boiler safety valve setting formula for sale

Boiler explosions have been responsible for widespread damage to companies throughout the years, and that’s why today’s boilers are equipped with safety valves and/or relief valves. Boiler safety valves are designed to prevent excess pressure, which is usually responsible for those devastating explosions. That said, to ensure that boiler safety valves are working properly and providing adequate protection, they must meet regulatory specifications and require ongoing maintenance and periodic testing. Without these precautions, malfunctioning safety valves may fail, resulting in potentially disastrous consequences.
Boiler safety valves are activated by upstream pressure. If the pressure exceeds a defined threshold, the valve activates and automatically releases pressure. Typically used for gas or vapor service, boiler safety valves pop fully open once a pressure threshold is reached and remain open until the boiler pressure reaches a pre-defined, safe lower pressure.
Boiler relief valves serve the same purpose – automatically lowering boiler pressure – but they function a bit differently than safety valves. A relief valve doesn’t open fully when pressure exceeds a defined threshold; instead, it opens gradually when the pressure threshold is exceeded and closes gradually until the lower, safe threshold is reached. Boiler relief valves are typically used for liquid service.
There are also devices known as “safety relief valves” which have the characteristics of both types discussed above. Safety relief valves can be used for either liquid or gas or vapor service.
Nameplates must be fastened securely and permanently to the safety valve and remain readable throughout the lifespan of the valve, so durability is key.
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors offers guidance and recommendations on boiler and pressure vessel safety rules and regulations. However, most individual states set forth their own rules and regulations, and while they may be similar across states, it’s important to ensure that your boiler safety valves meet all state and local regulatory requirements.
The National Board published NB-131, Recommended Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Legislation, and NB-132, Recommended Administrative Boiler and Pressure Vessel Safety Rules and Regulationsin order to provide guidance and encourage the development of crucial safety laws in jurisdictions that currently have no laws in place for the “proper construction, installation, inspection, operation, maintenance, alterations, and repairs” necessary to protect workers and the public from dangerous boiler and pressure vessel explosions that may occur without these safeguards in place.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) governs the code that establishes guidelines and requirements for safety valves. Note that it’s up to plant personnel to familiarize themselves with the requirements and understand which parts of the code apply to specific parts of the plant’s steam systems.
High steam capacity requirements, physical or economic constraints may make the use of a single safety valve impossible. In these cases, using multiple safety valves on the same system is considered an acceptable practice, provided that proper sizing and installation requirements are met – including an appropriately sized vent pipe that accounts for the total steam venting capacity of all valves when open at the same time.
The lowest rating (MAWP or maximum allowable working pressure) should always be used among all safety devices within a system, including boilers, pressure vessels, and equipment piping systems, to determine the safety valve set pressure.
Avoid isolating safety valves from the system, such as by installing intervening shut-off valves located between the steam component or system and the inlet.
Contact the valve supplier immediately for any safety valve with a broken wire seal, as this indicates that the valve is unsafe for use. Safety valves are sealed and certified in order to prevent tampering that can prevent proper function.
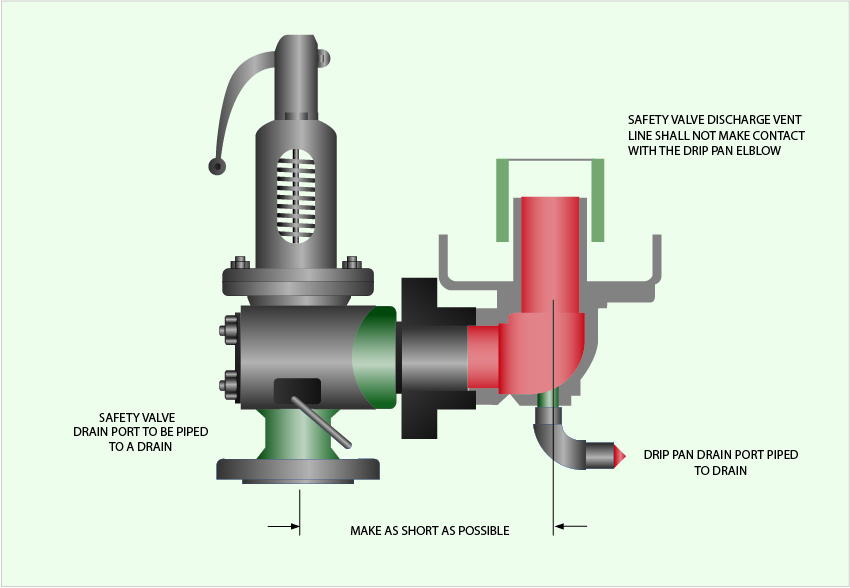
Avoid attaching vent discharge piping directly to a safety valve, which may place unnecessary weight and additional stress on the valve, altering the set pressure.

As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.
Safety valves and pressure relief valves are crucial for one main reason: safety. This means safety for the plant and equipment as well as safety for plant personnel and the surrounding environment.
Safety valves and pressure relief valves protect vessels, piping systems, and equipment from overpressure, which, if unchecked, can not only damage a system but potentially cause an explosion. Because these valves play such an important role, it’s absolutely essential that the right valve is used every time.
The valve size must correspond to the size of the inlet and discharge piping. The National Board specifies that the both the inlet piping and the discharge piping connected to the valve must be at least as large as the inlet/discharge opening on the valve itself.
The connection types are also important. For example, is the connection male or female? Flanged? All of these factors help determine which valve to use.
The set pressure of the valve must not exceed the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of the boiler or other vessel. What this means is that the valve must open at or below the MAWP of the equipment. In turn, the MAWP of the equipment should be at least 10% greater than the highest expected operating pressure under normal circumstances.
Temperature affects the volume and viscosity of the gas or liquid flowing through the system. Temperature also helps determine the ideal material of construction for the valve. For example, steel valves can handle higher operating temperatures than valves made of either bronze or iron. Both the operating and the relieving temperature must be taken into account.
Back pressure, which may be constant or variable, is pressure on the outlet side of the pressure relief valve as a result of the pressure in the discharge system. It can affect the set pressure of the upstream valve and cause it to pop open repeatedly, which can damage the valve.
For installations with variable back pressure, valves should be selected so that the back pressure doesn’t exceed 10% of the valve set pressure. For installations with high levels of constant back pressure, a bellows-sealed valve or pilot-operated valve may be required.
Different types of service (steam, air, gas, etc.) require different valves. In addition, the valve material of construction needs to be appropriate for the service. For example, valves made of stainless steel are preferable for corrosive media.
Safety valves and relief valves must be able to relieve pressure at a certain capacity. The required capacity is determined by several factors including the geometry of the valve, the temperature of the media, and the relief discharge area.
These are just the basic factors that must be considered when selecting and sizing safety valves and relief valves. You must also consider the physical dimensions of the equipment and the plant, as well as other factors related to the environment in which the valve will operate.

Relief valves are designed to open at a preset pressure (or temperature) level and relieve the system when it has exceeded the desired level. The valve"s relief of elevated liquid, gas, or steam pressures prevents damage to the system. We offer a wide selection of relief valves for any application.
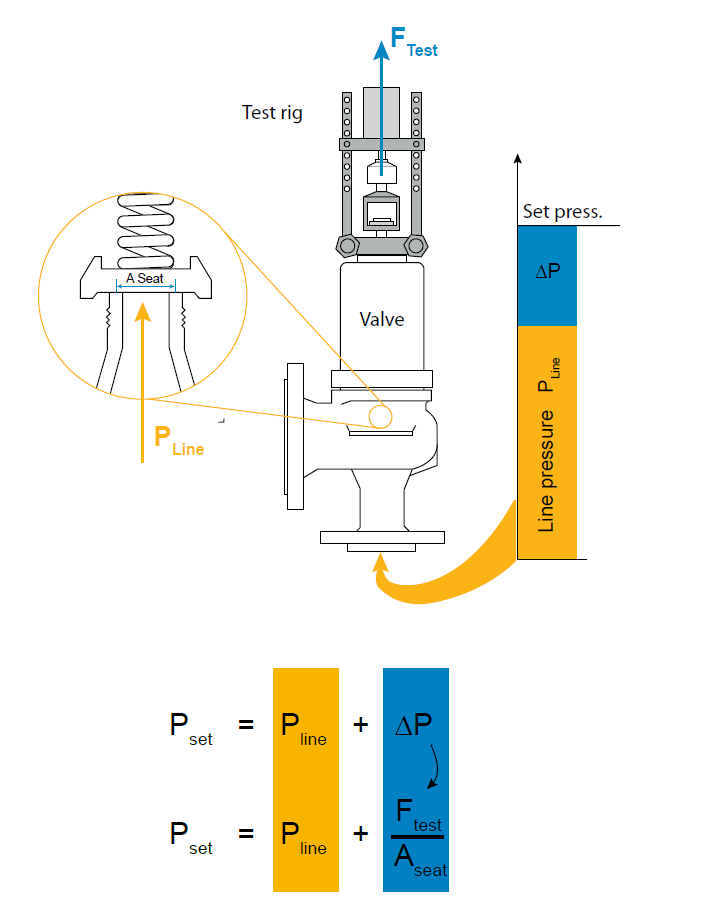
but not more than 3% above working pressure. Also the safety Valve re-sits at 5% below working pressure. There are 2 safety valves. Both the safety valves are to be set at a pressure not exceeding 3% of the normal working pressure (stamped on name plate). Let us say the working pressure of the boiler is 7 bar. 3% of 7 bar is (7+0.21) = 7.21 bar. which means, both the safety valves have to be set at a pressure not exceeding 7.21 bar. Apart from that, let us say one of the valves have been set at a pressure say 7.15 bar (assuming two digit decimal even though the practice is not referring to 2 digits), then the other valve must be set at a pressure range of 10% within this. i.e the other valve setting must be 7.16 bar. I used two digit decimal only for understanding the precision of calculation. The second safety valve must be set within 10 % of the setting of the first safety valve. If any one has any other understanding please do discuss.




 8613371530291
8613371530291