difference between pressure relief valve and pressure safety valve manufacturer

As you already know, there are a multitude of pressure relief valves out there. In the industry, we tend to use terms like safety valve and relief valve interchangeably. And for the most part, this makes sense. Most pressure relief valves are designed to do the same thing — release pressure in a system.
But is there a difference between some of these commonly used terms, and if so, what does it mean for you? Here’s a quick breakdown of two popular terms: safety valve vs. relief valve.
While both terms refer to valves used to release pressure from a pressurized system, their technical definitions are a bit different. In general, the term relief valve refers to a valve within a pressurized system that is used to control pressure for the optimal functionality of the system. Relief valves are designed to help your facility avoid system failures, and protect equipment from overpressurized conditions.
The term safety valve, on the other hand, refers to pressure valves that are designed to protect people, property, and processes. In other words, the term safety valve refers to a failsafe, last resort valve that will release pressure to prevent a catastrophe, usually in the event that all other relief valves have failed to adequately control pressure within a system.
The general purpose of both safety valves and relief valves are the same. Both are pressure relief valves, and they are designed to let off pressure in any situation where a system becomes overpressurized. That said, relief valves and safety valves do function slightly differently:
Relief Valves are designed to control pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air systems. These valves open in proportion to the increase in system pressure. This means they don’t fly all the way open when the system is slightly overpressure. Instead, they open gradually, allowing the system to return to the preset pressure level. When that level is reached, the valve shuts again.
Safety Valves are used for one reason — safety. Instead of controlling the pressure in a system, they’re designed to immediately release pressure in the event of an emergency or system failure. Unlike relief valves, safety valves open immediately and completely to avoid a disaster, rather than to control the pressure of a system.
While both safety valves and relief valves work to release excess pressure, the way they go about it is a little different. Check out this table, courtesy of Difference Between, for a little more information about the differences between the two valves:

Industrial equipment often uses either safety or relief valves to prevent damaging pressure levels from building up. Though they perform similar functions, there are some critical differences between safety and relief valves. Understanding these two valves’ differences is essential for proper pressure system operation. So here we discuss the pressure safety valve vs pressure relief valve.
A pressure relief valve is a device that releases pressure from a system. The relief valve is generally immune to the effects of back pressure and must be periodically stripped down. Pressure relief valves are one the essential parts of a pressure system to prevent system failures. They are set to open at a predetermined pressure level. Each pressure system has a setpoint that is a predetermined limit. The setpoint determines when the valve will open and prevents overpressure.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in gas or liquid systems where there is a need to prevent excessive pressure from building up. When the pressure in the system reaches a certain level, the valve will open and release the pressure. Pressure relief valves are an essential safety feature in many designs and can help to prevent damage to the system or components.
PRVs are generally considered to be safe and reliable devices. However, before installing a PRV in a system, some potential disadvantages should be considered. Here are five pros and cons of pressure relief valves:
Pros: Pressure relief valves are anessential safety feature in many systems. They protect against over-pressurization by relieving excess pressure from the system. This can help to prevent severe damage or even explosions.
Pressure relief valves can help to improve the efficiency of a system. The system can operate at lower overall pressure by relieving excess pressure and saving energy.
Pressure relief valves can be used as a safety device in systems that are susceptible to overpressurization. By relieving pressure before it builds up to a dangerous level, they can help to prevent accidents and injuries.
Cons: Pressure relief valves can be a potential source of leaks. If not properly maintained, the valve may not seat properly and can allow fluids or gasses to escape.
Pressure relief valves can sometimes cause problems if they do not open or close properly. This can lead to process disruptions and may cause safety issues.
A pressure safety valve is a device used to release pressure from a system that has exceeded its design limit. This safety valve is a fail-safe device. This type of valve is typically used in systems that contain fluids or gasses under high pressure. Pressure safety valves are designed to open and release pressure when the system has exceeded its maximum pressure limit. This helps to prevent the system from rupturing or exploding.
Pressure safety valves are an essential part of many different types of systems and can help keep both people and property safe. If anyone is ever in a situation where they need to release pressure from a system, it is essential to know how to use a pressure safety valve correctly.
A pressure safety valve (PSV) is a type used to relieve a system’s pressure. PSVs are commonly used in chemical and process industries, as well as in some kinds of pressure vessels. There are both advantages and disadvantages to using a PSV. Some of the pros of using a PSV include: PSVs can help to prevent overpressurization, which can be dangerous.
A safety valve is a pressure relief device used to prevent the over-pressurization of a system. On the other hand, a relief valve is a device used to relieve pressure from a system that is already overpressurized. Function Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Valve
The function of a pressure relief valve is to protect a system or component from excess pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, is designed to protect from overpressurization. Both types of valves are used in various industries, but each has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Pressure relief valves are typically used in systems where a small amount of overpressure can cause damage. On the other hand, safety valves are designed for systems where overpressurization could be catastrophic. Both valves have advantages and disadvantages, so choosing the right type of valve for the specific application is essential.
Relief valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure and will close once the pressure has been relieved. Safety valves are similar in that they are also used to protect equipment from excessive pressure. However, safety valves are designed to stay open until they are manually closed. This is because safety valves are typically used in applications where it is not safe to have a closed valve, such as in a gas line. Operation Of Safety Relief Valve Vs Pressure Relief Valve
Two types of valves are commonly used in industrial settings: relief valves and safety valves. Both of these valves serve essential functions, but they operate in different ways.
Relief valves are designed to relieve pressure build-up in a system. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released. On the other hand, safety valves are designed to prevent accidents by preventing system pressure from getting too high. They open when the system pressure reaches a certain point, which allows excess pressure to be released before an accident can occur.
So, which valve is better? That depends on the situation. A relief valve is the better option to protect the system from pressure build-up. If anyone need to protect the system from accidents, then a safety valve is the better option Setpoint Of Pressure Relief Valve Vs Safety Relief Valve
The relief valve is made to open when it reaches a specific pressure, commonly described as a “setpoint”. Setpoints shouldn’t be misinterpreted as the pressure set. A setpoint on a relief valve is set to the lowest possible pressure rating, which means it is set to the lowest system pressure before an overpressure situation is observed. The valve will open as the pressure increases to a point higher than the setpoint. The setting point is determined as pounds per square inch (PSIG) and should be within the maximum allowed operating pressure (MAWP) limits. In safety valves, the setpoint is typically placed at about 3 percent over the working pressure level, whereas relief valves are determined at 10 percent.
No, the safety valve and relief valve can not be used interchangeably. Though both valves are seal butterfly valve and used for safety purposes, they serve different functions. A safety valve relieves excess pressure that builds up in a system, while a relief valve regulates the pressure in a system.
Knowing the difference between these two types of valves is essential, as using the wrong valve for the intended purpose can potentially be dangerous. If unsure which type of valve to use, it is always best to consult with a professional.
A few key points help us understand the safety valve vs pressure relief valve. Safety valves are designed to relieve pressure in a system when it gets too high, while relief valves are designed to relieve pressure when it gets too low. Safety valves are usually set to open at a specific pressure, while relief valves are generally open at a particular vacuum. Safety valves are typically intended for one-time use, while relief valves can be used multiple times. Choose the trusted valve manufactureraccording to the specific business needs.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

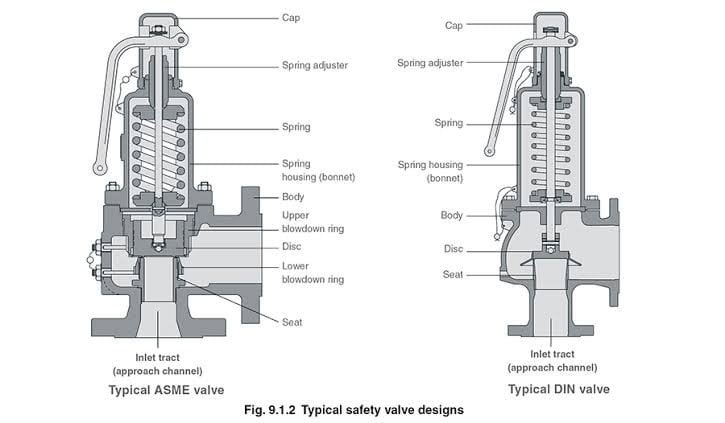
Safety valves and relief valves have similar structure and performance, both of which discharge internal media automatically when the pressure exceeds the set value to ensure the safety of the production device. Because of this essential similarity, the two are often confused and their differences are often overlooked as they are interchangeable in some production facilities. For a clearer definition, please refer to the ASME boiler and pressure vessel specifications.
Safety Valve: An automatic pressure control device driven by the static pressure of the medium in front of the valve is used for gas or steam applications, with full open action.
The basic difference in their operating principle: The safety valve relieves the pressure into the atmosphere i.e. out of the system, it can be a pressure relief device of fluid vessels, when the set pressure value reached then the valve opens almost fully. On the contrary, relief valve relieves the pressure by relieving the fluid back into the system, that’s the low-pressure side. Relief valve opens gradually if the pressure increased gradually.
The difference is also generally shown in capacity and setpoint. A relief valve is used to relieve pressure to prevent an overpressure condition, the operator may be needed to assist in opening the valve in response to a control signal and close back once it relieves the excess pressures and continues to operate normally.
A safety valve can be used to relieve the pressure that does not need a manual reset. For example, a thermal relief valve is used to bleed off pressure in a heat exchanger if it is isolated but the possibility of thermal expansion of the fluid could cause overpressure conditions. The safety valve on a boiler or other types of fired pressure vessels must be capable of removing more energy that is possible to be put into the vessel.
In short, Safety valves and relief valves are the two most commonly used types of control valves. The safety valve belongs to the pressure release device, which can only operate when the working pressure exceeds the allowable range to protect the system. The relief valve can make the high-pressure medium quickly to meet the pressure requirements of the system and its working process is continuous.

Thus, its operation is automatic; it will open only to release the pressure and not exceed the liquid force; therefore, its use is more common with fluids (although, they can also be used with vapours or moderate gases). In terms of capacity, they can withstand low pressures and their processes are continuous.
Whenever we talk about the pressure in the process industries we come across two types of safety equipments and that is the safety v/v and the relief v/v.
Most of us think that both are same thing but that’s not the case. Though their functions are same yet there are certain differences among them. Both of them are used in the industry to prevent the accumulation of excess pressure, but there are operational differences between them.
Relief valves which are also known as Pressure relief valves are one of the protective devices which are used to protect a pressurize working system and equipments from getting damaged due to an over-pressure or excessive pressure conditions.
In every pressurized working system there is a set pressure under which the system works properly and efficiently, this set pressure is known as set point and when the pressure is above set point the relief valve opens and the excess pressure is released.
It is made very sensitive such that even for a slight increment in the pressure lifts the safety valve and gets closed quickly as soon as the pressure is released to maintain the desired pressure in the vessel.
1. A relief valve is a device used to limit the pressure in the system within certain specified limit or a set level.A safety valve is a device designed to actuate automatically when the pressure becomes excess.
2. The opening of a relief Valve is directly proportional to the increase in the vessel pressure.2. A safety valve opens almost immediately and fully in order to prevent over pressure condition.
3. A relief valve opens when the pressure reached the specific limit and it is usually operated by an operator.3. The purpose of the safety valve is mainly to safeguard people, property and the environment. It operates without any human intervention.
4. The set point of a relief valve is usually set at 10% above working pressure.4. The set point of safety valve is usually set at 3 % above working pressure.
5. Relief valves are categorized into pop-type, direct-operated, pilot-operated, and internal relief valves.5. Safety valves are divided into wide variety of types based on their applications and performance in different areas of use.
From the definition of both the valves we can conclude that the relief v/v which is also known as the pressure relief v/v is a safety device which is used to maintain a proper preset pressure in the vessel or the system within a prescribed limit condition to prevent a situation of over pressure.
On the other hand, the safety valve is a protective device which is used in a system to control the pressure inside the system under a predetermined limit.
The pressure relief valves are generally used in the hydraulic systems to control the pressure within specified limit and when the pressure increases than the preset value.
It lifts up and provide an escape of the excess pressure through an alternate channel or bypass provided in the system back to the source from where the input is coming or may be a different chamber provided to accept the excess of the liquid.
On contrary in case of safety valve, the main function of the safety valve is to provide safety to the property, life, and the environment which can get damaged due to failure of the system because of the excess pressure.
The pressure relief valves are generally used in the hydraulic systems to control the pressure within specified limit and when the pressure increases than the preset value, it lifts up and provide an escape of the excess pressure through an alternate channel or bypass provided in the system back to the source from where the input is coming or may be a different chamber provided to accept the excess of the liquid.
On contrary in case of safety valve, the main function of the safety valve is to provide safety to the property, life, and the environment which can get damaged due to failure of the system because of the excess pressure.
We used the set point in case of the relief valve, the “Set Point” basically refers to a point set to the lowest maximum pressure rating which means that the pressure is set below the maximum operative pressure which is allowed for a system to operate without being get into the state of overpressure.
In Simple words we can say that the relief valve pressure is set to maintain and control the pressure inside the system, the set pressure is dependent on the working pressure of the system.
On the other hand , the pressure of safety valve is set on the basis of various factors of consideration like the material used, the environment in which it has to be used, the type of work it has to perform.
The boilers material used for 6 Bar will have the materials which can withstand upto 12 Bar (it depends on the manufacturer) So the Safety valve will be set to 7-8 bar so as to prevent the boiler failure.

A pressure relief valve is one that is used to limit the pressure in a system within a specific set level. However, a pressuresafety valveactuates automatically to release excessive pressure.Relief valveopens only when the pressure reaches the specific set pressure limit and is usually operated by an operator. It does not require operator assistance to release excessive pressure.
The similarity between thepressure relief valveand thesafety valveis that they both are spring-loaded valves. Usually, the valve is forced shut by the spring. When the pressure increases, the force of the spring has overcome that forces the valve to open.
Pressure Relief Valves are essential for controlling the flow rate of fluid, thereby facilitating the practical use of the system and providing additional safety to pressurized vessels or systems. There are three types of Pressure relief Valves.
Relief valve: – A valve that is used in a hydraulic system as pressure over sill devices. They can further be into adjustable relief valves and safety relief valves. They are usually used in naval ships for generating thermal electricity.
Safety Relief valve: – A valve that is used either for liquid or compressible fluids in a pressurized vessel is called a safety relief valve. These are generally used in boilers.
Conventional(spring-loaded):- The main components of traditional spring-loaded safety relief valve are the nozzle, seat disc, disc holder, bonnet, spring, set pressure adjusting screw, body, and blowdown adjustment ring.
Pilot operated:-The main component of pilot-operated hydraulic valve is inlet from the system, orifice, main spool spring, dart, pilot spring, adjustment screw, pilot drain, the skirt of the spool, and
Balanced bellows:-The essential components of Balanced bellows relief valve are nozzle, body, adjusting ring, disk, seating surface, bellows, balanced piston, bonnet, spring, adjusting screw, stem, and cap.
SKG Pneumatics is the best supplier ofindustrial valves in Delhi. The company has been into pneumatic industries for several years. The company manufactures different types of relief and safety valves that can be used in the industrial production unit. The pressuresafety relief valvecan prevent damage to property, life, and environment to a great extent and shall be used in every industry for additional safety. The pressure relief valves can be used in pressurized vessels, boiler, and other pressurized systems.

Both the terms are used interchangeably in the process industry as every pressurized system requires safety devices to protect life, property, and environment. Relief valves and safety valves are the two principle safety devices designed to prevent overpressure conditions in process industries. Although, both the devices are used almost for the same purpose, the difference lies mainly in how they operate.
Relief valves, or commonly known as pressure relief valves (PRVs), belong to the family of protective devices specifically designed to protect pressure-sensitive systems and equipment from the damaging effects of overpressure conditions. A relief valve device is basically immune to the back pressure effects of a system and is subject to periodic stripdown. Pressure relief valves are one of the most critical parts of a pressure system that are set to open at a preset pressure level in order to avoid system failures. Every pressure system is set with a predetermined design limit called a setpoint, above which the valve begins to open to prevent overpressure conditions.
A safety valve is the last resort of people, property, and processes in the process industry comprising of power plants, petrochemicals, boilers, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and many more. It’s kind of a fail-safe device that actuates automatically in order to prevent the accumulation of pressure in a vessel or system beyond a preset limit. The device is so designed so that the safety valve trips automatically when the given pressure is attained. It simply allows the excess pressure to escape in order to prevent any damage to the vessel. Additionally, it also makes sure the pressure remains within the limits in the future. Even a slight increment in pressure lifts the safety valve and it closes as soon as the pressure is reduced to the prescribed limit.
A relief valve, also known as pressure relief valve (PRV) or safety relief valve, is type of a safety valve device used to limit or control the pressure level in a system within a safe threshold limit to avoid an overpressure condition. In simple terms, a relief valve is a device designed to control the pressure in a vessel or system to a specific set level. A safety valve, on the other hand, is a device used to let go excess pressure from a vessel or equipment when the pressure crosses a certain predetermined limit. It simply allows liquids or gases to escape if the pressure gets too high to prevent any damage.
Pressure relief valves are mainly used in hydraulic systems to limit the pressure in the system to a specific preset level and when the pressure reaches the safety design limit, the relief valve responds by releasing the excess flow from an auxiliary passage from the system back to the tank in order to prevent equipment failure. The main purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property, and environment against failure in the control system pressure. Simply put, a safety valve opens when the pressure exceeds the designed set pressure limit.
For a safety relief valve, the opening is directly proportional to the increase in the vessel pressure. This means the opening of the valve is rather gradual than sudden, allowing it to open only at a preset pressure level and release fluids until the pressure drops to the desired set pressure. A safety valve, on the other hand, will open immediately when the system pressure reaches the set pressure level in order to system failure. It is safety device capable of operating at all times and is the last resort to prevent catastrophic failure in systems under overpressure conditions.
A pressure relief valve is designed to open at a certain pressure level which is generally called as a “setpoint”. A setpoint should not be confused with the set pressure. In fact, a setpoint of a relief valves is adjusted to the lowest maximum pressure rating meaning it is set below the maximum system pressure allowed before the overpressure condition occurs. The valve begins to open when the pressure reaches up to some level above the setpoint. The setpoint is measured in pounds per square inch (PSIG) and must not exceed the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). In safety valves, the setpoint is usually set at 3 percent above the working pressure level whereas in relief valves, it is set at 10 percent.
Both relief valves and safety valves are high-performance pressure-sensitive safety devices so designed to control or limit the pressure inside the system or vessel by releasing the excessive pressure from the auxiliary passage out of the system. Although both are common terms used for safety valves, the difference lies mainly in the capacity and setpoint. While the former is operator-assisted and is designed to relieve pressure in order to avoid overpressure condition, the latter is a self-operated device which opens automatically when the maximum allowable pressure is reached. Relief valves are mostly used in fluid or compressed air systems, whereas safety valves are mainly used to release vapor or steam into the atmosphere.
Sagar Khillar is a prolific content/article/blog writer working as a Senior Content Developer/Writer in a reputed client services firm based in India. He has that urge to research on versatile topics and develop high-quality content to make it the best read. Thanks to his passion for writing, he has over 7 years of professional experience in writing and editing services across a wide variety of print and electronic platforms.
Outside his professional life, Sagar loves to connect with people from different cultures and origin. You can say he is curious by nature. He believes everyone is a learning experience and it brings a certain excitement, kind of a curiosity to keep going. It may feel silly at first, but it loosens you up after a while and makes it easier for you to start conversations with total strangers – that’s what he said."

Both pressure relief valves (PRV) and pressure safety valves (PSV) are used for process safety to relieve excess pressure. Although they’re often used interchangeably, they do have different functions and it’s important to know the difference.
If the PRV fails to maintain optimal pressure, the PSV kicks in. This valve opens quickly to avoid overpressurization when a set pressure is reached, preventing a potential safety incident.
Industrial Valve offers new PSVs and PRVs from Farris. Our Farris Authorized Service Team (FAST) can conduct pre-installation testing, install your valve, and perform regularly scheduled maintenance to keep your workflow operating at peak efficiency. Should you ever need an emergency repair, just call us – our technicians are available 24 hours a day!

Pressure Relieving Devices (PRD) are components used in refineries, chemical plants, and other similar facilities to prevent pressure vessels and other equipment from over pressurization by relieving excess pressure when necessary. They can be used to release gas, steam, liquids, or vapours. Properly functioning pressure relief devices are essential for protecting plant personnel and equipment, since unexpected overpressure events can potentially cause equipment damage, loss of containment, and result in costly plant shutdowns.
Pressure relieving devices include mechanisms such as Pressure Safety Valves (PSV) and Pressure Relief Valves (PRV), although there are other types of pressure relieving devices as well, such as Rupture Disk Devices and Pin-Actuated Devices. These devices can come in many different sizes and shapes and allow pressurized fluids or gasses to escape through a secondary passage out of the system so that pressure cannot build up beyond safe operating limits.
A Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) is a type of valve used to quickly release gasses from equipment in order to avoid over pressurization and potential process safety incidents. PSVs are activated automatically when pressure exceeds prescribed pressure limits in order to return equipment pressure to a safe operating level.
A Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) is a type of valve used to release stored gas in various equipment in order to maintain an optimal pressure level. PRVs open gradually as pressure builds up in order to release the necessary amount of pressure. While the term PRV is sometimes used interchangeably with PSV, there is a difference between the two. A PRV opens gradually in relation to the pressure, while a PSV is opened suddenly once the pressure hits a certain level in order to avoid over pressurization and a potential process safety incident.
The function of both PSV and PRV is that they relieve the excess pressure from the system by opening automatically and they get closed automatically when the pressure in the system normalizes.
The valve has a spring which is attached to adjusting screw. The screw can be adjusted to compress the spring thus imparting flexibility in adjusting the spring force. The spring is attached to a disc using a spindle. The location of the disk is where the fluid enters the valve when the system is over pressurized.
If the pressure force is less than the spring force then the fluid will not be able to move the disc. Such condition represents normal operating condition. If the pressure force is equal to the spring force then the disc starts to move. The fluid enters from the equipment to the valve and starts moving out of the system.
In case of PSV, when the pressure force becomes greater than the spring force the valve opens instantly and a ‘pop’ sound occurs whereas the PRV opens proportionally to the increasing pressure. It can be said that the opening is relatively gradual as compared to PSV.
The escaping fluid results in decrease of the pressure. When the pressure force becomes smaller than the spring force again then the disc returns to the same location again and seals the equipment.

Curtiss-Wright"s selection of Pressure Relief Valves comes from its outstanding product brands Farris and Target Rock. We endeavor to support the whole life cycle of a facility and continuously provide custom products and technologies. Boasting a reputation for producing high quality, durable products, our collection of Pressure Relief Valves is guaranteed to provide effective and reliable pressure relief.
While some basic components and activations in relieving pressure may differ between the specific types of relief valves, each aims to be 100% effective in keeping your equipment running safely. Our current range includes numerous valve types, from flanged to spring-loaded, threaded to wireless, pilot operated, and much more.
A pressure relief valve is a type of safety valve designed to control the pressure in a vessel. It protects the system and keeps the people operating the device safely in an overpressure event or equipment failure.
A pressure relief valve is designed to withstand a maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). Once an overpressure event occurs in the system, the pressure relief valve detects pressure beyond its design"s specified capability. The pressure relief valve would then discharge the pressurized fluid or gas to flow from an auxiliary passage out of the system.
Below is an example of one of our pilot operated pressure relief valves in action; the cutaway demonstrates when high pressure is released from the system.
Air pressure relief valves can be applied to a variety of environments and equipment. Pressure relief valves are a safety valve used to keep equipment and the operators safe too. They"re instrumental in applications where proper pressure levels are vital for correct and safe operation. Such as oil and gas, power generation like central heating systems, and multi-phase applications in refining and chemical processing.
At Curtiss-Wright, we provide a range of different pressure relief valves based on two primary operations – spring-loaded and pilot operated. Spring-loaded valves can either be conventional spring-loaded or balanced spring-loaded.
Spring-loaded valves are programmed to open and close via a spring mechanism. They open when the pressure reaches an unacceptable level to release the material inside the vessel. It closes automatically when the pressure is released, and it returns to an average operating level. Spring-loaded safety valves rely on the closing force applied by a spring onto the main seating area. They can also be controlled in numerous ways, such as a remote, control panel, and computer program.
Pilot-operated relief valves operate by combining the primary relieving device (main valve) with self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief valves, also known as the pilot control. This pilot control dictates the opening and closing of the main valve and responds to system pressure. System pressure is fed from the inlet into and through the pilot control and ultimately into the main valve"s dome. In normal operating conditions, system pressure will prevent the main valve from opening.
The valves allow media to flow from an auxiliary passage and out of the system once absolute pressure is reached, whether it is a maximum or minimum level.
When the pressure is below the maximum amount, the pressure differential is slightly positive on the piston"s dome size, which keeps the main valve in the closed position. When system pressure rises and reaches the set point, the pilot will cut off flow to the dome, causing depressurization in the piston"s dome side. The pressure differential has reversed, and the piston will rise, opening the main valve, relieving pressure.
When the process pressure decreases to a specific pressure, the pilot closes, the dome is repressurized, and the main valve closes. The main difference between spring-loaded PRVs and pilot-operated is that a pilot-operated safety valve uses pressure to keep the valve closed.
Pilot-operated relief valves are controlled by hand and are typically opened often through a wheel or similar component. The user opens the valve when the gauge signifies that the system pressure is at an unsafe level; once the valve has opened and the pressure has been released, the operator can shut it by hand again.
Increasing pressure helps to maintain the pilot"s seal. Once the setpoint has been reached, the valve opens. This reduces leakage and fugitive emissions.
At set pressure the valve snaps to full lift. This can be quite violent on large pipes with significant pressure. The pressure has to drop below the set pressure in order for the piston to reseat.
The pilot is designed to open gradually, so that less of the system fluid is lost during each relief event. The piston lifts in proportion to the overpressure.
At Curtiss-Wright we also provide solutions for pressure relief valve monitoring. Historically, pressure relief valves have been difficult or impossible to monitor. Our SmartPRV features a 2600 Series pressure relief valve accessorized with a wireless position monitor that alerts plant operators during an overpressure event, including the time and duration.
There are many causes of overpressure, but the most common ones are typically blocked discharge in the system, gas blowby, and fire. Even proper inspection and maintenance will not eliminate the occurrence of leakages. An air pressure relief valve is the only way to ensure a safe environment for the device, its surroundings, and operators.
A PRV and PSV are interchangeable, but there is a difference between the two valves. A pressure release valve gradually opens when experiencing pressure, whereas a pressure safety valve opens suddenly when the pressure hits a certain level of over pressurization. Safety valves can be used manually and are typically used for a permanent shutdown. Air pressure relief valves are used for operational requirements, and they gently release the pressure before it hits the maximum high-pressure point and circulates it back into the system.
Pressure relief valves should be subject to an annual test, one per year. The operator is responsible for carrying out the test, which should be done using an air compressor. It’s imperative to ensure pressure relief valves maintain their effectiveness over time and are checked for signs of corrosion and loss of functionality. Air pressure relief valves should also be checked before their installation, after each fire event, and regularly as decided by the operators.
Direct-acting solenoid valves have a direct connection with the opening and closing armature, whereas pilot-operated valves use of the process fluid to assist in piloting the operation of the valve.
A control valve works by varying the rate of fluid passing through the valve itself. As the valve stem moves, it alters the size of the passage and increases, decreases or holds steady the flow. The opening and closing of the valve is altered whenever the controlled process parameter does not reach the set point.
Control valves are usually at floor level or easily accessible via platforms. They are also located on the same equipment or pipeline as the measurement and downstream or flow measurements.
An industrial relief valve is designed to control or limit surges of pressure in a system, most often in fluid or compressed air system valves. It does so as a form of protection for the system and defending against instrument or equipment failure. They are usually present in clean water industries.
A PRV is often referred to as a pressure relief valve, which is also known as a PSV or pressure safety valve. They are used interchangeably throughout the industry depending on company standards.

The primary purpose of a safety valve is to protect life, property and the environment. Safety valves are designed to open and release excess pressure from vessels or equipment and then close again.
The function of safety valves differs depending on the load or main type of the valve. The main types of safety valves are spring-loaded, weight-loaded and controlled safety valves.
Regardless of the type or load, safety valves are set to a specific set pressure at which the medium is discharged in a controlled manner, thus preventing overpressure of the equipment. In dependence of several parameters such as the contained medium, the set pressure is individual for each safety application.

A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.
Safety valves were first developed for use on steam boilers during the Industrial Revolution. Early boilers operating without them were prone to explosion unless carefully operated.
Vacuum safety valves (or combined pressure/vacuum safety valves) are used to prevent a tank from collapsing while it is being emptied, or when cold rinse water is used after hot CIP (clean-in-place) or SIP (sterilization-in-place) procedures. When sizing a vacuum safety valve, the calculation method is not defined in any norm, particularly in the hot CIP / cold water scenario, but some manufacturers
The earliest and simplest safety valve was used on a 1679 steam digester and utilized a weight to retain the steam pressure (this design is still commonly used on pressure cookers); however, these were easily tampered with or accidentally released. On the Stockton and Darlington Railway, the safety valve tended to go off when the engine hit a bump in the track. A valve less sensitive to sudden accelerations used a spring to contain the steam pressure, but these (based on a Salter spring balance) could still be screwed down to increase the pressure beyond design limits. This dangerous practice was sometimes used to marginally increase the performance of a steam engine. In 1856, John Ramsbottom invented a tamper-proof spring safety valve that became universal on railways. The Ramsbottom valve consisted of two plug-type valves connected to each other by a spring-laden pivoting arm, with one valve element on either side of the pivot. Any adjustment made to one of valves in an attempt to increase its operating pressure would cause the other valve to be lifted off its seat, regardless of how the adjustment was attempted. The pivot point on the arm was not symmetrically between the valves, so any tightening of the spring would cause one of the valves to lift. Only by removing and disassembling the entire valve assembly could its operating pressure be adjusted, making impromptu "tying down" of the valve by locomotive crews in search of more power impossible. The pivoting arm was commonly extended into a handle shape and fed back into the locomotive cab, allowing crews to "rock" both valves off their seats to confirm they were set and operating correctly.
Safety valves also evolved to protect equipment such as pressure vessels (fired or not) and heat exchangers. The term safety valve should be limited to compressible fluid applications (gas, vapour, or steam).
For liquid-packed vessels, thermal relief valves are generally characterized by the relatively small size of the valve necessary to provide protection from excess pressure caused by thermal expansion. In this case a small valve is adequate because most liquids are nearly incompressible, and so a relatively small amount of fluid discharged through the relief valve will produce a substantial reduction in pressure.
Flow protection is characterized by safety valves that are considerably larger than those mounted for thermal protection. They are generally sized for use in situations where significant quantities of gas or high volumes of liquid must be quickly discharged in order to protect the integrity of the vessel or pipeline. This protection can alternatively be achieved by installing a high integrity pressure protection system (HIPPS).
In the petroleum refining, petrochemical, chemical manufacturing, natural gas processing, power generation, food, drinks, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industries, the term safety valve is associated with the terms pressure relief valve (PRV), pressure safety valve (PSV) and relief valve.
The generic term is Pressure relief valve (PRV) or pressure safety valve (PSV). PRVs and PSVs are not the same thing, despite what many people think; the difference is that PSVs have a manual lever to open the valve in case of emergency.
Relief valve (RV): an automatic system that is actuated by the static pressure in a liquid-filled vessel. It specifically opens proportionally with increasing pressure
Pilot-operated safety relief valve (POSRV): an automatic system that relieves on remote command from a pilot, to which the static pressure (from equipment to protect) is connected
Low pressure safety valve (LPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the difference between the vessel pressure and the ambient atmospheric pressure is small.
Vacuum pressure safety valve (VPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the pressure difference between the vessel pressure and the ambient pressure is small, negative and near to atmospheric pressure.
Low and vacuum pressure safety valve (LVPSV): an automatic system that relieves static pressure on a gas. Used when the pressure difference is small, negative or positive and near to atmospheric pressure.
In most countries, industries are legally required to protect pressure vessels and other equipment by using relief valves. Also, in most countries, equipment design codes such as those provided by the ASME, API and other organizations like ISO (ISO 4126) must be complied with. These codes include design standards for relief valves and schedules for periodic inspection and testing after valves have been removed by the company engineer.
Today, the food, drinks, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals industries call for hygienic safety valves, fully drainable and Cleanable-In-Place. Most are made of stainless steel; the hygienic norms are mainly 3A in the USA and EHEDG in Europe.
The first safety valve was invented by Denis Papin for his steam digester, an early pressure cooker rather than an engine.steelyard" lever a smaller weight was required, also the pressure could easily be regulated by sliding the same weight back and forth along the lever arm. Papin retained the same design for his 1707 steam pump.Greenwich in 1803, one of Trevithick"s high-pressure stationary engines exploded when the boy trained to operate the engine left it to catch eels in the river, without first releasing the safety valve from its working load.
Although the lever safety valve was convenient, it was too sensitive to the motion of a steam locomotive. Early steam locomotives therefore used a simpler arrangement of weights stacked directly upon the valve. This required a smaller valve area, so as to keep the weight manageable, which sometimes proved inadequate to vent the pressure of an unattended boiler, leading to explosions. An even greater hazard was the ease with which such a valve could be tied down, so as to increase the pressure and thus power of the engine, at further risk of explosion.
Although deadweight safety valves had a short lifetime on steam locomotives, they remained in use on stationary boilers for as long as steam power remained.
Weighted valves were sensitive to bouncing from the rough riding of early locomotives. One solution was to use a lightweight spring rather than a weight. This was the invention of Timothy Hackworth on his leaf springs.
These direct-acting spring valves could be adjusted by tightening the nuts retaining the spring. To avoid tampering, they were often shrouded in tall brass casings which also vented the steam away from the locomotive crew.
The Salter coil spring spring balance for weighing, was first made in Britain by around 1770.spring steels to make a powerful but compact spring in one piece. Once again by using the lever mechanism, such a spring balance could be applied to the considerable force of a boiler safety valve.
The spring balance valve also acted as a pressure gauge. This was useful as previous pressure gauges were unwieldy mercury manometers and the Bourdon gauge had yet to be invented.
Paired valves were often adjusted to slightly different pressures too, a small valve as a control measure and the lockable valve made larger and permanently set to a higher pressure, as a safeguard.Sinclair for the Eastern Counties Railway in 1859, had the valve spring with pressure scale behind the dome, facing the cab, and the locked valve ahead of the dome, out of reach of interference.
In 1855, John Ramsbottom, later locomotive superintendent of the LNWR, described a new form of safety valve intended to improve reliability and especially to be tamper-resistant. A pair of plug valves were used, held down by a common spring-loaded lever between them with a single central spring. This lever was characteristically extended rearwards, often reaching into the cab on early locomotives. Rather than discouraging the use of the spring lever by the fireman, Ramsbottom"s valve encouraged this. Rocking the lever freed up the valves alternately and checked that neither was sticking in its seat.
A drawback to the Ramsbottom type was its complexity. Poor maintenance or mis-assembly of the linkage between the spring and the valves could lead to a valve that no longer opened correctly under pressure. The valves could be held against their seats and fail to open or, even worse, to allow the valve to open but insufficiently to vent steam at an adequate rate and so not being an obvious and noticeable fault.Rhymney Railway, even though the boiler was almost new, at only eight months old.
Naylor valves were introduced around 1866. A bellcrank arrangement reduced the strain (percentage extension) of the spring, thus maintaining a more constant force.L&Y & NER.
All of the preceding safety valve designs opened gradually and had a tendency to leak a "feather" of steam as they approached "blowing-off", even though this was below the pressure. When they opened they also did so partially at first and didn"t vent steam quickly until the boiler was well over pressure.
The quick-opening "pop" valve was a solution to this. Their construction was simple: the existing circular plug valve was changed to an inverted "top hat" shape, with an enlarged upper diameter. They fitted into a stepped seat of two matching diameters. When closed, the steam pressure acted only on the crown of the top hat, and was balanced by the spring force. Once the valve opened a little, steam could pass the lower seat and began to act on the larger brim. This greater area overwhelmed the spring force and the valve flew completely open with a "pop". Escaping steam on this larger diameter also held the valve open until pressure had dropped below that at which it originally opened, providing hysteresis.
These valves coincided with a change in firing behaviour. Rather than demonstrating their virility by always showing a feather at the valve, firemen now tried to avoid noisy blowing off, especially around stations or under the large roof of a major station. This was mostly at the behest of stationmasters, but firemen also realised that any blowing off through a pop valve wasted several pounds of boiler pressure; estimated at 20 psi lost and 16 lbs or more of shovelled coal.
Pop valves derived from Adams"s patent design of 1873, with an extended lip. R. L. Ross"s valves were patented in 1902 and 1904. They were more popular in America at first, but widespread from the 1920s on.
Although showy polished brass covers over safety valves had been a feature of steam locomotives since Stephenson"s day, the only railway to maintain this tradition into the era of pop valves was the GWR, with their distinctive tapered brass safety valve bonnets and copper-capped chimneys.
Developments in high-pressure water-tube boilers for marine use placed more demands on safety valves. Valves of greater capacity were required, to vent safely the high steam-generating capacity of these large boilers.Naylor valve) became more critical.distilled feedwater and also a scouring of the valve seats, leading to wear.
High-lift safety valves are direct-loaded spring types, although the spring does not bear directly on the valve, but on a guide-rod valve stem. The valve is beneath the base of the stem, the spring rests on a flange some height above this. The increased space between the valve itself and the spring seat allows the valve to lift higher, further clear of the seat. This gives a steam flow through the valve equivalent to a valve one and a half or twice as large (depending on detail design).
The Cockburn Improved High Lift design has similar features to the Ross pop type. The exhaust steam is partially trapped on its way out and acts on the base of the spring seat, increasing the lift force on the valve and holding the valve further open.
To optimise the flow through a given diameter of valve, the full-bore design is used. This has a servo action, where steam through a narrow control passage is allowed through if it passes a small control valve. This steam is then not exhausted, but is passed to a piston that is used to open the main valve.
There are safety valves known as PSV"s and can be connected to pressure gauges (usually with a 1/2" BSP fitting). These allow a resistance of pressure to be applied to limit the pressure forced on the gauge tube, resulting in prevention of over pressurisation. the matter that has been injected into the gauge, if over pressurised, will be diverted through a pipe in the safety valve, and shall be driven away from the gauge.
There is a wide range of safety valves having many different applications and performance criteria in different areas. In addition, national standards are set for many kinds of safety valves.
Safety valves are required on water heaters, where they prevent disaster in certain configurations in the event that a thermostat should fail. Such a valve is sometimes referred to as a "T&P valve" (Temperature and Pressure valve). There are still occasional, spectacular failures of older water heaters that lack this equipment. Houses can be leveled by the force of the blast.
Pressure cookers are cooking pots with a pressure-proof lid. Cooking at pressure allows the temperature to rise above the normal boiling point of water (100 degrees Celsius at sea level), which speeds up the cooking and makes it more thorough.
Pressure cookers usually have two safety valves to prevent explosions. On older designs, one is a nozzle upon which a weight sits. The other is a sealed rubber grommet which is ejected in a controlled explosion if the first valve gets blocked. On newer generation pressure cookers, if the steam vent gets blocked, a safety spring will eject excess pressure and if that fails, the gasket will expand and release excess pressure downwards between the lid and the pan. Also, newer generation pressure cookers have a safety interlock which locks the lid when internal pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure, to prevent accidents from a sudden release of very hot steam, food and liquid, which would happen if the lid were to be removed when the pan is still slightly pressurised inside (however, the lid will be very hard or impossible to open when the pot is still pressurised).
These figures are based on two measurements, a drop from 225 psi to 205 psi for an LNER Class V2 in 1952 and a smaller drop of 10 psi estimated in 1953 as 16 lbs of coal.
"Trial of HMS Rattler and Alecto". April 1845. The very lowest pressure exhibited "when the screw was out of the water" (as the opponents of the principle term it) was 34 lb, ranging up to 60 lb., on Salter"s balance.




 8613371530291
8613371530291