what is a swab on a mud pump manufacturer

Oil drilling is a challenging and highly mechanical profession. Oil rig operators need to have extensive knowledge of the tools they use, the correct processes for resource collection and how to recognize potential issues or risks and mitigate them. From drilling to worker safety, they"re responsible for many areas. One of the processes they need to know is swabbing.
Swabbing is a process that"s different for every well. It depends on preexisting pressurization, wellbore depth, fluid production from the reservoir and more. As you"re drilling, you may hit a point where you need to use a swabbing rig. At the very least, you can use the process to rejuvenate an old well. This guide will take you through the basics of oil well swabbing, why it"s important, how it works and some ways to decrease your chances of needing to swab a well.
As far as the oil and gas industry is concerned, swabbing is the act of accessing the production zones of wells and removing accumulated fracking fluids. It"s a method of well control that drilling companies use to release the well"s bottom hole pressure, allowing them to "kick" it off. When a drilling company creates a new well, they use pressurized liquids to fracture the site, creating channels and production zones where the oil and gas can travel. Swabbing follows as a second step.
To efficiently remove the remaining liquids from the well, teams use specific swabbing rigs, which consist of a winch, cable, swab cup, foldable mast and a pulley at the top. Once they"re ready to carry out the process, the rig operator will back the machine up to the edge of the well, as close as possible while still maintaining safety. They then adjust the rig"s mast and position it over the center point of the well. Using the winch, the operator lowers and raises the cable into and out of the well, keeping in mind control and the well"s characteristics.
In general, the standard for fluid removal is pulling about six barrels out of the well by way of the swabbing rig. In some cases, it only takes a single run, while other wells may require multiple repeats to remove all the fluids. As the operator pulls the fluids, the bottom pressure of the well builds, allowing the oil or gas to flow and push out of the well. Once you"ve reestablished the adequate pressure, your oilfield workers and operators can begin to pull resources from the well and store them.
However, the pressure doesn"t always last after the first swabbing. Over time, the pressure can decrease, causing the well to cease to produce oil or gas. If it depressurizes, the operator must apply the swabbing process again to build it back up. Swabbing rig operators must be highly skilled in their field, as they have to consider the soundness, pressure and depth of the well they"re working in, while also knowing the feel of their machine.
Well swabbing is essential to the production of oil and gas wells. For one, the process of swabbing and removing fluids from the production zone of the well creates the conditions for a gas and oil yield. The method introduces the pressure necessary for the well to push out the resources oilfield workers need to collect. If the well doesn"t have the required natural pressure to induce flowing on its own, swabbing makes it possible to access the resources regardless.
Additionally, as wells age, they collect fluids and lose their pressurization. But this doesn"t mean the well becomes unusable. If there are still resources left to pull, oilfield crews can use swabbing to rejuvenate the well"s pressurization multiple times. It removes those liquids that build up over time and with use.
When you pull resources from the reservoir, it also releases fluids that then collect at the bottom of the wellbore. As these liquids build up, they can prevent you from pulling oil or gas from the reservoir. Swabbing uses cups to remove the fluid, regaining you access to the oil well and allowing you to continue pulling resources. So, the process is necessary to get the most out of your wells.
If you aren"t sure why your well has ceased production, running an oil well swab test can provide you with a potential answer. Collecting fluid is a common reason for a reservoir production stoppage, and with a swab test, you can tell whether or not liquid is the problem. If it is, you can continue swabbing to pull as much as you need to remove from the reservoir area. If it"s not, you can rule it out as a possibility.
While swabbing is helpful in many cases, it isn"t always a necessary process. Some wells naturally have the required pressure to push oil out of themselves, and may not take on too much liquid over time. It all depends on the presence of particular factors and circumstances.
Fast pulling speeds: It takes a lot of energy to move mud at high speeds. Fast pulling from a well can create a more significant pressure drop and increase the need for swabbing. Monitoring the state of the well while tripping and making sure the pulling speed isn"t affecting well control are necessary to lessen the need for swabbing.
Balled-up bit or BHA: A balled-up bit and bottom hole assembly (BHA) creates a piston-like force and causes a much more significant swabbing effect. If you"re using a balled-up bit, you have to monitor the balance of the well"s condition. If the well has a nearly balanced status, it"s at a higher risk of becoming underbalanced due to the swabbing effect.
Large drilling tools: The size of the tools you use for tripping may significantly increase the potential need for swabbing. Using fishing tools, coring tools, mud motors, drill collars or any other form of large apparatus may cause a need for swabbing. You can still use these tools, but your operators and team need to understand how to use them carefully to trip the well. With proper attention, you can use them and prevent the need for swabbing.
Mud thickness and properties: The viscosity of the mud you"re moving comes into play as well. When mud is thick and has a high viscosity, it takes much more energy to move. That added thickness and energy use creates a pressure drop, which sometimes causes a need for swabbing. Beyond viscosity, several other mud properties can affect the pressure, such as high rheology and high gel strength, which can induce swab kick. Since these properties matter so much, it"s essential to keep an eye on the drilling fluids, monitor their properties and have a plan in place to keep the mud in the best condition possible.
Hydrostatic vs. formation pressure: The balance of your well"s condition includes hydrostatic and formation pressure. To create the best possible environment, you have to ensure there"s an overbalance margin with a higher formation pressure. If the hydrostatic pressure is above or equal to the formation, the chance of swabbing increases greatly.
Small hole clearance: The size of the access hole can also affect whether or not you may need swabbing. Moving mud through a bore with the proper amount of clearance should pose no problem, as long as the other elements align properly. But pulling mud through a hole with a smaller space uses much more energy, causing a more significant drop in pressure and a potential need for swabbing.
Formation movement: Sometimes, the formation itself can pose an issue. With swelling and heaving, the wellbore may decrease in size, creating a smaller diameter and a tighter space for the BHA or bit. Pulling out of the well with a small clearance can increase the chances of needing swabbing in drilling.
The process of swabbing involves specialized equipment and well-trained operators. To start, you should follow the recommended OSHA regulations and precautions, which include details like conducting swabbing during daylight hours, keeping oilfield workers significantly clear of the well and equipment at all times and locating swab tanks a proper distance from the well site.
First, you need to be able to recognize when swabbing is necessary. As you pull oil from your well, it is exiting the reservoirs through perforations. The openings may also produce fluids. But rather than travel up the pipe, they collect in the bottom of the well. As the fluid levels get higher, they block off the reservoir, causing it to stop producing. Swabbing equipment will help you remove the liquid without disturbing the reserve, allowing you to continue pulling from it.
Next, you need the right equipment. Swabbing cups are specifically for removing liquids from wells. As you push them into the well, they allow water to push past them, dipping into the collected fluids. However, they only allow fluids to pass in one direction. It works similarly to a loose plunger in a syringe tube, for the sake of visual representation.
As you pull the cups back out of the well, they pull the liquids that passed with them, effectively removing them from the wellbore. Depending on how much fluid has accumulated, you may need to repeat the process multiple times for the well to continue producing.
Once the fluid level is low enough, you can continue pulling from the well. The remaining bit of liquid will rise with the oil as you proceed and return the reservoir to full productivity. Over time, the fluid will gather again and require another swabbing treatment, but there are ways you can minimize the number of times you need to swab a particular well.
Swabbing a well can be time-consuming and costly for your company, as well as harmful for the environment. The act of swabbing a well can cause the well to vent a significant amount of methane emissions per year. A single well can create anywhere from 80 to 1,600 thousand cubic feet (Mcf) of methane in a year, depending on how often it requires swabbing. Minimizing the chances of swabbing is beneficial for your company and the environment.
Maintaining well control: One of the best ways to prevent the occurrence of swabbing is to retain control over the well by any means necessary. Continually monitor it and ensure all systems are working correctly. Whenever you observe any indications that swabbing might become necessary, it"s essential to have a plan to control the conditions. Whether you find signs of swelling, narrow access, imbalanced pressures or a difference in mud viscosity, having a way to regain control is imperative.
Monitoring mud condition:The conditions of the well as a whole are essential to maintaining safety and mitigating risks, but you should also keep a close eye on the status of your mud. The mud surrounding your equipment can make your job easier or much harder, depending on a few factors. If your mud has a high viscosity, rheology or gel strength, you"re dealing with poor conditions that can cause bit balling and induced swab kick. If you monitor it, you can help control these factors through proper lubrication and using the correct type of chemicals. Lowering the viscosity of the mud will help you mitigate swabbing risks.
Preventing bit balling:There are several reasons your bit and BHA can ball up during the drilling process. It could be due to clay and shale collecting on the equipment, too much weight on the bit, an imbalance in pressure where the hydrostatic pressure is too high or a poor bit design and structure. There are several ways you can recognize if your bit is balled up while drilling, such as a low drilling torque, a decreased rate of penetration or an increased standpipe pressure. Catching any of these early by consistent monitoring will reduce your chances of swabbing. You can also use preventative measures to decrease your chances before drilling, such as selecting reliable equipment, adding a reasonable amount of weight to the bit, using proper drilling fluid and lubricant and ensuring you have enough hydraulic horsepower.
Pull out of the well at reasonable speed: A simple way to avoid issues with swabbing is to monitor your speeds. Pulling out of your well too fast can affect its pressure balance, causing it to drop significantly. Well-balanced pressure is essential to keeping your oil well controlled and minimize the potential for swabbing.
Pumping instead of pulling: While monitoring your pulling speeds is a great way to mitigate any risks, you can also decrease the number of times you need to remove fluids by pumping instead. With pumping, there"s less risk for the damages associated with pulling, such as depressurization, making it useful for minimizing swabbing.
Having reliable equipment is essential to ensuring you can continue your oil pulling operations. High-quality apparatus can keep your rig from suffering downtime or many of the drilling-related hardware damages. With Global Elastomeric Products, you"ll have access to standard and custom oilfield equipment, proudly made in the U.S. with top quality materials. From swab cups and accessories to custom rubber molding, we can provide your company with the solutions it needs to keep your rigs up and running.
Global Elastomeric Products has over 50 years in the industry and ISO certification. Our team of in-house design engineers can help you through the process of choosing the right parts or customizing your mold. We make the process as straightforward as possible and guarantee a quick turnaround.

to change the supplier / type. The thinking is that "Bonded White Lightning" (Mission) components are designed for a bit higher temperature environment (230 deg F vs 208 deg F at section TD) and might be a bit "stiff" and have issues "adjusting" to the inner bore, bypassing fluid and eventually failing due to wash-out.

If you run a mud rig, you have probably figured out that the mud pump is the heart of the rig. Without it, drilling stops. Keeping your pump in good shape is key to productivity. There are some tricks I have learned over the years to keeping a pump running well.
First, you need a baseline to know how well your pump is doing. When it’s freshly rebuilt, it will be at the top efficiency. An easy way to establish this efficiency is to pump through an orifice at a known rate with a known fluid. When I rig up, I hook my water truck to my pump and pump through my mixing hopper at idle. My hopper has a ½-inch nozzle in it, so at idle I see about 80 psi on the pump when it’s fresh. Since I’m pumping clear water at a known rate, I do this on every job.
As time goes on and I drill more hole, and the pump wears, I start seeing a decrease in my initial pressure — 75, then 70, then 65, etc. This tells me I better order parts. Funny thing is, I don’t usually notice it when drilling. After all, I am running it a lot faster, and it’s hard to tell the difference in a few gallons a minute until it really goes south. This method has saved me quite a bit on parts over the years. When the swabs wear they start to leak. This bypass pushes mud around the swab, against the liners, greatly accelerating wear. By changing the swab at the first sign of bypass, I am able to get at least three sets of swabs before I have to change liners. This saves money.
Before I figured this out, I would sometimes have to run swabs to complete failure. (I was just a hand then, so it wasn’t my rig.) When I tore the pump down to put in swabs, lo-and-behold, the liners were cut so badly that they had to be changed too. That is false economy. Clean mud helps too. A desander will pay for itself in pump parts quicker than you think, and make a better hole to boot. Pump rods and packing last longer if they are washed and lubricated. In the oilfield, we use a petroleum-based lube, but that it not a good idea in the water well business. I generally use water and dish soap. Sometimes it tends to foam too much, so I add a few tablets of an over the counter, anti-gas product, like Di-Gel or Gas-Ex, to cut the foaming.
Maintenance on the gear end of your pump is important, too. Maintenance is WAY cheaper than repair. The first, and most important, thing is clean oil. On a duplex pump, there is a packing gland called an oil-stop on the gear end of the rod. This is often overlooked because the pump pumps just as well with a bad oil-stop. But as soon as the fluid end packing starts leaking, it pumps mud and abrasive sand into the gear end. This is a recipe for disaster. Eventually, all gear ends start knocking. The driller should notice this, and start planning. A lot of times, a driller will change the oil and go to a higher viscosity oil, thinking this will help cushion the knock. Wrong. Most smaller duplex pumps are splash lubricated. Thicker oil does not splash as well, and actually starves the bearings of lubrication and accelerates wear. I use 85W90 in my pumps. A thicker 90W140 weight wears them out a lot quicker. You can improve the “climbing” ability of the oil with an additive, like Lucas, if you want. That seems to help.
Outside the pump, but still an important part of the system, is the pop-off, or pressure relief valve. When you plug the bit, or your brother-in-law closes the discharge valve on a running pump, something has to give. Without a good, tested pop-off, the part that fails will be hard to fix, expensive and probably hurt somebody. Pop-off valve are easily overlooked. If you pump cement through your rig pump, it should be a standard part of the cleanup procedure. Remove the shear pin and wash through the valve. In the old days, these valves were made to use a common nail as the shear pin, but now nails come in so many grades that they are no longer a reliable tool. Rated shear pins are available for this. In no case should you ever run an Allen wrench! They are hardened steel and will hurt somebody or destroy your pump.
One last thing that helps pump maintenance is a good pulsation dampener. It should be close to the pump discharge, properly sized and drained after every job. Bet you never thought of that one. If your pump discharge goes straight to the standpipe, when you finish the job your standpipe is still full of fluid. Eventually the pulsation dampener will water-log and become useless. This is hard on the gear end of the pump. Open a valve that drains it at the end of every job. It’ll make your pump run smoother and longer.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

The 2,200-hp mud pump for offshore applications is a single-acting reciprocating triplex mud pump designed for high fluid flow rates, even at low operating speeds, and with a long stroke design. These features reduce the number of load reversals in critical components and increase the life of fluid end parts.
The pump’s critical components are strategically placed to make maintenance and inspection far easier and safer. The two-piece, quick-release piston rod lets you remove the piston without disturbing the liner, minimizing downtime when you’re replacing fluid parts.
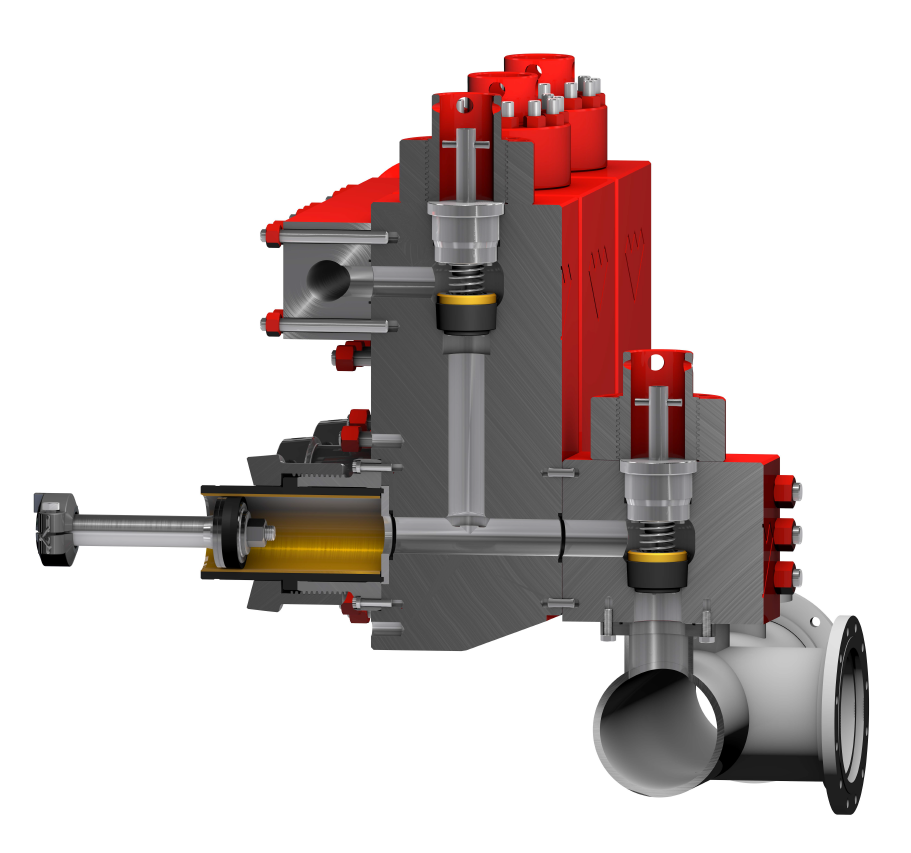
For the successful execution of your projects, it is important to find an appropriate company with a good track record. We help you in connecting with the top mud pump manufacturers and companies and get the best quotation.
We have designed affordable annual subscription plans which would help you get leads for your business. You can have a look at our pricing chart by clicking on this link: https://www.energydais.com/pricing/ . These plans are customized according to the specific needs and requirements of your business.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
Yes. We help you find the best mud pumps irrespective of your location. We simplify your search by connecting you with top mud pump manufacturers and mud pump companies in your location, according to your budget and business requirement.
Yes. We use third-party companies to provide best quotations for your shipment and inspection of manufactured goods. We make sure that you get quality products from the manufacturer at the best price.
The most widely used mud pumps across the industry are Triplex Reciprocating Pumps. Their application has gained immense popularity with time because they are 30% lighter than duplex reciprocating pumps with relatively less operational cost. Moreover, through these pumps the discharge of mud is smooth and they are capable of moving large volume of mud at higher pressure.
The different parts of a mud pump are Housing itself, Liner with packing, Cover plus packing, Piston and piston rod, Suction valve and discharge valve with their seats, Stuffing box (only in double-acting pumps), Gland (only in double-acting pumps), and Pulsation dampener. A mud pump also includes mud pump liner, mud pump piston, modules, hydraulic seat pullers along with other parts.
The wearing parts of a mud pump should be checked frequently for repairing needs or replacement. The wearing parts include pump casing, bearings, impeller, piston, liner, etc. Advanced anti-wear measures should be taken up to enhance the service life of the wearing parts. This can effectively bring down the project costs and improve production efficiency.

Drilling consumables such as mud pump systems and their components can drastically increase your uptime while reducing costs and health/safety/environmental (HSE) risks. To support your drilling needs, Forum’s patented P-Quip® mud pump system offers a single-source solution that integrates high-quality fluid end components for maximum longevity and performance.
With more than 20 years of successful operation in severe environments, P-Quip offers a proven track record for the lowest cost of ownership in the industry. As part of our commitment to quality, our mud pump parts use patented Banded Bore™ technology that significantly reduces stress concentrations and leads to longer module life.
One of Forum’s most committed core values is that “no one gets hurt,” and the P-Quip system is designed to support that principle. Streamlined and easy to use, it reduces or eliminates the need for manual force during maintenance, shrinking the time needed to replace high-use components and minimizing safety risks.

FET manufactures a full range of valves and seats for every drilling and well-servicing application as part of our full line of Osprey® mud pump system solutions. All of our valves and seats can be used in water, water base, oil base and synthetic base mud applications. FET offers additional valves and seats not listed below, including drilling valves, frac valves and well service valves. FET’s QC standards for the dimensional and material specs are extremely rigid in comparison to other manufacturers. Contact your FET representative to learn more.

Gardner Denver, Lewco, NOV, Oilwell, National, Varco, Woolley, Baash-Ross, Demco, Bomco, Oteco, Brown & Sharpe, Ideco, P-Quip, and Continental Emsco, and the product models referenced on this website are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. Premium Oilfield Technologies is not authorized by or affiliated with any of these companies, and no business relationship, affiliation, or endorsement is claimed or implied.

The RRP PINNACLE ASSEMBLED PISTON also known as Replaceable Rubber Piston or Supreme Piston is designed for use in the most demanding applications. The replaceable seal element is manufactured from a specially formulated elastomeric compound designed to be resistant to most chemical fluid found in the drilling industry today. These pistons can also be used in conditions where elevated temperatures can be problematic to other types of pistons in the market. The fabric anti-extrusion device on the piston is constructed from proprietary materials utilizing well researched process to reduce the extrusion of the rubber even at the pump’s maximum pressure rating.

Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features Power End The power pump shell is the structure of steel plate welding and has been tested with its intensity by authority. The crankshaft is a composed structure of straight shaft and eccentric wheel. Its airproof part of elastic ripple tube has been awarded a patent certificate by the state. The...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features Max single spare part weight is no more than 2t(4400lbs)which is a large convenient for helicopter transportation for located in jungle areas. The pinion shaft id herringbone gear, which means high strength and long service life. The main bearing carrier are closed annular type, the oil reservoir lies...
Product Features Max single spare part weight is no more than 2t(4400lbs)which is a large convenient for helicopter transportation for located in jungle areas. The pinion shaft id herringbone gear, which means high strength and long service life. The main bearing carrier are closed annular type, the oil reservoir lies...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features ● Its compact structure, lighter weight, and small size with high efficiency can be matched with kinds of pump devices according to drilling rig`s requirement and different conditions. ●Its durable and compact structure can ensure the smooth operation of pump, and meet the specific requirements of...
Product Features 1.Power end features Continuous tooth herringbone gear. One-piece alloy steel crank. Renewable crosshead guide. The frame is made of welded steel plate to provide the frame with high strength, good rigidity and lightweight. The extension rod packing is of duplex seal structure to provide the good seal...




 8613371530291
8613371530291