boiler safety valve testing brands

Tired of keeping track of your valve inventory’s annual certification records? We offer complete management of your safety relief valves. With an inventory of repair parts and in stock relief valves of all sizes, we can respond to any customer emergency. We offer annual certification services as well as repair of all major brands, including Kunkle, Conbraco, Consolidated, Dresser, Apollo and more.

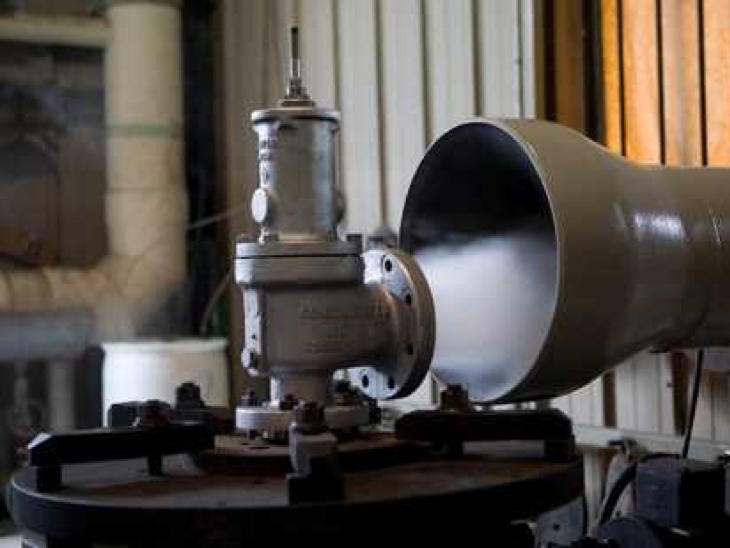
Safety valves are used in a variety of industrial applications to include air/gas, vapor, steam, and liquid service, among many more. These pressure relief valves are critical to the safe operation of our customer’s equipment and provide—as their name implies—a safety measure that can reduce the number of risks that can threaten both your personnel and facilities.
Millennium Power Services’ safety valve technicians will get your valves tested, repaired, and quickly set to the exact specifications. We serve as your knowledge partner and will also evaluate the repair condition of every valve and make recommendations as needed to help you make the best decisions.

Distributor of pipe, valves, piping accessories, industrial pumps & valve automation. Fluid handling products such as steam traps, control & high performance valves, corrosion resistant piping & grooved piping systems are also available. Valves include sanitary butterfly, plug, ball, check, gate, globe, sampling & rising stem valves. Instrumentation include actuators, limit switches, instrumentation fittings, transmitter manifolds, low pressure brass fittings, quick connectors, thermometers, gauges, RTDs, thermocouples, temperature & pressure sensors, pressure & temperature regulators, fluid & gas meters & sensors, positive displacement & turbine meters, positioners, switch boxes & pneumatic cylinders. Pumps & process equipment include rotary, positive displacement, air operated double diaphragm, progressive cavity, centrifugal, vertical & horizontal, end suction & submersible pumps.

IVI is a VR certified safety valve repair facility, approved by the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors as a VR certificate holder (stamp 179). We certify pressure relief valves in the shop and in the field for sections V and UV. We also perform on-site testing (while the plant operates) providing documented reports for all valves tested. We are also certified to administer special process conversions regarding machining, welding, heat treating, and N.D.T. (non-destructive testing) with our VR certificate.
With our VR stamp, we repair all types of pressure relief valves such as Consolidated, Crosby, Kunkle, Farris, Spence, Anderson Greenwood, and numerous other O.E.M. safety and pressure relief valves.

Certifies Allied Valve Inc. is qualified and approved to assemble Pressure Relief Valves (PRV) for use in Section I applications including boilers and pressure vessels.
Certifies Allied Valve Inc. is qualified and approved to assemble Pressure Relief Valves (PRV) for use in Section VIII applications including all uses outside of boilers and pressure vessels.
Certifies Allied Valve Inc. is qualified and approved to calibrate, test, and stamp Pressure Relief Valves (PRV) for use in Section I and Section VIII applications.
Certifies Allied Valve Inc. is qualified and approved to repair Pressure Relief Valves (PRV) of all brands for both Section I and Section VIII applications.
The National Board offers the Certificate of Authorization and T/O mark for the inservice testing of pressure relief valves. Requirements are described in NB-528. Accreditation of T/o Test Only Organizations.

Pressure safety valves are designed to protect process piping and equipment in case of an overpressure event. TEAM Valve Solutions inspects, tests, repairs and re-certifies safety valves at 17 service centers across three continents, and in our fleet of mobile facilities, all of which are audited under the jurisdiction of relevant governing bodies.
Our solutions cover all major safety valve brands and support our customers through an inventory of spare parts and loose-assembled valves. In addition, our facilities are audited and governed by the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors. Testing, repair, and assembly are performed under license and guidelines of NBIC, and ASME Section I and VIII.
To ensure accurate in-line setpoint verification, TEAM Valve Solutions utilizes Trevitest, the pioneering system for validating safety valve performance in Conventional and Nuclear Power plants, as well as in other industrial process facilities.

Vinson understands that complete reliability of all Pressure Relief Devices is essential to protect, not only a plant’s assets, but most importantly all personnel and the environment. Vinson offers both field and in-shop repair services, and is proud to be one of the nation’s leading National Board certified VR & TO Repair Facilities. With certifications on air/gas/liquid and steam service (Section I & VIII), Vinson provides setting, repair and testing services on all manufacturers valves up to 10,000 psi.

Ensure compliance, prevent overpressure and protect downstream equipment with industry regulated repairs for Section I & Section VIII Pressure and Safety Relief Valves. We offer rapid response and delivery times to minimize plant downtime while maximizing valve performance. We service all major makes and manufacturers for emergency, maintenance and scheduled outage needs. We also repair and replace conservation, tank and vacuum vents. Contact our sales team today to receive a quotation to repair, test or replace your safety relief valves.
Valsource is certified by The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors to repair and test Section I and Section VIII Pressure relief and Safety Relief Valves. Every valve is repaired to standards set by The National Board’s VR program. We provide 24/7 repair, testing and engineering services. We also maintain an extensive inventory and can provide replacement valves and parts with same day delivery options.
Valsource provides 24/7 repair and testing services in our shop or in the field. Our valve program allows our technicians to repair, remove, install and test your pressure relief and safety relief valves on-site. Using our AVK Electronic Test Vessel Package, our technicians are able to accurately test safety relief valves on-site without removing them from line. The primary function is to verify the set pressure in-line without having to shut down a system or unit. This service is a sure way to guarantee minimal downtime and peak valve performance. If you are preparing to service your boiler, Valsource technicians will come to your site and test each main steam safety valve to determine which valves require service. We will perform the repairs in-house or on-site using our 53’ field machining trailer, install and re-test back to calibrated set points.
If you need the best in valve repair and remanufacturing, Valsource can deliver the right options for your company. We offer rapid response times and emergency repair services available to resolve unplanned outages quickly. Our experienced technicians look forward to working with you to determine the most effective solutions for your valve repair needs.
Ensure compliance, prevent overpressure and protect downstream equipment with industry regulated repairs for Section I & Section VIII Pressure and Safety Relief Valves. We offer rapid response and delivery times to minimize plant downtime while maximizing valve performance. We service all major makes and manufacturers for emergency, maintenance and scheduled outage needs. We also repair and replace conservation, tank and vacuum vents. Contact our sales team today to receive a quotation to repair, test or replace your safety relief valves.
Valsource is certified by The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors to repair and test Section I and Section VIII Pressure relief and Safety Relief Valves. Every valve is repaired to standards set by The National Board’s VR program. We provide 24/7 repair, testing and engineering services. We also maintain an extensive inventory and can provide replacement valves and parts with same day delivery options.
Valsource provides 24/7 repair and testing services in our shop or in the field. Our valve program allows our technicians to repair, remove, install and test your pressure relief and safety relief valves on-site. Using our AVK Electronic Test Vessel Package, our technicians are able to accurately test safety relief valves on-site without removing them from line. The primary function is to verify the set pressure in-line without having to shut down a system or unit. This service is a sure way to guarantee minimal downtime and peak valve performance. If you are preparing to service your boiler, Valsource technicians will come to your site and test each main steam safety valve to determine which valves require service. We will perform the repairs in-house or on-site using our 53’ field machining trailer, install and re-test back to calibrated set points.
If you need the best in valve repair and remanufacturing, Valsource can deliver the right options for your company. We offer rapid response times and emergency repair services available to resolve unplanned outages quickly. Our experienced technicians look forward to working with you to determine the most effective solutions for your valve repair needs.

A relief valve is one of the most crucial pressured system components and often the last device to prevent catastrophic failures in high-pressured systems. That is why it is essential that relief valves are always certified and should work at all times.
Relief valves are pressure valves that are designed to open at a preset pressure and discharge fluid until the pressure drops to a safe and acceptable level. This means the relief valve is the last resort that releases pressure when other components in the system have failed to control the pressure.
Safety is of paramount importance when it comes to dealing with relief valves. So, it’s critical for industries to make sure the valves are working as designed.
The only way to do that is through periodic inspection and standardized testing. The standards about relief valves and associated assemblies like boilers and pressured vessels are regulated by ASME, API, OSHA, National Board, and individual State codes.
Standard requirements include periodic inspection, testing, and recertification. Certification assures that a valve’s condition and performance are essentially equal to that of a new valve.
Though ASME is the leading organization governing pressured systems’ standards and codes, the body itself does not certify the valves. Certification and recertification of relief valves are done by the National Board (NB).
Performing periodic testing on relief valves is the best practice to ensure that the valves are in good working condition and the employees and work environment is safe.
The above recommendations constitute correct inspecting and testing practices for efficient Relief Valve operations and, ultimately, a safe working environment. However, one crucial safety measure is to use a pressure indicator with a full-scale range higher than the valve’s relief pressure.
In fact, we believe proper valve inspection, testing, and maintenance is the best investment you make in the safety and security of your company and employees.
Our valve experts focus on getting your old valves tested and recertified for safe use. On top of that, we evaluate the repair condition of every valve and recommend the right solution to manage your equipment better.

Testing the safety relief valve is extremely important to the overall safety of your boiler system. In this post, we’ll be talking about what goes into testing a steam relief valve, but safety valve repairs should only be performed by a company holding a current Certificate of Authorization (VR) from the National Board of Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
Using certified and calibrated gauges is essential to accurate testing. WARE’s own Rick Walker recommends using two gauges, for maximum accuracy and in case one isn’t properly functioning.
Relief valves need to open and close at very specific pressures, and also need to open smoothly. A smooth opening contains a clean “pop” sound, and not a simmering or chattering sound. Responding to the appropriate pressures and opening and closing cleanly are both important signs a professional maintenance provider will look for in a safety valve.
Safety valves contain a compression screw, which puts pressure on a spring and causes the valve to function. The compression screw is where a maintenance provider will try to dial in your valve’s functionality and make set-pressure adjustments. It’s important to note if a valve is cold it might test higher, but as the valve gets hotter its metal will expand and its innerspring will slightly decompress.
Once the valve is warm and has stabilized, it’s best to give it more than one test (Rick does three) to make sure the valve is consistent and within ASME code.
ASME defines a safety valve as properly functioning at 150 psi if it tests within 3% of the set pressure. If your valve tests within 3% of the set pressure three times in a row on properly calibrated gauges, you’re likely good to go.
Remember, this procedure should only be done by professionals. If you’d like to schedule maintenance for your boiler, need assistance, or just want to learn more, contact us and check out our maintenance and service options at https://www.wareinc.com/boiler-services

Safety valves play an important role in keeping people and equipment safe. Building on the long legacy of the Consolidated Safety Valves, we work closely with customers and regulatory organizations to configure, engineer, and manufacture safety valves that can help maintain safer operating conditions in a full range of environments.
Our safety valves comply with the ASME Section I code for boiler applications. They are built with many features that meet ASME requirements for steam-compressible fluids. Baker Hughes’s Consolidated safety valves are known for exceptional quality, performance and dependability. It is important they are reliable even the in most demanding real-world applications. With a range of styles, models, options and configurations, our safety valves work in many different applications.
Not sure which valve you need for your application?Download ValSpeQ (Mooney regulators & Becker valves) or ValvStream™ (Masoneilan and Consolidated valves) to size, select and generate proposal documentation for your valves.
Consolidated Green Tag Centers (GTC) comprise one of the broadest OEM service networks in the industry. With more than 80 facilities located in more than 30 countries worldwide, the GTCNet™ network provides the aftermarket support you need. Our GTC customers receive responsive and effective service through OEM-certified repairs, innovative valve diagnostics from ValvKeep™- valve management and maintenance software, and the EVT-Pro, an electronic valve testing device. Each GTC location is staffed with highly qualified technicians, specifically trained and certified to deliver exceptional product support and technical expertise.

Thermoglide design improves the gliding characteristics of internal parts thus enabling the valve to achieve its full lift and re-seat point within the fastest possible time

At each of our 12 convenient locations, the Chalmers & Kubeck Valve and Actuation Technicians are factory trained and certified. Each expert Technician is required to meet stringent factory standards prior certification so you can be confident that we will provide the expert, efficient, and comprehensive service that you expect.
Our services include field trouble shooting, actuator refurbishment, control enhancement, electronic valve testing, torque verification, turnkey overhauls / repairs, retrofits, and valve testing / certification. We offer complete reconditioning of ball valves, butterfly valves, check valves, control valves, gate valves, globe valves, parallel slide valves, pilot operated valves, plug valves, pressure relief valves, pressure safety valves, vacuum break valves, and other specialty valves.
Baker Hughes manufactures the premier boiler safety valves and pressure relief valves in the industry, Consolidated®, and authorizes a very select group of companies to be their exclusive factory authorized repair and service centers, known as Green Tag Centers® (GTC). Ten of the 12 C&K Service Locations are GTCs, which means that you will receive best-in-class aftermarket product support. With our OEM trained and certified valve technicians, you know that your relief valves will be rebuilt correctly to exacting standards. Prior to certification, each of our valve technicians must go through Baker Hughes classroom training that includes applicable codes and standards, proprietary repair procedures, and practical hands-on instruction. The technician must prove their proficiency during both written and practical examinations covering relief valve repair, assembly, and testing. With our certified Green Tag Technicians, you can rest assured that your valves will be serviced in compliance with ASME and NBBI (National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors) standards so they perform their critical safety function as intended.
Each of our GTC service locations has compete machining capabilities, calibrated measuring and testing equipment, specialized electronic valve testing equipment, and ValvKeep, a proprietary electronic data management system, so you can track and trend the repair history of your valves. We also carry significant inventory of Consolidated pressure relief valves and OEM certified replacement parts ensuring rapid response to your urgent repair needs. If for some reason we don’t have a part in stock locally, we have access to all parts stocked by GTCs throughout the entire United States and can have them overnight shipped to one of our service centers. We are your trusted local pressure relief valve service center whether your valves are Consolidated or another manufacturer’s brand.
Since the first installation of its Limitorque Machine (limit & torque capable) in 1929, Limitorque has been manufacturing some of the most innovative and dependable motor-operated valve actuators for demanding industrial applications. Flowserve, the parent company of Limitorque, authorizes a select group of companies to be their “Limitorque Blue Ribbon” service and repair centers. Chalmers & Kubeck is proud to be the largest Limitorque Distributor east of the Mississippi River and that all twelve (12) of our locations are Limitorque Blue Ribbon Service Centers. With over 20 years providing outstanding Blue Ribbon Service, C&K is your go-to solution for actuator sizing, selection, adaptation, installation / certification, maintenance, repair, and field service.
This team of valve and instrument specialists works closely together to provide customer assistance in technical sales, quotations and delivery. Chalmers & Kubeck maintains around-the -clock service, which includes the assembly and test of new CONSOLIDATED® pressure relief valves, plus full machining and repair operations for industrial valves of many types and manufacturers. Additionally, C&K provides comprehensive design and manufacturing services to adapt your existing manual valve or a new manual valve to a motor operated actuator for enhanced process control and operator safety.

Industry leading pressure and safety relief valve designs with over 140 years of technical and application expertise providing custom engineered solutions for O&G, Refining, Chemical, Petrochemical, Process and Power applications. Our designs meet global and local codes and standards (API 526; ASME Section I, IV & VIII; EN ISO 4126; PED & more). Gain insight into the performance of your pressure relief valves with wireless monitoring.
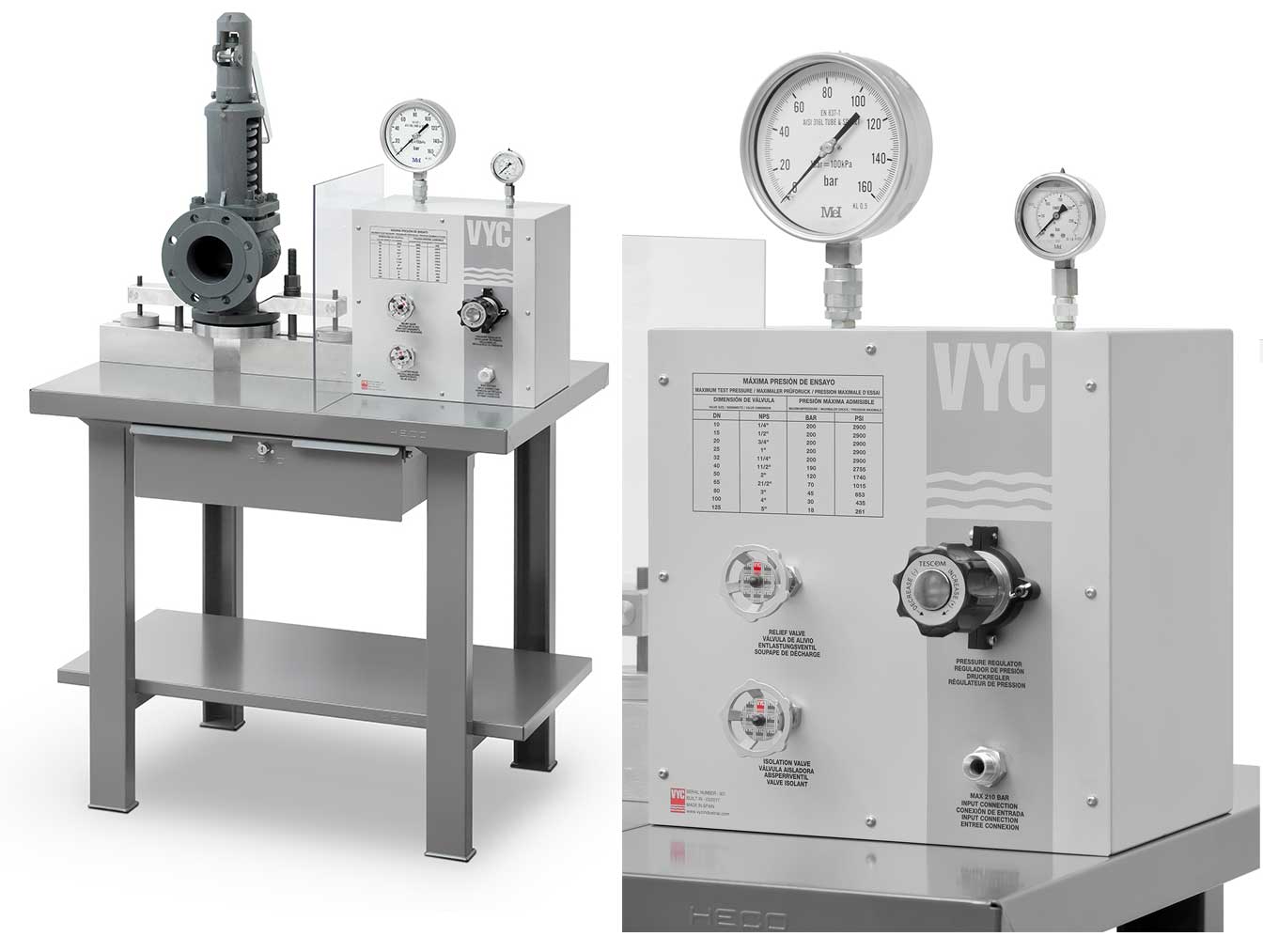

There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).

The National Board offers the Certificate of Authorization and VR Stamp for the repair of pressure relief valves. Requirements are included in the current mandatory edition of the National Board Inspection Code(NBIC), Part 4, and NB-514, Accreditation of VR Repair Organizations.
The National Board offers the Certificate of Authorization for use of the T/O mark which indicates accreditation as a pressure relief valve Testing Organization. The program includes provisions for minor adjustments to restore valve performance. Requirements are based upon the current mandatory edition of the National Board Inspection Code(NBIC), Part 2, Part 4, and NB-528, Accreditation of T/O Test Only Organizations.
The National Board supports members who request tests be conducted on pressure relief devices involved in boiler and pressure vessel accidents. This service is provided at no cost to the National Board member. Please contact Pressure Relief or Executive staff for more information.
Representatives from the National Board are assigned to visit company sites to select production sample valves for testing at National Board- and ASME- accepted labs.




 8613371530291
8613371530291