air compressor safety valve testing manufacturer

We are a leading manufacturer of high quality valves serving the compressed air, pressure washer, automotive, fluid power, fire protection, specialty gas, and pneumatic industries.
The Model “ST” safety valve is our standard safety valve for small air compressor systems and related applications. Even though the size is compact, flow capacities are high.
Resilient rubber pad, offered in silicone or flourocarbon, insures valve is bubble-tight to within 10% of set pressure. Three inlet sizes are available: 1/8″ NPT, 1/4″ NPT, and 3/8″ NPT.
Model “SV” ASME safety valves are designed for systems where large flow capacities are needed. Resilient pad insures valve is bubble-tight to within 10% of set pressure. Inlet size: 1/2″ NPT.
Model “SB” safety valves offer Control Devices value to users of high capacity ASME safety valves. Unique O-ring seal insures valve is bubble-tight to within 10% of set pressure. 1/2″ NPT and 3/4″ NPT inlets available.
The model “SW” valve is our highest capacity ASME safety valve. Unique O-ring seal insures valve is bubble-tight to within 10% of set pressure. 1″ NPT and 1¼” NPT inlets available.
The Super-Chek® design has been proven over the last 15 years to be the standard for air compressor in-tank check valves. One-piece brass bodies, stainless steel springs, and glass-filled fluoropolymer poppets all add up to long term reliability, while the eight discharge holes insure quiet operation.
Valves may be disassembled for cleaning or repair. Valves are 100% tested for backflow leakage performance. 450 PSI max pressure, 400 deg. F max temperature.
These cast-brass check valves have been specifically designed for installation into air compressor discharge lines. Extra-heavy walled cast brass bodies, glass-filled fluoropolymer poppets, and stainless springs resist corrosion and insure long life.
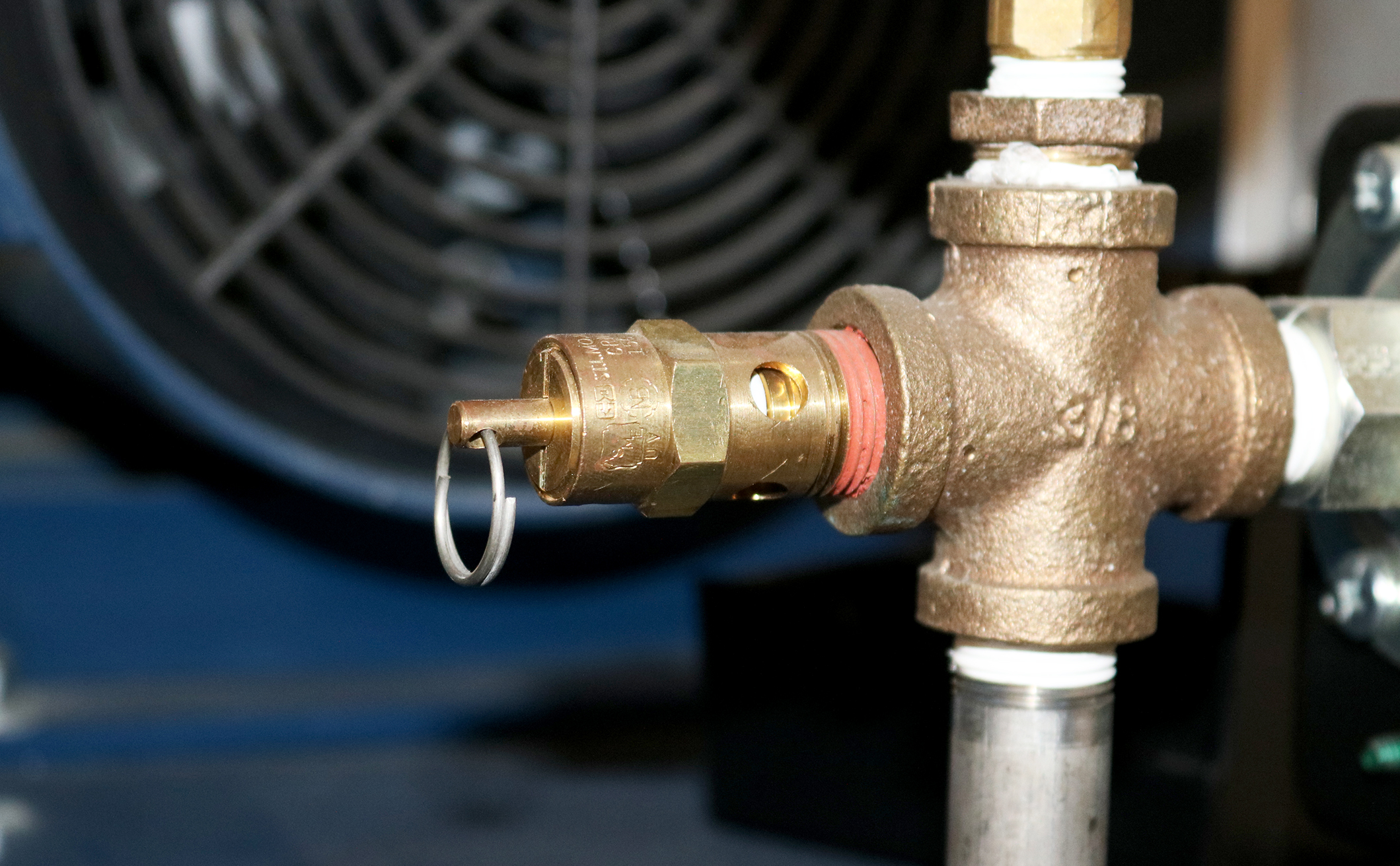

An OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES should be placed immediately after the air control shut off valve and before the hose on a compressor, and after each discharge port that a hose is connected to.
Before starting the compressor the air control valve should be closed completely. When the compressor unloads, open the air shut off control valve very slowly. Full port ball valves tend to work better than gate or butterfly type valves.
The air shut off control valve must be fully open for the OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES to work. Some portable air compressor manufacturers recommend start-up with the air control valve slightly open. In this case you may have to close the valve and reopen it slowly to the full open position, or wait for the safety shut-off valve to reset itself.
If the OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES fails to operate despite meeting all condi-tions, check the hose line for obstructions or a hose mender restricting normal air flow.
• Turn on air supply slowly (to avoid tripping OSHA safety valve). Prior to fully reaching operation conditions, the OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES should suddenly activate and stop air flow.
• If the OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVE is not activated the unit should be disconnected and the lower flow range OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES should be used. This means you need to use a different valve with a lower scfm range.
• At temperatures below 40°F ensure that OSHA COMPRESSED AIR SAFETY SHUT-OFF VALVES are not subject to icy conditions which may prevent proper functioning.

New replacement air compressor pressure safety relief valves. Using the correct one for your application is critical for safety. If you need help picking the right one, please call us for assistance.

IVI is a VR certified safety valve repair facility, approved by the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors as a VR certificate holder (stamp 179). We certify pressure relief valves in the shop and in the field for sections V and UV. We also perform on-site testing (while the plant operates) providing documented reports for all valves tested. We are also certified to administer special process conversions regarding machining, welding, heat treating, and N.D.T. (non-destructive testing) with our VR certificate.
With our VR stamp, we repair all types of pressure relief valves such as Consolidated, Crosby, Kunkle, Farris, Spence, Anderson Greenwood, and numerous other O.E.M. safety and pressure relief valves.

The Pressure Safety Valve Inspection article provides you information about inspection of pressure safety valve and pressure safety valve test in manufacturing shop as well as in operational plants.
Your pressure safety valve is a direct spring-loaded pressure-relief valve that is opened by the static pressure upstream of the valve and characterized by rapid opening or pop action.
Your construction code for pressure safety valve is API Standard 526 and covers the minimum requirements for design, materials, fabrication, inspection, testing, and commissioning.
These are:API Recommended Practice 520 for Sizing and SelectionAPI Recommended practice 521 Guideline for Pressure Relieving and Depressing SystemsAPI Recommended Practice 527 Seat Tightness of Pressure Relief Valves
For example if there is pressure vessel need to be installed in the state of Minnesota then the pressure vessel nameplate shall be U stamped and pressure vessel safety valve shall be UV stamped.
National Board Inspection Code (NBIC) have own certification scheme for pressure safety valves and using NB symbol. The NBIC code book for this certification is NB 18.
There are some other standards and codes which are used in pressure safety valve such as:ASME PTC 25 for pressure relief devices which majorly is used for assessment of testing facility and apparatus for safety valvesBS EN ISO 4126-1, 4126-2 and 4126-3 which is construction standard similar to API STD 526.
This API RP 527 might be used in conjunction of API RP 576 as testing procedure for seat tightness testing of pressure safety valve for periodical servicing and inspection.
These are only important points or summery of points for pressure safety valve in-service inspection and should not be assumed as pressure safety valve inspection procedure.
Pressure safety valve inspection procedure is comprehensive document which need to cover inspection methods to be employed, equipment and material to be used, qualification of inspection personnel involved and the sequence of the inspection activities as minimum.
You may use following content as summery of points for Pressure Safety Valve Inspection in operational plantDetermination pressure safety valve inspection interval based API STD 510 and API RP 576 requirementsInspection of inlet and outlet piping after pressure safety valve removal for any foulingInspection of pressure safety valve charge and discharge nozzles for possible deposit and corrosion productsTaking care for proper handling of pressure safety valves from unit to the valve shop. The detail of handling and transportation instruction is provided in API RP 576.Controlling of seals for being intact when the valves arrived to the valve shop.Making as received POP test and recording the relieving pressure.
If the POP pressure is higher than the set pressure the test need to be repeated and if in the second effort it was near to the set pressure it is because of deposit.If in the second effort it was not opened near to the set pressure either it was set wrongly or it was changed during the operationIf the pressure safety valve was not opened in 150% of set pressure it should be considered as stuck shut.If the pressure safety valve was opened below the set pressure the spring is weakenedMaking external visual inspection on pressure safety valve after POP test. The test need contain following item as minimum;the flanges for pitting and roughness
Making body wall thickness measurementDismantling of pressure safety valve if the result of as received POP test was not satisfactoryMaking detail and comprehensive visual and dimensional inspection on the dismantled valve parts (after cleaning)Making special attention to the dismantled valves seating surfaces inspection e.g. disk and seat for roughness, wear and damage which might cause valve leakage in serviceReplacing the damaged parts in dismantled valves based manufacture recommendation and API RP 576 requirementsMaking precise setting of the pressure safety valve after reassembly based manufacture recommendation or NB-18 requirements
Making at least two POP test after setting and making sure the deviation from set pressure is not more than 2 psi for valves with set pressure equal or less than 70 psi or 3% for valves with set pressure higher than 70 psiMaking valve tightness test for leakage purpose after approval of the setting pressure and POP tests. The test method and acceptance criteria must be according to the API RP 576.The API RP 527 also can be used for pressure safety valve tightness test.Recording and maintaining the inspection and testing results.
ACS stocks air compressor check valves and safety valves as two important parts of your air compressor. Our safety valves are designed to relieve pressure if the air compressor exceeds the maximum safe pressure level. Our air compressor check valves aredesigned to keep air from flowing back into the pump when the air compressor is not in use. This way, your air compressor won"t risk being damaged by excessive pressure.

1. Suncenter air compressor safety valve testing is made of durable and high quality material but with reasonable price. It can be used for a broad variety of liquids, such as oil, water, and chemical
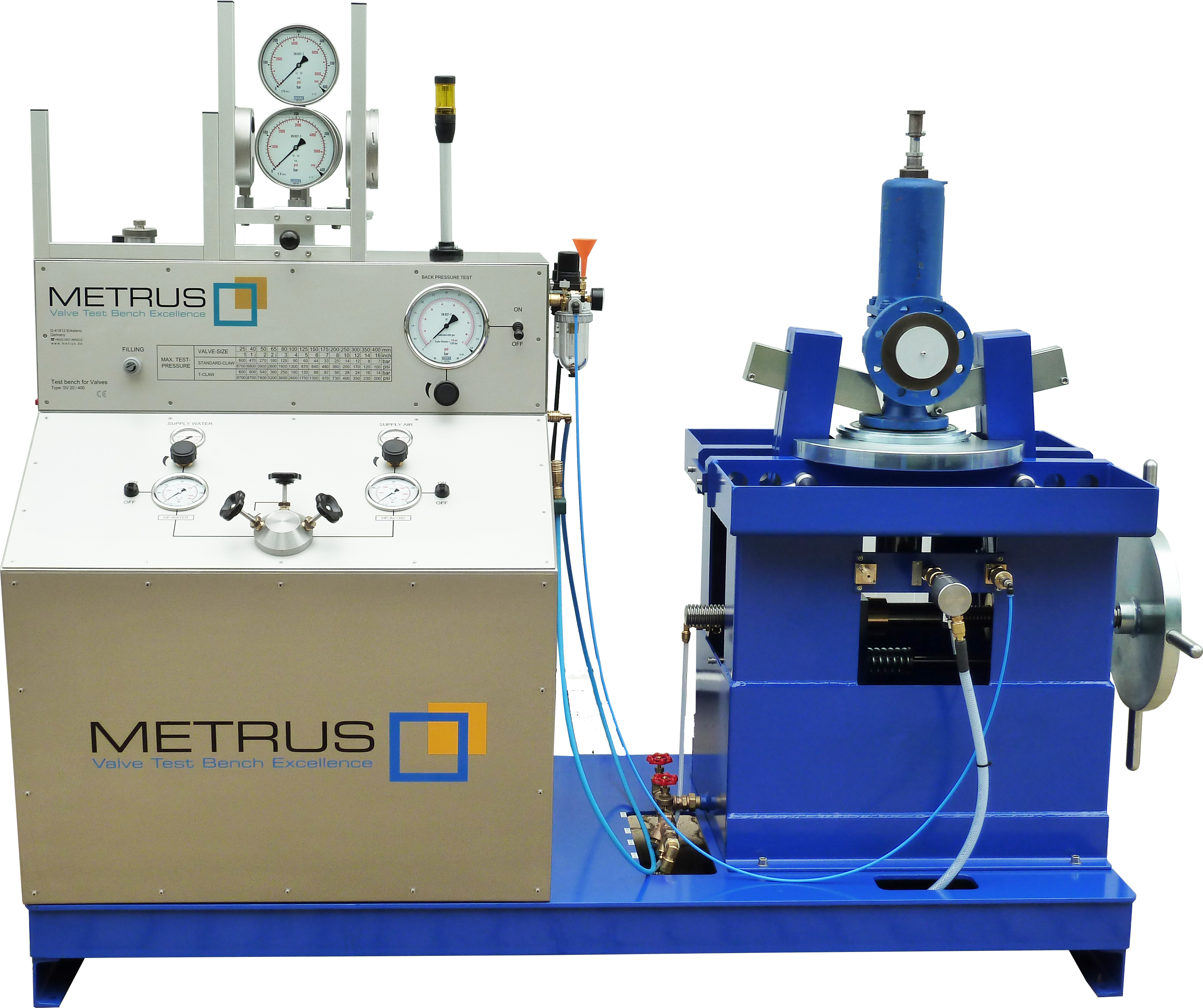
◪The safety valve test bench is a new type of pressure test device developed by our company for reference to GB/T 12242-2005 (pressure release device and performance test specification), which is used to adjust and test the setting pressure of the safety valve.
Safety valve test bench is used for various safety valve setting pressure adjustment, the whole set pressure detection, discharge pressure detection, back seat pressure testing, assessment of its pressure safety performance etc.. ,

Curtiss-Wright"s selection of Pressure Relief Valves comes from its outstanding product brands Farris and Target Rock. We endeavor to support the whole life cycle of a facility and continuously provide custom products and technologies. Boasting a reputation for producing high quality, durable products, our collection of Pressure Relief Valves is guaranteed to provide effective and reliable pressure relief.
While some basic components and activations in relieving pressure may differ between the specific types of relief valves, each aims to be 100% effective in keeping your equipment running safely. Our current range includes numerous valve types, from flanged to spring-loaded, threaded to wireless, pilot operated, and much more.
A pressure relief valve is a type of safety valve designed to control the pressure in a vessel. It protects the system and keeps the people operating the device safely in an overpressure event or equipment failure.
A pressure relief valve is designed to withstand a maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). Once an overpressure event occurs in the system, the pressure relief valve detects pressure beyond its design"s specified capability. The pressure relief valve would then discharge the pressurized fluid or gas to flow from an auxiliary passage out of the system.
Below is an example of one of our pilot operated pressure relief valves in action; the cutaway demonstrates when high pressure is released from the system.
Air pressure relief valves can be applied to a variety of environments and equipment. Pressure relief valves are a safety valve used to keep equipment and the operators safe too. They"re instrumental in applications where proper pressure levels are vital for correct and safe operation. Such as oil and gas, power generation like central heating systems, and multi-phase applications in refining and chemical processing.
At Curtiss-Wright, we provide a range of different pressure relief valves based on two primary operations – spring-loaded and pilot operated. Spring-loaded valves can either be conventional spring-loaded or balanced spring-loaded.
Spring-loaded valves are programmed to open and close via a spring mechanism. They open when the pressure reaches an unacceptable level to release the material inside the vessel. It closes automatically when the pressure is released, and it returns to an average operating level. Spring-loaded safety valves rely on the closing force applied by a spring onto the main seating area. They can also be controlled in numerous ways, such as a remote, control panel, and computer program.
Pilot-operated relief valves operate by combining the primary relieving device (main valve) with self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief valves, also known as the pilot control. This pilot control dictates the opening and closing of the main valve and responds to system pressure. System pressure is fed from the inlet into and through the pilot control and ultimately into the main valve"s dome. In normal operating conditions, system pressure will prevent the main valve from opening.
The valves allow media to flow from an auxiliary passage and out of the system once absolute pressure is reached, whether it is a maximum or minimum level.
When the pressure is below the maximum amount, the pressure differential is slightly positive on the piston"s dome size, which keeps the main valve in the closed position. When system pressure rises and reaches the set point, the pilot will cut off flow to the dome, causing depressurization in the piston"s dome side. The pressure differential has reversed, and the piston will rise, opening the main valve, relieving pressure.
When the process pressure decreases to a specific pressure, the pilot closes, the dome is repressurized, and the main valve closes. The main difference between spring-loaded PRVs and pilot-operated is that a pilot-operated safety valve uses pressure to keep the valve closed.
Pilot-operated relief valves are controlled by hand and are typically opened often through a wheel or similar component. The user opens the valve when the gauge signifies that the system pressure is at an unsafe level; once the valve has opened and the pressure has been released, the operator can shut it by hand again.
Increasing pressure helps to maintain the pilot"s seal. Once the setpoint has been reached, the valve opens. This reduces leakage and fugitive emissions.
At set pressure the valve snaps to full lift. This can be quite violent on large pipes with significant pressure. The pressure has to drop below the set pressure in order for the piston to reseat.
At Curtiss-Wright we also provide solutions for pressure relief valve monitoring. Historically, pressure relief valves have been difficult or impossible to monitor. Our SmartPRV features a 2600 Series pressure relief valve accessorized with a wireless position monitor that alerts plant operators during an overpressure event, including the time and duration.
There are many causes of overpressure, but the most common ones are typically blocked discharge in the system, gas blowby, and fire. Even proper inspection and maintenance will not eliminate the occurrence of leakages. An air pressure relief valve is the only way to ensure a safe environment for the device, its surroundings, and operators.
A PRV and PSV are interchangeable, but there is a difference between the two valves. A pressure release valve gradually opens when experiencing pressure, whereas a pressure safety valve opens suddenly when the pressure hits a certain level of over pressurization. Safety valves can be used manually and are typically used for a permanent shutdown. Air pressure relief valves are used for operational requirements, and they gently release the pressure before it hits the maximum high-pressure point and circulates it back into the system.
Pressure relief valves should be subject to an annual test, one per year. The operator is responsible for carrying out the test, which should be done using an air compressor. It’s imperative to ensure pressure relief valves maintain their effectiveness over time and are checked for signs of corrosion and loss of functionality. Air pressure relief valves should also be checked before their installation, after each fire event, and regularly as decided by the operators.
Direct-acting solenoid valves have a direct connection with the opening and closing armature, whereas pilot-operated valves use of the process fluid to assist in piloting the operation of the valve.
A control valve works by varying the rate of fluid passing through the valve itself. As the valve stem moves, it alters the size of the passage and increases, decreases or holds steady the flow. The opening and closing of the valve is altered whenever the controlled process parameter does not reach the set point.
Control valves are usually at floor level or easily accessible via platforms. They are also located on the same equipment or pipeline as the measurement and downstream or flow measurements.
An industrial relief valve is designed to control or limit surges of pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air system valves. It does so as a form of protection for the system and defending against instrument or equipment failure. They are usually present in clean water industries.
A PRV is often referred to as a pressure relief valve, which is also known as a PSV or pressure safety valve. They are used interchangeably throughout the industry depending on company standards.

You may not worry often, if at all, about whether or not your air compressor is running safely. And you really don’t have to, because compressor manufacturers do. From the pressure rating on the air storage tank to emergency stop buttons, air compressors are designed with safety in mind.
But that doesn’t mean you should never think about your compressor’s safety features. In most cases, they need to be inspected regularly to make sure they’re working properly. One key safety feature that should be inspected regularly is the air pressure relief valve (PRV), sometimes called a safety relief valve.
The pressure relief valve is a safety valve that protects the compressor component that it’s attached to from being exposed to a pressure above its rated maximum operating pressure. This rating, called the maximum working pressure (MWP), is the pressure that the vessel has been certified to continuously operate at safely.
So when a compressor is running at or below its maximum working pressure—in other words, when it’s running “normally”—the relief valve doesn’t do anything.
However, when the air pressure inside a compressor exceeds its MWP, the pressure relief valve will activate to “blow off” the excessive pressure within the compressor. Without a relief valve, the storage tank could rupture from the excessive pressure, damaging the compressor itself, possibly other property near it, and even causing injuries (or worse) to anyone standing nearby.
Before we can talk about how the air pressure relief valve works, we first need to look at how air pressure inside a compressor is managed when everything is running normally.
Under normal circumstances, the air pressure in a compressor is controlled by a pressure switch in an electro/mechanical control system or, in the case of an electronic controller, a pressure transducer and controller settings. When the cut-out set pressure for the pressure switch is reached, the compressor will stop compressing air (unload) until the cut-in set pressure is reached, at which time it will start compressing air again (load). If the pressure switch fails, the compressor would not be able to start compressing air again, or potentially worse, not be able to stop. Most compressors also have a high-pressure safety switch that should stop the compressor if the pressure exceeds the unload set point.
A pressure relief valve is a straightforward safety backup to the pressure switch and high-pressure switch, or the controller set points, should any of these components fail with the compressor running. The safety relief valve is set above the high-pressure safety switch and generally at or below the vessel’s maximum operating pressure. Inside the valve is a spring, and the pressure created by the spring’s tension keeps the valve closed under normal operating conditions. However, as the air pressure increases in pressure vessels (like the storage tank), it eventually exceeds the rated pressure of the relief valve, causing the relief valve to open and the excess pressure to be “blown off” to the atmosphere.
If the pressure relief valve fails open, air will continually vent to the atmosphere, preventing the air stream from becoming fully pressurized. The compressor should be shut down and the relief valve replaced before the compressor is restarted. The open relief valve will likely cause a loss of production and possible danger to personnel as a result of the flow of high-pressure air with flying debris and an unsafe sound level.
A pressure relief valve failing closed presents a potentially more dangerous situation. As noted earlier, the relief valve exists to allow excessive pressure to be “blown off” so that the air pressure inside the compressor’s pressure vessels don’t exceed their rated specifications. If the valve fails closed, this pressure venting can’t happen. Unless compressed air demand matches the compressed air supply, the pressure inside the compressor will continue to build. Eventually, the pressure increase would cause the storage tank to rupture, damaging the compressor and possibly causing additional damage and injury to property and people nearby.
If the relief valve is opening because the air pressure in the compressor has exceeded the valve’s pressure set point, that means the valve is working and doing what it was designed to do. But because this indicates the MWP of the compressor has been exceeded, the condition that’s causing excessive pressure should be diagnosed and corrected.
If the relief valve opening wasn’t caused by excessive pressure inside the compressor, then the valve is most likely “failing open”. Most likely, this is because the valve has become “soft” over time, i.e. the valve spring is providing less counterpressure, so it’s opening at a lower pressure than it should.
Whether the valve opened because of excessive pressure in the compressor or because the valve is failing, you should have your local air compressor distributor inspect your compressor before running it again for two reasons:
First, your distributor can determine whether the valve opened due to a failing relief valve or excessive compressors pressure and perform any needed maintenance or service to get your compressor running efficiently and safely again.
Second, regardless of why the pressure relief valve opened, replacing it may be recommended to ensure safe compressor operation, depending on the valve manufacturer. (Replacement is recommended for Sullair compressors.)
Important: Running the compressor after the relief valve has opened, regardless of the reason why it opened, can put both your property at risk of damage and people at risk of injury (or worse). While this may be obvious if the compressor is building up excess pressure, it also applies if the valve failed open. As noted above, even a valve that fails open poses some risk, and next time it could fail closed.
Given how critical a working air pressure relief valve is to the safe and efficient operation of your air compressor, you may wonder whether you need to do any regular inspecting or testing of the valve to make sure it is working. Because this can vary by manufacturer, you should consult your owner’s manual or contact your local air compressor distributor for frequency and type of inspection needed. For most Sullair compressors, inspection for damage or leakage is recommended, but testing is not recommended, as doing so may compromise the valve’s performance.
However, one thing you should do is schedule regular maintenance with your local air compressor distributor. As part of regular maintenance, a service technician can inspect the PRV and let you know it’s at an age or in a condition at which the manufacturer recommends replacement. Also, problems with the compressor’s performance, e.g. not reaching normal operating pressure, may help the service technician identify a failing relief valve after ruling out other possible causes.
When a pressure vessel like a receiver, sump tank or other storage vessel is purchased separately from the compressor, it may not be supplied with a pressure relief valve. To ensure its safe operation, you should add a PRV.
When selecting a PRV to add to the pressure vessel, you must choose a valve with a pressure set point set at or below the maximum working pressure of the vessel. You will find the MWP (and other useful information) on a tag welded to the pressure vessel. Also, flow capacity of the PRV must meet or exceed the total compressed air supplied to the vessel.
For example, if you have two compressors with capacities of 500 and 750 cfm (14.2 and 21.2 m³/min), and a pressure vessel with a maximum working pressure of 200 psi (13.8 bar), the minimum settings for a pressure relief valve would be 1250 cfm (35.4 m³/min) and a set point 200 psi (13.8 bar) or less.
Finally, when attaching the valve to the vessel, the porting must not be reduced to a size less than the size of the inlet port of the pressure relief valve.
Because the pressure relief valve is critical to the safe operation of your compressed air system, if you’re not sure how to select the correct PRV and properly and safely add it to the pressure vessel, contact your local air compressor distributor. They have the experience and expertise to ensure that the PRV is sized and installed correctly.

Compressor Safety Valve that decreases the volume of air or other gas by the application of air compressor safety valve from the simple hand pump and the piston-equipped compressor used to inflate tires to valves that use a rotating, bladed element to achieve compression. The four basic types of compressors are reciprocating, rotary screw. these are further classified by the number of compression stages, the cooling method, and lubrication.
HP Valve a Compressor Safety Valve is a gadget that permits liquid or air to stream in one and only bearing. At the point when your compressor achieves the empty weight, the check valves close to keep reverse of the air from the tank to the compressor safety valve head.
A valve in a compressor, typically programmed, which works by weight distinction on the two sides of a versatile, single loaded part and which has no mechanical linkage with the moving parts of the compressor component.
An energetic note on check valves: Many circumstances people will find air spilling from the weight switch. At the point when this happens, they instantly buy and introduce another weight switch. Since air still gaps, they call and express that the switch is defective.
In the event that air is spilling reliably? the issue is not the weight switch - it is the check valve. More than likely it is loaded with garbage and is not fixing. At the point when this happens the check valve either should be cleaned or supplanted.
Air compressors safety valve have much utilization, including providing high-weight clean air to fill gas chambers, providing moderate-weight clean air to a submerged surface provided jumper, providing moderate-weight clean air for driving some office and school building pneumatic HVAC control framework valves, providing a lot of direct weight air to control pneumatic devices, for example, jackhammers, filling high weight air tanks (HPA), for filling tires, and to convey immense volumes of direct weight air for broad scale current methodology, (for instance, oxidation for oil cooking or security plant pack house scrub systems).

Our range of products include Air Compressor Brass Safety Valve, Air Compressor Safety Valve, Brass Safety Valve, Brass Pressure Safety Valve, Brass Angle Valve and Pressure Relief Valves.
This is safety valve for use safetty perpuse , like air compressor ,pressure vasle,oil , gas etc. This is importent for every enginering machines , becose that is safety for machine and and human also.
This ispneumatic valve, It is made in ss mateiral wht many other material. I am manufactuiirng big range of this valve. This is fully auto matic valve.
This is brass pilot valve. It is use in all model like high preassure 12 hp to 25 hp with high pressure machine. This valve use for by pass air like body creat air to descharge by pilot valve.
This is auxliery valve.It is made by aluminum material.This is requirment high pressure compressor and low pressure air compressor. This valve is use in 90 to 100, 175 to 200, 200 to 300, 300 to 600, 600 to 1000.

Conventionally when we talk about oil lubricated screw air compressor maintenance, it is mostly about replacing consumables such as filters and lubricant on time. While these consumables have a defined usable life and have a direct effect on the efficiency and the life of the air compressor itself when not replaced on time, there are a few critical valves in the air compressor that require maintenance as well. Compressor valves directly affect the efficiency, safety, and the functionality of the screw air compressor. Let us understand some of the commonly available valves in a screw air compressor, why they need maintenance, and discuss some of the frequently asked questions about screw air compressor valves.
A screw air compressor is very similar to a human heart. While a human heart has tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves, a screw air compressor has four critical valves namely air inlet, minimum pressure, blow down, and safety valves.
Air inlet valve is also commonly known as the ‘Intake valve’ which is typically assembled on the airend’s intake. The air inlet valve of a conventional fixed speed screw air compressor controls the air intake into the compressor. It remains closed when the compressor starts to lower the starting load on the main motor and when the desired working pressure is attained in the compressed air circuit and thus enabling the compressor’s motor to run without any load. In some compressors that are capable of providing a variable output by modulating the amount of air it sucks in, the inlet valve holds various opening positions to regulate the volume of air entering the compressor. The effective performance of the inlet valve directly affects the compressor’s capacity and its power consumption during load and no-load conditions.
The minimum pressure valve is typically assembled on the exit of the air-oil separation tank of a compressor. The minimum pressure valve acts as a check valve preventing back flow of compressed air into the airend, retains a minimum pressure in the compressor system for lubrication, offers a restriction to avoid a collapse of the air-oil separation filter, and ensures a suitable velocity of flow across the air-oil separator that ensures efficient air-oil separation. The effective performance of the minimum pressure valve directly affects the compressor’s lubrication, air-oil separation efficiency, and power consumption during load and no-load conditions.
The blow down valve is typically found on a dedicated exhaust line from the air-oil separation tank. The blow down valve evacuates the compressed air in the air-oil separation tank each time the compressor runs on a no-load and when the compressor shuts down to ensure there is no back pressure when the compressor starts to load next time. The blow down valve of a conventional screw compressor is typically actuated by a solenoid valve. The effective performance of the blow down valve affects the compressor’s power consumption during un-load, capacity of the compressor when running on load, and the life of the motor.
The safety valve is typically mounted directly on the air-oil separator tank. The only function of the safety valve is to blow off the compressed air in the air-oil separation tank when the pressure in the air-oil separation tank exceeds the set pressure of the safety valve and there by prevents the tank from cracking under high pressure. A malfunctioning safety valve affects the safe operation of the air compressor or results in leakage of compressed air continuously.
Though each compressor manufacturer has their own unique valve design, compressor valves in general contain moving parts such as springs, valve plates, and plungers that affect the opening and closing of the valves and rubber seals / seats that offer perfect sealing when the valves remain closed. These moving parts wear or lose their mechanical properties over a period of time and the sealing components typically ‘age’ over time and lose their effectiveness and will need to be replaced.
Compressor manufacturers typically design these components to operate efficiently for several thousand or millions of operation cycles. However, several factors such as variability in the demand pattern, sizing of the air compressor against a certain air demand, the environment in which the air compressor operates, promptness of preventive maintenance, etc. determine how long these valves efficiently operate.
Many times, it is difficult to identify a malfunctioning valve or a valve operating with worn-out parts as the compressor continues to generate air. The typical symptoms of a malfunctioning valve are loss in compressor"s capacity, increase in power consumption during load or/and unload, drop in discharge pressure, increase in oil carry-over and more load on motor. These symptoms are either difficult to notice or have other frequently common assignable causes such as air leak before suspecting the compressor valves.
Case studies show that operating a screw air compressor with a worn-out / malfunctioning valve could increase its overall power consumption by 10 - 15%. Power cost contributes to more than 75% of the compressor’s total life cycle cost over ten years and hence this is a significant impact. Unserviced valves also lower the life span of downstream accessories by half. In some cases, a malfunctioning safety valve may result in a catastrophe.
Air compressor manufacturers typically offer convenient valve maintenance kits for customers that contain the internal parts of the valve that wear or age out. Changing the valve kits is a much more sensible and economical option than changing the complete valve.
It is difficult or almost impossible to identify a malfunctioning valve unless it is opened for inspection. Hence it is absolutely mandatory that these valves are inspected for effectiveness every year and the internal moving parts replaced as a part of preventive maintenance once every year or two depending on the operating conditions of the air compressor. It is typical for compressor manufacturers to mandate a valve kit replacement once every two years as a proactive measure.
In particular, the safety valve must be inspected and certified every year per the local safety laws to ensure they are functional and efficient. Sometimes, replacing the safety valve entirely with a valid certificate for one year is more economical as the certification procedures could be equally expensive on an existing valve.
As stated before, it is challenging to identify a valve that is worn out unless it is opened and inspected, but there are a few indicators that a qualified compressor technician can use to deduct a malfunctioning valve.
Low duty cycle operation: A sophisticated screw air compressor in today’s day and age carries a convenient microprocessor-based human-machine interface that keeps track of operating hours of the compressor under load and un-load conditions and the number of load/unload counts the compressor is subjected to over a period of time. A higher un-load hours and load/unload count indicates that the air compressor is oversized against the actual air demand. This in turn indicates the air compressor ‘cycles’ frequently between load and un-load mode as opposed to running continuously on load. Every time a compressor ‘cycles’, the inlet valve, blow down valve, and minimum pressure valve is brought into play where their internals ‘actuate’. Frequent actuation of these valves results in a faster wear of the internals and hence results in shorter life.
High operating temperature: A compressor that runs on a high operating temperature affects the life of the valve’s sealing components, which causes them to ‘age’ fast.
Compressor not building pressure: If the air demand has not changed over time and the facility is relatively free of any air leakage, the air compressor is probably not delivering the rated output. There is a high probability that there is a malfunctioning valve.
Increase in compressor’s power consumption: An increase in the air compressor’s power consumption profile over a period of time where there has been no abnormal change in the air demand and usage pattern indicates an increase in either the load or un-load power. There is a high probability that this is because of a malfunctioning valve.
Based on the design philosophy adopted by the air compressor manufacturer, the oil lubricated screw air compressors could have a few more valves that are critical to functional performance that must be maintained as well. Some of the other valves frequently used in an air compressor are as follows:
Temperature control valve (also known as thermal valve) is used to regulate the flow of oil through the oil cooler based on the operating temperature.
Drain valves are used to drain lubricant at the time of lubricant change over or cleaning. Air compressors equipped with a moisture trap at the outlet of the after cooler also has a drain valve (automatic or timer based) to discharge water collected.
The presence or absence of one of these valves and the type of actuation of these valves (electronic / mechanical) depends on air compressor’s design architecture. The Operation and Maintenance Manual (OMM) and the Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) supplied by the air compressor manufacturer are excellent resources that explain the purpose, functioning, and maintenance requirements of these valves.
Many of the air compressor valves are highly specialized and exclusive. Their designs are usually complex and some even need special tools to service them. The internal components" build quality and material selection are extremely important and proprietary. Hence it is highly critical that only genuine valve kits issued by the air compressor manufacturer are used to maintain the valves. An inferior after-market replacement will most certainly compromise the performance of the entire compressor, void the original manufacturer"s warranty of the compressor, cause consequential damage to other parts of the compressor, and above all, be a safety hazard.
In conclusion, while it is important to change the screw air compressor"s filters and lubricants on time, it is equally important to perform preventive maintenance on these critical valves in a screw air compressor as recommended by the air compressor manufacturer. While the intake valve, minimum pressure valve, safety valve, and blowdown valve are critical to the performance and safety of the compressor, there could be other valves in the compressor that are critical and need maintenance. The air compressors sizing and the environment in which it operates are crucial factors that affect the life of the air compressor. Finally, it is critical to proactively service these valves using genuine kits issued by the compressor manufacturer to enable the air compressor performs efficiently and safely.
Gershom Joel has over 15 years of experience in the compressed air field and specializes in helping industries such as Pharmaceuticals, Textile, Electronics, and Food and Beverage find compressed air solutions to meet their unique requirements. Gershom holds a Mechanical Engineering Degree from Anna University and a Masters in Business Administration from University of North Carolina.
ELGi North America, headquartered in Charlotte, NC, is a subsidiary of ELGi Equipments Limited, a leader in compressed air solutions for over 60 years. Established in 2012, ELGi North America, in conjunction with its subsidiaries, Pattons, Pattons Medical, and Michigan Air Solutions, offers a comprehensive range of compressed air products and services. Our product offering includes oil-lubricated and oil-free rotary screw and reciprocating compressors, dryers, filters, and ancillary accessories. ELGi and its subsidiaries serve multiple industry verticals spanning medical applications, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure. For more information, visit https://www.elgi.com/us/.




 8613371530291
8613371530291