mud pump liner function quotation
Alibaba.com offers 1111 mud pump liner products. About 56% % of these are mud pump, 7%% are mining machine parts, and 3%% are other oil field equipments.
A wide variety of mud pump liner options are available to you, You can also choose from oil well, mud pump liner,As well as from carbon steel, chromium, and iron. and whether mud pump liner is moulding, bending, or punching.

GDEP is the original creator of the drilling pump and continues to set the standard for durable, high-quality drilling pumps that can withstand the world’s toughest drilling environments. Starting with our PZ7 and rounding out with the market"s most popular pump, the PZ1600, our PZ Series of pumps are the perfect choice for today"s high-pressure drilling applications.

Electronic Pump Stroke Counters are a vital part to any drilling rig operation. When a mud pump is in operation, the driller must know how much mud is flowing down hole in order to keep the operation running at peak efficiency. Pump stroke counters assist the driller by measuring the mud pump’s strokes per minute and total strokes. So, how does a pump stroke counter tally the mud pump’s strokes
Electronic Pump Stroke Counters are a vital part to any drilling rig operation. When a mud pump is in operation, the driller must know how much mud is flowing down hole in order to keep the operation running at peak efficiency. Pump stroke counters assist the driller by measuring the mud pump’s strokes per minute and total strokes. So, how does a pump stroke counter tally the mud pump’s strokes, and why it is important? In order to understand that, you’ll need to know some basic information about mud pumps.
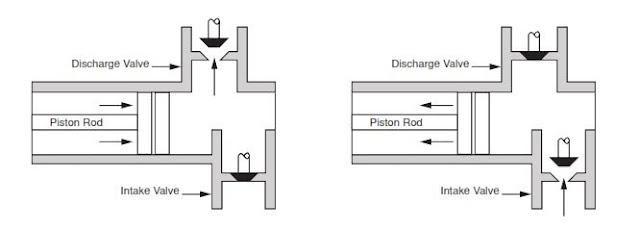
Knowing how a mud pump functions is important in understanding the role a pump stroke counter plays in rig operations. Mud pumps act as the heart of the drilling rig, similar to how our heart works. Just as our heart circulates blood throughout our bodies, a mud pump circulates essential drilling mud down the hole and back up to the surface. Mud tanks house drilling mud, and a mud pump draws the fluid from the mud pump. A piston draws mud in on the backstroke through the open intake valve and pushes mud through the discharge valve and sends it towards the rig. By circulating fluid, the mud pump ensures that the drill bit is cool and lubricated and that cuttings are flushed from the hole. The two main kinds of pumps used are duplex and triplex pumps, where the duplex pump has two pistons and the triplex pump has three. Whether the rig is using a duplex or triplex pump, it is important to know how many strokes per second the pistons are moving. The driller monitors strokes per minute to determine how much costly, yet essential, mud is being pumped into the system with the use of a mud pump stroke counter system. Now, that you know about mud pumps, you’ll need to know what’s in a stroke counter system.
Stroke Counter — The stroke counter stainless steel box is mounted on the driller’s console and is either square or rectangular in shape, depending on the number of pumps it is monitoring. Stroke counters will show strokes per minute and total strokes, and when a particular mud pump is operating the strokes/minute and total strokes will be displayed. Power is supplied by a 3.6 volt lithium battery, and the counter contains a crystal-controlled real time clock with 100 parts per million accuracy or better. Each counter is mounted to the console with 1/4” stainless steel hex head bolts, lock washers and nuts.
Micro Limit Switch — The micro switch is connected to a c clamp near the mud pump piston. The micro switch stainless steel rod (sometimes called a whisker) sticks out in the piston housing near the piston. As the piston passes the rod, it moves the rod and the switch sends an electronic signal back to the counter. The counter increases by one each time the piston moves the rod, counting the mud pump’s strokes. The switch’s signal is then transmitted to the stroke counter. These micro switches are built to stand up to demanding outdoor conditions. They can withstand shock, equipment vibration, extreme temperatures, water and dust.
Cable and Junction Box – A cable is connected to the back of the pump stroke counter and then to the junction box. From the junction box, the cables travel to the limit switches.
Pump Stroke Counters are like a blood pressure machine. Each time our heart pumps, a blood pressure machine reads our systolic and diastolic blood pressure by way of our pulse. A mud pump stroke counter functions in much the same way. Just as a blood pressure machine detects our pulse so too does a limit switch rod detect the movement of the piston. When the stainless steel rod is moved, the micro limit switch detects the movement. The signal is sensed as a contact closure, and it is transmitted to the stroke counter where the contact closure is converted to a logic pulse. The pulse feeds two separate circuits. The total strokes circuit reads and displays the closures one at a time, totaling them up to reveal the total strokes in the LED window. The second pulse is sent along a separate circuit which is a rate circuit. This rate circuit will average the closures against the real time clock. The result is displayed as the total strokes per minute.
Pump stroke counters are essential to drilling rig operations because they measure the efficiency of mud pumps. Knowing strokes per minute and total strokes of the pistons helps the driller to determine if the correct amount of mud is going down hole. Having this information aids in running a drilling rig at peak efficiency, assists in extending drill bit life, and avoids costly overuse of drilling rig mud. Unsure which pump stroke counter is right for your application? Give our friendly, knowledgeable staff a call or email. We’ll keep you turning right.

Function: Mud Pump Liner also called the cylinder liner. The cylinder liner is the core accessory of the mud pump, which has the functions of storing mud, bearing pressure and completing the suction and discharge of mud. Because the cylinder liner is in direct contact with the mud, it is easy to be worn and corroded by the tiny sand particles, acid and alkali liquid in the mud during work. As a result, the inner diameter of the cylinder liner becomes larger, leakage occurs in the seal between the cylinder liner and the piston, and the pressure is reduced. The cylinder liner is scrapped eventually. Cylinder liner is a one-time wearable part that cannot be reused, and its life span directly affects the normal operation and cost of the drilling operation.
Bimetal Liners are also known as double metal liners. Forged steel pipe 45# (ASTM1045) is used for the outer sleeve, the normalizing hardness: 160BHN (HB180-200); elongation: 17%; tensile strength is not less than 85000PSI; yield strength is not less than 60000 PSI; The inner sleeve material is high chromium wear-resistant cast iron, with chromium content of 26-28%; thickness is 0.25 to 0.35 inches (6.35-8.89 mm), and the standard thickness is 7 mm. Usually, the service life is 800 hours under normal drilling conditions.
The inner liner is made of zirconia or aluminium oxide, and the outer sleeve is made of 45# (ASTM1045) forged steel. It has the advantages of more wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high-pressure resistance, high-temperature resistance, high strength and high hardness than metal cylinder liners. The service life is more than 4000 hours under normal drilling conditions.
The piston assembly is one of the main parts of the hydraulic end system of the mud pump, and it is also one of the vulnerable parts of the drilling work. The discharge pressure of the mud pump is generated by the reciprocating linear movement of the piston assembly in the piston.
Polyurethane rubber has excellent oil resistance and wear resistance. The working temperature is not higher than 120℃, which is suitable for oil-based mud with working pressure below 35Mpa and working environment with high sand content.
Lake Petro has over 10 years of experience in Liners and Pistons, we export a large amount of mud pump parts to many countries and regions in the world. If you are interested in any of our products, please contact sales@lakepetro.com.

Lake Petro provides high quality Mud Pump Parts including Mud Pump Liners, Mud Pump Fluid End Module, piston, Valve and Seat etc. With more than 10 years of experience in the oil and gas industry, we are dedicated to help and support our loyal clients with the most cost-effective and quality Liners and Pistons. We also provide mud pump price and mud pump for sale.
We offer Liners with Ceramic (Zirconia and Aluminium oxide) and Steel (Metal and Bi-metal) materials for all common brands of the mud pump and triplex mud pump.
Bi-metal liners (double metal liners) are made of forged steel shell and wear-resistant sleeve of high chromium iron. In the production process, the size accuracy should be strictly controlled, which can ensure that they can be easily and stably installed. The inner sleeve with high finish and hardness is wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant and has a long service life. The bi-metal liners are suitable for a lot of bad working conditions. Its service life is more than 800 hours.
Ceramic Liners are made of a ceramic inner sleeve and a forged steel outer shell. The service life of ceramic liners is about 4000 to 10000 hours, the minimum time is at least 2000 hours, which is a lot more than bi-metal liners. Because of the phase transformation toughen technology, the ceramic liners have the features of wear-resistance, erosion-resistance, high-pressure-resistance, high hardness and strength. Zirconia type and Alumina type are common type of ceramic sleeve. Compared with Alumina type, Zirconia type liners have better toughness properties and a much longer service life. Piston wear and water consumption for lubrication can be reduced as well.
Seal Rings for Liner packing are also important. Liner Seal Rings is designed and made with hard corner which is an integral part of seal rings and soft nitrile element rubber center. We could provide reliable liner Seal Rings for our customers could order them at the same time.
All Lake Petro liner products are interchangeable with O.E.M. products. Meanwhile, we provide customized Liners according to drawings. Our liners, also with our other mud pump spares, are supplied for use in Honghua, F-Series, Bomco, Emsco and National lines of triplex drilling pumps. Let Lake Petro be your one-stop shop for your whole fleet of pumps. Please refer to “Suitable Pump Models” Lable for more details.

Mud Pump Pulsation Dampener is usually installed on the discharge line to reduce the fluctuation of pressure and displacement of the drilling mud pump.
Mud Pump Pulsation Dampener is a pneumatic device built into the outflow line of each UUD pump to dampen the pressure fluctuations resulting from the action of the pump. Although presented as a surge tank, this device is really a device that can be tuned to greatly diminish the output pulsations transmitted downstream from the mud pump. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of the pulsation dampener is a function of both output pump pressure and frequency of the pump pulsations.

A mud pump is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi (52,000 kPa)) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A duplex mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplex’s with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that Duplex mud pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better Measurement while drilling and Logging while drilling decoding.
Use duplex mud pumps to make sure that the circulation of the mud being drilled or the supply of liquid reaches the bottom of the well from the mud cleaning system. Despite being older technology than the triplex mud pump, the duplex mud pumps can use either electricity or diesel, and maintenance is easy due to their binocular floating seals and safety valves.
A mud pump is composed of many parts including mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers, and other parts. Parts of a mud pump:housing itself
Duplex pumps are used to provide a secondary means of fuel transfer in the event of a failure of the primary pump. Each pump in a duplex set is sized to meet the full flow requirements of the system. Pump controllers can be set for any of the following common operating modes:Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary): The lead (primary) pump is selected by the user and the lag (secondary pump operates when a failure of the primary pump is detected.
Alternating: Operates per Lead / Lag (Primary / Secondary) except that the operating pump and lead / lag status alternate on consecutive starts. A variation is to alternate the pumps based on the operating time (hour meter) of the lead pump.

NOV 12-P-160 Mud Pump is rated at 1600 input horsepower (1193 kw) at 120 strokes per minute, with a 12-inch (304.8 mm) stroke. Multiple liner sizes allow pressures and volumes to handle circulation requirements in deep drilling applications.
Flexibility: Compact engineering provides higher efficiency in less space. The NOV 12-P-160 Triplex Mud Pump light weight and flexible design make it easily adaptable to a variety of rig configurations. This provides flexibility as drilling requirements and conditions change.
Fluid End Modules: NOV offers a choice of fluid end modules and valve covers for every P Series pump model to select the fluid end module that exactly matches drilling requirements. All pump models can be equipped with either the standard or premium forged, two-piece interchangeable fluid modules
The drilling industry has roots dating back to the Han Dynasty in China. Improvements in rig power and equipment design have allowed for many advances in the way crude oil and natural gas are extracted from the ground. Diesel/electric oil drilling rigs can now drill wells more than 4 miles in depth. Drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to help transfer the dirt or drill cuttings from the action of the drilling bit back to the surface for disposal. Drill cuttings can vary in shape and size depending on the formation or design of the drill bit used in the process.
Watch the video below to see how the EDDY Pump outperforms traditional pumps when it comes to high solids and high viscosity materials commonly found on oil rigs.
The fluid is charged into high-pressure mud pumps which pump the drilling mud down the drill string and out through the bit nozzles cleaning the hole and lubricating the drill bit so the bit can cut efficiently through the formation. The bit is cooled by the fluid and moves up the space between the pipe and the hole which is called the annulus. The fluid imparts a thin, tough layer on the inside of the hole to protect against fluid loss which can cause differential sticking.
The fluid rises through the blowout preventers and down the flowline to the shale shakers. Shale shakers are equipped with fine screens that separate drill cutting particles as fine as 50-74 microns. Table salt is around 100 microns, so these are fine cuttings that are deposited into the half-round or cuttings catch tank. The drilling fluid is further cleaned with the hydro-cyclones and centrifuges and is pumped back to the mixing area of the mud tanks where the process repeats.
The drill cuttings contain a layer of drilling fluid on the surface of the cuttings. As the size of the drill cuttings gets smaller the surface area expands exponentially which can cause rheological property problems with the fluid. The fluid will dehydrate and may become too thick or viscous to pump so solids control and dilution are important to the entire drilling process.
One of the most expensive and troubling issues with drilling operations is the handling, processing, and circulation of drilling mud along with disposing of the unwanted drill cuttings. The drilling cuttings deposited in the half round tank and are typically removed with an excavator that must move the contents of the waste bin or roll-off box. The excavators are usually rented for this duty and the equipment charges can range from $200-300/day. Add in the cost for the day and night manpower and the real cost for a single excavator can be as much as $1800/day.
Offshore drilling rigs follow a similar process in which the mud is loaded into empty drums and held on the oil platform. When a certain number of filled drums is met, the drums are then loaded onto barges or vessels which take the drilling mud to the shore to unload and dispose of.
Oil field drilling operations produce a tremendous volume of drill cuttings that need both removal and management. In most cases, the site managers also need to separate the cuttings from the drilling fluids so they can reuse the fluids. Storing the cuttings provides a free source of stable fill material for finished wells, while other companies choose to send them off to specialty landfills. Regardless of the final destination or use for the cuttings, drilling and dredging operations must have the right high solids slurry pumps to move them for transport, storage, or on-site processing. Exploring the differences in the various drilling fluids, cutting complications, and processing options will reveal why the EDDY Pump is the best fit for the job.
The Eddy Pump is designed to move slurry with solid content as high as 70-80 % depending on the material. This is an ideal application for pumping drill cuttings. Drill cuttings from the primary shakers are typically 50% solids and 50% liquids. The Eddy Pump moves these fluids efficiently and because of the large volute chamber and the design of the geometric rotor, there is very little wear on the pump, ensuring long life and greatly reduced maintenance cost for the lifetime of the pump.
plumbed to sweep the bottom of the collection tank and the pump is recessed into a sump allowing for a relatively clean tank when the solids are removed. The Eddy Pump is sized to load a roll-off box in 10-12 minutes. The benefit is cuttings handling is quicker, easier, safer, and allows for pre-planning loading where the labor of the solids control technician is not monopolized by loading cuttings. Here, in the below image, we’re loading 4 waste roll-off bins which will allow the safe removal of cuttings without fear of the half-round catch tank running over.
Mud cleaning systems such as mud shaker pumps and bentonite slurry pumps move the material over screens and through dryers and centrifuges to retrieve even the finest bits of stone and silt. However, the pump operators must still get the raw slurry to the drill cuttings treatment area with a power main pump. Slurry pumps designed around the power of an Eddy current offer the best performance for transferring cuttings throughout a treatment system.
Options vary depending on whether the company plans to handle drill cuttings treatment on-site or transport the materials to a remote landfill or processing facility. If the plan is to deposit the cuttings in a landfill or a long-term storage container, it’s best to invest in a pump capable of depositing the material directly into transport vehicles. Most dredging operations rely on multiple expensive vacuum trucks, secondary pumps, and extra pieces of equipment.
Using an EDDY Pump will allow a project to eliminate the need for excavators/operators to load drill cuttings, substantially lowering both labor and heavy equipment costs. The EDDY Pump also allows a company to eliminate vacuum trucks once used for cleaning the mud system for displacing fluids. Since the pump transfers muds of all types at constant pressure and velocity throughout a system of practically any size, there’s little need for extra equipment for manual transfer or clean up on the dredge site.
The EDDY Pump can fill up a truck in only 10 minutes (compared to an hour) by using a mechanical means such as an excavator. For this reason, most companies can afford one piece of equipment that can replace half a dozen other units.
This application for the Eddy Pump has the potential to revolutionize the drilling industry. Moving the excavator out of the “back yard” (the area behind the rig from the living quarters) will make cuttings handling a breeze. Trucking can be easier scheduled during daylight hours saving on overtime and incidences of fatigued driving. Rig-site forklifts can move the roll-off boxes out of the staging area and into the pump loading area. The operator can save money on excavators rental, damages, and keep the technician operating the solids control equipment.
The EDDY Pump is ideal for drilling mud pump applications and can be connected directly onto the drilling rigs to pump the drilling mud at distances over a mile for disposal. This eliminates the need for costly vacuum trucks and also the manpower needed to mechanically move the drilling mud. The reasons why the EDDY Pump is capable of moving the drilling mud is due to the hydrodynamic principle that the pump creates, which is similar to the EDDY current of a tornado. This tornado motion allows for the higher viscosity and specific gravity pumping ability. This along with the large tolerance between the volute and the rotor allows for large objects like rock cuttings to pass through the pump without obstruction. The large tolerance of the EDDY Pump also enables the pump to last many times longer than centrifugal pumps without the need for extended downtime or replacement parts. The EDDY Pump is the lowest total life cycle pump on the market.

The piston is one of the parts that most easily become worn out and experience failure in mud pumps for well drilling. By imitating the body surface morphology of the dung beetle, this paper proposed a new type (BW-160) of mud pump piston that had a dimpled shape in the regular layout on the piston leather cup surface and carried out a performance test on the self-built test rig. Firstly, the influence of different dimple diameters on the service life of the piston was analyzed. Secondly, the analysis of the influence of the dimple central included angle on the service life of the piston under the same dimple area density was obtained. Thirdly, the wear of the new type of piston under the same wear time was analyzed. The experimental results indicated that the service life of the piston with dimples on the surface was longer than that of L-Standard pistons, and the maximum increase in the value of service life was 92.06%. Finally, the Workbench module of the software ANSYS was used to discuss the wear-resisting mechanism of the new type of piston.
The mud pump is the “heart” of the drilling system [1]. It has been found that about 80% of mud pump failures are caused by piston wear. Wear is the primary cause of mud pump piston failure, and improving the wear-resisting performance of the piston-cylinder friction pair has become the key factor to improve the service life of piston.
Most of the researchers mainly improve the service life of piston through structural design, shape selection, and material usage [1, 2]. However, the structure of mud pump piston has been essentially fixed. The service life of piston is improved by increasing piston parts and changing the structures of the pistons. However, the methods have many disadvantages, for example, complicating the entire structure, making piston installation and change difficult, increasing production and processing costs, and so on. All piston leather cup lips use rubber materials, and the material of the root part of the piston leather cup is nylon or fabric; many factors restrict piston service life by changing piston materials [3]. Improving the component wear resistance through surface texturing has been extensively applied in engineering. Under multiple lubricating conditions, Etsion has studied the wear performance of the laser surface texturing of end face seal and reciprocating automotive components [4–6]. Ren et al. have researched the surface functional structure from the biomimetic perspective for many years and pointed out that a nonsmooth surface structure could improve the wear resistance property of a friction pair [7, 8]. Our group has investigated the service life and wear resistance of the striped mud pump piston, and the optimal structure parameters of the bionic strip piston have improved piston service life by 81.5% [9]. Wu et al. have exploited an internal combustion engine piston skirt with a dimpled surface, and the bionic piston has showed a 90% decrease in the average wear mass loss in contrast with the standard piston [10]. Gao et al. have developed bionic drills using bionic nonsmooth theory. Compared with the ordinary drills, the bionic drills have showed a 44% increase in drilling rate and a 74% improvement in service life [11]. The present researches indicate that microstructures, like superficial dimples and stripes, contribute to constituting dynamic pressure to improve the surface load-carrying capacity and the wear resistance of the friction pair [12–21].
In nature, insects have developed the excellent wear-resistant property in the span of billions of years. For instance, the partial body surface of the dung beetle shows an irregularly dimpled textured surface with the excellent wear-resistant property that is conducive to its living environment [7, 8, 22]. The dung beetle, which is constantly active in the soil, shows a body surface dimple structure that offers superior drag reduction. These dimples effectively reduce the contact area between the body surface and the soil. Moreover, the friction force is reduced. Therefore, the dung beetle with the nonsmooth structure provides the inspiration to design the bionic mud pump piston. This paper proposed a new type of piston with dimpled morphology on its surface and conducted a comparative and experimental study of different surface dimpled shapes, thus opening up a new potential to improve the service life of the mud pump piston.
A closed-loop circulatory system was used in the test rig, which was built according to the national standard with specific test requirements. The test rig consisted of triplex single-acting mud pump, mud tank, in-and-out pipeline, reducer valve, flow meter, pressure gauge, and its principle, as shown in Figure 1. Both the pressure and working stroke of the BW-160 mud pump are smaller than those of the large-scale mud pump, but their operating principles, structures, and working processes are identical. Therefore, the test selected a relatively small BW-160 triplex single-acting mud pump piston as a research object, and the test results and conclusion were applicable to large-scale mud pump pistons. The cylinder diameter, working stroke, reciprocating motion velocity of piston, maximum flow quantity, and working pressure of the BW-160 triplex single-acting mud pump were 70 mm, 70 mm, 130 times/min, 160 L/min, and 0.8–1.2 MPa, respectively.
The mud pump used in the test consisted of water, bentonite (meeting the API standard), and quartz sand with a diameter of 0.3–0.5 mm according to actual working conditions. The specific gravity of the prepared mud was 1.306, and its sediment concentration was 2.13%. Whether mud leakage existed at the venthole in the tail of the cylinder liner of the mud pump was taken as the standard of piston failure. Observation was made every other half an hour during the test process. It was judged that the piston in the cylinder failed when mud leaked continuously; its service life was recorded, and then it was replaced with the new test piston and cylinder liner. The BW-160 mud pump is a triplex single-acting mud pump. The wear test of three pistons could be simultaneously conducted.
The mud pump piston used in the test consisted of a steel core, leather cup, pressing plate, and clamp spring. The leather cup consisted of the lip part of polyurethane rubber and the root part of nylon; the outer diameter on the front end of the piston was 73 mm, and the outer diameter of the piston tail was 70 mm, as shown in Figure 2. We proceeded in two parts during the design of the dimpled layout pattern because the piston leather cup consisted of two parts whose materials were different. The dimples at the lip part of the leather cup adopted an isosceles triangle layout pattern, and the dimples at the root part were arranged at the central part of its axial length, as shown in Figure 3(a). Dimple diameter (D, D′), distance (L), depth (h), and central included angle (α) are shown in Figure 3. The dimples on the piston surface were processed by the CNC machining center. Since then, the residual debris inside the dimples was cleaned.
Table 1 shows that average service lives of L-Standard, L-D1, L-D2, and L-D3 were 54.67 h, 57.17 h, 76.83 h, and 87.83 h, respectively. Therefore, the mud pump pistons with dimples provide longer service life than the L-Standard piston. As the dimple diameter increases, the piston service life was improved, and the largest percentage increase of the service life was 60.65%. The service life of the L-D4 piston was about 81.17 h, which increased by 7.94% compared with that of the L-D2 piston, indicating that the piston with dimples at the leather cup root could improve piston service life.
Figure 4 illustrates the surface wear patterns of pistons with different dimple diameters in the service life test. Figures 4(a) and 4(a′) show wear patterns on the surface of the L-Standard piston. This figure shows that intensive scratches existed in parallel arrangement on the piston leather cup surface, enabling high-pressure mud to move along the scratches from one end of the piston to the other easily, which accelerated the abrasive wear failure with the abrasive particles of the piston. Figures 4(b), 4(b′), 4(c), 4(c′), 4(d), and 4(d′) show the wear patterns of the leather cup surfaces of L-D1, L-D2, and L-D3 pistons, respectively. Figures 4(b), 4(b′), 4(c), 4(c′), 4(d), and 4(d′) show that the scratches on the leather cup surface became shallower and sparser and the surface wear patterns improved more obviously as the dimple diameter increased. If the piston leather cup surface strength was not affected to an extent as the dimple diameter increased, the reduced wear zone near the dimple would become greater and greater, indicating that the existence of dimples changed the lubricating status of the leather cup surface, their influence on nearby dimpled parts was more obvious, and they played active roles in improving the service life of the piston.
Figure 5 displays the wear patterns of the leather cup root parts of the L-D4 and L-D2 test pistons. The wear patterns of the nylon root parts of the L-D4 pistons are fewer than those of the L-D2 pistons, as shown in Figure 5. When the leather cup squeezed out high-pressure mud as driven by the piston steel core, it experienced radial squeezing while experiencing axial wear. Therefore, the area with the most serious wear was the piston leather cup root part, and the friction force at the leather cup root was much greater than that at the other areas. The rapid wear at the root decreased the piston load-carrying capacity and then affected the service life of piston. The dimples at the piston leather cup root could reduce the wear of the piston leather cup root and improve the service life of piston.
Figure 6 shows the surface wear patterns of the L-S1 and L-S2 test pistons. In Figures 6(a) and 6(a′), the scratches on the piston leather cup surface became sparse and shallow in the dimpled area. Figures 6(b) and 6(b′) show that the wear was slight in the area close to the dimples. The farther the scratches were from the dimpled area, the denser and deeper the scratches would be. The L-S1 piston had a small dimple central included angle, which was arranged more closely on the piston surface. The lubricating effects of oil storage in each row of dimples were overlaid very well, which was equivalent to amplifying the effect of each row of dimples in Figure 6(b), making the wear on the whole piston leather cup surface slight, preventing the entry of high-pressure mud into the frictional interface, and lengthening the service life of piston.
During the operation of the mud pump piston, the outside surface of the piston leather cup comes in contact with the inner wall of the cylinder liner and simultaneously moves to push the mud. The lip part of the piston leather cup mainly participated in the piston wear and exerted a sealing effect, while the piston root part mainly exerted centralizing and transitional effects. In the mud discharge stroke, the lip part of the piston experienced a “centripetal effect,” and a gap was generated between the lip part and the cylinder liner. The greater the contact pressure between the lip part and cylinder liner of the piston was, the smaller the gap was, and the entry of high-pressure mud into the contact surface between the piston and cylinder liner was more difficult. The piston root easily experienced squeezing under high pressure, and the smaller the equivalent stress caused by the piston root was, the more difficult the squeezing to occur. Hence, the contact pressure at the lip part of the piston and the equivalent stress at the root were analyzed, and they would provide a theoretical basis for the piston wear-resisting mechanism. The ANSYS Workbench module was used to perform a comparative analysis between the contact pressure at the lip part and the equivalent stress at the root of the three kinds of pistons (i.e., L-Standard piston, L-S1 piston, and L-D1 piston). The service life of the L-S1 piston exhibited the best improvement effect, whereas that of the L-D1 piston demonstrated the worst improvement effect. The piston adopted a 1 mm hexahedral grid, and the grid nodes and elements are as shown in Table 4.
The contact pressure nephograms of the three pistons indicate that the dimpled structure on the piston surface changed the distribution state of contact pressure. Three nodes were selected at the same position of each piston to obtain the contact pressure values. The node positions are shown in Figure 8(c), and the average pressure value of three nodes was the pressure value at the lip part of this piston. The contact pressure value of the L-Standard piston was 0.6027 MPa and that of the L-D1 and L-S1 pistons was 0.6840 MPa and 1.0994 MPa, respectively. Compared with the L-Standard piston, the contact pressure at the lip part of the L-S1 piston increased, the gap between the piston and cylinder liner became small, which could effectively prevent abrasive particles from participating in the wear and resulting in piston failure, and there was greater improvement in the service life of piston. The contact pressure of the L-D1 piston did not increase too much, and the degree of improvement of the piston service life was not obvious.
The lubricating oil on the mud pump piston surface could reduce the wear of piston and cylinder liner and improve the service life of pistons with the reciprocating movement. The lubricating oil would eventually run off and lose lubricating effect, which would result in piston wear. The finite element fluid dynamics software CFX was used to establish the fluid domain model of the dimpled and L-Standard pistons and analyze the lubricating state on the piston surface. The piston surface streamlines are shown in Figure 10. This figure shows that the lubricating fluid did not experience truncation or backflow phenomenon when passing the surface of the L-Standard piston. When the lubricating fluid flowed through the surface of the dimpled piston, it presented a noncontinuous process. Its flow velocity at the dimpled structure slowed down obviously because it was blocked by the dimpled structure.
Figure 11 shows the piston cross section streamline. This figure shows that the existence of dimples changed the distribution status of the lubricating flow fields on the contact surface between the piston and cylinder liner. The lubricating oil entered the dimpled structure in a large quantity, and the flow velocity slowed down. The dimpled structure on the piston surface enlarged the storage space of the lubricating oil and made it difficult for the lubricating oil inside the dimpled structure to be taken away by the cylinder liner to improve the lubricating conditions of the friction pair interface, reduce the frictional resistance between the piston and cylinder liner, reduce wear, and improve the piston service life.
When the piston moved in the cylinder liner, a small quantity of solid particles in mud entered gap of piston and cylinder liner and participated in abrasion. The dimpled structure on the piston surface could store some abrasive particles (as shown in Figure 6(a′)) during the piston wear process to prevent these particles from scratching the piston and cylinder liner and generating gullies, thus avoiding secondary damage to the piston and cylinder liner and improving the piston service life.
This paper presented a dimpled-shape mud pump piston; that is, the piston leather cup surface had a dimpled array morphology in regular arrangement. The experimental results can provide the basic data for design engineering of the mud pump piston with a long service life. The comparative analyses of service life and wear patterns for dimpled mud pump pistons and L-Standard pistons were conducted. The main results and conclusions were summarized as follows:(1)The service life of the mud pump piston with dimpled morphology on the surface improved in comparison with that of the L-Standard piston, and the service life increase percentages were from 4.57% to 92.06%.(2)The piston service life would increase with the dimple diameter under the same dimpled arrangement pattern, and the maximum increase in the value of service life was 60.65%.(3)The service life of the piston with dimples increased by 7.94% in comparison with that with none.(4)Under the same dimpled arrangement patterns and area densities, the tighter and closer the dimples were arranged on the piston surface, the longer the service life of piston was, and the maximum increase in the value of service life was 92.06%.(5)Under the same wear time, the wear of the dimpled piston slightly decreased in comparison with that of the L-Standard piston, and the minimum value of wear mass percentage was 3.83%.(6)The dimpled shape could not only change the stress state of the piston structure, improve piston wear resistance, and reduce root squeezing, but also increase oil storage space, improve lubricating conditions, and enable the accommodation of some abrasive particles. Furthermore, the dimpled shape was the key factor for the service life improvement of the mud pump piston.

Weir provides the oil and gas industry with the best in full open valve and seat technology and manufactures a wide variety of valves and seats for workover pumps, high pressure well service fracturing pumps, cementing pumps and mud pumps through its Novatech™ pressure pumping equipment line.
Novatech leads the industry in full open valve and seat technology and manufactures valves and seats for workover pumps, high pressure well service fracturing pumps, cementing pumps and mud pumps. Novatech also manufactures caged assemblies for almost all well service pumps and applications, including workover, cementing, acidizing and fracking. Novatech developed the first valve and seat in the industry rated for continuous service at 7,500 psi. Products are 100% made in U.S.A.
Reasontek carry Weir/Novatech products for oilfield applications including valves, seats, inserts replacement of pump maintenance. Please check the catalogue below and let us know your request.

Our pumps can be used for numerous industrial and oil field applications, including oil-line pumping, mine-dewatering, chemical and petroleum products transfer, well servicing, cementing, mud drilling, water well drilling and salt water injection.




 8613371530291
8613371530291