kelly bushing oil and gas supplier

Please send us your inquiry with detail item description or with Model number. If there is no packing demand we take it as our regular exported standard packing. We will offer you an order form for filling. We will recommend you the most suitable model according to information you offered.
We can give you really high quality products with competitive price. We have a better understanding in Chinese market, with us your money will be safe.

The Kelly Drive Bushing acts as an adapter that serves to connect the rotary table to the Kelly. The Kelly bushing has an inside diameter profile that matches that of the Kelly, usually square or hexagonal. It is connected to the rotary table by four large steel pins that fit into mating holes in the rotary table. The rotary motion from the rotary table is transmitted to the bushing through the pins, and then to the kelly itself through the square or hexagonal flat surfaces between the Kelly and the Kelly drive bushing. The Kelly then turns the entire drillstring because it is screwed into the top of the drillstring itself.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

All CategoriesAdapters (20)B.O.P. (4)Bit Breakers (4)Casing (52)Drill Collars (51)Drill Pipe (77)Downhole/Tubulars (1)Elevators (10)Flanges (13)Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (49)Hooks (5)Insert Bowl (1)Kelly Bushing (5)Kellys (3)Pony Collars (4)Pumps (1)Pup Joints (5)Rams (10)Rotary Tables (1)Spools (6)Stabilizers (1)Stabilizers, Non-Mag (2)Subs, Bits (24)Subs, Cross-Over (43)Subs, Double Pin (22)Subs, Double Pin Kick (2)Subs, Lift (23)Subs, Pump-In Outlet (3)Subs, Saver (4)Tubing (8)Valves (2)Wash Pipe (1)

Jiangsu Xinxiang share Co., Ltd was founded in 1994, its predecessor was established in 1955, it‘s located in high-tech industrial concentration zone of Nantong City, Jiangsu Province; near to a new developing international deep-water port Yangkou Port which commitment to ship 200,000 tons goods; world famous modern city Shanghai is only 2.5 hours away from it by car; company registered capital is 60,000,000 RMB, the total assets is 119.85 million RMB, it covers an area of 160,000 square meters and currently over 500 employees. Jiangsu Xinxiang Share Co., Ltd is "self-import and export enterprise", "private technology enterprises in Jiangsu Province", "high-tech enterprises in Jiangsu Province", it is top ten companies of the first national large and medium-sized industrial enterprises in independent innovation capacity of the industry; it accessed to API7, 7K, 8A, 8C, and has the right to use the logo, and also passed the ISO9001:2000 quality system certification in the earlier stage within the same industry.

Our company produces all kinds of bushings, including casing bushings, kelly bushings and so on. Casing bushings are manufactured with high-strength heat treated steel. They"re specially designed to work with NOV rotary equipment and handling tools. With interchangeable insert bowls, these casing bushings can accommodate casing sizes from 16 inches up to 42 inches in diameter. There are three standard types for choice. Models CU and CUL are solid bushings, while the Model CB is a split bushing. These bushings are available for 17 1/2 in to 49 1/2 in rotary tables. In the operation, casing bushings are inserted directly into the rotary table to ensure that the casing runs perfectly with the center of the hole.
As a professional China casing bushings, kelly bushings and other oil drilling tools manufacturer, Jiangsu Kayson Petrol- Machinery Co., Ltd becomes a first-level supply member of Chinese Petroleum & Natural Gas Consortium. At the same time, it"s also the member of China Petrochemical Material Resources Market. And it has achieved the right for products import and export.

A large valve, usually installed above the ram preventers, that forms a seal in the annular space between the pipe and well bore. If no pipe is present, it forms a seal on the well bore itself. See blowout preventer.†
One or more valves installed at the wellhead to prevent the escape of pressure either in the annular space between the casing and the drill pipe or in open hole (for example, hole with no drill pipe) during drilling or completion operations. See annular blowout preventer and ram blowout preventer.†
A heavy, flanged steel fitting connected to the first string of casing. It provides a housing for slips and packing assemblies, allows suspension of intermediate and production strings of casing, and supplies the means for the annulus to be sealed off. Also called a spool.†
A pit in the ground to provide additional height between the rig floor and the well head to accommodate the installation of blowout preventers, ratholes, mouseholes, and so forth. It also collects drainage water and other fluids for disposal.†
The arrangement of piping and special valves, called chokes, through which drilling mud is circulated when the blowout preventers are closed to control the pressures encountered during a kick.†
A centrifugal device for removing sand from drilling fluid to prevent abrasion of the pumps. It may be operated mechanically or by a fast-moving stream of fluid inside a special cone-shaped vessel, in which case it is sometimes called a hydrocyclone.†
A centrifugal device, similar to a desander, used to remove very fine particles, or silt, from drilling fluid. This keeps the amount of solids in the fluid to the lowest possible level.†
The hoisting mechanism on a drilling rig. It is essentially a large winch that spools off or takes in the drilling line and thus raises or lowers the drill stem and bit.†
The cutting or boring element used in drilling oil and gas wells. Most bits used in rotary drilling are roller-cone bits. The bit consists of the cutting elements and the circulating element. The circulating element permits the passage of drilling fluid and uses the hydraulic force of the fluid stream to improve drilling rates.†
A heavy, thick-walled tube, usually steel, used between the drill pipe and the bit in the drill stem. It is used to put weight on the bit so that the bit can drill.†
The heavy seamless tubing used to rotate the bit and circulate the drilling fluid. Joints of pipe 30 feet long are coupled together with tool joints.†
A wire rope hoisting line, reeved on sheaves of the crown block and traveling block (in effect a block and tackle). Its primary purpose is to hoist or lower drill pipe or casing from or into a well. Also, a wire rope used to support the drilling tools.†
On diesel electric rigs, powerful diesel engines drive large electric generators. The generators produce electricity that flows through cables to electric switches and control equipment enclosed in a control cabinet or panel. Electricity is fed to electric motors via the panel.†
A large, hook-shaped device from which the elevator bails or the swivel is suspended. It is designed to carry maximum loads ranging from 100 to 650 tons and turns on bearings in its supporting housing.†
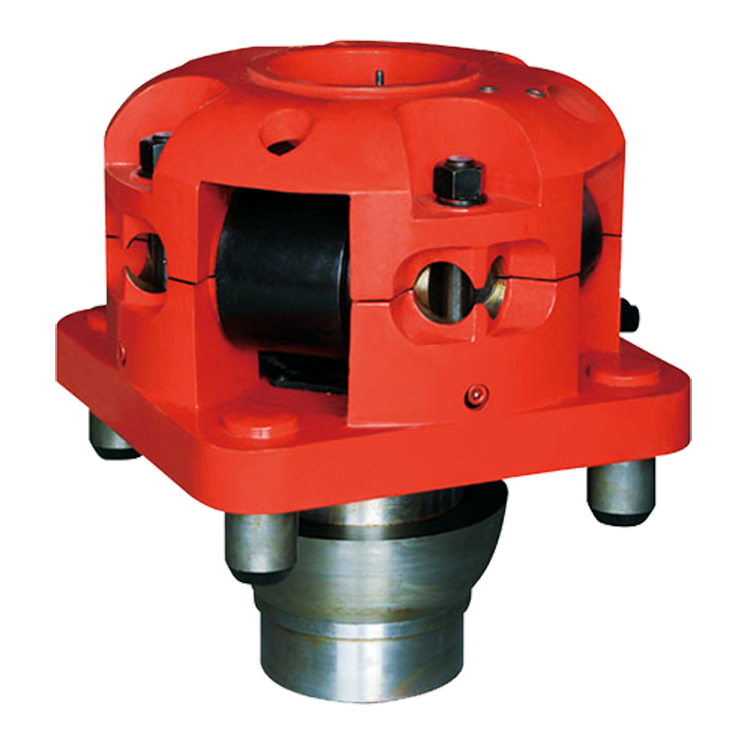
A device fitted to the rotary table through which the kelly passes. It is the means by which the torque of the rotary table is transmitted to the kelly and to the drill stem. Also called the drive bushing.†
A portable derrick capable of being erected as a unit, as distinguished from a standard derrick, which cannot be raised to a working position as a unit.†
A series of open tanks, usually made of steel plates, through which the drilling mud is cycled to allow sand and sediments to settle out. Additives are mixed with the mud in the pit, and the fluid is temporarily stored there before being pumped back into the well. Mud pit compartments are also called shaker pits, settling pits, and suction pits, depending on their main purpose.†
A trough or pipe, placed between the surface connections at the well bore and the shale shaker. Drilling mud flows through it upon its return to the surface from the hole.†
A diesel, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), natural gas, or gasoline engine, along with a mechanical transmission and generator for producing power for the drilling rig. Newer rigs use electric generators to power electric motors on the other parts of the rig.†
A hole in the rig floor 30 to 35 feet deep, lined with casing that projects above the floor. The kelly is placed in the rathole when hoisting operations are in progress.†
A mud pit in which a supply of drilling fluid has been stored. Also, a waste pit, usually an excavated, earthen-walled pit. It may be lined with plastic to prevent soil contamination.†
The hose on a rotary drilling rig that conducts the drilling fluid from the mud pump and standpipe to the swivel and kelly; also called the mud hose or the kelly hose.†
The principal component of a rotary, or rotary machine, used to turn the drill stem and support the drilling assembly. It has a beveled gear arrangement to create the rotational motion and an opening into which bushings are fitted to drive and support the drilling assembly.
A series of trays with sieves or screens that vibrate to remove cuttings from circulating fluid in rotary drilling operations. The size of the openings in the sieve is selected to match the size of the solids in the drilling fluid and the anticipated size of cuttings. Also called a shaker.†
Wedge-shaped pieces of metal with teeth or other gripping elements that are used to prevent pipe from slipping down into the hole or to hold pipe in place. Rotary slips fit around the drill pipe and wedge against the master bushing to support the pipe. Power slips are pneumatically or hydraulically actuated devices that allow the crew to dispense with the manual handling of slips when making a connection. Packers and other down hole equipment are secured in position by slips that engage the pipe by action directed at the surface.†
A relatively short length of chain attached to the tong pull chain on the manual tongs used to make up drill pipe. The spinning chain is attached to the pull chain so that a crew member can wrap the spinning chain several times around the tool joint box of a joint of drill pipe suspended in the rotary table. After crew members stab the pin of another tool joint into the box end, one of them then grasps the end of the spinning chain and with a rapid upward motion of the wrist "throws the spinning chain"-that is, causes it to unwrap from the box and coil upward onto the body of the joint stabbed into the box. The driller then actuates the makeup cathead to pull the chain off of the pipe body, which causes the pipe to spin and thus the pin threads to spin into the box.†
A vertical pipe rising along the side of the derrick or mast. It joins the discharge line leading from the mud pump to the rotary hose and through which mud is pumped going into the hole.†
A rotary tool that is hung from the rotary hook and traveling block to suspend and permit free rotation of the drill stem. It also provides a connection for the rotary hose and a passageway for the flow of drilling fluid into the drill stem.†
The large wrenches used for turning when making up or breaking out drill pipe, casing, tubing, or other pipe; variously called casing tongs, rotary tongs, and so forth according to the specific use. Power tongs are pneumatically or hydraulically operated tools that spin the pipe up and, in some instances, apply the final makeup torque.†
The top drive rotates the drill string end bit without the use of a kelly and rotary table. The top drive is operated from a control console on the rig floor.†

The NOV CUL & CB Casing Bushings are inserted directly into the rotary table and insure that the casing being run is perfectly aligned with the center of the hole. Model CU is a solid bushing and model CB is a split bushing. All of the bushings accept bowls of different sizes to accommodate a wide range of casing. Using CMS-XL or CP-S slips, since these bushings fit into the rotary table, the casing string can be easily rotated during cementing operations.
The NOV CUL & CB Casing Bushings are inserted directly into the rotary table and insure that the casing being run is perfectly aligned with the center of the hole. Model CU is a solid bushing and model CB is a split bushing. All of the bushings accept bowls of different sizes to accommodate a wide range of casing. Using CMS-XL or CP-S slips, since these bushings fit into the rotary table, the casing string can be easily rotated during cementing operations.

The JOTKB MODEL 27 PDHD OR 20 PDHD are developed for pin drive master bushing for rotary table sizes from 27-1/2" to 49-1/2" having 25-3/4" and 23" dia pin center. This unit is used for heavy duty drilling operations and high torque conditions on off shore as well as on shore drilling operations, and handle Kelly sizes from 3" to 6" Square or Hexagonal.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
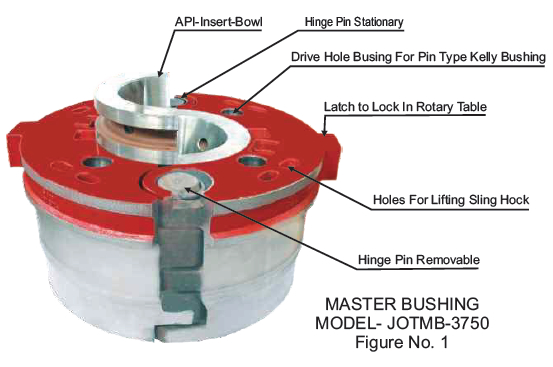
Kelly bushing is that elevated device positioned right on top of the rotary table and used to transmit torque from the rotary table to the kelly. The kelly bushing is designed to be the connection between the rotary table and the kelly. The kelly is a 4 or 6 sided steel pipe.
The purpose of the rotary table is to generate the rotary action (torque) and power necessary to rotate the drillstring and drill a well. The torque generated by the rotary table is useless if it is not transferred to the kelly (the drillstring is connected to the kelly).
Hence, through the kelly bushing the torque generated at the rotary table is transferred to the kelly. To achieve this connection, the inside profile of the kelly bushing matches the outer profile of the kelly so that the kelly fits or “sits” comfortably in the kelly bushing.
There are various designs for the kelly bushing including the split type, the pin-drive type and the square-drive type. Each of these designs has different ways in which they are connected and disconnected from the rotary table.
The internal diameter of the kelly bushing can be cut into the shape of a square (4-sided) or a hexagon (6-sided) depending on the outer shape of the kelly that will be used. The internals of a Kelly bushing is designed to resemble the outer shape of a Kelly just like the insides of a key lock is cut to exactly match the outer shape of the key.
The kelly bushing is not designed to hold tightly onto the Kelly; the kelly is still permitted to move up and down through the kelly bushing. This requirement is a must since drilling cannot progress if the kelly remains on a fixed spot. As the well is drilled deeper, the kelly also moves downward through the Kelly bushing.
The kelly bushing is sometimes used as a reference point from which depth measurements can be taken. All depths must be recorded with respect to a reference point; the kelly bushing (KB) is one of the depth references used in the oil and gas industry.
The top of the kelly bushing is normally used as the depth reference.For example, 7500ft KB means 7500ft below the kelly bushing or 7500ft measured from the top of the kelly bushing down to that point in the well.
In some other cases, depths could be recorded as 7500ft MDBKB meaning 7500ft measured depth below the kelly bushing. This is mostly used when the measured depth is different from the true vertical depth of the well, common with deviated and horizontal wells.

A. Hexagonal Kelly Conforming To API Spec 7-1 & Bearing the API Monogram Mark, Manufactured from AISI 4145 H API Modified Alloy Steel from Specially Straightened Kelly Bars, Full Length Quenched and Tempered, Brinell Hardness: 285-341, and with the Following Specification:
A.3. The Connections shall be with Stress Relief Grooves on Pin End, Bore Back Box And Cold Rolled Phosphatised Threads, Complete with Pressed Steel Protectors on both ends.
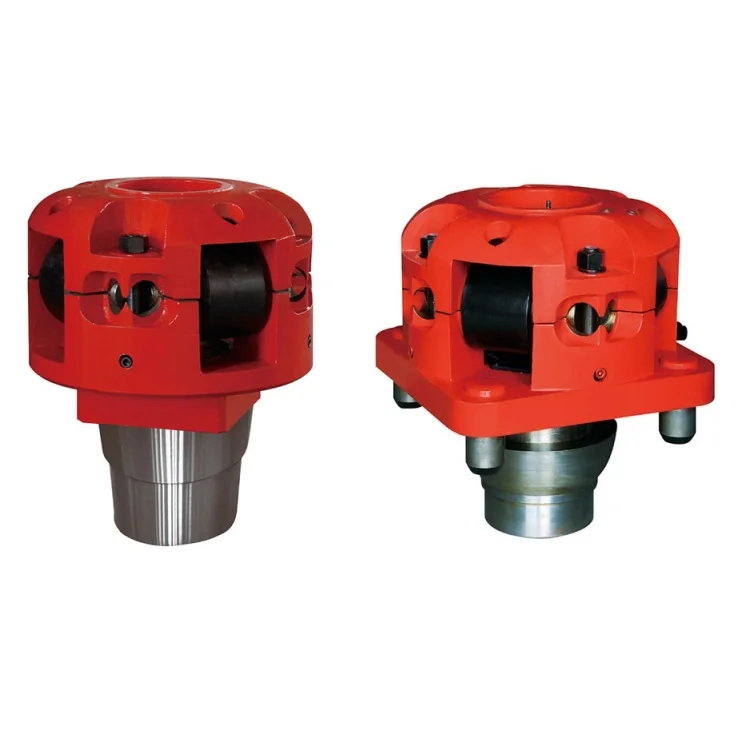
Square Drive Roller Kelly Bushing Conforming To API Spec 7k & Suitable for 5.1/4" (133.35 Mm) Hexagonal Kelly, Complete with Rollers Wrench and Wiper Assembly. The Kelly is to be Used with 27.1/2" (698.50 Mm) Rotary Table with Square Drive Master Bushing.
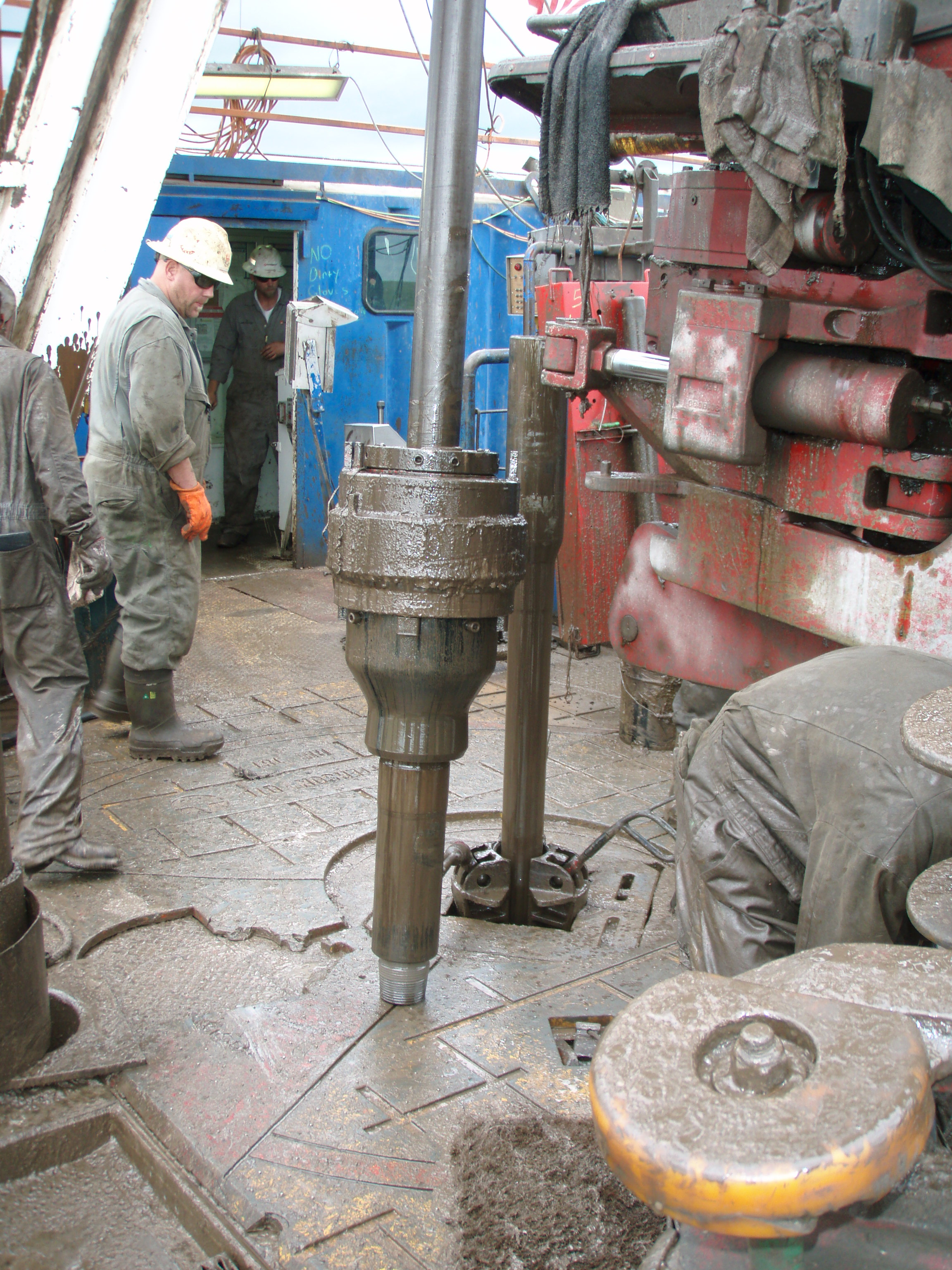

Roller Kelly Bushings are designed and manufactured as per API Spec 7K "Drilling and Well Servicing Equipment" for driving Kelly in the drilling operation.
Roller kelly bushings are constructed in upper body half, low body half, rollers, rollers pin and etc., can be available in square drive or pin drive. Square drive roller kelly bushing designed with taper contact surface in low body half, while pin drive roller kelly bushing designed with pin to be installed in low body half.
According to torque of drilling, roller kelly bushing can be available in heavy duty, medium duty and light duty, heavy duty bushings are for high torque and high speed drilling operations while medium duty and light duty are for medium or shadow depth drilling operations.
Roller kelly bushings can accommodate square Kelly or hex Kelly, for square Kelly, the bushing is designed with four flat rollers, and for hex Kelly, the bushing is designed with two V-shaped rollers and two flat rollers. By changing roller size, roller kelly bushing can accommodate square Kelly from 2½" to 5¼" or hex Kelly from 3" to 6", and can be installed in rotary table range from 17½" to 37½".

Figure 8.06 shows a schematic diagram of a typical top-drive rig. In a top-drive drilling rig, the top-drive (Item 6 in Figure 8.06) is suspended from the traveling block (Item 5 in Figure 8.06) and attached to a guide system (gear train and rail system) on the derrick. The top-drive is an electrical motor that has the ability to travel vertically up and down and to impart torque to the drill pipe. These drilling rigs began to appear in the late 1990s. Although the top-drive supplies the torque for the system, a rotary table is still used to supply stability to the drill string and as a redundant (back-up) rotary system.
As we saw in our discussion of a Conventional Rotary Table Rigs, the next 30-foot joint of drill pipe to be added to the drill string is temporarily stored in the mousehole on the rig floor. This joint of drill pipe is added to the drill string when drilling ahead or tripping into the wellbore. Tripping is the process of running drill pipe into or out of the hole for purposes other than drilling ahead. For example, if a drill bit needs to be changed due to wear, then the entire drill string needs to be pulled from the wellbore (tripping out of the hole), the drill bit needs to be replaced, and the drill string needs to be run back into the wellbore (tripping into the hole) to resume normal drilling operations. You can imagine how much ineffective rig time (in terms of not drilling ahead) is used tripping into or out of the wellbore and making or breaking connections in the drill string–particularly if the well"s TD (Total Depth) is 10,000–15,000 feet (or a shallower well has a 10,000-foot horizontal section).
Note: On the website linked above, you can select a name from the list or a number on the graphic to see a definition and a more detailed photo of the object.
The improved efficiencies coming from a top-drive is that an entire 90-foot stand (or triple) of drill pipe can be connected to the drill string rather than a single 30-foot joint. This is because the top-drive can go to the full height of the derrick using the traveling block to connect to the entire stand of drill pipe. Note, however, that not all top-drives use a triple when connecting drill pipe; some use a Double (two joints), while others use a single joint from a mousehole.
Figure 8.07: Rig Components - showing Kelly, Kelly Bushing, Rotary Table, Mousehole, and Rat Hole (screen capture at 9 seconds of the Drilling Training video)
In the screen capture shown in Figure 8.07, we see many of the components discussed in this lesson: the kelly, kelly bushing, rotary table, mousehole, and rat hole. Throughout the video, you can see these components of the rig used in action.
In the screen capture shown in Figure 8.09, we see the mechanical tongs (red). As shown in the video, the mechanical tongs are used to grip the kelly and drill string to aid in uncoupling (unscrewing) the two.
What I like about this clip, and the reason that I selected it, was because of the “non-standard operating procedure” that seems to be occurring in the video. Did you spot it?
At around 2:52 into the video, it appears that while two of the roughnecks were trying to remove the slips from the master bushing, the hoist system on the derrick was attempting to assist them by lifting the kelly and drill pipe to release pressure from the slips. Instead of freeing the slips, the hoist appears to have lifted the entire section of the rig floor covering the rotary table, along with the two roughnecks. You can hear someone laughing in the video.
At around 3:31 into the video, one of the roughnecks and the hoist appear to use a piece of drill pipe to tamp the section of rig floor back into place. This piece of drill pipe is then placed into the mousehole as the next piece of drill pipe to be connected to the drill string. This is not a standard operating procedure on the rig floor. After this incident, you can see the rotary table and kelly bushing rotating in the manner discussed in these lesson notes.
In this video, you can see two roughnecks connecting Doubles (two joints) of drill pipe to the drill string as they trip into the wellbore. You can tell that they are connecting doubles by counting the joints as they go into the wellbore. You can also tell that they are tripping into the hole because as they add the new drill pipe, they just run it into the hole and do not drill.
The improved efficiency of the top-drive rigs comes from its ability to connect longer sections of drill pipe during tripping and drilling operations. This is done in less rig time and with less cost than a conventional rig. The two major advantages of a top-drive drilling rig are:
Extended Reach Drilling enables wells with long horizontal or near-horizontal lengths to be drilled through the reservoir in a more efficient manner than in the past. These long horizontal wells are one of the technology enhancements that has resulted in the “shale boom” in the U.S. domestic oil and gas industry in formations such as the low permeability Marcellus Shale in western Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. The other technological advancement required for the shale boom was the ability to stimulate these extended reach wells with multiple hydraulic fractures (as we discussed in Lesson 7).




 8613371530291
8613371530291