rongsheng refinery capacity brands

Rongsheng Petrochemical (brand value up 43% to US$2.3 billion) achieved very strong growth this year, rising two places in the chemicals ranking and jumpingfrom 10th to 8th place amongst global chemicals brands. The Chinese brand owns various globally significant facilities, including an integrated refining-petrochemical complex with the refining capacity of 40 million tons per annum.

SINGAPORE, Oct 14 (Reuters) - Rongsheng Petrochemical, the trading arm of Chinese private refiner Zhejiang Petrochemical, has bought at least 5 million barrels of crude for delivery in December and January next year in preparation for starting a new crude unit by year-end, five trade sources said on Wednesday.
Rongsheng bought at least 3.5 million barrels of Upper Zakum crude from the United Arab Emirates and 1.5 million barrels of al-Shaheen crude from Qatar via a tender that closed on Tuesday, the sources said.
Rongsheng’s purchase helped absorbed some of the unsold supplies from last month as the company did not purchase any spot crude in past two months, the sources said.
Zhejiang Petrochemical plans to start trial runs at one of two new crude distillation units (CDUs) in the second phase of its refinery-petrochemical complex in east China’s Zhoushan by the end of this year, a company official told Reuters. Each CDU has a capacity of 200,000 barrels per day (bpd).
Zhejiang Petrochemical started up the first phase of its complex which includes a 400,000-bpd refinery and a 1.2 million tonne-per-year ethylene plant at the end of 2019. (Reporting by Florence Tan and Chen Aizhu, editing by Louise Heavens and Christian Schmollinger)

BEIJING, Aug 14 (Reuters) - Rongsheng Petrochemical , the listed arm of a major shareholder in one of China’s biggest private oil refineries, expects demand for energy and chemical products to return to normal in the country in the second half of this year.
Rongsheng expects to start trial operations of the second phase of the refining project, adding another 400,000 bpd of refining capacity and 1.4 million tonnes of ethylene production capacity in the fourth quarter of 2020.
“We expect the effects of the coronavirus pandemic on energy and chemicals to have basically faded in spite of the possibility of new waves of outbreak,” said Quan Weiying, board secretary of Rongsheng, in response to Reuters questions in an online briefing.
But Li Shuirong, president of Rongsheng, told the briefing that it was still in the process of applying for an export quota and would adjust production based on market demand. (Reporting by Muyu Xu and Chen Aizhu; Editing by Jacqueline Wong)
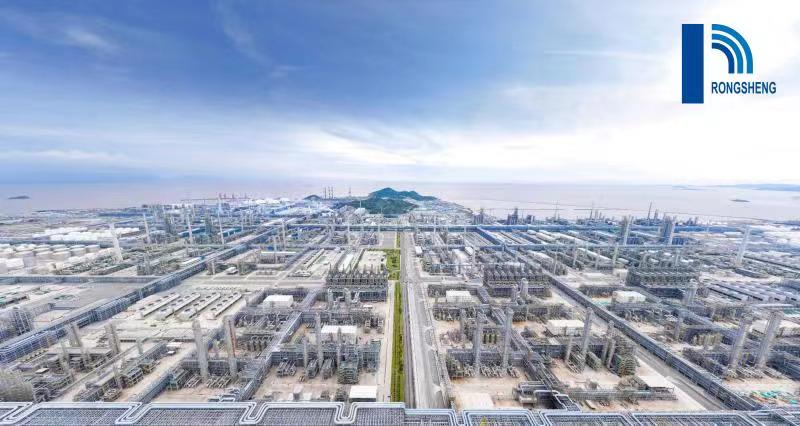

(Reuters) Chinese conglomerate Zhejiang Rongsheng Holding Group plans to double capacity of a joint venture refining project to 800 Mbpd in 2020, two years after the first phase starts up, senior company officials said Thursday.
The project, a venture among private companies led by Rongsheng, is planning to start up the 400 Mbpd first phase in 2018, aiming to meet the group"s requirements for petrochemical feedstocks.

China"s private refiner Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical is set to start trial runs at its second 200,000 b/d crude distillation unit at the 400,000 b/d phase 2 refinery by the end of March, a source with close knowledge about the matter told S&P Global Platts March 9.
"The company targets to commence the phase II project this year, and run both the two phases at above 100% of their capacity, which will lift crude demand in 2021," the source said.
ZPC cracked 23 million mt of crude in 2020, according the the source. Platts data showed that the utilization rate of its phase 1 refinery hit as high as 130% in a few months last year.
Started construction in the second half of 2019, units of the Yuan 82.9 billion ($12.74 billion) phase 2 refinery almost mirror those in phase 1, which has two CDUs of 200,000 b/d each. But phase 1 has one 1.4 million mt/year ethylene unit while phase 2 plans to double the capacity with two ethylene units.
ZPC currently holds about 6 million cu m (37.74 million barrels) in crude storage tanks, equivalent to 47 days of the two plants" consumption if they run at 100% capacity.
With the entire phase 2 project online, ZPC expects to lift its combined petrochemicals product yield to 71% from 65% for the phase 1 refinery, according to the source.
Zhejiang Petroleum, a joint venture between ZPC"s parent company Rongsheng Petrochemical and Zhejiang Energy Group, planned to build 700 gas stations in Zhejiang province by end-2022 as domestic retail outlets of ZPC.
Established in 2015, ZPC is a JV between textile companies Rongsheng Petrochemical, which owns 51%, Tongkun Group, at 20%, as well as chemicals company Juhua Group, also 20%. The rest 9% stake was reported to have transferred to Saudi Aramco from the Zhejiang provincial government. But there has been no update since the agreement was signed in October 2018.

The higher throughput in 2021 was attributed to refining capacity expansion, and as refineries produced more oil products to compensate for the reduction in imports of blending materials for gasoline and gasoil, analysts said.
The integrated Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical refinery continued to raise its crude throughput to around 2.84 million mt in December, up 7.2% from 1.72 million mt in November, which was up 54% from October, according to JLC data. The refinery ramped up throughput after it was allocated more quotas in late October.
The Hengli Petrochemical (Dalian) Refinery in Liaoning province also raised its throughput by 3.6% month on month to 1.7 million mt in December. This comes after the completion of the maintenance at its secondary units, according to refinery sources.
However, Shandong independent refineries have gradually started to cut crude throughput from around Jan. 22 in response to a directive to cap utilization below 70% during the Winter Olympics, as Beijing aims to ensure that emissions remain under control, refinery sources told S&P Global Platts. But some refinery sources believe the overall impact will not be much more than what occurs every year since the Winter Olympics will be held around the Lunar New Year holidays, when independent refineries are forced to cut crude throughput due to logistics and manpower constraints.
In other news, Sinopec"s Hainan Petrochemical refinery in southern China is expected to export about 50,000 mt of refined oil products in January 2022, according to a refinery source. This was down 55% from 110,000 mt planned for export in December 2021.
PetroChina"s West Pacific Petrochemical Corp. refinery will skip gasoil exports in January after skipping them in December and November due to good demand in the domestic market.
PetroChina"s flagship refinery Dalian Petrochemical in northeastern Liaoning province will raise its gasoline exports to 160,000 mt in January, according to sources with knowledge of the matter. This will be about 357% higher than its planned exports in December. Dalian will double jet fuel exports to 80,000 mt in January, from 40,000 mt last month. Dalian plans to process around 1.3 million mt of crudes in January, translating to 75% of its nameplate capacity, stable on the month.
** Sinochem has been in the process of starting up its 12 million mt/year CDU and related refining units at its Quanzhou Petrochemical facility in southern Fujian province, according to a source with knowledge of the matter Jan. 19. The refining and petrochemical units were shut at around Dec. 1, 2021 for maintenance, which lasted for about 40-50 days, according to the maintenance schedule. The refinery will likely process about 450,000 mt to 500,000 mt of crudes for the remainder of February, compared with around 1.2 million mt during normal months.
** Sinopec"s Fujian Refining and Chemical Co. refinery in southeastern Fujian province has been in the process of restarting from a scheduled maintenance this week, according to a source with knowledge of the matter Jan. 19. The refinery was expected to return to normal operations around Jan. 20, about nine days behind schedule, mainly due to the slow progress in procuring some parts, the source added. The 4 million mt/year crude distillation unit, as well as some secondary units, including the aromatics units, were to be restarted along the way. Following the restart of the CDU, the crude throughput at the refinery will likely increase to around 750,000 mt in January, or 63% of its nameplate capacity. This compares with a run rate of 56%, or 660,000 mt, in December 2021.
** Japan"s ENEOS said Dec. 28 it plans to shut the sole crude distillation unit at its Marifu refinery in the west in late January for scheduled maintenance until early March 2022.
** Idemitsu Kosan restarted the sole 160,000 b/d crude distillation unit at its Aichi refinery in central Japan on Dec. 5 after completing planned maintenance, a spokesperson said Dec. 20.
** PetroChina"s Yunnan Petrochemical refinery in southwestern Yunnan province, has shut its 4 million mt/year residual hydrogenation unit and some of its relative downstream facilities due to a blast. The blast hit the residual hydrogenation unit Dec. 13 morning, according to a press release issued by the Anning city local government in Yuannan. A refining engineer said the closure of residual hydrogenation unit would cut about 30% of the refinery"s daily production.
** Sinopec"s Hainan Petrochemical refinery in southern China plans to completely shut for scheduled maintenance over March-April 2022, a source with the refinery said. This is a routine maintenance that is normally carried out by Chinese refineries every three to four years, according to the source. Sinopec Hainan refinery last carried out complete maintenance over November 2017-January 2018.
** Japan"s ENEOS said it will decommission the 120,000 b/d No. 1 CDU at its 270,000 b/d Negishi refinery in Tokyo Bay in October 2022. It will also decommission secondary units attached to the No. 1 CDU, including a vacuum distillation unit and fluid catalytic cracker. ENEOS will also decommission a 270,000 mt/year lubricant output unit at the Negishi refinery.
** Sinopec is looking to launch its 2 million mt/year crude distillation unit expansion at Luoyang Petrochemical in central China in January, with a new crude pipeline able to supply sufficient feedstock, a refinery source said late December. "We have reconfigured an existing crude pre-treater into a 2 million mt/year CDU to increase the primary capacity to 10 million mt/year. The start-up will be in the next month with the crude pipeline having been put into use in November," the refinery source said. The expansion was initially set to be put into use in H2 2020, but was delayed to H1 2021 due to construction of the 10 million mt/year Rizhao-Puyang-Luoyang crude pipeline and weak demand in oil product market, Platts reported. The source said the expansion needs more crude supplies discharged from Rizhao port in Shandong province and transmitted through the Rizhao-Puyang-Luoyang crude pipeline.
** Chinese Sinopec"s refinery Zhenhai Refining and Chemical currently has a 27 million mt/year refining capacity and a 2.2 million mt/year ethylene plant, after its phase 1 expansion project of 4 million mt/year crude distillation unit and a 1.2 million mt/year ethylene unit was delivered end-June.
** PetroChina"s Guangxi Petrochemical in southern Guangxi province plans to start construction at its upgrading projects at the end of 2021, with the works set to take 36 months. The projects include upgrading the existing refining units as well as setting up new petrochemical facilities, which will turn the refinery into a refining and petrochemical complex. The project will focus on upgrading two existing units: the 2.2 million mt/year wax oil hydrocracker and the 2.4 million mt/year gasoil hydrogenation refining unit. For the petrochemicals part, around 11 main units will be constructed, which include a 1.2 million mt/year ethylene cracker.
** Axens said its Paramax technology has been selected by state-owned China National Offshore Oil Corp. for the petrochemical expansion at the plant. The project aims at increasing the high-purity aromatics production capacity to 3 million mt/year. The new aromatics complex will produce 1.5 million mt/year of paraxylene in a single train.
** China"s privately held refining complex, Shenghong Petrochemical, is likely to start feeding crudes into its newly built 16 million mt/year crude distillation unit, according to a company source in early January. The refinery initially planned to start up at the end of August, but this was postponed to the end of December due to slower-than-expected construction work, and then again to around the Lunar New Year. The construction of the complex started in December 2018. Located in the coastal city of Lianyungang in Jiangsu province, the company"s 16 million mt/year CDU is the country"s single biggest by capacity.
** Chinese privately owned refining and petrochemical complex Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical has fully started up commercial operation at it 400,000 b/d Phase 2 refining and petrochemical project, parent company Rongsheng Petrochemical said in a document Jan. 12. There are two crude distillation units in the Phase 2 project, each with a capacity of 200,000 b/d. ZPC started trial run at one of the CDUs in November 2020. Due to tight feedstock supplies, the refiner could not feed the other CDU until the end of November 2021, when it gained crude import quota for the project. The nameplate capacity of the company doubled to 800,000 b/d in Phase 2. It will run four CDUs at about 82% of nameplate capacity in January. Rongsheng said Phase 2 adds 6.6 million mt/year aromatics and 1.4 million mt/year ethylene production capacity.
** Saudi Aramco continues to pursue and develop the integrated refining and petrochemical complex in China with Norinco Group and Panjin Sinchen. The joint venture plans to build an integrated refining and petrochemical complex in northeast China"s Liaoning province Panjin city with a 300,000 b/d refinery, 1.5 million mt/year ethylene cracker and a 1.3 million mt/year PX unit.
Construction work is expected to be completed in 24 months. The complex has been set up with the aim of consolidating the outdated capacities in Shandong province. A total of 10 independent refineries, with a total capacity of 27.5 million mt/year, will be mothballed over the next three years. Jinshi Petrochemical, Yuhuang Petrochemical and Zhonghai Fine Chemical, Yuhuang Petrochemical and Zhonghai Fine Chemical will be dismantled, while Jinshi Asphalt has already finished dismantling.
** PetroChina officially started construction works at its greenfield 20 million mt/year Guangdong petrochemical refinery in the southern Guangdong province on Dec. 5, 2018.
This year, China is expected to overtake the United States as the world’s largest oil refining country.[1] Although China’s bloated and fragmented crude oil refining sector has undergone major changes over the past decade, it remains saddled with overcapacity.[2]
Privately owned unaffiliated refineries, known as “teapots,”[3] mainly clustered in Shandong province, have been at the center of Beijing’s longtime struggle to rein in surplus refining capacity and, more recently, to cut carbon emissions. A year ago, Beijing launched its latest attempt to shutter outdated and inefficient teapots — an effort that coincides with the emergence of a new generation of independent players that are building and operating fully integrated mega-petrochemical complexes.[4]
China’s “teapot” refineries[5] play a significant role in refining oil and account for a fifth of Chinese crude imports.[6] Historically, teapots conducted most of their business with China’s major state-owned companies, buying crude oil from and selling much of their output to them after processing it into gasoline and diesel. Though operating in the shadows of China’s giant national oil companies (NOCs),[7] teapots served as valuable swing producers — their surplus capacity called on in times of tight markets.
Four years later, the NDRC adopted a different approach, awarding licenses and quotas to teapot refiners to import crude oil and granting approval to export refined products in exchange for reducing excess capacity, either upgrading or removing outdated facilities, and building oil storage facilities.[10] But this partial liberalization of the refining sector did not go exactly according to plan. Swelling with new sources of feedstock that catapulted China into the position of the world’s largest oil importer, teapots increased their production of refined fuels and, benefiting from greater processing flexibility and low labor costs undercut larger state rivals and doubled their market share.[11]
Meanwhile, as teapots expanded their operations, they took on massive debt, flouted environmental rules, and exploited taxation loopholes.[12] Of the refineries that managed to meet targets to cut capacity, some did so by double counting or reporting reductions in units that had been idled.[13] And when, reversing course, Beijing revoked the export quotas allotted to teapots and mandated that products be sold via state-owned companies, it trapped their output in China, contributing to the domestic fuel glut.
2021 marked the start of the central government’s latest effort to consolidate and tighten supervision over the refining sector and to cap China’s overall refining capacity.[14] Besides imposing a hefty tax on imports of blending fuels, Beijing has instituted stricter tax and environmental enforcement[15] measures including: performing refinery audits and inspections;[16] conducting investigations of alleged irregular activities such as tax evasion and illegal resale of crude oil imports;[17] and imposing tighter quotas for oil product exports as China’s decarbonization efforts advance.[18]
The politics surrounding this new class of greenfield mega-refineries is important, as is their geographical distribution. Beijing’s reform strategy is focused on reducing the country’s petrochemical imports and growing its high value-added chemical business while capping crude processing capacity. The push by Beijing in this direction has been conducive to the development of privately-led mega refining and petrochemical projects, which local officials have welcomed and staunchly supported.[20]
Yet, of the three most recent major additions to China’s greenfield refinery landscape, none are in Shandong province, home to a little over half the country’s independent refining capacity. Hengli’s Changxing integrated petrochemical complex is situated in Liaoning, Zhejiang’s (ZPC) Zhoushan facility in Zhejiang, and Shenghong’s Lianyungang plant in Jiangsu.[21]
As China’s independent oil refining hub, Shandong is the bellwether for the rationalization of the country’s refinery sector. Over the years, Shandong’s teapots benefited from favorable policies such as access to cheap land and support from a local government that grew reliant on the industry for jobs and contributions to economic growth.[22] For this reason, Shandong officials had resisted strictly implementing Beijing’s directives to cull teapot refiners and turned a blind eye to practices that ensured their survival.
But with the start-up of advanced liquids-to-chemicals complexes in neighboring provinces, Shandong’s competitiveness has diminished.[23] And with pressure mounting to find new drivers for the provincial economy, Shandong officials have put in play a plan aimed at shuttering smaller capacity plants and thus clearing the way for a large-scale private sector-led refining and petrochemical complex on Yulong Island, whose construction is well underway.[24] They have also been developing compensation and worker relocation packages to cushion the impact of planned plant closures, while obtaining letters of guarantee from independent refiners pledging that they will neither resell their crude import quotas nor try to purchase such allocations.[25]
To be sure, the number of Shandong’s independent refiners is shrinking and their composition within the province and across the country is changing — with some smaller-scale units facing closure and others (e.g., Shandong Haike Group, Shandong Shouguang Luqing Petrochemical Corp, and Shandong Chambroad Group) pursuing efforts to diversify their sources of revenue by moving up the value chain. But make no mistake: China’s teapots still account for a third of China’s total refining capacity and a fifth of the country’s crude oil imports. They continue to employ creative defensive measures in the face of government and market pressures, have partnered with state-owned companies, and are deeply integrated with crucial industries downstream.[26] They are consummate survivors in a key sector that continues to evolve — and they remain too important to be driven out of the domestic market or allowed to fail.
In 2016, during the period of frenzied post-licensing crude oil importing by Chinese independents, Saudi Arabia began targeting teapots on the spot market, as did Kuwait. Iran also joined the fray, with the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) operating through an independent trader Trafigura to sell cargoes to Chinese independents.[27] Since then, the coming online of major new greenfield refineries such as Rongsheng ZPC and Hengli Changxing, and Shenghong, which are designed to operate using medium-sour crude, have led Middle East producers to pursue long-term supply contracts with private Chinese refiners. In 2021, the combined share of crude shipments from Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, and Kuwait to China’s independent refiners accounted for 32.5%, an increase of more than 8% over the previous year.[28] This is a trend that Beijing seems intent on supporting, as some bigger, more sophisticated private refiners whose business strategy aligns with President Xi’s vision have started to receive tax benefits or permissions to import larger volumes of crude directly from major producers such as Saudi Arabia.[29]
The shift in Saudi Aramco’s market strategy to focus on customer diversification has paid off in the form of valuable supply relationships with Chinese independents. And Aramco’s efforts to expand its presence in the Chinese refining market and lock in demand have dovetailed neatly with the development of China’s new greenfield refineries.[30] Over the past several years, Aramco has collaborated with both state-owned and independent refiners to develop integrated liquids-to-chemicals complexes in China. In 2018, following on the heels of an oil supply agreement, Aramco purchased a 9% stake in ZPC’s Zhoushan integrated refinery. In March of this year, Saudi Aramco and its joint venture partners, NORINCO Group and Panjin Sincen, made a final investment decision (FID) to develop a major liquids-to-chemicals facility in northeast China.[31] Also in March, Aramco and state-owned Sinopec agreed to conduct a feasibility study aimed at assessing capacity expansion of the Fujian Refining and Petrochemical Co. Ltd.’s integrated refining and chemical production complex.[32]

Zhejiang Petrochemical operates the Dayushan Island refinery, which is located in Zhejiang, China. It is an integrated refinery owned by Zhejiang Rongsheng Holding Group, Tongkun Group, Jihua Group, and others. The refinery, which started operations in 2019, has an NCI of 12.06.
Information on the refinery is sourced from GlobalData’s refinery database that provides detailed information on all active and upcoming, crude oil refineries and heavy oil upgraders globally. Not all companies mentioned in the article may be currently existing due to their merger or acquisition or business closure.

With the new issue, ZPC, China"s largest refiner with 800,000 barrels per day crude processing capacity, has obtained 40 million tonnes of quotas for the year, fully matching its refining capacity.
In a move to encourage higher refinery production to help a struggling economy, authorities earlier this month issued a small portion of the first-batch crude oil import quotas for 2023, months ahead of the usual timeline.

Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) has signed a broad framework agreement with China’s Rongsheng Petrochemical to explore domestic and international growth opportunities in support of ADNOC’s 2030 growth strategy.
The companies will examine opportunities in the sale of refined products from ADNOC to Rongsheng, downstream investment opportunities in both China and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the supply of liquified natural gas (LNG) to Rongsheng.
Under the terms of the deal, the companies will also study chances to increasing the volume and variety of refined product sales to Rongsheng as well as ADNOC’s participation as the China firm’s strategic partner in refinery and petrochemical projects. This could include an investment in Rongsheng’s downstream complex.
In return, Rongsheng will also look at investing in ADNOC’s downstream industrial ecosystem in Ruwais, UAE, including a proposed gasoline-to-aromatics plant as well as reviewing the potential for ADNOC to supply LNG to Rongsheng for use within its own complexes in China.
Rongsheng’s chairman Li Shuirong added that the cooperation will ensure that its project, which will have a refining capacity of up to 1 million bbl/day of crude oil, has adequate supplies of feedstock.

Abu Dhabi, UAE – November 12, 2019: The Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) announced, today, it has signed a broad Framework Agreement with China’s Rongsheng Petrochemical Co., Ltd. (Rongsheng) to explore domestic and international growth opportunities which will support the delivery of its 2030 smart growth strategy.
The agreement will see both companies explore opportunities in the sale of refined products from ADNOC to Rongsheng, downstream investment opportunities in both China and the United Arab Emirates, and the supply and delivery of liquified natural gas (LNG) to Rongsheng.
The agreement was signed by His Excellency Dr. Sultan Al Jaber, UAE Minister of State and ADNOC Group CEO, and Li Shuirong, Chairman of Rongsheng Group.
H.E. Dr. Al Jaber said: “This Framework Agreement builds on the existing crude oil supply relationship between ADNOC and Rongsheng, which we are keen to enhance. The agreement covers domestic and international growth opportunities across a range of sectors, which have the potential to open new markets for our growing portfolio of products and attract investment to support our downstream and gas expansion plans.
Under the terms of the Framework Agreement, ADNOC and Rongsheng will explore opportunities for increasing the volume and variety of refined products sales to Rongsheng as well as ADNOC’s active participation as Rongsheng’s strategic partner in refinery and petrochemical opportunities, including an investment in Rongsheng’s downstream complex. In return Rongsheng will also explore potential investments in ADNOC’s downstream industrial ecosystem in Ruwais, including the proposed Gasoline Aromatics Plant (GAP) and the potential for ADNOC to supply and deliver liquified natural gas (LNG) for utilization by Rongsheng within its production complexes in China.
Shuirong said: “This Framework Agreement is a key milestone in Rongsheng Petrochemical’s strategic international expansion. ADNOC is an important trading partner, and we are confident of the win-win benefits of this partnership, particularly in realizing opportunities in the downstream space in Asia.
“The strategic cooperation with ADNOC will ensure that our ZPC project, which will have a refining capacity of up to 1 million barrels per day (mbpd) of crude, has adequate supplies of feedstock. Our valued partnership will enable Rongsheng Petrochemical to continue its expansion into the international oil market and we are confident Rongsheng Petrochemical will achieve enhanced market share and recognition in the global marketplace.”
Rongsheng Petrochemical Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in China’s petrochemical and textile industry. In recent years, Rongsheng has been committed to developing both vertically and horizontally across the value chain, investing massively in multiple high-value oil and gas projects. Amongst them, Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical Co., Ltd. (ZPC), in which Rongsheng has a controlling interest, is a 40 million tons per annum mega integrated refining and chemical project. Once operational, ZPC will be one of the largest-scale plants in the world.
China is the world"s second-largest oil consumer, and Chinese energy companies have steadily increased their participation in ADNOC’s Upstream and Downstream operations. At the same time, ADNOC has identified China as an important growth market for its crude oil and petrochemical products, as it moves towards boosting its oil production capacity to 4 million barrels per day (mbpd) by the end of 2020 and 5mbpd in 2030 and accelerates the implementation of its downstream expansion and international investment strategies.

Saudi Aramco today signed three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) aimed at expanding its downstream presence in the Zhejiang province, one of the most developed regions in China. The company aims to acquire a 9% stake in Zhejiang Petrochemical’s 800,000 barrels per day integrated refinery and petrochemical complex, located in the city of Zhoushan.
The first agreement was signed with the Zhoushan government to acquire its 9% stake in the project. The second agreement was signed with Rongsheng Petrochemical, Juhua Group, and Tongkun Group, who are the other shareholders of Zhejiang Petrochemical. Saudi Aramco’s involvement in the project will come with a long-term crude supply agreement and the ability to utilize Zhejiang Petrochemical’s large crude oil storage facility to serve its customers in the Asian region.
Phase I of the project will include a newly built 400,000 barrels per day refinery with a 1.4 mmtpa ethylene cracker unit, and a 5.2 mmtpa Aromatics unit. Phase II will see a 400,000 barrels per day refinery expansion, which will include deeper chemical integration than Phase I.

Earlier this month, Royal Dutch Shell pulled the plug on its Convent refinery in Louisiana. Unlike many oil refineries shut in recent years, Convent was far from obsolete: it’s fairly big by US standards and sophisticated enough to turn a wide range of crude oils into high-value fuels. Yet Shell, the world’s third-biggest oil major, wanted to radically reduce refining capacity and couldn’t find a buyer.

The United States has the most complex and efficient refining industry in the world, but we also have less refining capacity than we used to. After more than two decades of growth in which the United States became the world’s largest refiner by volume, our industry has contracted. We’ve lost 1.1 million barrels of daily refining capacity over the course of the global pandemic with at least seven facilities shuttering, closing units or beginning the transition away from petroleum processing.
With a global energy crunch underway, much focus has been placed on crude oil supply and demand. And while this is the primary driver of our current price challenges, it’s not the only factor. Refining matters too. Crude oil has no utilitarian value until it runs through a refinery and gets processed into fuels like wholesale gasoline, diesel and jet fuel. Because of this, it’s not an overstatement to say that energy security requires a strong refining sector.
Where the issue of refining capacity is concerned, it’s important to understand what refining capacity is, why we’ve lost capacity in the United States and how policies can advance the competitiveness of our refineries in the global market. Let’s take a look:
How much refining capacity does the United States have?At the start of 2020, the United States had the largest refining industry in the world by a stretch, with 135 operable petroleum refineries and total refining capacity of 19 million barrels per day. Today, we have 128 operable refineries with total crude distillation capacity of 17.9 million barrels per day—a loss of 1.1 million barrels.
In this same period of time, the world lost a total of 3.3 million barrels of daily refining capacity. Roughly 1/3 of these losses occurred in the United States. With this realignment, and planned refinery openings and capacity expansions in Asia, trade press reports suggest China will overtake the United States as the country with the most refining capacity by year’s end.
Is COVID the only reason why the U.S. is losing refining capacity?No. A combination of factors is responsible for the United States’ loss of refining capacity. Choices to convert or shutter refineries are made very carefully—factoring in present and projected future fuel demand, the political environment as well as facility locations and their individual market access. Political and financial pressure to move away from petroleum derived fuels, costs associated with federal and state regulatory compliance and facilities’ singular economic performance all inform these decisions. The sharp drop in fuel demand over the course of the pandemic certainly sped up the timeframe for refining contractions, closures and transitions, but many of these moves were already planned or underway, something Chevron CEO Mike Wirth acknowledged in a recent interview.
Even if that wasn’t the case, reopening a refinery is a major effort. It would require significant lead time to inspect machinery and attain necessary operating permits. Staff would need to be reassembled and/or recruited and trained. And the facilities themselves would need to be reintegrated with supply chains. A hypothetical restart is not a quick-turn project, and the investment cannot be based on short-term data.
How is lost refining capacity affecting fuel prices and production?Less refining capacity means less maximum fuel production globally. As a result of tighter supply, fuel purchasers are willing to pay more for refined products. They have increased bids to buy and secure finished fuel which has pushed prices up throughout the global market.
In regions that have been most affected by refining capacity losses—such as the U.S. West Coast and Mid-Atlantic—the loss of local petroleum fuel production is contributing to higher prices and affecting regional demand for imports of gasoline, diesel and jet fuel from the global market. Because of infrastructure limitations and an uncompetitive shipping environment, economic access to domestic crude oil and refined products is limited.
Even with less capacity, United States refiners are working around the clock to produce fuel for consumers. Our refining sector is unmatched in terms of utilization. Nationally, and even with some regions undergoing planned facility maintenance, American refiners are running at 93% capacity. Along the Gulf Coast, utilization is 95%, and on the East Coast, 98%.
What does lost capacity say about the future of liquid fuels?In much of the world, demand for liquid fuels is almost back to pre-pandemic levels. Refining capacity is not. This mismatch has created a shortfall in refined product that has been exacerbated by the sudden decrease in oil and refined product from Russia and China’s decision to stop contributing fuel to the global market. New capacity is coming, though it is intended to satisfy demand growth in Asia, the Middle East and Africa, rather than replace what’s recently been lost. In these markets, roughly three million barrels of new daily capacity will come online by the end of 2022, with an additional 1.3 million barrels per day to follow in 2023.
Capacity expansions at existing refineries—rather than new facility construction—are underway in the United States as well, primarily aimed at increasing refinery throughput of U.S. light sweet crude oil.
The U.S. refining sector has experienced significant capacity losses over the last few years for reasons beyond COVID, though the pandemic certainly did fast-track decisions to repurpose or shutter facilities. Restarting those facilities is not an option in most cases as they have already been dismantled, converted or are in the conversion process. In other cases, returning idled capacity to safe operation would be so labor intensive and time consuming that any market impact would be years out.
Refiners remain focused on maximizing the production of fuelsfrom our operable facilities, ensuring that the capacity we do have isrunning efficiently and cost effectively to supply U.S. consumersand meet global energy demand.




 8613371530291
8613371530291