power steering pump as hydraulic pump brands
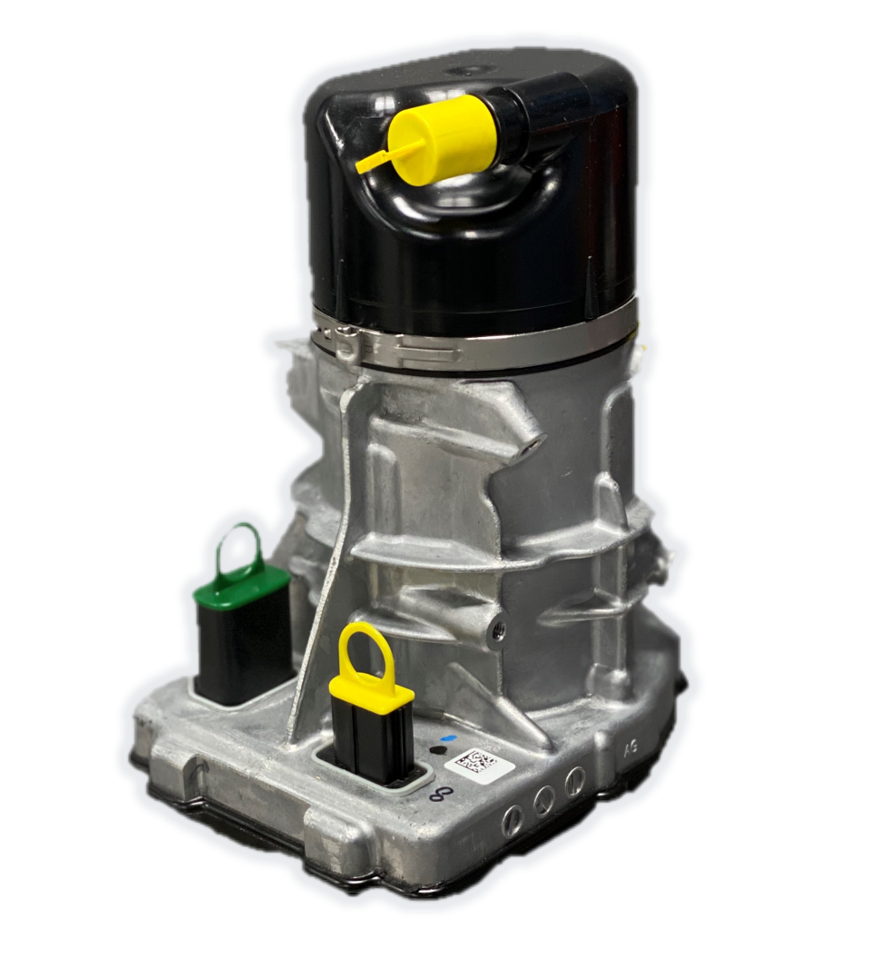

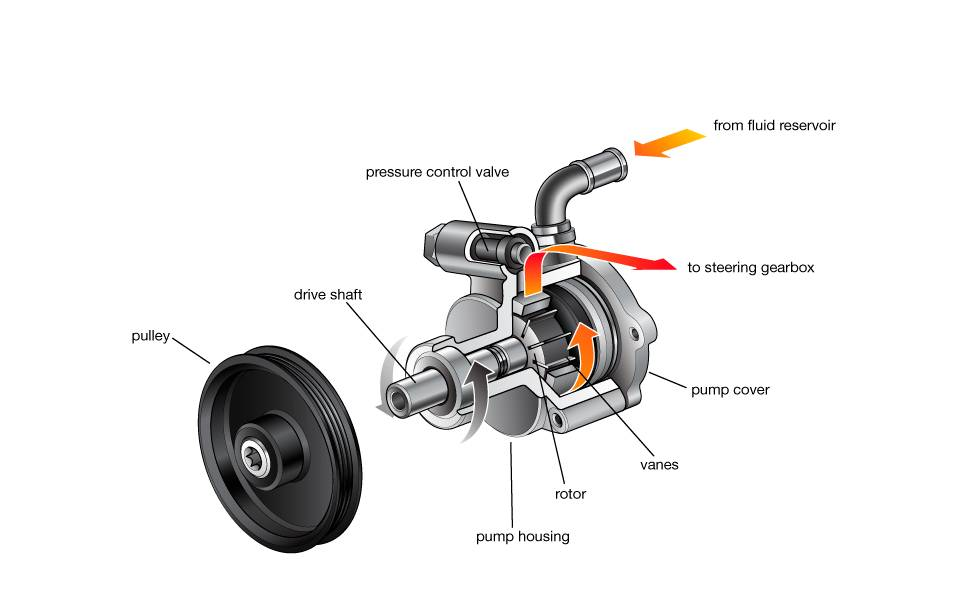
A power steering pump provides the required hydraulic pressure to steer your vehicle with minimal effort on the steering wheel. The power steering pump is driven by the engine’s crankshaft via a belt-pulley. The pump is usually located in the front of the engine, opposite to the alternator or AC compressor. The steering pump compresses the hydraulic fluid at a rate directly proportional to the speed of the engine.

This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience.

This product carries our 12 Month Limited Warranty. All warranties are limited to the original purchaser and are not transferable to subsequent owners of the product. The warranty period begins on the purchase date.
Specifically excluded from this warranty are failures caused by lack of maintenance, misuse, negligence, modification, abuse, improper application, crash damage, installation or operation, or failures caused by unauthorized service or use of unauthorized parts.
Additionally excluded from this warranty are parts which are subject to normal wear and tear, such as bushings, fluids, hoses, gaskets, belts, etc. Products not manufactured by Trail-Gear Inc. are excluded from any warranty and shall be handled with the original manufacturer.
All parts used in a competitive racing environment are excluded from this warranty. If, after inspection, a part returned, under any warranty, is deemed to be ineligible for warranty repair or replacement, the part may be repaired or replaced for a discounted cost. Return shipping charges will apply. Any part for which a warranty replacement is sought must be returned to Trail-Gear Inc. before any replacement items can be shipped. All replacement parts shipped before the suspect part has been received and evaluated by Trail-Gear, MUST BE PAID IN FULL. In such a case, after the suspect part has been received and approved for a warranty replacement, the purchase price for the replacement will be refunded.
Please contact Trail-Gear Inc. at 559-252-4950 or email sales@trail-gear.com prior to returning any product(s) under warranty to verify that warranty is still in effect.

As the term suggests, the function of a power steering pump is to deliver pressurized fluid to the steering rack in order to decrease the amount of effort required to steer the vehicle at low road speeds. In modern designs, the amount of power assistance is modulated such that maximum assistance is delivered at low road speeds, and power assistance decreases progressively as the road speed increases. In most cases, power assistance is removed completely at road speeds above about 30 – 35 miles per hour to improve steering feedback to the driver.
In purely hydraulic power steering systems, fluid is pressurized by a belt-driven, positive displacement pump, and the pressure of the power steering fluid is therefore dependent on the engine speed. However, in practice, all power steering pumps are fitted with pressure regulating valves that both maintain the minimum required pressure/volume and prevent excessive pressure from being developed at high engine speeds.
When the pressure in the power steering system approaches or exceeds a maximum allowable threshold, the pressure overcomes the tension of a spring, which opens the pressure relief valve, thereby causing most or all of the pressurized fluid to be diverted directly back into the system reservoir. Similarly, when the steering system is idle while the engine is running (i.e. there are no steering inputs), the pressure relief valve allows the fluid to circulate from the reservoir, through the pump, and back to the reservoir.
When a steering input occurs, the fluid volume in the steering rack increases, which causes a pressure drop in the high-pressure side of the system that results in partial closure of the pressure relief valve. In this condition, some pressurized fluid is directed to the steering rack, where the effective hydraulic steering input is increased to decrease the steering effort of the driver.
How much fluid is directed into the steering rack at any given moment depends on the signal that is generated by a torque sensor (located in the steering column) that detects both whether the steering wheel is turned as well as the magnitude of the steering input.
It must be noted though that the above description applies to power steering systems in their simplest form, and not to more advanced systems like electro-hydraulic and purely electric power steering systems. Purely electrical systems use electric motors and various sensors to multiply and control steering inputs, while electro-hydraulic systems use two or more load/torque sensors, typically two electrical motors to drive a single hydraulic pump, and a microprocessor for control purposes. These types of systems can be significantly more complex and as such, fall outside the scope of this article.
For some vehicles, the power steering system is fitted with pressure sensors to monitor the operation of the pump. Therefore, a complete loss or serious reduction of the working pressure could cause a check engine light to illuminate. If a check engine light illuminates, you can easily find out what trouble code it is associated with using an inexpensive OBD code reader.
Mechanical failures of power steering pumps can cause a complete loss of pressure, and while this is rarely dangerous in itself so long as the driver is aware (since non-power steering functionality will still usually be available), the sudden loss of power steering assistance can require significant effort to steer the vehicle at low speeds which can surprise a driver if pressure is lost while the vehicle is in motion.
Low fluid levels, dirty or contaminated fluid, or the incorrect type of power steering fluid can cause rapid and severe mechanical wear of moving and rotating parts within a power steering pump, which typically manifests as whining, rumbling, or grinding noises in the pump. These noises will typically vary with engine speed since the pump is most often belt driven off the engine. If not addressed immediately, pump failure is likely to follow shortly thereafter.
Low fluid levels and some mechanical failure modes can cause intermittent pressure losses in the system, which typically manifests as points where the steering wheel “sticks” or binds when it is turned from lock-to-lock, regardless of the direction in which it is being turned. This is a significant safety concern and the vehicle should not be driven under these circumstances until a repair is completed.
Depending on the application, replacement procedures can vary from easy, to moderately difficult, to extremely challenging, since working space is extremely limited on some vehicles.
Note: The example steps below are intended for general informational purposes solely to help give you an idea of project difficulty and tools required. As all cars are engineered differently, repair procedures and safety hazards vary from vehicle to vehicle. To ensure that you have a vehicle specific repair procedure and an exhaustive list of potential safety hazards, we advise you reference a factory service manual for your vehicle. Similarly, referencing a repair manual such as Chilton or Haynes might serve as a less expensive alternative.
Step 1 – Make sure the engine is cold to prevent scalds and burns. Locate the power steering pump, and spend a few minutes studying the general layout of the system. It is important to locate all brackets and fasteners, some of which may be hidden behind unrelated brackets and or components. Also, use this time to remove as much fluid from the reservoir as possible to minimize spills later on. A fluid pump or a large syringe can make this happen with relative ease. Drain the power steering fluid into an oil drain pan and dispose of the old fluid in an environmentally responsible way (many oil change shops accept old power steering fluid and will recycle it safely on your behalf). If your steering pump is underneath your vehicle, you will likely need to raise it using an appropriately rated floor jack and support it using an appropriately rated set of jack stands.
Step 2 – Study the routing of the serpentine (drive) belt, and if a manual is not available, take as many pictures of the belt’s routing around pulleys and tensioning devices as it takes to give you a clear picture of how the belt fits relative to all driven components. Some belts can be extremely tricky to fit back on, so if you do not have a clear picture of how it fits, you can spend several hours trying to work it out. Taking a picture or two will give you something to reference to make sure you reinstall properly when the time comes.
Step 4 – Take a moment to ensure that you understand your steering system. Depending on the system, you may have to take precautions to depressurize the system prior to continuing to avoid injury associated with highly pressurized fluid. Refer to a factory service manual to make sure you are aware of any safety concerns. Remove both the low and high-pressure hoses from the pump using flare nut wrenches or combination wrenches, as well as any electrical connectors if any are present. The electrical connectors can often be removed by hand, although you may require a small set of screwdrivers depending on the connector type. Remove all fasteners using a socket set, and remove the old pump from the engine.
Step 7 – Once you are sure the belt is fitted correctly and all hose connections are free of leaks, fill the power steering fluid reservoir up to the indicated “FULL” mark using the correct type of power steering fluid for your vehicle. Be sure to replace the cap before starting the engine. Start the engine, and turn the steering wheel from lock-to-lock SLOWLY to allow the new fluid to fill the system, topping off as necessary.
Step 8 – After adding fluid and confirming that the steering operates normally with no noises present, turn off the engine. Adjust the steering fluid level as required. Test-drive the vehicle to verify that the steering system functions correctly. If something isn’t right, stop immediately, troubleshoot, and repair as necessary.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

A liquid reservoir powers hydraulic steering pump manufacturers at neutral pressure (atmospheric pressure), then this latter compresses it to reach an outlet pressure at the order of 60-80 bars. If you opt for belt power steering systems, this is your lucky day as we bring you some of the best power steering pulleys at preferential wholesale prices. We also have some pumps with integrated power steering pump reservoirs. This type of steering pump connects to the rack through a high-pressure steering pump hose.
There are two main types of hydraulic steering pump manufacturers. The hydraulic power steering pumps are considered as an old version of steering pumps, and they need to be equipped with the belt to run properly. Electric power steering pumps, on the other hand, don"t require any accessories circuit. As the name suggests, they have an electric motor to pressurize the steering fluid.
You should replace your power steering pump when observing any of the following signs: growls in the direction, the steering system no longer works, or fluid leakage in the power steering system. Once you identify that your steering pump is faulty, you can search for a new hydraulic steering pump manufacturers in our collections. We are sure you will be pleased with the affordable cost of our hydraulic steering pump manufacturers.

The mechanical hydraulic steering pump, also called servo pump, power steering pump or hydraulic pump, is driven by the vehicle engine via a V-belt. In this way, the pump generates the hydraulic pressure required by the power steering system to make the vehicle easier and thus more comfortable to steer when driving.
Two types of steering pumps, single and tandem, can be installed in commercial vehicles. Both have the same function, but tandem pumps also have an attached fuel pump driven by the same shaft.

Nexteer’s power steering pumps are designed for most car and light-duty truck applications. Power steering pumps are available in displacements from 6.8 cc/rev. to 20 cc/rev.
Nexteer pumps are designed to operate at speeds of 10,000 rpm and belt loads up to 2000N. Improved fuel efficiency can be achieved with variable-flow devices.
The most complete range of steering pumps for the main models of trucks (VOLVO, SCANIA, MB, VW, FORD, AGRALE, IVECO, etc). Pumps 100% interchangeable with the original pump, with easy installation with no need for adaptions.
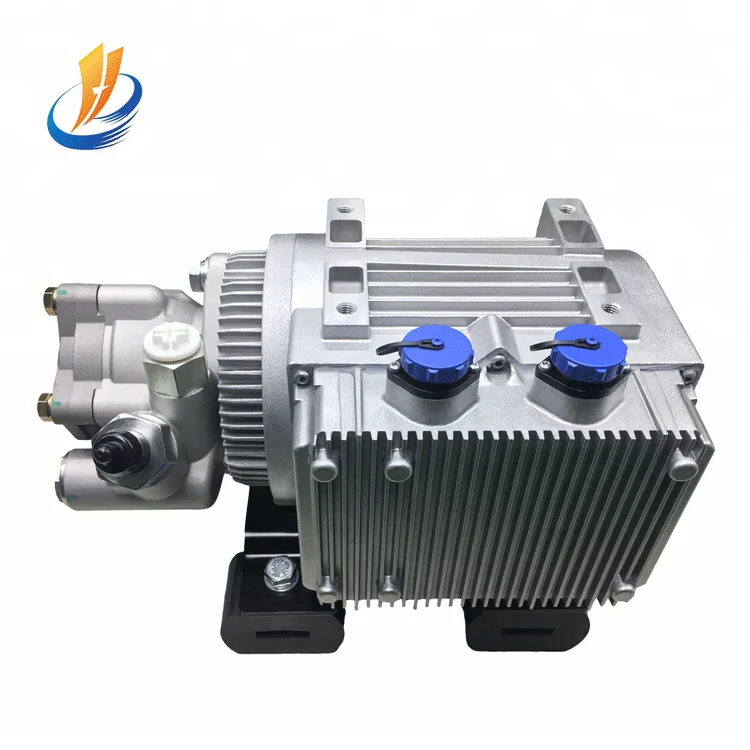

The FN4 power steering pump is designed for connection to the air compressor or a power take-off on the engine. The shaft connects by means of a cross-slotted disk or spline toothing. It can be driven by either a gear or belt. For these cases, an anti-friction bearing is used for the drive shaft. The ball bearing needed for this can be integrated into the housing.
The rotor set is comprised of the rotor, ten radially-guided blades as well as the cam ring with two symmetrically arranged suction and pressure zones. The fixed geometric delivery volume of the pump is defined by the design of the cam ring.
The conveyed volume flow is limited to a defined value by the integrated volume flow control. The maximum system pressure must be limited by a pressure control valve installed on the pump or in the system. If required, a pressure level of up to 200 bar is available as a special version.




 8613371530291
8613371530291