zhejiang rongsheng refinery price

SINGAPORE, Oct 14 (Reuters) - Rongsheng Petrochemical, the trading arm of Chinese private refiner Zhejiang Petrochemical, has bought at least 5 million barrels of crude for delivery in December and January next year in preparation for starting a new crude unit by year-end, five trade sources said on Wednesday.
Rongsheng bought at least 3.5 million barrels of Upper Zakum crude from the United Arab Emirates and 1.5 million barrels of al-Shaheen crude from Qatar via a tender that closed on Tuesday, the sources said.
Rongsheng’s purchase helped absorbed some of the unsold supplies from last month as the company did not purchase any spot crude in past two months, the sources said.
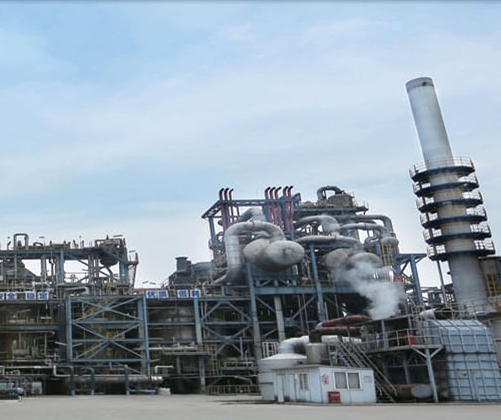
Zhejiang Petrochemical plans to start trial runs at one of two new crude distillation units (CDUs) in the second phase of its refinery-petrochemical complex in east China’s Zhoushan by the end of this year, a company official told Reuters. Each CDU has a capacity of 200,000 barrels per day (bpd).
Zhejiang Petrochemical started up the first phase of its complex which includes a 400,000-bpd refinery and a 1.2 million tonne-per-year ethylene plant at the end of 2019. (Reporting by Florence Tan and Chen Aizhu, editing by Louise Heavens and Christian Schmollinger)

China"s private refiner Zhejiang Petroleum & Chemical is set to start trial runs at its second 200,000 b/d crude distillation unit at the 400,000 b/d phase 2 refinery by the end of March, a source with close knowledge about the matter told S&P Global Platts March 9.
ZPC cracked 23 million mt of crude in 2020, according the the source. Platts data showed that the utilization rate of its phase 1 refinery hit as high as 130% in a few months last year.
Started construction in the second half of 2019, units of the Yuan 82.9 billion ($12.74 billion) phase 2 refinery almost mirror those in phase 1, which has two CDUs of 200,000 b/d each. But phase 1 has one 1.4 million mt/year ethylene unit while phase 2 plans to double the capacity with two ethylene units.
With the entire phase 2 project online, ZPC expects to lift its combined petrochemicals product yield to 71% from 65% for the phase 1 refinery, according to the source.
Zhejiang Petroleum, a joint venture between ZPC"s parent company Rongsheng Petrochemical and Zhejiang Energy Group, planned to build 700 gas stations in Zhejiang province by end-2022 as domestic retail outlets of ZPC.
Established in 2015, ZPC is a JV between textile companies Rongsheng Petrochemical, which owns 51%, Tongkun Group, at 20%, as well as chemicals company Juhua Group, also 20%. The rest 9% stake was reported to have transferred to Saudi Aramco from the Zhejiang provincial government. But there has been no update since the agreement was signed in October 2018.

BEIJING (Reuters) - Rongsheng Petrochemical , the listed arm of a major shareholder in one of China"s biggest private oil refineries, expects demand for energy and chemical products to return to normal in the country in the second half of this year.
The Zhejiang-based Chinese private refiner saw profit more than triple in the first half of 2020, bolstered by the launch of its 400,000 barrel-per-day Zhejiang Petrochemical Co (ZPC), according to a stock exchange filing earlier this week.
Rongsheng expects to start trial operations of the second phase of the refining project, adding another 400,000 bpd of refining capacity and 1.4 million tonnes of ethylene production capacity in the fourth quarter of 2020.
"We expect the effects of the coronavirus pandemic on energy and chemicals to have basically faded in spite of the possibility of new waves of outbreak," said Quan Weiying, board secretary of Rongsheng, in response to Reuters questions in an online briefing.
But Li Shuirong, president of Rongsheng, told the briefing that it was still in the process of applying for an export quota and would adjust production based on market demand. (Reporting by Muyu Xu and Chen Aizhu; Editing by Jacqueline Wong)

(Reuters) Chinese conglomerate Zhejiang Rongsheng Holding Group plans to double capacity of a joint venture refining project to 800 Mbpd in 2020, two years after the first phase starts up, senior company officials said Thursday.
The project, a venture among private companies led by Rongsheng, is planning to start up the 400 Mbpd first phase in 2018, aiming to meet the group"s requirements for petrochemical feedstocks.

Third MoU with Zhejiang Energy aimed at exploring potential investment in retail network in Eastern Region of China, in addition to other related downstream investments
Saudi Aramco today signed three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) aimed at expanding its downstream presence in the Zhejiang province, one of the most developed regions in China. The company aims to acquire a 9% stake in Zhejiang Petrochemical’s 800,000 barrels per day integrated refinery and petrochemical complex, located in the city of Zhoushan.
The first agreement was signed with the Zhoushan government to acquire its 9% stake in the project. The second agreement was signed with Rongsheng Petrochemical, Juhua Group, and Tongkun Group, who are the other shareholders of Zhejiang Petrochemical. Saudi Aramco’s involvement in the project will come with a long-term crude supply agreement and the ability to utilize Zhejiang Petrochemical’s large crude oil storage facility to serve its customers in the Asian region.
An integral part of the project includes a third agreement with Zhejiang Energy to invest in a retail fuel network. The companies plan to build a large scale retail network over the course of the next five years in the Zhejiang province. The retail business will be integrated with the Zhejiang Petrochemical complex as an outlet for the refined products produced.
Saudi Aramco CEO, Amin Nasser said: “The agreements demonstrate our commitment to the Chinese market and help enhance the strategic integration of our downstream network in Asia. They will further strengthen our relationship with China and the Zhejiang province, setting the stage for more cooperation in the future.”
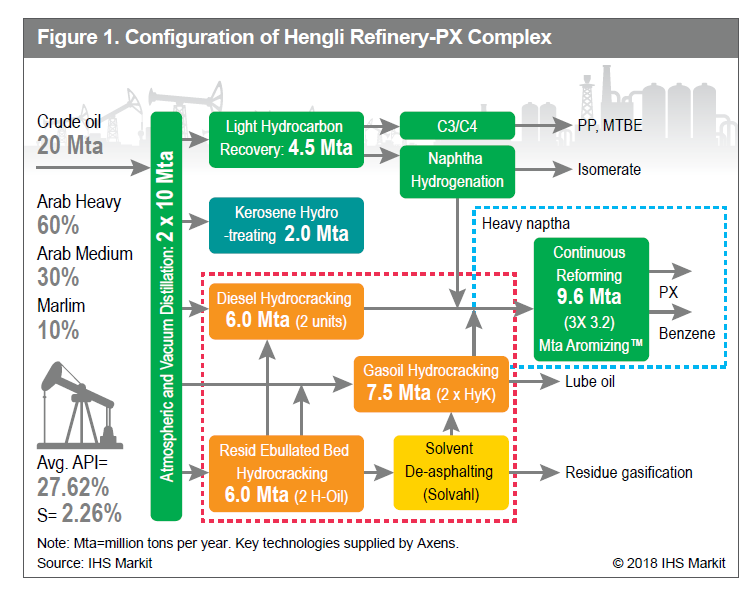
Phase I of the project will include a newly built 400,000 barrels per day refinery with a 1.4 mmtpa ethylene cracker unit, and a 5.2 mmtpa Aromatics unit. Phase II will see a 400,000 barrels per day refinery expansion, which will include deeper chemical integration than Phase I.
2021 marked the start of the central government’s latest effort to consolidate and tighten supervision over the refining sector and to cap China’s overall refining capacity.[14] Besides imposing a hefty tax on imports of blending fuels, Beijing has instituted stricter tax and environmental enforcement[15] measures including: performing refinery audits and inspections;[16] conducting investigations of alleged irregular activities such as tax evasion and illegal resale of crude oil imports;[17] and imposing tighter quotas for oil product exports as China’s decarbonization efforts advance.[18]
Yet, of the three most recent major additions to China’s greenfield refinery landscape, none are in Shandong province, home to a little over half the country’s independent refining capacity. Hengli’s Changxing integrated petrochemical complex is situated in Liaoning, Zhejiang’s (ZPC) Zhoushan facility in Zhejiang, and Shenghong’s Lianyungang plant in Jiangsu.[21]
As China’s independent oil refining hub, Shandong is the bellwether for the rationalization of the country’s refinery sector. Over the years, Shandong’s teapots benefited from favorable policies such as access to cheap land and support from a local government that grew reliant on the industry for jobs and contributions to economic growth.[22] For this reason, Shandong officials had resisted strictly implementing Beijing’s directives to cull teapot refiners and turned a blind eye to practices that ensured their survival.
In 2016, during the period of frenzied post-licensing crude oil importing by Chinese independents, Saudi Arabia began targeting teapots on the spot market, as did Kuwait. Iran also joined the fray, with the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) operating through an independent trader Trafigura to sell cargoes to Chinese independents.[27] Since then, the coming online of major new greenfield refineries such as Rongsheng ZPC and Hengli Changxing, and Shenghong, which are designed to operate using medium-sour crude, have led Middle East producers to pursue long-term supply contracts with private Chinese refiners. In 2021, the combined share of crude shipments from Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, and Kuwait to China’s independent refiners accounted for 32.5%, an increase of more than 8% over the previous year.[28] This is a trend that Beijing seems intent on supporting, as some bigger, more sophisticated private refiners whose business strategy aligns with President Xi’s vision have started to receive tax benefits or permissions to import larger volumes of crude directly from major producers such as Saudi Arabia.[29]
The shift in Saudi Aramco’s market strategy to focus on customer diversification has paid off in the form of valuable supply relationships with Chinese independents. And Aramco’s efforts to expand its presence in the Chinese refining market and lock in demand have dovetailed neatly with the development of China’s new greenfield refineries.[30] Over the past several years, Aramco has collaborated with both state-owned and independent refiners to develop integrated liquids-to-chemicals complexes in China. In 2018, following on the heels of an oil supply agreement, Aramco purchased a 9% stake in ZPC’s Zhoushan integrated refinery. In March of this year, Saudi Aramco and its joint venture partners, NORINCO Group and Panjin Sincen, made a final investment decision (FID) to develop a major liquids-to-chemicals facility in northeast China.[31] Also in March, Aramco and state-owned Sinopec agreed to conduct a feasibility study aimed at assessing capacity expansion of the Fujian Refining and Petrochemical Co. Ltd.’s integrated refining and chemical production complex.[32]

In Asia and the Middle East, at least nine refinery projects are beginning operations or are scheduled to come online before the end of 2023. At their current planned capacities, they will add 2.9 million barrels per day (b/d) of global refinery capacity once fully operational.
The scheduled expansions follow a period of reduced global refining capacity. Net global capacity declined in 2021 for the first time in 30 years, according to the IEA. The new refinery projects would increase production of refined products, such as gasoline and diesel, and in turn, they might reduce the current high prices for these products.
China’s refinery capacity is scheduled to increase significantly this year. The Shenghong Petrochemical facility in Lianyungang has an estimated capacity of 320,000 b/d, and they report that trial crude oil-processing operations began in May 2022. In addition, PetroChina’s 400,000 b/d Jieyang refinery is expected to come online in the third quarter of 2022. A planned 400,000 b/d Phase II capacity expansion also began operations earlier this year at Zhejiang Petrochemical Corporation’s (ZPC) Rongsheng facility. More information on these expansions is available in our Country Analysis Executive Summary: China.
Outside of China, the 300,000 b/d Malaysian Pengerang refinery (also known as the RAPID refinery) restarted in May 2022 after a fire forced the refinery to shut down in March 2020. In India, the Visakha Refinery is undergoing a major expansion, scheduled to add 135,000 b/d by 2023.
New projects in the Middle East are also likely to be an important source of new refining capacity. The 400,000 b/d Jizan refinery in Saudi Arabia reportedly came online in late 2021 and began exporting petroleum products earlier this year. More recently, the 615,000 b/d Al Zour refinery in Kuwait—the largest in the country when it becomes fully operational—began initial operations earlier this year. A new 140,000 b/d refinery is scheduled to come online in Karbala, Iraq, this September, targeting fully operational status by 2023. A new 230,000 b/d refinery is set to come online in Duqm, Oman, likely in early 2023.
These estimates do not necessarily include all ongoing refinery capacity expansions. Moreover, many of these projects have already been subject to major delays, and the possibility of partial starts or continued delays related to logistics, construction, labor, finances, political complications, or other factors may cause these projects to come online later than estimated. Although the potential for project complications and cancellations is always a significant risk, these projects could otherwise account for an increase of nearly 3.0 million b/d of new refining capacity by the end of 2023.

The fact that this landmark refinery joint venture is back under serious consideration underlines the extremely significant shift in Saudi Arabia’s geopolitical alliances in the past few years – principally away from the U.S. and its allies and towards China and its allies. Up until the 2014-2016 Oil Price War, intended by Saudi Arabia to destroy the then-nascent U.S. shale oil sector, the foundation of U.S.-Saudi relations had been the deal struck on 14 February 1945 between the then-U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Saudi King Abdulaziz. In essence, but analyzed in-depth inmy new book on the global oil markets,this was that the U.S. would receive all of the oil supplies it needed for as long as Saudi had oil in place, in return for which the U.S. would guarantee the security both of the ruling House of Saud and, by extension, of Saudi Arabia.
Later, the first discussions about the joint Saudi-China refining and petrochemical complex in China’s northeast began, with a bonus for Saudi Arabia being that Aramco was intended to supply up to 70 percent of the crude feedstock for the complex that was to have commenced operation in 2024. This, in turn, was part of a multiple-deal series that also included three preliminary agreements to invest in Zhejiang province in eastern China. The first agreement was signed to acquire a 9 percent stake in the greenfield Zhejiang Petrochemical project, the second was a crude oil supply deal signed with Rongsheng Petrochemical, Juhua Group, and Tongkun Group, and the third was with Zhejiang Energy to build a large-scale retail fuel network over five years in Zhejiang province.




 8613371530291
8613371530291