mud pump pressure calculation in stock

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.

NOTE: Max RPM in the above equation varies according to type of pump, size of stroke, and other variables. Duplex pumps often run about 100 RPM Max. while triplex pumps will run somewhere between 100 RPM Max and 400 RPM Max.
I have a reciprocating pump and I know what my max rated rod load is (in foot pounds). I also know what size plunger size my pump has. What PSI will my pump produce?
Specific Gravity is used when sizing a centrifugal pump. Liquids with a specific gravity greater than 1.0 are heavier than water and conversely, liquids with a specific gravity lower than 1.0 are lighter weight than water and will generally float on water.

Oil and Gas drilling process - Pupm output for Triplex and Duplex pumpsTriplex Pump Formula 1 PO, bbl/stk = 0.000243 x ( in) E.xample: Determine the pump output, bbl/stk, at 100% efficiency for a 7" by 12". triplex pump: PO @ 100%,= 0.000243 x 7 x12 PO @ 100% = 0.142884bbl/stk Adjust the pump output for 95% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 95 + 100 = 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.142884bbl/stk x 0.95 PO @ 95% = 0.13574bbl/stk Formula 2 PO, gpm = [3(D x 0.7854)S]0.00411 x SPM where D = liner diameter, in. S = stroke length, in. SPM = strokes per minute Determine the pump output, gpm, for a 7" by 12". triplex pump at 80 strokes per minute: PO, gpm = [3(7 x 0.7854) 1210.00411 x 80 PO, gpm = 1385.4456 x 0.00411 x 80 PO = 455.5 gpm
Example:Duplex Pump Formula 1 0.000324 x (liner diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk -0.000162 x (rod diameter, in) x ( stroke lengh, in) = ________ bbl/stk Pump out put @ 100% eff = ________bbl/stk Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2" by 14" duplex pump at 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0": 0.000324 x 5.5 x 14 = 0.137214bbl/stk -0.000162 x 2.0 x 14 = 0.009072bbl/stk Pump output @ 100% eff. = 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: Decimal equivalent = 85 100 = 0.85 PO@85%)= 0.128142bbl/stk x 0.85 PO@ 85% = 0.10892bbl/stk Formula 2
PO. bbl/stk = 0.000162 x S[2(D) - d] where S = stroke length, in. D = liner diameter, in. d = rod diameter, in. Example: Determine the output, bbl/stk, of a 5 1/2". by 14". duplex pump @ 100% efficiency. Rod diameter = 2.0in.: PO@100%=0.000162 x 14 x [ 2 (5.5) - 2 ] PO @ 100%)= 0.000162 x 14 x 56.5 PO@ 100%)= 0.128142bbl/stk Adjust pump output for 85% efficiency: PO@85%,= 0.128142bb/stkx 0.85 PO@8.5%= 0.10892bbl/stk Metric calculation Pump output, liter/min = pump output. liter/stk x pump speed, spm. S.I. units calculation Pump output, m/min = pump output, liter/stk x pump speed, spm. Mud Pumps Mud pumps drive the mud around the drilling system. Depending on liner size availability they can be set up to provide high pressure and low flow rate, or low pressure and high flow rate. Analysis of the application and running the Drill Bits hydraulics program will indicate which liners to recommend. Finding the specification of the mud pumps allows flow rate to be calculated from pump stroke rate, SPM. Information requiredo Pump manufacturer o Number of pumps o Liner size and gallons per revolution Weight As a drill bit cutting structure wears more weight will be required to achieve the same RoP in a homogenous formation. PDC wear flats, worn inserts and worn milled tooth teeth will make the bit drill less efficiently. Increase weight in increments of 2,000lbs approx. In general, weight should be applied before excessive rotary speed so that the cutting structure maintains a significant depth of cut to stabilise the bit and prevent whirl. If downhole weight measurements are available they can be used in combination with surface measurements to gain a more accurate representation of what is happening in the well bore.

Density of the Kick, ppg = initial mud weight, ppg – (initial stabilized drillpipe pressure, psi – initial stabilized casing pressure, psi)/(0.052 x Length of the kick, ft)
Riser margin is = (drilling fluid gradient to control the formation pressure with riser, psi/ft x depth of the hole (TVD), ft – seawater gradient, psi/ft
The purpose of this article is to present some guidelines and simplified techniques to size pumps and piping typically used in mud systems. If unusual circumstances exist such as unusually long or complicated pipe runs or if very heavy or viscous drilling muds are used, a qualified engineer should analyze the system in detail and calculate an exact solution.
To write about pumps, one must use words that are known and well understood. For example, the label on the lefthand side of any centrifugal pump curve is Total Head Feet. What does this mean?
Total Head remains constant for a particular pump operated at a constant speed regardless of the fluid being pumped. However, a pump’s pressure will increase as the fluid density (mud weight) increases according to the following relationship:
Note that the pump pressure almost doubled. It follows that the required pump horsepower has increased by the same percentage. If the pump required 50 HP for water service, it will require the following horsepower for 16 lb/gal mud:
To summarize, a pump’s Total Head remains constant for any fluid pumped, only the pump pressure and pump horsepower will change. Therefore, a pump motor must be sized according to the heaviest weight mud to be pumped.
In our example problem, the required desilter pressure head is 75 ft. for any mud weight. However, the pressure would be 30.3 PSIG for water or 43.6 PSIG for 12 lb mud or 58.1 PSIG for 16 lb mud. A good rule of thumb is that the required pressure (PSIG) equals 4 times the mud weight (12 LB/GAL x 4 = 48 PSIG).
Determine the required pressure head and flow rate. If the pump is to supply a device such as a mud mixing hopper or a desilter, consult the manufacturer’s information or sales representative to determine the optimum flow rate and pressure head required at the device. (On devices like desilters the pressure head losses downstream of the device are considered negligible and are usually disregarded.)
Select the basic pump to pump the desired flow rate. Its best to refer to a manufacturer’s pump curve for your particular pump. (See example – Figure 3).
The pump’s impeller may be machined to a smaller diameter to reduce its pressure for a given application. Refer to the manufacturer’s pump curves or manufacturer’s representative to determine the proper impeller diameter. Excessive pressure and flow should be avoided for the following reasons:
The pump must produce more than 75 FT-HD at the pump if 75 FT-HD is to be available at the desilter inlet and the pump’s capacity must be at least 800 GPM. Therefore, we should consider using one of the following pumps from the above list: 4″ x 5″ Pump 1750 RPM – 1000 GPM at 160 FT-HD; or 5″ x 6″ Pump 1750 RPM – 1200 GPM at 160 FT-HD.
The pump suction and discharge piping is generally the same diameter as the pump flange diameters. The resulting fluid velocities will then be within the recommended ranges of 4 to 10 FT/SEC for suction lines and 4 to 12 FT/
SEC for discharge lines. Circumstances may dictate that other pipe diameters be used, but remember to try to stay within the above velocity guidelines. Smaller pump discharge piping will create larger pressure drops in the piping
and the pump may not be able to pump the required amount of fluid. (For example, don’t use a 4″ discharge pipe on a 6″ x 8″ pump and expect the pump’s full fluid flow.)
6″ pipe may be used for the suction pipe since it is relatively short and straight and the pump suction is always flooded. 6″ pipe is fully acceptable for the discharge pipe and is a good choice since the desired header is probably 6″ pipe.
8″ pipe may be used for the suction pipe (V = 5.13 FT/SEC) since V is still greater than 4 FT/SEC. 8″ pipe would be preferred if the suction is long or the suction pit fluid level is low with respect to the pump.

Pumps tend to be one of the biggest energy consumers in industrial operations. Pump motors, specifically, require a lot of energy. For instance, a 2500 HP triplex pump used for frac jobs can consume almost 2000 kW of power, meaning a full day of fracking can cost several thousand dollars in energy costs alone!
So, naturally, operators should want to maximize energy efficiency to get the most for their money. Even a 1% improvement in efficiency can decrease annual pumping costs by tens of thousands of dollars. The payoff is worth the effort. And if you want to remotely control your pumps, you want to keep efficiency in mind.
In this post, we’ll point you in the right direction and discuss all things related to pump efficiency. We’ll conclude with several tips for how you can maintain pumping efficiency and keep your energy costs down as much as possible.
In simple terms, pump efficiency refers to the ratio of power out to power in. It’s the mechanical power input at the pump shaft, measured in horsepower (HP), compared to the hydraulic power of the liquid output, also measured in HP. For instance, if a pump requires 1000 HP to operate and produces 800 HP of hydraulic power, it would have an efficiency of 80%.
Remember: pumps have to be driven by something, i.e., an electric or diesel motor. True pump system efficiency needs to factor in the efficiency of both the motor AND the pump.
Consequently, we need to think about how electrical power (when using electric motors) or heat power (when using combustion engines) converts into liquid power to really understand pump efficiency.
Good pump efficiency depends, of course, on pump type and size. High-quality pumps that are well-maintained can achieve efficiencies of 90% or higher, while smaller pumps tend to be less efficient. In general, if you take good care of your pumps, you should be able to achieve 70-90% pump efficiency.
Now that we have a better understanding of the pump efficiency metric, let’s talk about how to calculate it. The mechanical power of the pump, or the input power, is a property of the pump itself and will be documented during the pump setup. The output power, or hydraulic power, is calculated as the liquid flow rate multiplied by the "total head" of the system.
IMPORTANT: to calculate true head, you also need to factor in the work the pump does to move fluid from the source. For example, if the source water is below the pump, you need to account for the extra work the pump puts in to draw source water upwards.
*Note - this calculation assumes the pump inlet is not pressurized and that friction losses are minimal. If the pump experiences a non-zero suction pressure, or if there is significant friction caused by the distance or material of the pipe, these should be factored in as well.
Every foot of water creates an additional 0.434 PSI of pressure, so we"ll find the elevation head by converting the change in elevation in feet to the suction pressure created by the water.
You"ll notice that the elevation head is minimal compared to the discharge pressure, and has minimal effect on the efficiency of the pump. As the elevation change increases or the discharge pressure decreases, however, elevation change will have a greater impact on total head.
Obviously, that’s a fair amount of math to get at the pump efficiency, considering all of the units conversions that need to be done. To avoid doing these calculations manually, feel free to use our simple pump efficiency calculator.
Our calculations use static variables (pump-rated horsepower and water source elevation) and dynamic variables (discharge flow and pressure). To determine pump efficiency, we need to measure the static variables only once, unless they change.
If you want to measure the true efficiency of your pump, taking energy consumption into account, you could add an electrical meter. Your meter should consist of a current transducer and voltage monitor (if using DC) for electrical motors or a fuel gauge for combustion. This would give you a true understanding of how pump efficiency affects energy consumption, and ultimately your bank account.
Up until this point, we’ve covered the ins and outs of how to determine pump efficiency. We’re now ready for the exciting stuff - how to improve pump efficiency!
One of the easiest ways to improve pump efficiency is to actually monitor pumps for signs of efficiency loss! If you monitor flow rate and discharge (output power) along with motor current or fuel consumption, you’ll notice efficiency losses as soon as they occur. Simply having pump efficiency information on hand empowers you to take action.
Another way to increase efficiency is to keep pumps well-maintained. Efficiency losses mostly come from mechanical defects in pumps, e.g., friction, leakages, and component failures. You can mitigate these issues through regular maintenance that keeps parts in working order and reveals impending failures. Of course, if you are continuously monitoring your pumps for efficiency drops, you’ll know exactly when maintenance is due.
You can also improve pump efficiency by keeping pumps lubricated at all times. Lubrication is the enemy of friction, which is the enemy of efficiency (“the enemy of my enemy is my friend…”).
A fourth way to enhance pump efficiency is to ensure your pumps and piping are sized properly for your infrastructure. Although we’re bringing this up last, it’s really the first step in any pumping operation. If your pumps and piping don’t match, no amount of lubricant or maintenance will help.
Pipes have physical limits to how much fluid they can move at a particular pressure. If pipes aren’t sized properly, you’ll lose efficiency because your motor will have to work harder. It’s like air conditioning - if your ductwork isn’t sized appropriately for your home, you’ll end up paying more on your energy bill.
In this post, we’ve given you the full rundown when it comes to calculating and improving pump efficiency. You can now calculate, measure, and improve pump efficiency, potentially saving your business thousands of dollars annually on energy costs.
For those just getting started with pump optimization, we offer purpose-built, prepackaged solutions that will have you monitoring pump efficiency in minutes, even in hazardous environments.

A measure of the energy per unit of time that is being expended across the bit nozzles. It is commonly calculated with the equation HHP=P*Q/1714, where P stands for pressure in pounds per square in., Q stands for flow rate in gallons per minute, and 1714 is a conversion factor necessary to yield HHP in terms of horsepower. Bit manufacturers often recommend that fluid hydraulics energy across the bit nozzles be in a particular HHP range, for example 2.0 to 7.0 HHP, to ensure adequate bit tooth and bottom-of-hole cleaning (the minimum HHP) and to avoid premature erosion of the bit itself (the maximum HHP).
How do you control a kick when drilling a well? In today’s video blog we learn what kill weight mud is, why it is useful, and how to calculate it. Be sure to watch the video above and subscribe to our youtube channel, but if you’re pressed for time, feel free to utilize the quick summary below.
A kill weight mud is a mud with a density high enough to produce a hydrostatic pressure at the point of influx, or where the kick is entering the wellbore, that will be sufficient enough to shut in the well and thus killing the well. Your kill weight mud (KWM) is the mud weight that will allow you to keep control of your well during times where a kick may be occurring.

REASON: This is the mud engineers Bible on the rig. It is based on prior knowledge of all drilling parameters and gives you a step by step plan for present well being drilled. It would guide you all though the drilling process.
Study your silos, pits, mud tanks, storage tank names, its contents, volume, dead volume capacity, properties of their contents (mud: especially Mud weight).
REASON: You don’t want to be taken unawares, you need to know the type of mud you have in each pit (where your backup mud is, kill mud if any, premix, etc.), you need to be sure you have enough mud to reach TD (Total depth) most especially if the logistics of transporting mud to the rig n’est pas facile, or takes days to arrive. Finally without knowing the properties of the mud you are introducing to the active system you would not be sure if what is affecting your active mud system is coming from the formation or from the mud you are introducing to the active mud.
REASON: You need to be sure the shaker screens can handle the flow if the mud is cold if not temporarily screen down to a lower size mesh or ask the driller to reduce the flow rate if permissible.
REASON: Drilling fluids would normally splash the rig crew on the rig floor while pulling and racking back pipes when a stand is removed from the drill string. So a slug (same mud but with 2-2.5 ppg higher density) would be prepared in the slug tank, and pumped into the drill string. This keeps the fluids level inside the drill pipe below the surface when tripping drill pipe.
For a leak off test (LOT), the mud has to be circulated to obtain uniform weight and condition. The primary concern for the mud engineer is to ensure an equal mud weight all through the mud. Mud weight going in to the hole should be equal to mud weight coming out of the hole at the shakers.
REASON: The well needs to be properly monitored. Instead speak with the mud loggers to convert the pit you want to transfer fluid from to the active system from a Reserve pit to an Active pit on their system then you can gradually make your transfers that way all volumes would be shown as active pit volume.
REASON: If the amount and average specific gravity of the solids in both fluids (i.e. the density) are different the mud weight would be a good indicator of the fluids interface during a displacement.
REASON: Calculate your hole volume, that means equal amount of mud on surface will leave you pit, so get the derrick man or personnel assisting you in the pit room to inform you when hole volume has been pumped.
REASON: Using a technique called nephelometry the turbidity can be measured. When light hits a particle the energy is scattered in all directions, it measures the level of light scattered by particles at right angles to the incident light beam. Initial NTU readings of both fluids would be the reference point for identification. After the Hi-vis passes through the driller should be told to stop pumping when the initial NTU of the filtered brine has been achieved.
For water based mud with a low alkalinity use phenolphthalein also. Add it to the mud and check for change of color to pink to know when traces of cement are on surface.
REASON: Note differences in weight between mud, spacer and cement before displacement of cement. The mud weight difference between the three fluids is a good indicator of the fluids interface on surface.
REASON: The first step is removal of cuttings from the borehole and the drilling fluid after which the mud should be condition before placing cement in the wellbore, either the density (not compromising well control) or the rheology depending on the situation. For the rheology, the yield stress, gel strength and plastic viscosity would be reduced hence reducing the driving forces necessary to displace mud with increased mud flexibility while being careful to prevent barite settling.
REASON: With no pit space to store the equivalent mud volume being replaced down hole, all pit levels should be recorded at all stages during the cement job. You would need to visit the pit room and return to the cement unit (while measuring cement density) at appropriate moments.
Measure all tank volumes before cement job i.e. when the mud has been thinned down and pump has been stopped (pit static). In case of leaks or valve mistakes all pits should be recorded.
If we get full returns during cementing it means that the cement displaced equal amount of mud and there was no loss down hole due to the cement job or due to displacement.
Prior to running casing, calculate the displacement of the casing first to know the volume it would displace, calculating from the mud line up to the casing depth.
REASON: From the cement program calculate the total volume of the fluids /cement that would be pumped into the hole that is not mud so as to confirm tank space to receive equal volume from the hole. If no available tank space/storage space then OBM should be back-loaded before the cement job to create space.
REASON: If it’s the pay zone, losses would require the use of acid-soluble LCM to prevent formation damage. Also considering down hole tools and motors, certain concentrations of LCM pills would not be pumped to avoid plugging/damaging the tools unless a bypass tool is part of the BHA.
Bit balling occurs in soft gumbo / swelling shales while drilling, the shale adsorbs water from the mud it then becomes plastic with a ball of compacted shale building up and covering the whole bit, stabilizers and drill collars, thus preventing further drilling progress.
To be certain it’s a bit balling issue we are dealing with the mud engineer should observe some of the following or collect the following information from the following rig personnel, with the first 3 information from the driller being very important:
To prevent bit balling from occurring it is advisable to adopt procedures that worked in your geographical area in overcoming bit balling by always reviewing previous drilling mud report (DMR).
· Use mud system that can inhibit clay swelling example: Formulating KCl mud with PHPA (to avoid using higher concentrations of KCl) in which KCl prevents clay swelling while PHPA (partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide ) coats the shales surfaces (encapsulates) thereby inhibiting their dispersion and incorporation into the mud.7
· “When drilling gumbo, the pH should be maintained at 9.0-10.0. If bit balling occurs, increase the mud alkalinity (PM) to 5 or more with lime”.8
· “If all else fails, before you trip out of the hole, you might pump a walnut-hull sweep. It will tend to sandblast the bit and remove the ball, and won’t hurt the mud. Don’t try this if you are running small jets in the bit, as plugging can be an issue.”11
A Drilling fluids Engineer should be able to observe or carry out a test and subsequently identify the reason for a high or a low mud weight in a water-base mud or an oil-base mud system.
Before looking at the reason why the mud weight reduced or increased from the given mud program specification, it’s good to know that the major function of drilling fluids is to provide sufficient pressure to check influx of gas, oil, and water into the well bore from the drilled formation.
The hydrostatic head of the mud column must be at least equal to that of the formation pressure, and hopefully greater, but not so high as to cause loss of circulation (except where an over balanced / under balanced drilling are specifically desired).
The mud weight materials could be barite, calcium carbonate or soluble salts such as sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl) and calcium chloride (CaCl2). Sometimes the desired mud weight can be achieved by combining additions of salts and barite.
a. Mud Weight (Density) Test: The mud balance may indicate that mud weight is too high or too low. b. Retort Test: The test may indicate that the percent solids by volume is high, and your solids content calculations (lb/bbl low and high gravity solids) may indicate that barite content is too high or too low. c. Rheology tests: Indicates increase or decrease in viscosity
a. Increase in pump pressure: This can indicate an increase in Mud weight. b. Change in penetration rate: Increase in penetration rate may indicate decrease in mud weight while decrease in penetration rate may indicate increase in mud weight. c. Gas bubbles: This definitely indicates decrease in mud weight.

Formulas displayed in this section are commonly used in wellcontrol calculation. The first formulas (1-29) have similar reference numbers to those used in the IWCF formula sheets
Overbalance (bar) x [Riser or Casing Capacity (l/m)- Closed End Displacement (l/m))] / [Drilling Mud Gradient (bar/m) x Closed End Displacement (l/m)]

Pump Output per Stroke (PO): The calculator returns the pump output per stroke in barrels (bbl). However this can be automatically converted to other volume units (e.g. gallons or liters) via the pull-down menu.
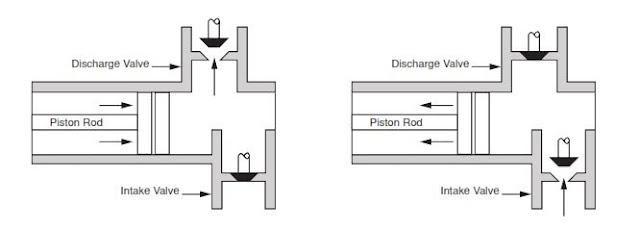
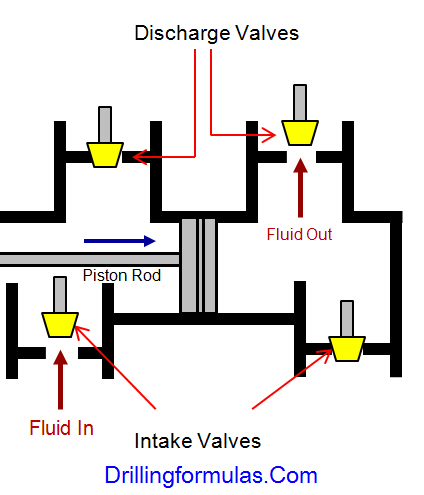
A triplex mud (or slush) pump has three horizontal plungers (cylinders) driven off of one crankshaft. Triplex mud pumps are often used for oil drilling.




 8613371530291
8613371530291