how mud pump works in stock
A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling and manufactured according to API specification 7K.
The advantages of the drilling mud pump include the ability to move high-solids-content fluids laden with abrasives, the ability to pump large particles, ease of operation and maintenance, reliability, and the ability to operate over a wide range of pressures and flow rates by changing the diameter of pump liners and pistons.
As an important equipment for oilfield drilling operation, a drilling mud pump delivers circulating high-pressure drilling fluid or drilling mud to the bottom of the oil well, flushes the bottom of the well, breaks the rock, cools, lubricates and clean the drill bit, and carries the cuttings back to the ground.
The drilling mud is also used to suspend and carry out drill cuttings from the drill bits as it is brought in and out of the hole. This ensures that the drill bit does not clog and overheat, and makes the entire drilling operation smooth and safe.
Rotational power is supplied to the mud pump through an external power source like a diesel engine or electric motor. The power end of the mud pump converts the rotational energy through a crankshaft to a reciprocating motion of pistons.
The pistons move back and forth in mud pump liners, exerting a force on the cylinder chamber. During the retraction of the piston, valves open to allow the fluid to be drawn into the cylinder. Once the piston has fully retracted, it is pushed back into the cylinder.
Drilling for oil and gas exploration is an involved and complicated operation requiring specialized machinery to accomplish. Drilling rig mud pumps are one of the fundamental pieces of machinery needed for a successful drilling operation. Waters International supplies drilling rig mud pumps and other specialized boring equipment for the oil and gas exploration industry.
A drilling rig mud pump is used to circulate drilling fluid or drilling mud into the bore hole to help cool, lubricate and clean the drill head as it bores into the ground. The drilling mud is also used to suspend and carry out drill cuttings from the drill head as it is brought in and out of the hole. This ensures that the drill does not clog and overheat, and makes the entire drilling operation smooth and safe.
Drilling rig mud pumps are usually reciprocating type pumps that basically work by drawing a fluid into a chamber or cylinder by the action of a piston, plunger or diaphragm, and then pushing it out to the needed direction through the use of one-way or check valves, resulting in the pulsed flow of the liquid in one direction. Ganging multiple pumps together increases the pump efficiency and provides a smoother liquid flow for better performance.
The action of the pump is used to draw out the drilling fluid from the bore hole, which is then filtered and cleared of impurities before being sent back in to cool and lubricate the drill head, and remove more drill cuttings. A failed pump will cause a disrupted flow of the drilling mud, which can cause the drill head to overheat or jam from cuttings and possibly even break. This can result in damage to the drilling equipment, and potentially cause injury to the drilling crew near the drilling rig.

A mud pump is a piston driven pump design that can produce high-pressure operations to safely transfer high viscosity fluids over an extended depth. The mud pump has many applications in industrial service, but it has proven to be invaluable in many drilling operations. Let"s take a look at mud pumps and why they are such a good fit for the industries they serve.
A Mud pump is a reciprocal pump design utilizing a piston in a cylinder to transfer fluids under high pressure. A mud pump can generate up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa) during normal operations. Mud pumps are a positive displacement design.
Mud pumps are available in a variety of configurations and sizes. However, mud pumps tend to be one of two main types: the duplex and the triplex. The duplex mud pump features two pistons (or plungers) in constant action to move the fluid.
The triplex mud pump has all but replaced the duplex version in most applications, although you will still find the latter in use in some smaller countries. The triplex mud pump features a triple piston (plunger) design that is more efficient than the duplex design.
The latest designs of the mud pump are the quintuplex and hex versions. As the name suggests, these designs feature five or six pistons in a reciprocating design. Although not in widespread use as compared to the triplex design, these mud pumps spread the pumping action across the rotational cycle, creating less mud noise. This allows for better measurements and logging to take place while in operation.
There are two main parts to a mud pump: the fluid end and the power end. The fluid end is where the actual pumping takes place. The components of the fluid end consist of valves, pistons (or plungers), and liners.
Since the fluid end is in constant contact with the material being pumped, most modern designs allow for quick replacement of worn components as needed. This dramatically extends the life of a unit without having to completely replace the pump.
The power end of a mud pump is responsible for taking the input power, typically through a driveshaft, and converting it into the reciprocating motion needed for the pistons. In most mud pump applications, the power end uses a crosshead crankshaft for this conversion.
Rotational power is supplied to the mud pump through an external power source. The power end of the pump converts this rotational energy through a crankshaft to a reciprocating motion that moves the pistons.
Due to the pressure and material being pumped, most mud pump applications can create a lot of vibration. To combat this, many mud pump applications incorporate pulsation dampeners. These are typically used on both suction and discharge sides of the pump.
In some cases, a positive displacement pump may pull the fluids at a pressure lower than its vapor pressure. When this happens, damaging cavitation can take place. In these cases, a charge pump might be required at the inlet side to maintain a positive pressure on the suction stream.
When selecting a mud pump, there are two main parameters to be used, pressure and displacement. Pressure is the net pumping pressure that the pump can safely provide. The requirement for pressure increases as the drilling depth and fluid (or slurry) viscosity increases.
Displacement is the volume of fluid that the pump can transfer within a given time period. In most applications, this is rated as discharged liters per minute.
Mud pumps are ideal wherever a lot of fluid needs to be pumped under high pressure. They are considered an essential part of most oil well drilling rigs. Mud pumps can deliver high concentration and high viscosity slurry in a stable flow, making them adaptable to many uses.
Mud pumps are an invaluable tool when high pressure and high viscosity fluids are needing to be transferred. Mader Electric, Inc. specializes in mud pump repair and installation, as well as pump training. Contact us to see how we can help with your pumping needs.

Positive displacements pumps are generally used on drilling rigs to pump high pressure and high volume of drilling fluids throughout a drilling system. There are several reasons why the positive displacement mud pumps are used on the rigs.
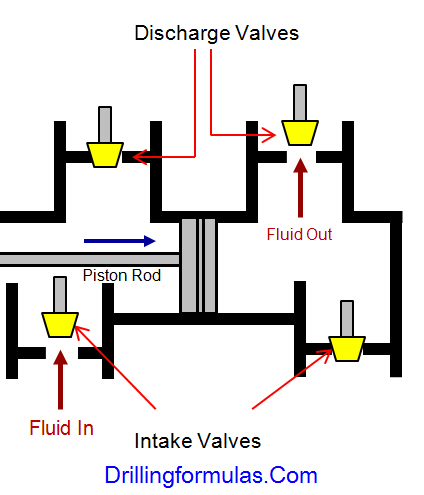
The duplex pumps (Figure 1) have two cylinders with double acting. It means that pistons move back and take in drilling mud through open intake valve and other sides of the same pistons, the pistons push mud out through the discharge valves.
When the piston rod is moved forward, one of intake valves is lift to allow fluid to come in and one of the discharge valve is pushed up therefore the drilling mud is pumped out of the pump (Figure 2).
On the other hand, when the piston rod is moved backward drilling fluid is still pumped. The other intake and discharge valve will be opened (Figure 3).
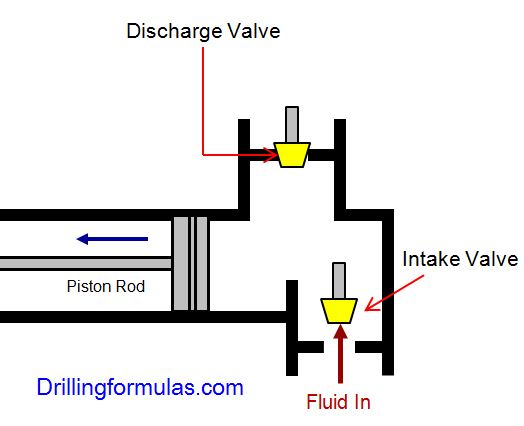
The triplex pumps have three cylinders with single acting. The pistons are moved back and pull in drilling mud through open intake valves. When the pistons are moved forward and the drilling fluid is pushed out through open discharge valves.
On the contrary when the piston rods are moved backward, the intake valve are opened allowing drilling fluid coming into the pump (Figure 6). This video below shows how a triplex mud pump works.
Because each pump has power rating limit as 1600 hp, this will limit capability of pump. It means that you cannot pump at high rate and high pressure over what the pump can do. Use of a small liner will increase discharge pressure however the flow rate is reduces. Conversely, if a bigger liner is used to deliver more flow rate, maximum pump pressure will decrease.
As you can see, you can have 7500 psi with 4.5” liner but the maximum flow rate is only 297 GPM. If the biggest size of liner (7.25”) is used, the pump pressure is only 3200 psi.
Finally, we hope that this article would give you more understanding about the general idea of drilling mud pumps. Please feel free to add more comments.

Mud pump is one of the most critical equipment on the rig; therefore personnel on the rig must have good understanding about it. We’ve tried to find the good training about it but it is very difficult to find until we’ve seen this VDO training and it is a fantastic VDO training about the basic of mud pumps used in the oilfield. Total length of this VDO is about thirteen minutes and it is worth to watch it. You will learn about it so quickly. Additionally, we also add the full detailed transcripts which will acceleate the learning curve of learners.
Powerful mud pumps pick up mud from the suction tank and circulate the mud down hole, out the bit and back to the surface. Although rigs usually have two mud pumps and sometimes three or four, normally they use only one at a time. The others are mainly used as backup just in case one fails. Sometimes however the rig crew may compound the pumps, that is, they may use three or four pumps at the same time to move large volumes of mud when required.
Rigs use one of two types of mud pumps, Triplex pumps or Duplex pumps. Triplex pumps have three pistons that move back-and-forth in liners. Duplex pumps have two pistons move back and forth in liners.
Triplex pumps have many advantages they weight 30% less than a duplex of equal horsepower or kilowatts. The lighter weight parts are easier to handle and therefore easier to maintain. The other advantages include;
• One of the more important advantages of triplex over duplex pumps, is that they can move large volumes of mud at the higher pressure is required for modern deep hole drilling.
Triplex pumps are gradually phasing out duplex units. In a triplex pump, the pistons discharge mud only when they move forward in the liner. Then, when they moved back they draw in mud on the same side of the piston. Because of this, they are also called “single acting.” Single acting triplex pumps, pump mud at a relatively high speeds. Input horsepower ranges from 220 to 2200 or 164 to 1641 kW. Large pumps can pump over 1100 gallons per minute, over 4000 L per minute. Some big pumps have a maximum rated pressure of over 7000 psi over 50,000 kPa with 5 inch/127 mm liners.
Here is a schematic of a triplex pump. It has three pistons each moving in its own liner. It also has three intake valves and three discharge valves. It also has a pulsation dampener in the discharge line.
Look at the piston at left, it has just completed pushing mud out of the liner through the open discharge valve. The piston is at its maximum point of forward travel. The other two pistons are at other positions in their travel and are also pumping mud. But for now, concentrate on the left one to understand how the pump works. The left piston has completed its backstroke drawing in mud through the open intake valve. As the piston moved back it instead of the intake valve off its seat and drew mud in. A strong spring holds the discharge above closed. The left piston has moved forward pushing mud through the now open discharge valve. A strong spring holds the intake valve closed. They left piston has completed its forward stroke they form the length of the liner completely discharging the mud from it. All three pistons work together to keep a continuous flow of mud coming into and out of the pump.
Crewmembers can change the liners and pistons. Not only can they replace worn out ones, they can also install different sizes. Generally they use large liners and pistons when the pump needs to move large volumes of mud at relatively low pressure. They use a small liners and pistons when the pump needs to move smaller volumes of mud at a relatively high pressure.
In a duplex pump, pistons discharge mud on one side of the piston and at the same time, take in mud on the other side. Notice the top piston and the liner. As the piston moves forward, it discharges mud on one side as it draws in mud on the other then as it moves back, it discharges mud on the other side and draws in mud on the side it at had earlier discharge it. Duplex pumps are therefore double acting.
Double acting pumps move more mud on a single stroke than a triplex. However, because of they are double acting they have a seal around the piston rod. This seal keeps them from moving as fast as a triplex. Input horsepower ranges from 190 to 1790 hp or from 142 to 1335 kW. The largest pumps maximum rated working pressure is about 5000 psi, almost 35,000 kPa with 6 inch/152 mm linings.
A mud pump has a fluid end, our end and intake and the discharge valves. The fluid end of the pump contains the pistons with liners which take in or discharge the fluid or mud. The pump pistons draw in mud through the intake valves and push mud out through the discharge valves.
The power end houses the large crankshaft and gear assembly that moves the piston assemblies on the fluid end. Pumps are powered by a pump motor. Large modern diesel/electric rigs use powerful electric motors to drive the pump. Mechanical rigs use chain drives or power bands (belts) from the rig’s engines and compounds to drive the pump.
A pulsation dampener connected to the pump’s discharge line smooths out surges created by the pistons as they discharge mud. This is a standard bladder type dampener. The bladder and the dampener body, separates pressurized nitrogen gas above from mud below. The bladder is made from synthetic rubber and is flexible. When mud discharge pressure presses against the bottom of the bladder, nitrogen pressure above the bladder resists it. This resistance smoothes out the surges of mud leaving the pump.
Here is the latest type of pulsation dampener, it does not have a bladder. It is a sphere about 4 feet or 1.2 m in diameter. It is built into the mud pump’s discharge line. The large chamber is form of mud. It has no moving parts so it does not need maintenance. The mud in the large volume sphere, absorbs this surges of mud leaving the pump.
A suction dampener smooths out the flow of mud entering into the pump. Crewmembers mount it on the triplex mud pump’s suction line. Inside the steel chamber is a air charged rubber bladder or diaphragm. The crew charges of the bladder about 10 to 15 psi/50 to 100 kPa. The suction dampener absorbs surges in the mud pump’s suction line caused by the fast-moving pump pistons. The pistons, constantly starts and stops the mud’s flow through the pump. At the other end of the charging line a suction pumps sends a smooth flow of mud to the pump’s intake. When the smooth flow meets the surging flow, the impact is absorbed by the dampener.
Workers always install a discharge pressure relief valve. They install it on the pump’s discharge side in or near the discharge line. If for some reason too much pressure builds up in the discharge line, perhaps the drill bit or annulus gets plugged, the relief valve opens. That opened above protects the mud pump and system damage from over pressure.
Some rig owners install a suction line relief valve. They install it on top of the suction line near the suction dampener. They mount it on top so that it won’t clog up with mud when the system is shut down. A suction relief valve protects the charging pump and the suction line dampener. A suction relief valve usually has a 2 inch or 50 mm seat opening. The installer normally adjusts it to 70 psi or 500 kPa relieving pressure. If both the suction and the discharged valves failed on the same side of the pump, high back flow or a pressure surge would occur. The high backflow could damage the charging pump or the suction line dampener. The discharge line is a high-pressure line through which the pump moves mud. From the discharge line, the mud goes through the stand pipe and rotary hose to the drill string equipment.

The policy set forth below outlines the personal data that Power Zone Equipment may collect, how Power Zone Equipment uses and safeguards that data, and with whom we may share it. This policy is intended to provide notice to individuals regarding personal data in an effort to be compliant with the data privacy laws and regulations of the jurisdictions in which Power Zone Equipment operates.
If you have a comment, question, or complaint about how Power Zone Equipment is handling your personal data, we invite you to contact us in order to allow us to resolve the matter. In addition, individuals located in the EU may submit a complaint regarding the processing of their personal data to the EU data protection authorities (DPAs). The following link may assist you in finding the appropriate DPA:http://ec.europa.eu/justice/data-protection/bodies/authorities/index_en.htm.

Mud pumps are large reciprocating pumps that are used to move heavy drilling fluid within the hole during oil drilling. The pump works by circulating the mud; it pushes the fluid down into the hole and then moves it back up again. Being reciprocating by design, they use plungers or oscillating pistons in order to displace the drilling fluid. Mud pumps are single acting pumps, which means that the fluid moves only in one direction.
The mud pump them pushes the mud down the piping and into the bottom of the well, and the pressure forces the mud up the space surrounding the piping (called the annulus). During oil and gas explorations, the mud used consists of clay, emulsified oil or water, and chemicals. It’s tailor-made for the particular conditions of the drilling for safety reasons. The purpose of this mud is to float clean the bottom of the well by floating out rock cuttings. It also cools the drilling equipment and functions as a barrier should there be a blowout.
Mud pumps, such as a Gardner Denver PZ 11, are crucial equipment for drilling oil. As drills cut through rocks, mud pumps move cuttings up the hole. These rock cuttings are then put through shakers that remove them from the drilling fluid or mud, which is them reused by the mud pumps. The process continues until the hole is drilled to the full depth. Modern mud pumps are typically triplex-style with three cylinders. Duplex pumps are still used sometimes in older oil rigs. Some of the newest mud pumps have six cylinders.
If you need a mud pump for sale, don’t hesitate to contact Henderson where we specialize in the procurement and brokerage of capital drilling equipment. Known for the transparency of their procurement process, if we don’t have what you need in stock we can recommend alternative sourcing options to help you cut costs as well as increase efficiency.

Electronic Pump Stroke Counters are a vital part to any drilling rig operation. When a mud pump is in operation, the driller must know how much mud is flowing down hole in order to keep the operation running at peak efficiency. Pump stroke counters assist the driller by measuring the mud pump’s strokes per minute and total strokes. So, how does a pump stroke counter tally the mud pump’s strokes
Electronic Pump Stroke Counters are a vital part to any drilling rig operation. When a mud pump is in operation, the driller must know how much mud is flowing down hole in order to keep the operation running at peak efficiency. Pump stroke counters assist the driller by measuring the mud pump’s strokes per minute and total strokes. So, how does a pump stroke counter tally the mud pump’s strokes, and why it is important? In order to understand that, you’ll need to know some basic information about mud pumps.
Knowing how a mud pump functions is important in understanding the role a pump stroke counter plays in rig operations. Mud pumps act as the heart of the drilling rig, similar to how our heart works. Just as our heart circulates blood throughout our bodies, a mud pump circulates essential drilling mud down the hole and back up to the surface. Mud tanks house drilling mud, and a mud pump draws the fluid from the mud pump. A piston draws mud in on the backstroke through the open intake valve and pushes mud through the discharge valve and sends it towards the rig. By circulating fluid, the mud pump ensures that the drill bit is cool and lubricated and that cuttings are flushed from the hole. The two main kinds of pumps used are duplex and triplex pumps, where the duplex pump has two pistons and the triplex pump has three. Whether the rig is using a duplex or triplex pump, it is important to know how many strokes per second the pistons are moving. The driller monitors strokes per minute to determine how much costly, yet essential, mud is being pumped into the system with the use of a mud pump stroke counter system. Now, that you know about mud pumps, you’ll need to know what’s in a stroke counter system.
Stroke Counter — The stroke counter stainless steel box is mounted on the driller’s console and is either square or rectangular in shape, depending on the number of pumps it is monitoring. Stroke counters will show strokes per minute and total strokes, and when a particular mud pump is operating the strokes/minute and total strokes will be displayed. Power is supplied by a 3.6 volt lithium battery, and the counter contains a crystal-controlled real time clock with 100 parts per million accuracy or better. Each counter is mounted to the console with 1/4” stainless steel hex head bolts, lock washers and nuts.
Micro Limit Switch — The micro switch is connected to a c clamp near the mud pump piston. The micro switch stainless steel rod (sometimes called a whisker) sticks out in the piston housing near the piston. As the piston passes the rod, it moves the rod and the switch sends an electronic signal back to the counter. The counter increases by one each time the piston moves the rod, counting the mud pump’s strokes. The switch’s signal is then transmitted to the stroke counter. These micro switches are built to stand up to demanding outdoor conditions. They can withstand shock, equipment vibration, extreme temperatures, water and dust.
Cable and Junction Box – A cable is connected to the back of the pump stroke counter and then to the junction box. From the junction box, the cables travel to the limit switches.
Pump Stroke Counters are like a blood pressure machine. Each time our heart pumps, a blood pressure machine reads our systolic and diastolic blood pressure by way of our pulse. A mud pump stroke counter functions in much the same way. Just as a blood pressure machine detects our pulse so too does a limit switch rod detect the movement of the piston. When the stainless steel rod is moved, the micro limit switch detects the movement. The signal is sensed as a contact closure, and it is transmitted to the stroke counter where the contact closure is converted to a logic pulse. The pulse feeds two separate circuits. The total strokes circuit reads and displays the closures one at a time, totaling them up to reveal the total strokes in the LED window. The second pulse is sent along a separate circuit which is a rate circuit. This rate circuit will average the closures against the real time clock. The result is displayed as the total strokes per minute.
Pump stroke counters are essential to drilling rig operations because they measure the efficiency of mud pumps. Knowing strokes per minute and total strokes of the pistons helps the driller to determine if the correct amount of mud is going down hole. Having this information aids in running a drilling rig at peak efficiency, assists in extending drill bit life, and avoids costly overuse of drilling rig mud. Unsure which pump stroke counter is right for your application? Give our friendly, knowledgeable staff a call or email. We’ll keep you turning right.

As an integral part of onshore and offshore drilling, mud pumps circulate the drilling fluid used to facilitate the drilling of oil and gas wells. Drilling fluids are used to stabilize pressure and support the well during drilling, as well as to reduce friction and remove rock chips.
Drilling fluids have come a long way since the early days of drilling and offshore mud pumps are constantly being taxed to help operators find and develop hydrocarbons in tougher, deeper, and more difficult locations.
The mud pump is one of the keys and essential pieces of equipment on land or offshore drilling rig. Offshore, where real estate is at a premium, mud pumps are equipped with compact top-mounted drive systems, reducing the overall length in a smaller package and strategically placed in the pump room for permanent installation.
Both jack-up semi-subs and drillships use the same mud pumps; however, the number of pumps installed in the pump room will vary depending on the drilling specifications.
In addition, the formations and pressures encountered while drilling may vary; HT/HP and environmental conditions may also affect the drilling process, as well as the drilling fluid selected and the mud pump required.
As drilling projects require higher flow rates and higher pressures, it is necessary to increase the pressure rating, either by increasing the number of mud pumps required or by using larger capacity mud pumps. Most early jack-up rigs used two mud pumps and piping systems rated at 5000 psi and 1600 HP working pressure, while most jack-up rigs today have 7500 psi working pressure and up to four 2200 HP pump piping systems.
Mud pumps are integrated into the rig, so they are not usually stand-alone units. The mud pump has a drive motor and is connected to a mixing tank to supply mud as required. The input and output fluid ends of the pump are piped directly to the drill column and borehole annulus. The pump usually has pulsation dampers at both the fluid inlet and outlet ends to eliminate pressure variations in the mud flow.
Mud pumps are usually driven by electric or diesel engines. Diesel engines are best suited to remote areas. The motor is slowed down as most pumps run at around 100 to 200 rpm as the motor usually spins much faster. Most electric pumps use AC motors, but DC motor units are also available. The largest mud pumps are rated at over 2,500 hp.
The drilling fluid or mud is circulated through the fluid end of the pump. It is pumped through the center hole of the drill pipe and through the drill column of its bit. The mud is returned to the surface through the borehole annulus or the space between the shaft and the borehole ID. Deep wells, such as offshore oil rigs, require 7,500 psi to force the mud downwards and backward. These wells can be at the surface and up to 10 miles below the seabed. Drilling mud is usually a water-based viscous slurry of suspended clay-like colloids, but it may vary depending on where it is used or the purpose of the well being drilled. It can also be a fluid mixture based on oil or synthetic fluids. The mud mixture is usually stored in a large mixing tank.

The drilling industry has roots dating back to the Han Dynasty in China. Improvements in rig power and equipment design have allowed for many advances in the way crude oil and natural gas are extracted from the ground. Diesel/electric oil drilling rigs can now drill wells more than 4 miles in depth. Drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to help transfer the dirt or drill cuttings from the action of the drilling bit back to the surface for disposal. Drill cuttings can vary in shape and size depending on the formation or design of the drill bit used in the process.
Watch the video below to see how the EDDY Pump outperforms traditional pumps when it comes to high solids and high viscosity materials commonly found on oil rigs.
The fluid is charged into high-pressure mud pumps which pump the drilling mud down the drill string and out through the bit nozzles cleaning the hole and lubricating the drill bit so the bit can cut efficiently through the formation. The bit is cooled by the fluid and moves up the space between the pipe and the hole which is called the annulus. The fluid imparts a thin, tough layer on the inside of the hole to protect against fluid loss which can cause differential sticking.
The fluid rises through the blowout preventers and down the flowline to the shale shakers. Shale shakers are equipped with fine screens that separate drill cutting particles as fine as 50-74 microns. Table salt is around 100 microns, so these are fine cuttings that are deposited into the half-round or cuttings catch tank. The drilling fluid is further cleaned with the hydro-cyclones and centrifuges and is pumped back to the mixing area of the mud tanks where the process repeats.
The drill cuttings contain a layer of drilling fluid on the surface of the cuttings. As the size of the drill cuttings gets smaller the surface area expands exponentially which can cause rheological property problems with the fluid. The fluid will dehydrate and may become too thick or viscous to pump so solids control and dilution are important to the entire drilling process.
One of the most expensive and troubling issues with drilling operations is the handling, processing, and circulation of drilling mud along with disposing of the unwanted drill cuttings. The drilling cuttings deposited in the half round tank and are typically removed with an excavator that must move the contents of the waste bin or roll-off box. The excavators are usually rented for this duty and the equipment charges can range from $200-300/day. Add in the cost for the day and night manpower and the real cost for a single excavator can be as much as $1800/day.
Offshore drilling rigs follow a similar process in which the mud is loaded into empty drums and held on the oil platform. When a certain number of filled drums is met, the drums are then loaded onto barges or vessels which take the drilling mud to the shore to unload and dispose of.
Oil field drilling operations produce a tremendous volume of drill cuttings that need both removal and management. In most cases, the site managers also need to separate the cuttings from the drilling fluids so they can reuse the fluids. Storing the cuttings provides a free source of stable fill material for finished wells, while other companies choose to send them off to specialty landfills. Regardless of the final destination or use for the cuttings, drilling and dredging operations must have the right high solids slurry pumps to move them for transport, storage, or on-site processing. Exploring the differences in the various drilling fluids, cutting complications, and processing options will reveal why the EDDY Pump is the best fit for the job.
The Eddy Pump is designed to move slurry with solid content as high as 70-80 % depending on the material. This is an ideal application for pumping drill cuttings. Drill cuttings from the primary shakers are typically 50% solids and 50% liquids. The Eddy Pump moves these fluids efficiently and because of the large volute chamber and the design of the geometric rotor, there is very little wear on the pump, ensuring long life and greatly reduced maintenance cost for the lifetime of the pump.
plumbed to sweep the bottom of the collection tank and the pump is recessed into a sump allowing for a relatively clean tank when the solids are removed. The Eddy Pump is sized to load a roll-off box in 10-12 minutes. The benefit is cuttings handling is quicker, easier, safer, and allows for pre-planning loading where the labor of the solids control technician is not monopolized by loading cuttings. Here, in the below image, we’re loading 4 waste roll-off bins which will allow the safe removal of cuttings without fear of the half-round catch tank running over.
Mud cleaning systems such as mud shaker pumps and bentonite slurry pumps move the material over screens and through dryers and centrifuges to retrieve even the finest bits of stone and silt. However, the pump operators must still get the raw slurry to the drill cuttings treatment area with a power main pump. Slurry pumps designed around the power of an Eddy current offer the best performance for transferring cuttings throughout a treatment system.
Options vary depending on whether the company plans to handle drill cuttings treatment on-site or transport the materials to a remote landfill or processing facility. If the plan is to deposit the cuttings in a landfill or a long-term storage container, it’s best to invest in a pump capable of depositing the material directly into transport vehicles. Most dredging operations rely on multiple expensive vacuum trucks, secondary pumps, and extra pieces of equipment.
Using an EDDY Pump will allow a project to eliminate the need for excavators/operators to load drill cuttings, substantially lowering both labor and heavy equipment costs. The EDDY Pump also allows a company to eliminate vacuum trucks once used for cleaning the mud system for displacing fluids. Since the pump transfers muds of all types at constant pressure and velocity throughout a system of practically any size, there’s little need for extra equipment for manual transfer or clean up on the dredge site.
The EDDY Pump can fill up a truck in only 10 minutes (compared to an hour) by using a mechanical means such as an excavator. For this reason, most companies can afford one piece of equipment that can replace half a dozen other units.
This application for the Eddy Pump has the potential to revolutionize the drilling industry. Moving the excavator out of the “back yard” (the area behind the rig from the living quarters) will make cuttings handling a breeze. Trucking can be easier scheduled during daylight hours saving on overtime and incidences of fatigued driving. Rig-site forklifts can move the roll-off boxes out of the staging area and into the pump loading area. The operator can save money on excavators rental, damages, and keep the technician operating the solids control equipment.
The EDDY Pump is ideal for drilling mud pump applications and can be connected directly onto the drilling rigs to pump the drilling mud at distances over a mile for disposal. This eliminates the need for costly vacuum trucks and also the manpower needed to mechanically move the drilling mud. The reasons why the EDDY Pump is capable of moving the drilling mud is due to the hydrodynamic principle that the pump creates, which is similar to the EDDY current of a tornado. This tornado motion allows for the higher viscosity and specific gravity pumping ability. This along with the large tolerance between the volute and the rotor allows for large objects like rock cuttings to pass through the pump without obstruction. The large tolerance of the EDDY Pump also enables the pump to last many times longer than centrifugal pumps without the need for extended downtime or replacement parts. The EDDY Pump is the lowest total life cycle pump on the market.

When choosing a size and type of mud pump for your drilling project, there are several factors to consider. These would include not only cost and size of pump that best fits your drilling rig, but also the diameter, depth and hole conditions you are drilling through. I know that this sounds like a lot to consider, but if you are set up the right way before the job starts, you will thank me later.
Recommended practice is to maintain a minimum of 100 to 150 feet per minute of uphole velocity for drill cuttings. Larger diameter wells for irrigation, agriculture or municipalities may violate this rule, because it may not be economically feasible to pump this much mud for the job. Uphole velocity is determined by the flow rate of the mud system, diameter of the borehole and the diameter of the drill pipe. There are many tools, including handbooks, rule of thumb, slide rule calculators and now apps on your handheld device, to calculate velocity. It is always good to remember the time it takes to get the cuttings off the bottom of the well. If you are drilling at 200 feet, then a 100-foot-per-minute velocity means that it would take two minutes to get the cuttings out of the hole. This is always a good reminder of what you are drilling through and how long ago it was that you drilled it. Ground conditions and rock formations are ever changing as you go deeper. Wouldn’t it be nice if they all remained the same?
Centrifugal-style mud pumps are very popular in our industry due to their size and weight, as well as flow rate capacity for an affordable price. There are many models and brands out there, and most of them are very good value. How does a centrifugal mud pump work? The rotation of the impeller accelerates the fluid into the volute or diffuser chamber. The added energy from the acceleration increases the velocity and pressure of the fluid. These pumps are known to be very inefficient. This means that it takes more energy to increase the flow and pressure of the fluid when compared to a piston-style pump. However, you have a significant advantage in flow rates from a centrifugal pump versus a piston pump. If you are drilling deeper wells with heavier cuttings, you will be forced at some point to use a piston-style mud pump. They have much higher efficiencies in transferring the input energy into flow and pressure, therefore resulting in much higher pressure capabilities.
Piston-style mud pumps utilize a piston or plunger that travels back and forth in a chamber known as a cylinder. These pumps are also called “positive displacement” pumps because they literally push the fluid forward. This fluid builds up pressure and forces a spring-loaded valve to open and allow the fluid to escape into the discharge piping of the pump and then down the borehole. Since the expansion process is much smaller (almost insignificant) compared to a centrifugal pump, there is much lower energy loss. Plunger-style pumps can develop upwards of 15,000 psi for well treatments and hydraulic fracturing. Centrifugal pumps, in comparison, usually operate below 300 psi. If you are comparing most drilling pumps, centrifugal pumps operate from 60 to 125 psi and piston pumps operate around 150 to 300 psi. There are many exceptions and special applications for drilling, but these numbers should cover 80 percent of all equipment operating out there.
The restriction of putting a piston-style mud pump onto drilling rigs has always been the physical size and weight to provide adequate flow and pressure to your drilling fluid. Because of this, the industry needed a new solution to this age-old issue.
As the senior design engineer for Ingersoll-Rand’s Deephole Drilling Business Unit, I had the distinct pleasure of working with him and incorporating his Centerline Mud Pump into our drilling rig platforms.
In the late ’90s — and perhaps even earlier — Ingersoll-Rand had tried several times to develop a hydraulic-driven mud pump that would last an acceptable life- and duty-cycle for a well drilling contractor. With all of our resources and design wisdom, we were unable to solve this problem. Not only did Miller provide a solution, thus saving the size and weight of a typical gear-driven mud pump, he also provided a new offering — a mono-cylinder mud pump. This double-acting piston pump provided as much mud flow and pressure as a standard 5 X 6 duplex pump with incredible size and weight savings.
The true innovation was providing the well driller a solution for their mud pump requirements that was the right size and weight to integrate into both existing and new drilling rigs. Regardless of drill rig manufacturer and hydraulic system design, Centerline has provided a mud pump integration on hundreds of customer’s drilling rigs. Both mono-cylinder and duplex-cylinder pumps can fit nicely on the deck, across the frame or even be configured for under-deck mounting. This would not be possible with conventional mud pump designs.
The second generation design for the Centerline Mud Pump is expected later this year, and I believe it will be a true game changer for this industry. It also will open up the application to many other industries that require a heavier-duty cycle for a piston pump application.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

Mud pumps are the pumps deployed in the oil and gas industry, mainly to circulate drilling fluids and other kinds of fluids in and out of the drilled wells for exploration. The mud pumps transfer the fluids at a very high pressure inside the well using the piston arrangement. The number of pistons decides the displacement and efficiency of working of the mud pumps, originally only dual piston pumps and three-piston pumps were used, but the technological advancements have seen pumps with five and six pistons to come up. Currently the triplex pumps which have three pistons are used, but the duplex pumps having two pumps are still deployed in the developing countries.
Based on its types, global mud pump market can be segmented into duplex, triplex, and others. The triplex mud pumps will dominate the mud pump marking in the given forecast period owing to its advantages and ongoing replacement of duplex pumps with triplex pumps. Based on operation, the global mud pumps market can be segmented into electric and fuel engine.
The electric mud pumps will dominate the market during the given forecast period due to the advantage of eliminating the harmful carbon emission which is done in the case of fuel engine pumps. Based on its application, the global mud pumps market can be segmented into oil & gas, mining, construction, and others.
The major market driver for the global mud pumps market is the increasing exploration activities taking place in various regions of the world to satisfy the increased energy demand. The number of drilled wells has increased in recent years, which has certainly impacted the growth of the mud pumps market in both oil & gas and mining sectors.
Key market restraint for the global mud pumps market is the drift towards the cleaner sources of energy to reduce the carbon emissions, which will certainly decrease the demand for oil & gas and therefore will have a negative impact on the growth of the global mud pumps market.
Some of the notable companies in the global mud pump market are Mud King Products, Inc. Gardner Denver Pumps, Weatherford, Schlumberger, National Oilwell Varco, China National Petroleum Corporation, Flowserve Corporation, MHWirth, American Block, Herrenknecht Vertical Gmbh, Bentec GmbH Drilling & Oilfield Systems, Drillmec Inc, Sun Machinery Company, Shale Pumps, and Dhiraj Rigs.
The global mud pump market has been segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. Owing to the well-established production sector and stable exploration industry North America holds the largest market for the mud pumps. The onshore exploration activities of oil & gas have increased at a good rate in the North America region, which has certainly boosted the growth of the mud pumps market in the region.
The demand from Europe and Asia Pacific has also increased due to exploration activities in both the regions owing to the increased energy demand. The energy demand specifically in the Asia Pacific has increased due to the increased population and urbanization. The Middle East and Africa also hold significant opportunities for the mud pumps market with increased exploration activities in the given forecast period.
In August 2018, Henderson which is a leading company in sales and service of drilling rigs, and capital drilling equipment in Texas signed a contract with Energy Drilling Company for the purchase and upgrade of oil field equipment’s which included three 1600hp × 7500psi mud pumps. This will be the first refurbishment completed at Henderson’s new service center and rig yard.
In January 2018, Koltek Energy Services launched the 99-acre facility for the testing of the oil field equipment in Oklahoma. This will allow the oil field equipment manufacturers to test their equipment at any given time. The company has deployed the MZ-9 pump which has a power rating of 1000Hp.

RM2MF3D54–Kikuube, Uganda. 24th Jan, 2023. A worker operates the Mud Pump Unit at the Kingfisher Oil Field in Kikuube, Uganda, on Jan. 24, 2023. Uganda on Tuesday started the drilling of oil for commercial production in the Western Region district of Kikuube on the shores of Lake Albert. Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni launched the drilling process at the Kingfisher Oil Field, operated by the Chinese oil giant China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC). Credit: Hajarah Nalwadda/Xinhua/Alamy Live News

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Mud pumps can be divided into single-acting pump and double-acting pump according to the completion times of the suction and drainage acting in one cycle of the piston"s reciprocating motion.
Mud pumps come in a variety of sizes and configurations but for the typical petroleum drilling rig, the triplex (three piston/plunger) mud pump is used. Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplexes with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that these new pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better measurement while drilling (MWD) and logging while drilling (LWD) decoding.
The fluid end produces the pumping process with valves, pistons, and liners. Because these components are high-wear items, modern pumps are designed to allow quick replacement of these parts.
To reduce severe vibration caused by the pumping process, these pumps incorporate both a suction and discharge pulsation dampener. These are connected to the inlet and outlet of the fluid end.
The pressure of the pump depends on the depth of the drilling hole, the resistance of flushing fluid (drilling fluid) through the channel, as well as the nature of the conveying drilling fluid. The deeper the drilling hole and the greater the pipeline resistance, the higher the pressure needed.
With the changes of drilling hole diameter and depth, the displacement of the pump can be adjusted accordingly. In the mud pump mechanism, the gearbox or hydraulic motor is equipped to adjust its speed and displacement. In order to accurately measure the changes in pressure and displacement, a flow meter and pressure gauge are installed in the mud pump.
The construction department should have a special maintenance worker that is responsible for the maintenance and repair of the machine. Mud pumps and other mechanical equipment should be inspected and maintained on a scheduled and timely basis to find and address problems ahead of time, in order to avoid unscheduled shutdown. The worker should attend to the size of the sediment particles; if large particles are found, the mud pump parts should be checked frequently for wear, to see if they need to be repaired or replaced. The wearing parts for mud pumps include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be adopted to increase the service life of the wearing parts, which can reduce the investment cost of the project, and improve production efficiency. At the same time, wearing parts and other mud pump parts should be repaired rather than replaced when possible.




 8613371530291
8613371530291