workover rig components pdf price

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Jereh truck/trailer mounted workover rig is mechanically and hydraulically driven. The power system, drawworks, mast, travelling system and transmission mechanism of the workover rig are mounted on the self-propelled chassis, which improves the moving efficiency greatly. Now, Jereh truck mounted workover rig series cover the workover depth from 2500m to 7000m and drawworks power from 250HP to 1000HP, featuring high operation load, reliable performance, excellent off-road performance, convenient movement and low operation/moving cost. Besides, workover rigs for arctic, desert and highland applications are available.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Workover Rig is available for both onshore as well as offshore Workover purposes at affordable prices. There are a number of companies that manufacture the Workover Rig as well as Rig packages that are required for different kinds of drilling jobs and meet the standards that have been set by the American Petroleum Institute or the API. The Rig packages are shipped worldwide. The rigs are included other than the simple Workover and they include the following:
Workover Rig is known as the Workover the different types of rigs include the offshore and onshore Rig that range from 150 horsepower to 1000 horsepower. Workover rigs have a surface depth that is equipped with diesel engines and transmissions and is available from 8000 ft to 30000 ft. Workover rigs contain a full line of drilling packages. Rig takes into account the skid mounted drilling rigs and the ones that are trailer mounted. Workover skid mounted drilling rigs incorporate the diesel-electric AC/VFD or the DC/SCR drive rigs, mechanical drive rigs and the combination drive Rig that ranges from 1000 horsepower to 6000 horsepower; while the trailer mounted Rig ranges from 450 horsepower to 1000 horsepower.
A lot of Workover Rig uses the double telescopic mast with the help of a single mast and is operated by wide wheel base axels, high strength steel beam, low cross section tires, dual pipeline brakes as well as hydraulic assist steering for the Workover. Rig mast is a double section type and uses a telescopic mast for dual safety protection. The gear shift and throttle of the engine can be remote controlled.
Workover types of Rig are available in the form of the single drum as well as the double drum. The groove ensures the alignment of in place as well as for long life. The optional Workover accessories for the auxiliary brakes include air thrust disc type clutch, brakes for the braking of the main drum, forced water circulating cooling with the brake rims as well as the optional brakes. Workover rigs are centrally controlled with electricity. The other kinds of drilling equipment include drilling equipment, triplex mud pumps, well control equipment; solids control equipment, oil control tubular goods and quality equipment. Work over rigs run casing tools and clean outs inside and outside a hole already drilled.

To ensure our website performs well for all users, the SEC monitors the frequency of requests for SEC.gov content to ensure automated searches do not impact the ability of others to access SEC.gov content. We reserve the right to block IP addresses that submit excessive requests. Current guidelines limit users to a total of no more than 10 requests per second, regardless of the number of machines used to submit requests.

WILSON WELL SERVICE RIG (Ref#3000Ta) 103’ x 248,000# derrick, Out of service since 2017, lot of rust, will start and run and/or drive down the road POR
Refurbished, 700 hp, Double drum 2042 drawwroks with Parmac 202 brake assist, (2) Caterpillar 3406 Engines, (2) rebuilt Allison 750 6 speed auto transmission with reverse. 112" x 300,000 # hook load capacity on 8 lines, clear height 97 feet, leg spread 7" 6-1/2", racking board, oil bath chain case, elevated rotary drive, all raising lines and guidelines. The Draw-works, hydro-mantic break, and crown assembly have been rebuilt. Heavy duty Draw works drive propeller shaft through right angle gear box, rotary drive propeller shaft, heavy duty reverse gear box and oil bath roller chain, and a self-locking handling winch. Mounted on triple front axle mechanical 6 axle carrier with 134,000# capacity designed to meet highway safety standards with necessary toughness for off road operations. Price: $265,000
Derrick fell onto rig when being raised, derrick would need to be replaced or repaired. Built 1981, double drum, 42 x 12, 42 x 8, swab drum removed from jack shaft, 5-axle back in carrier, 250,000# derrick with double racking board and triple rod basket, Cat 3408, CLT 5860 transmission, Cooper right angle box, 4 hydraulic leveling jacks, air rod transfer in derrick, hydraulic winch, Kerr 6 cyd 10000 psi Mustang pump powered from jack shaft, Kerr 3-valve release 10,000 psi, tong carrier f/Foster, steel work platform, Parmac 22 SR hydromatic brake. Extra rebuilt 3408 Cat engine. Price as is: $112,500
Manufactured 1981, mounted on 5 axle carrier, double triple service rig, 96’ x 250,000# derrick, Detroit Series 60 12.7 diesel engine, Allison transmission, 9/16” sandline, 1” drill line, hydraulic jacks, hydraulic catwalk, travelling block, tubing bard, rod basket and all necessary lines. Tooling not included. Price: $115,000
Manufactured 1983, double drum, 96’ x 180,000# derrick, mounted on 5 axle carrier with 92T engine, Allison transmission Price rig only: $300,000 Price with tooling:$340,000
WILSON 42 WELL SERVICE RIG(Ref#7562Ta) Manufactured 1975, 180,000# Pemco double/triple derrick, mounted on Wilson carrier with Detroit 8V71 engine, 4 hydraulic leveling jacks, ready to work Price rig only: $74,500 Price with tooling: $94,500
Manufactured 1983, 70" x 120,000# non telescoping stiff mast, double drum 26 x 8, Detroit 6V71 diesel engine, 740 Allison transmission with Spicer power divider, mounted on 4 axle carrier. Rig runs and truck drives, stacked for several years, good condition Price: $93,500 USD
FRANKS 500 WORKOVER RIG(Ref#7615Tc) Built 1980, refurbished 2018, 102’ derrick, 150 ton blocks, 15,000’ sandline, new engine and transmission, ready to work Price: $430,000
FRANKS 400 WORKOVER RIG(Ref#7615Ta) Built 1979, refurbished 2017, 102’ x 215,000# derrick, 100 ton blocks, 15,000’ sandline, 4 lines Price: $390,000
FRANKS 300 SERVICE RIG(Ref#1169Ta) 4-legged derrick, Series 60 Detroit engine, 6850 Allison transmission, blocks, Foster tongs, mounted on 4 axle carrier, working condition Price: $37,500
WILSON MOGUEL 42 WELL SERVICE RIG(Ref#3177Tb) Two available, 96" x 280,000# mast, Detroit Series 60 engine, 5860 Allison transmission, mounted on 5 axle Wilson carrier, handling tools Price: $315,000
Workover rig with 83’ telescoping derrick, 10’ crown extension, 200,000# lift capacity, 100,000# snubbing capacity. Catwalk with 42’ reach, forward and revere motion, hydraulic pipe slide, six portable pipe racks, powered by workover rig. 5000 ft/lb hydraulic rotary, 15k psi working pressure capability kelly hose, 300 ton mast with 5 x 5 heavy wall box tubing and 2 x 2 heavy wall cross sections, (2) mast raising cylinders, 9-1/8 x 25’ telescoping cylinders/crown sheaves with cable guides, (2) winch sheaves/snubbing sheaves, SRS fall protection, retractable flow tube design, non-swivel boom pole on curb side winch, (2) mast supports, 1” lifting cables, mounted on 5 axle Crane Carrier (3rd axle drop), with 375k Volvo Penta engine, 150 gal fuel capacity, hydraulic self-leveling components, 6 speed Allison transmission, 1:1 gear box, (2) 65 gpm pumps, (2) 30 gpm pumps, (1) 28 gpm Commercial shearing pump, 40 gal accumulator storage, single man cab, hydraulic leveling jacks Price on Request
Manufactured 1960’s, double drum, single rig mast, 64’ x 250,000# (tubing and rod racks), 70 ton blocks, 2 lines, Detroit diesel 60 gpm @ 2000 psi, hydraulic system, air clutch. Rig was refurbished 2013/2014 at a cost of $130,000: repairs included used 65’ derrick installed, new 1” main line, repairs to air system, hydraulic system upgrade, leveling jacks, derrick ljghting, tires, 70 ton blocks installed. But the rig has been sitting since 2015 and now needs rebuilding. It doesn’t run. Price as is: $19,500
Manufactured 1980, completely refurbished 2004, 5 axle double drum well service unit, double 15 Parmac brake on main drum, 96" x 180,000# hydraulic raised mast, mast lighting, Detroit 60 Sereis engine, 5860 Allison 6 speed transmission, 4 hydraulic leveling jacks, dual manual outriggers, PD12 Braden utility winch, McKissick 100 ton tubing block 21-31 diving, 1000" of 1" tubing line, 13000" of 9/16" sandline Price: $225,000
CARDWELL KB200B SERVICE RIG(Ref#11674Ta) 72’ x 140,000# stiff mast, 40 x 10 double drum drawworks, 2 aux deck winches, tubing board, rod board, cat walks, railing, stairs, floor BOP controls and accumulator bottles, McKissick 75 ton tubing block and hook, mounted on 5 axle carrier, Detroit 8V71 diesel engine, Alliston CLBT4460 auto transmission PRICE: $127,500
Rig manufacture 1980, mounted on 1980 GMC Brigadier with Cat 3208 engine, includes elevators & misc tools, also includes 1996 1-ton Super Duty tool truck, tandem axle, Cat 3208 diesel, sitting 1-1/2 years Price: $92,500
1980, 475 hp, single drum (new), reworked, 96" x 205,000# hydraulically raised mast, 6 lines, crown block: 3 new sheaves blocks and bearings, racking board, guide wires, (2) hydraulic hoist, weight indicator, block, elevator links, fall safety device, work platform, mounted on 4 axle carrier with Detroit Series 60 diesel engine, Allison transmission, rig in excellent condition and has been well maintained, ready for use PRICE: $115,000
SKYTOP BREWSTER RR400(Ref#13190T) Mounted on 4 axle carrier, single drum drawworks, 8x7 disc assisted brakes, tubing board, Cat3406B engine, Allison 860DB transmission, 100 ton McKissick block, Foster 58-92R tongs, misc hand tools, approx 36" base beam for rig, ready to work Price: $110,000
Refurbished 2017, 4 lines, 96’ x 205,000# mast, 8V71 Detroit engine, mounted on CCC, 75 ton McKissick blocks, tubing board, rod basket, work platform, rigged up and working in field Price: $295,000
Manufactured 1977, 72’ x 125,000# derrick, 8V71 Detroit engine (rebuilt), Allison 750 transmission, 6500’ of new 5/8” sand line, tubing line new, drum brakes new, new style McKissick blocks, working daily Price rig only: $157,500
Double drum drawworks with hydromatic brake, 10" brakes, 96" x 180,000# derrick, mounted on 4-axle PEMCO carrier with hydraulic support legs, 8V71 Detroit, 4460 Allison transmission, Spicer 784 split shaft gearbox, 250 hp right angle drive, 650" of 7/8" tubing line, 8000" of 9/16" swab line, 100 ton Sowa block, hydraulic winch, hydraulic weight indicator, 84" links, 2-3/8" and 2-7/8" tubing elevators, BJ tubing slips, Foster 5893R power tongs with lift in derrick, rod hook, rod stripper, rod elevators, wrenches, transfers, rod fishing tools, misc hand tools and connections Price: $140,000
Manufactured 1974, double drum drawworks, double triple 96" x 180,000# derrick with a hydromatic. The rig has working line with heavy traveling block and approx. 12,000" 9/16 sand line. Mounted on Skytop carrier with tandem steering and rear ends 4 axles W/ tag axle, 4 leveling jacks, powered by an 8V-71 with a Allison 4460 transmission, (note transmission was overhauled in early 2000"s) and the engine has a new head on right bank. The rig has two leveling jacks on the rear and two leveling jacks on the front which are located right behind the steering axels. Tooled out with hydraulic rod and hydraulic tubing tongs, air slips, rod and tubing elevators, hand tools and misc over items. PRICE REDUCED: $115,000
10 x 13 pole, double Drum, Franks 33” air over grease, brakes in good shape, 7/8” tubing line, tubing blocks, tong pressure adjustment, hi/low on tubing, air slips control, master kill on drawworks, Foster 36 with 8’ lift ram, air backup, swing around tong rack, mounted on 2001 Freightliner F80 truck, Cat C12 Series 3125, Fuller 9-speed transmission, PTO, winch for pole scope Tulsa 48, blocks raise pole, dual fuel tank, dual battery, 50 gal hyd tank, toolboxes, hydraulic outriggers, BJ rod tongs, ¾” and 7/8” heads, tools, swabs, extra tongs, orbits, drilling head Price: $242,500
Double drum (second drum is removed, rig is running as single drum), hyd pole and down riggers, mounted on 1990 Crane Carrier, 9 sp Eaton Fuller transmission, 100,000 miles, 8 x 10 telescoping poles, 3/4” cable, no tooling Price: $52,500
10 x 13” pole, single drum, mounted on 1980 Brigadier 9500 Series truck with 671 inline Detroit, drop box, travelling blocks, tubing lines, hyd jacks, no tooling, sitting since 2000 PRICE: $49,500
Cable Tool Drilling and Completion Rig, 60" double poles rated to 150,000#, 5000" drill capacity, 10,000" pull capacity, propane Waukesha 145 engine, 500 gal propane tank, trailer moutned with International 4300 truck, last drilled 2012, 2300" drill line on drum, 3500" on spool casing drum, heavy block sandline drum, cat heads each side, tooling, spare engine Price: $72,500
400’ of 7/8” block line, 9/16” sandline drum (no cable), 2000’ of ¾” drilling drum, 3 McKissick sheaves, air clutches and controls, mounted on 1961 Mack truck with 250 hp Cummins engine, older rig but runs good. Includes elevators, oil saver pump, no BJ tongs, currently working. Price: $87,500 - Pennsylvania
Triple drum, friction clutch, cathead (sandline holds 2400’ of 5/8” line), mounted on tandem axle Chevy truck with 427 gasoline engine, 8-5/8” x 45’ single pole, new tires, power steering, wireline unit, good usable rig for shallow oil/gas lease, drills, workover, swab capabilities, no tools Price: $112,500 - Oklahoma

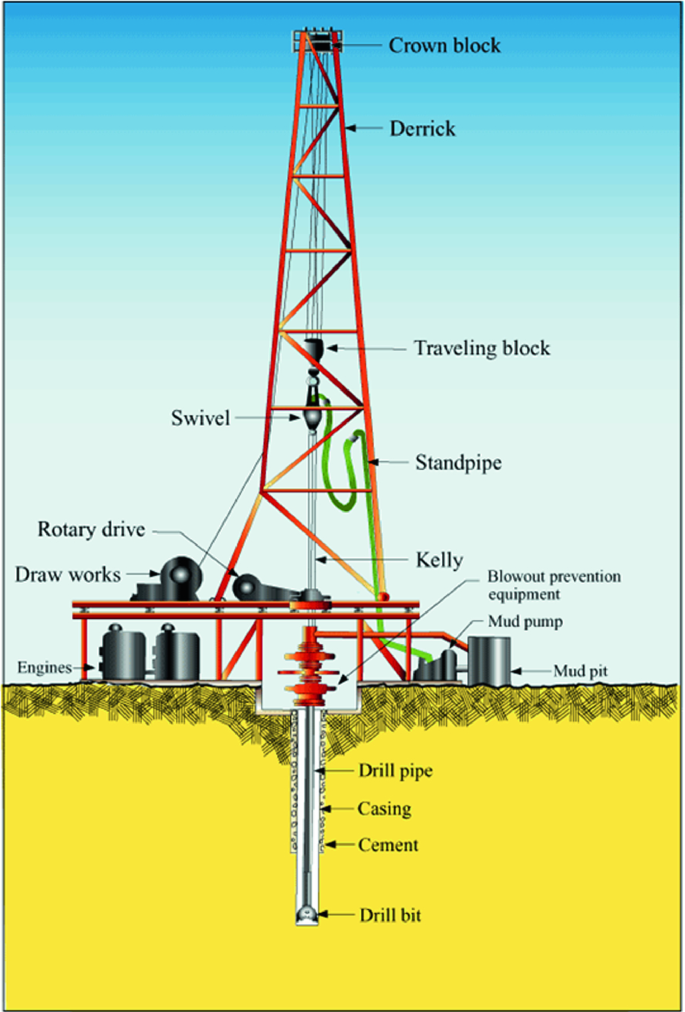
This comprehensive training manual, updated my drilling expert Mike Marcom, acquaints the reader with the standard equipment and crew on a rotary drilling rig. Topics include the power, hoisting, rotating, and circulating systems; well-control equipment, auxiliaries, and the crew. This book is recommended for floorhands, motorhands, derrickhands, drillers, and toolpushers. Readable language, clearly labeled illustrations and photographs, a glossary, helpful appendixes, and self-test review questions help the reader to comprehend the material. ISBN 978-0-88698-255-3. 2015, 160 pp.

For most operators, improving profitability on their wells is an ongoing battle between getting the right equipment, making the job easier, and keeping a strict eye on the bottom line.
A perfect example of this is that many operators go with a full-size drilling rig for surface interval drilling because it is more convenient. Often, they are already engaged with the service provider and the equipment is already on site — so it seems like this is the most cost-effective decision. In the end, though, operators end up paying more in fuel and personnel costs, and increasing their HSE risks, with this option.
Full-size rigs are made for constructing wells with total depths over 20,000 feet. These are enormous machines for enormous jobs. As a result, they have an enormous footprint in terms of costs and risks. When drilling surface intervals and running surface casing, a full-size rig is not the right equipment for the job. While it may seem more effective at the time, a surface drilling rig or spudder rig is the better choice.
Less fuel consumption and lower fuel costs: Surface drilling rigs are highly engineered for surface drilling and running surface casing. They are smaller in size as compared to full-size rigs, which means they use a lot less fuel. To be exact, spudder rigs actually burn up to 50% less diesel compared to full-size rigs, which means they also cost about 50% less to operate.
Equipment optimization:When operators use full-size rigs for surface drilling and running surface casing, they aren’t able to reserve the machines for their intended use. If operators have a separate spudder rig, then the full-size rigs can be used for applications better suited for them, reducing overall operating costs.
Lower personnel costs: Typically, a full-size rig requires a crew of 16 people to operate, while a top hole rig only has a crew of nine. With a lower personnel count, there are lower payroll costs. Not only that, the costs for personnel transportation are lower as well, in addition to the HSE risks.
Safer work environment: With a full-size rig, operators must switch between mud systems, which means that the crew has to mix different muds on location. Handling more fluids increases the chances of spills, which is detrimental to the environment and to the crew. A top hole drilling rig uses a closed-loop mud system, so there is no need to switch between different mud systems or handle different types of mud on location.
A smaller, fit-for-purpose preset surface drilling rig is a more economical choice than a full-size rig when it comes to drilling surface intervals and running preset surface casing.
A differentiating factor between EnerCorp’s surface drilling rigs and our competitors is the customized casing running tools (CRT) that enable us to be faster and more cost effective than other service providers.
Fit-for-purpose equipment: Our CRT’s are specifically designed for our RD20 XC rigs. This allows for the casing to be torqued up to proper torque specs per the casing manufacturer’s specifications.
Better processes:Competitors use alternative methods to run casing: Wishbone style casing elevators. In this process, a tool is used to run casing on our competitors rigs that does not keep the casing full and requires a swedge to be rigged up to fill it. There is far greater exposure and risk to the man in the basket on a board suspended from the derrick. Plus, dry casing run with this method is far less efficient because each joint needs to be filled via the swedge on top of the casing, taking more time. The Wishbone is a far more dangerous method as sometimes it does not latch correctly and can cause the casing to be unsettled during the run.
When working with EnerCorp, operators not only get the benefits of using a surface drilling rig, but also the additional advantages of using fit-for-purpose equipment that is highly optimized as compared to competitor options.

Independent producers and operators ramping up shale exploration and development programs are pushing the limits of conventional drilling equipment. Whether they are drilling multiple long-lateral horizontal wells from single pads, testing new bits and mud motors to boost penetration rates, or deploying next-generation rig floor and automation systems to slash “spud to sales” times, independents and their service company partners continue to find ways to improve resource play economics and crack the unconventional drilling frontier wide open.
Goodrich Petroleum is a case in point. Over the past two years, the company has transitioned from vertical Cotton Valley wells to horizontal wells in the Cotton Valley and the underlying Haynesville Shale. To unlock the shale’s vast potential, the company worked with its partners and service providers to discover the right casing points and to choose bottom hole assemblies that could build at sufficient rates to maximize lateral lengths, reports Clarke Denney, the company’s vice president of drilling. He notes that in the Haynesville Shale, Goodrich is utilizing robust directional equipment and mud cooling units to drill laterals at vertical depths of 15,000 feet, where circulating temperatures can reach upward of 340 degrees Fahrenheit.
Drilling wells in either play requires rigs with the right equipment, says Denney. He says top drives are important because they allow pumping and rotating the drill string while coming out of the hole, which is necessary at times for hole cleaning. This reduces drag and the chance of getting stuck. Top drives also maximize directional drilling performance.
Drawworks that can deliver at least 1,500 horsepower are also key, Denney adds. “We believe in high horsepower,” he stresses. “A 1,500-horsepower rig carries a premium over a 1,000-horsepower rig, but it speeds trips and puts less strain on the equipment. We get our money’s worth.”
Just as important as the drawworks and top drive is having powerful mud pumps on the rig, Denney says. “In the Eagle Ford, we would prefer to have at least 1,600-horsepower pumps, especially when drilling long laterals,” he relates. “That horsepower is needed for mud hydraulics to keep the hole clean, and to drive the downhole motor and other equipment. We have achieved up to 6,000-foot laterals to date, and we are targeting 9,000-foot long laterals in the near future.”
In many cases, it makes sense for the rig to have the ability to skid, Denney says. He explains that drilling multiple horizontal well bores on one pad reduces construction costs and rig transit times. “In the Eagle Ford, if we can skid, our drilling costs can be reduced as much as $500,000 a well,” he says.
Goodrich Petroleum is far from the only company that needs “high-spec” rigs with powerful top drives, hoisting systems and pumps. According to industry sources, rigs with larger (+1,000) horsepower ratings account for an estimated 60 percent of the active rig fleet. Moreover, rigs with at least 1,000 horsepower account for nine of every 10 rigs that are under construction or planned for the near future.
With its operational focus transitioning from the Cotton Valley trend to the Haynesville Shale, and more recently to the Eagle Ford Shale, Goodrich Petroleum is achieving consistent production and reserve growth through horizontal drilling with high-spec land rigs and advanced downhole tools. Even during the economic recession of 2009, the company increased average net daily production 24 percent and proved reserves 5 percent. Over the past four years, it has more than doubled its daily production while expanding its reserves 30 percent.
Trent Latshaw, the founder and head of Latshaw Drilling in Tulsa, can verify that the demand for 1,000-2,000 horsepower rigs is high. He says the company’s fleet, which includes 15 rigs within that range, has 100 percent utilization. In fact, Latshaw reports that the only unused rig his company has on the books is a new, 1,700-horsepower diesel electric that is still under construction.
Many of today’s high-spec rigs have closed-loop mud systems, Latshaw notes. “Closed-loop mud systems do away with the need for a reserve pit,” he says. “The systems also processes drilling fluid more efficiently. They are able to take more solids from the drilling fluid, which enables more fluid to be reused and makes the solids dryer and easier to dispose of. That becomes very important when dealing with oil-based mud, which often is used in horizontal wells.”
Latshaw encourages operators to consider using high-horsepower rigs when the class they want is difficult to obtain. “We consider our 2,000-horsepower rig to be identical to our 1,500-horsepower rigs, except for the drawworks size and the mast/substructure capacity,” he says. “The 2,000-horsepower rigs have the same footprint and move as fast as the 1,500-horsepower units, and for all practical purposes, the day rates are the same.”
He also says diesel-electric SCR rigs are comparable to AC rigs. “They have the same top drives, the same mud pumps, the same mud systems, the same engines, and the same blowout preventers,” he reports. “From the customers’ perspective, they drill wells as fast as AC rigs.”
In reference to safety, Latshaw says people matter more than technology. “You can try to design a piece of equipment that is accident proof, but safety comes down to the people on the rig floor and what their mindsets are,” he insists. “We are putting more money into training, beefing up our safety department, and having more safety coaches go around the rigs to work with the hands.”
He points out that many rigs, including several of Latshaw Drilling’s units, use automated iron roughnecks to improve safety. “Those are expensive, high-maintenance pieces of equipment,” he says. “We decided to take some of them off our rigs, then track closely to see if we had more finger and hand accidents on the rigs using manual tongs and a drill pipe spinner versus the rigs that had iron roughnecks. We have not seen a difference.”
For Joe Hudson, the president of Nabors Drilling USA, the future looks bright. “We have at least 103 AC rigs deployed at this point,” he reports. “We are in the process of building 25 more, and we always are looking for opportunities to expand further, be it in the Bakken, the Mid-Continent, West Texas, the Eagle Ford, or the Marcellus.”
Hudson says the new rigs include larger pumps, AC top drives, and tubular handling tools such as automatic catwalks and floor wrenches. “With the automatic catwalk, there is no need for a rig hand to pick pipe off the catwalks, pull it up with a hoist, and drag it to the rig floor,” he says. “Instead, the catwalk picks up pipe and elevates it to the rig floor. No one is touching the pipe or rolling pipe onto the catwalk, which keeps people away from tubulars, reducing the risk of pinch-point injuries.”
The rigs also employ advanced software. “With conventional rigs, the driller would drill ahead with a hand on the brake handle. He had only basic drilling information available to him, and his skill and his experience with the area dictated his ability to drill the well,” Hudson recalls. “Today, the software associated with smart drilling systems allows him to drill the well with a better understanding of the factors that influence drilling performance, such as delta P, hydraulic horsepower, weight on bit and rate of penetration. That translates to a faster rate of penetration.”
To ensure that its employees work as safely and efficiently as possible, Nabors has fully functional training rigs in Williston, N.D., Casper, Wy., and Tyler, Tx., where it trains personnel with no previous experience, Hudson reports. He adds that the company carefully defines the training and competency individuals need to be promoted.
The newest generation of high-spec land rigs purpose-built for horizontal drilling in unconventional resource plays features integrated subsystems to automate key processes such as pipe handling. Automated catwalks and floor wrenches not only increase operating efficiency, but also improve rig floor safety and extend pipe longevity by reducing handling damage.
When downturns do occur, Nabors tries to keep competent people and trainers on staff, Hudson says. By doing so during the last economic downturn, he says the company managed to go from 92 rigs in fall 2009 to 190 rigs today without compromising its personnel or safety standards.
Regardless of the market condition, Hudson says it is vital to design rigs for specific areas. “Every area is unique,” he says. “Carrying the top drive in the mast is a great way to reduce the number of loads needed, but in areas where road weights are critical, other approaches have to be adopted.”
To illustrate regional developments, Hudson points to Nabors’ B-series rigs, which were designed to accommodate pad drilling in the Bakken Shale. “We built a box-on-box substructure because we can close in that substructure, which makes it easier to winterize,” Hudson says. “Also, the way we can rotate the substructure lets the company conduct completion and production-related operations on one well while we are drilling another on the same location.”
Dealing with cold weather is also important, he observes. “We protect the rig floor from wind by putting the dog house and wind walls around it, then put heaters on the floor,” he says.
Like other contractors, Cyclone is expanding its fleet. “We built five rigs in 2010 and we are scheduled to build four more in 2011,” Hladky details. “They all have 1,600-horsepower pumps, with 270- and 500-ton AC top drives.”
Hladky says Cyclone tries to keep the rigs’ designs simple. “We engineer all the rigs similarly,” he adds. “Even if they are different sizes or different applications, the basics are all the same. That lets employees move from rig to rig efficiently and safely.”
Like the other drilling contractors, Hladky stresses the importance of good people. “A high-spec rig is nothing without good people,” he declares. “We are drilling with mechanical rigs built in the 1980s and 1990s with good people right next to and as efficiently as high-spec rigs.
Cyclone skids its rigs with hydraulic feet rather than rails because rigs can get slightly off target each time they move from one well to the next. “If you are on a rail system, the error is difficult to deal with. A walking rig can move in any direction needed to position exactly over the well bore,” he says.
“We started looking at these pads primarily from a surface usage viewpoint,” Cox says. “Since the terrain in North Dakota can be difficult, we wanted to reduce the number of pads, handling facilities, power lines, and pipelines we had to build. As we dug into the process, we began to ask if we would save any money beyond the cost of building the location and moving the rigs. The batch process provided the cost savings that gave us the impetus to keep working on the project.”
To explain the process’s economic and environmental benefits to investors, Continental dubbed it ECO-Pad® and produced a video, which is now available on its website. “It’s been amazing how many people have watched the video and asked to show it to others,” says Brian Engel, Continental’s vice president of public affairs. “The walking rig is something almost no one has seen before, especially in the investor community.”
As drilling contractors build their fleets and train employees, equipment manufacturers are coming up with better ways to design and manufacture components. These include downhole motor manufacturers. “We are dedicating significant resources toward boosting overall motor performance, with specific focus on increased power and equipment reliability,” says Mpact Downhole Motors Vice President David Stuart.
To maximize reliability, Stuart says manufacturers are designing downhole motors that can operate under increasingly higher loads. In addition, they must ensure motors are designed to be compatible with ever-changing drilling conditions. “Drilling motors have to be designed and calibrated for each specific application to compensate for changes in temperature and other downhole conditions, which will cause the components to expand and contract during drilling,” Stuart remarks.
The ideal operating range varies with motor sizes and configurations, Stuart says. “Experience goes a long way in determining the right range, and it comes not only from the drilling motor provider, but also from the service companies and operators. Collaboration among the three is important for efficient drilling operations,” he advises.
Drilling contractors are expanding their fleets to accommodate growing demand for high-horsepower land rigs equipped with powerful mud pumps, heavy-duty drawworks, closed-loop mud systems, automated rig floor equipment and ‘smart’ data management systems. As with this 1,500-horsepower electric rig, these new high-spec units often are fitted with top drives to rotate the drill string to optimize drilling efficiency and reduce the chance of pipe sticking while coming out of long horizontal laterals.
“Getting hydration right can be tricky,” Anderson says. “The coagulants and flocculants typically used to dewater drilling fluid have long, fragile chains, so they are sensitive to high mechanical shear forces and temperatures. Low pressure is also a concern; it increases residence times.”
Latshaw Drilling’s Trent Latshaw says improvements in rig designs, downhole motors, and fluids handling equipment are only a small part of a larger effort to improve drilling efficiency. “Polychrystalline diamond compact bits, measurement-while-drilling tools and rotary steerables will continue to be major drivers,” he predicts.

Oil rig equipment is expensive due to the size and operations carried out by such large machinery. Purchasing a newly constructed drill rig is a huge investment.
As such, you’ll want to be sure you have the right expectations before you begin searching for one to complete your assignment. This article will discuss just what a drill rig does and the estimated costs involved in the drilling process.
When you need a machine powerful enough to bore through the earth’s crust to retrieve minerals, gas, or any other natural resources, a drill rig will get the job done. Each rig is designed for the environment they’re operating in and the product being extracted. Those two factors greatly affect the cost of the rig you’re looking to purchase.
A standard land rig with 1,500 to 1,700 horsepower will cost between $14 million and $25 million to own. An offshore oil rig cost is much higher, starting at $20 million and going as high as $1 billion. Owning your drill rig will save you money in the long run, especially when considering the daily cost of operations.
Your daily rate depends on the rig type, distance from shore, drilling depth, and water depth. Onshore drilling rates range from $200,000 to $310,000 each day. Offshore drilling can cost between $600,000 to $800,000 per day.
Several factors impact the oil rig cost, including construction, including materials, market conditions, equipment prices, and more. We’ll cover the basics, so you have a realistic expectation when searching for a rig price.
Cost and demand go hand-in-hand. When there is a high demand for building new rigs, the cost rises because a limited number of shipyards can provide the service.
For example, in the early 2000s, there wasn’t a demand for new rig construction, so rates were low. In the mid-2000s, demand increased, and prices rose, but after the 2008 recession, demand decreased. But the prices didn’t drop significantly as the recession wasn’t expected to last long.
The materials used in making a drill rig are a key component in construction costs. The material used most, steel, comes in various strengths, and the stronger the steel, the higher it’s priced. When steel prices are low, rigs will be cheaper to produce; when steel prices rise, so do the costs of the rigs.
The cost of additional services needed for constructing wells will begin to add up. Phone bills and fees for transferring data are part of your communication cost. For those working offshore, rig positioning will be another fee.
There are two types of oil rigs, jackups, and floaters. Floaters aren’t attached to or resting on the seafloor. Jackups have support legs that allow the rig to be raised or lowered. Each type has different equipment to assist with the drilling process.
The engines, generators, cranes, and other oil rig components are purchased from a third party and assembled by the rig builder. Non-drilling related equipment is about 30% to 60% of the total cost.
Since most of the parts used are made from steel, the fluctuations in the steel market will influence the rig’s price. Demand for the additional equipment to fit on the rig will also play a part in costs.
Where your rig is built impacts the labor costs, which affect the price of the drill rig. It’s estimated that labor is 10% to 15% of the total cost of the rig is built internationally. While the U.S. and Korea have similar costs, Singapore charges three times less.
Each dollar spent on labor in the U.S. generates $3 in revenue, while in Singapore and South Korea, every dollar generates $7 to $10 in revenue. Since labor costs are typically lower internationally, the cost of your rig won’t be as high.
Always expect and prepare for the unexpected by setting aside a portion of the budget for allowances. Once you start drilling, you can’t be sure what you’re going to find, and variances in the geological structure could require different equipment and delay the process. Both of these instances will increase the cost of the rig being used.
The drilling depth and well complexity are primary cost influencers. Once the drill rig is moved into position, it can take a team of 30 to 40 companies to complete the process. Costs can easily top $4 million during the drilling phase and take about three weeks to finish.
Positioning drilling rigs isn’t an easy task. It takes 3 to 5 days to move in and assemble a rig for well digging. Once the job is complete, the rig has to be disassembled and moved again. Rates hover between $100,000 and $350,000 depending on how far the rig is being transported.
The oil industry is very lucrative, and the machines used to drill for the resource are not cheap. Oil rigs are heavy-duty machines needed to reach extreme depths.
The harsh environments they’re in demand that they are built with the best materials available. If you need a drill rig, it’s important to keep in mind all the factors that contribute to the cost of the equipment so you can budget correctly.




 8613371530291
8613371530291