kelly bushing diagram in stock

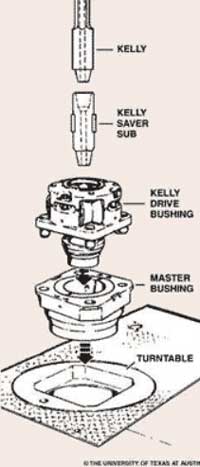
A long square or hexagonal steel bar with a hole drilled through the middle for a fluid path. The kelly is used to transmit rotary motion from the rotary table or kelly bushing to the drillstring, while allowing the drillstring to be lowered or raised during rotation. The kelly goes through the kelly bushing, which is driven by the rotary table. The kelly bushing has an inside profile matching the kelly"s outside profile (either square or hexagonal), but with slightly larger dimensions so that the kelly can freely move up and down inside.

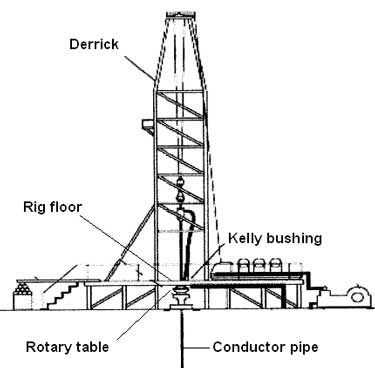
Because wells are not always drilled vertically, there may be two “depths” for every given point in a wellbore: the measured depth (MD) measured along the path of the borehole, and the true vertical depth (TVD), the absolute vertical distance between the datum and the point in the wellbore. In perfectly vertical wells, the TVD equals the MD; otherwise, the TVD is less than the MD measured from the same datum. Common datums used are ground level (GL), drilling rig floor (DF), rotary table (RT), kelly bushing (KB) and mean sea level (MSL). [1]
Kelly Bushing Height (KB):The height of the drilling floor above the ground level. Many wellbore depth measurements are taken from the Kelly Bushing. The Kelly bushing elevation is calculated by adding the ground level to the Kelly bushing height.

The NOV CUL & CB Casing Bushings are inserted directly into the rotary table and insure that the casing being run is perfectly aligned with the center of the hole. Model CU is a solid bushing and model CB is a split bushing. All of the bushings accept bowls of different sizes to accommodate a wide range of casing. Using CMS-XL or CP-S slips, since these bushings fit into the rotary table, the casing string can be easily rotated during cementing operations.
The global kelly drive market was valued at $1.6 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 3.7% from 2022 to 2031.
Report Key HighlightersThe kelly drive market is consolidated in nature with few players such as NOV Inc., SANY Group, BAUER Maschinen GmbH (Subsidiary of BAUER Group), Jereh Global Development LLC (As a Subsidiary of Jareh Group) and Liebherr-International Deutschland GmbH. that hold significant share of the market.
The study covers in-depth analysis of 16 countries from different regions including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. In addition, country-wise data of every country has been provided for better understanding of kelly drive market dynamics in every country.
A kelly drive is a particular kind of well drilling tool which uses a section of pipe with a polygonal or splined outer surface and feeds it through a rotary table and matching kelly (mating) bushing which have the same shape or splines. The Kelly is a long, four- or six-sided steel bar having a hole bored through the center to allow drilling fluid to pass through. The kelly bushing allows the drill string to be lifted or lowered while it rotates by transferring rotating motion from the rotary table or kelly bushing to the drill string. Crewmembers make up several attachments to the kelly. The attachments include the upper kelly cock, the lower kelly cock (drill pipe safety valve), and the kelly saver sub.
Kelly drilling is one of the most used dry rotary drilling techniques. The kelly drive is used to create large-diameter bored piles (from a size of approx. 500 mm). With the increasing drilling activities is booting the kelly drive market share in coming year. The kelly drive works with almost any kind of rock and soil. According to kelly drive market forecast, the demand for short rotary drilling instruments, such as augers, core barrels, buckets, and specialized drilling tools which are used to move the dirt will be more in the market. The drill rod which is also known as a kelly bar, is a typical component of this drilling technique. The strong kelly bars enables deep drilling and help in boosting the kelly drive market trend in forecast period.
Globally, there has been a surge in oil exploration activity, which is driving the demand for kelly drive in rig and drilling industry. Apart from the pandemic time, a boom in exploration has tripled over the last five years. Kelly drive market analysis showcase the owing to a global boom in exploration of oil reserves, several oil companies are getting into the rig sector. With the ongoing expansion in petroleum products, large oil extraction companies are contracting with drilling equipment manufacturers for the rent and sale of drilling equipment. Oil exploration companies and equipment companies collaborate to provide offshore support services that can increase production. Factor such as oil exploration activities is likely to boost the market for kelly drive in near future.
Advances in technology and equipment have enabled more oil and natural gas to be recovered from the length of each well, improving production and reducing the environmental footprint of energy production. Kelly drive is cheaper however, technology is slow, inefficient, and unsafe as compared to the other technology which are present or coming in the market. These factors may restrain customers from using kelly drive; thus, hampering the market growth.
With combination of seismic surveys and drilling wells, companies are doing the search of oil reserve and deposits beneath the surface of the earth. Exploration projects can be expensive, time-consuming, and risky, drilling a well may cost tens of millions of dollars. Several factors are considered the number of wells to be drilled, recovery method, type of installation to be used, separation systems for the gas & fluids, and how the oil and gas will be transported to a processing facility. High demand for the petroleum products in the market resulting into several new excavations projects in different regions. This factor is anticipated to increase the sales of kelly drive; thus, creating lucrative kelly drive market opportunities.
The kelly drive market is segmented into product type, and region. On the basis of product type, the market is bifurcated into cleaners, braking oil, grease and lubes, degreaser, and others. Region-wise, the market is studied across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
In 2021, the square kelly segment was the largest revenue generator, and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.6% during the forecast period. With the increasing horizontal drilling operations result in increasing demand for square kelly in the market. To increase the output from a single well, drilling square kelly equipment are being used frequently in the market. Square Kelly is advantageous for end-users, however equipment can be used for both onshore and offshore drilling operations. Drilling activities are becoming more challenging which are demanding the high quality of kelly equipment. Several oil firms engage in new types of drilling on land, such as horizontal well drilling which covers a significantly larger area under the earth. With the increasing horizontal well drilling creates the opportunity for square kelly segment in global kelly drive market.
In 2021, the kelly bar segment was the largest revenue generator, and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.0% during the forecast period. With the increasing number of excavation projects and finding of deep oil reserves will increase the demand for kelly bars in the market. Companies are entering into the agreement for the drilling operations which is driving the kelly bars market. Today, reserves are found very deep under the land of sea which require the high strength bars for handling the pressure. Vertical and horizontal drilling activities are increasing which is increasing the demand for different shapes of kelly bars.
The North America kelly drive market size is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The region is experiencing more drilling activities of oil and gas extraction as the demand for oil-related goods rises worldwide. Kelly drive equipment is particularly helpful for drilling through hard rock and getting to the oil deposits. The Kelly Drive can be used to reduce operational expenses in drilling operations. For field operators and engineers, it ensures long-term project success and a high rate of return.
LAMEA was the second-largest contributor in terms of revenue in the global kelly drive market in 2021, and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% during the forecast period. Accelerated investment across the upstream sector along with crude oil price recovery will foster the drilling activities in the region. Robust growth in petrochemical products demand along with increase in industrial and commercial activities across the developing economies will boost the kelly drive market growth in LAMEA region.
The leading players operating in the global kelly drive market include, NOV Inc., SANY Group, BAUER Maschinen GmbH (Subsidiary of BAUER Group), Jereh Global Development LLC (As a Subsidiary of Jareh Group) and Liebherr-International Deutschland GmbH, Bridges Equipment LTD, Lake Petro., TEXAS INTERNATIONAL OILFIELD TOOLS, LTD, Goldman, Tianhe Oil Group Co. Ltd., XI"AN KINGWELL OILFIELD MACHINERY CO.,LTD, El Didi Group.
It outlines the current Kelly drive market trends and future estimations from 2021 to 2031 to understand the prevailing opportunities and potential investment pockets.
The invasion of Russia has further worsened an already precarious scenario for the energy and drilling markets, notably in Europe. To minimize the possibility of an interruption in Russian oil and gas supply, oil and gas corporations must collaborate with governments. In longer term, the sector needs to increase its adaptability and relevance in a rapidly evolving energy environment. The scenario brought about by the conflict between Russia and Ukraine influences the Kelly Drive market as well. Many projects that were previously underway in the nations are now on hold, and new projects are being delayed, which has slowed the market"s expansion in recent years.

KELLY WIPERS Kelly Size HOP, HOS Weight Hex Wt [inches] Square P/N [lbs/kg] P/N [lbs/kg] 3" API 8-0260 4 / 1.8 8-0320 4 / 1.8 3.1 /2" API 8-0265 4 / 1.8 8-0285 4 / 1.8 4.1 /4" API 8-0170 3.5 / 1.6 8-0275 3.5 / 1.6 5.1 /2" API 8-0300 3 / 1.4 8-0305 3 / 1.4 6" API 8-0200 3 / 1.4 8-0240 3 / 1.4KELLY BUSH ING SAFETY GUARDFits Rotary Tables with HOP-HOS kelly Bushings.For 17.1/2" - 27.1/2" Rotary Table P/N 15794For 37.1 /2" Rotary Table P/N 16951For 49.1 /2" Rotary Table P/N 16953
MPCH MASTER BUSHrNGThe 37. 1/2" MPCH is a Pin Drive Hinged Master Bushing specially designed for floating andsemi-submersible drilling operations.With insert bowl No. 3 and optional insert bowls No. 1 and No. 2, the MPCH will handle 2.3/8" to13.3/8" OD drill collars, tubing and casing.Unit come complete with No. 3 insert bowl, bit breaker adapter plate and lifting sling PN 6699.
Part P/N Weight [lbs/kg] Complete 4200 / 1905 MPCH with # 3 bowl and SDXL slips Body only 3200 / 1452 Insert Bowl No. 1: 13.3/8" to 11.3/4" 6610 336 / 152 Insert Bowl No. 2: 10.3/4" to 9.5/8" 6609 470 / 213 Insert Bowl No. 3: API 8.5/8" and smaller 6608 625 1283 Lifting sling for insert bowls 1021 46 / 22* See selection chartMSPC MASTER BUSHINGThe 27.1 /2" MSPC is a solid Body Pin Drive Master Bushing designed for all drilling operations.The pin drive allows the kelly bushing to ride on top of the rotary table and permits extendedbowls to be used for better slip back up. With the extended API insert bowl No. 3, the MSPC MPCH with bit breaker adapter platewill handle 2.3/8" thru 8.5/8" OD drill pipe, drill collars, tubing and casing . Insert bowl No. 2 canhandle tubulars from 9.5/8" to 10.3/4" OD; while insert bowl No. 1 is good for 11.3/4" to 13.3/8"OD. Unit comes with No. 3 insert bowl, bit breaker adapter plate and lifting sling PN 6699.
MSP MASTER BUSHINGSMSP 27 .1/2" SPLIT PIN DRIVE BUSHINGS*MSP 27.1 /2 Split Pin Drive bushings are also available. With the larger rotary opening thestandard No. 3 Extended API taper is used. This allows the use of extra-long SDXL slips required MSPfor heavier loads. Weight 1600 lbs / 726 kg.* See selection chart

DEN-CON 27 RPH Kelly Bushing is used with Den-Con Pin Drive Master-Casing Bushings for 23" through 49 1/2" Rotary Tables. The 27 RPH has 3 5/16 " diameter drive pins (API) and 25 3/4" pin centers (API) and will handle Kelly sizes 3" to 6" square and 3" to 6" hex.
DEN-CON 20 RPH Kelly Bushing is used with Den-Con Pin Drive Master Casing Bushings for 20 1/2" to 22 1/2" Rotary Tables. The 20 RPH has 2 1/2" diameter drive pins (API) and 23" pin centers (API).
SSB Master Bushings and all Master Bushings having a drive square dimension of 13 9/16" (API). This bushing uses the same roller assemblies, components and wiper assemblies as the 27 RPH. All RH Series Parts & Components Interchange with Varco HD Series Bushing Parts.
A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

All CategoriesAdapters (20)B.O.P. (4)Bit Breakers (4)Casing (52)Drill Collars (51)Drill Pipe (77)Downhole/Tubulars (1)Elevators (10)Flanges (13)Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (49)Hooks (5)Insert Bowl (1)Kelly Bushing (5)Kellys (3)Pony Collars (4)Pumps (1)Pup Joints (5)Rams (10)Rotary Tables (1)Spools (6)Stabilizers (1)Stabilizers, Non-Mag (2)Subs, Bits (24)Subs, Cross-Over (43)Subs, Double Pin (22)Subs, Double Pin Kick (2)Subs, Lift (23)Subs, Pump-In Outlet (3)Subs, Saver (4)Tubing (8)Valves (2)Wash Pipe (1)

A 27-year-old gas drilling rig worker died on May 23, 2003 from blunt force trauma to the head, neck, and chest during a cleanout operation at the well. At the time of the incident, the victim was working within eight feet of the kelly on the drilling rig floor. Compressed air was used to blow out the conductor pipe, but due to a lack of communication, the compressor was turned on before the valves were prepared to control the flow of debris out of the hole. The excess pressure caused the kelly bushing, drillpipe slips, and debris to be blown out of the rotary table. The victim was struck by these objects and was pronounced dead on arrival to the hospital.
A 27-year-old gas drilling rig worker died on May 23, 2003 from blunt force trauma to the head, neck, and chest after he was struck by the kelly bushing and drillpipe slips. OKFACE investigators reviewed the death certificate, related local news articles, and reports from the sheriff’s office, Medical Examiner, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA),
At the time of the incident, the rig floor and working surfaces were level and dry; the weather was warm with light to no wind. The victim was working with four other crew members on a gas drilling rig, wearing the necessary personal protective equipment (e.g., steel toe boots, hard hat, eye protection). Prior to the incident, the decedent was assigned the task of driller and was asked to find the bottom of the conductor hole with the kelly (Figure 2). The kelly is used to transmit power (rotary motion) from the rotary table and kelly bushing to the drillstring (Table 1). After unlatching the brake handle, the driller allowed the kelly to free fall to the bottom. The uncontrolled fall caused the kelly to become jammed with debris, such as water, mud, and other material, that had collected in the conductor hole since the time it was originally drilled for the well. As a result, a cleanout operation became necessary. Cleanout procedures involving air or mud drilling fluid are acceptable norms in the oil and gas drilling industry; however, drilling fluid is more commonly used than compressed air.
a long square or hexagonal steel bar with a hole drilled through the middle for a fluid path; goes through the kelly bushing, which is driven by the rotary table
After the kelly became jammed, a senior driller was assigned to take over the brake handle and kelly; however, the decedent remained approximately eight feet away on the rig floor. A newly hired, yet experienced, derrickman had the job of running the air compressor. While the drillers were switching positions, the derrickman realized that he had not started that particular type of compressor in quite some time and left the rig floor to seek help from another driller onsite.
In normal cleanout operation procedures, certain valves are closed prior to turning on the compressed air, which allows control over the flow of debris out of the hole and into a catch pond. Once the valves are prepared, the driller indicates to the derrickman that the area is ready for the compressed air. At some point between the senior driller preparing for cleanout and the derrickman leaving the floor to turn on the air compressor, there was a lack of communication and the air compressor was activated without the senior driller’s knowledge, prior to the prescribed valves being shut. After starting the air compressor, the derrickman returned to the rig floor and, as he walked to his next assignment, the rotary table erupted. The pressure normally used to complete the cleanout work is a minimum of 20 pounds per square inch. Within minutes, the kelly had pressurized well beyond this point to 150 pounds per square inch. The victim, who was still on the rig floor in close proximity to the kelly, was also unaware that the air compressor had been turned on. The compressed air, at full pressure with no valves closed to control or direct the flow, blew the kelly bushing, drillpipe slips, and debris out of the rotary table; all of which struck and landed on the victim.




 8613371530291
8613371530291