rope.
Strands of wire rope consist of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and supports the strands and helps to maintain their relative position under loading and bending stresses. Cores can be made from a number of different materials including natural or synthetic fibers and steel.
Lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process and penetrates all the way to the core. Wire rope lubrication has two primary benefits:Reduces friction as the individual wires and strands move over each other
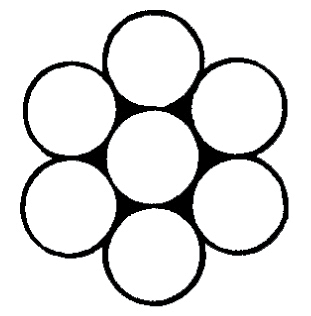
The number of layers of wires, the number of wires per layer, and the size of the wires per layer all affect the strand pattern type. Wire rope can be constructed using one of the following patterns, or can be constructed using two or more of the patterns below.Single Layer – The most common example is a 7 wire strand with a single-wire center and six wires of the same diameter around it.
Filler Wire – Two layers of uniform-size wire around a center with the inner layer having half the number of wires as the outer layer. Small filler wires, equal to the number in the inner layer, are laid in valleys of the inner wire.
Seale – Two layers of wires around a center with the same number of wires in each layer. All wires in each layer are the same diameter. The large outer wires rest in the valleys between the smaller inner wires.
Warrington – Two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of wire in the inner layer, and two diameters of wire alternating large and small in the outer later. The larger outer-layer wires rest in the valleys, and the smaller ones on the crowns of the inner layer.
On a preformed wire rope, the strands and wires are formed during the manufacturing process to the helical shape that they will take in a finished wire rope.
Preformed rope can be advantageous in certain applications where it needs to spool more uniformly on a drum, needs greater flexibility, or requires more fatigue-resistance when bending.
Direction and type of lay refer to the way the wires are laid to form a strand (either right or left) and how the strands are laid around the core (regular lay, lang lay, or alternate lay).Regular Lay – The wires line up with the axis of the rope. The direction of the wire lay in the strand is opposite to the direction of the strand lay. Regular lay ropes are more resistant to crushing forces, are more naturally rotation-resistant, and also spool better in a drum than lang lay ropes.
Lang Lay– The wires form an angle with the axis of the rope. The wire lay and strand lay around the core in the same direction. Lang Lay ropes have a greater fatigue-resistance and are more resistant to abrasion.
A steel core can be an independent wire rope or an individual strand. Steel cores are best suited for applications where a fiber core may not provide adequate support, or in an operating environment where temperatures could exceed 180° F.
The classifications of wire rope provide the total number of strands, as well as a nominal or exact number of wires in each strand. These are general classifications and may or may not reflect the actual construction of the strands. However, all wire ropes of the same size and wire grade in each classification will have the SAME strength and weight ratings and usually the same pricing.
Besides the general classifications of wire rope, there are other types of wire rope that are special construction and designed for special lifting applications.
Some types of wire rope, especially lang lay wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation when under load. Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or rotating and can be used in a single line or multi-part system.
Special care must be taken when handling, unreeling, and installing rotation resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce twist into the rope which can cause uncontrolled rotation.
Compacted strand wire rope is manufactured using strands that have been compacted, reducing the outer diameter of the entire strand, by means of passing through a die or rollers. This process occurs prior to closing of the rope.
This process flattens the surface of the outer wires in the strand, but also increases the density of the strand. This results in a smoother outer surface and increases the strength compared to comparable round wire rope (comparing same diameter and classification), while also helping to extend the surface life due to increased wear resistance.
A swaged wire rope differs from a compacted strand wire rope, in that a swaged wire rope’s diameter is compacted, or reduced, by a rotary swager machine after the wire rope has been closed. A swaged wire rope can be manufactured using round or compacted strands.
The advantages of a swaged wire rope are that they are more resistant to wear, have better crushing resistance, and high strength compared to a round strand wire rope of equal diameter and classification. However, a swaged wire rope may have less bending fatigue resistance.
A plastic coating can be applied to the exterior surface of a wire rope to provide protection against abrasion, wear, and other environmental factors that may cause corrosion. However, because you can’t see the individual strands and wires underneath the plastic coating, they can be difficult to inspect.
Plastic filled wire ropes are impregnated with a matrix of plastic where the internal spaces between the strands and wires are filled. Plastic filling helps to improve bending fatigue by reducing the wear internally and externally. Plastic filled wire ropes are used for demanding lifting applications.
This type of wire rope uses an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) that is either filled with plastic or coated in plastic to reduce internal wear and increase bending fatigue life.
Remember, wire rope is a complex piece of mechanical machinery. There are a number of different specifications and properties that can affect the performance and service life of wire rope. Consider the following when specifying the best type of wire rope for your lifting application:Strength
When you select a piece of rope that is resistant to one property, you will most likely have a trade-off that affects another property. For example, a fiber core rope will be more flexible, but may have less crushing resistance. A rope with larger diameter wires will be more abrasion resistant, but will offer less fatigue resistance.
At Mazzella Companies, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.
If you’re looking for a standard or custom specified wire rope for your lifting project, contact a Lifting Specialist at a Mazzella Companies location near you.
We stock well over 2,000,000 feet of wire rope in our various locations … ready for immediate delivery! We provide wire rope assemblies, and manufacture bridge cables, crane cables, steel mill cables, and thousands of OEM assemblies.
There are several different ways to construct wire rope. Each different construction offers its own pros and cons. Knowing the difference between the construction types allows for users and purchasers to get the most from their wire.
Spiral ropes are less common, but are still very useful. The construction is made of round strands that are laid helically over the center. One wire will be laid in the opposite direction, but this is on the outer layer. The biggest boon this construction offers is its ability to lock out dirt and water. It also holds lubricants at higher raters.
Strand ropes lay helically in multiple layers around a single core. These constructions normally only have a single layer over the core, which makes it less durable.
Wire ropes are constructed with steel wires. This is arguably the strongest of all the construction types. It has high tensile forces, and it is able to run over sheaves with small diameters.
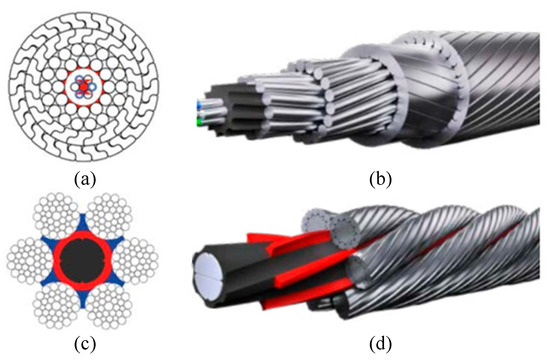
In order to avoid twisting of the wire rope by the drum, the drum rule should be obeyed. A right hand drum should be operated with a left hand lay rope, a left hand drum should be operated with a right hand lay rope.
In multi-layer drums, the direction of the drum changes with every layer. Here the direction of the lay of the steel wire rope should either be chosen to suit the direction of the reeving (a left hand reeving should have a right hand rope and a right hand reeving should have a left hand rope) or the lay direction of the steel wire rope should be chosen for the most used layer of the drum (see also page 52 & 53).

Did you know wire ropes were used as far back as the 1830s for mining hoist applications? Nowadays, we can use steel ropes for many different applications such as lifting and hoisting in elevators and cranes, and for mechanical power transmission. US Cargo Control’s wire rope slings are an excellent choice for heavy-duty jobs as their fabrication offers excellent abrasion resistance and heat resistance for extreme conditions.
Although these slings are beneficial for the lifting and rigging industry, there are a few specifications to know before purchasing them. Continue reading what is wire rope, what are important specifications to look for, and how it’s different from cable rope.
These slings carry different properties that can determine their performance. Wire rope is constructed where a strand consists of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope. Once the wires are formed, they all come together to create greater strength and flexibility.
These slings work well for lifting, hoisting, towing, or anchoring loads. They’re manufactured in a variety of configurations, with 6×19 and 6×36 being the most common. When you see 6×19 or 6×36 from our website, these numbers represent the number of wires making up the strand and the number of strands wrapped around the core.
For example, a 6×19 indicates that there are 19 wires making up a strand, and 6 strands wrapping around the core. To learn more about our 6×19 wire ropes, look into our bestselling 1/2″ Galvanized Wire Rope EIPS IWRC, 1/2″ Stainless Steel Wire Rope IWRC T304, and 1/2″ Bright Wire Rope EIPS FC.
The configurations will offer different benefits for certain applications. In general, a smaller number of large outer wires offers better wear and corrosion resistance, while a larger number of small wires provides a better level of flexibility and fatigue resistance. Continue reading to learn which wire rope fits your job.
There are different versions of wire rope slings, ranging from single leg to 4 legs, as well as braided wire rope and domestic wire rope slings (manufactured in the U.S. with Crosby® hardware). When looking at the types of slings we offer at US Cargo Control, be sure to consider how much versatility and capability you need.
For example, a braided wire rope has increased flexibility and friction to grip loads over a regular wire rope. Adding an additional leg to the sling can add additional versatility and strength.
This is the measurement of the rope’s diameter and can be displayed in inches or millimeters. These sizes commonly display different strand patterns where the number of layers, wires per layer, and size of the wires per layer all affect the strand pattern. Wire rope can be constructed using one of the following patterns below or using two or more patterns.
Warrington – this construction has two layers of wires around a center with one diamter of wire in the inner layer, and two diameteres of wire alternating large and small in the outer layer.
The type of lay refers to the way the wires are laid to form a strand. They’re how the strands are laid around the core which can be regular lay, long lay, or alternate lay.
The wires line up with the axis of the rope. This is where the wires are twisting in one direction, and the strands in the opposite direction create the rope. Regular lay is less likely to untwist and less likely to crush.
This is the opposite of regular lay where the wires form an angle with the axis of the rope. The wires and strands spiral in the same direction and run at a diagonal to the centerline of the rope. Lang lay is more flexible and resistant to abrasion than regular lay wire ropes. The only con is this type of lay will be more likely to twist and crush than the regular lay.
Sometimes known as reverse lay, this type of lay consists of alternating regular lay and long lay strands. This unites the best features of both types, and it’s using relatively large outer wires to provide an increase of abrasion resistance.
This refers to the protective coating that’s applied to the wire rope. There are three types of finishes which are galvanized (zinc-coated), stainless steel, and bright (unfinished steel).
The grade of the rope means the grade of steel being used. The plow steel strength calculates the strengths of most steel wire ropes. Some classifications include Improved Plow Steel (IPS), Extra Improved Plow Steel (EIPS), Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel (EEIPS), Galvanized Improved Plowed Steel (GIPS), and Drawn Galvanized Imrpoved Plow Steel (DGEIP).
EIPS is 15% stronger than IPS, and EEIPS is 10% stronger than EIPS. Along with that, GIPS and DGEIP wires can add corrosion resistance to your application, but DGEIP wires have a higher break load than GIPS.
The type of core is what makes up the center of the wire rope. There are three types of core: Fiber Core (FC), Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC), and Wire Strand Core (WSC).
A steel core can either be an independent wire rope or individual strand. The steel cores can provide adequate support, or in an operating environment where temperatures can exceed very high heat.
Wire and cable ropes are terms that are often interchangeable but do have one varying difference. Wire rope refers to the diameters that are larger than 3/8 inch. Sizes smaller than this are classified as cable rope or even cords. Regardless of the size difference, cable and wire rope are still classified as a “machine.” Even a group of strands laid around a core would still be called a cable or wire rope.

Understanding the basics of wire rope will help guide you on how to choose the right wire rope for your job. Application, required strength, and environmental conditions all play a factor in determining the type of wire rope that is best for you.
But when it comes to buying wire rope, the various numbers and abbreviations that describe the different types of wire rope can be confusing. EIPS wire rope, 6X19 IWRC wire rope, and lang lay wire rope are just some of the many variations available. But what does it all mean?
Displayed as inch or fractional inch measurements, the size indicates the diameter of the rope. Industry standards measure the rope at its widest point. A wide range of sizes are available from 1/8” wire rope to 2-1/2” wire rope. Thicker sized wire rope has a higher break strength. For example, our Wire Rope has a 15,100 lb. break strength while our Wire Rope has a 228,000 lb. break strength.
The numbers indicate its construction. For example: in wire rope, as shown above the first number is the number of strands (6); the second number is how many wires make up one strand (19).
When it comes to wire rope basics, regular lay also refers to right lay or ordinary lay. This indicates that the strands pass from left to right across the rope and the wires in the rope lay in opposite direction to the lay of the strands. This type of construction is the most common and offers the widest range of applications for the rope.
This term indicates that the wires twist in the same direction as the strands. These ropes are generally more flexible and have increased wearing surface per wire than right lay ropes. Because the outside wires lie at an angle to the rope’s axis, internal stress is reduced making it more resistant to fatigue from bending. This type of rope is often used in construction, excavating, and mining applications.
Independent wire rope cores offer more support to the outer strands and have a higher resistance to crushing and heat. Independent wire rope core also has less stretch and more strength.
Many of our customers use our rope and our wire rope clips to create rope assemblies. Check out of video blog on Wire Rope Clips to Wire Rope Assemblies to learn more.
For any questions on our wire rope products, call (877) 923-0349 or email customerservice@uscargocontrol.com to speak with one of our product experts.
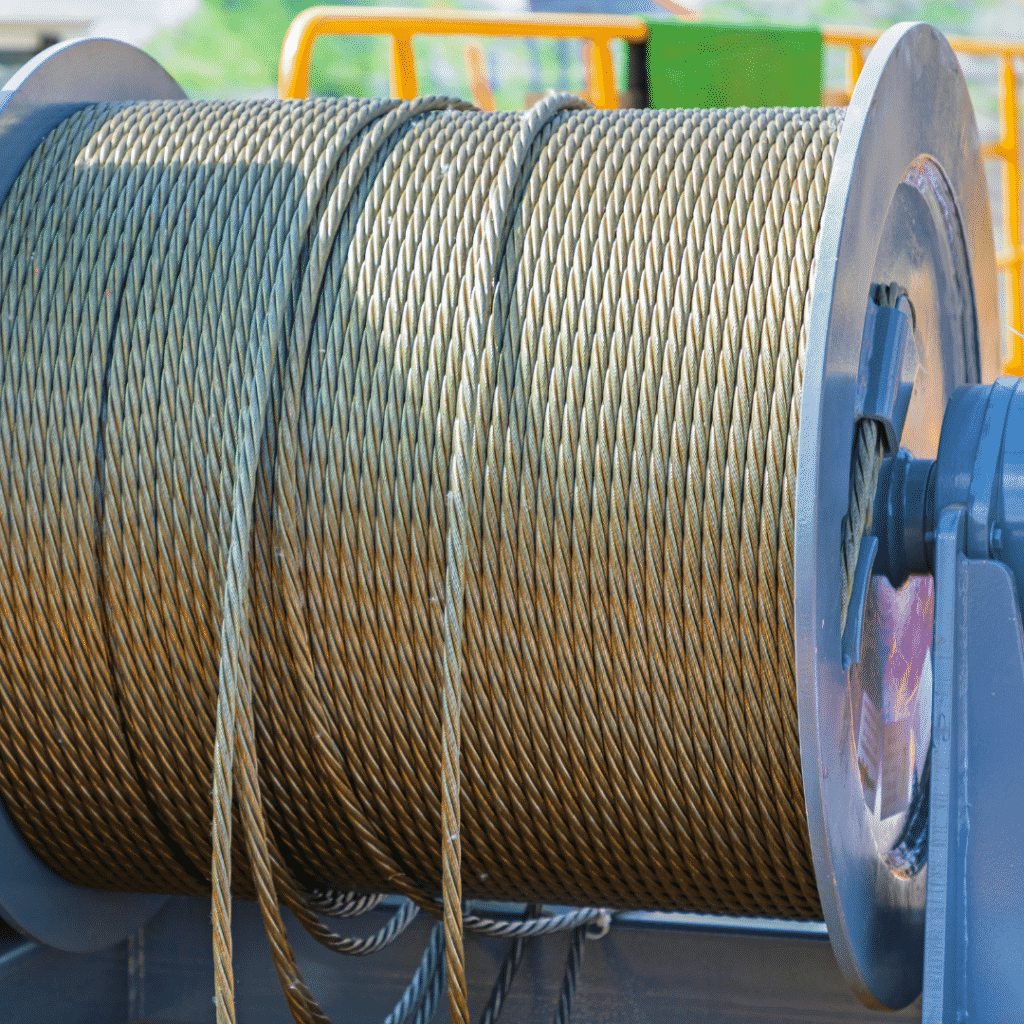
The actual diameter of a wire rope is the diameter of a circumscribed circle that will enclose all the strands. It’s the largest cross-sectional measurement as shown here. You should make the measurement carefully with calipers.
The rope diameter should be measured on receipt for conformity with the specification. British Standard (B.S. 302:1987, standard steel wire rope, Part 1. Clause 5.1) allow for a tolerance of - 1% to 4 % of the nominal rope diameter.
The generally accepted method of measuring rope diameter for compliance with the standard is to use a caliper with jaws broad enough to cover not less than two adjacent stands. The measurement must be taken on a straight portion of rope at two points at least 1 meter apart. At each point two diameters at right angles should be measured. The average of the four measurement is the actual diameter.
After the rope has made the first few cycles under low load, the rope diameter should be measured at several points. The average value of all the measurements at each point must be recorded and will form the basis of comparison for all future measurements.
The measurements of the rope diameter an essential part of all inspections and examinations. It ensures the maximum diameter reduction does not exceed the recommended figure. As stated in 5.2 British standard 6570 recommends that a wire rope should be discarded when the diameter of the rope is reduced to 90% of the nominal diameter.
A comparison of the measured data with the recorded previous values can detect an abnormal rate of reduction in diameter. Coupled with assessment of previous rope examination data, the probable date of rope renewal can be predicted.
If we examine the cross-section of a six-stand wire rope, we will find that measuring the thickness of the rope over the crowns (Fig-a) will produce a higher value than measuring it over the valleys (Fig-b). The actual diameter of the rope is defined as the diameter of the circumscribing circle.
When using a conventional caliper, wire rope with an even number of outer strands (four-, six, eight-, and multi strand) ropes must be measured from crown to crown. The advantage of a proper wire rope caliper with measuring plates is that even if the measurement is carried out "incorrectly", adjacent crowns are always included, so that the actual diameter is determined at any section. (Fig-c)
Measuring the diameter of wire rope with an uneven number of outer strands (three, five, seven, or nine-strand ropes) is more complicated: a crown on the one side of the wire rope always has a valley as a counterpart on the other side of the wire rope. A conventional caliper, therefore, has to be applied diagonally to the axis of the rope, so that at any time a crown adjacent to a valley is covered. Again a wire rope caliper with measuring plate is definitely to be preferred as it always includes strands crowns.
In all cases during periodic examinations where the measurements are to be recorded, the rope should be measured as already described. Where the roundness is being checked to detect potential faults, two diameters, one at right angles to the other can be taken and noted in the records. The entry into the records might read rope diameter : 20.4/20.5mm.
After a rope has been fitted to the appliance, its length cannot be measured again accurately, with out a great deal of trouble. The purpose of measuring the length of lay is to detect any increase in the rope length which may have been caused by corrosion, core deterioration or rope rotation (unlaying). With n new rope the wire and strands should be allowed to settle into their permanent position. Six or seven lifting cycles with a light to medium load are recommended before measuring error, the measurement should be made over four lays and the length divided by four lays and the length divided by four to find the average lay length.
On eight strand ropes the eight, sixteen, twenty-four and thirty-second strands must be marked. Using a straight length of the rope and with the rope under no load, first mark any strand on the crown with a piece of chalk; this strand now become"" crown zero"". Excluding this strands, count the next eight strands and mark the eight strand with chalk. Exclude the eight strand and repeat the procedures further two times. The measured length between the outer chalk marks is then divided by four to give the lay length.
As a rough check on the overall accuracy of the chalk marking, the length of lay for eight strand ropes is approximately between 6.25 and 6.5 x the diameter of the rope e.g. using a lay length of 6.5 x rope diameter, four lay length of a 32mm diameter rope will be 32mm x 6.5 x 4=832mm.
An alternate method of measuring the rope lay is to secure the free end of the roll of adding machine paper to the rope with adhesive tape. The paper is rolled out over the rope and simultaneously the wax pencil is drawn over the paper, providing a clear print of the outer wires of the rope. The finished print can be field for comparison with later measurements.
A third method is to wrap typing carbon papers round the rope under the roll of paper. By rubbing along the paper with a piece of cardboard, the carbon marking on the underside of the paper can be confined to the tops of the strand crowns.

Based on 135 years of experience CERTEX Danmark A/S is your reliable partner and supplier of steel wire rope, lifting applications and related services. We are experts in both standard and customized products and solutions and we offer everything from service and inspection to installation and testing. We look forward to solving your next lifting challenge!




 8613371530291
8613371530291