how many safety valve in boiler in stock
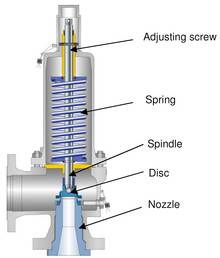
Years ago, it was not uncommon to read news about tragic boiler explosions, sometimes resulting in mass destruction. Today, boilers are equipped with important safety devises to help protect against these types of catastrophes. Let’s take a look at the most critical of these devices: the safety valve.
The safety valve is one of the most important safety devices in a steam system. Safety valves provide a measure of security for plant operators and equipment from over pressure conditions. The main function of a safety valve is to relieve pressure. It is located on the boiler steam drum, and will automatically open when the pressure of the inlet side of the valve increases past the preset pressure. All boilers are required by ASME code to have at least one safety valve, dependent upon the maximum flow capacity (MFC) of the boiler. The total capacity of the safety valve at the set point must exceed the steam control valve’s MFC if the steam valve were to fail to open. In most cases, two safety valves per boiler are required, and a third may be needed if they do not exceed the MFC.
There are three main parts to the safety valve: nozzle, disc, and spring. Pressurized steam enters the valve through the nozzle and is then threaded to the boiler. The disc is the lid to the nozzle, which opens or closes depending on the pressure coming from the boiler. The spring is the pressure controller.
As a boiler starts to over pressure, the nozzle will start to receive a higher pressure coming from the inlet side of the valve, and will start to sound like it is simmering. When the pressure becomes higher than the predetermined pressure of the spring, the disc will start to lift and release the steam, creating a “pop” sound. After it has released and the steam and pressure drops below the set pressure of the valve, the spring will close the disc. Once the safety valve has popped, it is important to check the valve to make sure it is not damaged and is working properly.
A safety valve is usually referred to as the last line of safety defense. Without safety valves, the boiler can exceed it’s maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and not only damage equipment, but also injure or kill plant operators that are close by. Many variables can cause a safety valve on a boiler to lift, such as a compressed air or electrical power failure to control instrumentation, or an imbalance of feedwater rate caused by an inadvertently shut or open isolation valve.
Once a safety valve has lifted, it is important to do a complete boiler inspection and confirm that there are no other boiler servicing issues. A safety valve should only do its job once; safety valves should not lift continuously. Lastly, it is important to have the safety valves fully repaired, cleaned and recertified with a National Board valve repair (VR) stamp as required by local code or jurisdiction. Safety valves are a critical component in a steam system, and must be maintained.
All of Nationwide Boiler’s rental boilers include on to two safety valves depending on the size; one set at design pressure and the other set slightly higher than design. By request, we can reset the safeties to a lower pressure if the application requires it. In addition, the valves are thoroughly checked after every rental and before going out to a new customer, and they are replaced and re-certified as needed.

Above certification pressure no one can guaranty the systems safety - and especially for a steam system with a very hot gas with a huge amount of latent heat the consequence with a failure can be dramatically.
The size of a safety valve depends primarily on the maximum boiler output and the operation pressure of the system. The safety valve must as minimum have the evacuation capacity of all the vapor the boiler can produce running at full power at the working (or certification) pressure. for a higher pressure the steam is compressed and requires less volume and the size of the valve can be reduced
The tables below can be used to select a typical safety valve in a high pressure system. Before the final design - always consult manufacturing documentation.
Note! The table above is based on steam with pressure 300 kPa (3 bar) (or 50 psiin imperial units). Latent heat of saturated steam is 1 N/m2 = 1 Pa = 1.4504 x 10-4 lb/in2 (psi) = 1x10-5 bar

After a boiler has been engineered, built and tested for a given operating pressure there is only one reliable way to prevent operation of the boiler above this design pressure. This is a safety valve. The safety valve should be sized so that a single valve can handle the maximum steam production rate of the boiler and once open prevent boiler pressure to continue to rise. Standard operating procedure for the last century has been to install two safety valves on the boiler, one set 3-5 lbs below the design pressure and one valve set at the design pressure.
The 1st valve listed below is a true adjustable differential pop valve. The differential is adjured through the differential rings lock screw hole, from 3 PSI to whatever the operator desires. The pressure of the valve can be adjusted from 40 to 200 PSI.
The other valves listed are adjustable for release pressure and have a "pop" action: The pressure differential is not adjustable on these valves. If the valves are operated above their nominal pressure, the set-reset differential increases. If operated at lower pressure, the differential decreases to the point of disappearing about 10-15% below nominal pressure.

As soon as mankind was able to boil water to create steam, the necessity of the safety device became evident. As long as 2000 years ago, the Chinese were using cauldrons with hinged lids to allow (relatively) safer production of steam. At the beginning of the 14th century, chemists used conical plugs and later, compressed springs to act as safety devices on pressurised vessels.
Early in the 19th century, boiler explosions on ships and locomotives frequently resulted from faulty safety devices, which led to the development of the first safety relief valves.
In 1848, Charles Retchie invented the accumulation chamber, which increases the compression surface within the safety valve allowing it to open rapidly within a narrow overpressure margin.
Today, most steam users are compelled by local health and safety regulations to ensure that their plant and processes incorporate safety devices and precautions, which ensure that dangerous conditions are prevented.
The principle type of device used to prevent overpressure in plant is the safety or safety relief valve. The safety valve operates by releasing a volume of fluid from within the plant when a predetermined maximum pressure is reached, thereby reducing the excess pressure in a safe manner. As the safety valve may be the only remaining device to prevent catastrophic failure under overpressure conditions, it is important that any such device is capable of operating at all times and under all possible conditions.
Safety valves should be installed wherever the maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) of a system or pressure-containing vessel is likely to be exceeded. In steam systems, safety valves are typically used for boiler overpressure protection and other applications such as downstream of pressure reducing controls. Although their primary role is for safety, safety valves are also used in process operations to prevent product damage due to excess pressure. Pressure excess can be generated in a number of different situations, including:
The terms ‘safety valve’ and ‘safety relief valve’ are generic terms to describe many varieties of pressure relief devices that are designed to prevent excessive internal fluid pressure build-up. A wide range of different valves is available for many different applications and performance criteria.
In most national standards, specific definitions are given for the terms associated with safety and safety relief valves. There are several notable differences between the terminology used in the USA and Europe. One of the most important differences is that a valve referred to as a ‘safety valve’ in Europe is referred to as a ‘safety relief valve’ or ‘pressure relief valve’ in the USA. In addition, the term ‘safety valve’ in the USA generally refers specifically to the full-lift type of safety valve used in Europe.
Pressure relief valve- A spring-loaded pressure relief valve which is designed to open to relieve excess pressure and to reclose and prevent the further flow of fluid after normal conditions have been restored. It is characterised by a rapid-opening ‘pop’ action or by opening in a manner generally proportional to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure. It may be used for either compressible or incompressible fluids, depending on design, adjustment, or application.
Safety valves are primarily used with compressible gases and in particular for steam and air services. However, they can also be used for process type applications where they may be needed to protect the plant or to prevent spoilage of the product being processed.
Relief valve - A pressure relief device actuated by inlet static pressure having a gradual lift generally proportional to the increase in pressure over opening pressure.
Relief valves are commonly used in liquid systems, especially for lower capacities and thermal expansion duty. They can also be used on pumped systems as pressure overspill devices.
Safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve characterised by rapid opening or pop action, or by opening in proportion to the increase in pressure over the opening pressure, depending on the application, and which may be used either for liquid or compressible fluid.
In general, the safety relief valve will perform as a safety valve when used in a compressible gas system, but it will open in proportion to the overpressure when used in liquid systems, as would a relief valve.
Safety valve- A valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored.

There is a wide range of safety valves available to meet the many different applications and performance criteria demanded by different industries. Furthermore, national standards define many varying types of safety valve.
The ASME standard I and ASME standard VIII for boiler and pressure vessel applications and the ASME/ANSI PTC 25.3 standard for safety valves and relief valves provide the following definition. These standards set performance characteristics as well as defining the different types of safety valves that are used:
ASME I valve - A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section I of the ASME pressure vessel code for boiler applications which will open within 3% overpressure and close within 4%. It will usually feature two blowdown rings, and is identified by a National Board ‘V’ stamp.
ASME VIII valve- A safety relief valve conforming to the requirements of Section VIII of the ASME pressure vessel code for pressure vessel applications which will open within 10% overpressure and close within 7%. Identified by a National Board ‘UV’ stamp.
Full bore safety valve - A safety valve having no protrusions in the bore, and wherein the valve lifts to an extent sufficient for the minimum area at any section, at or below the seat, to become the controlling orifice.
Conventional safety relief valve -The spring housing is vented to the discharge side, hence operational characteristics are directly affected by changes in the backpressure to the valve.
Balanced safety relief valve -A balanced valve incorporates a means of minimising the effect of backpressure on the operational characteristics of the valve.
Pilot operated pressure relief valve -The major relieving device is combined with, and is controlled by, a self-actuated auxiliary pressure relief device.
Power-actuated safety relief valve - A pressure relief valve in which the major pressure relieving device is combined with, and controlled by, a device requiring an external source of energy.
Standard safety valve - A valve which, following opening, reaches the degree of lift necessary for the mass flowrate to be discharged within a pressure rise of not more than 10%. (The valve is characterised by a pop type action and is sometimes known as high lift).
Full lift (Vollhub) safety valve -A safety valve which, after commencement of lift, opens rapidly within a 5% pressure rise up to the full lift as limited by the design. The amount of lift up to the rapid opening (proportional range) shall not be more than 20%.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the opening force underneath the valve disc is opposed by a closing force such as a spring or a weight.
Proportional safety valve - A safety valve which opens more or less steadily in relation to the increase in pressure. Sudden opening within a 10% lift range will not occur without pressure increase. Following opening within a pressure of not more than 10%, these safety valves achieve the lift necessary for the mass flow to be discharged.
Diaphragm safety valve -A direct loaded safety valve wherein linear moving and rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluid by a diaphragm
Bellows safety valve - A direct loaded safety valve wherein sliding and (partially or fully) rotating elements and springs are protected against the effects of the fluids by a bellows. The bellows may be of such a design that it compensates for influences of backpressure.
Controlled safety valve - Consists of a main valve and a control device. It also includes direct acting safety valves with supplementary loading in which, until the set pressure is reached, an additional force increases the closing force.
Safety valve - A safety valve which automatically, without the assistance of any energy other than that of the fluid concerned, discharges a quantity of the fluid so as to prevent a predetermined safe pressure being exceeded, and which is designed to re-close and prevent further flow of fluid after normal pressure conditions of service have been restored. Note; the valve can be characterised either by pop action (rapid opening) or by opening in proportion (not necessarily linear) to the increase in pressure over the set pressure.
Direct loaded safety valve -A safety valve in which the loading due to the fluid pressure underneath the valve disc is opposed only by a direct mechanical loading device such as a weight, lever and weight, or a spring.
Assisted safety valve -A safety valve which by means of a powered assistance mechanism, may additionally be lifted at a pressure lower than the set pressure and will, even in the event of a failure of the assistance mechanism, comply with all the requirements for safety valves given in the standard.
Supplementary loaded safety valve - A safety valve that has, until the pressure at the inlet to the safety valve reaches the set pressure, an additional force, which increases the sealing force.
Note; this additional force (supplementary load), which may be provided by means of an extraneous power source, is reliably released when the pressure at the inlet of the safety valve reaches the set pressure. The amount of supplementary loading is so arranged that if such supplementary loading is not released, the safety valve will attain its certified discharge capacity at a pressure not greater than 1.1 times the maximum allowable pressure of the equipment to be protected.
Pilot operated safety valve -A safety valve, the operation of which is initiated and controlled by the fluid discharged from a pilot valve, which is itself, a direct loaded safety valve subject to the requirement of the standard.
The common characteristic shared between the definitions of conventional safety valves in the different standards, is that their operational characteristics are affected by any backpressure in the discharge system. It is important to note that the total backpressure is generated from two components; superimposed backpressure and the built-up backpressure:
Subsequently, in a conventional safety valve, only the superimposed backpressure will affect the opening characteristic and set value, but the combined backpressure will alter the blowdown characteristic and re-seat value.
The ASME/ANSI standard makes the further classification that conventional valves have a spring housing that is vented to the discharge side of the valve. If the spring housing is vented to the atmosphere, any superimposed backpressure will still affect the operational characteristics. Thiscan be seen from Figure 9.2.1, which shows schematic diagrams of valves whose spring housings are vented to the discharge side of the valve and to the atmosphere.
By considering the forces acting on the disc (with area AD), it can be seen that the required opening force (equivalent to the product of inlet pressure (PV) and the nozzle area (AN)) is the sum of the spring force (FS) and the force due to the backpressure (PB) acting on the top and bottom of the disc. In the case of a spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve (an ASME conventional safety relief valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a)), the required opening force is:
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
In both cases, if a significant superimposed backpressure exists, its effects on the set pressure need to be considered when designing a safety valve system.
Once the valve starts to open, the effects of built-up backpressure also have to be taken into account. For a conventional safety valve with the spring housing vented to the discharge side of the valve, see Figure 9.2.1 (a), the effect of built-up backpressure can be determined by considering Equation 9.2.1 and by noting that once the valve starts to open, the inlet pressure is the sum of the set pressure, PS, and the overpressure, PO.
Balanced safety valves are those that incorporate a means of eliminating the effects of backpressure. There are two basic designs that can be used to achieve this:
Although there are several variations of the piston valve, they generally consist of a piston type disc whose movement is constrained by a vented guide. The area of the top face of the piston, AP, and the nozzle seat area, AN, are designed to be equal. This means that the effective area of both the top and bottom surfaces of the disc exposed to the backpressure are equal, and therefore any additional forces are balanced. In addition, the spring bonnet is vented such that the top face of the piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure, as shown in Figure 9.2.2.
The bellows arrangement prevents backpressure acting on the upper side of the disc within the area of the bellows. The disc area extending beyond the bellows and the opposing disc area are equal, and so the forces acting on the disc are balanced, and the backpressure has little effect on the valve opening pressure.
Bellows failure is an important concern when using a bellows balanced safety valve, as this may affect the set pressure and capacity of the valve. It is important, therefore, that there is some mechanism for detecting any uncharacteristic fluid flow through the bellows vents. In addition, some bellows balanced safety valves include an auxiliary piston that is used to overcome the effects of backpressure in the case of bellows failure. This type of safety valve is usually only used on critical applications in the oil and petrochemical industries.
In addition to reducing the effects of backpressure, the bellows also serve to isolate the spindle guide and the spring from the process fluid, this is important when the fluid is corrosive.
Since balanced pressure relief valves are typically more expensive than their unbalanced counterparts, they are commonly only used where high pressure manifolds are unavoidable, or in critical applications where a very precise set pressure or blowdown is required.
This type of safety valve uses the flowing medium itself, through a pilot valve, to apply the closing force on the safety valve disc. The pilot valve is itself a small safety valve.
The diaphragm type is typically only available for low pressure applications and it produces a proportional type action, characteristic of relief valves used in liquid systems. They are therefore of little use in steam systems, consequently, they will not be considered in this text.
The piston type valve consists of a main valve, which uses a piston shaped closing device (or obturator), and an external pilot valve. Figure 9.2.4 shows a diagram of a typical piston type, pilot operated safety valve.
The piston and seating arrangement incorporated in the main valve is designed so that the bottom area of the piston, exposed to the inlet fluid, is less than the area of the top of the piston. As both ends of the piston are exposed to the fluid at the same pressure, this means that under normal system operating conditions, the closing force, resulting from the larger top area, is greater than the inlet force. The resultant downward force therefore holds the piston firmly on its seat.
If the inlet pressure were to rise, the net closing force on the piston also increases, ensuring that a tight shut-off is continually maintained. However, when the inlet pressure reaches the set pressure, the pilot valve will pop open to release the fluid pressure above the piston. With much less fluid pressure acting on the upper surface of the piston, the inlet pressure generates a net upwards force and the piston will leave its seat. This causes the main valve to pop open, allowing the process fluid to be discharged.
When the inlet pressure has been sufficiently reduced, the pilot valve will reclose, preventing the further release of fluid from the top of the piston, thereby re-establishing the net downward force, and causing the piston to reseat.
Pilot operated safety valves offer good overpressure and blowdown performance (a blowdown of 2% is attainable). For this reason, they are used where a narrow margin is required between the set pressure and the system operating pressure. Pilot operated valves are also available in much larger sizes, making them the preferred type of safety valve for larger capacities.
One of the main concerns with pilot operated safety valves is that the small bore, pilot connecting pipes are susceptible to blockage by foreign matter, or due to the collection of condensate in these pipes. This can lead to the failure of the valve, either in the open or closed position, depending on where the blockage occurs.
The terms full lift, high lift and low lift refer to the amount of travel the disc undergoes as it moves from its closed position to the position required to produce the certified discharge capacity, and how this affects the discharge capacity of the valve.
A full lift safety valve is one in which the disc lifts sufficiently, so that the curtain area no longer influences the discharge area. The discharge area, and therefore the capacity of the valve are subsequently determined by the bore area. This occurs when the disc lifts a distance of at least a quarter of the bore diameter. A full lift conventional safety valve is often the best choice for general steam applications.
The disc of a high lift safety valve lifts a distance of at least 1/12th of the bore diameter. This means that the curtain area, and ultimately the position of the disc, determines the discharge area. The discharge capacities of high lift valves tend to be significantly lower than those of full lift valves, and for a given discharge capacity, it is usually possible to select a full lift valve that has a nominal size several times smaller than a corresponding high lift valve, which usually incurs cost advantages.Furthermore, high lift valves tend to be used on compressible fluids where their action is more proportional.
In low lift valves, the disc only lifts a distance of 1/24th of the bore diameter. The discharge area is determined entirely by the position of the disc, and since the disc only lifts a small amount, the capacities tend to be much lower than those of full or high lift valves.
Except when safety valves are discharging, the only parts that are wetted by the process fluid are the inlet tract (nozzle) and the disc. Since safety valves operate infrequently under normal conditions, all other components can be manufactured from standard materials for most applications. There are however several exceptions, in which case, special materials have to be used, these include:
Cast steel -Commonly used on higher pressure valves (up to 40 bar g). Process type valves are usually made from a cast steel body with an austenitic full nozzle type construction.
For all safety valves, it is important that moving parts, particularly the spindle and guides are made from materials that will not easily degrade or corrode. As seats and discs are constantly in contact with the process fluid, they must be able to resist the effects of erosion and corrosion.
For process applications, austenitic stainless steel is commonly used for seats and discs; sometimes they are ‘stellite faced’ for increased durability. For extremely corrosive fluids, nozzles, discs and seats are made from special alloys such as ‘monel’ or ‘hastelloy’.
The spring is a critical element of the safety valve and must provide reliable performance within the required parameters. Standard safety valves will typically use carbon steel for moderate temperatures. Tungsten steel is used for higher temperature, non-corrosive applications, and stainless steel is used for corrosive or clean steam duty. For sour gas and high temperature applications, often special materials such as monel, hastelloy and ‘inconel’ are used.
A key option is the type of seating material used. Metal-to-metal seats, commonly made from stainless steel, are normally used for high temperature applications such as steam. Alternatively, resilient discs can be fixed to either or both of the seating surfaces where tighter shut-off is required, typically for gas or liquid applications. These inserts can be made from a number of different materials, but Viton, nitrile or EPDM are the most common. Soft seal inserts are not generally recommended for steam use.
Standard safety valves are generally fitted with an easing lever, which enables the valve to be lifted manually in order to ensure that it is operational at pressures in excess of 75% of set pressure. This is usually done as part of routine safety checks, or during maintenance to prevent seizing. The fitting of a lever is usually a requirement of national standards and insurance companies for steam and hot water applications. For example, the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code states that pressure relief valves must be fitted with a lever if they are to be used on air, water over 60°C, and steam.
Where it is not acceptable for the media to escape, a packed lever must be used. This uses a packed gland seal to ensure that the fluid is contained within the cap, (see Figure 9.2.5 (b)).
For service where a lever is not required, a cap can be used to simply protect the adjustment screw. If used in conjunction with a gasket, it can be used to prevent emissions to the atmosphere, (see Figure 9.2.6).
A test gag (Figure 9.2.7) may be used to prevent the valve from opening at the set pressure during hydraulic testing when commissioning a system. Once tested, the gag screw is removed and replaced with a short blanking plug before the valve is placed in service.
The amount of fluid depends on the particular design of safety valve. If emission of this fluid into the atmosphere is acceptable, the spring housing may be vented to the atmosphere – an open bonnet. This is usually advantageous when the safety valve is used on high temperature fluids or for boiler applications as, otherwise, high temperatures can relax the spring, altering the set pressure of the valve. However, using an open bonnet exposes the valve spring and internals to environmental conditions, which can lead to damage and corrosion of the spring.
When the fluid must be completely contained by the safety valve (and the discharge system), it is necessary to use a closed bonnet, which is not vented to the atmosphere. This type of spring enclosure is almost universally used for small screwed valves and, it is becoming increasingly common on many valve ranges since, particularly on steam, discharge of the fluid could be hazardous to personnel.
Some safety valves, most commonly those used for water applications, incorporate a flexible diaphragm or bellows to isolate the safety valve spring and upper chamber from the process fluid, (see Figure 9.2.9).
An elastomer bellows or diaphragm is commonly used in hot water or heating applications, whereas a stainless steel one would be used on process applications employing hazardous fluids.

PPI™ and Power Plus International™, and related marks and logos displayed on the Site, are our trademarks and may not be used in any way without our prior express written permission.
Disclaimer: This Code of Ordinances and/or any other documents that appear on this site may not reflect the most current legislation adopted by the Municipality. American Legal Publishing Corporation provides these documents for informational purposes only. These documents should not be relied upon as the definitive authority for local legislation. Additionally, the formatting and pagination of the posted documents varies from the formatting and pagination of the official copy. The official printed copy of a Code of Ordinances should be consulted prior to any action being taken.
For further information regarding the official version of any of this Code of Ordinances or other documents posted on this site, please contact the Municipality directly or contact American Legal Publishing toll-free at 800-445-5588.
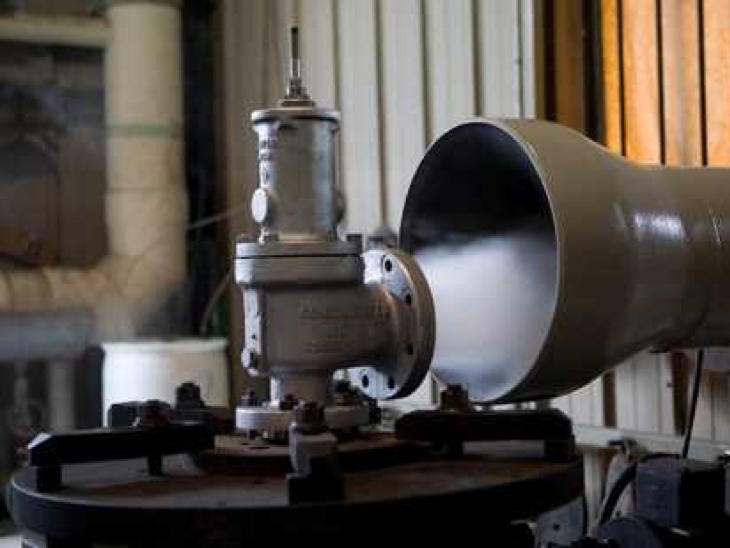

Tired of keeping track of your valve inventory’s annual certification records? We offer complete management of your safety relief valves. With an inventory of repair parts and in stock relief valves of all sizes, we can respond to any customer emergency. We offer annual certification services as well as repair of all major brands, including Kunkle, Conbraco, Consolidated, Dresser, Apollo and more.

A series of anomalies occurred in the boiler room that evening. The steel compression tank for the hydronic loop flooded, leaving no room for expansion. Water will expand at 3% of its volume when heated from room temperature to 180° F. When the burner fired, the expansion of the water increased the system pressure within the boiler. The malfunctioning operating control did not shut off the burner at the set point which caused the relief valve to open.
The brass relief valve discharge was installed with copper tubing piped solid to a 90° ell on the floor and the tubing further extended to the floor drain. The combination of hot water and steam from the boiler caused the discharge copper tubing to expand, using the relief valve as a fulcrum. The expansion of the copper discharge tubing pressing against the floor was enough to crack the brass relief valve, flooding the boiler room. The damage was not discovered until the next morning, several hours after the leak occurred. Thousands of dollars in damage was sustained and luckily no one was injured.
Each boiler requires some sort of pressure relieving device. They are referred to as either a safety, relief or safety relief valve. While these names are often thought of as interchangeable, there are subtle differences between them. According to the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors, the following are the definitions of each:
• Safety valve— This device is typically used for steam or vapor service. It operates automatically with a full-opening pop action and recloses when the pressure drops to a value consistent with the blowdown requirements prescribed by the applicable governing code or standard.
• Relief valve— This device is used for liquid service. It operates automatically by opening farther as the pressure increases beyond the initial opening pressure and recloses when the pressure drops below the opening pressure.
• Safety relief valve— This device includes the operating characteristics of both a safety valve and a relief valve and may be used in either application.
• Temperature and pressure safety relief valve— This device is typically used on potable water heaters. In addition to its pressure-relief function, it also includes a temperature-sensing element which causes the device to open at a predetermined temperature regardless of pressure. The set temperature on these devices is usually 210°.
• Relief valve piping— The boiler contractor installed a bushing on the outlet of the safety relief valve. Instead of 1 1/2-in. pipe, the installer used 3/4-in. pipe. When asked about it, he answered that he did not have any 1 1/2-in. pipe but had plenty of 3/4-in. pipe. I explained and then had to show the disbelieving contractor the code that states that the relief valve discharge piping has to be the same diameter as the relief valve outlet (see 2012 International Mechanical Code, 1006.6). By reducing the discharge pipe size, the relieving capacity of the safety valve may not be adequate to properly relieve the pressure inside the boiler, causing a dangerous situation.
The code also states that the discharge material shall be of rigid pipe that is approved for the temperature of the system. The inlet pipe size shall be full diameter of the pipe inlet for the relief valve. Some manufacturers suggest using black iron pipe rather than copper tubing. If using copper, it should have an air space that allows expansion should the relief valve open to avoid the accident that I referenced above. The discharge piping has to be supported and the weight of the piping should not be on the safety relief valve. Valves are not permitted in the inlet piping to or discharge piping from the relief valve. If you are using copper tubing on discharge piping, verify that there is room for expansion.
• Installation— Read the manufacturer’s installation manual as each may have different requirements. For instance, Conbraco requires that the discharge piping must terminate with a plain end and use a material that can handle temperatures of 375° or greater. This will preclude PVC or CPVC pipe for the discharge piping. The instruction manual for its model 12-14 steam relief valve stipulates that you cannot use a pipe wrench to install it. That would be good to know.
I once visited Boiler Utopia as the floor was clean and waxed. All the pipes were covered and exposed pipes were painted. There were large stickers detailing what was inside each pipe as well as directional arrows. Nothing was stacked next to the boilers. Yellow caution lines were painted on the floor around each boiler. I was in heaven. As I walked around the rear of the boiler, something clicked and triggered a warning bell. The discharge of the relief valve piping was about 6 in. from the floor but instead of a plain or angled cut end, the pipe had a threaded pipe cap on the termination. I asked the maintenance person about it and he said that the valve was leaking all over his newly waxed floor and this was the only way he could stop it. When I said that the discharge pipe should not have been threaded, he explained that it was not threaded and he had to take it to the local hardware store to thread it. I informed him that the cap had to be removed. We cut the pipe on an angle to prevent this.
• Steam boiler— Most manufacturers recommend a drip pan ell on the discharge of the steam boiler relief valve to eliminate the weight of the discharge piping on the relief valve. Some codes require the discharge to be vented outdoors.
• Testing— I will ask the attendees in my classes, “How often do you test the relief valves?” Most do not make eye contact and when I follow up with, “Why are they not tested?” I often hear that opening the relief valve will cause it to leak. I suggest that you refer to each manufacturer’s directions for testing. For instance, one will recommend once a year while another recommends twice a year. One manufacturer says, “Safety/relief valves should be operated only often enough to assure they are in good working order.” I am not sure what that even means. You want to also verify the proper test procedure as some will only want the relief valve tested when the boiler is at 75% of the rated pressure or higher of the relief valve.

“Our safety valves keep popping. We’ve had a contractor replace them, but they keep going bad.” It was late on a Friday afternoon and the boiler operator was angry. “We need this fixed right away!”
“Well, today they installed the fourth one,” he said. “But it also popped right after we fired the boiler. That contractor can’t fix this. Maybe you can.”
“Yes, four new ones, and they’re all crap!” he said. “I kept telling the contractor they’re getting a bad batch from their supplier, but he just doesn’t listen. Can you order us a different brand?”
“Let’s check everything first to see what is going on,” I said. “The safety valve is set to pop at 150 psi. What is the pressure gauge showing when that happens?”
“That pressure gauge stopped working around the same time the first safety valve went bad,” he said. “We haven’t had time to replace it. We need to get this safety valve replaced with a good one first. Then I’ll worry about the pressure gauge.”
I removed the gauge and opened the vent on top of the boiler so I could see steam as soon as it started to leave the boiler. After a few minutes, the steam appeared. It came out of the vent, but there was still nothing coming out of the gauge port.
“On this boiler, the pressuretrols and gauge are mounted on the branches of what we call a control tree,” I said. “See how the contractor tapped the tree off the side of the low-water cutoff? If it doesn’t get proper maintenance, the fitting that connects the tree to the low-water cutoff will clog and the controls won’t operate.”
After disassembling the control tree and removing the low-water cutoff’s head assembly, I confirmed the nipple and the elbow coming directly off the low-water cutoff were fully clogged. I don’t like the design of having all of the pressuretrols on a common pipe for this exact reason. One clog can take them all out and leave the boiler in a very unsafe condition. Only good maintenance can keep this from happening.
This was a high-pressure steam boiler, operating at 100 psi. The safety valve was popping at its set pressure of 150 psi. Instead of being piped outdoors, the safety valve’s discharge line was piped to the floor. When it popped, the entire boiler room filled with steam, which is a very dangerous condition that can lead to injury and even asphyxiation. I mentioned that to the operator.
There was nothing wrong with that pressure gauge. I sensed that because I have seen this happen before. I believe that you should never assume any device on a system is bad until you check everything. That relief valve was just doing its job. And in this case, that was a very good thing. It prevented a possible explosion.
Mike Sheppard is a commercial service technician in the Washington DC area. Mike specializes in commercial boilers and burners as well as large hydronic and steam systems.
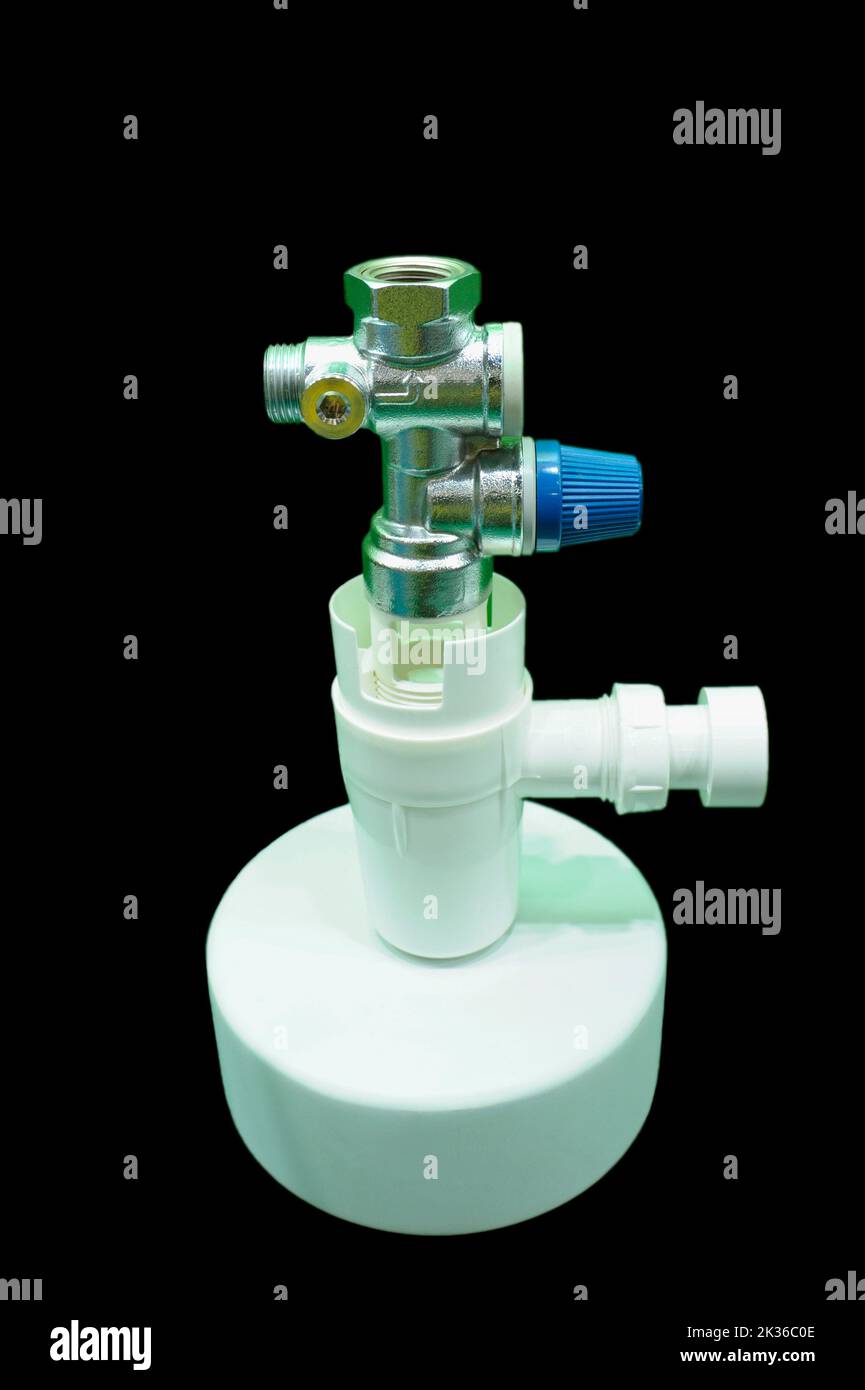

As per SOLAS chapter II-1 regulation 32 “Every steam boiler and every un-fired steam generator shall be provided with not less than 2 safety valves of adequate capacity. However, having regard to the output or any other features of any boiler or un-fired steam generator, the administration may permit only one safety valve to be fitted if it is satisfied that adequate protection against over pressure is thereby provided”.
Generally on boilers used on ship two safety valves are fitted. These safety valves are o/hauled in dry-dock and set to open at 3% more than the max allowable pressure, in presence of a surveyor. In case of economiser safety valves the valves are set by the chief engineer at sea and the surveyor is informed.
Easing gear is fitted basically to allow for manual operation of the safety valve, in case of failure to open when the boiler has been over pressurised. The easing gear also allows for regular testing of the valves at sea to ensure correct operation.
a): For a normal ship, unless there has been an incident where the boiler safety valves have been affected, the only time these valves are o/hauled and set are in dry dock in presence of a surveyor or if the survey is planned not in a drydock Or at sea in the case of economiser, these are set by the chief engineer. After the setup these valves are not adjusted until the next dry dock. In other words no maintenance is carried out on these valves.
The valve may fail to operate due to a broken spring, or if the set point has changed due to excessive vibration. If the drain line is choked then fluid can accumulate above the valve causing the set pressure to change, in such a case the valve will operate at a higher pressure than the set point. If these things occur then the easing gear can be used to manually operate the valve and prevent a catastrophe from taking place.
b): Preventive maintenance is very important for proper operation of a ship. Part of an efficient PMS is to try out all standby and passive equipment, especially safety devices like relief valves and safety valves. Same goes for the safety valve of the boiler. Even though the valves have been o/hauled and tried out in front of class surveyor, it is very important to try out these valves at regular intervals. It would be highly dangerous and impractical to try out these valves by over pressurising the boiler.
The easing gear allows the ship staff to try out the safety valve during normal operation, without interfering with ship operations. The condition of the spring can also be determined by this. Operating the safety valve a few times by the easing gear helps in freeing up the mechanism which can be jammed due to it being at standstill for long time. The condition of the easing gear can also be determined during this test. The easing gear consists of levers, cables and pulleys, which have to be regularly lubricated and cleaned. Operating the safety valve with easing gear also gives the condition of easing gear.

As a design engineer responsible for developing and specifying boilers, dryers, furnaces, heaters, ovens and other industrial heating equipment, you face a daunting labyrinth of standards and industry regulations. Regulatory bodies sound a bit like alphabet soup, with acronyms like UL, FM, CSA, UR, AGA, ASME, ANSI, IRI, CE and NFPA tossed about. This article will help explain a common task for many thermal processing equipment specifiers: meeting the requirements of key codes — including Underwriters Laboratories (UL), Factory Mutual Insurers (FM) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) — for safety valve equipment used in process heating applications.
Key to designing safety into your fuel train configurations are familiar technologies such as safety shutoff valves and vent valves as well as visual-indication mechanisms and proof-of-closure switches.
Your design skills come into play with how you take advantage of the wide range of products available. You can mix and match solenoid and safety shutoff valves — within designs from catalytic reactors to multi-zone furnaces — to create easily installed, cost-effective solutions that comply with all necessary standards. (See table.)
Make sure, however, that you start with a good grasp of valve element fundamentals. For example, examining a proof-of-closure (POC) switch underlines how reliably modern valves can ensure combustion safety. The POC unit provides an electrical contact interlocked with the controller safety circuit. In a typical design, the switch is located at the bottom of the valve, positioned to trace the stroke of the valve disc. When the disc seal reaches the fully closed position, it triggers the mechanism to push down on the contact, closing it and triggering the unit’s visual indicator to show open or closed status. As a result, the operator can act with full confidence in situations where it is critical that a safety valve be safely closed.
To provide ease of installation, many users prefer valves with modular capabilities. For example, to reduce mounting complexity, you can choose modular gas safety shut-off valves — combining a solenoid valve with an electrohydraulic motorized valve for a compact double-valve footprint, a slow-open feature and high flow rates. An accompanying actuator can provide on/off or high/low/off firing rates as well as visual indication and proof of closure for compliance with most industry standards.
Also, you may want to look for valves that include useful features such as pipe taps, which can facilitate accurate pressure readings and leakage testing.
Knowing your valve choices — and how they meet given codes and standards — can reduce the time required for design and production while facilitating compliance. This results in safer, more efficient and cost-effective heating process installations.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

To provide a designed-to-fail pressure-relief valve so that the entire system does not explode. In general, redundant systems are designed such that the first one fails at a system-wide safe level, the second one fails at some specified point below the failure point of the boiler itself. For example, the heating system in our house has elements within it that are designed for up to3 bar of pressure. The boiler itself is designed at4 bar. The TPRV is designed at2 bar @120C as a single device to cover the boiler/heat loop. However, the internal domestic water heating loop TPRV is set at7, bar but only95C and the loop is designed at10 bar.

We are passionate about making great espresso based beverages. It all start with the top quality brands we offer our residential and commercial customers.




 8613371530291
8613371530291