wire rope inspection pdf made in china

A competent person must begin a visual inspection prior to each shift the equipment is used, which must be completed before or during that shift. The inspection must consist of observation of wire ropes (running and standing) that are likely to be in use during the shift for apparent deficiencies, including those listed in paragraph (a)(2) of this section. Untwisting (opening) of wire rope or booming down is not required as part of this inspection.
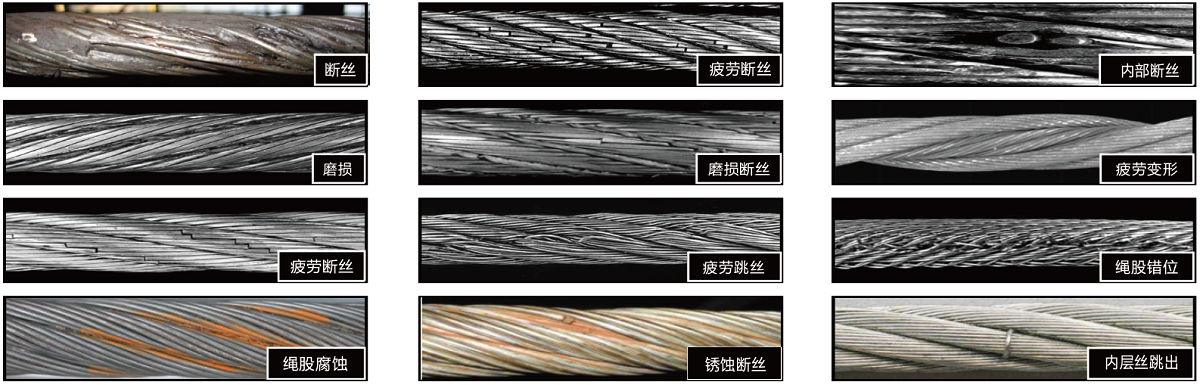
Significant distortion of the wire rope structure such as kinking, crushing, unstranding, birdcaging, signs of core failure or steel core protrusion between the outer strands.
In running wire ropes: Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay or three broken wires in one strand in one rope lay, where a rope lay is the length along the rope in which one strand makes a complete revolution around the rope.
In rotation resistant ropes: Two randomly distributed broken wires in six rope diameters or four randomly distributed broken wires in 30 rope diameters.
In pendants or standing wire ropes: More than two broken wires in one rope lay located in rope beyond end connections and/or more than one broken wire in a rope lay located at an end connection.
If a deficiency in Category I (see paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section) is identified, an immediate determination must be made by the competent person as to whether the deficiency constitutes a safety hazard. If the deficiency is determined to constitute a safety hazard, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If a deficiency in Category II (see paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section) is identified, operations involving use of the wire rope in question must be prohibited until:
The employer complies with the wire rope manufacturer"s established criterion for removal from service or a different criterion that the wire rope manufacturer has approved in writing for that specific wire rope (see § 1926.1417),
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the deficiency (other than power line contact) is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. Repair of wire rope that contacted an energized power line is also prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
Where a wire rope is required to be removed from service under this section, either the equipment (as a whole) or the hoist with that wire rope must be tagged-out, in accordance with § 1926.1417(f)(1), until the wire rope is repaired or replaced.
The inspection must include any deficiencies that the qualified person who conducts the annual inspection determines under paragraph (c)(3)(ii) of this section must be monitored.
Wire ropes on equipment must not be used until an inspection under this paragraph demonstrates that no corrective action under paragraph (a)(4) of this section is required.
At least every 12 months, wire ropes in use on equipment must be inspected by a qualified person in accordance with paragraph (a) of this section (shift inspection).
The inspection must be complete and thorough, covering the surface of the entire length of the wire ropes, with particular attention given to all of the following:
Exception: In the event an inspection under paragraph (c)(2) of this section is not feasible due to existing set-up and configuration of the equipment (such as where an assist crane is needed) or due to site conditions (such as a dense urban setting), such inspections must be conducted as soon as it becomes feasible, but no longer than an additional 6 months for running ropes and, for standing ropes, at the time of disassembly.
If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope in two; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited. If a rope is shortened under this paragraph, the employer must ensure that the drum will still have two wraps of wire when the load and/or boom is in its lowest position.
If the qualified person determines that, though not presently a safety hazard, the deficiency needs to be monitored, the employer must ensure that the deficiency is checked in the monthly inspections.
All documents produced under this section must be available, during the applicable document retention period, to all persons who conduct inspections under this section.

As consumables in mine, wire ropes have great significance for safe operation of coal mines. The complex structure makes the nondestructive testing particularly difficult. This paper summarizes the existing methods of analysis at home and abroad from the perspective of strong magnetic and weakly magnetic; introduc- es the main methods of wire rope at the present, including principle and current status. At last, several critical problems in nondestructive testing of wire rope are discussed.
Any wire rope in use should be inspected on a regular basis. You have too much at stake in lives and equipment to ignore thorough examination of the rope at prescribed intervals.
The purpose of inspection is to accurately estimate the service life and strength remaining in a rope so that maximum service can be had within the limits of safety. Results of the inspection should be recorded to provide a history of rope performance on a particular job.
On most jobs wire rope must be replaced before there is any risk of failure. A rope broken in service can destroy machinery and curtail production. It can also kill.
Because of the great responsibility involved in ensuring safe rigging on equipment, the person assigned to inspect should know wire rope and its operation thoroughly. Inspections should be made periodically and before each use, and the results recorded.
When inspecting the rope, the condition of the drum, sheaves, guards, cable clamps and other end fittings should be noted. The condition of these parts affects rope wear: any defects detected should be repaired.
To ensure rope soundness between inspections, all workers should participate. The operator can be most helpful by watching the ropes under his control. If any accident involving the ropes occurs, the operator should immediately shut down his equipment and report the accident to his supervisor. The equipment should be inspected before resuming operation.
The Occupational Safety and Health Act has made periodic inspection mandatory for most wire rope applications. If you need help locating the regulations that apply to your application, please give our rigging experts a call.
(3) Operational aids. Operations must not begin unless operational aids are in proper working order, except where the owner or lessee meets the specified temporary alternative measures. See WAC 296-155-53412 for the list of operational aids.Note:All accredited crane certifiers must meet and follow the requirements relating to fall protection, located in chapter 296-880 WAC, Unified safety standards for fall protection.
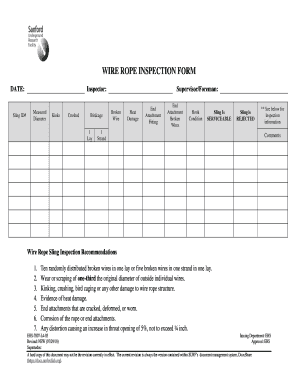
(a) Wire ropes must meet the crane or wire rope manufacturer"s specifications for size, type and inspection requirements. In the absence of the manufacturer"s specifications, follow the requirements for removal criteria located in this section, including Table 1.
Derricks63Consult rope mfg.Consult rope mfg.32*Also remove if you detect 1 wire broken at the contact point with the core or adjacent strand; so called valley breaks or evidence from any heat damage from any cause.Note:xd means times the "diameter."
(b) The accredited crane certifier must perform a complete and thorough inspection covering the surface of the working range plus 3 additional wraps on the drum of the wire ropes.
(ii) If the deficiency is localized, the problem is corrected by severing the wire rope; the undamaged portion may continue to be used. Joining lengths of wire rope by splicing is prohibited.
(e) Replacement rope must be of a compatible size and have a strength rating at least as great as the original rope furnished or recommended by the crane manufacturer.
(a) Sheave grooves must be free from surface defects that could damage the rope. The cross-sectional radius at the bottom of the groove should be such as to form a close fitting saddle for the size of rope used. The sides of the groove must be tapered outward and rounded at the rim to facilitate entrance of the rope into the groove. Flange rims must run true about the axis of rotation.
(a) A safe test area must be selected and all traffic and unauthorized personnel and equipment must be cleared from test area. This test area must be roped off or otherwise secured to prevent entry of unauthorized personnel and equipment;




 8613371530291
8613371530291