wire rope inspection pdf pricelist
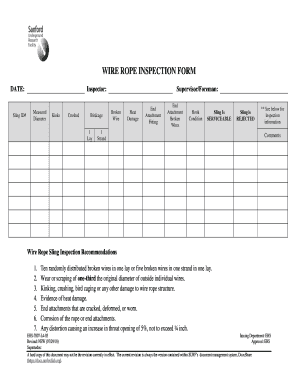
A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
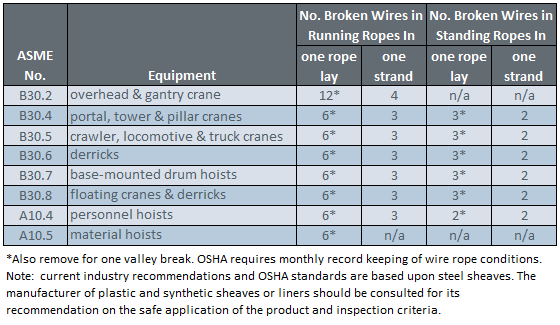
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
The inspection must include any deficiencies that the qualified person who conducts the annual inspection determines under paragraph (c)(3)(ii) of this section must be monitored.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the qualified person determines that, though not presently a safety hazard, the deficiency needs to be monitored, the employer must ensure that the deficiency is checked in the monthly inspections.
All documents produced under this section must be available, during the applicable document retention period, to all persons who conduct inspections under this section.
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. Wire rope comes in a variety of strand patterns including single layer, filler wire, seale, warrington, and combination. Wire rope strands can be laid around the core in different configurations including regular lay wire rope, lang lay wire rope, and alternate lay wire rope. There also many types of grades of wire rope, including: improved plow steel (IPS), extra improved plow steel (EIPS), and extra extra improved plow steel (EEIPS). Some types of wire rope is preferred over others due to the unique properties, including: rotation resistant wire rope, compacted strand wire rope, swaged wire rope, plastic coated wire rope, plastic impregnated (PI) wire rope.

Wire rope isa type of cablewhich is made up of several strands of metal wirelaid or twisted into a braid or helix.Do you know how often your wire rope needs to be inspected? Wire rope inspections are vital to industries that use wire rope.
One of the most important purposes of carrying out wire rope inspections or testing is to oversee the process of depreciation in the wire rope. When any depreciation or deterioration is identified these wire ropes can cease to be used immediatelybefore it becomes a hazard. A great advantage of conducting these examinations is to analyse and identify if there is unexpected corrosion and destruction.
Commonly, there is a constant increase rate in the amount of wire rope breaks, during the lifespan of that wire rope. Wire ropes need to be inspected and tested as they have a limited life, like all consumable products. Early in the life of the wire rope (when it is starting to be used), the wires and strands of the rope settle into position and the breaking strength increases. Once it has hit its maximum, the breaking strength then decreases rapidly.
Wire rope inspections should only be carried out by highly trained professionals. There are 2 ways that these inspections are carried out on crane wire rope: Visual and Non-Destructive. Visual and no-destructive examinations are equally as important but a non-destructive wire rope test is a lot less frequent than a visual wire rope inspection. Destructive testing only takes place when specifically required by a company to find out what type of wire rope something is that has not been labelled and is not common practice in the general testing/inspections.
Visual inspection of wire ropeThe visual method is a simple yet effective method to check for external damage to a crane wire rope. Visually inspecting the entire length of rope is very important. The rope should be inspected 2 to 3 feet at a time and examined carefully at each stop. Whilst inspecting the wire rope it also cleaned with Lanotec and a wire brush.
Although tedious, it can determine many visual signs of wire rope damage, such as; kinks, bird caging, cutting, knots, flattening, crushing & heat damage (burn marks, discolouration of the metal). Wearing heavy duty gloves, an inspector will grab the rope and lightly move a rag slowly along the length of rope. Broken wires will often stick out (porcupine) and will therefore snag on the rag. Should the rag snag on a wire, the inspector should the stop and visually assess the rope condition. Broken wires do not always ‘porcupine’. Visual inspections should not be the only method relied on for inspecting crane wire ropes.
Due to the composition of a wire rope, the outer layer only represents approximately 40% of the metallic cross section of the rope and only approximately half of this is visible due to the strand twisting inside and out. That means you are only able to visually examine approximately 20% of the entire rope composition. You can only assume that the other 80% is in good condition.
Although the external 20% may look in good condition it may be concealing a great number of wire breaks and internal damage. Wire ropes with internal damage that have no signs of external damage can be extremely dangerous. This is why an internal wire rope inspection should also be completed. Internal deterioration is the primary cause of many rope failures, mainly due to corrosion and the normal progress of fatigue. Single-layer stranded ropes may be opened up slightly to allow an assessment of their internal condition, provided that they are at zero tension; though, some restrictions occur with large rope sizes. Permanent damage can be caused to multi-layer wire ropes if they are opened.
Internal inspection should always be carried out by a capable person. The method of inspection consists of firmly attaching two clamping jaws of appropriate size at a suitable distance apart to the rope. During the inspection of sections of rope adjacent to terminations, it is adequate to use a single clamping jaw, since the end anchorage system, or a bar suitably located through the end portion of the termination, may be used as the second clamp.
By the application of a force to the clamping jaws in the opposite direction to the rope lay, the outer strands separate and move away from the core. Care should be taken during the opening process to ensure that the clamping jaws do not slip about the outside of the rope. The strands should not be displaced excessively. When a limited opening is achieved, a small probe, such as a screwdriver, may be used to remove grease or debris that could obstruct observation of the interior of the rope. The crucial points that should be observed are as follows:
After inspection, a service dressing should be introduced into the opened part and the clamping jaws rotated with moderate force to ensure correct replacement of the strands around the core. After removal of the jaws, the outer surface of the rope should be greased. Since it is impossible to inspect the interior of the wire rope over the whole of its length, suitable sections shall be selected.
For wire ropes that wind onto a drum, or pass over pulleys or rollers, it is recommended that the lengths that engage the pulley grooves when the appliance is in a loaded condition be inspected. Those localised lengths in which shock forces are arrested (i.e., adjacent to drum and jib head pulleys) and those lengths that are particularly exposed to the weather for long periods should be inspected. Attention should be given to the length of rope close to its termination, and this is particularly important for fixed ropes, such as stays or pendants. This is where a visual inspection is complimented by a non-destructive test. .

At CERTEX USA, we set the standard for rigging supplies, lifting products and world-class fall protection as well as the top industrial rescue courses and critical testing services. Many companies and workers around the country rely on our expansive line of quality lifting equipment and products. From wire rope to wire mesh slings, to hoists, clamps, blocks and sheaves, CERTEX USA has the lifting equipment you will need to get the job done correctly, safely and on schedule. When it comes to rigging equipment, supplies and lifting products, you shouldn’t have to worry about choosing between the highest-quality products available and the products offered at affordable prices. At CERTEX USA, we have you covered with quality lifting products at competitive prices.




 8613371530291
8613371530291