steel wire rope lifting capacity chart factory

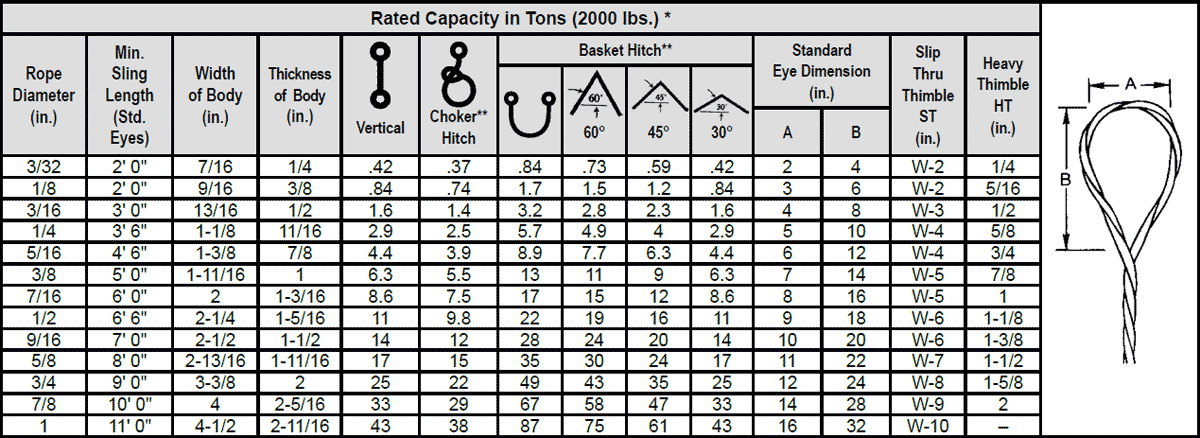
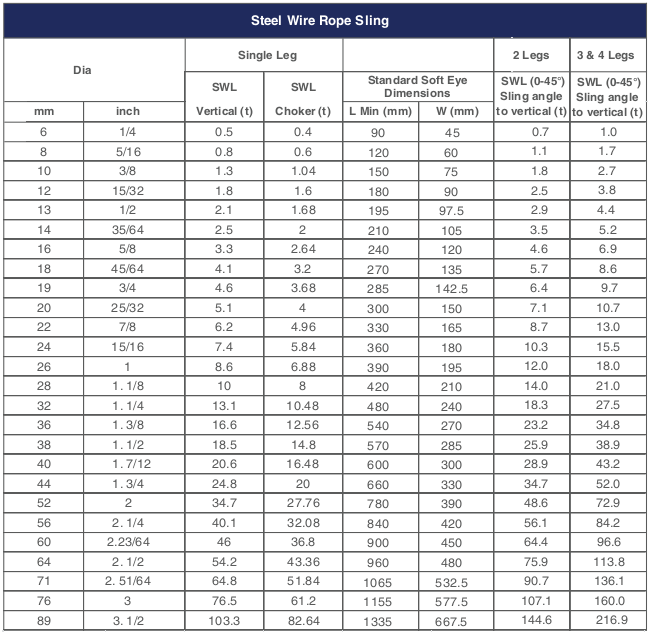
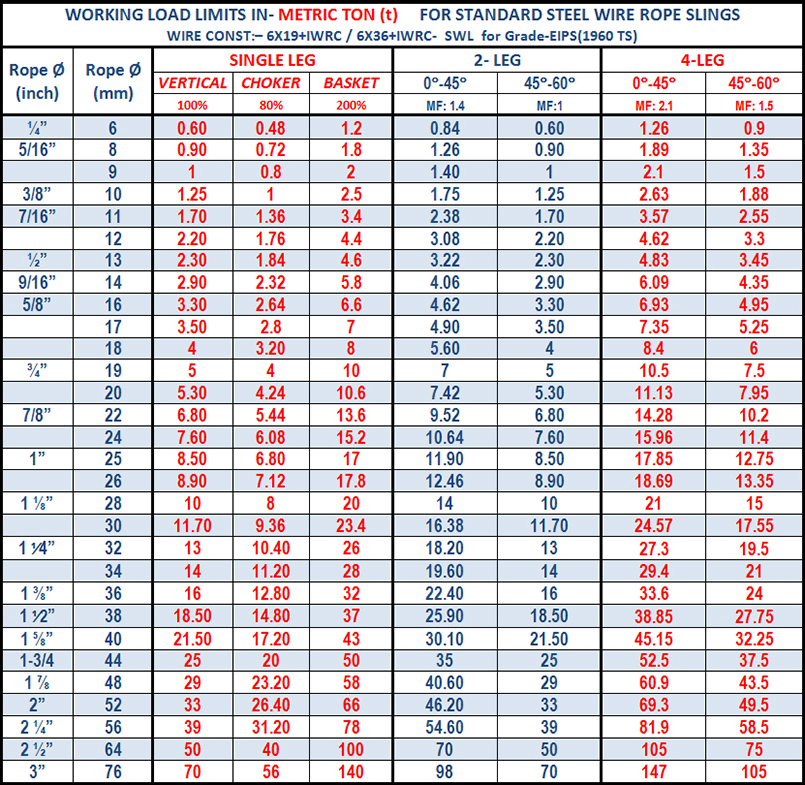
Large Loads Require Large Slings Whatever the load you are lifting. YuanBo Wire Rope Factory can supply a steel wire rope sling to do the task. Sling up to 12" (305mm) diameter can be supplied with minimum braking loads up to tons. There arethree distinct types of Wire Rope Sling.
Slings manufactured from cable laid ropes, 4" diameter to 12" diameter. hand spliced or by combination of hand splicing and socketing with eye at each end.
Slings manufactured from 6 strand equal laid ropes. up to 3.5 " diameter with soft eyes spliced each end. terminated by either hand splicing or mechanical means.
The most common size: wire rope slings having soft eyes at both end used for heavy lifting operations with safety factor of 7, length 6m, 12m, 16m, 20m, and the swl from 5 ton to 40 ton.

When a wire rope is bent around any sheave or other object there is a loss of strength due to this bending action. As the D/d ratio becomes smaller this loss of strength becomes greater and the rope becomes less efficient. This curve relates the efficiency of a rope diameter to different D/d ratios. This curve is based on static loads and applies to 6-strand class 6×19 and 6×37 wire rope.
In most cases the shackle or hook over which the sling is placed will have a sufficient D/d ratio. On the other hand, do not place too LARGE an object into the sling eye as this will result in splitting forces affecting the sling splice and sling safety. The object (a shackle, a crane hook, a steel bar, etc.) you place into the sling eye must not be larger than 1/2 of the sling eye length.
When a sling is used in a BASKET- or CHOKER HITCH with D/d ratios smaller than listed in the capacity tables, the rated capacities (or WLLs) must be decreased.
For example: The BASKET and CHOKER hitch capacities listed (in all Standards and Regulations) for 6-strand ropes are based on a minimum D/d ratio of 25:1.
An object you place into a 1" diameter 6-strand wire rope sling using a basket- or choker hitch must have a minimum diameter of 25". If the object is smaller than the listed 25:1 D/d ratio the capacity (or WLL) must be decreased. Table A) illustrates the percentage of decrease to be expected.
If the object lifted with a 6-strand wire rope sling in a basket hitch is at least 25 x larger than the sling diameter (D/d 25:1) the basket capacity need not to be adjusted.
It is better to use a larger shackle or a Wide Body shackle type. If the shackle or object has at least 5x the sling diameter (D/d 5:1) the basket sling capacity must still be reduced by about 25%.
Load Hooks must have sufficient thickness to ensure proper sling D/d ratio, particularly when using slings in an inverted basket hitch; that is the sling BODY is placed into the hook and the sling EYES are facing downwards.
Endless (or Grommet) slings DO NOT HAVE A LOOP which has double the strength of the sling body. Prior to EVERY lift, YOU, the user, has to determine if the D/d ratio is equal or higher than the ones listed in the capacity tables.
The wires of wire rope are made of high-carbon steel. These carbon steel wires come in various grades. Wire ropes are usually made of Extra Improved Plow Steel (EIPS) or Extra Extra Improved Plow Steel (EEIPS) which roughly equivalents to a wire tensile strength of 1960N/mm² and 2160N/mm².
The fill factor measures the metallic cross section of a rope and compares this with the circumscribed area given by the rope diameter. Traditional rope constructions ‘fill’ the rope diameter only up to about 58% with steel. Python® and Compac® wire rope ‘fill’ the rope diameter up to 80% with steel. That is an metallic increase of about 38% which results in a similar increase in rope strength.
Wire ropes are essential for safety purposes on construction sites and industrial workplaces. They are used to secure and transport extremely heavy pieces of equipment – so they must be strong enough to withstand substantial loads. This is why the wire rope safety factor is crucial.
You may have heard that it is always recommended to use wire ropes or slings with a higher breaking strength than the actual load. For instance, say that you need to move 50,000 lbs. with an overhead crane. You should generally use equipment with a working load limit that is rated for weight at least five times higher – or 250,000 lbs. in this case.
This recommendation is all thanks to the wire rope safety factor. This calculation is designed to help you determine important numbers, such as the minimum breaking strength and the working load limit of a wire rope.
The safety factor is a measurement of how strong of a force a wire rope can withstand before it breaks. It is commonly stated as a ratio, such as 5:1. This means that the wire rope can hold five times their Safe Work Load (SWL) before it will break.
So, if a 5:1 wire rope’s SWL is 10,000 lbs., the safety factor is 50,000 lbs. However, you would never want to place a load near 50,000 lbs. for wire rope safety reasons.
The safety factor rating of a wire rope is the calculation of the Minimum Break Strength (MBS) or the Minimum Breaking Load (MBL) compared to the highest absolute maximum load limit. It is crucial to use a wire rope with a high ratio to account for factors that could influence the weight of the load.
The Safe Working Load (SWL) is a measurement that is required by law to be clearly marked on all lifting devices – including hoists, lifting machines, and tackles. However, this is not visibly listed on wire ropes, so it is important to understand what this term means and how to calculate it.
The safe working load will change depending on the diameter of the wire rope and its weight per foot. Of course, the smaller the wire rope is, the lower its SWL will be. The SWL also changes depending on the safety factor ratio.
The margin of safety for wire ropes accounts for any unexpected extra loads to ensure the utmost safety for everyone involved. Every year there aredue to overhead crane accidents. Many of these deaths occur when a heavy load is dropped because the weight load limit was not properly calculated and the wire rope broke or slipped.
The margin of safety is a hazard control calculation that essentially accounts for worst-case scenarios. For instance, what if a strong gust of wind were to blow while a crane was lifting a load? Or what if the brakes slipped and the load dropped several feet unexpectedly? This is certainly a wire rope safety factor that must be considered.
Themargin of safety(also referred to as the factor of safety) measures the ultimate load or stress divided by theallowablestress. This helps to account for the applied tensile forces and stress thatcouldbe applied to the rope, causing it to inch closer to the breaking strength limit.
A proof test must be conducted on a wire rope or any other piece of rigging equipment before it is used for the first time.that a sample of a wire rope must be tested to ensure that it can safely hold one-fifth of the breaking load limit. The proof test ensures that the wire rope is not defective and can withstand the minimum weight load limit.
First, the wire rope and other lifting accessories (such as hooks or slings) are set up as needed for the particular task. Then weight or force is slowly added until it reaches the maximum allowable working load limit.
Some wire rope distributors will conduct proof loading tests before you purchase them. Be sure to investigate the criteria of these tests before purchasing, as some testing factors may need to be changed depending on your requirements.
When purchasing wire ropes for overhead lifting or other heavy-duty applications, understanding the safety dynamics and limits is critical. These terms can get confusing, but all of thesefactors serve an important purpose.
Our company has served as a wire rope distributor and industrial hardware supplier for many years. We know all there is to know about safety factors. We will help you find the exact wire ropes that will meet your requirements, no matter what project you have in mind.

6x36 is a flexible general engineering wire rope readily available in galvanised, ungalvanised and marine grade stainless steel. The wire rope has an equal lay construction (warrington seale) and achieves a superior breaking load to the 6x19 construction range. The construction has been designed to give a flexible rope with a good fatigue life. A 6x36 wire rope is available with either FC (fibre core) or IWRC (independent wire rope core) and is used for a wide range of applications, examples of which are shown below:

Wire rope is a complex mechanical device that has many moving parts all working in tandem to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. This structure provides strength, flexibility, and the ability to handle bending stresses. Different configurations of the material, wire, and strand structure will provide different benefits for the specific lifting application, including:Strength
However, selecting the proper wire rope for your lifting application requires some careful thought. Our goal is to help you understand the components of a wire rope, the construction of wire rope, and the different types of wire rope and what they might be used for. This will allow you to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
A wire rope is, in reality, a very complicated machine. A typical 6 x 25 rope has 150 wires in its outer strands, all of which move independently and together in a very complicated pattern around the core as the rope bends. Clearances between wires and strands are balanced when a rope is designed so that proper bearing clearances will exist to permit internal movement and adjustment of wires and strands when the rope has to bend. These clearances will vary as bending occurs, but are of the same range as the clearances found in automobile engine bearings.
Understanding and accepting the “machine idea” gives a rope user a greater respect for rope, and enables them to obtain better performance and longer useful life from rope applications. Anyone who uses a rope can use it more efficiently and effectively when they fully understand the machine concept.
Wires are the smallest component of wire rope and they make up the individual strands in the rope. Wires can be made from a variety of metal materials including steel, iron, stainless steel, monel, and bronze. The wires can be manufactured in a variety of grades that relate to the strength, resistance to wear, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and curve of the wire rope.
Strands of wire rope consist of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and supports the strands and helps to maintain their relative position under loading and bending stresses. Cores can be made from a number of different materials including natural or synthetic fibers and steel.
Lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process and penetrates all the way to the core. Wire rope lubrication has two primary benefits:Reduces friction as the individual wires and strands move over each other
The number of layers of wires, the number of wires per layer, and the size of the wires per layer all affect the strand pattern type. Wire rope can be constructed using one of the following patterns, or can be constructed using two or more of the patterns below.Single Layer – The most common example is a 7 wire strand with a single-wire center and six wires of the same diameter around it.
Filler Wire – Two layers of uniform-size wire around a center with the inner layer having half the number of wires as the outer layer. Small filler wires, equal to the number in the inner layer, are laid in valleys of the inner wire.
Seale – Two layers of wires around a center with the same number of wires in each layer. All wires in each layer are the same diameter. The large outer wires rest in the valleys between the smaller inner wires.
Warrington – Two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of wire in the inner layer, and two diameters of wire alternating large and small in the outer later. The larger outer-layer wires rest in the valleys, and the smaller ones on the crowns of the inner layer.
On a preformed wire rope, the strands and wires are formed during the manufacturing process to the helical shape that they will take in a finished wire rope.
Preformed rope can be advantageous in certain applications where it needs to spool more uniformly on a drum, needs greater flexibility, or requires more fatigue-resistance when bending.
Direction and type of lay refer to the way the wires are laid to form a strand (either right or left) and how the strands are laid around the core (regular lay, lang lay, or alternate lay).Regular Lay – The wires line up with the axis of the rope. The direction of the wire lay in the strand is opposite to the direction of the strand lay. Regular lay ropes are more resistant to crushing forces, are more naturally rotation-resistant, and also spool better in a drum than lang lay ropes.
Lang Lay– The wires form an angle with the axis of the rope. The wire lay and strand lay around the core in the same direction. Lang Lay ropes have a greater fatigue-resistance and are more resistant to abrasion.
A fiber core can be made of natural or synthetic polypropylene fibers. Fiber cores offer greater elasticity than a steel core but are more susceptible to crushing and not recommended for high heat environments.
A steel core can be an independent wire rope or an individual strand. Steel cores are best suited for applications where a fiber core may not provide adequate support, or in an operating environment where temperatures could exceed 180° F.
The classifications of wire rope provide the total number of strands, as well as a nominal or exact number of wires in each strand. These are general classifications and may or may not reflect the actual construction of the strands. However, all wire ropes of the same size and wire grade in each classification will have the SAME strength and weight ratings and usually the same pricing.
Besides the general classifications of wire rope, there are other types of wire rope that are special construction and designed for special lifting applications.
Some types of wire rope, especially lang lay wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation when under load. Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or rotating and can be used in a single line or multi-part system.
Special care must be taken when handling, unreeling, and installing rotation resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce twist into the rope which can cause uncontrolled rotation.
Compacted strand wire rope is manufactured using strands that have been compacted, reducing the outer diameter of the entire strand, by means of passing through a die or rollers. This process occurs prior to closing of the rope.
This process flattens the surface of the outer wires in the strand, but also increases the density of the strand. This results in a smoother outer surface and increases the strength compared to comparable round wire rope (comparing same diameter and classification), while also helping to extend the surface life due to increased wear resistance.
A swaged wire rope differs from a compacted strand wire rope, in that a swaged wire rope’s diameter is compacted, or reduced, by a rotary swager machine after the wire rope has been closed. A swaged wire rope can be manufactured using round or compacted strands.
The advantages of a swaged wire rope are that they are more resistant to wear, have better crushing resistance, and high strength compared to a round strand wire rope of equal diameter and classification. However, a swaged wire rope may have less bending fatigue resistance.
A plastic coating can be applied to the exterior surface of a wire rope to provide protection against abrasion, wear, and other environmental factors that may cause corrosion. However, because you can’t see the individual strands and wires underneath the plastic coating, they can be difficult to inspect.
Plastic filled wire ropes are impregnated with a matrix of plastic where the internal spaces between the strands and wires are filled. Plastic filling helps to improve bending fatigue by reducing the wear internally and externally. Plastic filled wire ropes are used for demanding lifting applications.
This type of wire rope uses an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) that is either filled with plastic or coated in plastic to reduce internal wear and increase bending fatigue life.
Remember, wire rope is a complex piece of mechanical machinery. There are a number of different specifications and properties that can affect the performance and service life of wire rope. Consider the following when specifying the best type of wire rope for your lifting application:Strength
When you select a piece of rope that is resistant to one property, you will most likely have a trade-off that affects another property. For example, a fiber core rope will be more flexible, but may have less crushing resistance. A rope with larger diameter wires will be more abrasion resistant, but will offer less fatigue resistance.
At Mazzella Companies, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.
If you’re looking for a standard or custom specified wire rope for your lifting project, contact a Lifting Specialist at a Mazzella Companies location near you.
We stock well over 2,000,000 feet of wire rope in our various locations … ready for immediate delivery! We provide wire rope assemblies, and manufacture bridge cables, crane cables, steel mill cables, and thousands of OEM assemblies.
For customers who require peak rope performance levels in mission critical applications, Casar manufactures and supplies highly-engineered ropes that exceed industry standards while providing record-setting service life.
Our proprietary and innovative German-engineered rope designs deliver the highest levels of performance and safety, superior breaking strength values, the highest bending fatigue resistance, superior crushing resistance, and the best rotational resistance characteristics for high lifts.We have decades of global experience and on-site engineering support in the crane, OEM and underground mining sectors.
CASAR has an extensive range of products available and we can customize to your application.Our wire rope specialists will assist customers in design, selection, installation and operation to improve rope performance and maximize service life.




 8613371530291
8613371530291