nozzle reaction safety valve price

300LPM01-L is a safety relief valve for steam service on unfired pressure vessels. It is also used on Pressure Reducing Stations, Accumulators, Cleaners, and Distillers. Meets ASME code, Section VIII.
Model 300LPM01-K is a safety relief valve for air, gas and vapors. It is used on compressors, receivers, burners, dryers and other piping systems. Meets ASME code, Section VIII.

The new TFT Working Fire nozzle delivers revolutionary performance when you need maximum flows for a “working fire.” For everyday use, it is a 150 gpm @ 75 psi Fixed GPM Nozzle, but when you need even more GPM, the nozzle’s exclusive pressure relief system dramatically limits nozzle reaction.
The exclusive TFT pressure relief feature maximizes GPM when you over pump the nozzle. The pressure relief feature keeps reaction force manageable as GPM increases versus a nozzle without a pressure relief feature that builds up massive nozzle pressure and reaction force.
At low flows, just like every other fixed GPM nozzle, it is clear from the stream quality that optimum flow has not yet been reached. When you achieve the 150gpm rate, the nozzle flows great, and there is about 65lbs of nozzle reaction force. However when you need a lot more GPM, that is where the Working Fire excels. By integrating pressure relief, a 33% increase in flow rates only yields a 33% increase in reaction force. Compare that to a traditional fixed nozzle, which increases 78%. With the Working Fire nozzle, TFT is able to deliver high GPM (200 gpm) with about 30lbs less reaction force than other nozzles!

The new TFT Working Fire nozzle delivers revolutionary performance when you need maximum flows for a “working fire.” For everyday use, it is a 150 gpm @ 75 psi Fixed GPM Nozzle, but when you need even more GPM, the nozzle’s exclusive pressure relief system dramatically limits nozzle reaction.
At low flows, just like every other fixed GPM nozzle, it is clear from the stream quality that optimum flow has not yet been reached. When you achieve the 150gpm rate, the nozzle flows great, and there is about 65lbs of nozzle reaction force. However when you need a lot more GPM, that is where the Working Fire excels. By integrating TFT’s exclusive pressure relief, a 33% increase in flow rates only yields a 33% increase in reaction force. Compare that to a traditional fixed nozzle, which increases 78%! With the Working Fire nozzle, TFT is able to deliver high GPM (200 gpm) with about 30lbs less reaction force than other nozzles!
There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
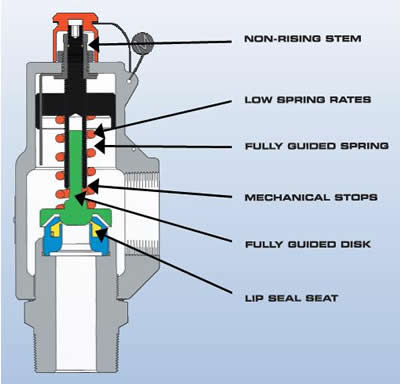
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
For process applications, austenitic stainless steel is commonly used for seats and discs; sometimes they are ‘stellite faced’ for increased durability. For extremely corrosive fluids, nozzles, discs and seats are made from special alloys such as ‘monel’ or ‘hastelloy’.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).

In addition to the small installation space of the above-mentioned compressors, they should be completely covered by an acoustic enclosure to reduce noise emissions. In order to reduce the size of the very cost-intensive sound enclosure, AERZEN requires special valves that are adapted to the available small installation space. Compressors are discontinuous machines for pressure generation.
In order to ensure that occurring pulsations do not impair the function of the safety valve, the set pressure of the valve is adjusted accordingly and an appropriate distance to the pressure line is ensured by design.
The LESER solutionAs a renowned manufacturer of safety valves, it is advantageous to be able to react flexibly to the above-mentioned concerns, primarily to the small installation space, with its portfolio. Being able to change the installation position of safety valves is a clear advantage for the compressor designer. They are much more variable in their design and construction options and can also respond more flexibly to special customer specifications. If the progressive modularization of compressors requires more compact designs, safety valves in different mounting positions, for example, can be an answer to the problem, unlike the classic upright position. In addition, the spindle guide plays a special role here. The friction at the guiding points must be reduced as much as possible so that the spindle runs smoothly. Otherwise, a safety valve can only be installed vertically.
Why LESER safety valves?For a global acting OEM like AERZEN, a specialist like LESER, who has not only the knowledge but also the necessary approvals, is an important component for success. LESER offers a global approval concept that allows safety valves to be used regardless of location. When ordering safety valves, only the applicable regulations must be specified in order to ensure appropriate labeling and material selection. In addition, LESER has tested and approved further installation positions in addition to the conventional installation situation, standing on the inlet pipeline. For example, some types of valves may be installed with a horizontal stem or even upside down, e.g. Types 526 and 441. For horizontal installation, care must be taken to align the outlet. Liquids, e.g. in the form of condensate, should be able to drain off downwards to avoid back pressures and even corrosion. When installed upside down, the inverted weight forces are corrected by correction factors. LESER offers not only safety valves with basic documentation and accessories but also other special documentation and options. From the “Fugitive Emission Test” with helium up to 3.2 ship class castings and from back pressures up to more than 200 bar-g to high pressure heating jackets for up to 30 bar-g, LESER sales engineers develop solutions for customer specific applications as described above for AERZEN.

Pentair Valves & Controls’ newly introduced Crosby HCI ISOFLEX is a high-capacity safety valve to help power plant operators reduce lifecycle costs and minimize shutdown periods. The valve ensures cost-effective power plant operation with a unique full-nozzle, flanged design and adjustable lift option that reduces maintenance costs while maximizing plant efficiency. Specifically designed for 300 to 3,000 psig steam generators, the HCI ISOFLEX can withstand temperatures up to 1,100F/593C and is available in various inlet sizes, ranging from 1½ inch (38.1 mm) to 6 inches (15.24 cm). An extensive range of interchangeable spare parts enables operators to repair or exchange components individually, avoiding costly replacements and minimizing shutdown time.
The valve is also available with an optional restricted lift feature to eliminate overcapacity and ensure a more economic distribution of relieving capacity between the drum and superheater safety valves. This design not only reduces reaction forces for a greater lifespan but also allows for the use of smaller superheater safety valves in some operations, reducing overall installation costs. Additional benefits include precise blowdown control due to a two-ring design and exceptional seat tightness up to 95% of valve set pressure. (valves.pentair.com/valves)

Nozzle reaction is the force exerted by a fire nozzle on a firefighter. The NFPA reports there are an average 13,795 firefighting injuries annually associated with handling charged hose lines.
Nozzle reactions can limit a firefighter’s water application rate and increase his or her air consumption rate. Firefighters may incorrectly assume a high nozzle reaction implies a high water application rate.
A new paper published in Fire Technology, Firefighter nozzle reaction, explains nozzle reaction fluid mechanics for the first time. This is an interesting engineering problem that has defied a general solution for more than 100 years. This paper makes several simplifying assumptions. For example, it neglects hose stiffness, friction between the ground and the hose, gravity and fluid friction.
Nozzle reaction and hose tension are analyzed using fluid momentum conservation and assuming steady, inviscid flow and a flexible hose in frictionless contact with the ground.
An expression independent of the bend angle is derived for the hose tension. If this tension is exceeded owing to anchor forces, the hose becomes straight. The nozzle reaction is found to equal the jet momentum flow rate, and it does not change when an elbow connects the hose to the nozzle.
Three reaction expressions are derived, allowing it to be determined in terms of hose diameter, jet diameter, flowrate and static pressure upstream of the nozzle. The nozzle reaction predictions used by the fire service are 56 percent to 90 percent of those obtained here for typical firefighting hand lines.
where A2 is the discharge diameter, Q is the volumetric flow rate, R is the magnitude of the nozzle reaction, and r is the water density. This equation shows that the reaction is proportional to the flow rate squared, divided by the nozzle diameter.
This equation is plotted in Fig. 1. Three different curves are shown, for different nozzle diameters (d2). The plot and equation show that nozzle reaction increases with flow rate squared. The vertical lines in Fig. 1 are the NFPA requirements for the initial attack line and the backup line. NFPA 1964, Standard for Spray Nozzles, provides performance requirements for firefighting spray nozzles suitable for fire suppression use. The horizontal line is the maximum reaction that a typical firefighter can handle alone. This limit can easily be surpassed with a high flow rate and/or a small nozzle diameter.
This equation shows that for a fully open bale valve and a hose area much larger than the nozzle area, the reaction is proportional to the flow rate times the square root of pressure.
The paper shows the same nozzle reaction occurs no matter how bent or straight the hose is. This conclusion contradicts some advice, published recently, that firefighters should try to hold their hose end straight.
The nozzle reaction equations published by the NFPA are reasonably accurate when the hose area is much larger than the smallest part of the nozzle. However, otherwise these lead to large underpredictions.
One limitation of the work is that hose stiffness and ground friction are neglected. Firefighters kneeling or sitting on the fire hose while spraying, is an effective strategy to reduce nozzle reaction tremendously.




 8613371530291
8613371530291