non rotation vs rotation resistant wire rope for sale

Rotation resistant wire rope refers to a series of steel ropes which minimizes the tendency to spin or rotation under load. These wire ropes boast special design - the outer layer is twisted in the reverse direction of inner layers for counteracting torsional forces generated from multi-layers of strands.
To achieve the resistance against the spin and rotation, all wire ropes are composed of at least two layers of strands. In general, more layers a rotation resistant wire rope has, more resistance it will boast. For example, 2-layer ropes is much easier to spin and rotate than 3-layer ones. Meanwhile, if one end of free rotation is allowed, 2-layer rope can only develop 55% to 75% of its breaking strength comparing with 95% to 100% of 3-layer ropes.
The 3-layer rope with more outer strands is capable to distribute more radial pressure onto inner layers and ideal for larger mobile such as all tower cranes.
Wire ropes with 8 to 10 strands & 2-layer constructions without reversely twisted inner strands have very similar appearance to rotation resistant wire ropes, but they are not.
Rotation resistant wire ropes are considered to be less stable needing to be handled and installed with great care. They must be taken to avoid high loads with small diameter sheaves.
Rope Services Direct supplies a variety of anti-spin non rotating wire rope (also called rotation resistant wire-rope). All standard rope wirehas a tendency to develop torque and therefore prone to rotation, whereas non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force. This is in the event that a rope is subjected to a load.
Rope elongation and rotation occurs on standard ropes when loaded, which can therefore spin the load, quite possibly out of control, which can be dangerous. When the rope rotates in this way the strands will begin to unravel. This causes the rope to lose strength and will undoubtedly fail, which could be catastrophic. It is for these reasons that non rotating wire rope is commonly used for many types of lifting applications including main hoist rope, whip rope,crane rope, off-shore and deck rope and more.
Non rotating wire rope or rotation resistant wire rope has a different construction to standard. as wires and strands are not laid in the same direction like they would be on standard rope. Inner and outer strands of wires are laid in opposite directions. For example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. The nature of this construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires/strands will counteract each other and therefore minimising the risk of unraveling.
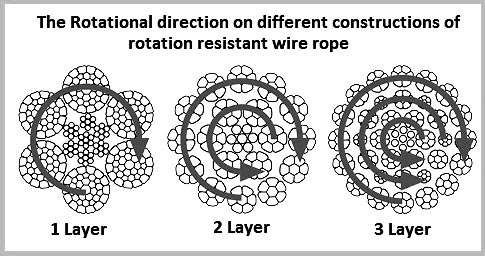
It is worth noting that the number of strand layers will have an effect of the resistance of rotation. A 2 layer rope has less resistance than a 3 layer rope. Therefore the more layers the rope has the greater rotation resistance it will have.
These types of ropes can be classified as spin resistant, rotation resistant or non rotation resistant. Classed on the basis of the number of rotations a certain length of rope does when a force of 20% of the MBF is applied; with 1 turn or less the rope will be classified as non rotating; with rotations between 1 & 4 the rope is classed as low rotation and for rotations between 4 & 10 the rope will be classified as spin resistant, any higher and the rope is NOT rotation resistant at all.
Correct usage and care with handling will prolong the working life. This is due to the friction on the inner wires caused by the strand crossover’s which will eventually cause the inner wires to break up. This is more apparent on non rotating wire rope with two layers. Ropes with 3 or more strand layers will distribute the radial pressures more evenly. Which will reduce friction and stress on the inner wires.
Regular,thorough inspectionsof non rotating rope are essential due to the fact that it is the inner strands that often break first and broken internal wires often go unnoticed as they are difficult to see.Rope Services Direct offer inspectionson all rope with certification issued on completion.
Holding both ends of the rope will prevent unraveling. Correctly fitted terminations will help to prevent damage. Kinking and unraveling may occur and they can also have an effect on the rotational balance if not fitted correctly.
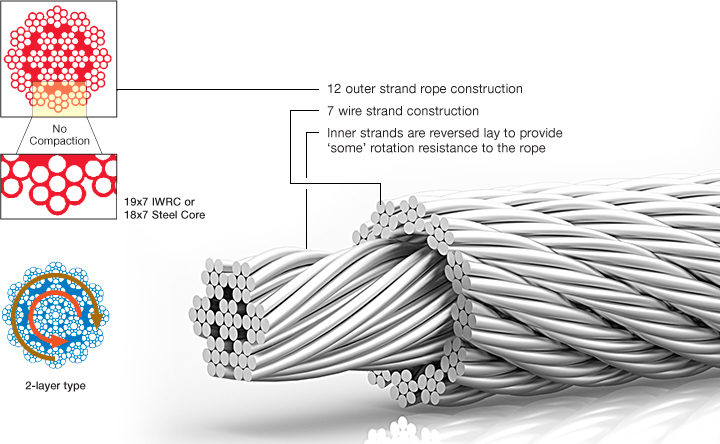
The characteristic of these wire ropes are that the outer layer is twisted in the opposite direction of their inner layers. The sometimes confusing issue is that many 8-, 9- and 10 strand constructions are 2-layer types but their inner strands are NOT twisted in the opposite direction and therefore these rope are NOT spin-resistant; plus, for the untrained eye these ropes look very much alike their spin-resistant variants. These and regular 6-strand ropes will spin violently and unlay themselves when loaded when one rope end is allowed to spin freely. They may also develop a significant drop in breaking strength and an even larger drop in their fatigue life characteristic (Torsion Fatigue).
To achieve any degree of resisting the tendency of a rope to spin and unlay under load all such rope types (other than 4-strand ones) are constructed with 2 or more layers of opposite twisted strands (see picture on right).
2-layer ropes (MULTI, COMPAC 18) have a larger tendency to rotate than 3-layer ones (e.g. Class 34 x 7, COMPAC® 35). Furthermore, 2-layer spin-resistant and rotation resistant ropes will develop only about 55% to 75% of their breaking strength when one end is allowed to rotate freely. This number increases to between 95% to 100% for 3-layer (e.g. COMPAC® 35) non-rotating ropes.
Another important issue is that 2-layer rotation resistant and 2-layer spin-resistant rope types have shown to break up from the inside. The 8 (e.g. 8×25 spin-resistant) or 12 outer strands (19×7, 19×19, COMPAC®18) are not able to evenly distribute the radial forces and because of the inherent internal strand cross overs (which make the rope spin- or rotation resistant) the resultant severe notching stresses cause the rope core to break up premature (unless the core is plastic coated, e.g. Python® Multi). Unexpected and sudden rope failures may be the result. Moreover, 2-layer spin-resistant or rotation resistant ropes satisfy only low to moderate rotational resistance demands.
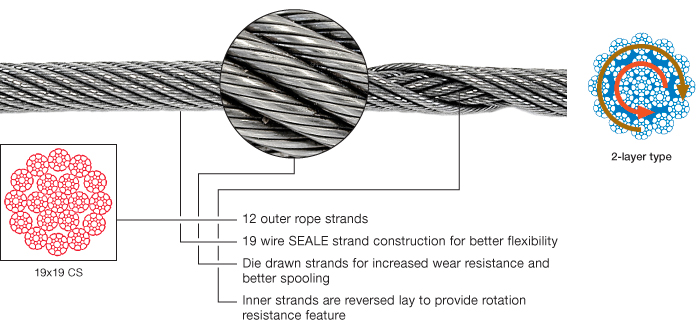
3-layer rope constructions (e.g. COMPAC® 35) have many more outer strands which can much better distribute the radial pressures onto the reverse lay inner strands. These ropes should be selected for larger mobile- and ALL tower cranes.

SWR supply a large range of non-rotating wire ropes in both galvanised and ungalvanised finish with either ordinary or langs lay. Depending upon your requirement for higher breaking load or better wear characteristics, these wire ropes are available in different finishes and lubrications as well as being available with plastic impregnated.

This wire rope construction is available in both galvanised and ungalvanised finish with either ordinary or langs lay. The construction family includes 17X7, 18X7 and 19X7. For further flexibility and other performance characteristics we also supply 32X7, 35X7 and 37X7.
Depending upon your requirement for higher breaking load or better wear characteristics, these wire ropes are available in different finishes and lubrications as well as being available with plastic impregnated.

Non-rotating wire ropes are designed so that the wire-rope outer rotational force naturally counteracts the inner strands rotational force in the event of a load applied.
Rather than all wires and strands being laid in the same direction, a rotation resistant wire rope consists of inner strands being laid in the opposite direction to the outer layers, for example the inner may be constructed in left hand lay whilst the outer layer is in right hand lay. This construction means that torsional forces on the inner and outer wires / strands will counteract each other and so minimise the risk of unraveling.
Using an ordinary lifting wire rope for a job or equipment which demand a non-rotating wire rope si very dangerous and it presents the following risks:
We understand that there are many factors that go into choosing the correct sling, wire rope, rigging hardware or lifting device for a lift! Let our sales team help!

Main and auxiliary hoist line for mobile and for all types of construction tower cranes which require a high strength rotation resistant rope construction.
The large number of outer strands distribute the pressures introduced by sheaves and drum more evenly onto the core minimizing the danger of unexpected rope failures because of undetected core deterioration.
Aside from this safety issue PYTHON® COMPAC 35 satisfies the high-strength requirements of late model tower and mobile cranes which can NOT be met with neither 19 x 7 nor 19 x 19 style ropes.

19x7 Rotation- Resistant Wire Rope is a special class of wire rope designed to resist the tendency to spin or rotate under load. This is achieved by laying 6 strands around the core in one direction, then laying 12 strands around the first in another direction. It is often used for hoisting unguided loads with a single part rope. Commonly used as a crane wire rope and hoist cable.
Frequent and regular inspection for broken wires is critical when using this rope. Due to its design, the 19 x 7 construction has relatively low reserve strength and this can result in short service life.
Inspect regularly for visible damage, distortion, elongation, corrosion, cracks, nicks or abrasion, which may cause failure or reduce the strength of the Wire Rope.

19x7 Rotation- Resistant Wire Rope is a special class of wire rope designed to resist the tendency to spin or rotate under load. This is achieved by laying 6 strands around the core in one direction, then laying 12 strands around the first in another direction. It is often used for hoisting unguided loads with a single part rope. Commonly used as a crane wire rope and hoist cable.
Frequent and regular inspection for broken wires is critical when using this rope. Due to its design, the 19 x 7 construction has relatively low reserve strength and this can result in short service life.
Inspect regularly for visible damage, distortion, elongation, corrosion, cracks, nicks or abrasion, which may cause failure or reduce the strength of the Wire Rope.

Our company is the major in offering Rotation Resistant Wire Rope to the clients. Rotation Resistant Wire Rope is manufactured using superior grade galvanized iron and latest technologies for ensuring its quality. Our product is known for its excellent tensile strength, corrosion resistance, finest finish and superb performance.

Rotation resistant wire rope is a special category (class) of wire rope designed to resist the tendency to spin or rotate under load. In general these ropes are used as single part lines, or in situations where operating conditions require a rope that will resist cabling in a multipart system. The essential nature of rotation resistant rope designs impose certain limitations on their application and necessitate special handling requirements not encountered with other rope constructions.
2) Multilayer strand (Multistrand)-consisting of two or more strand layers closed in opposing directions. Torsional forces generated by each layer of the rope counteract one another to minimize rotation.
The multistrand classification includes ropes with between eight and twenty outer strands. Table 1 of this manual describes some of the more commonly available rotation resistant multistrand rope classification. In addition to these, a wide variety of special multistrand ropes is available. See (Figure 9). It would be impractical to cover the specific features of each in this manual.
In multistrand rotation resistant ropes the crossover points between strand layers are points of high stress concentration. Relative motion of the strands at these points results in accelerated deterioration of the internal components of the rope. Because of this design characteristic of the multistrand construction, care must be taken to avoid high loads with small diameter sheaves. Design factors less than five are not recommended.




 8613371530291
8613371530291