non rotation vs rotation resistant wire rope in stock

Rotation resistant wire rope refers to a series of steel ropes which minimizes the tendency to spin or rotation under load. These wire ropes boast special design - the outer layer is twisted in the reverse direction of inner layers for counteracting torsional forces generated from multi-layers of strands.
To achieve the resistance against the spin and rotation, all wire ropes are composed of at least two layers of strands. In general, more layers a rotation resistant wire rope has, more resistance it will boast. For example, 2-layer ropes is much easier to spin and rotate than 3-layer ones. Meanwhile, if one end of free rotation is allowed, 2-layer rope can only develop 55% to 75% of its breaking strength comparing with 95% to 100% of 3-layer ropes.
The 3-layer rope with more outer strands is capable to distribute more radial pressure onto inner layers and ideal for larger mobile such as all tower cranes.
Wire ropes with 8 to 10 strands & 2-layer constructions without reversely twisted inner strands have very similar appearance to rotation resistant wire ropes, but they are not.
Rotation resistant wire ropes are considered to be less stable needing to be handled and installed with great care. They must be taken to avoid high loads with small diameter sheaves.

Rope Services Direct supplies a variety of anti-spin non rotating wire rope (also called rotation resistant wire-rope). All standard rope wirehas a tendency to develop torque and therefore prone to rotation, whereas non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force. This is in the event that a rope is subjected to a load.
Rope elongation and rotation occurs on standard ropes when loaded, which can therefore spin the load, quite possibly out of control, which can be dangerous. When the rope rotates in this way the strands will begin to unravel. This causes the rope to lose strength and will undoubtedly fail, which could be catastrophic. It is for these reasons that non rotating wire rope is commonly used for many types of lifting applications including main hoist rope, whip rope,crane rope, off-shore and deck rope and more.
Non rotating wire rope or rotation resistant wire rope has a different construction to standard. as wires and strands are not laid in the same direction like they would be on standard rope. Inner and outer strands of wires are laid in opposite directions. For example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. The nature of this construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires/strands will counteract each other and therefore minimising the risk of unraveling.
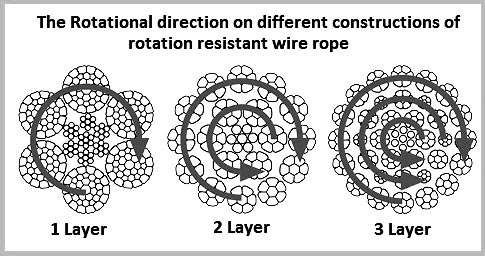
It is worth noting that the number of strand layers will have an effect of the resistance of rotation. A 2 layer rope has less resistance than a 3 layer rope. Therefore the more layers the rope has the greater rotation resistance it will have.
These types of ropes can be classified as spin resistant, rotation resistant or non rotation resistant. Classed on the basis of the number of rotations a certain length of rope does when a force of 20% of the MBF is applied; with 1 turn or less the rope will be classified as non rotating; with rotations between 1 & 4 the rope is classed as low rotation and for rotations between 4 & 10 the rope will be classified as spin resistant, any higher and the rope is NOT rotation resistant at all.
Correct usage and care with handling will prolong the working life. This is due to the friction on the inner wires caused by the strand crossover’s which will eventually cause the inner wires to break up. This is more apparent on non rotating wire rope with two layers. Ropes with 3 or more strand layers will distribute the radial pressures more evenly. Which will reduce friction and stress on the inner wires.
Regular,thorough inspectionsof non rotating rope are essential due to the fact that it is the inner strands that often break first and broken internal wires often go unnoticed as they are difficult to see.Rope Services Direct offer inspectionson all rope with certification issued on completion.
Holding both ends of the rope will prevent unraveling. Correctly fitted terminations will help to prevent damage. Kinking and unraveling may occur and they can also have an effect on the rotational balance if not fitted correctly.
Non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force in the event of a load applied.
Rather than all wires and strands being laid in the same direction, a rotation resistant wire rope consists of inner strands being laid in the opposite direction to the outer layers, for example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. This construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires / strands will counteract each other and so minimise the risk of unraveling.
Using an ordinary lifting wire rope for a job or equipment which demand a non-rotating wire rope si very dangerous and it presents the following risks:
The most important factor in selecting the right wire rope for the job in hand is deciding whether a rope type is to be rotation resistant or non-rotation resistant. This point needs to be considered very carefully as using the wrong rope type can have serious consequences, for example, shortened service life, changes in the rope structure, unintentional rope breaks.
Rotation resistant ropes must be used for the lifting of an unguided load on a single fall,the lifting of an unguided load on several falls at a great lifting height
Non-rotation resistant ropesmust be used for the lifting of a guided load,the lifting of unguided loads on several falls at low lifting heights,the lifting of loads with right-handed and lefthanded ropes operating in pairs, Non-rotation resistant ropes must not be used with a swivel.
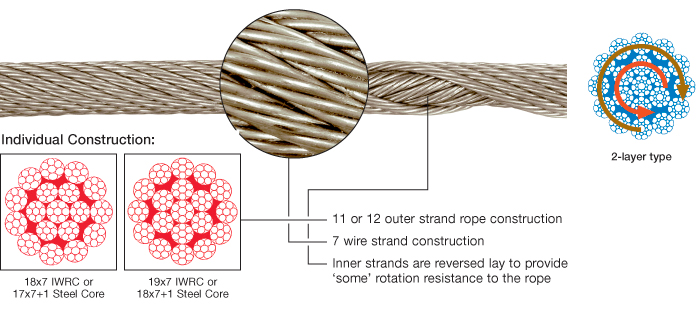
The characteristic of these wire ropesare that the outer layer is twisted in the opposite direction of their inner layers. The sometimes confusing issue is that many 8-, 9- and 10 strand constructions are 2-layer types but their inner strands are NOT twisted in the opposite direction and therefore these rope are NOT spin-resistant; plus, for the untrained eye these ropes look very much alike their spin-resistant variants. These and regular 6-strand ropes will spin violently and unlay themselves when loaded when one rope end is allowed to spin freely. They may also develop a significant drop in breaking strength and an even larger drop in their fatigue life characteristic (Torsion Fatigue).
To achieve any degree of resisting the tendency of a rope to spin and unlay under load all such rope types (other than 4-strand ones) are constructed with 2 or more layers of opposite twisted strands (see picture on right).
2-layer ropes (MULTI, compacted 18xk7) have a larger tendency to rotate than 3-layer ones (e.g. Class 34 x 7, compacted 35WXK7). Furthermore, 2-layer spin-resistant and rotation resistant ropes will develop only about 55% to 75% of their breaking strength when one end is allowed to rotate freely. This number increases to between 95% to 100% for 3-layer (e.g. 35WXK7 compacted) non-rotating ropes.
Another important issue is that 2-layer rotation resistant and 2-layer spin-resistant rope types have shown to break up from the inside. The 8 (e.g. 8×25 spin-resistant) or 12 outer strands (19×7, 19×19, 18XK7) are not able to evenly distribute the radial forces and because of the inherent internal strand cross overs (which make the rope spin- or rotation resistant) the resultant severe notching stresses cause the rope core to break up premature (unless the core is plastic coated). Unexpected and sudden rope failures may be the result. Moreover, 2-layer spin-resistant or rotation resistant ropes satisfy only low to moderate rotational resistance demands.
3-layer rope constructions (e.g. compacted 35WXK7) have many more outer strands which can much better distribute the radial pressures onto the reverse lay inner strands. These ropes should be selected for larger mobile- and ALL tower cranes.
Non-rotating (non-rotational) wire ropes are used in various on and offshore cranes, various machinery, winches and trolleys, in the maritime and fisheries sector, on and offshore oil exploitation, civil and industrial construction, engineering and infrastructure works, underground and surface mining, timber mining and numerous other industries and applications.

The term “rotation resistant wire rope” refers to a type of wire rope that is designed to resist the inclination to spin or rotate under stress. These ropes are typically used as single-part lines or in instances where the operating requirements need a rope that can withstand cabling in a multipart system. The basic nature of rotation resistant rope designs places certain restrictions on their use and necessitates certain handling requirements not seen in other rope types.
Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to minimize load rotation during a lift. When lifting with other types of wire rope, elongation and rotation is normal. This can cause a load to spin, possibly out of control, which is a serious safety issue. Thus, rotation resistant wire rope is essential for any application where a load is lifted by a single line.
Rotation resistant wire rope is created by twisting the outer layer of the rope in the opposite direction to the inner layers of the rope. When under tension the opposing rotational forces cancel each other out.
2) Multilayer strand (Multistrand): two or more strand layers that are closed in opposite directions. Each layer of the rope generates torsional pressures that balance each other out, reducing rotation.
It’s important to remember that the amount of strand layers has an impact on rotational resistance. The resistance of a two-layer rope is lower than that of a three-layer rope. As a result, the more layers a rope has, the greater its rotation resistance.
Hercules SLR offers a wide selection of rotation resistant wire rope products and can custom fabricate rotation resistant wire rope products for specific requirements.
The inner core in rotation resistant wire rope can twist more tightly when a swivel is used. This significantly reduces rope strength and possibly causing early rope failure. Only during the initial installation phase, a swivel may be employed as a temporary device to help prevent any twisting of cabling caused by the installation process.
Once the rope installation is finished and the crane is operational, the swivel needs to be taken out of the reeving. With some rotation-resistant ropes, a swivel may be utilised; always check with the manufacturer.

Rotation resistant ropes are known to provide the best and most economical services for specific applications. When the correct ropes are selected and appropriately used, they are unmatched in the lifting market. Elephant hoists greatly benefit from rotation resistant wires.
Rotation resistance is created when wires are laid in a contra-helical position. These ropes are different from standard construction types because rotation resistant ropes are required to meet a different and higher set of service requirements. The modes of wear and failure for these ropes vary more than standard constructions. Special operational needs make specific limitations and special handling necessary. These are not encouraged with standard constructions.
Testing on ropes that are resistant to rotation commonly shows that the total length of service for these ropes is shorter than that of standard construction ropes. The tests show that there is a need for separate guidelines for the use, inspection, retirement, and application of resistant ropes.
Using a swivel at the load hook for rotation resistant ropes results in unpredictable service life. This type of practice can potentially lead to unbalanced loading between outer and inner layers of strands. This typically results in core failure. Any significant changes in diameter found in a small length of operating rope should be retired and replaced. Make sure to use appropriate rigging supplies for all crane wire rope applications.
For more information on the benefits of rotation resistant ropes, you should not hesitate to give our team a call. Do not forget to ask about our V rope options.

The characteristic of these wire ropes are that the outer layer is twisted in the opposite direction of their inner layers. The sometimes confusing issue is that many 8-, 9- and 10 strand constructions are 2-layer types but their inner strands are NOT twisted in the opposite direction and therefore these rope are NOT spin-resistant; plus, for the untrained eye these ropes look very much alike their spin-resistant variants. These and regular 6-strand ropes will spin violently and unlay themselves when loaded when one rope end is allowed to spin freely. They may also develop a significant drop in breaking strength and an even larger drop in their fatigue life characteristic (Torsion Fatigue).
To achieve any degree of resisting the tendency of a rope to spin and unlay under load all such rope types (other than 4-strand ones) are constructed with 2 or more layers of opposite twisted strands (see picture on right).
2-layer ropes (MULTI, COMPAC 18) have a larger tendency to rotate than 3-layer ones (e.g. Class 34 x 7, COMPAC® 35). Furthermore, 2-layer spin-resistant and rotation resistant ropes will develop only about 55% to 75% of their breaking strength when one end is allowed to rotate freely. This number increases to between 95% to 100% for 3-layer (e.g. COMPAC® 35) non-rotating ropes.
Another important issue is that 2-layer rotation resistant and 2-layer spin-resistant rope types have shown to break up from the inside. The 8 (e.g. 8×25 spin-resistant) or 12 outer strands (19×7, 19×19, COMPAC®18) are not able to evenly distribute the radial forces and because of the inherent internal strand cross overs (which make the rope spin- or rotation resistant) the resultant severe notching stresses cause the rope core to break up premature (unless the core is plastic coated, e.g. Python® Multi). Unexpected and sudden rope failures may be the result. Moreover, 2-layer spin-resistant or rotation resistant ropes satisfy only low to moderate rotational resistance demands.
3-layer rope constructions (e.g. COMPAC® 35) have many more outer strands which can much better distribute the radial pressures onto the reverse lay inner strands. These ropes should be selected for larger mobile- and ALL tower cranes.

This wire rope construction is available in both galvanised and ungalvanised finish with either ordinary or langs lay. The construction family includes 17X7, 18X7 and 19X7. For further flexibility and other performance characteristics we also supply 32X7, 35X7 and 37X7.
Depending upon your requirement for higher breaking load or better wear characteristics, these wire ropes are available in different finishes and lubrications as well as being available with plastic impregnated.

Non rotation resistant steel wire ropes are usually made of 6 or 8 outer strands. They are the most commonly used to perform lifting operations that do not present specific problems or require high performance such as standard overhead cranes or traction winches. They are used as well to manufacture any kind of slings, pennants and grommets.
SIRTEF usually has on stock a large stock of ropes of almost any kind, either with fiber core or steel core, either in bright or galvanized finishing and even in stainless steel un-magnetic. Our ropes may be supplied either fully or partially lubricated ( dry outside and lubricated inside).
As mentioned before it is quite common that the 8 strands ropes are manufactured with a plastic extrusion between the core and the outer strands. This technical feature has several advantages as it protect the core from wear and corrosion (weatherproof), it guarantees a better geometrical stability of the construction and maintain the inside always lubricated.

We stock a wide variety of rotation resistant wire ropes from several manufacturers.Some types of wire rope, especially lang lay wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation when under load. Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or rotating and can be used in a single line or multi-part system.Special care must be taken when handling, unreeling, and installing rotation resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce twist into the rope which can cause uncontrolled rotation.Call us at 800.362.4601 or click here to get the rotation resistant wire rope you need!

Non-rotating wire ropes are made so that the outer rotational force of the wire rope naturally balances the rotational force of the inner strands. Standard rope wire has a tendency to create torque and is thus prone to rotation.
In the past, wrought iron chains, which had a history of mechanical failure, gave rise to wire rope. Defects in solid steel bars or chain links can result in catastrophic failure, whereas flaws in the wires that make up a steel cable are less important because the other wires can readily carry the strain. Although friction between the various wires and strands wears the rope over time, it also aids in temporary repair of minor flaws.
This pertains to the scenario in which a load is applied to a rope. In order to create a composite rope known as wire rope, numerous strands of metal wire are twisted into a helix in a pattern called lay rope. A larger diameter wire rope is made up of several strands of this lay rope arranged in a style called cable laid.
The global non rotating wire rope marketaccounted for $XX Billion in 2021 and is anticipated to reach $XX Billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of XX% from 2022 to 2030.
In terms of value, Regular Type of Lay is the fastest-growing Type of Lay for Steel Wires.Lang lay ropes spool poorly in a drum and are less naturally rotation-resistant and resistant to crushing forces than regular lay ropes.
They are employed in a variety of fields, including mining, oil and gas, construction, fishing, and marine. To address the unique wire rope needs of the new cranes, South Korean speciality high carbon steel wire products producer “Kiswire” is growing its operations in India. They not only serve as OEM suppliers to numerous global crane manufacturers, like Tadano and Kobelco, but they also actively pursue the Indian Replacement Market.

The very basic rotation resistant wire rope mostly used as hoisting rope (Single Point Line) and lifeboat falls. It can be widely found on small working capacity of electric wire rope hoist and winches. 35X7 is then invented to provide better performance comparing to 19X7 and other similiar rotation resistant rope. The rotation resistant characteristic of 19x7 rope is acheived by laying six strands around one core strand in one direction and then laying 12 strands around the first wire strand in the opposite direction. Opposing rotational forces are created at inner and outer layer when the rope is in tension. It has a relatively low reserve strength comparing to other rotation resistant rope. Using the rope to it’s maximum fatigue life will cause the rope to deteriorate from the inside out. Sudden rope failures may be the result. For this reason we do not recommend this construction for tower cranes.

Main and auxiliary hoist line for mobile and for all types of construction tower cranes which require a high strength rotation resistant rope construction.
The large number of outer strands distribute the pressures introduced by sheaves and drum more evenly onto the core minimizing the danger of unexpected rope failures because of undetected core deterioration.
Aside from this safety issue PYTHON® COMPAC 35 satisfies the high-strength requirements of late model tower and mobile cranes which can NOT be met with neither 19 x 7 nor 19 x 19 style ropes.




 8613371530291
8613371530291