mud pump cap wrench quotation
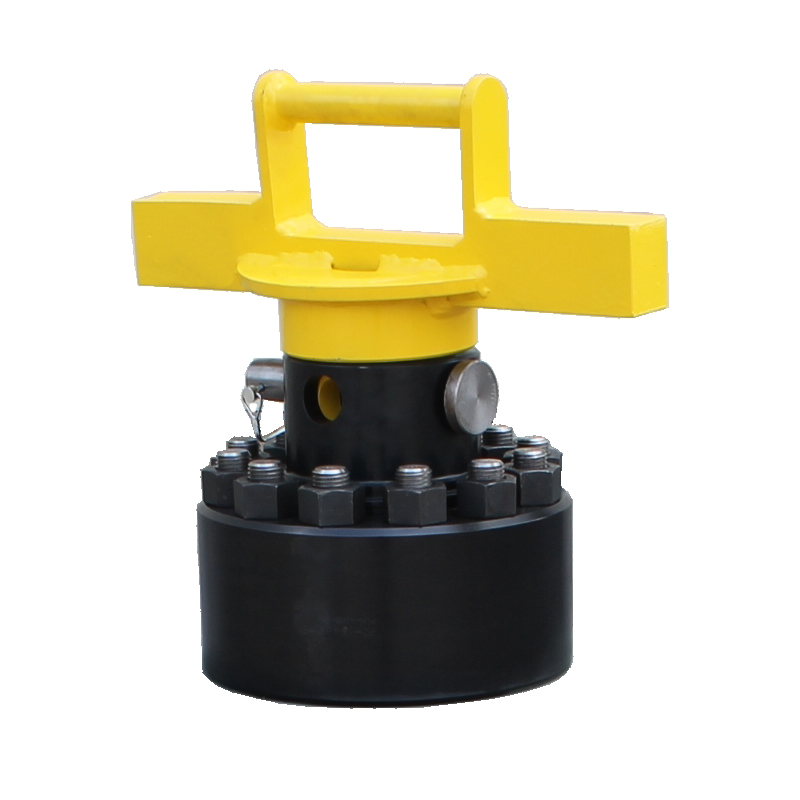

Designed for easier removal of mud pump caps with less damage than the most traditional methods. These wrenches feature heavy handle design for greater strength and a fitted safety lock pin to help prevent injuries.

Browse through more than 1,500 duplex piston rods and 200 duplex pony rods in our inventory. EC Tool gives you a quote before your order, so you know what you’re getting for your money every time. While we primarily keep connecting rods for GA550 and GA750 models in stock, there are other options at your disposal as well. This includes custom connecting rods for most duplex and triplex mud pumps.
We now offer new crossheads and capsules for both EMSCO D-375 and DB-550 duplex pumps. You can also find slides and shoes for certain models. Available parts currently in our inventory include:
We carry a large inventory of valve cap plugs made for OEM and MATTCO fluid ends. You’ll also find different drop-in plugs for most gland-type valve caps.

A Mud Pump may have many changeable parts, such as liner, piston, extension rod, pulsation dampener, valve, clamp, etc. Lake Petro could provide 100% interchangeable parts of many common brands of pump. We offer Liners with Ceramic (Zirconia and Aluminium oxide) and Steel (Metal and Bi-metal) materials. Piston assembly is the important spare parts and expendable parts of oil drilling mud pumps. Mud pump valve assy include valve body, valve seat, valve insert (valve rubber ). Pulsation Dampener is usually installed on the discharge line to reduce the fluctuation of pressure and displacement of the drilling mud pump. Fluid End Module is an important component of the hydraulic pump end of the mud pump.
It includes the hexagon spanner, cover puller, plunger installation tool, plunger removal, packing nut wrench, cover wrench speed tool, cover installation tool, packing removal, drain tool. We have everything you need for your plunger pump installation and removal jobs.
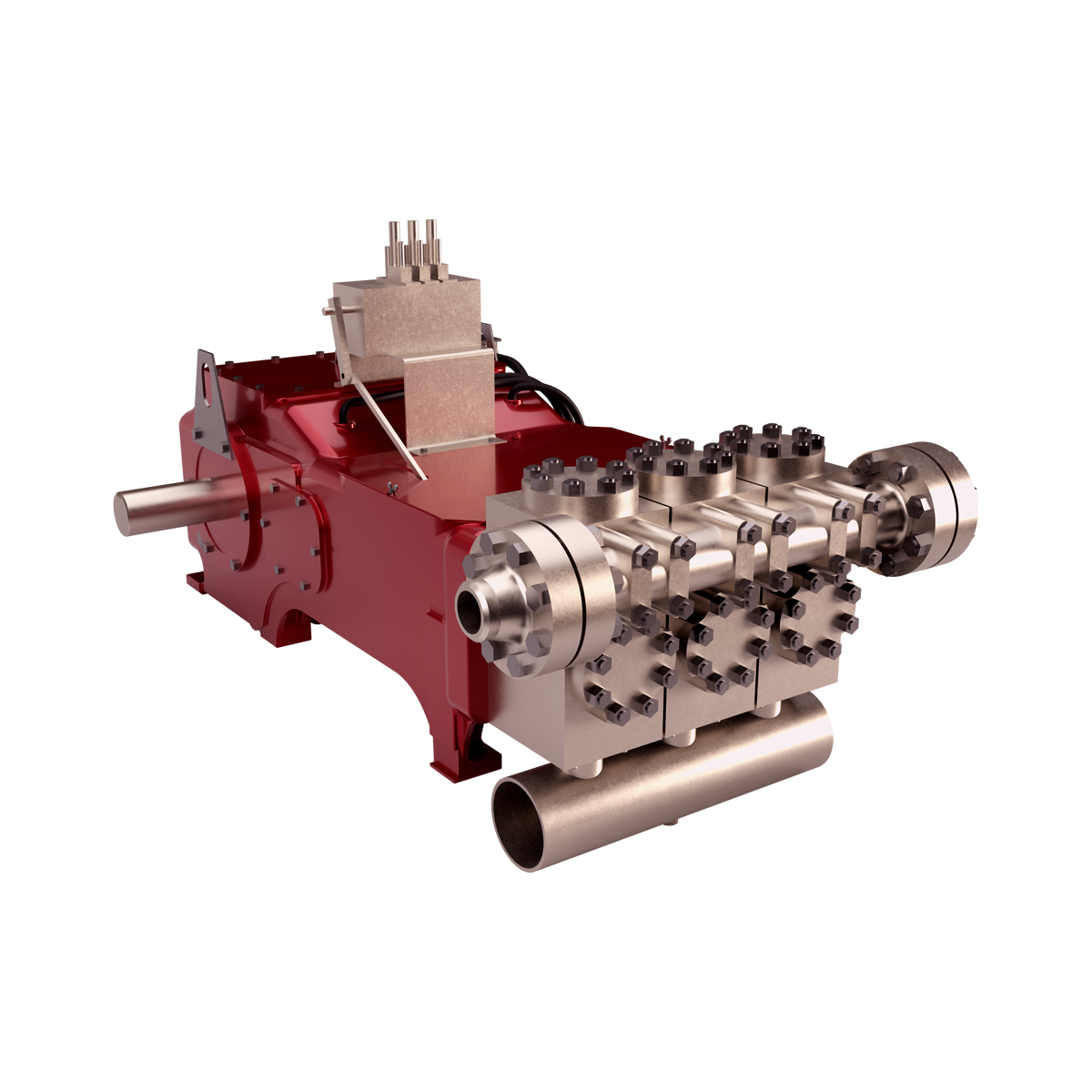
SafeLock is offered as an optional upgrade on new GD Energy Products drilling pumps and modules, and can also be used for retrofit on GD Energy Products HD, F and Y series drilling pump modules with bore seal technology.
Simple Operation -No tools, no problems. SafeLock’s quarter-turn design eliminates the need for hydraulic pumps, torque wrenches, drills, or impact guns for installation and removal. To install or remove SafeLock, simply grab the handles and turn 25 degrees, it’s that easy!
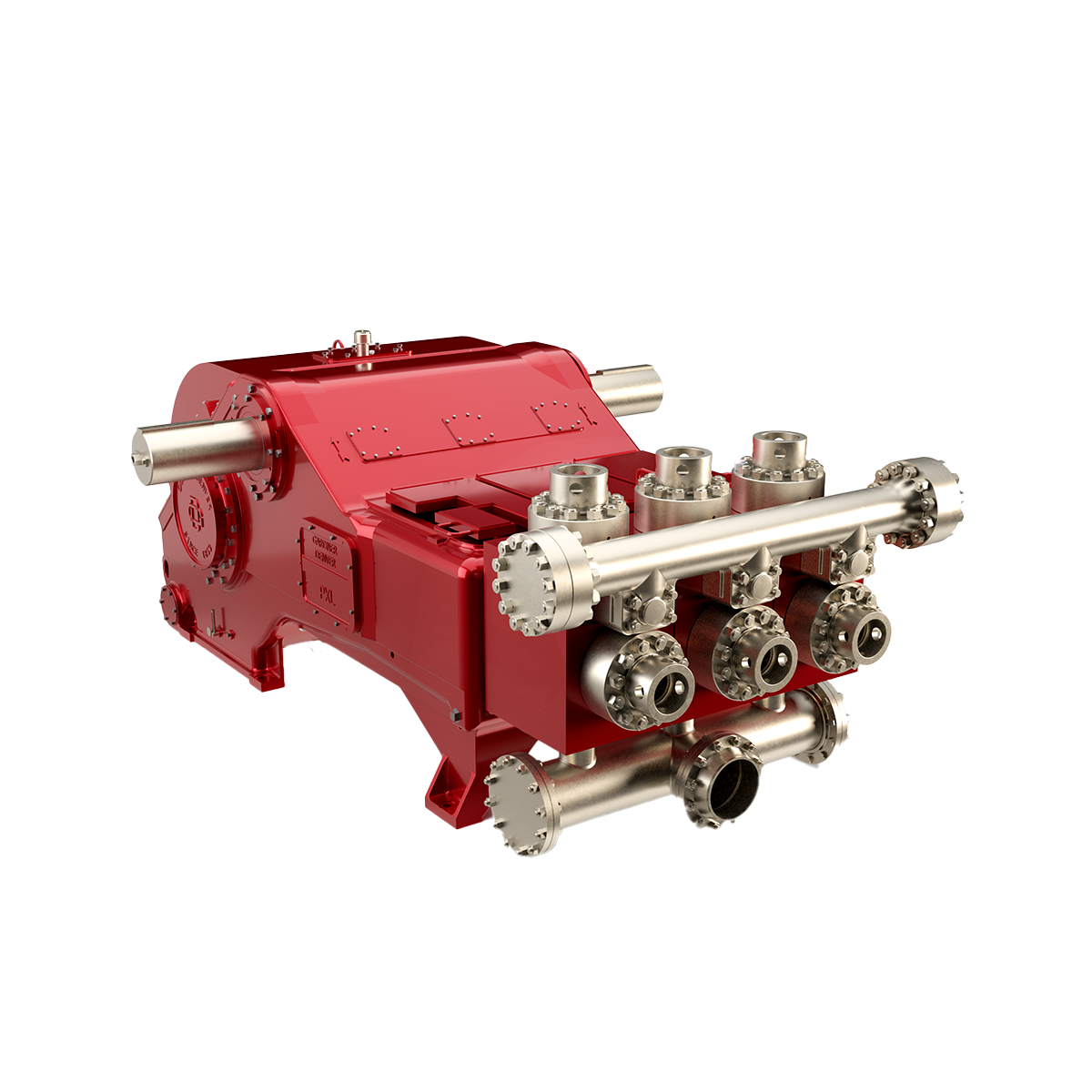

Powerful, durable and lightweight, the GD-1600 is ideal for offshore applications, but features the versatility to be used in skid, or truck mounted configurations, even being staggered for a double pump unit within the road legal 102” limit. A patented connecting rod assembly allows for maximum thrust bearing area, and standard autofrettaged fluid end options provide exceptional fluid end life.

For the successful execution of your projects, it is important to find an appropriate company with a good track record. We help you in connecting with the top mud pump manufacturers and companies and get the best quotation.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
Yes. We help you find the best mud pumps irrespective of your location. We simplify your search by connecting you with top mud pump manufacturers and mud pump companies in your location, according to your budget and business requirement.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
The different parts of a mud pump are Housing itself, Liner with packing, Cover plus packing, Piston and piston rod, Suction valve and discharge valve with their seats, Stuffing box (only in double-acting pumps), Gland (only in double-acting pumps), and Pulsation dampener. A mud pump also includes mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers along with other parts.
The wearing parts of a mud pump should be checked frequently for repairing needs or replacement. The wearing parts include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be taken up to enhance the service life of the wearing parts. This can effectively bring down the project costs and improve production efficiency.

Backed by the industry"s best delivery, customer service, and technical support, Cat Pumps products and service parts are readily available when you need them. A worldwide network of highly qualified distributors provides sales and service support for pumps, parts and accessories when servicing is required.

Adjust or replace these bearings at first sign of wear. The bearings in the crank end are babbitt lined steel shells, adjustable for wear by removing shims and easily replaced when completely worn. These bearings should be watched closely and adjusted at first signs of looseness.. You will note on series 3400, 3800, 3500, and 3900 pumps, that the shims do not completely fill the outer gap between rod and cap casting, although the connecting rod bolts are tight. This is because the faces of the shell bearings project slightly beyond the faces of the rod and cap castings, and the shims are gripped only between the faces of the bearing halves. Do not try to close this outer gap by tightening the connecting rod bolt as it will put an excessive strain on the bolts.
To check for wear, place a wrench on the top connecting rod bolt and shake the rod parallel to the crankshaft. (The pressure must be relieved from the liquid end of the pump, so that the pump"s mechanism is free to move.) If the rod bearing moves without resistance, the bearing may be too loose and need adjusting. If the bearing does need adjusting, remove shims until you cannot shake the rod, then add .005" shims one at a time until there is little side movement. Be sure to torque rod bolt nuts to proper value for each adjustment. Oil clearance should be checked with Plastigage (available in most parts stores). Wipe crankshaft journal clean of any oil, place a strip of Plastigage on the crankshaft journal and tighten rod cap to the proper torque value. Once tightened, remove rod cap and measure oil clearance with scale on Plastigage package. See oil clearance chart. (NOTE: If you are making this adjustment after having had the crossheads out, be sure that the oil holes in the rod are pointing up. The "up" side is indicated by matching numbers stamped on the cap and rod at the split between them. These numbers should be the same on each rod and should be on the top side of the crankshaft.) Rotate the shaft by hand and if there is any hard drag or tight spots in the bearing, add another 0.005" shim. After this bearing is properly adjusted, loosen bolts a few turns and repeat the above operation on the other bearings. After all bearings have been adjusted.
Torque all connecting rod bolt nuts back to proper value. Again rotate the pump by hand to check for excessive drag and tight spots. If none, the pump should be ready for operation.
If the pump cannot be rotated by hand due to the drive being enclosed, care must-be taken: not to over-tighten the bearings, since they cannot be checked by rotating the pump. When bearings are adjusted by this method, watch carefully for overheating when the pump is put into operation.
It is usually better to have a bearing a little too loose than too tight. A slightly loose bearing will cause very little trouble because of the slow operating speeds of the pump, but a tight bearing will overheat and the babbitt may melt or pull. Normal precautions must be taken to insure cleanliness of parts upon their assembly.
Inspect connecting rod bearings and adjust as necessary every six months or when crankcase lubricant is changed. The bearings in the crank end are babbitt lined steel shells, adjustable for wear by removing shims and easily replaced when completely worn. These bearings should be watched closely and adjusted to compensate for wear. You will note that shims do not completely fill the outer gap between rod and cap casting although the connecting rod bolts are tight. This is because the faces of the shell bearings project slightly beyond the faces of the rod and cap castings and the shims are gripped only between the faces of the bearing halves. Do not try to close this outer gap by tightening the connecting rod bolt as it will put an excessive strain on them.
To check for wear, place a wrench on the top connecting rod bolt and shake the rod parallel to the crankshaft. (The pressure must be relieved from the liquid end of the pump so that the pump"s mechanism is free to move.) If the rod bearing moves without resistance, the bearing may be too loose and need adjusting. If the bearing does need adjusting, remove shims until you cannot shake the rod, then add .005" shims one at a time until there is a little side movement. Be sure to torque rod bolt nuts to proper value for each adjustment. (NOTE: If you are making this adjustment after having had the crossheads out, be sure that the oil holes in the rod are pointing up. The "up" side is indicated by matching numbers stamped on the cap and rod at the split between them. These numbers should be the same on each rod and should be on the top side of the crankshaft.) Turn the shaft by hand and if there is any hard drag or tight spots in the bearing, add another .005"" shim. After this bearing is properly adjusted, loosen bolts a few turns and repeat the above operation on the other bearings. After all bearings have been adjusted, torque all connecting rod bolt nuts back to proper amount. Again turn the pump by hand to check for excessive drag and tight spots. If none, the pump should then be ready for operation.
If the pump cannot be rotated by hand due to the drive being enclosed, the bearings may be completely adjusted by shaking the bearing on the shaft as stated above. Care must be taken not to over-tighten the bearings since they cannot be checked by rotating the pump by hand. When bearings are adjusted by this method, they must be watched carefully for overheating when the pump is put into operation.
Alternatively, plastic gauge strips, found in most parts stores may be used to adjust these bearings. It is usually better to have a bearing a little too loose than too tight. A slightly loose bearing will cause very little trouble because of the slow operating speeds of the pump, but a tight bearing will overheat and the babbitt may melt or pull. with experience, an operator can tell by feel when the bearings are properly adjusted. Normal precautions must be taken to insure cleanliness of parts upon their assembly. All wrenches used in adjusting these bearings are standard wrenches.

Crown Oilfield Instrumentation offers Standpipe Pressure Gauges & Unitized Pressure Gauges (UMG) that come standard with a 2″ male NPT, 2” 1502 hammer union type, flanged type and threaded. These mud pump pressure gauges (also known as Standpipe Manifold Gauges) are easily view-able at distances and provide the same reliability as our standard6” gauges. Just like reading a large clock at a distance, Crown UMGs offer provide an easy-to-view, full-faced, liquid-filled dial, unlike a Type F or D that only has a half-moon shaped dial. With built in dampener assembly and blow-out plug safety feature, these gauges stand up to over-pressure situations, kicks, and rig vibrations. This style of gauge is ideal for mud pumps, stand pipes, choke manifolds and pump trucks and can be used in cementing, fracturing, and acidizing gravel-packing trucks, blowout preventers, and mud pump pressure gauge applications.




 8613371530291
8613371530291