drilling mud pump selection quotation
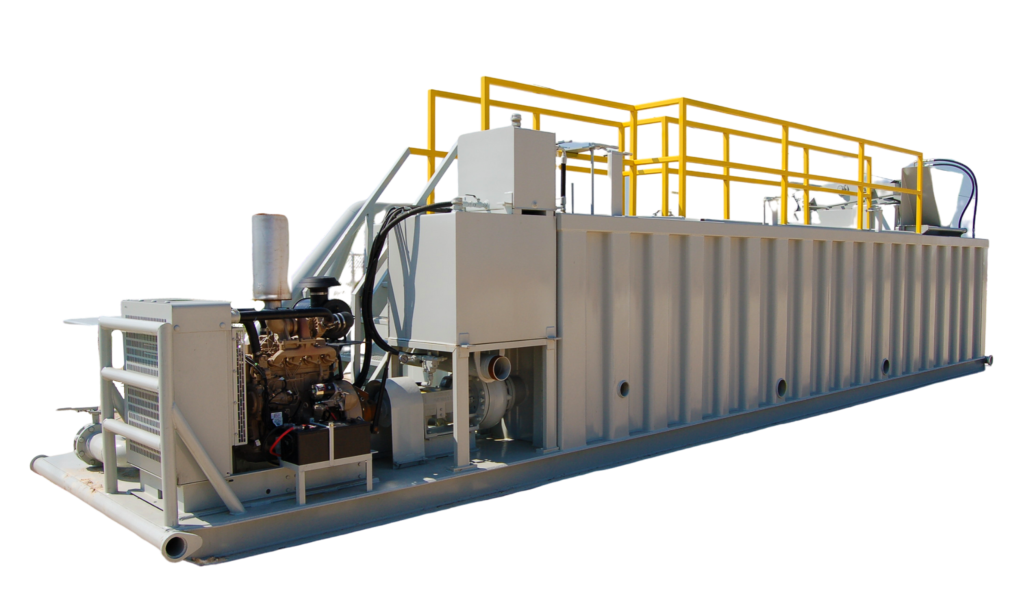
Having a quality mud pump is a critical part of keeping your oil well drilling system running as smoothly as possible. Dragon carries a wide range of mud pumps for systems of all kinds and jobs of all sizes. We also carry a 50 BPM mud mixing table to make drilling fluid mixing more efficient and accurate so you can always get the job done safely and correctly. View our full well service pump and mud pump selection to find the right system for your job site, or check out the rest of our drilling rigs for even more options.

During drilling in Oil and Gas exploration, drilling mud or Bentonite is pumped into boreholes for multiple reasons. Pumping drill mud into boreholes cools the drill bit as well as bringing drill cuttings to the surface as the way in which mud is pumped into boreholes forms a closed loop system. The use of drilling mud also provides hydrostatic pressure to prevent liquids such as oil and gas rising to the surface, as drilling mud is thixotropic meaning when it is not agitated it stiffens forming a mud which is an effective liquid and gas barrier.
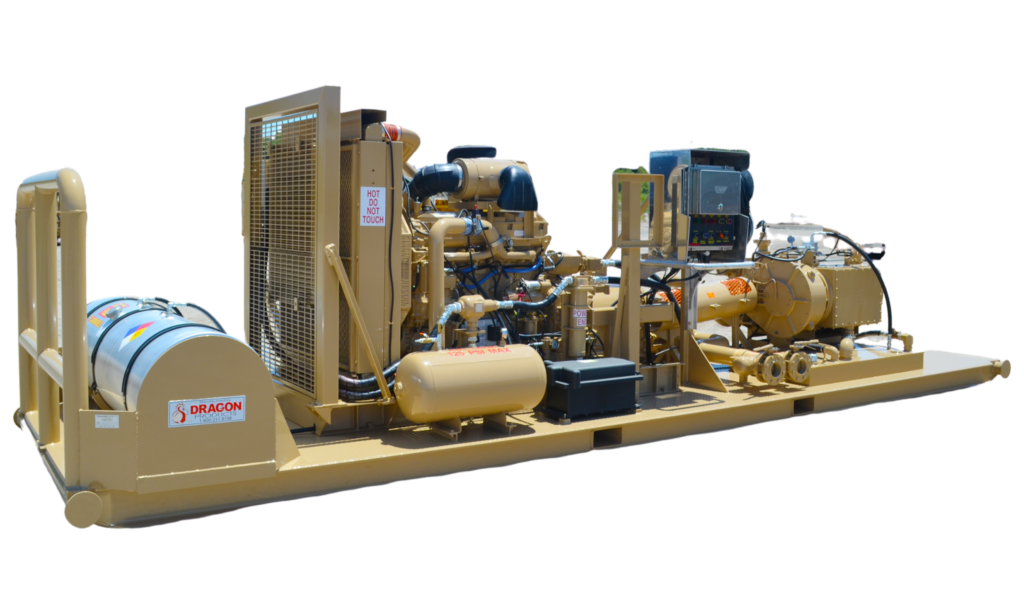

Welcome to Pickett Oilfield’s mud pumps web page. Our company has been in the oil & gas drilling equipment industry for over 38 years, supplying new and used mud pumps and mud pump parts to customers in practically every producing region in the world. We are here to serve all your drilling equipment needs – if you don’t see it on this site, just give us a call or email. We can get it, if you need it!
Pickett Oilfield, LLC offers prospective buyers and extensive selection of quality new and used oil & gas drilling equipment, including mud pumps and parts to choose from at competitive prices. Browse our inventory of mud pumps and mud pump parts for sale at competitive rates.For more information or to request a quote, please Contact Us at 936-336-5154 or email to Sales@PickettOilfield.com.
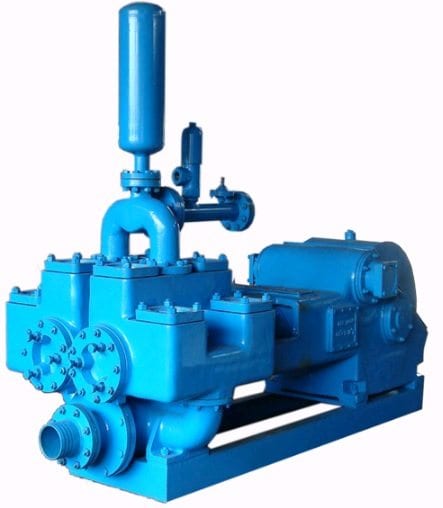

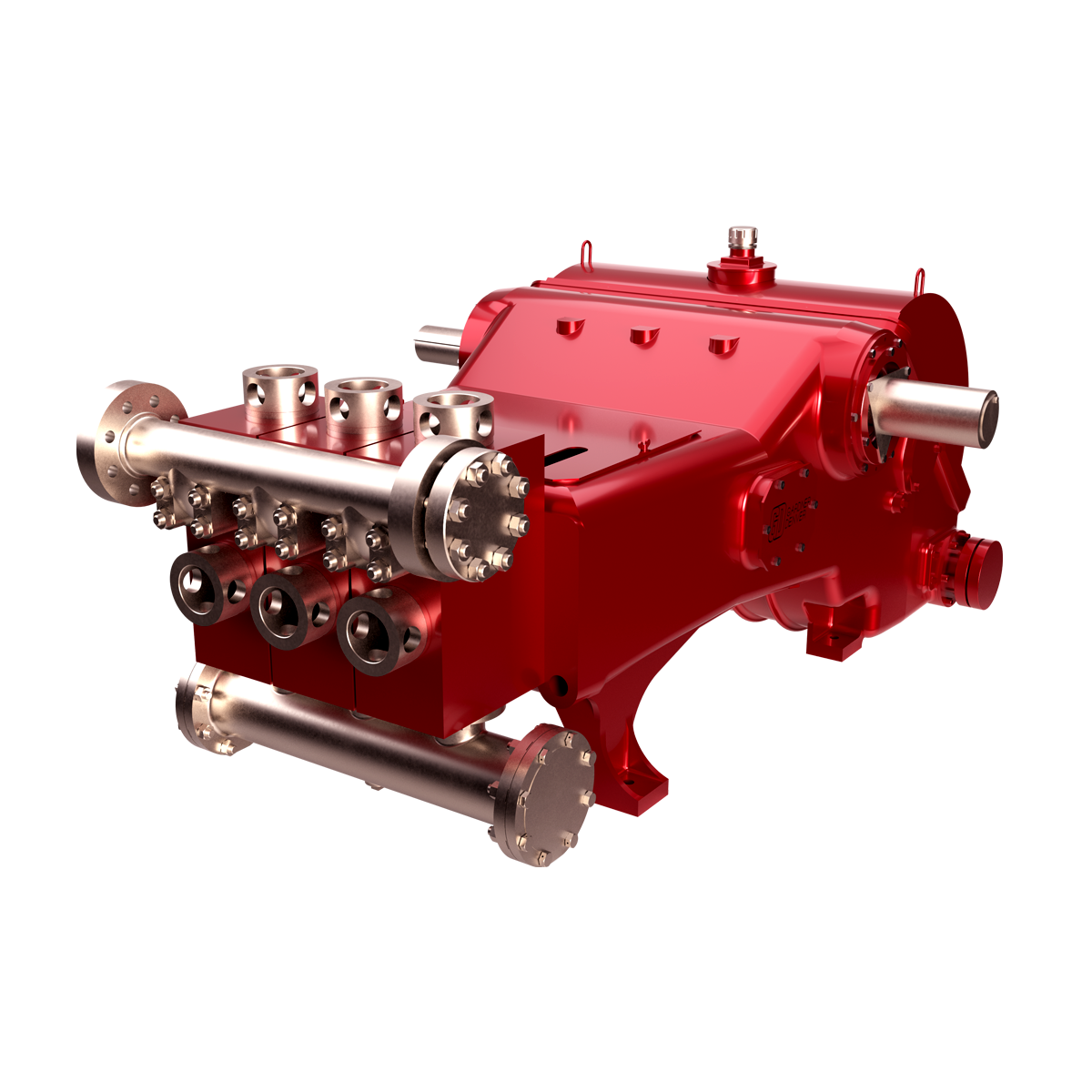
A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.

Mud pump liner selection in today"s drilling operations seldom (at best) considers electrical implications. Perhaps, with more available useful information about the relationships between mud pump liner size and operational effects on the electrical system, certain potential problems can be avoided. The intent of this paper is to develop those relationships and show how they affect an electrical system on example SCR rigs.Introduction
There, seems to be little consideration for the relationships between liner size and demand on a rig"s engine/generator set(s). Yet, consideration for this relationship can prove to be very helpful to drillers and operators in efficiency of a rig"s electrical system. In order to develop the relationships and help drillers and operators understand the importance of each, relationships between liner size, pump speed, pump pressure, and electrical power will be developed. Only basic physical laws will be used to develop the relationships; and, once developed, the relationships are readily applied to realistic examples utilizing a mud pump manufacturer"s pump data. Finally, conclusions will be drawn from the examples.DEVELOPMENT OF RELATIONSHIPS BASIC RELATIONSHIPS
where HHP= Hydraulic horsepower, GPM = Mud pump volumetric flow rate in gallons per minute, and PST Mud pump output pressure in pounds peer square inch.
Hydraulic horsepower is reflected to the mud pump motor via a multiplier for mechanical efficiency. it follows that motor horsepower is then represented by
AfghanistanAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntarcticaAntigua and BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBonaire, Sint Eustatius and SabaBosnia and HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCabo VerdeCambodiaCameroonCanadaCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos IslandsColombiaComorosCongoCongo, Democratic Republic of theCook IslandsCosta RicaCroatiaCubaCuraçaoCyprusCzechiaCôte d"IvoireDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEswatiniEthiopiaFalkland IslandsFaroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard Island and McDonald IslandsHoly SeeHondurasHong KongHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIranIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, Democratic People"s Republic ofKorea, Republic ofKuwaitKyrgyzstanLao People"s Democratic RepublicLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacaoMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesiaMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorth MacedoniaNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayOmanPakistanPalauPalestine, State ofPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarRomaniaRussian FederationRwandaRéunionSaint BarthélemySaint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da CunhaSaint Kitts and NevisSaint LuciaSaint MartinSaint Pierre and MiquelonSaint Vincent and the GrenadinesSamoaSan MarinoSao Tome and PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint MaartenSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth SudanSpainSri LankaSudanSurinameSvalbard and Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandSyria Arab RepublicTaiwanTajikistanTanzania, the United Republic ofThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad and TobagoTunisiaTurkmenistanTurks and Caicos IslandsTuvaluTürkiyeUS Minor Outlying IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuelaViet NamVirgin Islands, BritishVirgin Islands, U.S.Wallis and FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweÅland Islands

The drilling industry has roots dating back to the Han Dynasty in China. Improvements in rig power and equipment design have allowed for many advances in the way crude oil and natural gas are extracted from the ground. Diesel/electric oil drilling rigs can now drill wells more than 4 miles in depth. Drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to help transfer the dirt or drill cuttings from the action of the drilling bit back to the surface for disposal. Drill cuttings can vary in shape and size depending on the formation or design of the drill bit used in the process.
Watch the video below to see how the EDDY Pump outperforms traditional pumps when it comes to high solids and high viscosity materials commonly found on oil rigs.
Solids control equipment including shakers, hydro-cyclones, and centrifuges are utilized to clean the drill cuttings from the drilling fluid, which then allows it to be reused and recirculated. The circuit includes the mixing of the drilling fluid in the rig tanks.
The drilling fluid is prepared to control fluid loss to the formation by the addition of chemicals or mineral agents. Commercial barite or other weighting agents are added to control the hydrostatic pressure exuded on the bottom of the well which controls formation pressures preventing fluid or gas intrusion into the wellbore.
The fluid is charged into high-pressure mud pumps which pump the drilling mud down the drill string and out through the bit nozzles cleaning the hole and lubricating the drill bit so the bit can cut efficiently through the formation. The bit is cooled by the fluid and moves up the space between the pipe and the hole which is called the annulus. The fluid imparts a thin, tough layer on the inside of the hole to protect against fluid loss which can cause differential sticking.
The fluid rises through the blowout preventers and down the flowline to the shale shakers. Shale shakers are equipped with fine screens that separate drill cutting particles as fine as 50-74 microns. Table salt is around 100 microns, so these are fine cuttings that are deposited into the half-round or cuttings catch tank. The drilling fluid is further cleaned with the hydro-cyclones and centrifuges and is pumped back to the mixing area of the mud tanks where the process repeats.
The drill cuttings contain a layer of drilling fluid on the surface of the cuttings. As the size of the drill cuttings gets smaller the surface area expands exponentially which can cause rheological property problems with the fluid. The fluid will dehydrate and may become too thick or viscous to pump so solids control and dilution are important to the entire drilling process.
One of the most expensive and troubling issues with drilling operations is the handling, processing, and circulation of drilling mud along with disposing of the unwanted drill cuttings. The drilling cuttings deposited in the half round tank and are typically removed with an excavator that must move the contents of the waste bin or roll-off box. The excavators are usually rented for this duty and the equipment charges can range from $200-300/day. Add in the cost for the day and night manpower and the real cost for a single excavator can be as much as $1800/day.
Offshore drilling rigs follow a similar process in which the mud is loaded into empty drums and held on the oil platform. When a certain number of filled drums is met, the drums are then loaded onto barges or vessels which take the drilling mud to the shore to unload and dispose of.
Oil field drilling operations produce a tremendous volume of drill cuttings that need both removal and management. In most cases, the site managers also need to separate the cuttings from the drilling fluids so they can reuse the fluids. Storing the cuttings provides a free source of stable fill material for finished wells, while other companies choose to send them off to specialty landfills. Regardless of the final destination or use for the cuttings, drilling and dredging operations must have the right high solids slurry pumps to move them for transport, storage, or on-site processing. Exploring the differences in the various drilling fluids, cutting complications, and processing options will reveal why the EDDY Pump is the best fit for the job.
The Eddy Pump is designed to move slurry with solid content as high as 70-80 % depending on the material. This is an ideal application for pumping drill cuttings. Drill cuttings from the primary shakers are typically 50% solids and 50% liquids. The Eddy Pump moves these fluids efficiently and because of the large volute chamber and the design of the geometric rotor, there is very little wear on the pump, ensuring long life and greatly reduced maintenance cost for the lifetime of the pump.
plumbed to sweep the bottom of the collection tank and the pump is recessed into a sump allowing for a relatively clean tank when the solids are removed. The Eddy Pump is sized to load a roll-off box in 10-12 minutes. The benefit is cuttings handling is quicker, easier, safer, and allows for pre-planning loading where the labor of the solids control technician is not monopolized by loading cuttings. Here, in the below image, we’re loading 4 waste roll-off bins which will allow the safe removal of cuttings without fear of the half-round catch tank running over.
Mud cleaning systems such as mud shaker pumps and bentonite slurry pumps move the material over screens and through dryers and centrifuges to retrieve even the finest bits of stone and silt. However, the pump operators must still get the raw slurry to the drill cuttings treatment area with a power main pump. Slurry pumps designed around the power of an Eddy current offer the best performance for transferring cuttings throughout a treatment system.
Options vary depending on whether the company plans to handle drill cuttings treatment on-site or transport the materials to a remote landfill or processing facility. If the plan is to deposit the cuttings in a landfill or a long-term storage container, it’s best to invest in a pump capable of depositing the material directly into transport vehicles. Most dredging operations rely on multiple expensive vacuum trucks, secondary pumps, and extra pieces of equipment.
Using an EDDY Pump will allow a project to eliminate the need for excavators/operators to load drill cuttings, substantially lowering both labor and heavy equipment costs. The EDDY Pump also allows a company to eliminate vacuum trucks once used for cleaning the mud system for displacing fluids. Since the pump transfers muds of all types at constant pressure and velocity throughout a system of practically any size, there’s little need for extra equipment for manual transfer or clean up on the dredge site.
The EDDY Pump can fill up a truck in only 10 minutes (compared to an hour) by using a mechanical means such as an excavator. For this reason, most companies can afford one piece of equipment that can replace half a dozen other units.
This application for the Eddy Pump has the potential to revolutionize the drilling industry. Moving the excavator out of the “back yard” (the area behind the rig from the living quarters) will make cuttings handling a breeze. Trucking can be easier scheduled during daylight hours saving on overtime and incidences of fatigued driving. Rig-site forklifts can move the roll-off boxes out of the staging area and into the pump loading area. The operator can save money on excavators rental, damages, and keep the technician operating the solids control equipment.
The EDDY Pump is ideal for drilling mud pump applications and can be connected directly onto the drilling rigs to pump the drilling mud at distances over a mile for disposal. This eliminates the need for costly vacuum trucks and also the manpower needed to mechanically move the drilling mud. The reasons why the EDDY Pump is capable of moving the drilling mud is due to the hydrodynamic principle that the pump creates, which is similar to the EDDY current of a tornado. This tornado motion allows for the higher viscosity and specific gravity pumping ability. This along with the large tolerance between the volute and the rotor allows for large objects like rock cuttings to pass through the pump without obstruction. The large tolerance of the EDDY Pump also enables the pump to last many times longer than centrifugal pumps without the need for extended downtime or replacement parts. The EDDY Pump is the lowest total life cycle pump on the market.

BW1500-12 mud pump used for various engineering drilling rigs, geological drilling rig when drilling would like to nip the circulating fluid (mud or water), which is equipped with drilling rigs to drill holes with mud. During drilling mud pump pumps slurry to the hole to provide coat to the wall, to lubricate the drilling tools and to carry the rock debris up to the ground.
BW1500-12 mud pump is a horizontal single-acting cylinder reciprocating piston pump with variable speed to change the displacement and pressure selected for use.
They are also the main equipment of the geological survey,the main role in the process of core drilling boreholes is to supply fluid(mud or water),making it circulate during drilling and carry rock waste back to the ground,in order to achieve and maintain the bottom hole clean and lubricate drill bits and drilling tools with cooling.
Drilling-fluid costs can constitute a significant fraction of the overall costs of drilling a well. Often the cost is quoted per unit length drilled, which takes into account any problems encountered (and avoided), such as stuck pipe. In many cases, the cost ascribed to the fluid also includes costs associated with solids control/management and waste disposal.
Thus, it is just as important to minimize costs associated with these two aspects as it is to ensure that the drilling fluid fulfills its primary functions [Young & Robinson]. Muds that require special attention and equipment to control the levels and types of solids frequently incur higher costs. Likewise, muds that generate waste fluid and cuttings, which must be hauled off (and perhaps treated) rather than discharged directly into the environment, generally incur higher costs.
Until recently, waste WBMs did not require any treatment and could be discharged directly into the environment. However, a number of components in WBMs are becoming increasingly restricted or prohibited. Chrome-containing materials, such as chrome lignosulfonates, are prohibited in many areas by governmental regulations. Tight restrictions are imposed in many areas on chloride, nitrate, and potassium salts, or, more generally, on the total electrical conductivity of the mud. In the North Sea, use of polyacrylamide polymers, such as partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (PHPA), is also severely restricted. OBMs tend to be restricted even more than WBMs, especially offshore, and in many places they can be used only if a zero discharge strategy (sometimes called a closed loop system) is adopted [Lal & Thurber].

Selecting the right pump type can be challenging. Azcue Pumps has a variety of pump types to choose from including variations in orientation, priming capabilities, motor configuration, suction method to name a few. In addition to the variety in pump capabilities, Azcue Pumps offers different metal construction to fit your needs. Browse the selection of pumps below or contact usand let one of our experts assist you in finding the right pump for your needs.

When choosing a size and type of mud pump for your drilling project, there are several factors to consider. These would include not only cost and size of pump that best fits your drilling rig, but also the diameter, depth and hole conditions you are drilling through. I know that this sounds like a lot to consider, but if you are set up the right way before the job starts, you will thank me later.
Recommended practice is to maintain a minimum of 100 to 150 feet per minute of uphole velocity for drill cuttings. Larger diameter wells for irrigation, agriculture or municipalities may violate this rule, because it may not be economically feasible to pump this much mud for the job. Uphole velocity is determined by the flow rate of the mud system, diameter of the borehole and the diameter of the drill pipe. There are many tools, including handbooks, rule of thumb, slide rule calculators and now apps on your handheld device, to calculate velocity. It is always good to remember the time it takes to get the cuttings off the bottom of the well. If you are drilling at 200 feet, then a 100-foot-per-minute velocity means that it would take two minutes to get the cuttings out of the hole. This is always a good reminder of what you are drilling through and how long ago it was that you drilled it. Ground conditions and rock formations are ever changing as you go deeper. Wouldn’t it be nice if they all remained the same?
Centrifugal-style mud pumps are very popular in our industry due to their size and weight, as well as flow rate capacity for an affordable price. There are many models and brands out there, and most of them are very good value. How does a centrifugal mud pump work? The rotation of the impeller accelerates the fluid into the volute or diffuser chamber. The added energy from the acceleration increases the velocity and pressure of the fluid. These pumps are known to be very inefficient. This means that it takes more energy to increase the flow and pressure of the fluid when compared to a piston-style pump. However, you have a significant advantage in flow rates from a centrifugal pump versus a piston pump. If you are drilling deeper wells with heavier cuttings, you will be forced at some point to use a piston-style mud pump. They have much higher efficiencies in transferring the input energy into flow and pressure, therefore resulting in much higher pressure capabilities.
Piston-style mud pumps utilize a piston or plunger that travels back and forth in a chamber known as a cylinder. These pumps are also called “positive displacement” pumps because they literally push the fluid forward. This fluid builds up pressure and forces a spring-loaded valve to open and allow the fluid to escape into the discharge piping of the pump and then down the borehole. Since the expansion process is much smaller (almost insignificant) compared to a centrifugal pump, there is much lower energy loss. Plunger-style pumps can develop upwards of 15,000 psi for well treatments and hydraulic fracturing. Centrifugal pumps, in comparison, usually operate below 300 psi. If you are comparing most drilling pumps, centrifugal pumps operate from 60 to 125 psi and piston pumps operate around 150 to 300 psi. There are many exceptions and special applications for drilling, but these numbers should cover 80 percent of all equipment operating out there.
The restriction of putting a piston-style mud pump onto drilling rigs has always been the physical size and weight to provide adequate flow and pressure to your drilling fluid. Because of this, the industry needed a new solution to this age-old issue.
As the senior design engineer for Ingersoll-Rand’s Deephole Drilling Business Unit, I had the distinct pleasure of working with him and incorporating his Centerline Mud Pump into our drilling rig platforms.
In the late ’90s — and perhaps even earlier — Ingersoll-Rand had tried several times to develop a hydraulic-driven mud pump that would last an acceptable life- and duty-cycle for a well drilling contractor. With all of our resources and design wisdom, we were unable to solve this problem. Not only did Miller provide a solution, thus saving the size and weight of a typical gear-driven mud pump, he also provided a new offering — a mono-cylinder mud pump. This double-acting piston pump provided as much mud flow and pressure as a standard 5 X 6 duplex pump with incredible size and weight savings.
The true innovation was providing the well driller a solution for their mud pump requirements that was the right size and weight to integrate into both existing and new drilling rigs. Regardless of drill rig manufacturer and hydraulic system design, Centerline has provided a mud pump integration on hundreds of customer’s drilling rigs. Both mono-cylinder and duplex-cylinder pumps can fit nicely on the deck, across the frame or even be configured for under-deck mounting. This would not be possible with conventional mud pump designs.
The second generation design for the Centerline Mud Pump is expected later this year, and I believe it will be a true game changer for this industry. It also will open up the application to many other industries that require a heavier-duty cycle for a piston pump application.

abstractNote = {Based on extensive research, development, and field testing of mud pumps and accessory equipment, this book offers cost-saving methods in operation and maintenance of triplex and duplex pumps. It covers practical engineering concerns such as pressure losses from friction in the piping and inertia in the drilling mud; suction dampeners in pump operation; charging the suction pipe for greater efficiency and smoother operation; hydraulic and mechanical knocking; hydraulic pressure losses; discharge lines.},

For the successful execution of your projects, it is important to find an appropriate company with a good track record. We help you in connecting with the top mud pump manufacturers and companies and get the best quotation.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
Yes. We help you find the best mud pumps irrespective of your location. We simplify your search by connecting you with top mud pump manufacturers and mud pump companies in your location, according to your budget and business requirement.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
The different parts of a mud pump are Housing itself, Liner with packing, Cover plus packing, Piston and piston rod, Suction valve and discharge valve with their seats, Stuffing box (only in double-acting pumps), Gland (only in double-acting pumps), and Pulsation dampener. A mud pump also includes mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers along with other parts.
The wearing parts of a mud pump should be checked frequently for repairing needs or replacement. The wearing parts include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be taken up to enhance the service life of the wearing parts. This can effectively bring down the project costs and improve production efficiency.




 8613371530291
8613371530291