gwr safety valve free sample

The Supreme Court has reinforced the theory of the First Amendment as a "safety valve," reasoning that citizens who are free to to express displeasure against government through peaceful protest will be deterred from undertaking violent means. The boundary between what is peaceful and what is violent is not always clear. For example, in this 1965 photo, Alabama State College students participated in a non-violent protest for voter rights when deputies confronted them anyway, breaking up the gathering. (AP Photo/Perry Aycock, used with permission from the Associated Press)
Under the safety valve rationale, citizens are free to make statements concerning controversial societal issues to express their displeasure against government and its policies. In assuming this right, citizens will be deterred from undertaking violent means to draw attention to their causes.
The First Amendment, in safeguarding freedom of speech, religion, peaceable assembly, and a right to petition government, embodies the safety valve theory.
These and other decisions rest on the idea that it is better to allow members of the public to judge ideas for themselves and act accordingly than to have the government act as a censure. The Court has even shown support in cases concerning obscenity or speech that incites violent action. The safety valve theory suggests that such a policy is more likely to lead to civil peace than to civil disruption.
Justice Louis D. Brandeis recognized the potential for the First Amendment to serve as a safety valve in his concurring opinion in Whitney v. California (1927) when he wrote: “fear breeds repression; . . . repression breeds hate; . . . hate menaces stable government; . . . the path of safety lies in the opportunity to discuss freely supposed grievances and proposed remedies; and the fitting remedy for evil counsels is good ones.”

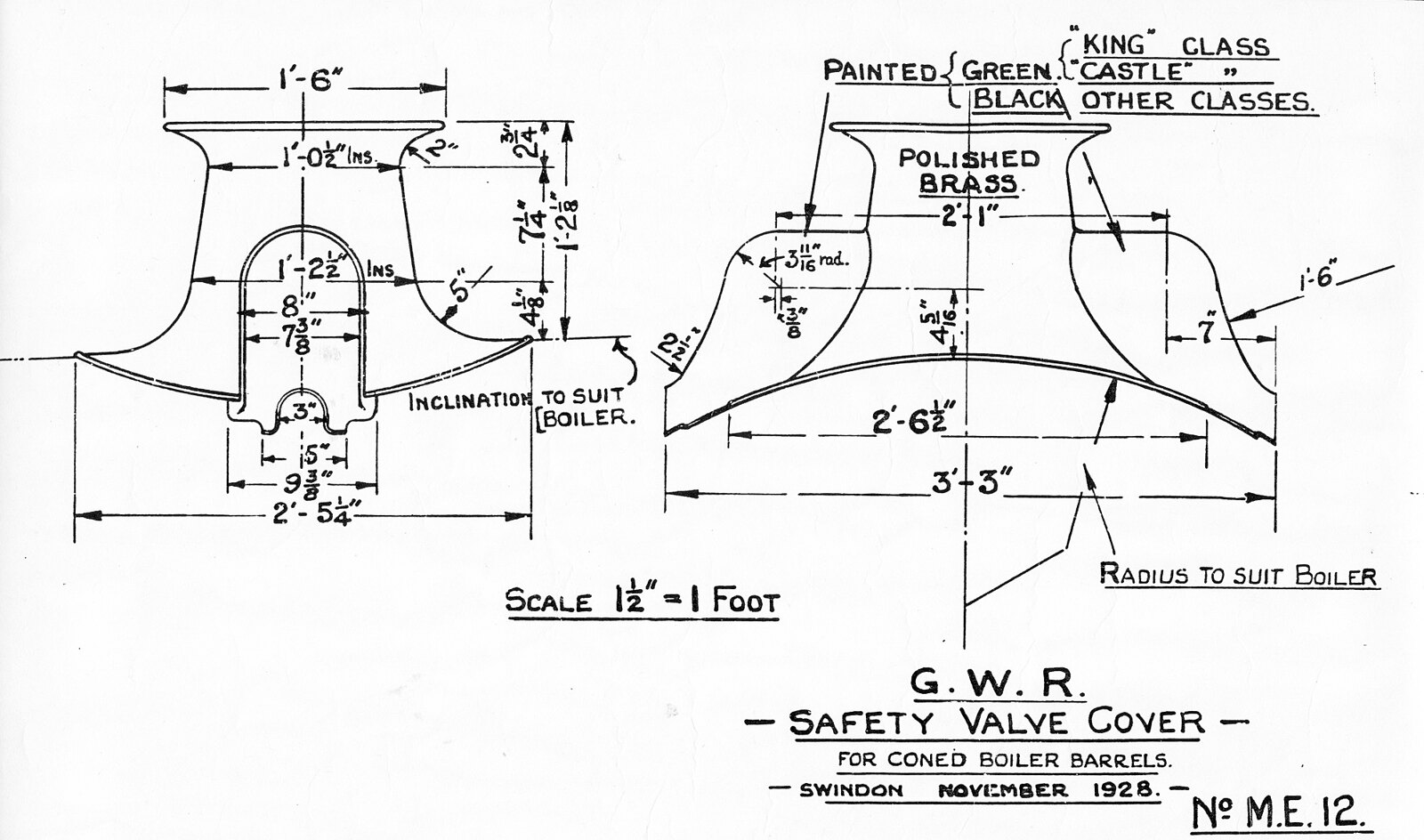
Dapol has revealed the first engineering sample for its all-new "OO" gauge model of the GWR "Manor" 4-6-0 together with confirmation of the identities for its first production run.
The "Manor" 4-6-0s were built in 1938-1939 by the GWR at Swindon Works with a further batch following in the early 1950s. In total 30 were built and they were seen in the West Country as well as on the Cambrian lines.
Dapol"s new "Manor" follows the specification laid out for the recently released GWR "Mogul" for "OO" including the slide out Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in the smokebox for decoder installation and wire-free tender to locomotive connection.
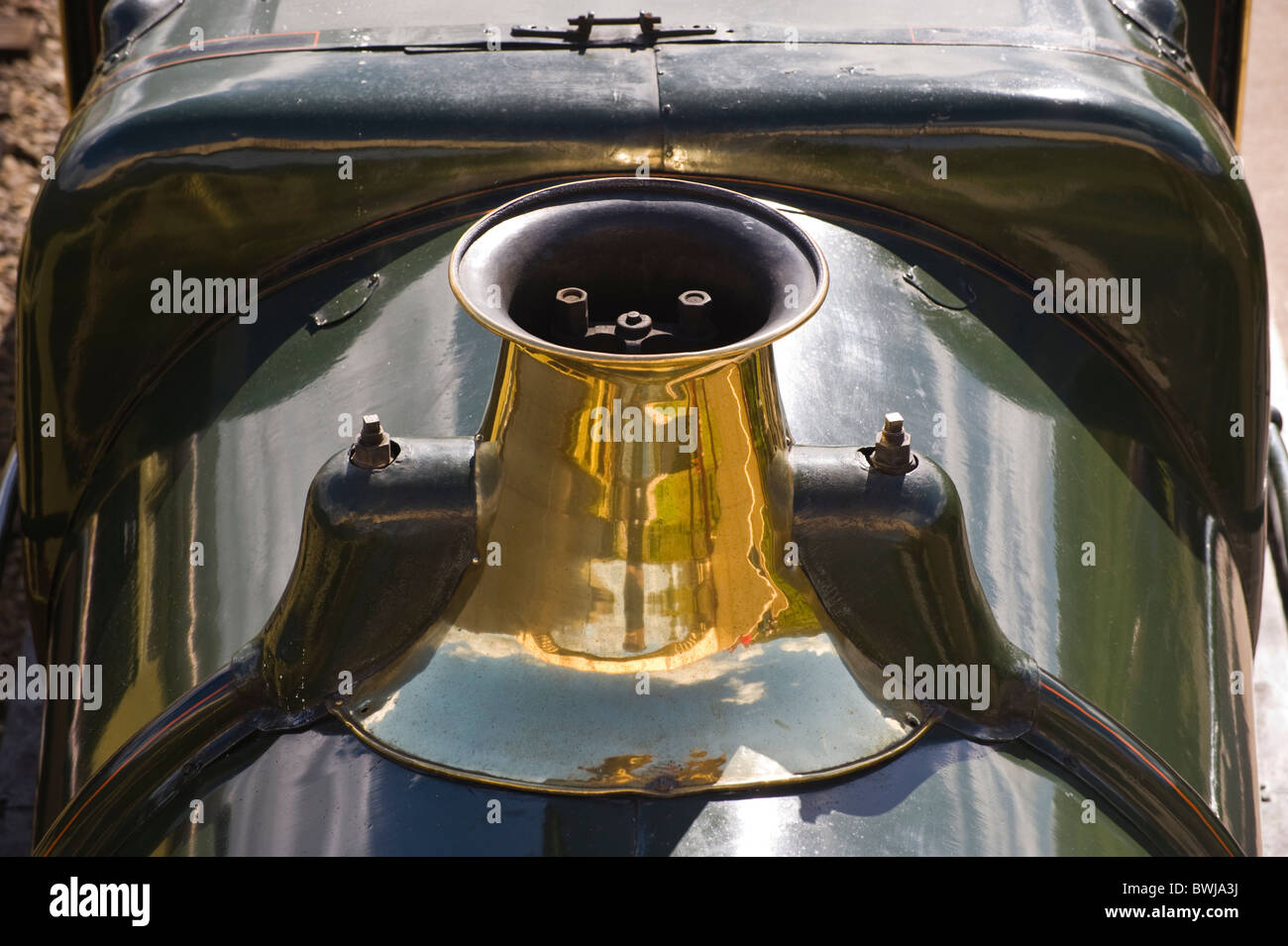
The specification for the "Manor" includes a die-cast compensated chassis, detailed cab interior, full relief cylinder blocks, brass plated safety valve casing, original and redraughted chimneys, a Next18 decoder socket for tool free decoder and sound installation, electrical pick up from 12 wheels and the option for factory fitted sound examples with Dapol"s own RealDrive sound profile.
Prices are set at £159.95 DCC ready, £185.95 DCC fitted and £259.95 DCC sound fitted with a choice of seven main releases and one Dapol exclusive. These will model 7800 Torquay Manor in GWR green with Monogram crests (Cat No. 4S-001-001), 7814 Fringford Manor in GWR lettered green (4S-001-002), 7807 Compton Manor in GWR green with crests (4S-001-003), 7823 Hook Norton Manor in BR lined black with small early crests (4S-001-004), 7819 Hinton Manor in BR black with large early crests (4S-001-005), 7810 Draycott Manor in BR lined green with small early crests (4S-001-006) and 7827 Lydham Manor in BR lined green with late crests (4S-001-007).
A “safety valve” is an exception to mandatory minimum sentencing laws. A safety valve allows a judge to sentence a person below the mandatory minimum term if certain conditions are met. Safety valves can be broad or narrow, applying to many or few crimes (e.g., drug crimes only) or types of offenders (e.g., nonviolent offenders). They do not repeal or eliminate mandatory minimum sentences. However, safety valves save taxpayers money because they allow courts to give shorter, more appropriate prison sentences to offenders who pose less of a public safety threat. This saves our scarce taxpayer dollars and prison beds for those who are most deserving of the mandatory minimum term and present the biggest danger to society.
The Problem:Under current federal law, there is only one safety valve, and it applies only to first-time, nonviolent drug offenders whose cases did not involve guns. FAMM was instrumental in the passage of this safety valve, in 1994. Since then, more than 95,000 nonviolent drug offenders have received fairer sentences because of it, saving taxpayers billions. But it is a very narrow exception: in FY 2015, only 13 percent of all drug offenders qualified for the exception.
Mere presence of even a lawfully purchased and registered gun in a person’s home or car is enough to disqualify a nonviolent drug offender from the safety valve,
Even very minor prior infractions (e.g., careless driving) that resulted in no prison time can disqualify an otherwise worthy low-level drug offender from the safety valve, and
The Solution:Create a broader safety valve that applies to all mandatory minimum sentences, and expand the existing drug safety valve to cover more low-level offenders.

Pressure relief valve is related to Microchek.com. We offer competitive pricing and reliability because we are the manufacture. Parts are molded and assembled in the U.S. The Microchek system incorporates this cartridge and a wide selection of end pieces to accommodate most connection requirements. The Microchek valve is a cartridge check valve incorporating an innovative guided poppet design. Relief valves are used to hold a fluid circuit or reservoir at a positive or negative pressure. We can select valves that fall into a specific cracking pressure range if needed. The Microchek valve has a low pressure drop and can be specified with a wide variety of cracking pressures.
The Microchek valve is a cartridge check valve incorporating an innovative guided poppet design. Relief valves are used to hold a fluid circuit or reservoir at a positive or negative pressure. We want the opportunity to help you solve your flow control applications and we can build special configurations.

In order to ensure that the maximum allowable accumulation pressure of any system or apparatus protected by a safety valve is never exceeded, careful consideration of the safety valve’s position in the system has to be made. As there is such a wide range of applications, there is no absolute rule as to where the valve should be positioned and therefore, every application needs to be treated separately.
A common steam application for a safety valve is to protect process equipment supplied from a pressure reducing station. Two possible arrangements are shown in Figure 9.3.3.
The safety valve can be fitted within the pressure reducing station itself, that is, before the downstream stop valve, as in Figure 9.3.3 (a), or further downstream, nearer the apparatus as in Figure 9.3.3 (b). Fitting the safety valve before the downstream stop valve has the following advantages:
• The safety valve can be tested in-line by shutting down the downstream stop valve without the chance of downstream apparatus being over pressurised, should the safety valve fail under test.
• When setting the PRV under no-load conditions, the operation of the safety valve can be observed, as this condition is most likely to cause ‘simmer’. If this should occur, the PRV pressure can be adjusted to below the safety valve reseat pressure.
Indeed, a separate safety valve may have to be fitted on the inlet to each downstream piece of apparatus, when the PRV supplies several such pieces of apparatus.
• If supplying one piece of apparatus, which has a MAWP pressure less than the PRV supply pressure, the apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve, preferably close-coupled to its steam inlet connection.
• If a PRV is supplying more than one apparatus and the MAWP of any item is less than the PRV supply pressure, either the PRV station must be fitted with a safety valve set at the lowest possible MAWP of the connected apparatus, or each item of affected apparatus must be fitted with a safety valve.
• The safety valve must be located so that the pressure cannot accumulate in the apparatus viaanother route, for example, from a separate steam line or a bypass line.
It could be argued that every installation deserves special consideration when it comes to safety, but the following applications and situations are a little unusual and worth considering:
• Fire - Any pressure vessel should be protected from overpressure in the event of fire. Although a safety valve mounted for operational protection may also offer protection under fire conditions,such cases require special consideration, which is beyond the scope of this text.
• Exothermic applications - These must be fitted with a safety valve close-coupled to the apparatus steam inlet or the body direct. No alternative applies.
• Safety valves used as warning devices - Sometimes, safety valves are fitted to systems as warning devices. They are not required to relieve fault loads but to warn of pressures increasing above normal working pressures for operational reasons only. In these instances, safety valves are set at the warning pressure and only need to be of minimum size. If there is any danger of systems fitted with such a safety valve exceeding their maximum allowable working pressure, they must be protected by additional safety valves in the usual way.
In order to illustrate the importance of the positioning of a safety valve, consider an automatic pump trap (see Block 14) used to remove condensate from a heating vessel. The automatic pump trap (APT), incorporates a mechanical type pump, which uses the motive force of steam to pump the condensate through the return system. The position of the safety valve will depend on the MAWP of the APT and its required motive inlet pressure.
This arrangement is suitable if the pump-trap motive pressure is less than 1.6 bar g (safety valve set pressure of 2 bar g less 0.3 bar blowdown and a 0.1 bar shut-off margin). Since the MAWP of both the APT and the vessel are greater than the safety valve set pressure, a single safety valve would provide suitable protection for the system.
Here, two separate PRV stations are used each with its own safety valve. If the APT internals failed and steam at 4 bar g passed through the APT and into the vessel, safety valve ‘A’ would relieve this pressure and protect the vessel. Safety valve ‘B’ would not lift as the pressure in the APT is still acceptable and below its set pressure.
It should be noted that safety valve ‘A’ is positioned on the downstream side of the temperature control valve; this is done for both safety and operational reasons:
Operation - There is less chance of safety valve ‘A’ simmering during operation in this position,as the pressure is typically lower after the control valve than before it.
Also, note that if the MAWP of the pump-trap were greater than the pressure upstream of PRV ‘A’, it would be permissible to omit safety valve ‘B’ from the system, but safety valve ‘A’ must be sized to take into account the total fault flow through PRV ‘B’ as well as through PRV ‘A’.
A pharmaceutical factory has twelve jacketed pans on the same production floor, all rated with the same MAWP. Where would the safety valve be positioned?
One solution would be to install a safety valve on the inlet to each pan (Figure 9.3.6). In this instance, each safety valve would have to be sized to pass the entire load, in case the PRV failed open whilst the other eleven pans were shut down.
If additional apparatus with a lower MAWP than the pans (for example, a shell and tube heat exchanger) were to be included in the system, it would be necessary to fit an additional safety valve. This safety valve would be set to an appropriate lower set pressure and sized to pass the fault flow through the temperature control valve (see Figure 9.3.8).




 8613371530291
8613371530291