wire rope construction types in stock
Wire rope is a complex mechanical device that has many moving parts all working in tandem to help support and move an object or load. In the lifting and rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist and fitted with swivels, shackles or hooks to attach to a load and move it in a controlled matter. It can also be used to lift and lower elevators, or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers.
Wire rope is a preferred lifting device for many reasons. Its unique design consists of multiple steel wires that form individual strands laid in a helical pattern around a core. This structure provides strength, flexibility, and the ability to handle bending stresses. Different configurations of the material, wire, and strand structure will provide different benefits for the specific lifting application, including:Strength
However, selecting the proper wire rope for your lifting application requires some careful thought. Our goal is to help you understand the components of a wire rope, the construction of wire rope, and the different types of wire rope and what they might be used for. This will allow you to select the best performing and longest-lasting wire rope for the job at hand.
A wire rope is, in reality, a very complicated machine. A typical 6 x 25 rope has 150 wires in its outer strands, all of which move independently and together in a very complicated pattern around the core as the rope bends. Clearances between wires and strands are balanced when a rope is designed so that proper bearing clearances will exist to permit internal movement and adjustment of wires and strands when the rope has to bend. These clearances will vary as bending occurs, but are of the same range as the clearances found in automobile engine bearings.
Understanding and accepting the “machine idea” gives a rope user a greater respect for rope, and enables them to obtain better performance and longer useful life from rope applications. Anyone who uses a rope can use it more efficiently and effectively when they fully understand the machine concept.
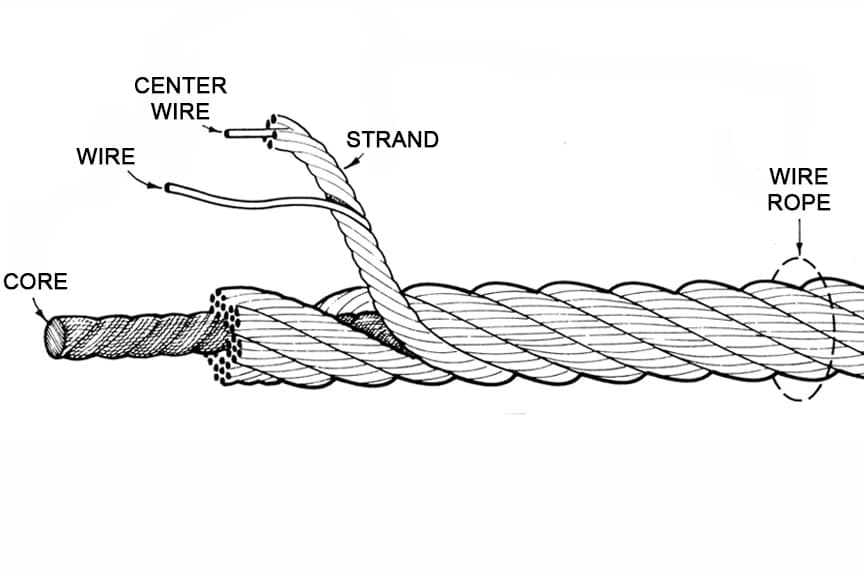
Wires are the smallest component of wire rope and they make up the individual strands in the rope. Wires can be made from a variety of metal materials including steel, iron, stainless steel, monel, and bronze. The wires can be manufactured in a variety of grades that relate to the strength, resistance to wear, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and curve of the wire rope.
Strands of wire rope consist of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope and supports the strands and helps to maintain their relative position under loading and bending stresses. Cores can be made from a number of different materials including natural or synthetic fibers and steel.
Lubrication is applied during the manufacturing process and penetrates all the way to the core. Wire rope lubrication has two primary benefits:Reduces friction as the individual wires and strands move over each other
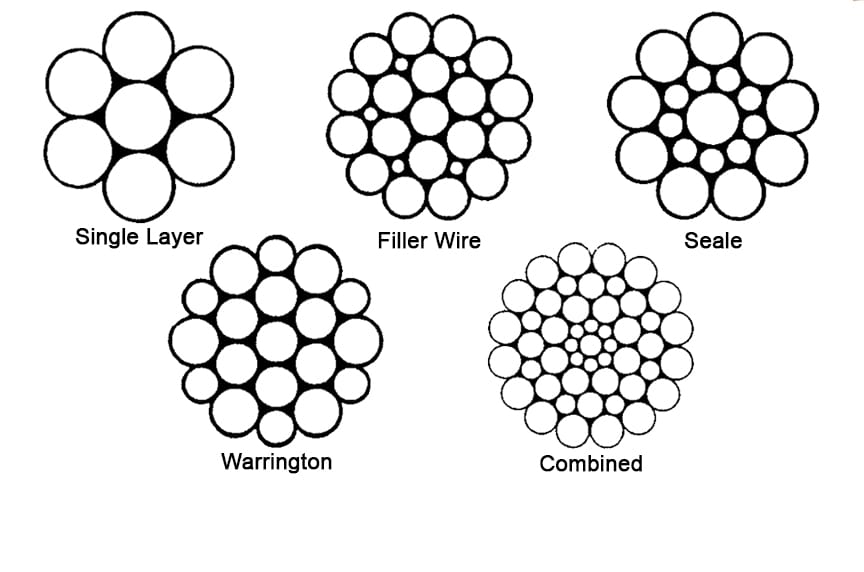
The number of layers of wires, the number of wires per layer, and the size of the wires per layer all affect the strand pattern type. Wire rope can be constructed using one of the following patterns, or can be constructed using two or more of the patterns below.Single Layer – The most common example is a 7 wire strand with a single-wire center and six wires of the same diameter around it.
Filler Wire – Two layers of uniform-size wire around a center with the inner layer having half the number of wires as the outer layer. Small filler wires, equal to the number in the inner layer, are laid in valleys of the inner wire.
Seale – Two layers of wires around a center with the same number of wires in each layer. All wires in each layer are the same diameter. The large outer wires rest in the valleys between the smaller inner wires.
Warrington – Two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of wire in the inner layer, and two diameters of wire alternating large and small in the outer later. The larger outer-layer wires rest in the valleys, and the smaller ones on the crowns of the inner layer.
On a preformed wire rope, the strands and wires are formed during the manufacturing process to the helical shape that they will take in a finished wire rope.
Preformed rope can be advantageous in certain applications where it needs to spool more uniformly on a drum, needs greater flexibility, or requires more fatigue-resistance when bending.
Direction and type of lay refer to the way the wires are laid to form a strand (either right or left) and how the strands are laid around the core (regular lay, lang lay, or alternate lay).Regular Lay – The wires line up with the axis of the rope. The direction of the wire lay in the strand is opposite to the direction of the strand lay. Regular lay ropes are more resistant to crushing forces, are more naturally rotation-resistant, and also spool better in a drum than lang lay ropes.
Lang Lay– The wires form an angle with the axis of the rope. The wire lay and strand lay around the core in the same direction. Lang Lay ropes have a greater fatigue-resistance and are more resistant to abrasion.
A steel core can be an independent wire rope or an individual strand. Steel cores are best suited for applications where a fiber core may not provide adequate support, or in an operating environment where temperatures could exceed 180° F.
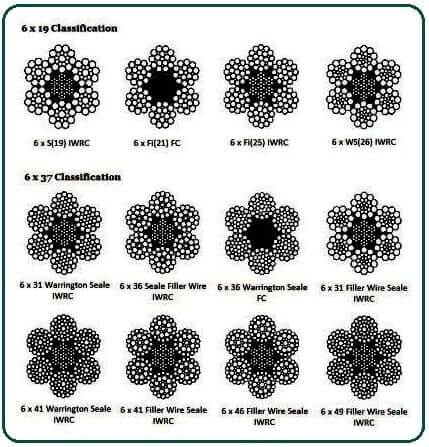
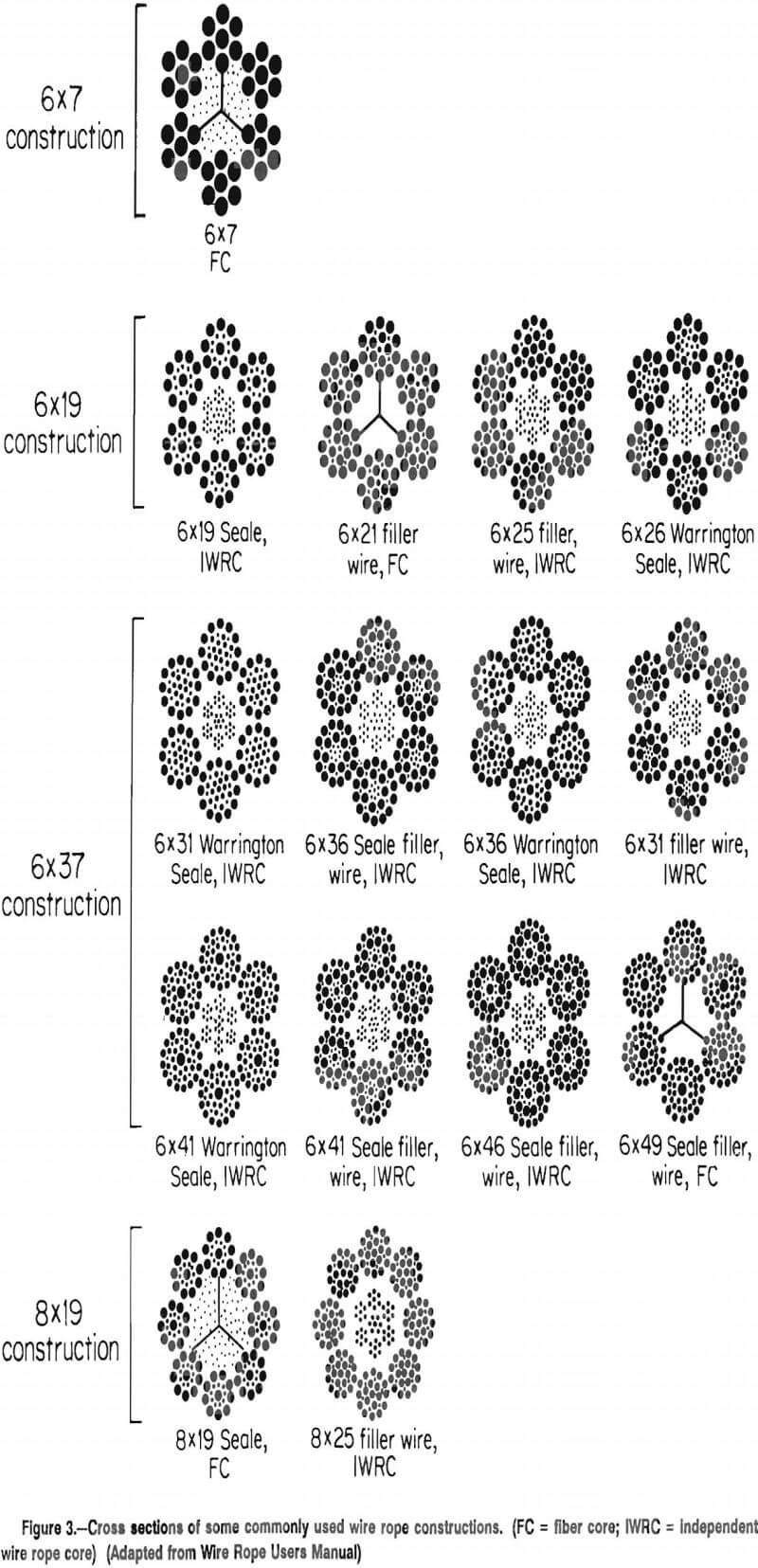
The classifications of wire rope provide the total number of strands, as well as a nominal or exact number of wires in each strand. These are general classifications and may or may not reflect the actual construction of the strands. However, all wire ropes of the same size and wire grade in each classification will have the SAME strength and weight ratings and usually the same pricing.
Besides the general classifications of wire rope, there are other types of wire rope that are special construction and designed for special lifting applications.
Some types of wire rope, especially lang lay wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation when under load. Rotation resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or rotating and can be used in a single line or multi-part system.
Special care must be taken when handling, unreeling, and installing rotation resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce twist into the rope which can cause uncontrolled rotation.
Compacted strand wire rope is manufactured using strands that have been compacted, reducing the outer diameter of the entire strand, by means of passing through a die or rollers. This process occurs prior to closing of the rope.
This process flattens the surface of the outer wires in the strand, but also increases the density of the strand. This results in a smoother outer surface and increases the strength compared to comparable round wire rope (comparing same diameter and classification), while also helping to extend the surface life due to increased wear resistance.
A swaged wire rope differs from a compacted strand wire rope, in that a swaged wire rope’s diameter is compacted, or reduced, by a rotary swager machine after the wire rope has been closed. A swaged wire rope can be manufactured using round or compacted strands.
The advantages of a swaged wire rope are that they are more resistant to wear, have better crushing resistance, and high strength compared to a round strand wire rope of equal diameter and classification. However, a swaged wire rope may have less bending fatigue resistance.
A plastic coating can be applied to the exterior surface of a wire rope to provide protection against abrasion, wear, and other environmental factors that may cause corrosion. However, because you can’t see the individual strands and wires underneath the plastic coating, they can be difficult to inspect.
Plastic filled wire ropes are impregnated with a matrix of plastic where the internal spaces between the strands and wires are filled. Plastic filling helps to improve bending fatigue by reducing the wear internally and externally. Plastic filled wire ropes are used for demanding lifting applications.
This type of wire rope uses an Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) that is either filled with plastic or coated in plastic to reduce internal wear and increase bending fatigue life.
Remember, wire rope is a complex piece of mechanical machinery. There are a number of different specifications and properties that can affect the performance and service life of wire rope. Consider the following when specifying the best type of wire rope for your lifting application:Strength
When you select a piece of rope that is resistant to one property, you will most likely have a trade-off that affects another property. For example, a fiber core rope will be more flexible, but may have less crushing resistance. A rope with larger diameter wires will be more abrasion resistant, but will offer less fatigue resistance.
At Mazzella Companies, we offer all different kinds of wire rope from all of the leading manufacturers. We sell the highest-quality domestic and non-domestic rigging products because product quality and operating safety go hand-in-hand. We have one of the largest and most complete inventories of both domestic and non-domestic rigging and lifting products to suit your lifting needs.
If you’re looking for a standard or custom specified wire rope for your lifting project, contact a Lifting Specialist at a Mazzella Companies location near you.
We stock well over 2,000,000 feet of wire rope in our various locations … ready for immediate delivery! We provide wire rope assemblies, and manufacture bridge cables, crane cables, steel mill cables, and thousands of OEM assemblies.

Wire ropes are several strands of metal wire that are twisted into a helix to form a composite rope, known as a laid rope. Large diameter wire rope consists of several strands of rope laid in what is known as cabling. Wire ropes are complex mechanical devices consisting of several moving parts that work together to help support & move an object or load.
In the lifting & rigging industries, wire rope is attached to a crane or hoist & fitted with a swivel, shackle, or hook to attach to a load and move it into a controlled case. It can also be used for lifting and lowering elevators or as a means of support for suspension bridges or towers. Wire rope is a preferred lifting tool for many reasons.
Its unique design consists of several steel wires that form separate strands placed in a helical pattern around a core. These structures provide strength, flexibility, & the ability to handle bending stresses. In the strictest sense, the term wire rope refers to a diameter larger than 3/8 inch (9.52 mm), with a smaller gauge specified cable or cord.
Initially, iron wires were used, but today the main material used for wire ropes is steel. Wire rope is made from cold-drawn wires to increase strength & durability. It may be noted that as its size decreases, the strength of the wire ropes increases.
The various materials used for wire ropes are iron, cast steel, extra strong cast steel, steel, and alloy steel, in order of increasing strength. For some purposes, wire rope can also be made from copper, bronze, aluminum alloys, and stainless steel. Wire ropes were developed in the 1830s with mining hoist applications.
Wire ropes are used in cranes and elevators for dynamic lifting and lifting and for transmission of mechanical power. It is also used to transmit forces to mechanisms, such as Bowden cables or the control surface of an airplane connected to levers and pedals in the cockpit.
Wire rope is made of threads of metal wire that are braided together to form a helix. Due to its heavy, flexible and tough characteristics, as well as being weather- and corrosion-resistant, it is commonly used in the building and construction, engineering, agriculture, aircraft, and marine industries.
Each wire strand bringing equal pressure to the bundle contributes to its strength and flexibility, making it an ideal material for pulleys. In Australia, wire rope was made of iron; Today, the materials used are mainly steel. Different industries use different types of wire ropes.
This is because the suitability of a specific wire rope for an application depends on the design, size, type of braids, and other characteristics. For example, marine-grade 316 wire rope is suitable for a variety of marine applications and settings.
Stainless steel is the standard alloy used in rope and cable. Its resistance to corrosions is much higher than that of galvanized & coated ropes, although there are no differences in strength. Therefore, it is the preferred material uses in marines and water-based salt industries.
It does not readily react to chemicals from food processing, textiles, and photographic settings. Its high resistance to corrosion, heat & cold, and pulp & paper chemicals makes stainless steel wire rope a much-needed material for manufacturing precision instruments, automobiles, fishing vessels, petrochemical equipment, & other fields.
Galvanized wire ropes are also steel wire materials that have undergone a galvanizing process to increase their corrosion resistance. The finished wire is immersed in a zinc bath to coat the product completely, i.e., it is galvanized.
Zinc is used in this process because cathode protection increases the life expectancy of the wire. Although the coating will degrade over time, it is still resistant to rust, corrosion, and other harsh chemicals. Galvanized wire can be found in the industrial and construction sectors as well as in agricultural and DIY projects.
Stainless steel and galvanized wire can be PVC coated with poly-vinyl-chloride or vinyl. Coated wire rope comes in various colors such as clear, black, white, or any other color that is required in various industries. PVC coated wire is flexible, weather-resistant, and very cost-effective.
Nylon-coated wire, although not as flexible as PVC, is abrasion-resistant and ideal for businesses in extremely cold regions. Wire ropes can be assembled to suit specific applications. If you have a project requiring a specific type of wire rope, send us an inquiry, and we’ll send you a special quote.
The wire is the smallest component of wire rope, and they form the individual strands in the rope. Wire can be made from a variety of metal materials, including steel, iron, stainless steel, Monel, and bronze. Wires can be manufactured in varieties of grades that are related to wire rope strength, wear resistance, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and curve.
These strings symbolize the smallest component of a wire rope and are tied together around a core to form complete wire ropes. The wire themselves can be coated but are usually available in “bright” or uncoated finishes.
Wire rope strings form two or more wires wrapped around an axial member in a geometric pattern or in combination with steel wires and other materials. These individual strands are then placed around the core in a helical pattern. Strands represent the major part that serves as the primary load-bearing unit.
A typical strand can form any number of strands, and the same goes for a rope that can have an ‘n’ number of strands. Wires made from larger diameter wires are more resistant to abrasion, while wires made of smaller diameter wires are more flexible.
The core of a wire rope runs through the center of the rope & supports the wires and helps them maintain their relative position under loading and bending stress. Cores can be made from many different materials, including natural or synthetic fibers and steel. It supports the strands and helps maintain their relative position under loading and bending stress.
Wire ropes are made from the various grades of steel wires with tensile strengths ranging from 1200 to 2400 MPa. The wires are first given special heat treatment & then cold drawn for the high strength and durability of the rope. Steel wire ropes are manufactured by special machines.
First, strands of wire such as 7, 19, or 37 are routed into a single strand, and then several strands, usually 6 or 8, are twisted around the core or center to form a rope. The core may be made of loops of hemp, jute, mica, or soft steel wire.
The core must be continuously saturated with lubricants for the long lives of the core as well as the entire rope. Asbestos or soft wire core is used when a rope is subjected to radiant heat, such as cranes working near furnaces.
However, a wire core reduces the rope’s flexibility, and such ropes are only used where they are subject to high compression, as in the case of multiple layers being injured on a rope drum.
The number of layers of wires, the numbers of wires per layer, & the size of the wire per layer all affect the strand pattern type. Wire ropes can be constructed using any one of the following patterns or can be made using two or more of the pattern below.
The Two-layer of similarly sized wire around a center whose inner layer is half the number of wires as the outer layer. Small fillers wires, equal to the numbers in the inner layer, are placed in the valleys of the inner wire.
Two layers of wires around centers with the same numbers of wires in each layer. All wire in each layer is of the same diameter. The larger outer strings rest in the valleys between the smaller inner strings.
The inner layer consists of two layers of wires around a center with one diameter of the wire, and the latter alternates two diameters of the larger and smaller wire in the outer. The larger wires in the outer layer are placed in the valleys & the smaller ones on the crowns of the inner layer.
On a prefabricated wire rope, the wire and wire are formed during the manufacturing process into the helical shape that they will take into a finished wire rope. Prefabricated rope can be beneficial in some applications where it needs to be spooled more evenly over the drum, more flexibility is required, or greater fatigue resistance is required when bending.
Direction and laying type refer to how the wires are laid to form a strand, either right or left & how the strands are laid around the regular core lay, lang lay, or alternate lay.
The wires are lined up with the axis of the rope. The direction of the wire held in the strand is opposite to the direction in the strand lay. Regular lat ropes are more resistant to crushing forces, are more naturally rotation-resistant, and also have a better spool in the drum than lang lat ropes.
The wires make an angle with the axis of the rope. The wire lay down, and the strand lay around the core in the same direction. Lang le ropes have greater fatigue resistance and are more resistant to abrasion.
A fiber core may be made of natural or synthetic polypropylene fibers. Fiber cores offer greater elasticity than steel cores but are more susceptible to crushing and are not recommended for high heat environments. A steel core can be independent wire ropes or an individual strand.
Steel cores are bests suited for applications where the fiber core cannot provide adequate support or in an operating environment where temperatures may exceed 180 degrees Fahrenheit. Based on what we have learned above, this wire rope description will provide the following information to the user:
Wire rope classifications provide the total number of wires in each strand, as well as the nominal or an exact number of wires. These are general classifications & may or may not reflect the actual constructions of the strands. However, all wires rope of the same size & wires grade in each classification will have similar strength and weight ratings and generally similar pricing.
Some types of wire rope, particularly lang le wire rope, are more susceptible to rotation under load. Rotation-resistant wire rope is designed to resist twisting, spinning, or twisting and can be used in a single-line or multi-part system. Special care should be taken when handling, unrolling, and installing rotation-resistant wire rope. Improper handling or spooling can introduce a twist in the rope, which can lead to uncontrolled twisting.
Compact Strand Wire Rope is manufactured using strands that have been compacted, by means of passing through a die or rollers, reducing the outside diameter of the entire strand. This process occurs before the rope is closed. This process flattens the surfaces of the outer strands in the strand but also increases the density of the strand.
This resulted in a smoother outer surface and increased strength compared to comparable round wire rope compare similar diameters and assortments while also helping to increase surface life due to increased wear resistance.
A swaged wires rope differs from a compacted strand wires rope in that the diameter of a swaged wire rope is compacted or reduced by a rotary swagger machine after the wire rope is closed. A curved wire rope can be manufactured using rounded or narrower wires.
The advantages of a swaged wires rope are that they are more resistant to wear, has better crushing resistance, and has higher strength than a round strand wire rope of similar diameter and assortment. However, a swaged wire rope may have low bending fatigue resistance.
The plastic coating may be applied to the outer surface of a wire rope to provide protection from abrasion, wear, and other environmental factors that can cause corrosion. However, because you can’t see the individuals strand & wires beneath the plastic coating, they can be difficult to inspect.
Plastic-filled wire ropes are fitted with a plastic matrix where the wires and the internal spaces between the wires are filled. Plastic fillings help improve bending fatigue by reducing wear internally and externally. Plastics-filled wire rope is used for demanding lifting applications.
This type of wires rope uses an independent wires rope core (IWRC) that is either filled with plastics or coated in plastic to reduce internal wear & increase bending fatigue life.
Strands of wire rope consist of two or more wires arranged and twisted in a specific arrangement. The individual strands are then laid in a helical pattern around the core of the rope. Strands made of larger diameter wires are more resistant to abrasion, while strands made of smaller diameter wires are more flexible.
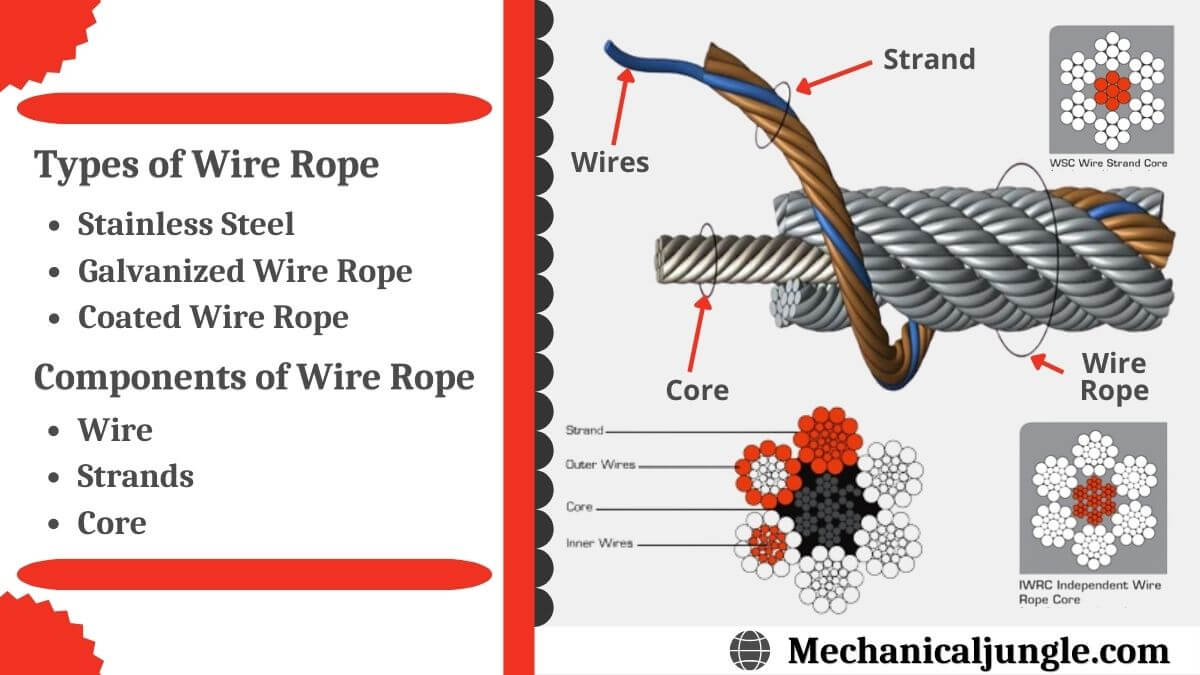
The Three Basic Wire Rope Components · Fiber Core (F.C.), usually polypropylene, sometimes hemp (H.C.) and sisal, Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC), Wire Strand Core (WSC)
The term cable is often used interchangeably with wire rope. However, in general, wire rope refers to diameters larger than 3/8 inch. Sizes smaller than this are designated as cables or cords. Two or more wires concentrically laid around a center wire are called a strand.
The term cable is often used interchangeably with wire rope. However, in general, wire rope refers to diameters larger than 3/8 inch. Sizes smaller than this are designated as cables or cords. Two or more wires concentrically laid around a center wire are called a strand.
A fiber core can be made of natural or synthetic polypropylene fibers. Fiber cores offer greater elasticity than a steel core but are more susceptible to crushing and not recommended for high heat environments. A steel core can be an independent wire rope or an individual strand.
Rotation-resistant wire rope refers to a series of steel ropes that minimizes the tendency to spin or rotate under load. These wire ropes boast a special design – the outer layer is twisted in the reverse direction of the inner layers for counteracting torsional forces generated from multi-layers of strands.
The helix or spiral of the wires and strands in a rope is called the lay. Regular lay denotes rope in which the wires are twisted in one direction and the strands in the opposite direction from the rope. The wires appear to run roughly parallel to the center line of the rope.
Understanding the basics of wire rope will help guide you on how to choose the right wire rope for your job. Application, required strength, and environmental conditions all play a factor in determining the type of wire rope that is best for you.
But when it comes to buying wire rope, the various numbers and abbreviations that describe the different types of wire rope can be confusing. EIPS wire rope, 6X19 IWRC wire rope, and lang lay wire rope are just some of the many variations available. But what does it all mean?
Displayed as inch or fractional inch measurements, the size indicates the diameter of the rope. Industry standards measure the rope at its widest point. A wide range of sizes are available from 1/8” wire rope to 2-1/2” wire rope. Thicker sized wire rope has a higher break strength. For example, our Wire Rope has a 15,100 lb. break strength while our Wire Rope has a 228,000 lb. break strength.
The numbers indicate its construction. For example: in wire rope, as shown above the first number is the number of strands (6); the second number is how many wires make up one strand (19).
When it comes to wire rope basics, regular lay also refers to right lay or ordinary lay. This indicates that the strands pass from left to right across the rope and the wires in the rope lay in opposite direction to the lay of the strands. This type of construction is the most common and offers the widest range of applications for the rope.
This term indicates that the wires twist in the same direction as the strands. These ropes are generally more flexible and have increased wearing surface per wire than right lay ropes. Because the outside wires lie at an angle to the rope’s axis, internal stress is reduced making it more resistant to fatigue from bending. This type of rope is often used in construction, excavating, and mining applications.
Independent wire rope cores offer more support to the outer strands and have a higher resistance to crushing and heat. Independent wire rope core also has less stretch and more strength.
Many of our customers use our rope and our wire rope clips to create rope assemblies. Check out of video blog on Wire Rope Clips to Wire Rope Assemblies to learn more.
For any questions on our wire rope products, call (877) 923-0349 or email customerservice@uscargocontrol.com to speak with one of our product experts.
HSI is a leader in the wire rope manufacturing industry. Since 1930 when founder Ted Hanes began splicing wire rope for local contractors in Buffalo, we have been dedicated to constructing the highest quality wire rope available.
Wire rope is a durable piece of machinery consisting of several multi-wired strands wrapped around a central core. It is ideal for indoor and outdoor environments, as an incredibly strong and durable rope with resistance to environmental hazards like water, sunlight, heat, and chemicals.
Wire rope consists of a core around which a number of multi-wired strands are “laid” or helically bent. There are two types of cores for wire rope: fiber and wire cores. Fiber cores are made of synthetic fibers, while wire cores are either an Independent Wire Rope Core or a Strand Core. The core provides support and maintains the position of the outer strands during operation.
Any number of multi-wired strands can be laid around the core. The most common arrangement is six strands around the core, as this construction gives the best balance of positive attributes. In general, ropes constructed with more wires have increased flexibility, while ropes constructed with fewer wires have superior resistance to abrasion.
The size, grade, and construction of wire rope needed should be considered when choosing a rope for your application. To learn more about selecting the correct wire rope, wire rope design factors, and to see a comprehensive overview of wire rope, see our Wire Rope Information page.
If you have questions about which wire rope is best suited for your job, please call our product experts at 1-888-426-3755 and we will be happy to advise you on a solution.
HSI standard wire ropes come in a full range of sizes, grades, and constructions. The most common classifications for standard wire rope are 6x7, 6x19, and 6x37. They may be ordered in bright or galvanized finishes, IPS and EIPS grades, right or left lay, and regular lay or lang lay.
While all wire ropes are constructed of multi-wired strands wrapped around a core, cable laid wire ropes take this construction a step further, wrapping several wire ropes, each with their own core, around a central wire rope. This results in a rope constructed with very small wires in reference to its finished nominal dimension which will offer greatly improved flexibility and kinking resistance.
Compact wire rope consists of wire rope strands that have been compacted to reduce the diameter of the strand and increase its density. The resulting rope has superior strength and abrasion resistance compared to standard wire rope, as well increased lateral compression strength. Typical applications for compact wire rope include crane lines, as compact rope can more easily fit into a sheave; and logging applications.
Extra high strength and corrosion resistant galvanized guy strand cable is an extremely sturdy wire rope used to hold structures in place in the construction and transmission industries, as well as a safety barrier cable and guard rail strand. Typical applications include telephone poles and other positioning applications where a sturdy and non-flexible rope is needed.
Commercial grade galvanized aircraft cable is a general purpose wire rope that is used in many industries for its increased corrosion resistance and strength. The galvanized coating on this wire rope provides lubrication while adding a protective layer against abrasive environments. Contrary to its common name, aircraft control cable, commercial grade GAC cannot be used in aircraft control applications.
Rotation resistant wire ropes are constructed with outer strands twisted in the opposite direction of the inner strands, causing the layers to counteract each other’s twist. This prevents rotation of the load during applications where precise lifting or positioning is required. Rotation resistant ropes are available in a full range of sizes, grades and constructions. Swivels are not recommended for use with rotation resistant wire rope.

Working safely with wire rope, for riggingand other purposes, requires an understanding of some of the characteristics of wire rope. Characteristics you should understand include lay, classification, and construction. We"ll explain each in this article.
The second is the relationship between the direction in which the strands are wrapped around the core and the direction that the wires within the strand are wrapped. This can be regular or lay.
And the third is the linear, or straight-line, distance a strand travels while making a single revolution around the core of the wire rope. This is known as the lay length.
The different lays and lay lengths of wire rope all have a functional purpose, and wire ropes with specific lays have different advantages and disadvantages for specific applications at work.
Another way to characterize wire rope is by the number of wires in each strand and the number of strands in the rope itself. This is known as wire rope classification.
A wire rope"s classification includes two numbers (such as 6 x 19). The first number (6, in this example) represents the exact number of strands in the rope. The second number represents the number of wires in each strand, but this number identifies a class, or range and may not be an exact number of wires.For example, a 6 x 19 class wire rope always has six strands, but may have 15-26 wires in each strand.
Hope you found this brief introduction to some aspects of wire rope, including the different parts of a wire rope and the rope"s lay, classification, and construction, helpful.
Remember there"s a lot more to learn about wire rope in order to work with it properly and safely, and thankfully, we offer two online learning courses for it--our wire rope basics online course and our wire rope safety and operations online course.

Finding the right wire rope and rigging supplies for your company needs is one of the most important safety precautions you can take. While you may assume that all types of wire rope are practically the same, understanding the individual wire rope specifications and uses is crucial. Without this information, you’ll never make the right decisions to keep your employees and premises suitably protected.
Available in a variety of sizes, diameters, and strengths, general purpose rope offers great flexibility and wear resistance. It is commonly found throughout a host of industries and can be used with a diverse range of equipment and machines.
A 6 x 26 rope is the most popular option within the 6 x 19 classification due to its flexibility. Meanwhile, products within the 6 x 37 classification, including the 6 x 49 SWS Warrington Seale, boast a third layer making them a regular choice for traveling cranes and mining equipment.
Special wire ropes take many forms but commonly share anti-spin and non-rotating properties. This makes them a great option when handling heavy loads, although they aren’t quite as flexible which can lead to some limitations regarding their function.
The special wire rope is designed by using six strands wrapped around the core in one direction. This is then wrapped by an additional layer of 12 strands in the opposite direction. They are available in various sizes and grades, giving you control when finding the right solution for your needs.
Galvanized cable shares many of the same properties as general purpose rope. However, it is coated in zinc to make it less vulnerable to rust and corrosion. It is a more affordable alternative to stainless steel solutions, although it might not be suited to harsher situations.
Stainless steel wire ropes boast the same pulling strength as the galvanized and general purpose rope options. But the corrosion resistant materials make it the strongest option under tough conditions, which can lead to greater longevity and safety in tough working environments.
Ultra-Pac wire ropes are built to offer an even greater breaking strength as well as superior fatigue. They boast a larger rope wire that has been put through a rotary swager to bring it back to size. Meaning it packs a far mightier punch than its size would suggest.
Tech-35 wire ropes are designed to offer the greatest rotation resistance possible. This makes it the perfect option when using a Swivel or similar machinery. In fact, persisting with the general purpose rope solution could be putting your employees and assets at risk.
If you’re still unsure of whichwire ropeand rigging supplies you need, our experts are here to help. We can provide guidance on the safest and most secure wire rope supplies for your project or business. Contact us to discuss your options today.
Small diameter 7×7 and 7×19 construction wire rope is commonly referred to as “aircraft cable”. IT IS NOT INTENDED FOR AIRCRAFT USE but designed for industrial and marine applications. According to Federal Specifications RR-W-410D, preformed, right regular lay, strand core, drawn galvanized. Aircraft cable is very versatile and is used for everything from hoisting ropes and tie-backs to safety barricades. It is available galvanized, stainless, or vinyl coated.
When browsing the General Purpose Wire Rope page of our website, you may notice that we offer two different6x19 highly flexible cables, and two different 6x37 flexible cables. When looking at the product illustrations, commonly referred to as snowflakes, you may notice a large black area in the center of some wire ropes, and an additional strand in the center of others. How can they be so similar yet so different at the same time? What sets them apart is their cores, and the distinctions betweenIWRC and Fiber Core.
The term IWRC stands for Independent Wire Rope Core. An IWRC is a full wire rope that can be either the same, or different construction as the outer layer strands. It adds strength to the total length of rope, and withstands crushing forces more effectively than other types of cores. It also reduces the amount of stretch a wire rope may undergo during service. IWRC wire ropes are often found in heavy lifting applications such as dredging and logging due to these strength qualities.
To learn more about 6x19 IWRC or 6x19 Fiber Core wire rope, visit https://strandcore.com/products/general-purpose-wire-rope/ or contact us with any questions.
Stainless Steel, galvanised or coated wire rope? Learn about these types of wire rope and select the one most suited for your application. Read on to learn more.
Wire rope is made of metal wire threads braided together to form a helix. Because of its heavy, pliable, and tough characteristics, as well as being weather- and corrosion-resistant, it is commonly used in building and construction, engineering, agriculture, aircraft, and marine industries. Each wire strand bringing equal pressure throughout the bundle contributes to its strength and flexibility, making it an ideal material for pulleys. In Australia, wire rope used to be made of wrought iron; today, the material used is mainly steel.
Different industries use different types of wire rope. This is because suitability of a specific wire rope for an application depends on the design, size, types of braids, and other characteristics. For example, marine grade 316 wire rope is suitable for various marine applications and settings.
Stainless steel is the standard alloy utilized in rope and cable. Its resistance to corrosion is much higher than galvanized and coated ropes, although there is no difference in strength. Therefore, it is the preferred material used in marine and salt-water based industries. It does not react easily to chemicals from food processing, textile, and photographic settings. Its high resistance to corrosion, heat and cold, pulp and paper chemicals make stainless steel wire rope a very essential material for creating precise instruments, automobiles, fishing vessels, petrochemical equipment, and other fields.
Galvanized wire rope is also a steel wire material that has undergone a galvanizing process to enhance its corrosion-resistance. The finished wire product is submerged into a zinc bath to coat its entirety, that is, galvanize it. Zinc is utilized in the process because the cathode preservation increases the life expectancy of the wire. Though the coating will wear off as time goes by, it is still resistant to rust, corrosion, and other harsh chemicals. Galvanized wire can be found in industrial and construction fields as well as agricultural and DIY projects.
Stainless steel and galvanized wire can be coated with PVC (poly-vinyl-chloride) or vinyl. Coated wire rope comes in various colours such as clear, black, white, or any other colour that is required in different industries. PVC coated wire is flexible, weather-resistant, and very cost-effective. Nylon coated wire, though not as flexible as PVC, is abrasion-resistant and is ideal for businesses in extremely cold regions.
Wire rope can be assembled to suit specific applications. If you have a project requiring specific types of wire rope, send us an enquiry and we’ll send you a specialised quote.

The majority of steel wires used for making wire ropes are usually manufactured from non-alloy carbon steel having a carbon content of between 0.4 and 0.95%. Since rope wires have a very high strength, they are able to offer support to large tensile forces. They can also run over sheaves even if the diameters are relatively small.
Cross lay strands has several layers, with the wires crossing each other. The parallel lay strands are prevalently used. Here, the lay length of practically all the wire layers have equal measurements. The wires of any two layers that are superimposed are also parallel. This makes for the linear contact.
However, two inner layer wires support the outer layer wire. Throughout the entire length of the strand, these wires are neighbors. Parallel lay strands are manufactured in a single operation. They have a greater endurance than cross lay strands. Parallel lay strands having two wire layers feature the construction Filler, Seale or Warrington.
The strands of spiral ropes are round. They feature an assembly of wire layers, laid helically through a center. At least a single wire layer is laid in the direction opposite to the outer layer. The dimension of spiral ropes can be non-rotating. They have a negligible rope torque under tension.
The open spiral rope is made up of round wires only. The center of the full-locked coil rope and half-locked coil rope is made of round wires, while the locked coil ropes come with at least a single outer layers of profile wires.
The major advantage is that they are constructed in such a way that dirt and water penetration is prevented to a large extent. Hence, protecting them from losing their lubrication. That’s not all, with the proper dimension, the ends of a broken outer wire will be unable to leave the rope.
Stranded ropes are a combination of several strands laid around a core in one or more layers in a helical shape. The core can be a fiber core, wire strand core, or independent wire rope core (IWRC). The fiber core features a synthetic material or natural fibers like Sysal.
Even though synthetic fibers are stronger and more uniform, they are unable to absorb many lubricants. Nonetheless, natural fibers are able to absorb about 15% of their weight in lubricant. This helps in protecting the inner wires against corrosion. Fiber cores are very elastic and flexible. The only problem is that they can easily get crushed.
Wire strand core consists an extra wire strand. It is basically used for suspension. The independent wire rope core (IWRC) is very durable regardless of the type of environments it is used in.
The majority of stranded ropes possess only a single one strand layer on top of the core. It is denoted with symbol Z when the strands in the rope are laid in the right direction, while symbol S represents left direction. Regular lay denotes that individual wires were wrapped around centers in a single direction, with the strands wrapped around the core in opposite direction.
Wire ropes featuring multiple strands are less resistant to rotation. They possess more than one strand layers, laid helically around the center. The outer strands are laid in an opposite direction to the underlying strands layers. Ropes having more than two strand layers can be non-rotating as well, while those with two strand layers are usually low-rotating.
Since they are used for carrying tensile forces, they are usually loaded by fluctuating and static tensile stresses. Wire ropes that are used for suspension are often referred to as cables.
They are used as rails for the cabin rollers or various other loads in cable cranes and aerial ropeways. Dissimilar to running ropes, the curvature of the rollers are not taken on by track ropes. When track ropes are used, the radius and the tensile force increases, as the stresses decrease.
They are used to bind together various kinds of goods. Wire rope slings are stressed by the tensile forces initially by bending stresses. They are bent over the blunt edges of the goods.




 8613371530291
8613371530291