how does a rotary table work factory
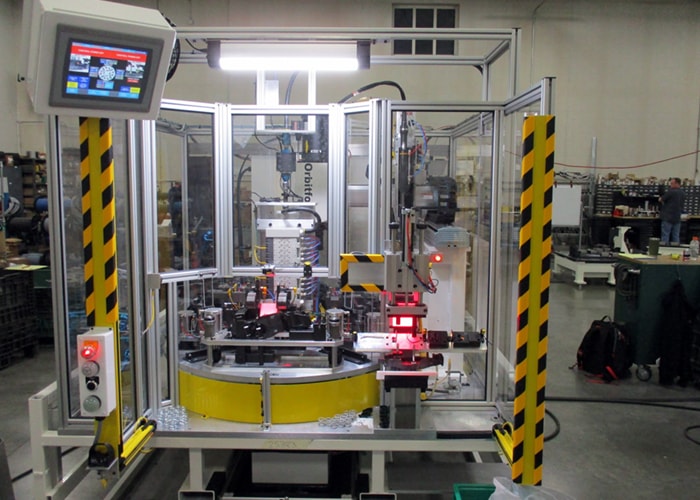
A rotary table is a precision work positioning device used in metalworking. It enables the operator to drill or cut work at exact intervals around a fixed (usually horizontal or vertical) axis. Some rotary tables allow the use of index plates for indexing operations, and some can also be fitted with dividing plates that enable regular work positioning at divisions for which indexing plates are not available. A rotary fixture used in this fashion is more appropriately called a dividing head (indexing head).
The table shown is a manually operated type. Powered tables under the control of CNC machines are now available, and provide a fourth axis to CNC milling machines. Rotary tables are made with a solid base, which has provision for clamping onto another table or fixture. The actual table is a precision-machined disc to which the work piece is clamped (T slots are generally provided for this purpose). This disc can rotate freely, for indexing, or under the control of a worm (handwheel), with the worm wheel portion being made part of the actual table. High precision tables are driven by backlash compensating duplex worms.
The ratio between worm and table is generally 40:1, 72:1 or 90:1 but may be any ratio that can be easily divided exactly into 360°. This is for ease of use when indexing plates are available. A graduated dial and, often, a vernier scale enable the operator to position the table, and thus the work affixed to it with great accuracy.
Rotary tables are most commonly mounted "flat", with the table rotating around a vertical axis, in the same plane as the cutter of a vertical milling machine. An alternate setup is to mount the rotary table on its end (or mount it "flat" on a 90° angle plate), so that it rotates about a horizontal axis. In this configuration a tailstock can also be used, thus holding the workpiece "between centers."
With the table mounted on a secondary table, the workpiece is accurately centered on the rotary table"s axis, which in turn is centered on the cutting tool"s axis. All three axes are thus coaxial. From this point, the secondary table can be offset in either the X or Y direction to set the cutter the desired distance from the workpiece"s center. This allows concentric machining operations on the workpiece. Placing the workpiece eccentrically a set distance from the center permits more complex curves to be cut. As with other setups on a vertical mill, the milling operation can be either drilling a series of concentric, and possibly equidistant holes, or face or end milling either circular or semicircular shapes and contours.
To create large-diameter holes, via milling in a circular toolpath, on small milling machines that don"t have the power to drive large twist drills (>0.500"/>13 mm)
with the addition of a compound table on top of the rotary table, the user can move the center of rotation to anywhere on the part being cut. This enables an arc to be cut at any place on the part.
Additionally, if converted to stepper motor operation, with a CNC milling machine and a tailstock, a rotary table allows many parts to be made on a mill that otherwise would require a lathe.
Rotary tables have many applications, including being used in the manufacture and inspection process of important elements in aerospace, automation and scientific industries. The use of rotary tables stretches as far as the film and animation industry, being used to obtain accuracy and precision in filming and photography.

rotary filing—that is, running a circular cutter withfile-like teeth in the headstock of alathe.Rotary filling and later,true milling were developed to reduce time and effort

An indexing table is a rotary table device that uses indexing to position a workpiece. CNC indexing tables are invaluable in milling and other industrial processes that require high precision cutting and shaping. They have a wide range of applications, including machining, positioning, inspection, and automation.
In manufacturing, indexing is the process of exposing a new edge or surface for use. An indexing table is used to convey and position workpieces during a manufacturing process.
The table’s indexing unit rotates the piece a precise distance into a specific position. It remains in place while the manufacturing tool cuts or drills the workpiece. Once the operation is completed, the table indexes the next section of the workpiece into position.
Indexing tables have a wide range of features. A basic indexing tool consists of a precision-machined steel plate with slots or mounting holes to secure workpieces during the machining process. They have either fixed or adjustable indexing angles. Parts can be loaded and unloaded manually or automatically.
There are three types of mounting: vertical, horizontal, and versatile. Indexing tables come with one or more spindles. Drive systems can be powered by pneumatic or electric motors, hydraulic drives, or even manually.
An indexing table is one of the most efficient ways to move and position a piece for precision machining. They can be used with small, medium, or large workpieces. Some of the benefits of using an indexing table include:
CNC indexing tables are used in the machining process for parts and components in a wide range of industrial applications, including food and beverage, printing, aerospace, defense, construction, medical, and automotive.
CNC Indexing & Feeding Technologies has been a premier importer/distributor of quality machine tool accessories such as hydrodynamic magazine-style bar feeders, short bar loaders, rotary tables, high-pressure coolant systems, and oil skimmers since 2007. Our line of TJR Precision rotary and indexing tables turn any 3-axis machining center into a 4 or 5-axis with customized faceplates available. In addition, we offer manufacturers our own CNC Indexing brand of hydrodynamic magazine bar feeders, short bar loaders, and gantry-style autoloaders.
If you’re looking for the best CNC accessories for your manufacturing operations, contact CNC Indexing & Feeding Technologies online or call us at 513-770-4200.
Indexing tables are used in a multitude of industries and in numerous applications. Their design is optimal for many manufacturing jobs, and they are a critical component in most automated manufacturing systems. Indexing tables are best defined as a machine tool positioning device. They carry components in a manufacturing environment with a repeating process of indexing (rotating) around an axis, stopping, dwelling while an operation is performed, then indexing again to repeat the process. They are usually made of circular steel plates, with one or more spindles, a drive system, encoders, sensors, controllers and slots or mounting holes to hold components.
Virtually any manufacturing operation can be performed on a part held by an indexing table including welding, grinding, drilling, assembly, painting, inspection, testing and more. In order to maximize operational efficiency, the machine doing the operation must also be built for the same intended application as the indexing table for them to work in synch. Similarly the machine that loads the indexing table with parts must also be synchronized. They must have the same capacity and be able to manage to the same dwell time for the system to work.
If the timing of these machines are coordinated, the time to operate on or assemble a product can be a fraction of that of workers assembling a product.
Industries that use indexing tables include automotive manufacturers, bottling companies, microchip manufacturers, pharmaceutical makers, consumer products companies and many more. They are invaluable to manufacturers pushing for automation and increased efficiency in their factories, turning work that used to take days into work that takes only hours. If a simple assembly task is required on small parts in a factory, there is no better way to complete the task than by coupling an assembly tool and an indexing table.
Many rotary index table end users need the flexibility afforded by having a fully programmable tool. A seemingly simple way to achieve this is by using a gear head coupled to a servo motor or an AC motor with an encoder. In reality though, while this seems simple and cost-effective, because of the physics described above, high inertia, combined with a goal of high accuracy can create a problematic mis-match.
With a servo-driven barrel cam rotary index table, it’s possible to deliver a wide range of table sizes, with zero backlash and unparalleled accuracy. Servo driven rotary indexers allow heavy inertial loads to be rotated in a very smooth and controlled manner.
Cam-driven rotary index tables can have significant advantages over other types of rotary index table drive systems such as gear drives. Cam-driven rotary index tables provide extremely high accuracy because they operate with no backlash. There are several types of commonly used cam-driven rotary index table systems, each is best for a specific application.
Barrel cams represent strength in indexing. Primarily found in rotary index tables, indexers utilizing barrel cams feature the greatest strength/size offering available.
Globoidal cams are similar to barrel cams in shape (and come from the same steel stock), but have considerably different profiles. Tapered walls in the grooves are designed to accommodate cam followers fixed to an output shaft in a "star" configuration.
Cam driven rotary table indexers are sometimes call "fixed indexers". With a fixed indexer, the cam drives receive constant power input from the motor. This rotates the cam which then rotates the output. Based upon the design of the drive, the output will have "dwell" periods (when the output is stopped) as well as acceleration, deceleration and peak velocity. Cam-driven rotary index tables have a number of advantages, however, they won"t meet the needs of every application.
Rotary index tables can also be "flexible". Flexible rotary index tables use a cam that has a constant lead, that is the output is at a constant velocity if the motor is running at a constant velocity. Constant lead cams provide a high-precision mechanical transition of power to the output and since acceleration and deceleration are still necessary, the logic controller for the index tables motor provides the necessary control.

When it comes to powered rotary table, it is the rotary tables widely used in CNC machining center which responsible for precisely locating the parts in the commanded angle in order to perform multi-face machining at one time.
For starters, we need to know what a rotary table is. Rotary table is a high precision positioning device which is widely used in machining and metalworking. With the rotation, the operators can perform drilling, milling, cutting and other applications at exact intervals around the horizontal or vertical axis. To achieve the high accuracy and efficiency, many rotary tables can incorporate with index plates or dividing plates. With the help of additional components, the rotary tables can be used for indexing application or even position the work piece at divisions on the dividing plates.
When it comes to powered rotary table, it is the rotary tables widely used in CNC machining center which responsible for precisely locating the parts in the commanded angle in order to perform multi-face machining at one time. Originally, in a 3-axis CNC machining center, there are only X, Y, Z working axes. The X, Y, Z axis are the linear lathe axes. Operating along the XYZ planes, the Z axis is the important axis that is aligned with the main axis of the machines. On the same plane, the Y axis works in horizontal direction while the X axis is the vertical operation direction.
In typical machining centers that have the 4th axis, the 4th axis is the 180° rotation axis around the X axis. With a CNC motors, the motorized rotary tables can play the role as the 4th axis in the machining centers to enhance the flexibility of metalworking applications. The arrangement of involving powered rotary table in 3-axis machining center is popular for cam machining, helical grooves producing, blade machining and other unique profile machining. Powered rotary tables have a wide range of applications, for example, utilizing in both manufacturing and inspection stage of essential components in aerospace industry, automobile manufacturing and other scientific industries.
The vital elements of a powered rotary table include a supporting disc where the work pieces are clamped for machining, a solid base for clamping onto another larger table, machine, or machining center, the CNC controller and motor. A through hole is machined into the CNC rotary table to fit the Morse taper center or fixture.
The precision-machined disc is the rotating surface where the work piece is positioned and fixed firmly. T slots are the typical parts to help clamping the work pieces. The chuck is used to hold the work piece with a dial indicator to ensure the chuck and product are centered. After installing the chuck with bolts and T-nuts then checking if the work piece is centered, the operator can position the job on the table. The disc can spin freely under the instructions from CNC controller and motor. It is also the components which the indexing plate or dividing plate can mount with. When CNC controller and the CNC motor provide inputs, the rotation of the worm gear is activated and the mating gear mounted beneath the table surface begins to spin, either. The worm gears perform the precise rotations of the rotary table and every parts of the disc are critically calibrated in degrees.
The computer numerical controller transport programmed commands to activate the powered rotary tables. The commands are conveyed in CAD files, which refers to Computer Aided Design files, and provide sequential instructions to ensure the smooth operation. Eliminating the human power, CNC provides reliable and precise high performance positioning for further machining applications.
The size and type of the CNC motors can determine the routers precision, the efficiency and also the accuracy. Following is the basic introduction of two classes of motors used in CNC rotary tables, which are the stepper motors and the servo motors. Within these 2 classes, there are more subtypes.
Servo motors use closed looping variable circuit which continuously run for maintaining smooth motor function. The brushes on this type of CNC motors should be replaced after two thousand hours of operation. The encoders may need to be checked and replaced, too. Servo motors feature the efficiency in power consumption. They perform with about 90 percent of efficiency when giving light loads.
Stepper motors only require the wires that connected with the motor driver, having simpler setup. The only wearing part in this type of CNC motors is the bearing mounted on the motor, which slightly reduce the equipment life. Compared to servo type, stepper motors consume a large amount of power to provide the output, and much of them is converted to heat. Depending on the stepper driver, the stepper motors are often seventy percent efficient.

A CNC rotary table is the precision positioning accessory that can provide a reliable 4th axis or even 5th axis for modern machining centers. Utilizing a computer-controlled rotary table can turn the original 3-axis machine tools into 5-axis CNC machines, expanding the accuracy as well as decreasing the costs while performing complex machining operations at one time.
A CNC rotary table is the precision positioning accessory that can provide reliable 4 or even 5 axis cutting operation capabilities for modern machining centers. Utilizing it can turn the original 3-axis machine tools into 5-axis CNC machines, expanding the accuracy as well as decreasing the costs while performing complex machining operations.
Rotary tables typically have rigid frames and coatings, and also excellent torque capacity, which makes the small device flexible and effective for a wide variety of turning, milling, drilling, and more metalworking operations. The easy setup and seamless interface allow the operators to easily add the rotary table to fit their 4-axis or 5-axis applications. .
The working principle is similar to the basic rotary tables, which is to support the workpiece by accurately rotating the workpieces on the axis in order to locate the parts for high precision tooling. Under rapid rotation, which is driven by CNC instructions, the cutting tools of larger machine tools or machining centers can remove the material and add the feature to the products at exact intervals. On rotary tables, there are vertical and horizontal axes for various tools to perform these high-performance metalworks. To enhance the accuracy and flexibility, there are models that employ additional dividing plates and come with additonal material handling mechanisms and features.
Since 4-axis and 5-axis machining is increasingly popular today, adding the CNC rotary table as the 4th axis is an ideal solution to easily open up more complex machining options at a lower cost. Due to the arrangement, they are widely also called the 4th or 5th axis or tilt rotary. The 4th axis, which is the rotational operational direction, is added to the original three linear axes which are known as X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis. In some cases, there are two rotational axes add to the original 3-axis machining center, achieving utmost accuracy as well as effective multiple face cutting to reach the difficult area on the surface. Rotary tables are usually mounted parallel to the ground or the bed, with the platter rotating around the vertical axis, for example with the most common vertical milling machine combination. Sometimes the machining application requires an alternative setup with the table mountet on its end so that it rotates around the horizontlal axis. Often, a tailstock is used in this configuration. Virtually all models today come with a clamping kit to mount it onto the bed of your machine tool.
The function of the high precision rotary table is also to rotate the workpiece so the cutting tool can create the contour we desired out of the workpiece. However, a rotary table with higher precision has the ability to achieve great accuracy just as its name implies. There is also a major misconception between the resolution and the accuracy.
A common example is that if a digital readout displays to four decimal places, then the high precision rotary table must also be capable of achieving the accuracy to that same value. Even though for higher accuracy to be achieved, the resolution has to also be high, but there is no guarantee that the accuracy is going to be high. The accuracy is the concept which is the difference between the actual position and the position measured by a reference measurement device. The feedback mechanism such as the rotary encoder, and the drive mechanism can influence the accuracy of the advanced rotary table.
A CNC rotary table can provide great rigidity for stable machining operations. It consists of the worktable where the metal parts are held, the rigid bearing that withstands the forces and loads during the rotation, the solid base which is used for attaching the rotary table to the machining center or other equipment, the motor, and the CNC system.
The worktable is the tooling surface where the workpieces are machined after accurate positioning. The worm gearing is the core mechanism of the table, which mesh with the steel worm which is submerged in the lubricants. Both the rigid bearings and the worm gears have large diameters. Excellent concentricity is the key to smooth operation, durability, and most importantly, accuracy. Driven by a computer and electric motor, the worktable can position the materials at exact intervals. For more flexible or critical operations, dividing plates can be added to this component.
A CNC system regulates the simultaneous 4-axis motion of the rotary table. The instructions are programmed and transmitted via CAD software, reducing the time for adjustment and monitoring by human workers.
The type and size of the electric motors utilized in can define the router accuracy as well as the efficiency of the device. Servo motor and stepper motor are two typical types that can be divided into more subtypes. The servo motor uses a closed looping variable circuit, the circuit will constantly run to keep the function. The brushes must be replaced every 2000 hours of operation in the servo motor. Compared to stepper motors, servo motors are more efficient in power consumption. On the other hand, the stepper motor has a simpler setup which are the wires that are attached to the driver. The bearing of the stepper motor is the only wearing component. However, the stepper motor consumes a great amount of energy.
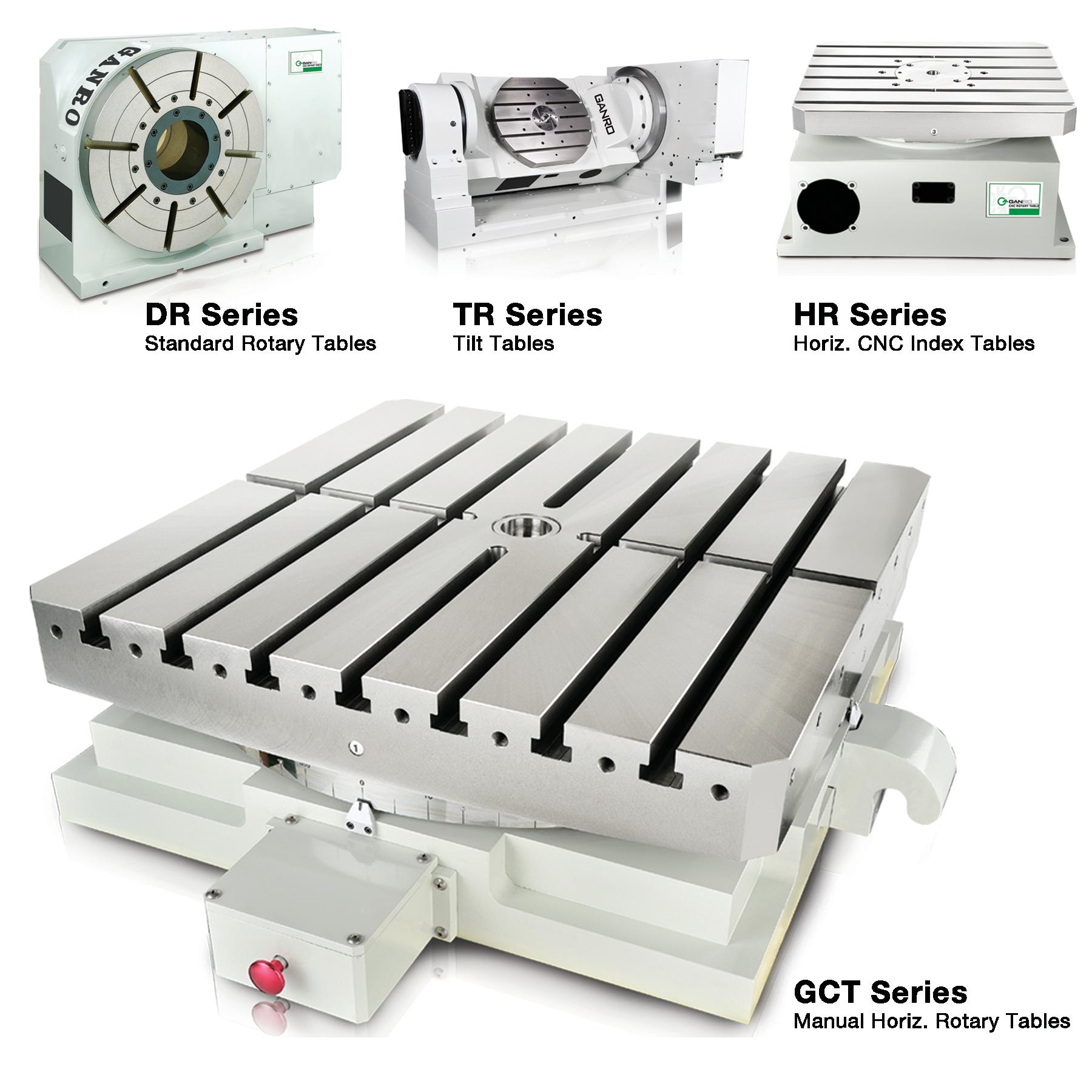
There are currently several different types and models available in the industries. Each of them possess its own traits and abilities. Let us take a look at the most common ones other than standard three axis tables
The 4 axis CNC rotary table will process the workpieces by holding them in the same position while the cutting tool performs along the XYZ plane to trim away the unwanted material. In general, a 4 axis model is very versatile equipment that can be used for several different industrial processes such as engraving curved surfaces, continuous cutting, and intermittent cutting. Besides, people can also add other devices such as cam machining, blade machining, and helical grooves to the 4 axes rotary table. Such a feature is simply impossible to achieve with the machining center which has only 3 axes.
Besides the 4 axis ones, there are also 5 axis models. They have the ability to allow the workpiece to be processed automatically from five sides at one time. people usually utilized the 5 axes rotary table in the industries such as the automobile, the aerospace, and the boating industries. The reason that the 5 axes rotary table is commonly used in heavy industries is that the 5 axis machining is an important technique to be used when the components need better intricacy and quick precision. All of these have more than three axes are called the multi-axis rotary table.
The installation method of the precision rotary table can be horizontal, vertical or inverted. When installed horizontally, the workbench surface is in a flat, vertical and horizontal position. When installed vertically, a rotary table is installed so that the surface of it can run up and down. In the reverse layout, itcan be rotated upside down in a horizontal position. The location of the drive of the rotary table can depend on the mount. The drive can be placed on the back, below, on the top or on the side.
When mounted horizontally, the spinning table top drive is positioned above the table floor. When the rotary table is horizontally placed, the side-mounted drive is located on the edge of the table board. The driving mechanism of the rotary table may be manual, electrical, pneumatic, hydraulic or non-driven. For manual revolving workbenches, release the workbenches and manually spin the workbenches with the crank.
Workpieces are gathered and machined through PC and fully programmed instructions. The 5-axis simultaneous operations will be measurably more reliable than products machined via different technologies. Also, the setup is simple and provides an indistinguishable process in every production cycle, the consistency of the quality of the metal products can be ensured under critical control and precision cutting.
Since the metalwork is driven by software, the preferred frameworks can be programmed and adapted by the rotary table. Saving both the cost and the room makes themis the ideal solution for potential users who don’t want to install larger equipment and new machines which may take up a great room for a wide variety of machining applications.
Another benefit is the utmost movements can be completed precisiely and faster. There are more favorable positions, operation angles as well as accessible machining that can be achieved through the technology. The complex operations are suitable for blade, helical grooves production, and other applications required to add complex features or require critical inspection in machining processes like the manufacturing of aerospace, automotive parts, and scientific equipment.
Addding a rotational table saves time because the extra finishing jobs or other sub-operations can also be performed at one time in the machining center.
A rotary table can be used in many applications including manufacturing, inspection, and assembly. Indicators are used, for example, for assembly, manufacturing, and bottling equipment. They typically use a single item in workspaces or move relatively small layouts of items around stations for sequential work or assembly.
In automated assembly machines, the rotary tables implementation is widespread, and choosing the right mechanism is important for both improving efficiency and reducing the cost of this vital component. This guide discusses two common devices for rotating indexing and offers guidance on the right range. There are several ways to get mass mobilization when it comes to the development of rotary indexing tables. Regardless of whether the load or load in centuries of thousands of kgm2 is incredibly light. When choosing a robust rotary index solution that will match or meet your standards, there are several factors to take into account when spinning, elevating, or pushing.
When determining the influencing factors on the postitioning accuracy, the first thing to look at is the mechanical properties of the table itself. A rotary table contains six degrees of freedom. Each of these movements increases the total risk of positioning errors. Usually, a rotary table is driven by a worm gear, which is connected to the motor through a rotary encoder on the back. The position of the table can be determined by the number of pulses transmitted from the encoder to the control device.
The four main sources of error due to the semi-closed position loop are geometric errors, thermal deformation, elasticity, and wear. The sum of these errors is called angular positioning error. To greatly reduce the angular positioning error, the ideal position for installing the angle encoder is on the rotating shaft under test. The angle encoder is installed under the rotary table, and the rotary encoder is installed under the rear motor, the position loop is now considered a closed-loop system.
Precision is a relative term. About a quarter of an inch is great and will meet the accuracy of its application. Others, for example, require micron-level accuracy in measuring and indexing devices. Then, some applications fall within these extreme ranges.
The misunderstanding is that you may have used an inaccurate indexing device and made it accurate by introducing a pin or wedge locking device. These devices increase the complexity and cycle time of use, and when they are used together with a high-precision positioning device, they may cause damage and reduce accuracy.
In the actual test, by selecting specific components, motion index drive, servo rotary indexer, the measurement accuracy is as high as 5-6 microns. These are not the results approved by Motion Index Drives, but the results of customer certification. When starting and stopping large amounts of data, it is important to know how fast it takes to stop the application with large amounts of data.
In a less rigid environment or the presence of higher recoil, a faster start and stop will bring many control problems. When moving masses (whether rotating mass or linear mass), starting and stopping in a system with a backlash of several arc minutes will cause a lot of back and forth movement in the gear system. The result is a force that is difficult or even impossible to calculate. In addition, when the gear head is used in rotating applications, the farther the mass is from the center of rotation, the greater the backlash. In applications with very slow deceleration times, recoil may not be a problem.
Backlash in the positioning process is a big issue – when it comes to the beginning and stopping volumes, it"s crucial to know how quickly you need to avoid the mass of your rotary indexing table applications. In a less rigid system or where there is an increased backlash, quicker start-ups and stops can cause a lot of control issues. When shifting a mass, whether rotary or linear, starting and stopping in a system with several minutes of backlash arc will create a lot of back-and-forth motion within the gearing system. The effect is a power that can be difficult and probably hard to quantify. In comparison, as the gear head is used for rotational applications, the more the mass is from the axis of rotation, the further the backlash is magnified.
The backlash may not be a concern in systems where deceleration times are incredibly long. In the case of cam indexers, there is " Zero Backlash." The cam indexer and rotary table dynamics give an incredibly rigid, highly regulated framework. A modern cam indexer system is capable of withstanding short cycle times with stop times in milliseconds.
So you want to get the smart manufacturing going but are not sure of what to look for in rotary tables. The information provided in this section may be able to help. The primary factor is to determine the mass snapshot of inactivity. This is often overlooked when measuring a rotary table for the machine.
Another significant factor is the size of the workpiece being rotated, including how big it is and how substantial it is. You want your rotary tables to be large enough to handle enormous pieces. This is where tilling rotary tables may become handy so that the pieces can be handled without causing interior harm. They allow the quickening and decelerating of machining at appropriate rates.
The last factor is accuracy, the applications for which, for instance, pivoting a gigantic part to allow welding highlights on it where the individual stop positions can be genuinely free. On an additional note, when choosing direct drive rotary tables, factors that you should consider when selecting a rotary table for your CNC machinery include accuracy, backlash, mass moment of inertia, acceleration and deceleration, speed, and environment.
Indexing system use is commonly possible in automatic assembly machines and the right process is important for both performance maximization and cost reduction.
Cam indexers are an omnipresent tool used for several decades for rotary indexing tables. They are suitable for applications that often index the same angle and need a high degree of accuracy at a relatively low cost. To place the load, a cam indexer uses a mechanical cam. A math curve is pushed onto the cam and provides incredibly smooth and repeatable movement.
Another popular alternative is a fully programmable rotary index table. A rotary table is advantageous in two different situations. Firstly, a versatile movement pattern is important. An example is if two components are running on one computer, each of which requires different index patterns. For incredibly fast placement accompanied by a long period, another condition that matches the servo pointer is. The need to accelerate the camshaft while the cam indexing mechanism was operating before starting the output movement reduced the on-demand cam indexer. Acceleration of the camshaft is possible, but there is a delay before the movement begins. There are realistic restrictions.
With an indexing table, the output rotates as soon as the servo starts moving. This is not difficult for a continuous cam indexer or a zero-backlash servo indexer, but it can also be difficult for an on-demand cam indexer. For applications with high-speed servo indexing, smooth movements are crucial. A zero-backlash preloaded reducer can achieve this. The ideal alternative for correct positioning with high dynamic response would be the zero-backlash reel drive system.
Application parameters, like a moment of inertia, indexing angle, indexing period, and residence time, are required for each indexer style. The rotary indexing table for the application should also be sized correctly by a reputable manufacturer.

At Rusach International,rotary table design, engineering and manufacturing & pallet system design, engineering and manufacturing is our specialty. We can supply rotary tables from 100mm up to 8 Meters in diameter. See our rotary table pages. We specialize in high accuracy, up to +/- 1 arc second, heavy load capacity, large work pieces, production style, heavy duty rotary tables and pallet shuttle/storage/transfer systems. We also have a line of standard small production tables that are very cost effective, yet can be customized per application.
Rusach International systems are not proprietary and therefore can be integrated into any machine, control system or application. We do not believe in “locking” a customer down with proprietary parts! We work with all the major industry control, motor and encoder manufacturers.

Thanks to Martin Power and Robert from Kitagawa Europe, I have another guest blog. Robert looks at rotary tables and how the small manual rotary table you might have for your drill press or milling table compairs with it’s bigger brother in the industrial world. For the model engineer, the rotary table would be for cutting curved slots say for an expansion link or rounding the ends of con rods. In industry there is a much wider range of tasks for the rotary table.
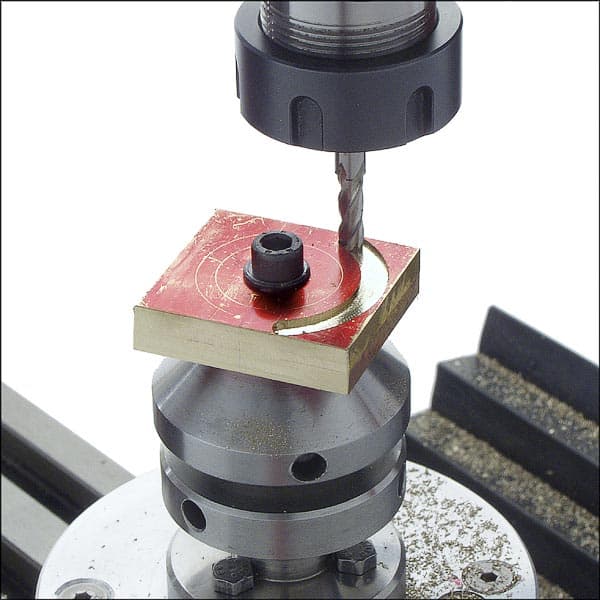
Those of you that have converted your shed or garage into a workshop will probably already know what a rotary table is may even have installed one. Even if you haven’t got your own personal workshop; there is a good chance that you have at some time used or at least come into contact with a rotary table. This will most likely have occurred in the school environment when in a Design and Technology class – or similar subject. The rotary table is of course a clamping mechanism that is used in the shaping of metal parts or components, in conjunction with various machines, including lathes, drill presses and milling machines.
In its most basic operation a rotary table is used to hold the object piece firmly in position whilst holes are made in an evenly spaced fashion. The image above shows such a task being carried out on a rotary table which has been mounted on a drill press. There are however much more advanced rotary tables available on the market, which are used in various manufacturing industries.
The photo above shows Kitagawa’s popular GT200 model, which is ideal for heavy machining. The complexity, accuracy and performance levels of such machines make their shed based cousins look like mere toys.
The top end rotary tables are commonly used in the manufacture of components that are used in cars, trains, planes and boats. Every time you travel somewhere in a vehicle you will be making use of metal work that has been created by a rotary table. It is of course important that every component of a vehicle is made precisely to ensure the safety of those using it. In order to deliver this precision, computer numerically controlled (CNC) rotary tables are used in the manufacturing world.
Rather than positioning and turning the rotary table manually; a CNC driven model operates using pre-programmed commands which are entered into a control module such as the one above. The rotary table is also able to communicate with the other end of the metalworking machine that holds the shaping tools. As a result both are able to work in unison; bringing precision and safety.
Whilst rotary tables play a key role in the manufacture of parts in the transport industry, it by no means the extent of their reach. Their usefulness stretches to many other areas of business, from construction to pipe laying. In order to fulfil their role in so many different environments it is important that rotary tables are both adaptable and available in various sizes and configurations.
In the example above we see a rotary table that has a huge through-hole capacity of 345mm. This allows long bar and tube shaped workpieces to be clamped effectively and is ideal for producing pipes to be used to move gas, water and oil. For such tasks, the standard three and four jawed chucks, such as the one below, are not suitable.
Such a clamping solution cannot deliver a suitable torque to hold the piece in place whilst it is being shaped. The result will be that shaping tools will deflect from their target, thus compromising the quality of the final component. Instead a collet chucks as shown below is more suitable for use when manufacturing pipes and bars.
The circular shape of the collet chuck allows pressure to be applied evenly to the outer surface of the workpiece. This allows larger gripping torque to be applied and also reduces the likelihood of surface damage to the workpiece that could otherwise be caused by standard jawed chucks. The clamping pressure is applied by tightening accompanying sleeve over the outside of the collet chuck.
The final main difference between manufacturing rotary tables and those used in schools and hobby workshops centres on the ability to choose tilting options. Standard rotary tables allow for the workpiece to be positioned along 3 axis in relation to the shaping tool. In contrast many models used in manufacturing include a manual or CNC tilting device that enables the workpiece to be positioned on a 4th and 5th axis. The image below shows a rotary table with tilting capabilities being use alongside a drill press.
As you can see, the machining tool is now able to approach the workpiece from different angles than would otherwise be possible. This allows for more much complex items to be produced, such as flute shaped ones.

Rotary indexing is a process where repeated angular displacement during a machine cycle is followed by motionless dwell. A rotary indexing table is specifically designed to make repetitive moves around a platform. Essentially, they are highly precise work-positioning devices that index parts to be worked or machined in multiple operations.
A rotary indexing table is an integrated motion system. They typically consist of motors and mechanical power transmission devices along with encoders, sensors and controllers. Tables use electric motors for either cam drives or servo tables. Mechanical cam indexers are relatively low cost and only index to set angles, but are capable of precision moves.
Important parameters for rotary indexing tables include the needed resolution of the application (or the smallest increment to move or measure), the required repeatability and accuracy, and other mechanical parameters such as acceptable levels of backlash or hysteresis. Another key parameter is the loading including torque, axial, radial, and moment loads. These can impact the type and size of the indexer used in a given application.
A rotary indexing table can be used in many applications including manufacturing, inspection, and assembly tasks. For instance, assembly, machining, and bottling machines all use indexers. Usually, they take one piece around to work areas or move arrays of relatively small parts around stations for sequential machining or assembly tasks.

This website or its third-party tools process personal data (e.g. browsing data or IP addresses) and use cookies or other identifiers, which are necessary for its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. To learn more, please refer to the cookie policy. In case of sale of your personal information, you may opt out by sending us an email via our Contact Us page. To find out more about the categories of personal information collected and the purposes for which such information will be used, please refer to our privacy policy. You accept the use of cookies or other identifiers by closing or dismissing this notice, by scrolling this page, by clicking a link or button or by continuing to browse otherwise.

Rotary indexing table use is widespread in automated assembly machinery and selecting the proper mechanism is essential for both maximizing performance and minimizing the cost of this critical component. This how-to-guide will explore two common devices that can be used for rotary indexing and give advice for proper selection. These two popular devices are cam indexing drives and servo rotary tables.
Cam indexers are a ubiquitous mechanism that have been used for rotary tables for many decades. They are a great fit for applications that will always index the same angle and that require high-precision positioning at a very reasonable cost. A cam indexer uses a mechanical cam to provide the motion control to position the load. A mathematical motion curve is machined onto the cam that provides extremely smooth and repeatable motion.
A cam indexer has two main modes of operation. One mode is referred to as “Cycle-on-Demand”. This indicates that the camshaft will be cycled one revolution at a time to advance the output one position at a time. This is typically achieved by using an inexpensive camshaft sensor package to detect camshaft position and a VFD to stop and start the motor. The camshaft dwell period offers a wide window for the camshaft to stop without affecting the position of the output. To cycle the indexer, a PLC gives a command to the VFD to accelerate the drive motor to a preset speed, the cam rotates one revolution indexing the output, a sensor sends an in-position signal to the PLC, and the PLC signals the VFD to stop the camshaft during the cam dwell position. The table will be in the dwell position for however long is necessary to complete the work at each station. The dwell time can range from a fraction of a second to several minutes or hours depending on the application. This combination allows very accurate positioning with an inexpensive drive system.
A cam indexer can also be run in a more traditional “Continuous” mode where the camshaft spins at a constant speed and the indexing and dwell time is controlled solely by the cam motion profile. Continuous mode is useful when other equipment will be mechanically synchronized with the camshaft timing or when the indexer needs to run at cycle rates faster than a motor can be stopped and started. A continuous indexer can run at rates in excess of 1,000 cpm. The limitation of continuous mode is that it may be impossible to machine a cam that requires a quick indexing motion followed by a long dwell time.
A fully programmable servo rotary table is another common option. There are two specific cases where a servo rotary table is advantageous. The first is when a flexible motion pattern is required. An example is two different products being run on one machine that each require different indexing patterns. The other situation that suits a servo indexer is when extremely fast positioning is required followed by a long dwell period. A cycle-on-demand cam indexer is limited by the need to accelerate the camshaft up to speed during the dwell period before output motion is started. There are practical limitations to how fast the camshaft can be accelerated so there will be a delay before motion is started. With a servo rotary table, the output rotates as soon as the servomotor starts moving. A practical example would be a load being indexed 90 degrees in 0.25 seconds. This is not difficult for a continuous cam indexer or a zero-backlash servo indexer, but a cycle-on-demand cam indexer may struggle with that motion. For quick servo indexing applications, a preloaded gear reducer with zero-backlash is critical to achieving smooth indexing motions with minimal settling time. A zero-backlash RollerDrive mechanism would be an optimal choice to achieve accurate positioning with great dynamic response.
For either style of indexer, application information including moment of inertia, indexing angle, indexing time, and dwell time is required. A reputable manufacture should then be able to properly size the rotary table for the application.

Rotary tables are a versatile tool found in many workshops and factories. There are various types of rotary tables, each with its own unique set of applications.
Air bearing rotary tables work by using air pressure to create air film between the table and the product. This film of air allows the table to rotate freely without friction. As a result, these tables are ideal for holding and turning products during manufacturing processes.
In addition, air-bearing rotary tables can be used in tandem with other machines, such as lathes and milling machines. This combination allows for even more precise and intricate work to be performed. Some of the products made with air-bearing rotary tables include medical implants, electronic components, and jewelry.
Rotary tables are used in hydrostatic piercing, which is a method of making oil wells. In this process, a table goes around while fluid finds its way into the well at high pressure. The fluid pierces the rock, and the table helps to stabilize the well.
Hydrostatic rotary tables also make other products, such as pipes and tubing. In this process, the table rotates while a metal rod goes into the center of the table. The rod is then cooled, and as it cools, it shrinks and forms a tight seal around the metal pipe.
A mechanical bearing rotary table essentially consists of a platform that can rotate around a central axis. The platform gains support from bearings, which allow it to rotate smoothly and without friction. Typically, you can control the platform"s rotational speed. You can stop the platform at specific intervals to work on it.
Common uses for a mechanical bearing rotary table include the production of circular saw blades. The blade blanks go on the rotating platform, and then they are cut to the desired size and shape using a saw.
Another common use for these devices is in the machining of metal parts. The parts are mounted on the table and then machined using various tools. Rotary tables can also be used for welding, assembling, and testing products.

As CNC machine tool technology has evolved it’s possible to do more operations better, faster and at lower cost than ever before. These advances also mean that there are more machine components and accessories to monitor and maintain. Often overlooked are rotary or trunnion tables that reduce setup and cycle times and, in many applications, enable the machining of complex parts.
Properly functioning rotaries and trunnions are essential to making accurate parts, and like other critical machine components should be checked regularly for signs of wear or damage. The most obvious tipoff that something is wrong with the rotary device is that you experience difficulty setting up a part, or begin producing out-of-tolerance parts. However there are 3 simple checks that, if done regularly, can help keep your rotary tables and trunnions in peak working order:
Check the oil sight glass for discolored or cloudy conditions. This may indicate that a seal has failed and coolant, dirt or other debris is in the lubrication system. Contaminated oil cannot properly protect the inner workings of the rotary device and can cause thousands of dollars in damage.
Inspect cables to make sure they aren’t broken or becoming soft and worn. A short in the electrical circuits caused by faulty cables can seriously damage electrical components.
Keep the control unit clean and free of moisture, oil and dirt. All electronic controls are subject to failure if the circuit boards are compromised. This is especially true in hot, humid conditions or when there is substantial oil residue in the air.
If you find that your Haas made rotary devices need maintenance or repair, contact your Torrance, CA Haas Factory Outlet for quick and reliable service. Since 1986 Haas has built and sold over 55,000 rotaries and trunnions for Haas and other machine tools, and provides comprehensive service on all 35 models.
Most jobs are turned around in 7 to 10 business days and include a thorough inspection to determine what components need attention to bring the rotary device back to factory specifications. This process includes:
Your Torrance, CA HFO technical service professionals will be happy to discuss your specific rotary device needs and can provide rentals or loaners to help minimize the impact on your production schedules. Learn more by calling Gabriel Monroy, 310-381-0750 Ext. 17526. Or email: gmonroy@haasfactoryoutlet.com. Visit www.haasfactoryoutlet.com for all the local Haas news.

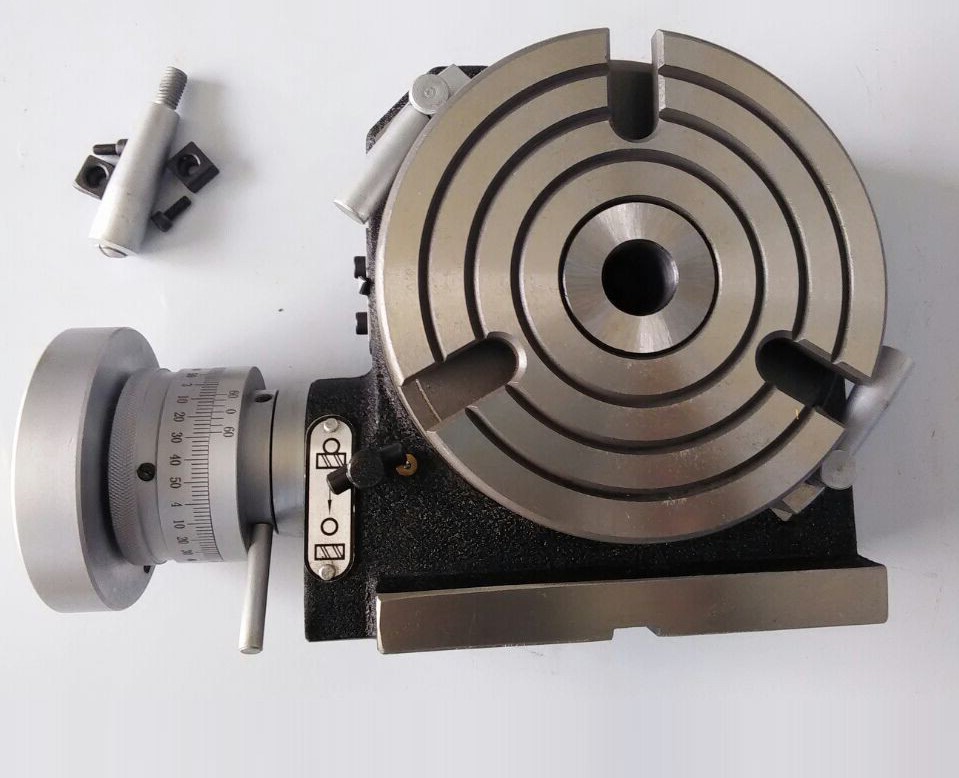
A rotary table is a precision device that is ideal for work positioning. Such table is used in metal works as it makes the job of drilling easier for the metal worker. Other than this, the metal worker can also cut the piece on fixed axes during specific interval with the help of a rotary table. Rotary Tables are available in varieties. Some of these tables use indexing plates for operations related to indexing whereas, others enables the user to fit dividing tables and leads to a better work positioning.
What make rotary tables important for metal industry are its numerous uses. Here is a list of few: Rotary tables are used for machining spanner flats on bolts. For cutting round pieces. For drilling holes at equal distance on circular flanges. A metal worker can also create large diameter holes on milling machines with these tables. Rotary tables are also used for cutting complex curves and mixing helixes.
There are different parts and components in rotary tables and all have different functions. Work table is the most important part of the table. It has spherical working area with four t-slots, which are used for mounting work pieces. There is a clank handle on rotary tables that enables the user to rotate the tables in clockwise and anti-clockwise directions. Rotary tables also have two bases, one is meant for vertical rotation whereas the other one is meant for horizontal rotation. At times, rotary tables are also mounted flat on planes similar to the way cutters are placed on vertical milling machines. If we look closely, rotary tables play a crucial role in the metal industry. Because they are used to perform different jobs, there is a specialized variety of rotary table to meet industry specific needs.

We combine rotary index tables with industrial automation systems so each task of your manufacturing process blends seamlessly into the next. For example, in the past we’ve created industrial automation systems that join rotary indexing machines with pick-and-place units for some of our clients. Contact us to see what we can do for you.
Rotary indexers are just one part of the equation when building a custom assembly cell. It’s important to remember the entire scope of the project and be cognizant that the rotary table should be able to move precise distances before stopping cleanly, with no backlash or wobbling. It needs to be balanced and capable of handling the tasks at hand.
Our automation experts have years of experience in consulting with our customers to create machines that suit their needs. We incorporate rotary tables from industry leaders like WEISS, Fibro, and Camco into our machines to create the perfect fusion of form and function. Our dedication to quality is unmatched in the world of custom machinery.
We seamlessly integrate rotary indexing tables into our automated machinery to provide you with custom solutions that work for your business. If you’re looking to take your manufacturing process to the next level, give the custom machine builders at Paramount Tool a call at (616) 582-5300 today. We’re always happy to answer any questions you may have about our rotary indexing machines or the machine building process as a whole. For a free quote, fill out our contact form and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.

Manufacturer of standard and custom 360 degree linear rotary tables for scanning, assembly, testing and production applications. Features vary depending upon model, including worm and gear drive design with central rotating ball bearings, manual and motorized operation, hollow spindles, four mounting holes, accessible adjustment clamps and graduated knobs. Accessories such as rotating table adapter plates, brackets, platform shelves, thumbscrew locks, alternative knobs, limit switches provided. Manually operated rotary motion turntables also available. Suitable for mounting and rotation of test specimens, cameras, transducers, sensors, mirrors and other components. Stock items and repair services are offered. One year warranty. Made in the USA.




 8613371530291
8613371530291