welding wire rope together quotation

Direct Wire’s welding cable ampacity chart intends to support and guide welding professionals toward the proper cable gauge and length. This information is for reference only, and it is highly recommended the user consult a licensed electrical engineer for a particular welding application.
For welding applications, using the proper cable gauge size is critical to ensure high-quality welds and protect the user and their welding equipment. Specifications that should be considered when selecting welding cable include:
AMPACITY: Welding cable ampacity (also known as current-carrying capacity or current rating) refers to the maximum amount of current (in amperes) that a cable conductor can continuously and safely carry without exceeding the operating temperature rating.
LENGTH: Welding cables should be long enough to provide the user with adequate length to reach all work areas—without becoming a hazard. It is essential to keep in mind (1) ampacity ratings decrease as length increases due to additional resistance, and (2) welding cable should be spread apart to allow heat to dissipate during use.
GAUGE SIZE: It is critical to select the proper gauge size for the given welding application. A longer, thinner welding cable will carry lower ampacity. If a longer cable is needed, the user should consider thicker gauge sizes. An improper gauge size will not carry the anticipated current, which can cause excessive heat absorption (melting and fire hazard), failure, and damage to equipment.
CONSTRUCTION: Welding cable construction uses a multi-stranded single conductor insulated (or jacketed) by a single layer of EPDM or neoprene thermoset with a temperature rating of -50°C (-58°F) to 105°C (221°F). Superior flexibility, durability, and resistance properties are also vital to a welding cable’s ability to perform in a range of demanding applications and environments.
STANDARDS & APPROVALS:Welders should look for key industry standards and approvals, ensuring quality and performance while protecting against substandard manufacturing. For welding cable, these may include SAE J1127 (battery), NFPA 70/NEC Article 630, UL 558 and 583 (and others), and CA Prop 65.
Direct Wire’s Flex-A-Prene® and Ultra-Flex® premium welding cables meet or exceed the SAE J1127 standard, which requires minimum copper amounts per gauge (i.e., guaranteed copper contents), appropriate sizing for specific applications, and testing for mechanical and performance characteristics.
FLEXIBILITY: Fine copper stranding and a high-quality outer insulation/jacket layer provide welding cable with increased flexibility, smoother pulling across various surfaces, and ease-of-movement on the job site.
COLOR & MARKINGS: Colored welding cable and customized markings can be used for various applications, including ownership and identification, accurate footage (or sequential) markings, industry standards and approvals, physical and mechanical characteristics, branding, and more.

Like GEN 99, GEN 55 is used for GMAW and GTAW welding of cast iron. It is also employed to weld cast irons to mild steels. The mixture of aluminum, silicon and iron makes it moderately hard, however, the wire can be machined using carbide tipped tools. To avoid cracking, a pre‐heat and minimum interpass temperature of 350°F (175°C) is recommended during welding.
All Welding products are supplied with a certificate of conformance stating physical and mechanical properties including alloy chemistry. Every welding product is manufactured to have its own unique lot identification number for full lot traceability.
Multiple packaging and shipping options are available from our facilities in the US, Canada, and the UK. Learn more about our products, the industries and applications we support, and how CWI Generation4™ welding wire can work for you.
While you’re looking at welding wire, here are Three Reasons To Source Your Welding Wire and Demister Pads Together. By ordering all your turnaround supplies from CWI, you can reduce downtime, perform maintenance all at once, and work confidently knowing you are receiving only the highest quality products from a trusted manufacturer.

GEN 625 is used for MIG, TIG and SAW for nickel‐chromium‐molybdenum alloys, such as 601, 690, 800 and 825. It may also be used for cladding and welding dissimilar base metals such as Ni‐Cr‐Mo alloys to stainless, carbon and low alloy steels. GEN 625 offers excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance against organic and phosphoric acids as well as seawater.
Low Heat Input Wire (LHIW) offers an optimized chemistry that requires lower heat input levels to achieve adequate material flow, improved weld penetration, and consistent material bonding while maintaining chemical stability. GEN 625LHIW welding wire burns clean and provides high feedability rates, making it perfect for thermal spray and laser metal deposition processing methods in cladding and hardfacing applications.
All Welding products are supplied with a certificate of conformance stating physical and mechanical properties including alloy chemistry. Every welding product is manufactured to have its own unique lot identification number for full lot traceability.
Multiple packaging and shipping options are available from our facilities in the US, Canada, and the UK. Learn more about our products, the industries and applications we support, and how CWI Generation4™ welding wire can work for you.
While you’re looking at welding wire, here are Three Reasons To Source Your Welding Wire and Demister Pads Together. By ordering all your turnaround supplies from CWI, you can reduce downtime, perform maintenance all at once, and work confidently knowing you are receiving only the highest quality products from a trusted manufacturer.

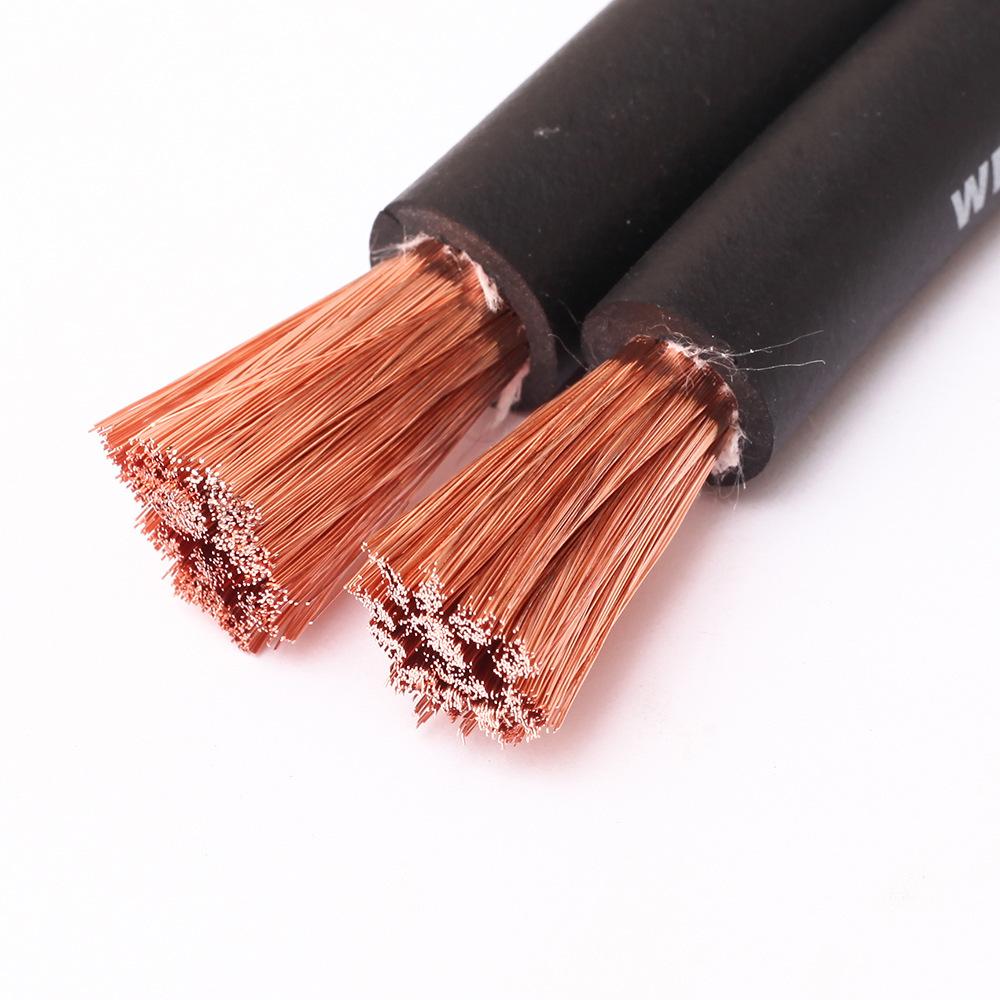
Welding cable is designed for use in electric arc-welding machines to power an electrode, a specially designed metal rod, that conducts a charge. The charge carried by the electrode is needed to produce an electric arc, the heat source, between the electrode and the metals being welded.
Welding cable is made to be extremely durable and flexible. Arc-welding requires a person to move the electrode around the shop and along the joints being welded, so it is essential to have a flexible welding cable that allows for ease of movement. A high strand count and rubber insulation help increase the cable"s flexibility.
TEMCo"s Welding Cable is highly flexible stranded No. 30 bare copper conductor insulated with high grade black EPDM. A paper separator is utilized to enhance stripability. Maximum conductor operating temperature is 105°C in circuits not exceeding 600 volts. Minimum temperature rating -50°C. View our guide below to learn more about welding cable sizing and applications. Our full product line is also available below.
This guide is meant to inform and support you in the proper selection and use of welding cable. We always recommend that you consult a licensed and competent electrician to help you with the sizing and selection of parts for your particular application.
Ampacity: The ampacity refers to the maximum amount of current your cable can handle safely. For more information, view the section on welding cable ampacity.
Length: Your cable should be long enough to reach every corner of the space you will be welding in. You will need to keep in mind (1) one cable connects from the welder to the elctrode and (2) another cable will connect from the welder to the piece that is being welded (also known as the work clamp or ground lead).
Gauge: The longer and thinner the welding cable, the lower the ampacity, so if you require a long cable, you may want to look at thicker sizes to compensate for the length and to prevent damage to your machine.
Insulation: Welding cable insulation is commonly made of neoprene, EPDM, or PVC. Both neoprene and EPDM jackets are flexible, resistant to harsh weather, abrasion, moisture, and water. However, they are not well suited for exposure to gas or other petroleum based liquid. PVC is less flexible but has high resistance to cuts and tears.
Arc-welding: For welding applications, two cables are required: one connects the machine to the electrode, while the other connects the machine to the workpiece that is being welded, and these two cables form a complete circuit.
Other uses: Welding cables are durable and flexible and are a popular choice for entertainment or stage lighting cables, lighting and sound systems, and communication vans. They can also function as battery cables for cars, inverter cables, and as a more cost-effective alternative to pendant (or reeling) cable on hoists and cranes.
This Portable Welder Instructables Tutorial is a great example of how you could use TEMCo welding cable for your own personal projects. This particular project uses 50 feet of 1/0 welding cable to create a connection cable from the batteries/vehicle to the welder.
The ampacity, or amperage capacity, is the maximum amount of electrical current that the welding cable can conduct safely. Different welding cable running on the same voltage will have different amp ratings depending on several factors, which include: cable length, wire size (gauge), insulation temperature rating, and the type of machine the cables are connected to.
Electrical resistance (in ohms) & insulation temperature rating: The more amps you run through your cable, the hotter it gets. The higher the resistance rating of the welding cable, the fewer amps you can safely run without overheating it. Overloading your welding cable will over heat it, which leads to damage to the insulation.
Welding cable size is measured by the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard. AWG sizes will have three numbers, for example, "2 AWG 625/30." This means that the welding cable has a total cross sectional area of 2 AWG and is made from 625 strands of 30 AWG wire.
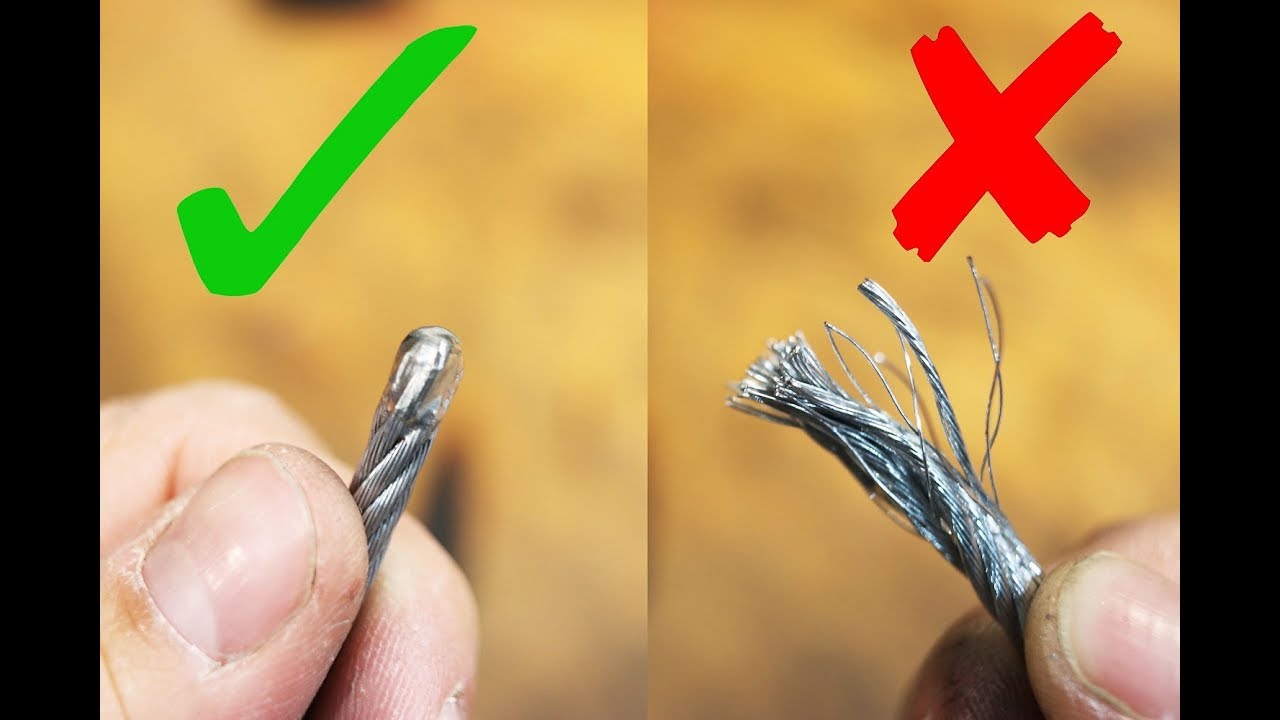
Welding two ropes together is common in the steel industry. If properly done, welding may develop sufficient strength to complete the rope installation. However, the welded portion of the rope is rather stiff, and the welded steel wire material may become brittle. Since the welded portion has to pass over sheaves, there is the danger that the weld may break.
If installing Python® wire rope as well as all non-rotating types we do not recommend the welding procedure. Welding might damage the seizings and the rope may unravel getting damaged beyond repair.
A common method for heavy crane rope installations. A steel sleeve only slightly larger than the rope diameter is swaged on to the rope end and a small auxiliary cable protrudes from the sleeve. Either, the old rope is furnished also with a becket loop, or the old rope will be connected to the becket loop with a cable grip.
Non-rotating rope must be installed with a swivel between old and new ropes. The old rope may have developed torque during it’s working life and we must ensure that this torque is not transferred to the new rope.
Python® types Multi and Super 8 may be installed with a swivel. In fact, if you have to change either of these constructions for a 6-strand rope, particularly when this rope has a different lay direction, a swivel is of definite benefit.
Python® Power 9 and Python® Ultra must not be installed with a swivel. Doing so will unlay the rope and damage it beyond repair. Use two cable grips and connect them with an auxiliary cable.
When using cable grips, the end of the grips have to be tightly seized on to the rope body to prevent accidental slip-out of the rope. Alternately, you may wrap the grip end with a strong reinforced industrial strength adhesive tape.
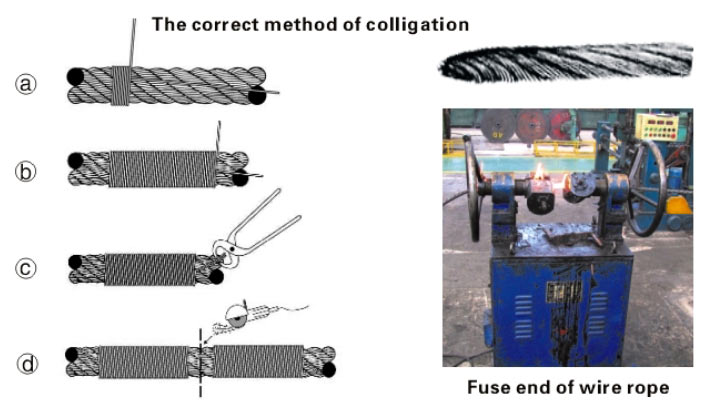
I"ve welded a lot of ends on cable by using a piece of pipe that will just slip over the end of the cable then welding the 2 together. you could put a collar on each end then weld the pipe collars together in a circle. Grind the weld smooth and it should hold whatever you put on it. We used to use 1" drilling cable that was covered w/ oil and had a rope core. it would smoke, bubble and just be generally nasty but the pipe added enough solid material that you could get the 2 to bond. We"d use that cable for fence anchors, putting a disc blade over the cable and burying that, and a rod loop on the other end to run the brace wire thru. Good Luck

Badger Wire manufactures a very popular, cost-effective TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer 105° C) alternative to welding cable. Badger Wire’s TPE is used in many welding cable applications offering added abrasion and oil resistance as well as flexibility over battery cable.

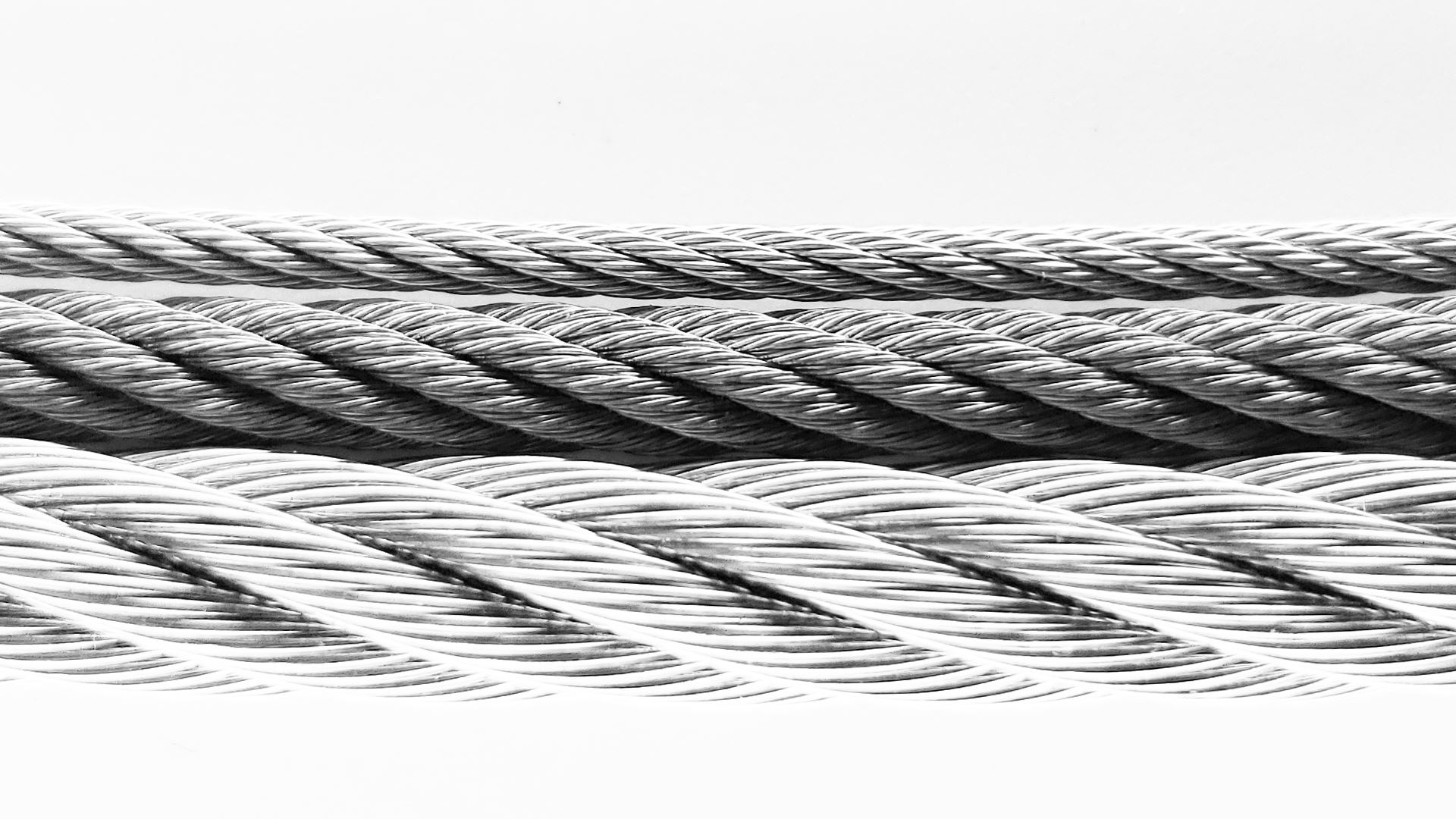
At Carl Stahl Sava Industries, our steel mechanical cable choices include 304 and 316 stainless steel and galvanized steel cable. Sava is both a wire rope supplier and a wire rope manufacturer that is able to work withexotic steel alternatives upon request, both stainless steel and galvanized steel mechanical cable offer distinct benefits, depending upon the application. Read on to learn the differences between galvanized vs. stainless steel wire ropeand determine which custom wire rope will better serve your application requirements.
One of the greatest benefits of stainless steel wire rope is that it is suitable for nearly any application. While it may have a slightly higher cost than galvanized steel cable, stainless steel cable provides customers with greater ROI and maintains its high-strength qualities over its lifespan under most conditions. While not as strong as tungsten or tolerant of excessive temperatures, stainless steel mechanical wire rope is an incredibly effective cable construction material.
Stainless steel has high corrosion resistance due to it being treated with chromium. This additional element makes stainless steel suitable for use in moist environments, even when harmful salty conditions are present. Specifically in marine environments, for instance, stainless steel wire rope can be used for years without corroding. And in the medical devices field, stainless steel is commonly the metal of choice for many medical device instruments like endoscopes because of its high sanitization level and durability over many cycles makes it ideal.
Galvanized steel is steel that has been dipped in a zinc coating, which gives it good corrosion-resistant qualities. But even with the addition of zinc, galvanized wire rope’s strength is weaker than stainless steel because of the presence of chromium, making the cable stronger and more tolerant of corrosive elements like saltwater. Galvanized cable will rust and corrode if salty wet conditions are present. And like stainless steel, galvanized steel cable ends will also weld together if they make contact with one another.
Galvanized steel cable is often found in industrial applications, since items may brush up against the wire rope in the field, which again, are environmental conditions that galvanized steel tolerates quite well over time. For this and other reasons, Galvanized steel wire rope works exceptionally well in aerospace applications.
Stainless steel wire rope is a cost-effective solution that works across a range of applications, is impervious to salty wetness and is stronger than galvanized steel cable. But galvanized steel wire rope is corrosion-resistant, except when salt is present and tolerates contact with itself far better than stainless steel cable.
It"s important to remember that since each application has unique needs, these comparisons are general guidelines. Contact Sava today to discuss your project, so we can help you determine whether a stainless steel wire rope or galvanized steel wire rope is best for your cable manufacturing needs.
As a leader in the resistance welding cable and accessory field, Flex-Cable is a major supplier to the global automobile industry and holds a strong presence with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) in the appliance, electronic, and consumer related product industries.
In today’s world of rapid growth and high technology, where a product can be here today and gone tomorrow; service, quality and technology are the key assets which separate the few from the many. For more than 55 years, Flex-Cable has developed these assets in order to be recognized as a leader in Resistance Welding Cable technology.
Flex-Cable offers exceptional design, assembly and energy. Our Resistance Welding Cables are low maintenance and provide a longer cable life. Size for size, the conductor arrangement gives approximately 10% more current for a given applied voltage than other available cable types.
Patented process with a six rope alternate polarity utilizing a unique, low wear point wire rope design. Providing the lowest inductive reactance and lowest impedance with the highest electrical power factor of all cables in today’s market place. The positive cooling paths maximize thermal efficiency and special water passageways reduce terminal heating.
The Color-Flex Resistance Welding Cable jacket is made up of a specially formulated, six layer, natural rubber compound with an abrasion resistant bumper as an integral part of the jacket, making it completely durable to overcome distress and flexure.
Available in both Standard and Flex-cel Process, these Resistance Welding Cables are made of specially designed rubber jacketing with ergonomics in mind, offering individually wrapped internal copper ropes with a perforated protective sleeve, which would improve water flow, decrease operating temperature and improve flexibility.
State-of-the-art, patent-pending process which incorporates a specially extruded ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber material covering each individual conductor rope within the cable. Then punched with symmetrical cooling channels to capture and isolate broken strands of copper wire to prevent cooling system contamination and obstructed water flow. Vortex water flow action causes increased heat transfer, resulting in higher cooling efficiency. The concept occupies less volume than standard separator cables resulting in increased flexibility as well as additional water volume to alleviate heat.
Combined with proper dress out and a good preventative maintenance program, this Resistance Welding Cable will virtually eliminate down time. The interior construction and outer hose make this cable a hard worker and a true value.
These Resistance Welding Cables have a rugged urethane outer jacket allowing for the combined advantage of safety, abrasion-resistance and long cable life into one unique design. Perforations and flow space between the wire and material create a sufficient Thermally Forced Cooling System.

With over a half-century of experience, dedicated in-house testing and ISO-certified manufacturing facilities, you can depend on Kalas to deliver the highest quality welding cable, wire and value add solutions. We offer you aone-stop service model for unprecedented value as an extension to our fully-integrated copper wire & compound facility. We go out of our way to meet your unique needsoffering custom print, sequential markings, proprietary packaging, quick ship order fulfillment for assemblies, stock cable & more.
As an EPDM cable, ToughFlex™ is designed for all welding applications where a stinger/whip, leads and grounds are used. Available in a range of colors, gauges, and in standard and custom lengths, we offer our customers the ability to custom print and sequentially mark their cable. Customers can also choose between proprietary shrink wrap packaging with easy to carry handles, coils, boxed or stocked as 250’ or 500’ reels.
As a highly flexible 34 gauge bare copper, FlexWhip™ is designed for all welding applications where a stringer/ whip, leads and grounds are used. Available in an industrial orange EPDM jacket in #2, #1, 1/0 and 2/0 gauges and both standard or custom lengths, we offer our customers the ability to custom print and sequentially mark their cable. Customers can also choose between proprietary shrink wrap packaging with easy to carry handles, coils, boxed or stocked as 250’ or 500’ reels.
Our SGR battery & welding cable features an EPDM jacket for superior durability and flexibility. It is RoHS compliant and constructed to meet both SAE and UL requirements. Appropriate for welding applications and use between the battery terminal and starter and grounding on boats, buses, cars, lift trucks, RVs, tractors and trucks, we offer our customers the ability to custom print their name and logo & sequentially mark their cable. Customers can also choose between proprietary shrink wrap packaging with easy to carry handles, coils, boxed, or 250’ or 500’ reels.
Kalas :Industrial offers a comprehensive assortment of pre-assembled leads, grounds, and stingers/ whips built to the specifications of our customers for optimal convenience and saving them time and money. Featuring welding connectors from both Lenco and Tweco, we offer assemblies in a range of cable colors and gauges. Customers can also choose between proprietary shrink wrap packaging with easy to carry handles, coils or boxed. All of our assemblies are made to the specifications of our customers, produced on site and shipped directly to you.
Buying your welding cable direct from Kalas is a decision you will immediately thank yourself for – Excellent customer service, the best quality cable, customizable finishing & purchasing plans to suit your needs…

In this post of This vs That, we compare DLO cable and welding cable. They are similarly categorized, but definitely have their differences in terms of usages and general construction. They are both used in power supply applications, but what exactly are they? Why are they frequently compared? To uncover their similarities and differences, let"s take a look at the construction and electrical specs for both DLO cable and welding cable, as well as the applications they"re used in.
DLO cable has a voltage rating of 2000V, making it ideal for heavy-duty, high-voltage applications. It also has a maximum temperature rating of 90°C in both wet and dry environments. Allied Wire and Cable carries Diesel Locomotive Cable in gauge sizes 14 AWG to 1111 MCM. These cables always feature a finely stranded tinned copper conductor, insulation, and a CPE jacket. Common insulation materials include EPR and EPDM.
Welding Cable is a portable cord typically used welder leads and power supply applications. Because of its rubber jacketing/insulation, it is resistant to abrasion, tears, and cuts. Welding Cable is also suitable for use in battery grounds, automotive starts, and marine applications because of its flexibility and versatility.
Welding cables have a voltage rating of 600V and a maximum temperature of +105°C. These cables also feature stranded copper conductors, but they come bare. This cable"s jacket acts as insulation as well, instead of having two separate materials like in Diesel Locomotive Cable. Allied Wire and Cable carries Welding Cable from 6 AWG to 500 MCM.
While these cables are suitable for use in similar applications, there are some major differences to consider. Both cables feature stranded copper conductors, but Welding Cable"s conductor is bare instead of tinned and has a higher strand count. This makes it more flexible, but harder to terminate. DLO"s tinned copper conductors provide extra corrosion resistance protection against environmental conditions.
Welding Cable usually has a red or black jacket but is available in other colors upon request. When it comes with an orange jacket, this signals it"s an extra durable cable construction. Diesel Locomotive Cables come only in black. They also carry some dual ratings that welding cable does not, including UL RHH/RHW-2 and CSA R90 approvals. Remember, voltage ratings differ for these approvals. UL RHH/RHW-2 is rated for 600V and CSA R90 is rated for 1000V.
When deciding between these two cables, it"s important to consider what exactly your application requires. DLO Cable has tinned conductors, insulation, a jacket, and a 2000V rating. This makes it more suitable for heavy-duty and industrial applications. Welding Cable features finely stranded conductors and a single jacket, making it more flexible and suitable for tighter spaces. If you still have questions, call one of our knowledgeable sales reps at 800-472-4655 for more details.
.png)
Welding and battery cables are often compared because of their similar ampacity. Can you use welding cables in batteries, and if so, what is the best way to do it? Read this blog to find out.
Welding cables are flexible and durable high-heat resistant cables typically with an EPDM insulation that were originally created for the welding leads. They are equipped with a stranded copper conductor. Today, welder’s cables with a RHH/RHW double rating are quite versatile and used in many applications, including industrial uses and other demanding environments. If you wish to learn more about welding lead wire applications, read thisblogon the topic.
Battery cables are designed to connect batteries with their starter. Automotive wires are a separate group of battery cables for cars. Common generalbattery cablesare SGT, SGX, and STX. Commonautomotive wiresinclude GXL, SXL, TXL, GPT, TWP, and HDT. The cables usually come with PVC or XLPE insulation and have limited flexibility. However, they are perfect for typical battery applications. To learn more about the subtypes of auto battery wiring, read thisblog.
Welder cables are compatible with battery applications. With most manufacturers, battery and welding cables have the same ampacity when their size is the same, which makes it easy to install welder’s cables in batteries in the same way battery cables are installed.
Welding cables have excellent high-heat resistance. With EPDM insulation, their temperature range is -50℃ - 105℃, which is perfect for batteries. In fact, welding cables rank higher than battery cables when it comes to flame retardance because they meet the UL 1581 flame-retardancy standard. Battery cables are also flame-resistant, but the standards they meet, UL 558 and UL 553, are inferior to a welder"s cable UL 1581. Both battery and welding cables are resistant to oil, grease, and harsh cuts, so they are both great for batteries in that regard.
Welding lead wire with EPDM insulation performs way better than PVC-insulated battery cables in freezing temperatures; therefore, you might consider using welding cables if your batteries are often exposed to cold. If the battery wire has an XLPE insulation instead, this comparison is not relevant as it is not likely to stiffen in the cold.
Note that in order to comply with the National Electrical Code Standard, welding cable needs to be double-rated as RHH/RHW for most uses, including batteries. Welding cables without an RHH/RHW rating can be used only in welding leads.
While welding cable is suitable for battery applications, this is not a two-way street. Battery cables cannot be used in welding arcs, as welding cables are the only type approved for welding arcs everywhere in the world.
Some say that welding cables are too expensive to replace cheaper battery cables in car applications, while others prefer to use them in car batteries and car amplifiers. To some, welder cables seem easier to install than battery ones. While it is true that welding cable is more expensive, it may be especially useful if you need a cable with a rating of 600 volts or one that is very flexible.
Properly rated welding cables can replace battery cables, but not vice versa. While it is not necessary to replace battery cables with welder"s, it is an option if you need a flexible cable with a higher voltage than a regular battery cable. Welding lead wire works for car batteries as well.
Nassau National Cable is a go-to platform forwelding cables,automotive wiring, andbattery cablesof all kinds. We have some of the best fares on the high-quality wire and cable in the industry thanks to the access to special rates from our suppliers.

When you have an application that requires wire splicing, or an application requiring that two or more wires be stacked together to be soldered into/onto a soldered application, ITC has the equipment and techniques to accomplish these needs in the form of ultrasonic wire welding.
The ultrasonic wire welding process process is simple, yet durable and effective. Copper wire is welded together ultrasonically, resulting in a very clean and neat weld.
The major benefit of ultrasonic wire welding is that it allows the presentation of a single leg to solder, rather than attempting to hold and align multiple conductors during the solder application process. Another major benefit of ultrasonic welding is its cost-effectiveness – this cost of ultrasonic welding is just a fraction of the cost of applying a mechanical crimp splice or a solder splice.
We utilize one of the finest ultrasonic welding machines in the industry, the Stapla ‘Raptor Series’ ultrasonic welder. It is fully programmable, and accommodates a wide range of wire sizes.

The short answer was “yes, you can, but you probably wouldn’t want to.” In most cases, if you need a corrosion-resistant wire form, it’s best to go all the way with stainless steel wire rather than mixing and matching metals.
Austenitic stainless steels such as grade 304 stainless or grade 316 stainless can be welded to plain carbon steel using MIG and TIG welding. When welding stainless steel to a dissimilar metal such as plain carbon steel, weld processes such as MIG welding that use filler material are preferred.
Resistance welding of stainless and carbon steel isn’t typically done, as the differences in electrical conductivity between the two metals make reaching the right weld temperature extremely difficult. When resistance welding is used, the carbon steel is usually preheated since it’s more electrically conductive and doesn’t heat up as fast as stainless steel.
When determining what form of welding is best for your custom wire basket, the answer depends on what type of metal is being used. If your custom basket is made from stainless steel, then there are certain methods that are superior compared to others for stainless steel welding.
The properties of stainless steel have to be considered before choosing a weld. For example, Marlin Steel makes most of its custom wire baskets from grade 304 or 316 stainless steel, they are corrosive-resistant and have a high tensile strength. Chrome-nickel stainless steel alloys have a high electrical resistance and cool off fast. Since stainless steel alloys bond and solidify quickly with minimal distortion, resistance weldingis the best welding technique for stainless steel.
Using a resistance weld for stainless steel welding is an easy, smoother process when compared to other metals. Due to its high resistance to current flow, heat at the weld joint is generated easier and quicker than mild steel.
Resistance welds can be completed incredibly fast since resistance welding works by passing electricity through a material and generating heat by resistance. Stainless steel tends to get up to weld temperature very quickly, which allows for quick welding. For example, Marlin’s IDEAL welding machine can complete a weld in two milliseconds (i.e. 2/1,000 of a second)—which makes it the best welder for stainless steel.
While resistance welding is similar to arc welding because both apply an electrical current to help join two pieces of metal together, it does not require a filler like arc welding. Instead, resistance welding uses pressureto bind the two materials being welded together. Resistance welding is also the best overall welding method for stainless steel since, without the use of a filler, there is much less risk of weld splatter and a much “cleaner” look to the product. Using resistance welding also reduces the risk of discoloration and burns around the weld site because a resistance-type stainless steel welding machine operates so quickly.
When welding stainless steel to other metals, other types of welding should be considered than resistance welding. For instance, MIG and TIG welding are preferred types of welding stainless steel to carbon steel together. When combining dissimilar metals together, such as welding stainless steel to carbon steel, a filler material is needed to bind the two metals. In MIG welding, a continuously-fed electrode wire melts into the weld, enabling two dissimilar metals to be joined without heating them to their melting points.
When welding stainless steel with MIG processes, the team at Marlin Steel programs a MIG welding robot to complete the weld. A filler must be used since the melting points of the two dissimilar metals may be very different. For instance, if one of the metals is overheated to reach the melting point of the other one, stress cracks and microfractures may result. Welding two dissimilar metals is possible, but a very difficult process with plenty of complications.
Difficulty.Combining dissimilar metals together, such as welding stainless steel to carbon steel, adds extra challenges to the process. This translates into increased labor, rejection/error rates, and costs.
Hot Cracking of the Stainless Steel. Because it is more electrically-resistant than carbon steel, welding stainless steel with resistance welding heats up the metal much faster than with carbon steel. While waiting for the carbon steel to reach weld temperature, the stainless can overheat and become riddled with hot cracks. Using filler-based welding or preheating the plain steel can ameliorate this, but these methods aren’t perfect.
Thermal Expansion in High Temperature Service Conditions. Another problem with using dissimilar metals in a welded wire form is that thermal expansion from heat will affect each metal differently. This difference in expansion rates between the two metals can cause extra fatigue to the welded joint—reducing the wire form’s structural integrity and useful life.
Reduced Weld Strength. Another problem with joining dissimilar metals is that it can lead to weaker welds—even with filler-based welding methods. The differences in weld temperatures and operational tolerances alone can easily compromise the strength of the welded joint.
To boil it down, welding dissimilar metals together is difficult to do right, and often produces inferior results to using metal alloys that are similar or the same.
By taking into account the long-term effects of using different metal alloys in a custom wire form, you can make sure that you get the right basket for the job.
If you have a question about stainless steel welding, wire forming issues, or need a custom wire form for a high-precision application with strict tolerance requirements, be sure to contact an experienced mechanical engineer!




 8613371530291
8613371530291