mud pump working principle price

A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling and manufactured according to API specification 7K.
The advantages of the drilling mud pump include the ability to move high-solids-content fluids laden with abrasives, the ability to pump large particles, ease of operation and maintenance, reliability, and the ability to operate over a wide range of pressures and flow rates by changing the diameter of pump liners and pistons.
As an important equipment for oilfield drilling operation, a drilling mud pump delivers circulating high-pressure drilling fluid or drilling mud to the bottom of the oil well, flushes the bottom of the well, breaks the rock, cools, lubricates and clean the drill bit, and carries the cuttings back to the ground.
The drilling mud is also used to suspend and carry out drill cuttings from the drill bits as it is brought in and out of the hole. This ensures that the drill bit does not clog and overheat, and makes the entire drilling operation smooth and safe.
Rotational power is supplied to the mud pump through an external power source like a diesel engine or electric motor. The power end of the mud pump converts the rotational energy through a crankshaft to a reciprocating motion of pistons.
The pistons move back and forth in mud pump liners, exerting a force on the cylinder chamber. During the retraction of the piston, valves open to allow the fluid to be drawn into the cylinder. Once the piston has fully retracted, it is pushed back into the cylinder.
Mud pumps are essential equipment for any oil or gas well. They are used to move drilling mud and other fluids needed during the drilling process. To select the right mud pump for your well, you need to understand the different types available and what each one can do.
In this article, we will take a comprehensive look at mud pumps and provide you with all the information you need to make an informed purchase. We will also discuss how mud pumps are used in drilling operations and highlight some of their key features. By the end of this article, you will clearly understand what mud pumps are and what they can do for your well.
A mud pump is a type of reciprocating positive displacement pump that is specifically designed for use in drilling operations. It helps to circulate the drilling fluid (or “mud”) through the drill bit and back up to the surface. The mud pump also provides pressure to keep the drill bit from becoming plugged.
The pump creates suction that pulls the drilling fluid from the pit and then uses its piston to push the fluid back up the well. This action not only circulates the fluid but also helps to remove any cuttings or debris that may have been generated during the drilling process. Mud pumps are an essential part of the drilling process and are typically used in conjunction with other pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, to create a complete pumping system. Without a mud pump, drilling would not be possible.
There are many different types of mud pumps, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. However, pump experts generally understand the requirement and then suggest which type of pump design would be more efficient. Here are five of the most popular types:
Piston mud pumps are the most common type of mud pump. They use a piston to draw mud from the pit and then force it to the drill bit through the hose. Piston mud pumps are very durable and can handle a lot of pressure. However, they are also very loud and can be challenging to operate.
Plunger mud pumps work similarly to piston mud pumps, but they use a plunger instead of a piston. As a result, plunger mud pumps are quieter than piston mud pumps and are easier to operate. However, plunger mud pumps are not as durable and can only handle a limited amount of pressure.
Hydraulic mud pumps use hydraulic power to draw mud from the pit. They are very powerful and can handle a lot of pressure. However, these types of pumps are generally costly and can be challenging to operate.
Diaphragm mud pumps use a diaphragm to draw mud from the pit. They are less powerful than hydraulic mud pumps but are much cheaper. They are also easier to operate. These merits make such pumps more used in small scale operations.
Peristaltic mud pumps use peristaltic action to draw mud from the pit. They are the most expensive type of mud pump but are also the most powerful. Unfortunately, they are also the most difficult to operate. But given their operational power, they are used in large-scale mining and drilling operations.
Even though mud pumps are very lucrative for mining and drilling purposes, they exhibit many more merits, making them useful in other industries. Following are some of the main advantages of mud pumps:
Mud pumps help to increase the efficiency of drilling operations by allowing for fluid circulation and cooling of the drill bit. This results in faster drilling and less wear on the equipment.
Mud pumps also help to improve safety during drilling operations by providing a means to circulate and cool the drill bit, which reduces the risk of overheating and fire.
Mud pumps can also help to improve the accuracy of drilling operations by preventing the drill bit from wandering off course due to excessive heat build-up.
The use of mud pumps can also help to reduce the costs associated with drilling operations by reducing the need for frequent replacement of drill bits and other worn items.
The use of mud pumps can also help to increase the productivity of drilling operations by reducing the downtime associated with the frequent replacement of drill bits and other worn items.
Mud pumps are an essential part of the oil and gas industry, as they are used to pump drilling fluid (mud) into the drill hole. There are many different mud pumps, each with its own unique set of features and applications. A reliable pump expert will help you choose which pump to use where. Here are 10 of the most common applications for mud pumps:
Mud pumps are extensively used to circulate drilling fluid during the drilling process. This helps to cool and lubricate the drill bit and remove cuttings from the hole.
Mud pumps are also used in hydraulic fracturing operations, where high-pressure fluid is injected into the rock formation to create fractures. The pump helps to circulate the fracturing fluid and keep the pressure at the desired level.
Mud pumps are sometimes used in geothermal operations to circulate water or other fluids through the drilled well. This helps extract heat from the rock and bring it to the surface.
In coal seam gas extraction, mud pumps are used to circulate water and chemicals through the coal seam to dissolve the methane gas and make it easier to extract.
In potash mining, mud pumps are used to circulate brine solution through the ore body to dissolve the potassium chloride (potash) and pump it out of the mine.
Mud pumps are often used in water well drilling operations to circulate water through the drill hole and help flush out any cuttings or debris. Pump experts can customize mud pumps to suit this application.
In tunnelling operations, mud pumps can circulate a slurry of water and clay through the drilling area. This helps to stabilize the walls of the tunnel and prevent collapse.
Mud pumps are sometimes used in pipeline operations to help clean and inspect the inside of the pipe. The pump circulates water or other fluids through the pipe to remove any build-up or debris.
In environmental remediation projects, mud pumps can circulate water or chemicals through contaminated soil or groundwater. This helps to break down contaminants and make them easier to remove.
Mud pumps can also be used in construction projects to help remove water from the site or stabilize the ground. For this application, they are extensively used in large construction sites.
Mud pumps are an essential part of many different industries and have various applications. If you need a mud pump for your next project, be sure to consult with a pump expert to find the right pump for your needs.

Mud pump, refers to the drilling process to the drilling mud or water and other washing liquid machinery. The main components are volute, impeller, pump seat, pump case, support cylinder, motor seat, motor and other components. Impeller nut is cast iron, so corrosion resistance is good, and convenient processing technology. Pump seat is equipped with four skeleton oil seal and shaft sleeve, prevent shaft wear, prolong the service life of the shaft.
High quality vertical mud pumps with thick, solid shaft and copper motor can be provided in ATO shop. Various models are available, such as 2 inch mud pump, 3 inch mud pump, 4 inch mud pump and 6 inch mud pump. Here is the price list of vertical mud pump.
Sewage mud pump is used in mining, papermaking, printing and dyeing, environmental protection, ceramics, refining, petroleum, chemical industry, farm, dyeing, brewing, food, construction, gold mine, mud, quicksand, mud pond, sewage pond, turbid fluid to send suction thick liquid, loading and suspended matter sewage operation, can also be used for mine drainage and fluid containing mud blocks.
If the mud pump and high-pressure water pump, water gun with the composition of hydraulic mechanized earthwork unit, can be used for land leveling, river and pond dredging, digging and other small water conservancy projects, as well as urban air defense engineering, underground engineering.
A mud pump (sometimes referred to as a mud drilling pump or drilling mud pump), is a reciprocating piston/plunger pump designed to circulate drilling fluid under high pressure (up to 7,500 psi or 52,000 kPa) down the drill string and back up the annulus. A mud pump is an important part of the equipment used for oil well drilling.
Mud pumps can be divided into single-acting pump and double-acting pump according to the completion times of the suction and drainage acting in one cycle of the piston"s reciprocating motion.
Mud pumps come in a variety of sizes and configurations but for the typical petroleum drilling rig, the triplex (three piston/plunger) mud pump is used. Duplex mud pumps (two piston/plungers) have generally been replaced by the triplex pump, but are still common in developing countries. Two later developments are the hex pump with six vertical pistons/plungers, and various quintuplexes with five horizontal piston/plungers. The advantages that these new pumps have over convention triplex pumps is a lower mud noise which assists with better measurement while drilling (MWD) and logging while drilling (LWD) decoding.
The fluid end produces the pumping process with valves, pistons, and liners. Because these components are high-wear items, modern pumps are designed to allow quick replacement of these parts.
To reduce severe vibration caused by the pumping process, these pumps incorporate both a suction and discharge pulsation dampener. These are connected to the inlet and outlet of the fluid end.
The pressure of the pump depends on the depth of the drilling hole, the resistance of flushing fluid (drilling fluid) through the channel, as well as the nature of the conveying drilling fluid. The deeper the drilling hole and the greater the pipeline resistance, the higher the pressure needed.
With the changes of drilling hole diameter and depth, the displacement of the pump can be adjusted accordingly. In the mud pump mechanism, the gearbox or hydraulic motor is equipped to adjust its speed and displacement. In order to accurately measure the changes in pressure and displacement, a flow meter and pressure gauge are installed in the mud pump.
The construction department should have a special maintenance worker that is responsible for the maintenance and repair of the machine. Mud pumps and other mechanical equipment should be inspected and maintained on a scheduled and timely basis to find and address problems ahead of time, in order to avoid unscheduled shutdown. The worker should attend to the size of the sediment particles; if large particles are found, the mud pump parts should be checked frequently for wear, to see if they need to be repaired or replaced. The wearing parts for mud pumps include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be adopted to increase the service life of the wearing parts, which can reduce the investment cost of the project, and improve production efficiency. At the same time, wearing parts and other mud pump parts should be repaired rather than replaced when possible.
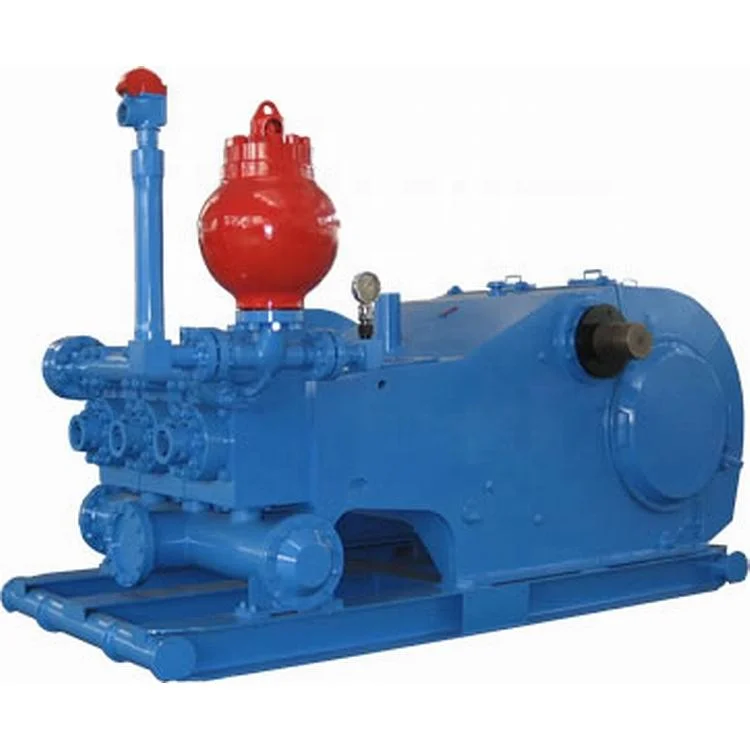

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.

Positive displacements pumps are generally used on drilling rigs to pump high pressure and high volume of drilling fluids throughout a drilling system. There are several reasons why the positive displacement mud pumps are used on the rigs.
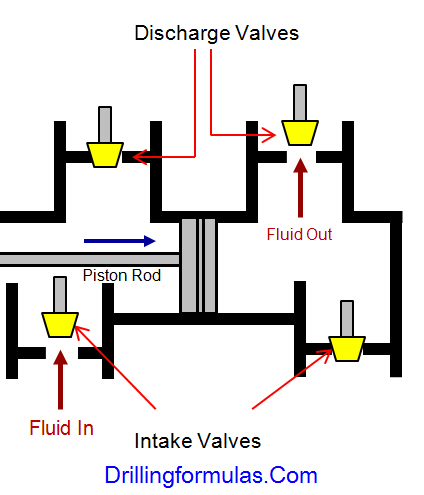
The duplex pumps (Figure 1) have two cylinders with double acting. It means that pistons move back and take in drilling mud through open intake valve and other sides of the same pistons, the pistons push mud out through the discharge valves.
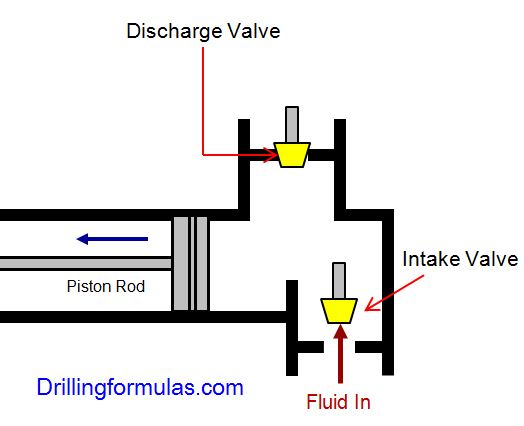
When the piston rod is moved forward, one of intake valves is lift to allow fluid to come in and one of the discharge valve is pushed up therefore the drilling mud is pumped out of the pump (Figure 2).
On the other hand, when the piston rod is moved backward drilling fluid is still pumped. The other intake and discharge valve will be opened (Figure 3).
The triplex pumps have three cylinders with single acting. The pistons are moved back and pull in drilling mud through open intake valves. When the pistons are moved forward and the drilling fluid is pushed out through open discharge valves.
On the contrary when the piston rods are moved backward, the intake valve are opened allowing drilling fluid coming into the pump (Figure 6). This video below shows how a triplex mud pump works.
Because each pump has power rating limit as 1600 hp, this will limit capability of pump. It means that you cannot pump at high rate and high pressure over what the pump can do. Use of a small liner will increase discharge pressure however the flow rate is reduces. Conversely, if a bigger liner is used to deliver more flow rate, maximum pump pressure will decrease.
As you can see, you can have 7500 psi with 4.5” liner but the maximum flow rate is only 297 GPM. If the biggest size of liner (7.25”) is used, the pump pressure is only 3200 psi.
Finally, we hope that this article would give you more understanding about the general idea of drilling mud pumps. Please feel free to add more comments.

Replaced by 337H-96. AMT line of 3" Diaphragm pumps features 2-stage, 44 to 1 gear reduction with a large diameter output gear and heavy duty ball bearing construction. Often referred to as Mud pumps or Sludge pumps, diaphragm pumps, mud suckers, oil collection are designed to pump mud, slurry, sewage, and thick liquids that have the ability to flow. AMT IPT Diaphragm pump Mud Hog w/Honda gasoline engines.
Built-in molded polyurethane flapper / check valve assures self-priming to 20 feet after initial prime. Heavy duty gear box is designed to operate pumps at 60 strokes per minute. Each unit includes a 3" NPT steel suction strainer, two 3" NPT nipples, and wheel kit with 10" semi-pneumatic transport wheels for portability. Pumps are designed for use with non-flammable liquids which are compatible with pump component materials. Suction and discharge port size cannot be reduced. 335H-96 4ta88
Suction and discharge port size cannot be reduced. Due to positive pumping action of diaphragm pumps, by all mfr"s, the discharge is recommended to only be 25FT long unless oversized. Discharge can not be restricted. There is no relief valve.

(1) The mud pump has advantages of high speed, small size, light weight, high efficiency, high fluidity, simple structure, no pulse infusion, stable performance, easy operation and convenient maintenance.
Therefore, in the following exceptions, centrifugal pumps should be used as much as possible: when metering is required, use a metering pump with high lift requirements; when the flow rate is small and there is no suitable small flow high lift centrifugal pump, a reciprocating pump such as cavitation vortex pump can also be used if the requirements are not high.
Select the pump according to high flow, axial and mixed flow. When the viscosity of the medium is greater than 650 to 1000 square mm/s, select the rotor pump or the reciprocating pump (gear pump, screw pump). In the case of 75% gas medium, if the flow rate is small and the viscosity is less than 37.4 square mm/s, the vortex pump can be used.
In the case of frequent irrigation pumps or inconvenient guidance, self-priming pumps, self-priming centrifugal pumps, self-priming eddy current pumps, and pneumatic (electric) diaphragm pumps should be used.
(2) Make the model and performance of the selected mud pump meet the requirements of technological parameters such as device flow, lift, pressure, temperature, cavitation flow, and suction range.
(3) The dielectric properties that must be met. For the transportation of flammable, toxic or explosive pump medium, it is necessary to have reliable seals for slurry pumps with no leakage, such as magnetic drive pumps, diaphragm pumps, and canned motor pumps.
For delivery pumps of corrosive media, the convection part requires corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel corrosion pumps AFB, the CQF plastic magnetic drive pumps.
A pump for conveying solid particles containing medium, wear-resistant materials requires a convection section. If necessary, seal and rinse it with the cleaning liquid.
(1) Packing is a common seal. The seal is injected with water in the form of continuous injection water under the pressure in the gasket to prevent the leakage of the mud pump. It is not suitable for the seal of multi-stage shaft seal mud pumps and packing. It has advantages of simple packaging and sealing structure, easy maintenance and low price.
(2) The impeller is sealed by the mud pump. The impeller with the reverse centrifugal generates the acting force to prevent the slurry from leaking out.
When the positive pressure value at the pump inlet is not greater than 10% of the pressure value at the outlet of the mud pump, the first-stage pump of a single-stage pump or a multi-stage pump can be designed with an impeller mechanical shaft seal, which does not dilute the slurry and has a good sealing effect.
(3) Mechanical seals of mud pumps generally have relatively high requirements for seals. Especially in some chemical and food fields, not only sealing is required, but it is important not to add additional components to the pump body. The disadvantage is that the mechanical seal of the mud pump is expensive and difficult to maintain.

Mud pump is mainly used for geological drilling, geological engineering construction and foundation treatment of low and medium pressure grouting pump, etc. Mud pump is a machine that sends mud or water to the borehole during the drilling process. Mud pump is an important part of drilling equipment. All major businesses have mud pump parts for sale.
The main function of mud pump is to inject mud into the well along with the bit during the drilling process. It plays the role of cooling the drill bit, cleaning the drilling tool, fixing the well wall, driving drilling, and bringing the cuttings back to the surface after drilling.
In the commonly used positive circulation drilling, the mud pump sends the surface flushing medium-- clean water, mud or polymer flushing fluid to the end of the drill bit through the high pressure hose faucet and the center hole of the drill string under a certain pressure. Therefore, the purpose of cooling the drill bit and removing and conveying the cuttings to the surface is achieved.
Petroleum drilling mud pump is a kind of volumetric mud pump. Its basic working principle is that the volume of the sealed working chamber (mud pump cylinder liner) is periodically changed to convert the original mechanical energy into the pressure energy of the liquid to complete the operation.
The specific process relies on the reciprocating motion of the mud pump piston in the cylinder liner to make the volume of the working chamber in the cylinder liner change periodically. The mud pump cylinder liner is isolated from the outside world by means of a sealing device such as a seal ring, and communicates or closes with the pipeline through the pump valve (suction valve or discharge valve), which shows the importance of the mud pump cylinder liner. The three-cylinder mud pumps currently on the market are equipped with three cylinder sleeves.

This rig features a Mission 4-by-5 centrifugal pump. Courtesy of Higgins Rig Co.Returning to the water well industry when I joined Schramm Inc. last year, I knew that expanding my mud pump knowledge was necessary to represent the company"s mud rotary drill line properly. One item new to me was the centrifugal mud pump. What was this pump that a number of drillers were using? I had been trained that a piston pump was the only pump of any ability.
As I traveled and questioned drillers, I found that opinions of the centrifugal pumps varied. "Best pump ever built," "What a piece of junk" and "Can"t drill more than 200 feet with a centrifugal" were typical of varying responses. Because different opinions had confused the issue, I concluded my discussions and restarted my education with a call to a centrifugal pump manufacturer. After that conversation, I went back to the field to continue my investigation.
For the past eight months, I have held many discussions and conducted field visits to understand the centrifugal pump. As a result, my factual investigation has clearly proved that the centrifugal pump has a place in mud rotary drilling. The fact also is clear that many drilling contractors do not understand the correct operational use of the pump. Following are the results of my work in the field.
High up-hole velocity - High pump flow (gpm) moves cuttings fast. This works well with lower viscosity muds - reducing mud expense, mixing time and creating shorter settling times.
Able to run a desander - The centrifugal"s high volume enables a desander to be operated off the pump discharge while drilling without adding a dedicated desander pump.
6. Sticky clays will stall a centrifugal pump"s flow. Be prepared to reduce your bit load in these conditions and increase your rpm if conditions allow. Yes, clays can be drilled with a centrifugal pump.
7. Centrifugal pumps cannot pump muds over 9.5 lbs./gal. Centrifugal pumps work best with a 9.0 lbs./gal. mud weight or less. High flow rate move cuttings, not heavy mud.
The goal of this article has been to increase awareness of the value of the centrifugal pump and its growing use. Although the centrifugal pump is not flawless, once its different operating techniques are understood, drilling programs are being enhanced with the use of this pump.
If you wish to learn more, please talk directly to centrifugal pump users. Feel free to call me at 314-909-8077 for a centrifugal pump user list. These drillers will gladly share their centrifugal pump experiences.

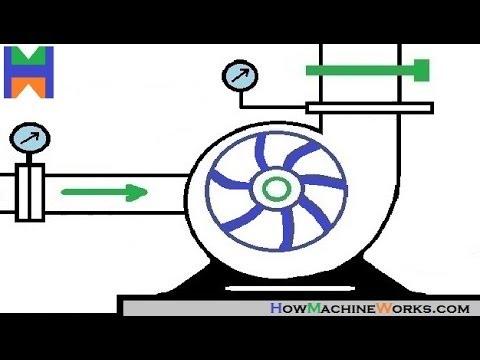
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move a fluid by means of the transfer of rotational energy from one or more driven rotors, called impellers. Fluid enters the rapidly rotating impeller along its axis and is cast out by centrifugal force along its circumference through the impeller’s vane tips. The action of the impeller increases the fluid’s velocity and pressure and also directs it towards the pump outlet. The pump casing is specially designed to constrict the fluid from the pump inlet, direct it into the impeller and then slow and control the fluid before discharge.
The impeller is the key component of a centrifugal pump. It consists of a series of curved vanes. These are normally sandwiched between two discs (an enclosed impeller). For fluids with entrained solids, an open or semi-open impeller (backed by a single disc) is preferred (Figure 1).
Fluid enters the impeller at its axis (the ‘eye’) and exits along the circumference between the vanes. The impeller, on the opposite side to the eye, is connected through a drive shaft to a motor and rotated at high speed (typically 500-5000rpm). The rotational motion of the impeller accelerates the fluid out through the impeller vanes into the pump casing.
There are two basic designs of pump casing: volute and diffuser. The purpose in both designs is to translate the fluid flow into a controlled discharge at pressure.
In a volute casing, the impeller is offset, effectively creating a curved funnel with an increasing cross-sectional area towards the pump outlet. This design causes the fluid pressure to increase towards the outlet (Figure 2).
The same basic principle applies to diffuser designs. In this case, the fluid pressure increases as fluid is expelled between a set of stationary vanes surrounding the impeller (Figure 3). Diffuser designs can be tailored for specific applications and can therefore be more efficient. Volute cases are better suited to applications involving entrained solids or high viscosity fluids when it is advantageous to avoid the added constrictions of diffuser vanes. The asymmetry of the volute design can result in greater wear on the impeller and drive shaft.
There are two main families of pumps: centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. In comparison to the latter, centrifugal pumps are usually specified for higher flows and for pumping lower viscosity liquids, down to 0.1 cP. In some chemical plants, 90% of the pumps in use will be centrifugal pumps. However, there are a number of applications for which positive displacement pumps are preferred.
The efficient operation of a centrifugal pump relies on the constant, high speed rotation of its impeller. With high viscosity feeds, centrifugal pumps become increasingly inefficient: there is greater resistance and a higher pressure is needed to maintain a specific flow rate. In general, centrifugal pumps are therefore suited to low pressure, high capacity, pumping applications of liquids with viscosities between 0.1 and 200 cP.
Slurries such as mud, or high viscosity oils can cause excessive wear and overheating leading to damage and premature failures. Positive displacement pumps often operate at considerably lower speeds and are less prone to these problems.
Any pumped medium that is sensitive to shearing (the separation of emulsions, slurries or biological liquids) can also be damaged by the high speed of a centrifugal pump’s impeller. In such cases, the lower speed of a positive displacement pump is preferred.
A further limitation is that, unlike a positive displacement pump, a centrifugal pump cannot provide suction when dry: it must initially be primed with the pumped fluid. Centrifugal pumps are therefore not suited to any application where the supply is intermittent. Additionally, if the feed pressure is variable, a centrifugal pump produces a variable flow; a positive displacement pump is insensitive to changing pressures and will provide a constant output. So, in applications where accurate dosing is required, a positive displacement pump is preferred.
Centrifugal pumps are commonly used for pumping water, solvents, organics, oils, acids, bases and any ‘thin’ liquids in both industrial, agricultural and domestic applications. In fact, there is a design of centrifugal pump suitable for virtually any application involving low viscosity fluids.
A centrifugal pump operates through the transfer of rotational energy from one or more driven rotors, called impellers. The action of the impeller increases the fluid’s velocity and pressure and directs it towards the pump outlet. With its simple design, the centrifugal pump is well understood and easy to operate and maintain.
Centrifugal pump designs offer simple and low cost solutions to most low pressure, high capacity pumping applications involving low viscosity fluids such as water, solvents, chemicals and light oils. Typical applications involve water supply and circulation, irrigation, and the transfer of chemicals in petrochemical plants. Positive displacement pumps are preferred for applications involving highly viscous fluids such as thick oils and slurries, especially at high pressures, for complex feeds such as emulsions, foodstuffs or biological fluids, and when accurate dosing is required.
Power Zone Equipment reserves the right to modify this policy from time to time in order that it accurately reflects the legal and regulatory environment and our data collection principles. When material changes are made to this policy, Power Zone Equipment will post the revised policy on our website.




 8613371530291
8613371530291