steel wire rope construction quotation

Understand that most of the people out from the industry always face the problem of having no idea with the terms of wire rope when receiving quotation. In this update, we will explain in the most simple way and hopefully it is applicable to anyone.
6X36 = Construction of wire rope (There are quite a lot different constructions available for different application for example like, 6X25, 6X29, 6X31, 4X39, 19X7, 8X26 etc.)
RHOL = Right hand ordinary lay, it is the wire lay direction and very important to select the right direction of wire when dealing with multi-reeving, crane and hoist application.
EIPS (1960) = Extra improved plow steel and 1960 stands for the tensile strength 1960N/mm2. The figure is telling you the grade of wire rope, lower or higher tensile strength will result in different breaking strength.
UNGALVD = Ungalvanized, the surface finishing of wire rope. Galvanized and Ungalvanized are the basic surface finishing selection with different grade of lubrication.
MECH SPLICED = Mechanical splicing is the process of using hydraulic pressure to press the aluminum sleeve or metal sleeve and a loop is formed. This phrase is always telling you the terminal of both end wire rope. It can be plain, socketed, fuse tapered or eye formed.
Wire rope could have a lot of variation upon the application which I will cover in the next update. The essay above is good enough to tell the basic and hope it helps for procurement department while dealing with steel wire rope. Last but not least, selecting the right wire rope is crucial to your company"s long term expenditure and safety purposes. Do not take the risk because of cheap.
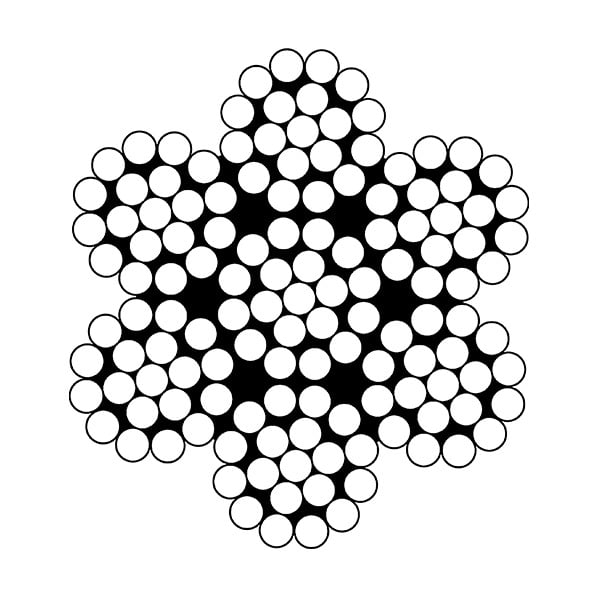
The 7×19 stainless steel wire rope construction is the most flexible of the multi-strand wire ropes and is used for a wide range of applications. Often found for guardrails and balustrade applications where the curves, corners or angles are required.
For larger sizes or any cable information not shown, please make contact with us. Our global sourcing arrangements allow us to secure a huge range of stainless-steel wire
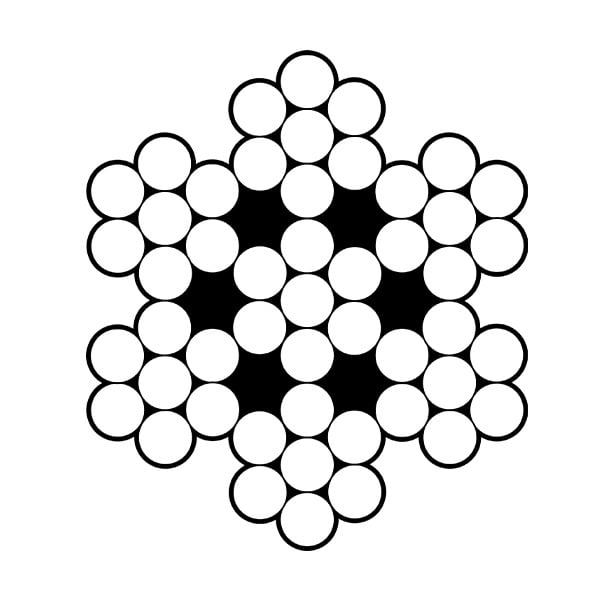
Wire ropes are identified primarily by construction. The number of strands and the geometric arrangement of wires within the strands make up the wire rope construction.
The more common constructions are shown above. Note that each construction can have more wires than shown, but the geometry remains the same. For example, there can be two operations ropes having more than 19 wires; there can be Seale ropes having more than 19 wires; there can be Warrington ropes having more than 19 wires and there can be Filler Wire types having more (or less) than 25 wires. Here are the basic constructions.
Each of the above possesses unique characteristics which must be considered when selecting rope or strand for a job. The specific geometric construction selected depends on the destructive factors present on the job.
The most common factors, abrasion and fatigue, create conflicting requirements. Small (more numerous) outer wires resist fatigue but are easily worn through by abrasion. Larger outer wires have superior abrasion resistance but are more quickly broken by bending and flexing. The difference in outer wire size is seen between the 6 x 19 Seal and 6 x 25 Filler Wire constructions. The nine outer wires in the Seale strands are clearly larger than the 12 outer wires in the Filler Wire strands. Other destructive factors must be considered: peening, corrosion, heat, crushing and shock loads.
Each wire rope construction falls within a classification. Classifications are identified by the number of strands and nominal number of wires. The actual number of wires must fall within a range specified for the given class. For example, ropes within the 6 x 19 class contain 6 strands made up of 15 through 26 wires of which no more than 12 are outside wire. The 6 x 19 Seale and 6 x 25 Filler Wire constructions therefore are both within this class. The more common classifications are 7 x 7, 7 x 19, 6 x 26, 6 x 36 and 19 x 7.

The 6×26 WS construction design feature compact construction with support for the wires, allowing it to withstand high crushing pressure. The 6×26 WS also has higher abrasion resistance compare to 6x25FW. The multiple inner wire and it size provide stability and fatigue resistance matching 6x25FW. The 6×26 proved to be a choice in application where 6x25FW is applicable.
ROPETEX steel wire rope products are developed by Axel Johnson International – Lifting solutions group (LSG) and sold through companies that belong to the group.
In the ROPETEX product range, our decades of experience and extensive knowledge have been brought together to bring you steel wire rope products with an excellent price / quality ratio.
The production of ROPETEX steel wire ropes takes place in carefully selected production centres that continuously meet our strict requirements with regard to technology, quality, social responsibility and sustainability.
The product range is constantly under development and currently consist of General Purpose wire ropes, PVC coated steel wire ropes in several colors and high quality stainless steel wire ropes as well. Browse them below - and use the filters above if needed.

Our steel cable construction and wire rope assemblies offer a high strength to weight ratio, are long lasting, low maintenance, flexible and a cost efficient solution for many mechanical needs.
Commercial quality “aircraft grade” cable is made from galvanized steel wire or stainless steel wire. Galvanized aircraft cable provides high tensile strength and adequate corrosion resistance for most applications. Stainless steel wire cable provides slightly lower tensile strength, but greater resistance to corrosion.
Industrial cable or wire rope is fabricated from individual wires put together in a uniform helical arrangement to form what is called a strand. A strand typically contains 7 wires (1x7) or 19 wires (1x19), although others are available. Cable or wire rope contains a varying number of these strands such as 7x7 and 7x19 (number of strands x wires per strand). The more strands and more wires per strand, the more flexible the cable and the higher the cost. The greater the cable diameter, the greater the diameter of each wire and the greater the breaking strength.
All steel wire cables can be coated with a number of different plastics such as vinyl (PVC) or nylon in various colors. Black, clear and white are typical stock colors but other colors can be ordered during the wire rope construction process.
The breaking strengths of various diameters of steel wire cable are listed here. Cable construction safety standards dictate a minimum of five to one safety factor when designing cables for most applications. If a cable is being designed for a 300 pound maximum weight load, then a 1/8 inch cable with a 1700 – 2000 pound breaking strength would be needed. For critical safety or shock load applications an 8 or 10 to one safety factor is needed. Request a quote on custom wire rope construction today and contact us with any questions about custom cable construction.
For more information or inquiries about our custom wire rope construction, get in touch with us today. Our team of experts are here to answer any of your questions. We look forward to hearing from you!

Left hand lay or right hand lay describe the manner in which the strands are laid to form the rope. To determine the lay of strands in the rope, a viewer looks at the rope as it points away from them. If the strands appear to turn in a clockwise direction, or like a right-hand thread, as the strands progress away from the viewer, the rope has a right hand lay. The picture of steel wire rope on this page shows a rope with right hand lay. If the strands appear to turn in an anti-clockwise direction, or like a left-hand thread, as the strands progress away from the viewer, the rope has a left hand lay. (The rope in the left hand lay photo shows one left hand lay rope from left to right and top to bottom, with 5 right hand lay strands, and part of a sixth in the upper left. It is not 5 right hand lay ropes adjacent to each other.)
Ordinary and Ducay"s lay describe the manner in which the wires are laid to form a strand of the wire rope. To determine which has been used, first identify if left or right hand lay has been used to make the rope. Then identify if a right or left hand lay has been used to twist the wires in each strand. (On ordinary lay, the outer wires approximately follow the alignment of the rope: with Lang"s lay they are cross at an angle of about 45�.) Lang"s laid rope is able to flex over sheaves more easily (with less damage) but it has the disadvantage of having a high torque tendency (it tends to untwist when tension load is applied) compared with ordinary laid rope. Untwisting can be dangerous with a steel-cored rope: load is shed from the strands and may cause the core to fail as it becomes higher loaded. For this reason, swivel termination units can be dangerous.
The specification of a wire rope type � including the number of wires per strand, the number of strands, and the lay of the rope � is documented using a commonly accepted coding system, consisting of a number of abbreviations.
The construction of your strand, aircraft cable, or wire rope defines a large percentage of the final performance characteristics. The strength, flexibility, fatigue life, and torque resistance all rely heavily on the manner in which wires and strands are laid together in the finished rope. When choosing the construction to use in your next product or project, take the time to review the difference between common constructions listed below and to understand the potential impact each can have in your application.
Strand Core produces strand, cable, and wire ropes up to 5/8" in diameter and can provide custom products and configurations meeting the most demanding specifications. All Wire Ropes are manufactured in stainless steel, galvanized, bright carbon steel, as well as other alloys. As a manufacturer, Customized constructions are available on request. If you have any questions about these constructions, or any aspect of selecting a strand, aircraft cable, or wire rope, please contact us today.

When looking for the highest quality domestic Wire Rope in stainless steel, galvanized, bright carbon steel and a variety of other alloys, Strand Core has the knowledge and experience to deliver. Strand Core manufactures Aircraft Cable right in the USA at our Milton, Florida facility. With over 40 years of industry experience, we understand how the right product makes all the difference. Whether you need high strength IWRC rigging wire ropes for a hoisting application or the flexibility and durability of a Fiber Core wire rope in heavy construction equipment, Strand Core is your manufacturer of choice.
With hard-won experience in Oil & Gas, Marine, Defense, Construction, and Rigging/Hoisting industries, Strand Core’s domestically made working wire ropes are made to the exacting standards of the latest revisions of Federal Specification RR-W-410 and ASTM 1023. When a standard design doesn"t meet your requirements, we have the equipment and process knowledge to build wire ropes in a range of materials and constructions. Sizes range from 3/16" to 5/8" in 6x19 and 6x36 class IWRC and Fiber Core constructions.
Strand Core strongly believes in the importance of sourcing domestic products. Our Wire Rope is domestically made and melted, here in America. All Strand Core Wire Ropes are Made in the USA, and available to Buy America, Buy American, and DFARS specifications. By buying domestically with Strand Core, you are guaranteed a well-made American product, while directly helping support American jobs and the manufacturing industry. Contact us today to learn more or start a quotation.

Wire rope manufacturers produce their products in order to provide a high load capacity, versatile alternative to weaker ropes like manila rope or hemp rope. Wire rope products are used for a wide variety of motion transmission applications, among them: lifting, baling, tie down, hoisting, hauling, towing, mooring, anchoring, rigging, cargo control, guidance and counterbalance. They can also be used as railing, fencing and guardrailing.
Wire rope is a must-have for many heavy duty industrial applications. From mining to forestry to marine and beyond, there’s wire rope for almost every job. Some of the many industries in which wire rope is popular include: construction, agriculture, marine, industrial manufacturing, fitness, sports and recreation (plastic coated cables for outdoor playground equipment and sports equipment), electronics, theater (black powder coated cables for stage rigging), mining, gas and oil, transportation, security, healthcare and consumer goods.
Wire rope as we know it was invented just under 200 years ago, between 1831 and 1834. At that time, the goal was to create a rope strong enough to support work in the mines of the Harz Mountains. Invented by Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, this wire rope consisted on four three-stranded wires. It was much stronger than older rope varieties, such as manila rope, hemp rope and metal chain rope.
While studying at Freiburg School of Mines, a man named L.D.B. Gordon visited the mines in the Harz Mountains, where he met Albert. After he left, Gordon wrote to his friend Robert Stirling Newall, urging him to create a machine for manufacturing wire ropes. Newall, of Dundee, Scotland, did just that, designing a wire rope machine that made wire ropes with four strands, consisting of four wires each. After Gordon returned to Dundee, he and Newall, along with Charles Liddell, formed R.S. Newall and Company. In 1840, Newall received a patent for “certain improvements in wire rope and the machinery for making such rope.”
In 1841, an American manufacturer named John A. Roebling began producing wire rope for suspension bridges. Soon after, another set of Americans, Josiah White and Erskine Hazard, started incorporating wire rope into coal mining and railroad projects, forming Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N Co.). In 1848, wire rope from their wire rope factory in Mauch Chunk, Pennsylvania provided the lift cables needed to complete the Ashley Planes Project. This project sought to improve the performance and appearance of the freight railroad that ran through Ashley, Pennsylvania, by adding lift cables. This increased tourism and increased the railroad’s coal capacity. Before, cars took almost four hours to return; after, they took less than 20 minutes.
Wire rope likewise changed the landscape (again) in Germany, in 1874, when an engineering firm called Adolf Bleichert & Co. used wire rope to build Bi-cable aerial tramways. These allowed them to mine the Ruhr Valley. Several years later, they also used wire rope to build tramways for the German Imperial Army and the Wehrmacht. These tramways were wildly successful, opening up roads in Germany and all over Europe and the USA.
Since the 1800s, manufacturers and engineers have found ways to improve wire rope, through stronger materials and material treatments, such as galvanization, and different rope configurations. Today, wire rope makes possible many heavy industrial processes. It has become a necessity of the modern world.
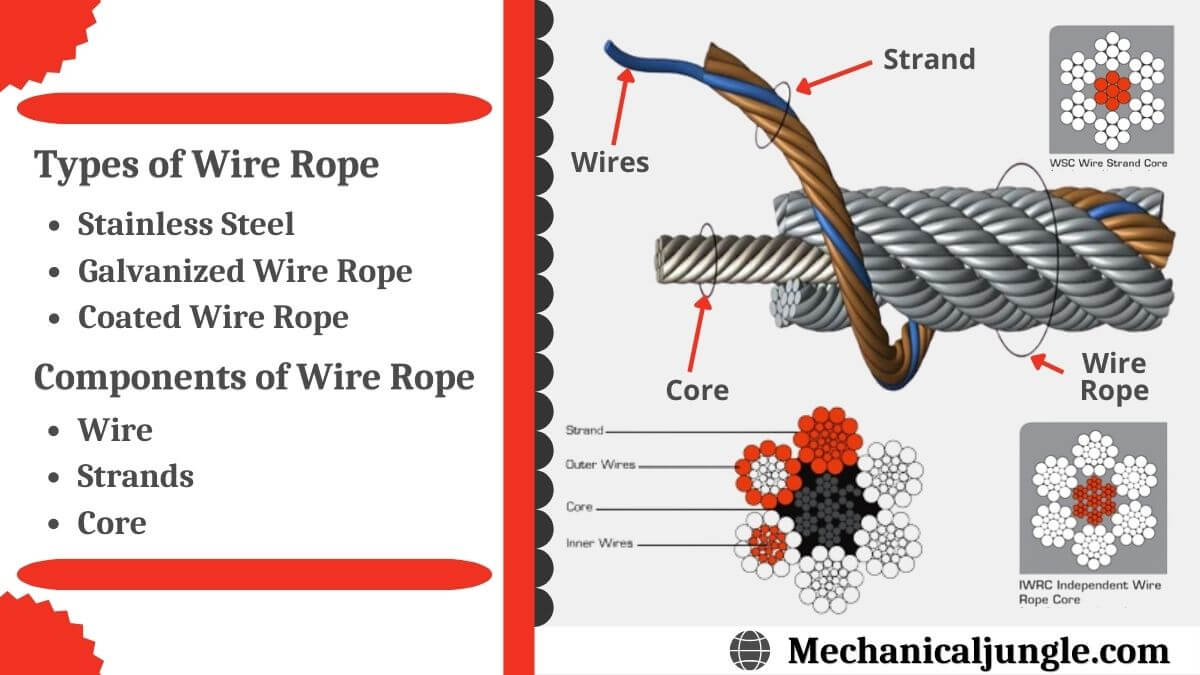
Strands are made by tightly twisting or braiding individual wire together. One strand could have anywhere between two and several dozen wire filaments depending on the necessary strength, flexibility, and weight capacity.
One of the most dynamic elements of wire cables is the inner core. The strands are wrapped around the core, and it can be made of different metals, fibers, or even impregnated fiber materials. For heavy applications, cores are often made of a different strand of wire called an independent wire rope core (IWRC). An IWRC has a considerable amount of flexibility and it is still very strong. In fact, at least 7.5% of the strength increase in a wire rope can be attributed to an IWRC.
While they sometimes use other metals, like aluminum, nickel, copper, titanium, and even bronze for some applications, manufacturers primarily produce wire rope from steel. This is because steel is very strong and stretchable. Among the most common types they use are: galvanized wire, bright wire, stainless steel and cold drawn steel.
Of the wire rope steels, cold drawn carbon steel wire is most popular, although stainless steel wire rope is sometimes employed as well. Stainless steel rope is most popular for its anti-corrosive properties. Bright wire rope, a type of ungalvanized steel wire rope, is also popular. For added strength and durability, galvanized steel wire rope/galvanized steel cables are a very popular choice. Galvanized aircraft cable, for example, is always a must in aerospace.
When choosing or designing a custom wire rope for your application, suppliers consider factors such as: the environment in which the rope will function, required rust resistance, required flexibility, temperature resistance, required breaking strength and wire rope diameter. To accommodate your needs, manufacturers can do special things like: make your rope rotation resistant, color code your rope, or add a corrosion resistant coating. For instance, sometimes they specially treat and coat a cable with plastic or some other compound for added protection. This is particularly important to prevent fraying if the wire rope is often in motion on a pulley.
Manufacturers and distributors identify the differences in wire cable by listing the number of strands and the amount of wires per strand so that anyone that orders understand the strength of the cable. Sometimes they are also categorized by their length or pitch. Common examples of this include: 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 19 x 7, 7 x 19, 7 x 7, 6 x 26 and 6 x 36.
More complex wire rope identification codes connote information like core type, weight limit and more. Any additional hardware like connectors, fasteners, pulleys and fittings are usually listed in the same area to show varying strengths and degrees of fray prevention.
Cable wire rope is a heavy-duty wire rope. To give it its high strength, manufacturers construct it using several individual filaments that are twisted in strands and helically wrapped around the core. A very common example of cable wire rope is steel cable.
Spiral rope is made up an assemblage of wires with round or curved strands. The assemblage features at least one outer layer cord pointed in the opposite direction of the wire. The big advantage of spiral ropes is the fact that they block moisture, water and pollutants from entering the interior of the rope.
Similarly, stranded rope steel wire is made up of an assemblage of spirally wound strands. Unlike spiral rope, though, its wire patterns have crisscrossing layers. These layers create an exceptionally strong rope. Stranded rope may have one of three core material types: wire rope, wire strand or fiber.
Wire rope chain, like all chains, is made up of a series of links. Because it is not solid, wire rope chain is quite flexible. At the same time, it is prone to mechanical failure.
Wire rope slings are made from improved plow wire steel, a strong steel wire that offers superior return loop slings and better security. The plow wire steel also shields rope at its connection points, which extends its working life. Wire rope slings, in general, provide their applications with increased safety, capacity and performance. Wire rope sling is a rope category that encompasses a wide range of sub-products, such as permaloc rope sling, permaloc bridle slings and endless slings. These and other wire rope slings may be accompanied by a wide variety of sling terminations, such as thimbles, chokers and hooks.
Wire rope offers its user many advantages. First, design of even distribution of weight among strands makes it ideal for lifting extremely heavy loads. Second, wire rope is extremely durable and, when matched properly to the application, can withstand great stress and elements like corrosion and abrasion. In addition, it is very versatile. Its many iterations and the ways in which the rope can treated means that users can get rope custom fit for virtually any application.
Depending on the type of wire rope with which you are working and your application, you may want to invest in different accessories. Among these accessories are: wire rope clips, steel carabiners, fittings, fasteners and connections.
To ensure that your wire rope quality remains high, you must regularly inspect them for wear and degradation. The right wire rope should be selected for a particular use. Watch out for performance-impacting damage like: rust, fraying and kinks. To make sure that they stay in tip-top shape, you should also clean and lubricate them as needed. Check for this need as a part of your regular inspection.
Rope care is about more than inspection. It’s also about making an effort to use and store them properly every time you use them. For example, never exceed your rope’s rated load and breaking strength. Doing so will not only cause the weakening of your cable, but it may even cause immediate breakage. In addition, always store your wire rope cable in a dry and warm area, away from those elements that could cause premature rusting or other damage. Finally, always carefully wind your wire rope when you’re done with it, so as to avoid kinks. If you follow all these tips and treat your wire rope assemblies well, they will reward you with a long and productive service life.
Always make sure that you purchase wire rope that matches your industry and regional standards. Some of the most widely referenced standards organizations for wire rope include: ISO, ASTM International and OSHA. Talk over your specifications and application with your wire rope supplier to figure out what’s best for you.
If you’re in the market for a wire rope or a wire rope assembly, the best way to know you’re getting something that will both perform well and be safe if by working with a vetted professional. Find one among the list we’ve provided on this page. Check out their profiles to get an idea of the services and products they offer. Pick out three or four to whom you’d like to speak, and reach out. Talk to them about your specifications, standard requirements and budget. Ask about lead times and delivery options. Once you’ve spoken with all of them, compare and contrast their answers. You’ll know you’ve found the one when you talk to a wire rope company that is willing to go above and beyond for your satisfaction.

We understand that there are many factors that go into choosing the correct sling, wire rope, rigging hardware or lifting device for a lift! Let our sales team help!
Wire rope is a collection of metal strands that have been twisted and wound to form the shape of a helix with the purpose of supporting and lifting heavy loads and performing tasks that are too rigorous for standard wire. On shipping docks, rigging, and load bearing equipment, wire rope is attached to swivels, shackles, or hooks to lift a load in a controlled, even, and efficient manner.
The uses for wire rope include adding support to suspension bridges, lifting elevators, and serving as additional reinforcement for towers. The design of wire rope, with its multiple strands wrapped around a stable core, provides strength, flexibility, and ease of handling for applications that have bending stress.
Individual designs of wire rope involve different materials, wire, and strand configurations as a means for supporting and assisting in the completion of lifting or supportive applications.
The term wire rope encompasses a wide range of mechanical tools that are made to perform heavy and extreme lifting jobs. Wire rope is a complicated and complex tool with multiple moving parts capable of moving in unison. A 6 by 25 wire rope has 150 outer strands that move as one in an intricate pattern supported by a flexible core.
An essential part of the design of wire rope is the required clearance between the strands to give each stand the freedom to move and adjust when the rope bends. It is this unique feature that differentiates wire rope from solid wire and other forms of cable.
The basic element of wire rope is wire that is used to configure, shape, and form the rope. Typically, steel, stainless steel, and galvanized wires are the first choice with aluminum, nickel alloy, bronze, copper, and titanium being second possibilities. The choice of wire is dependent on the type of work the wire is going to be used to perform with strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance being the major determining factors.
Stainless steel wire rope has all of the basic qualities of galvanized and general wire rope with the added benefits of corrosion and rust resistance; this makes it the ideal choice for harsh and stressful conditions.
Steel wire rope is classified as general purpose wire rope and comes in a wide variety of sizes, diameters, and strengths. It is the most common type of wire rope and is used for several industrial, manufacturing, and construction applications.
Before going further into the discussion of how wire rope is made, it is important to understand the numbers used to describe each type. All wire ropes have a core around which wires are wound. The various styles of cores vary according to the construction and design of the requirements of the wire rope that is being produced.
Wire rope is classified by the number of strands it has as well as the number of wires in each strand. The most common classification is a seven wire rope that has one strand in the center and six around its circumference. This type of wire rope is lightweight with a very simple construction. The majority of wire ropes are more complex and intricate with multiple intertwining strands and wires.
What must be understood about wire rope is that it has a complicated configuration. It is actually wires wrapped around wires to form bundles that are wrapped around other bundles. In the case of a seven wire wire rope, the core has bundles of wires wound around it; this can be seen in the image below.
The first step in wire rope creation is the production of wire strands where wires are wound around a single core wire. The number of wires included in the strand is dependent on the specified strength, flexibility, and size requirements of the rope. Once the strand is completed, it is straightened before being moved to wire rope construction.
Like wire ropes, strands have different patterns; patterns are the arrangements of the wires and their diameters. Though most strands have a core, there are strand patterns that have three or four wires without a core that are referred to as centerless strands. The design of each strand pattern is meant to enhance the strength of the wire rope and improve its performance.
For a multiple layer strand, the layers of wire are placed over one another in successive order. The placement of the wires on top of each other must be such that they fit smoothly and evenly.
The Warrington pattern is like the multiple layer pattern with one variation. Like the multiple layer pattern, the inner wires and the core are the same and have the same diameter. The difference is in the outer layer, which has wires of alternating sizes of large and small with larger diameter wires laying in the valleys of the inner wires.
All of the wires of a filler pattern are the same size. What makes this pattern unique is the insertion of small wires in the valleys of the inner wires to fill the gap between the inner and outer layer.
The flattened strand pattern is also known as the triangular strand, which can be triangular or oval. Three round wires form the core. The outer flattened surface has a greater sectional metallic area; this makes this pattern stronger and longer lasting.
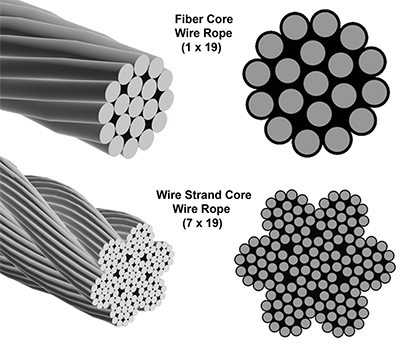
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and can be composed of a variety of materials, which include synthetic fibers, natural fibers, a single strand, or another wire rope. The core supports the wound strands, helps maintain their position, is an effective lubricant carrier, and provides support.
Wire ropes with fiber cores are restricted to light loads and are not used in severe, harsh, or stressful conditions. Polypropylene and nylon are types of synthetic fiber cores and can be used in conditions where there is exposure to chemicals.
Cores made of wire are classified as independent wire cores. The core of a wire rope with a wire core is actually a wire rope with another wire rope serving as the core, as can be seen in the diagram below. These types of wire ropes are used where the rope will be exposed to exceptional resistance and crushing.
A strand, or wire strand core, is exactly like the rest of the strands of the wire rope with wires of the same diameter and size as the other strands.
The choice of core and creation of the strands are the simplest yet most essential parts of wire rope construction. Wire rope lays, the method used to wind the strands, is more complex and involves several choices.
Lay is a term used to describe three of the main characteristics of wire rope: direction, relationship, and linear distance. The strands can be wrapped around the core going right or left. Right or left refers to the direction of the strands wrapped around the core and the wires within the strands. The linear distance is how far a strand moves when it is making a revolution around the core.
In a regular lay, the wires and strands spiral in opposite directions. With a right hand regular lay, the wires spiral to the left and the strands to the right. In the left hand regular lay, the wires spiral to the right and the strands to the left. This type of lay is easy to handle but wears out quickly because the crown wires are in contact with the bearing surface.
In the Lang, or Albert, lay, the wires and strands spiral in the same direction with right hand lay being the most common. The wires in a Lang lay appear to run parallel to the center line of the rope. The difficulty with Lang lay wire ropes is handling since they tend to kink, twist, and crush.
Wire rope is an exceptionally strong tool that has been configured and designed to withstand the stress placed upon it through rigorous and continual use. In most applications, wire rope has to endure extreme stress and strain. It is for these reasons that coatings have been developed to protect wire rope from abrasions, corrosion, UV rays, and harmful and damaging chemicals.
Three main types of coatings are used to protect wire rope: polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene, and nylon. Of the three types, PVC is the most popular.
In cases where there are severe and hazardous working conditions, polypropylene is the recommended choice since it is capable of protecting wire rope against corrosion and chemical leaching. Additionally, it is resistant to impact damage and abrasion. Polypropylene is a tough, rigid, and crystalline thermoplastic that is made from a propene monomer and is resilient as well as inexpensive.
Braided wires are electrical conductors made up of small wires that are braided together to form a round tubular braid. The braiding and configuration of braided wire makes them very sturdy such that they do not break when flexed or bent. Braided wires are widely used as conductors, are commonly made from copper due to copper"s exceptional conductivity, and can be bare or coated depending on the application.
Braided wire can be round and tubular or flat. Round tubular braids fit in most spaces where flat braided wire will not. Flat braided wire begins as round braided wire which is flattened on a capstan. They are exceptionally strong and designed for medical and aircraft applications.
Metals used to make wire rope are various grades of stainless steel, bright steel, and galvanized steel. Though the majority of wire rope manufacturers use these three metals, other metals such as copper, aluminum, bronze, and monel are also used on a limited basis.
The most important aspect of wire rope is the wire and the metal from which it is made. The strength and resilience of wire rope is highly dependent on the quality of metal used to make it, and these are essential factors to be considered when purchasing it.
Bright steel wire does not have a coating and is rotation resistant, (designed to not rotate when lifting a load). It is drawn from hot rolled rods that are put through a die to match its specific dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties, and finish. Bright wire is used as a single line in conditions that require a rope that will resist cabling.
Galvanized steel has a zinc coating for corrosion resistance and has the same strength and durability as bright steel. Environmental conditions determine the use of galvanized steel. In mildly severe and slightly harsh conditions, galvanized steel wire is an economical replacement for stainless steel.
In the manufacturing process, galvanized wire goes through the process of galvanization, a method of coating steel wire with a protective and rust resistant metal. Galvanized wire is exceptionally strong, rust resistant, and flexible enough to meet the needs of a variety of applications.
Stainless steel does not have the same strength and endurance as bright steel or galvanized steel but has the many benefits commonly associated with stainless steel, such as resistance to stains, wear, rust, and corrosion. More expensive than the other two metals, stainless steel has the added benefit of lasting longer and providing exceptional performance.
Wire rope made from copper is mostly used for electrical applications due to its exceptional electrical characteristics. The benefits of copper wire rope are its durability, flexibility, and resilience compared to standard copper wire. The strength of copper wire rope is seen in its use in applications where there are vibrations and shaking.
The wire rope lubrication process begins during its fabrication and continues during its use. Lubrication of wire rope is designed to lower the amount of friction it endures and provide corrosion protection. Continued lubrication increases the lifespan of wire rope by preventing it from drying up, rusting, and breaking.
The types of lubricants for wire rope are penetrating or coating with coatings covering and sealing the outside of the rope. Penetrating lubricants go deep into the rope and seep into the core where they evaporate to form a thick coating or film.
The application of the lubricant is dependent on the type of core. Fiber cores absorb the lubricant and serve as a reservoir that retains the lubricant for an extended period of time. With metal cores, the lubricant is applied as the wire is twisted into strands to give complete saturation and coverage of the wires.
There are several types of greases that are used as wire rope lubricating agents and are made up of oil, a thickener, and additives. The essential components are the base oil and additives, which influence the behavior of the grease. The thickener holds the base oil and additives together. The amount of base oil in a grease is between 70% and 95% with an additive of 10%.
The additive in grease enhances the positive properties of the oil and suppresses the negative properties. Common additives are oxidation and rust inhibitors as well as pressure, wear, and friction reducing agents.
Of the many choices for lubricants, vegetable oil is the easiest to use and penetrates the deepest. The design of the additives for vegetable oils gives them the necessary qualities required to penetrate deep into a wire rope. The exceptional penetration provides protection against wear and corrosion. Since vegetable oil is a fluid, it helps in washing the wire rope to remove external abrasive contaminants.
Wire rope is widely used in machines, structures, and varied lifting applications. Its type, size, and requirements are determined by how it will be used. Regardless of its use, wire rope guarantees exceptional strength and provides high quality and excellent performance.
The lifting of heavy loads for centuries involved the use of hemp rope or chains, neither of which was a guaranteed or substantial method. Early in the 18th Century, between 1824 and 1838, Wilhelm Albert, a German mining engineer, combined the twisting of hemp and strength of chains to create today‘s wire rope.
The most common use of wire rope is as a part of a crane hoist wherein it is attached to the hook of the hoist and wrapped around a grooved drum. The tensile strength and durability of wire rope makes an ideal tool for lifting and keeping loads secure. Though it is used in several industries, it is very popular for production environments wherein materials need to be lifted quickly and efficiently.
In addition to its many lifting applications, the strength and stability of wire rope is useful in other applications, especially in the aerospace industry. Pedals, levers, and connectors in the cockpit of an aircraft are connected with wire rope. The wires provide for the passage of power between systems and mechanisms; this allows control of the aircraft. Wire rope is used to control propeller pitch, cowl flaps, and the throttle. It also assists in lowering and minimizing vibrations.
Tires are reinforced with wire rope to increase their durability and strength. All automotive production environments make use of wire ropes for supplying materials, moving heaving loads, and positioning equipment. Wire rope can be found in the production of steering wheels, cables, exhausts, springs, sunroofs, doors, and seating components.
As surprising as it may seem, the place that wire rope has the greatest use is in the home, where its strength, long life, endurance, and resilience provide guaranteed protection and performance. The main reason wire ropes are so popular for home use is cost.
Inexpensive, easy to obtain, easy to install, and easy to maintain, wire ropes provide an additional method for performing home repairs and structural support. Their excellent flexibility and sturdiness combined with their invisibility has made wire rope an ideal solution to several home maintenance issues. It is used to support staircases, fences, decks, and hang plants.
The search and production of crude oil has relied on wire ropes for centuries to lift drill bits, insert shafts, and support oil rigs on land and the water. When equipment, machinery, and tools have to be lowered into the depths of the earth and sea, wire ropes are the tool that the oil industry relies on to do the job.
Many of the tasks of oil production require tools that are capable of enduring severe and harsh conditions. Wire ropes have to withstand enormous pressure, extraordinary stress, and a wide range of temperatures. The use of wire rope includes maintaining oil rig stability and moorings for offshore rigs.
Wire rope has long been a standard component for the transportation industry, from the cable cars of San Francisco to the lift chairs for ski resorts. For many years, cable cars have relied on heavy duty cables (wire ropes) to be pulled by a central motor from multiple locations. It is a method of transportation that has existed for centuries.
In Europe, funiculars use cables that hang from a support to move cars up and down a mountain with cables moving in opposite directions. The word funicular is from the French word funiculaire, meaning railway by cable. The terms wire rope and cable are used interchangeably when discussed by professionals. The first part of funicular, or funiculaire, is from the Latin word "funis," meaning rope.
The major use for wire ropes in the food and beverage industries is as a means for lifting and moving heavy loads. Wine barrels and containers full of ingredients are lifted and placed through use of cranes and wire ropes. They are also part of conveyor systems that move products from one station to another.
From the beginnings of amusement rides up to the present, wire ropes have been an essential part of attraction construction and safety. They pull cars on roller coasters, hold cabins that swing, and move carriages through haunted houses. The main concern of amusement parks is safety. The strength, stability, and guaranteed performance of wire ropes ensures that people who attend amusement parks will have a good time and stay safe.
The rigging used to complete the stunts in modern movies depends on wire rope for safety. Much like in amusement rides, wire ropes protect performers from injury and harm as they hang above a scene or carry out an impossible move.
The live theater industry uses wire ropes to raise and lower curtains, support overhead rigging, and hold backdrops and scenery pieces. During a production, rapid and efficient movement is a necessity that is facilitated by the use of wire ropes.
Wire rope is a tool that we tend to envision as indestructible, unable to succumb to any form of damage. Though it is exceptionally sturdy and strong as well as capable of enduring constant use, it is just as susceptible to breakdown as any other tool.
To avoid serious harm and damage, wire ropes should be scheduled for regular inspections. There are situations that can damage or break a wire rope; these should be understood prior to the problem arising.
Guide rollers have the potential to damage and cause abrasions on wire rope if they become rough and uneven. Of the various elements of a crane and lift, guide rollers have the greatest contact with the mechanism‘s wire rope. Regular inspection of guide rollers will ensure they are not damaging the rope or causing abrasions.
Bending is normally a regular part of wire rope usage; this occurs repetitively as the rope passes through a sheave. As a wire rope traverses the sheave, it is continually bent and develops cracks or breaks. The cracking and breaking are exacerbated by movement on and off the groove of the drum. Normally, the breakage happens on the surface and is visible. Once it appears, it accelerates to the core of the rope.
A bird cage is caused by a sudden release of tension and a rebound of the rope. This type of break requires that the rope be replaced since the place of the break will not return to its normal condition.
Wire ropes are multi-layered; this makes them flexible and torque balanced. The layering inside and outside creates flexibility and wear resistance. Relative motion between the wires causes wear over time, which leads to internal breakage. The detection of these breaks can be indicated by an electromagnetic inspection that calculates the diameter of the rope.
Kinked wire rope is caused by pulling a loop on a slack line during installation or operation; this causes a distortion in the strands and wires. This is a serious condition that necessitates rope replacement.
Corrosion damage is the most difficult cause of wire rope damage to identify, which makes it the most dangerous. The main reason for corrosion is poor lubrication that can be seen in the pitted surface of the rope.
The types of damage and problems listed here are only a small portion of the problems that can be caused if a wire rope is not regularly lubricated and inspected. Various regulatory agencies require that wire ropes be inspected weekly or monthly and provide a list of factors to examine.
As with any type of heavy duty equipment, wire rope is required to adhere to a set of regulations or standards that monitor and control its use for safety and quality reasons. The two organizations that provide guidelines for wire rope use are the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
All wire rope manufacturers and users closely follow the standards and guidelines established by OSHA and ASME. In the majority of cases, they will identify the specific standards they are following in regard to their products.
OSHA‘s regulations regarding wire rope fall under sections 1910, 1915, and 1926, with the majority of the stipulations listed in 1926 under material handling, storage, use, and disposal.
"Running rope in service shall be visually inspected daily, unless a qualified person determines it should be performed more frequently. The visual inspection shall consist of observation of all rope that can reasonably be expected to be in use during the day‘s operations. The inspector should focus on discovering gross damage that may be an immediate hazard."
"The inspection frequency shall be based on such factors as rope life on the particular installation or similar installations, severity of environment, percentage of capacity lifts, frequency rates of operation, and exposure to shock loads. Inspections need not be at equal calendar intervals and should be more frequent as the rope approaches the end of its useful life. Close visual inspection of the entire rope length shall be made to evaluate inspection and removal criteria."
ASTM A1023 covers the requirements for steel wire ropes with specifications for various grades and constructions from ¼ in. (6 mm) to 31/2 in. (89 mm) manufactured from uncoated or metallic coated wire. Included are cord products from 1/32 in. (0.8 mm) to 3/8 in. (10 mm) made from metallic coated wire.
United States Federal Spec RR W 410 covers wire ropes and wire seizing strands but does not include all types, classes, constructions, and sizes of wire rope and strands that are available. The purpose of Spec RR W 410 is to cover more common types, classes, constructions, and sizes suitable for federal government use.
Wire rope and wire seizing strand covered by United States Federal Spec RR W 410 are intended for use in general hauling, hoisting, lifting, transporting, well drilling, in passenger and freight elevators, and for marine mooring, towing, trawling, and similar work, none of which are for use with aircraft.
API 9A lists the minimum standards required for use of wire rope for the petroleum and natural gas industries. The types of applications include tubing lines, rod hanger lines, sand lines, cable-tool drilling and clean out lines, cable tool casing lines, rotary drilling lines, winch lines, horse head pumping unit lines, torpedo lines, mast-raising lines, guideline tensioner lines, riser tensioner lines, and mooring and anchor lines. Well serving wire ropes such as lifting slings and well measuring are also included in API 9A.
Wire rope is a collection of metal strands that have been twisted and wound to form the shape of a helix with the purpose of supporting and lifting heavy loads and performing tasks that are too rigorous for standard wire.
Individual designs of wire rope involve different materials, wire, and strand configurations as a means for supporting and assisting in the completion of a lifting or supportive task.

Communication Cable 1)Application: for detection of fiber optic lines, to be used in low voltage circuits. 2)Material: HDPE insulated stainless steel cables 3)Construction of inside stainless steel...
Stainless Steel Wire Rope1) Material: AISI304 AISI316 2) Construction: 7x37, 1x37, 7x19, 6x19+FE, 1x19, 7x7, 6x7+FE, 1x7. 3)Diameter 0.27mm - 30.00mm 4) Packing: on reels 5) Standard: DIN3055 ...
6x7 (6/1) - Fibre Core Wire Rope6x7 construction general purpose wire rope is available with either FC (fibre core) or WSC (wire strand core). When supplied with a WSC the rope is more commonly referr...
Coated Galvanised and Stainless Steel Wire Ropes We supply a full range of wire rope covered in a range of coatings including PVC, Polypropylene and Nylon as well as special coatings which we can cons...
Compacted Wire Rope Compacted Wire Rope has been subject to a compacting process suchas drawing rolling or swageing where by the metalic cross-sectional area of thewires remains unaltered whereas th...
Cable Inner Wire Thisis Inner Wire, available for Cars, Motorcycle, Tricycle, Bicycle. Etc. Wecan offer all kind of Inner wire. A:Φ8×10 Head 2.0mm Cable for MotorcycleB: Φ6×11 Head 1.5mm Cable for...
7x7 (6/1) - Wire Strand Core Wire Rope6x7 construction general purpose wire rope is available with either FC (fibre core) or WSC (wire strand core). When supplied with a WSC the rope is more commonly ...
1x19 - Marine Grade Stainless Steel Wire Rope 1x19 AISI316 (304) stainless steel strand is a very poplar stainless steel construction. Used heavily throughout the marine industry, 1x19’s ex...
6x19 (12/6/1) - Fibre Core Wire Rope6x19 construction wire rope is available with either FC (fibre core) or WSC (wire strand core). When supplied with a wsc the rope is more commonly referred to as 7x...

Bright steel wire rope refers to general wire rope without surface treatment, free from zinc, tin, copper and other types of metallic coatings. So they are normally lubricated with grease to protect the wire rope from corroding.




 8613371530291
8613371530291