mud pump pressure formula manufacturer

Rig pump output, normally in volume per stroke, of mud pumps on the rig is one of important figures that we really need to know because we will use pump out put figures to calculate many parameters such as bottom up strokes, wash out depth, tracking drilling fluid, etc. In this post, you will learn how to calculate pump out put for triplex pump and duplex pump in bothOilfield and Metric Unit.

Continental Emsco Drilling Products, Inc., which consisted of Emsco drilling machinery and Wilson mobile rigs, was purchased by National-Oilwell, Inc on July 7, 1999. To our knowledge, no pumps have been manufactured and sold under the Emsco brand name since National-Oilwell acquired them.
Fairbanks Morse pumps are currently manufactured in Kansas City, Kansas. Fairbanks Morse is a division of Pentair ever since August, 1997 when Pentair purchased the General Signal Pump Group.
Gaso pumps are manufactured by National Oilwell Varco. Gaso was acquired as "Wheatley Gaso" by National-Oilwell in the year 2000. At the time, Wheatley Gaso was owned by Halliburton.
Skytop Brewster pumps are no longer available as new pumps. Skytop Brewster(Cnsld Gold), a unit of Hansen PLC"s Consolidated Gold Fields subsidiary, was acquired while in bankruptcy by National-Oilwell, Inc. in November, 1999.

The purpose of this article is to present some guidelines and simplified techniques to size pumps and piping typically used in mud systems. If unusual circumstances exist such as unusually long or complicated pipe runs or if very heavy or viscous drilling muds are used, a qualified engineer should analyze the system in detail and calculate an exact solution.
To write about pumps, one must use words that are known and well understood. For example, the label on the lefthand side of any centrifugal pump curve is Total Head Feet. What does this mean?
Total Head remains constant for a particular pump operated at a constant speed regardless of the fluid being pumped. However, a pump’s pressure will increase as the fluid density (mud weight) increases according to the following relationship:
Note that the pump pressure almost doubled. It follows that the required pump horsepower has increased by the same percentage. If the pump required 50 HP for water service, it will require the following horsepower for 16 lb/gal mud:
To summarize, a pump’s Total Head remains constant for any fluid pumped, only the pump pressure and pump horsepower will change. Therefore, a pump motor must be sized according to the heaviest weight mud to be pumped.
In our example problem, the required desilter pressure head is 75 ft. for any mud weight. However, the pressure would be 30.3 PSIG for water or 43.6 PSIG for 12 lb mud or 58.1 PSIG for 16 lb mud. A good rule of thumb is that the required pressure (PSIG) equals 4 times the mud weight (12 LB/GAL x 4 = 48 PSIG).
Determine the required pressure head and flow rate. If the pump is to supply a device such as a mud mixing hopper or a desilter, consult the manufacturer’s information or sales representative to determine the optimum flow rate and pressure head required at the device. (On devices like desilters the pressure head losses downstream of the device are considered negligible and are usually disregarded.)
Select the basic pump to pump the desired flow rate. Its best to refer to a manufacturer’s pump curve for your particular pump. (See example – Figure 3).
The pump’s impeller may be machined to a smaller diameter to reduce its pressure for a given application. Refer to the manufacturer’s pump curves or manufacturer’s representative to determine the proper impeller diameter. Excessive pressure and flow should be avoided for the following reasons:
The pump must produce more than 75 FT-HD at the pump if 75 FT-HD is to be available at the desilter inlet and the pump’s capacity must be at least 800 GPM. Therefore, we should consider using one of the following pumps from the above list: 4″ x 5″ Pump 1750 RPM – 1000 GPM at 160 FT-HD; or 5″ x 6″ Pump 1750 RPM – 1200 GPM at 160 FT-HD.
The pump suction and discharge piping is generally the same diameter as the pump flange diameters. The resulting fluid velocities will then be within the recommended ranges of 4 to 10 FT/SEC for suction lines and 4 to 12 FT/
SEC for discharge lines. Circumstances may dictate that other pipe diameters be used, but remember to try to stay within the above velocity guidelines. Smaller pump discharge piping will create larger pressure drops in the piping
and the pump may not be able to pump the required amount of fluid. (For example, don’t use a 4″ discharge pipe on a 6″ x 8″ pump and expect the pump’s full fluid flow.)
6″ pipe may be used for the suction pipe since it is relatively short and straight and the pump suction is always flooded. 6″ pipe is fully acceptable for the discharge pipe and is a good choice since the desired header is probably 6″ pipe.
8″ pipe may be used for the suction pipe (V = 5.13 FT/SEC) since V is still greater than 4 FT/SEC. 8″ pipe would be preferred if the suction is long or the suction pit fluid level is low with respect to the pump.

Mud pump liner selection in today"s drilling operations seldom (at best) considers electrical implications. Perhaps, with more available useful information about the relationships between mud pump liner size and operational effects on the electrical system, certain potential problems can be avoided. The intent of this paper is to develop those relationships and show how they affect an electrical system on example SCR rigs.Introduction
There, seems to be little consideration for the relationships between liner size and demand on a rig"s engine/generator set(s). Yet, consideration for this relationship can prove to be very helpful to drillers and operators in efficiency of a rig"s electrical system. In order to develop the relationships and help drillers and operators understand the importance of each, relationships between liner size, pump speed, pump pressure, and electrical power will be developed. Only basic physical laws will be used to develop the relationships; and, once developed, the relationships are readily applied to realistic examples utilizing a mud pump manufacturer"s pump data. Finally, conclusions will be drawn from the examples.DEVELOPMENT OF RELATIONSHIPS BASIC RELATIONSHIPS
where HHP= Hydraulic horsepower, GPM = Mud pump volumetric flow rate in gallons per minute, and PST Mud pump output pressure in pounds peer square inch.
Hydraulic horsepower is reflected to the mud pump motor via a multiplier for mechanical efficiency. it follows that motor horsepower is then represented by

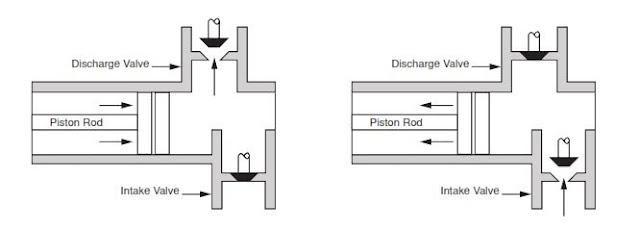
Whether onshore or offshore, well drilling sites rely on a multitude of systems to successfully perform the drilling operation. The mud pump is a key component tasked with circulating drilling fluid under high pressure downhole. The mud pump can be divided into two key sections: the power end or crosshead and the fluid end. Proper alignment of the pump’s crosshead to the fluid end liner is necessary to maximizing piston and liner life. Misalignment contributes to
accelerated wear on both the piston and the liner, and replacing these components requires downtime of the pump. Traditional methods of inspecting alignment range from using uncalibrated wooden rods, Faro Arms and micrometers to check the vertical and horizontal alignment of the piston rod OD to the piston liner ID. These are time consuming and cumbersome techniques that are ultimately not well suited to troubleshoot and solve alignment issues.
A “Mud Pump Laser Alignment Kit” enables you to measure where the piston will run through the liner at various positions along the pump’s stroke. It will also project a laser centerline from the fluid end back towards the rear power end of the pump that can be used to determine how much shimming is required to correct any alignment issues. The kit can include either a 2-Axis receiver or a 4-Axis which accepts the laser beam and documents where it falls on the active surface of the receiver. The 4-Axis receiver can decrease alignment time by as much as 50% as it will measure angularity as well as X and Y while the 2-Axis does not and will need multiple measurement locations to get the same information. In addition, the alignment system is a non-intrusive service requiring the removal of only the piston rod which allows for much quicker service and less down time on the pump. As the mud pumps in question are located globally both on and offshore, having a small, portable system is another great advantage. Our recommendation would be Pinpoint laser System’s “Mud Pump Alignment Kit”. They are being used by many of the leading repair service companies and have been their main alignment tool for over 15 years. Manufacturers are also utilizing these for new pump set-up.
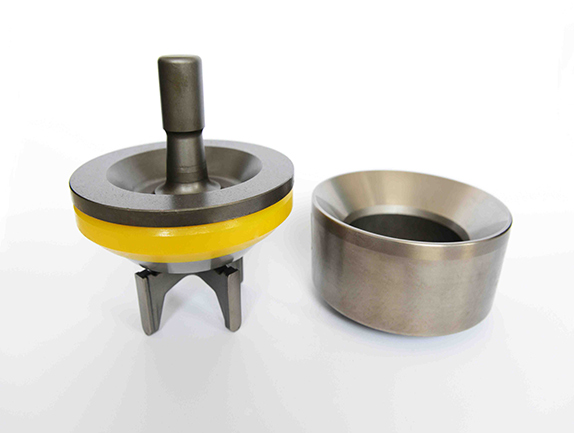

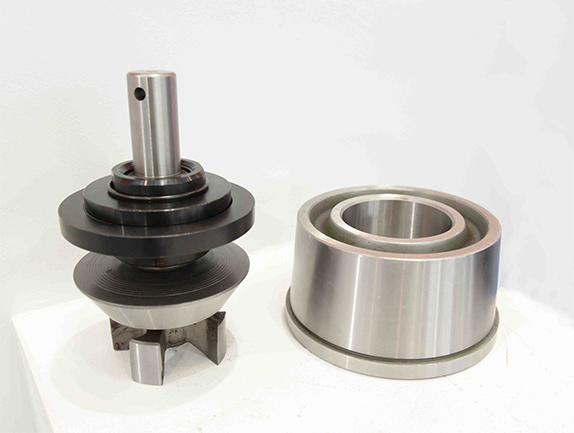
Centerline Manufacturing is committed to the highest level of customer service quality. Every Centerline pump is comprehensively and repeatedly tested at diverse pressure levels to assure that it goes to our customer in perfect operational order. Centerline technicians work to ensure that our customers fully understand the operation of the model being delivered. If a customer"s pump is down, we understand the importance of timely response and parts availability. Centerline technicians will assess the problem and make repairs to bring the pump back into new specification. The Centerline mud pump technicians are well versed and qualified to operate and repair any product that is provided to the customer.
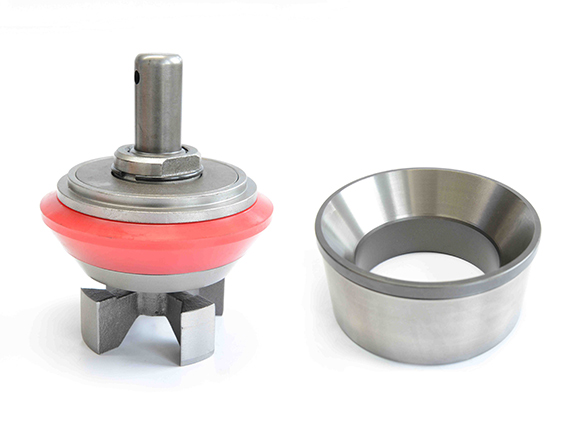

Centerline Manufacturing is committed to the highest level of customer service quality. Every Centerline pump is comprehensively and repeatedly tested at diverse pressure levels to assure that it goes to our customer in perfect operational order. Centerline technicians work to ensure that our customers fully understand the operation of the model being delivered. If a customer"s pump is down, we understand the importance of timely response and parts availability. Centerline technicians will assess the problem and make repairs to bring the pump back into new specification. The Centerline mud pump technicians are well versed and qualified to operate and repair any product that is provided to the customer.
When it comes to pumping terminology, one crucial term to know is GPM — a measurement that will help you determine if you’re choosing the right pump. So what is GPM, and how do you calculate it?
GPM stands for gallons per minute and is a measurement of how many gallons a pump can move per minute. It is also referred to as flow rate. GPM is variable based on another measurement known as the Head, which refers to the height the water must reach to get pumped through the system. It is also referred to as flow rate. GPM is variable based on another measurement known as the Head, which refers to the height the water must reach to get pumped through the system.
Pumps are typically measured by their GPM at a certain Head measurement. For example, a pump specification may read 150 GPM at 50 Feet of Head, which means the pump will work at 150 gallons per minute when pumping water at a height of 50 feet.
The GPM formula is 60 divided by the number of seconds it takes to fill a one gallon container. So if you took 10 seconds to fill a gallon container, your GPM measurement would be 6 GPM (60/10 seconds = 6 GPM). To most accurately calculate GPM, you use the pressure tank method and formula. For this calculation, you need to know the specifications of your pressure tank, including how many gallons it holds, the gallon drawdown and the PSI. The manufacturer specifies the gallon drawdown. Once you have that information, as well as a stopwatch to keep time, follow these steps:
For example, if it took four minutes for the pressure switch to turn off, and your gallon drawdown was 20 gallons, this would mean a GPM rate of five.
If you don’t have a pressure tank, you can also use a bucket or any other container, time how long it takes to fill up and then divide that by the volume the container holds.
GPM identifies the unique capabilities of a pump so you can select the right one for your specific needs. If you need a pump for a larger public area such as a golf course, marina or lake, you will need a pump with a much higher GPM than one used for your home’s well. Plus, choosing the correct pump is essential for reducing your costs and increasing your pump’s lifespan.
At GeoForm International, we are a leading manufacturer of high-quality submersible pumps, dredges, digester packages and aerators, all of which are made in the U.S. With our pump expertise, we know just how essential GPM is in the pumping and dredging industry from how much equipment costs to how long jobs will take.

Case story: Water and wastewater treatment plants Areas of application Transfer and dosing of lime milk and ACP, sludge, iron chloride, lixiviat. Sampling of treated water and chlorine water. Injection of bisulfite. Pumping of grease, wastewater with grease, oil and phosphoric acid and water with sand. Models from all four realax peristaltic pump series – the APY, ISI, IP and RP –...
Case story: Directional drilling Application: Drilling mud Pump: Realax ISI 22 Hose material: Natural Rubber Speed: 17 rpm Pressure: ...
Case story: Food manufacturer Application: Transfer of water based mustard suspension Pump: Realax RP 32 Hose material: NBR Speed: ...
Case story – Detergent manufacturer Problem description An Italian manufacturer of chemical detergent products for industrial cleaning faced several problems with flexible impeller pumps used for product filling. The high rotation speed of the pumps caused the product foaming. As a result, the storage tanks could therefore never be fully emptied due to pump cavitation, which caused impeller damage. Consequently for the customer,...
Case story: Passenger ship operator Application: Sewage treatment on passenger ships Pump: Realax IP 70 on a trolley Viscosity: Varying viscosity Abrasive/solids: High...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
One of the major titanium dioxide manufacturers in France, uses two realax RP 100 duplex and one realax RP60 duplex to transfer very abrasive product with a flow of 46M3/H, 55 cps and 35°C, 2 bars. About titanium dioxide Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. The most important application areas...
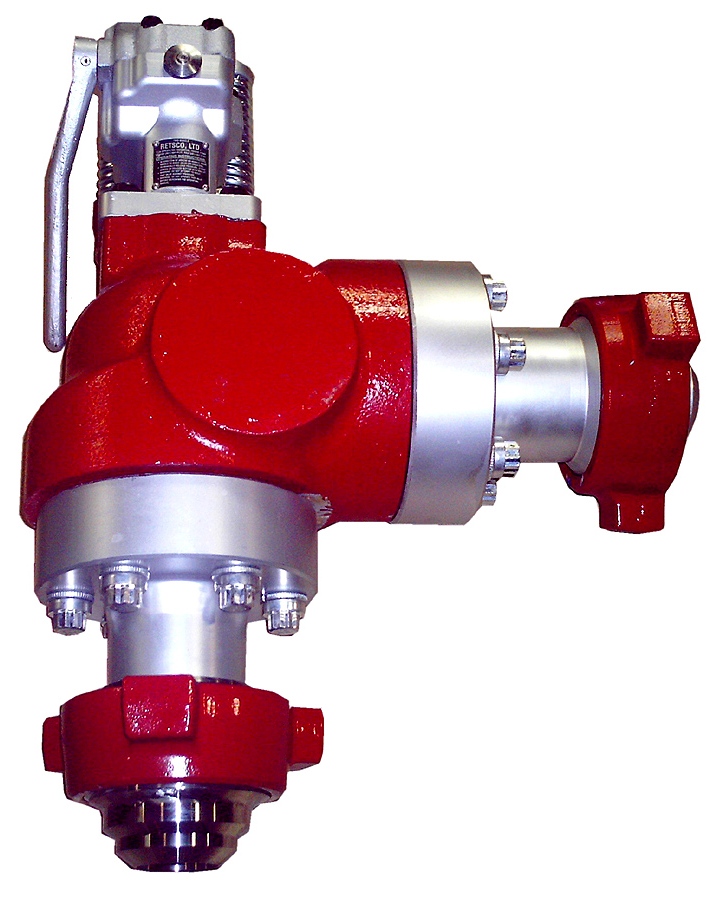
Pressure relief valves are installed on mud pumps in order to prevent an overpressure which could result in a serious damage of the pump and serious or fatal injury to personnel.
The discharge pressure is routed to the closer mud tank, via a 3” XXS line clamped strongly on tank side . Mud is flowing into the mud tank until line bled off, bearing in mind that minimum slope is required to avoid mud settling in pipe ( around 1 inch/meter).
Pressure relief valves are set usually to 90% of the maximum working pressure of the liners in use. Read carefully manufacturer chart for pressure setting versus size of liners.
With a low pressure setting, ie, 1000psi, by adjusting the top nylon self lock nut to move on the vertical scale to get the same setting than the scale.
Discharge pressure losses close to the maximum preset pressure.The Pressure relief valves are usually installed on a upper point of the discharge side of the mud pumps.
The pressure relief valve can be reset, if not damaged during the release of pressure. Special care should be taken if no working platform available to access the PRV.




 8613371530291
8613371530291