non rotation vs rotation resistant wire rope pricelist
Rope Services Direct supplies a variety of anti-spin non rotating wire rope (also called rotation resistant wire-rope). All standard rope wirehas a tendency to develop torque and therefore prone to rotation, whereas non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force. This is in the event that a rope is subjected to a load.
Rope elongation and rotation occurs on standard ropes when loaded, which can therefore spin the load, quite possibly out of control, which can be dangerous. When the rope rotates in this way the strands will begin to unravel. This causes the rope to lose strength and will undoubtedly fail, which could be catastrophic. It is for these reasons that non rotating wire rope is commonly used for many types of lifting applications including main hoist rope, whip rope,crane rope, off-shore and deck rope and more.
Non rotating wire rope or rotation resistant wire rope has a different construction to standard. as wires and strands are not laid in the same direction like they would be on standard rope. Inner and outer strands of wires are laid in opposite directions. For example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. The nature of this construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires/strands will counteract each other and therefore minimising the risk of unraveling.
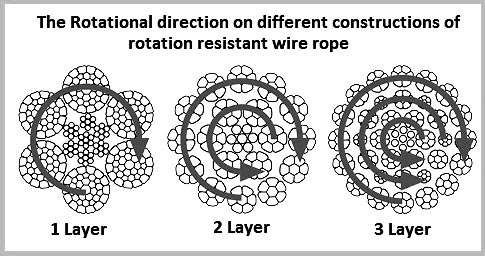
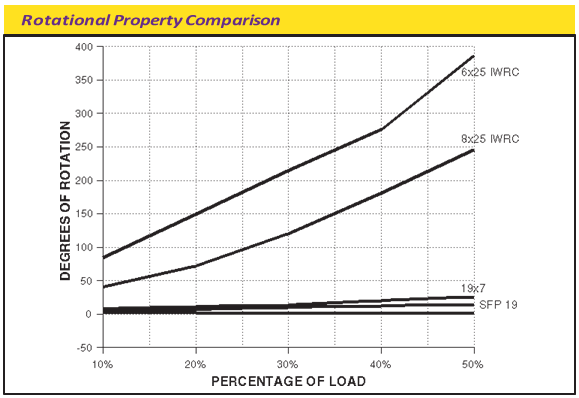
It is worth noting that the number of strand layers will have an effect of the resistance of rotation. A 2 layer rope has less resistance than a 3 layer rope. Therefore the more layers the rope has the greater rotation resistance it will have.
These types of ropes can be classified as spin resistant, rotation resistant or non rotation resistant. Classed on the basis of the number of rotations a certain length of rope does when a force of 20% of the MBF is applied; with 1 turn or less the rope will be classified as non rotating; with rotations between 1 & 4 the rope is classed as low rotation and for rotations between 4 & 10 the rope will be classified as spin resistant, any higher and the rope is NOT rotation resistant at all.
Correct usage and care with handling will prolong the working life. This is due to the friction on the inner wires caused by the strand crossover’s which will eventually cause the inner wires to break up. This is more apparent on non rotating wire rope with two layers. Ropes with 3 or more strand layers will distribute the radial pressures more evenly. Which will reduce friction and stress on the inner wires.
Regular,thorough inspectionsof non rotating rope are essential due to the fact that it is the inner strands that often break first and broken internal wires often go unnoticed as they are difficult to see.Rope Services Direct offer inspectionson all rope with certification issued on completion.
Holding both ends of the rope will prevent unraveling. Correctly fitted terminations will help to prevent damage. Kinking and unraveling may occur and they can also have an effect on the rotational balance if not fitted correctly.

Rotation resistant wire rope refers to a series of steel ropes which minimizes the tendency to spin or rotation under load. These wire ropes boast special design - the outer layer is twisted in the reverse direction of inner layers for counteracting torsional forces generated from multi-layers of strands.
To achieve the resistance against the spin and rotation, all wire ropes are composed of at least two layers of strands. In general, more layers a rotation resistant wire rope has, more resistance it will boast. For example, 2-layer ropes is much easier to spin and rotate than 3-layer ones. Meanwhile, if one end of free rotation is allowed, 2-layer rope can only develop 55% to 75% of its breaking strength comparing with 95% to 100% of 3-layer ropes.
The 3-layer rope with more outer strands is capable to distribute more radial pressure onto inner layers and ideal for larger mobile such as all tower cranes.
Wire ropes with 8 to 10 strands & 2-layer constructions without reversely twisted inner strands have very similar appearance to rotation resistant wire ropes, but they are not.
Rotation resistant wire ropes are considered to be less stable needing to be handled and installed with great care. They must be taken to avoid high loads with small diameter sheaves.

The characteristic of these wire ropes are that the outer layer is twisted in the opposite direction of their inner layers. The sometimes confusing issue is that many 8-, 9- and 10 strand constructions are 2-layer types but their inner strands are NOT twisted in the opposite direction and therefore these rope are NOT spin-resistant; plus, for the untrained eye these ropes look very much alike their spin-resistant variants. These and regular 6-strand ropes will spin violently and unlay themselves when loaded when one rope end is allowed to spin freely. They may also develop a significant drop in breaking strength and an even larger drop in their fatigue life characteristic (Torsion Fatigue).
To achieve any degree of resisting the tendency of a rope to spin and unlay under load all such rope types (other than 4-strand ones) are constructed with 2 or more layers of opposite twisted strands (see picture on right).
2-layer ropes (MULTI, COMPAC 18) have a larger tendency to rotate than 3-layer ones (e.g. Class 34 x 7, COMPAC® 35). Furthermore, 2-layer spin-resistant and rotation resistant ropes will develop only about 55% to 75% of their breaking strength when one end is allowed to rotate freely. This number increases to between 95% to 100% for 3-layer (e.g. COMPAC® 35) non-rotating ropes.
Another important issue is that 2-layer rotation resistant and 2-layer spin-resistant rope types have shown to break up from the inside. The 8 (e.g. 8×25 spin-resistant) or 12 outer strands (19×7, 19×19, COMPAC®18) are not able to evenly distribute the radial forces and because of the inherent internal strand cross overs (which make the rope spin- or rotation resistant) the resultant severe notching stresses cause the rope core to break up premature (unless the core is plastic coated, e.g. Python® Multi). Unexpected and sudden rope failures may be the result. Moreover, 2-layer spin-resistant or rotation resistant ropes satisfy only low to moderate rotational resistance demands.
3-layer rope constructions (e.g. COMPAC® 35) have many more outer strands which can much better distribute the radial pressures onto the reverse lay inner strands. These ropes should be selected for larger mobile- and ALL tower cranes.
The most important factor in selecting the right wire rope for the job in hand is deciding whether a rope type is to be rotation resistant or non-rotation resistant. This point needs to be considered very carefully as using the wrong rope type can have serious consequences, for example, shortened service life, changes in the rope structure, unintentional rope breaks.
Rotation resistant wire rope is a special category (class) of wire rope designed to resist the tendency to spin or rotate under load. In general these ropes are used as single part lines, or in situations where operating conditions require a rope that will resist cabling in a multipart system. The essential nature of rotation resistant rope designs impose certain limitations on their application and necessitate special handling requirements not encountered with other rope constructions.
2) Multilayer strand (Multistrand)-consisting of two or more strand layers closed in opposing directions. Torsional forces generated by each layer of the rope counteract one another to minimize rotation.
The multistrand classification includes ropes with between eight and twenty outer strands. Table 1 of this manual describes some of the more commonly available rotation resistant multistrand rope classification. In addition to these, a wide variety of special multistrand ropes is available. See (Figure 9). It would be impractical to cover the specific features of each in this manual.
In multistrand rotation resistant ropes the crossover points between strand layers are points of high stress concentration. Relative motion of the strands at these points results in accelerated deterioration of the internal components of the rope. Because of this design characteristic of the multistrand construction, care must be taken to avoid high loads with small diameter sheaves. Design factors less than five are not recommended.

Bayou City Wire Rope is an American owned and operated company based out of Humble, Texas. Bayou City Wire Rope is proud to distribute some of the industries most reliable specialty wire ropes for virtually every application. We distribute high-quality specialty wire ropes in the North American marketplace for construction, marine, oilfield and other diversified markets across the continent. Our high-performance steel wire ropes are used for Tower Cranes, Crawler Cranes, Truck Mounted Cranes, Foundation Cranes, Telescopic Mobile Cranes, Overhead Cranes, Still Mill Cranes, Gantry Cranes, as well as Ship Deck Cranes. With our location in Southeast Texas, we’re able to service the entire continent with the quickest delivery time possible. Bayou City Wire Rope is dedicated to delivering a quality product with efficient and effective service. “Quality Ropes Provided with Integrity”

19x7 wire rope is recommended for hoisting unguided loads with a single-part line. The rotation-resistant properties of this rope are superior to those of the 8x19 class wire ropes, and are secured by two layers of strands. The inner strands are left lay, while the 12 outer strands are right lay, which enables one layer to counteract the other layer’s rotation.
Galvanized wire rope (steel) features a compressed zinc coating for providing excellent corrosion resistance. With a higher break strength, yet lower price than stainless steel wire rope, galvanized steel wire rope is widely used in general engineering applications such as winches and security ropes.
The bright class of industrial wire rope is produced without a surface treatment—making the rope less likely to untwist or kink while giving it a stronger crush resistance than lay ropes. Generally, they are fully lubricated to protect the rope from rust and corrosion. Also available in USA-made.
Non-rotation resistant ropes usually achieve more bending cycles than rotation-resistant ropes or semi-rotation resistant ropes. However, they exert a torque on the end fitting when under load.
Non-rotation resistant ropes are always the right choice, when the characteristic “rotation-resistance”, which only rotation-resistant ropes offer, is not required. This is the case for many rope applications, e.g. for luffing ropes, trolley ropes, pendant ropes or installation.
Note: With coupling of non-rotation resistant ropes, e.g. pendant ropes or grab ropes, only identical ropes of the same construction, meaning: the same diameter, the same lay type and lay direction have to be used (figure 78). Combining ropes with different lay directions would turn up the ropes and thus destroy them.

There are a variety of cables and wires that are used for various purposes. They can either be hidden underground or pass overhead. Crane Cable is one such cable wire rope made out of several strands of metal wires that are twisted together into a helix form to make them into a single rope. Initially, wrought iron was used to make these Crane Cables however, these days steel is the primary material used. Apart from this high carbon steel and galvanized steel are also used in manufacturing these cables. Dents or flaws in the ordinary link chain can lead to severe failure whereas, damage in these EOT Crane Cablecan be easily covered up. Ther are ideally used for lifting elevators, in the transmission of mechanical power, and in cranes.
Crane Lifting Cables are resistant to corrosion and have excellent ductility for optimal fatigue. They have a high breaking strength compared to steel crane wire rope. The radially elastic rope structure absorbs the dynamic force thus giving it high impact resistance. Crane Cable Wires are said to be cost-effective as a strong and durable structure helps in reducing maintenance costs and downtime. They can be coated with bright phosphate or galvanized depending upon the customers’ requirements.
Crane Electrical Cable is available in rotating, rotation, compact, or non-compact structures. Most of the wire ropes have the tendency of developing torque and are thus prone to rotation. However, non-rotation wires are designed in a way that their outer rotation naturally counteracts the inner strands rotation. Crane Hoist Cable can be used in tower crane ropes or offshore crane ropes.
Overhead Crane Cable reel should be capable of winding it automatically. The drive torque of the crane cable should not be less than the max winding torque of the winding crane cable. The cable conductor should be as small as possible when the Crane Rope laying acts on the traction force.
The Crane Wire Rope does not have a reinforcement core, the maximum tension allowed on the copper conductor cross-section is 20N/mm2. We at Bhuwal Insulation Cable Pvt. Ltd. not only provide you the best quality Tower Crane Cable but also the parts required to assemble them. Our long-standing reputation in providing the best quality product at a competent price has made us one of the leading Crane Cable manufacturers in India.
Cables or cords are the wire ropes which have diameters smaller than 3/8 inches, While wire ropes have diameters greater than 3/8 inches. if there are two or more wire concentrically laid then it is known as strand
Warrington: Two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of wire in the inner layer and two diameters of wire alternating large and small in the outer later
6 by 19 is a type of wire rope which can withstand fatigue resistance, abrasion and prevents crushing on drums. it is available in diatmeter range of 3mm to 6 mm. While 7 by 19 are wire rope which has diameters ranging between 3 mm to 16 mm which can be use in different applications.

Ropes are materials produced to perform various tasks such as lifting, lowering, tying and carrying an item or load. The parts with the small rope structure bend in one direction and the arm is formed. These arms are brought together again and twisted to form ropes. Ropes are produced with different raw materials according to the usage area and the work to be done. It is among the rope types that are frequently used in steel ropes.
Steel core steel rope is a type of rope in which the arm in the core of the rope and the arms on the edges are produced by forming steel wires. Steel core steel ropes are very durable and strong ropes as they are produced entirely from steel. Each type of steel core wire rope offers the opportunity to do professional work in different areas of use with its features.
Ropes are used in different ways by undertaking various functions such as pulling, holding, lifting and lowering. The usage areas of steel core steel ropes are generally as follows;
Steel core steel ropes are produced in line with the needs of the usage area. Since it is different for each working area and shape, rope types with different properties are designed and produced. The most commonly used types of steel core steel rope are as follows;
Ropes offer various advantages to the user thanks to their features. Increasing work efficiency and quality is its most important advantage. In addition, they offer a great advantage in providing the necessary conditions for occupational safety. The properties of steel core steel ropes can be listed as follows;
Steel core steel ropes are different from each other in terms of design, production and use. The cost figure for each product also changes based on these reasons. The prices of steel core steel ropes are determined separately for each type. In this case, it is more accurate to obtain price information after determining the type of steel rope that is suitable for the operation and the work to be done.

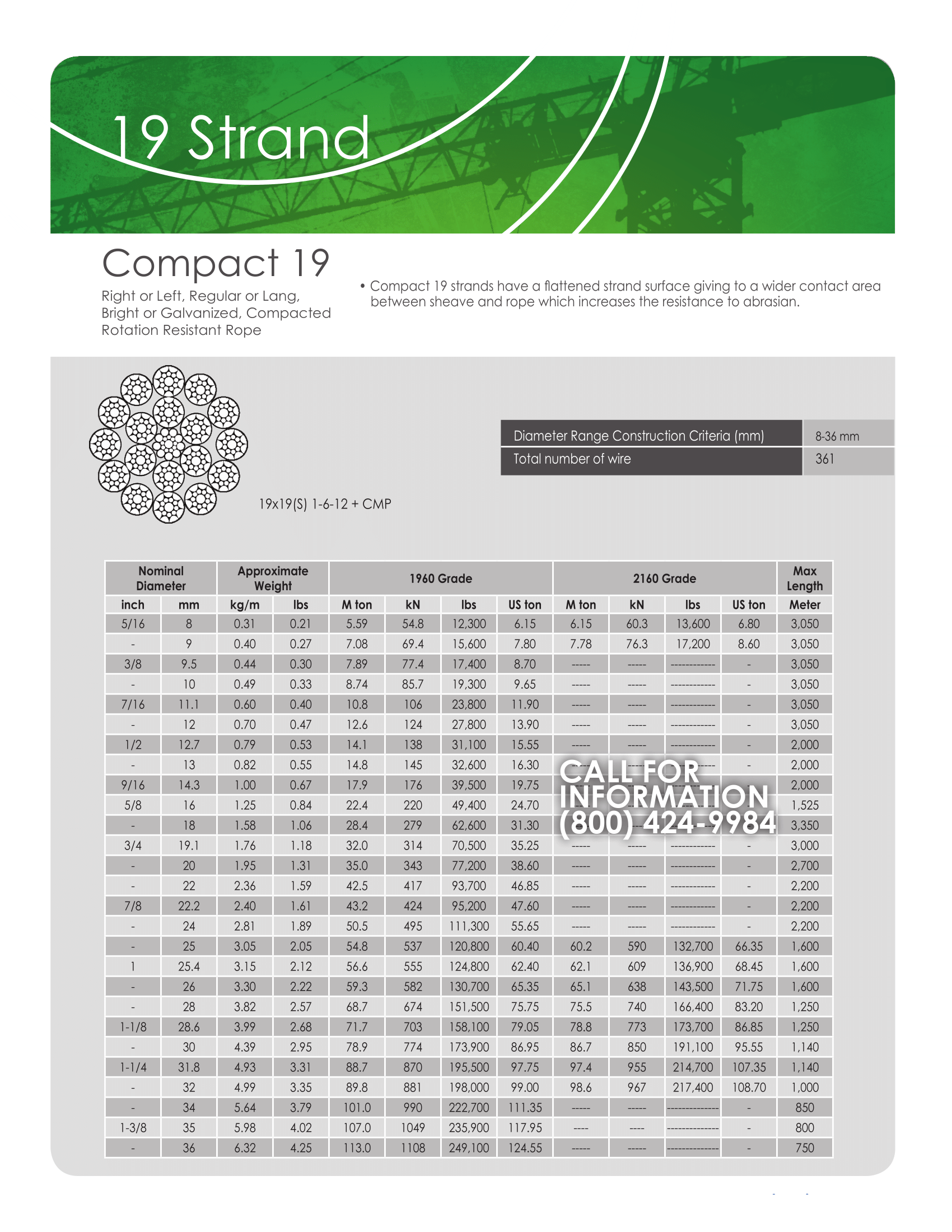
Assembled from 19 strands of wire, the Galvanised steel core anti-rotation wire rope is stiffer than a standard rope. Typically, the ropes consist of 7 to 61 strands with right-handed cross-wiring. Ropes of the same diameter may have different numbers of strands and wires. The more wires the rope has, the softer it is. However, a rope with large diameter wires will be stiffer than a rope with smaller diameter wires.
The 19x7 Galvanised Steel Rope is available in12mm diameter. Designed for the construction of treetop adventures courses t, it is especially used for the installation of zip lines. The 12mm diameter rope has abreaking load of 9 437kg. It belongs to the strength class 1960 N/mm2.
The wires rope is cut by our teams to the lengths you want. For the assembly of the19x7 galvanised steel non-rotating wire rope, remember to add the necessary accessories.
A wire rope requires a regular check of its condition. It is therefore important to check it in its entirety and more particularly in places where it is subjected to greater stress, leading to frequent damage. Broken wires, distortion of the strands, lengthening of the pitch or the appearance of rust are points to be checked regularly. Storage of the Galvanised steel Rope in a dry place without contact with the ground will preserve the material as much as possible and prevent wear.
SWR supply a large range of non-rotating wire ropes in both galvanised and ungalvanised finish with either ordinary or langs lay. Depending upon your requirement for higher breaking load or better wear characteristics, these wire ropes are available in different finishes and lubrications as well as being available with plastic impregnated.
Non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force in the event of a load applied.
Rather than all wires and strands being laid in the same direction, a rotation resistant wire rope consists of inner strands being laid in the opposite direction to the outer layers, for example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. This construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires / strands will counteract each other and so minimise the risk of unraveling.
Using an ordinary lifting wire rope for a job or equipment which demand a non-rotating wire rope si very dangerous and it presents the following risks:

The choice of the lay type must consider the specific use of the rope, the rope construction, crane components and the expected wear factors in use, which determine the lifetime of the rope substantially.
The aim of the rope choice is a high rope lifetime ensuring a high safety factor at the same time, which means the operator can recognize the secure operating condition of the rope reliably at any time, considering the discard criteria of the specific application. Therefore a general statement about the use of regular or lang’s lay ropes is not possible or not useful without knowledge of the specific case/application.
Ordinary lay ropes are widespread which are therefore presumably considered as universally applicable. Ordinary lay ropes have a very good structural stability due to the opposing stranding of the wires and strands which make them more resistant against external twist. The rope torque is lower than the one of lang’s lay ropes. Ordinary lay ropes also offer a good wear-resistance. Construction wise the externally visible wire breaks appear earlier of ordinary ropes than of lang’s lay ropes due to the higher pressure between wire and rope groove and a stronger wire bend within the strand, which makes it easier to recognize wire breaks and thus the rope state, making it easier to evaluate the discard criteria. Ordinary lay ropes are still no universal ropes for all applications under the abovementioned aims of the rope choice.
Lang’s lay ropes are more demanding not only in the production process, but also with the application, beginning with the installation. The reason for this lies in the stranding of wires and strands in the same direction, which raises the rope torque and makes lang’s lay ropes substantially more sensitively against every kind of external twist.
Lang’s lay ropes reach very high bending cycles until break because of the geometrically more favorable contact conditions between wire and rope groove which leads to the reduction of the pressure in the contact areas. This reduction of pressure is advantageous to the lifetime of the crane components and the rope itself.
However, it must also to be mentioned that in comparison to ordinary lay ropes the development of the externally visible wire breaks occurs more slowly. Therefore the recognition of the discard criteria due to externally visible wire breaks can be complvicated. For this reason the numbers of wire breaks until discard are clearly lower for lang’s lay ropes than for ordinary ropes with identical rope construction. Therefore also lang’s lay ropes are no universal ropes for all application under the abovementioned criteria of rope choice.
Important: As described in the “Lang’s Lay ropes” paragraph, these ropes can have an increased amount of internal wire breaks, which are not visible on the outside. This is expecially the case with rotation-resistant ropes in Lang Lay under bending cycle usage. This should always be clarified with a rope expert.
Besides the rope itself crane components and crane geometry are important criteria for the right rope choice. The applied drum system and the crane geometry constructively selected fleet angles are to mentioned particularly.
While on single-layer drums the rope gets stressed due to tensile load and substantially due to bend and lateral deflection and thus twists, dominates on multi-layer drums mechanical wear and lateral pressure stress between the touching ropes.
The crane geometry constructively selected fleet angle is a very important characteristic for a reliable rope spooling and the degree of rope wear. For multi-layer spooling a maximum fleet angle of 1,5° is recommended, while single-layer drums can work with higher fleet angels like for example up to 4°.
The following basic rules for the correct choice of rope lay types for ropes that spool on drums have proved themselves and therefore are also recommended by us:single-layer drums = ordinary lay ropes
On single-layer drums the ordinary lay ropes have clear advantages, because it can usually compensate the bigger fleet angle. Also the easier recognition of externally visible wire breaks is an important argument for the use of ordinary lay ropes on single-layer drums where strong mechanical rope wear, which also leads to wire breaks, does not or not substantially exist.
On multi-layer drums the bending fatigue resistance of the rope is not decisive for the rope lifetime but its resistance to mechanical impact is. Ordinary lay ropes are less suitable for multi-layer drum spooling because the wires of the neighboring ropes can rub with each other. This leads to high mechanical wear. The touch of the neighboring ropes during the spooling process is also well “audible”. The results are premature wire breaks. Lang’s lay ropes have proved themselves in the multi-layer spooling because neighboring ropes can not rub into each other, which raises the lifetime of the rope significantly.
The abovementioned statements have proved themselves in practice. Customer desired, occasionally divergences should therefore be analyzed thoroughly with regard to:specific operating conditions of the rope




 8613371530291
8613371530291