variable swash plate hydraulic pump factory
The displacement of a pump is defined by the volume of fluid that the gears, vanes or pistons will pump in one rotation. If a pump has a capacity of 30 cm3, it should treat 30 ml of fluid in one rotation.
In axial piston variable pumps, the flow is proportional to the drive speed and the displacement. The flow can be steplessly changed by adjusting the swivel angle. Axial piston variable ...
... axial piston pump type V60N is designed for open circuits in mobile hydraulics and operate according to the swash plate principle. They are available with the option of a thru-shaft for operating additional ...
Variable displacement axial piston pumps operate according to the bent axis principle. They adjust the geometric output volume from maximum to zero. As a result they vary the flow rate ...
... piston pump type V30D is designed for open circuits in industrial hydraulics and operate according to the swash plate principle. They are available with the option of a thru-shaft for operating additional ...
... circuit axial piston pumps are used as hydrostatic transmission components in self-propelled machines and for rotary drives in both fixed and mobile equipment of all kinds.
Axial piston twin flow pump. With a very high performance in all job conditions. Due to its twin flow configuration this pump allows a great variety of solutions in different job applications.
Air hydraulic pump, double pneumatic motor, double effect, foot operated with lock-up function, lever distributor valve (4/3), 10L tank, oil flow 8.5 / 0.26 l / min
... customer system options for mechanical, hydraulic and electric input solutions are available. Further special regulating features like torque control and pressure cut-off are also available. The reliable ...
... needs of truck hydraulics, the TXV variable displacement pumps with LS (Load Sensing) control allow flow regulation to suit the application requirements. The pump ...
... rev. displacements, these pumps are designed to operate in both directions of rotation (clockwise or counter-clockwise). Only one reference regardless of direction of rotation. The TXV indexable pumps ...
... PVG is a variable-displacement axial-piston pump designed to take on your most demanding applications. It offers high-pressure, superior performance in a compact design ...
Variable displacement pumps in closed loop; 3 basic design units and 8 max. displacement sizes of 14, 18, 21, 28, 35, 46, 56, 64 cc/rev; various control options; max. ...
Parker P2/P3 High Pressure Axial Piston Pumps are variable displacement, swashplate piston pumps designed for operation in open circuit, mobile hydraulic ...
... Series pump offers variable displacement axial piston pumps for open-circuit applications. Featuring a compact footprint and continuous operating pressure ...
The axial piston pump type V60N is designed for open circuits in mobile hydraulics and operate according to the swash plate principle. They are available with the option ...
Variable displacement axial piston pumps operate according to the bent axis principle. They adjust the geometric output volume from maximum to zero. As a result they vary the flow rate ...
The K3VG series are swash-plate type axial piston pumps which give excellent performance in high flow industrial applications in a compact and cost-effective package.
Closed circuit axial piston pumps are used as hydrostatic transmission components in self-propelled machines and for rotary drives in both fixed and mobile equipment of all kinds.
Twin flow axial piston pumps offers two different flows. In addition, we find several advantages such as lower weight or standar system solutions. BZT are available in ISO and SAE version.
Our variable volume, pressure compensated axial piston pumps continuously match output flow to the system demands. They’re designed to closely match the Eaton-Vickers PVB and PVQ and ...
The PFBA is a fixed displacement pump, axial-piston pump. It’s proven itself in a variety of operations—including die casting and injection molding machines, high-pressure ...
PMH high pressure axial piston pumps for closed loop are specifically designed to be used on heavy duty machines for traction and auxiliary functions, providing efficiency and durability.
Variable displacement pumps in closed loop; 3 basic design units and 8 max. displacement sizes of 14, 18, 21, 28, 35, 46, 56, 64 cc/rev; various control options; max. nominal pressure 300 bar, 350 bar peak; driving speed: ...
"C"" Axial Piston Pumps for high accuracy fluid metering with precision flow controls and high-pressure capability. Specifically designed for the Polyurethane Industry. Capacities from ...
Rotork offers a range of high quality hydraulic pumps for applications in the upstream and downstream oil and gas industries. These include an extensive range of axial piston ...
... Parker’s hydraulic truck pump series F1 featuring high self-priming speed and high efficiency and is one of the leading truck pumps in the market. The F1 pump provide ...
Parker P2/P3 High Pressure Axial Piston Pumps are variable displacement, swashplate piston pumps designed for operation in open circuit, mobile hydraulic ...
... Series pump offers variable displacement axial piston pumps for open-circuit applications. Featuring a compact footprint and continuous operating pressure ...

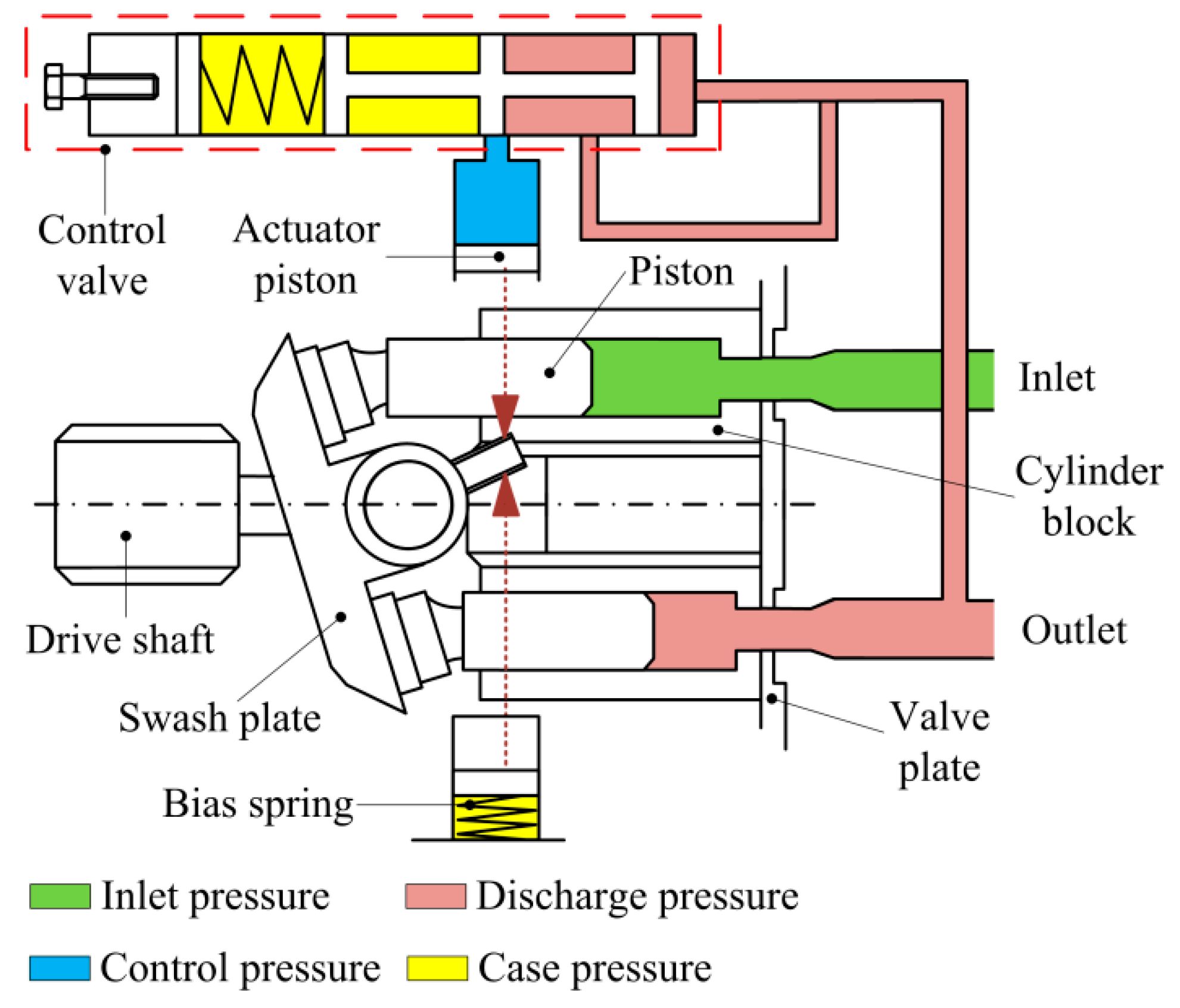
Swashplate hydraulic pumps have a rotating cylinder containing pistons. A spring pushes the pistons against a stationary swash plate, which sits at an angle to the cylinder. The pistons suck in fluid during half a revolution and push fluid out during the other half. The greater the slant the further the pump pistons move and the more fluid they transfer.
Electro-Hydraulic Controls for Model (A)A4VSO (Sizes 40...1,000), Model A4VSH (Sizes 40...250), Model (A)A4VSG (Sizes 40...1000) and Model (A)A4CSG (Sizes 250...750) Swashplate pumps

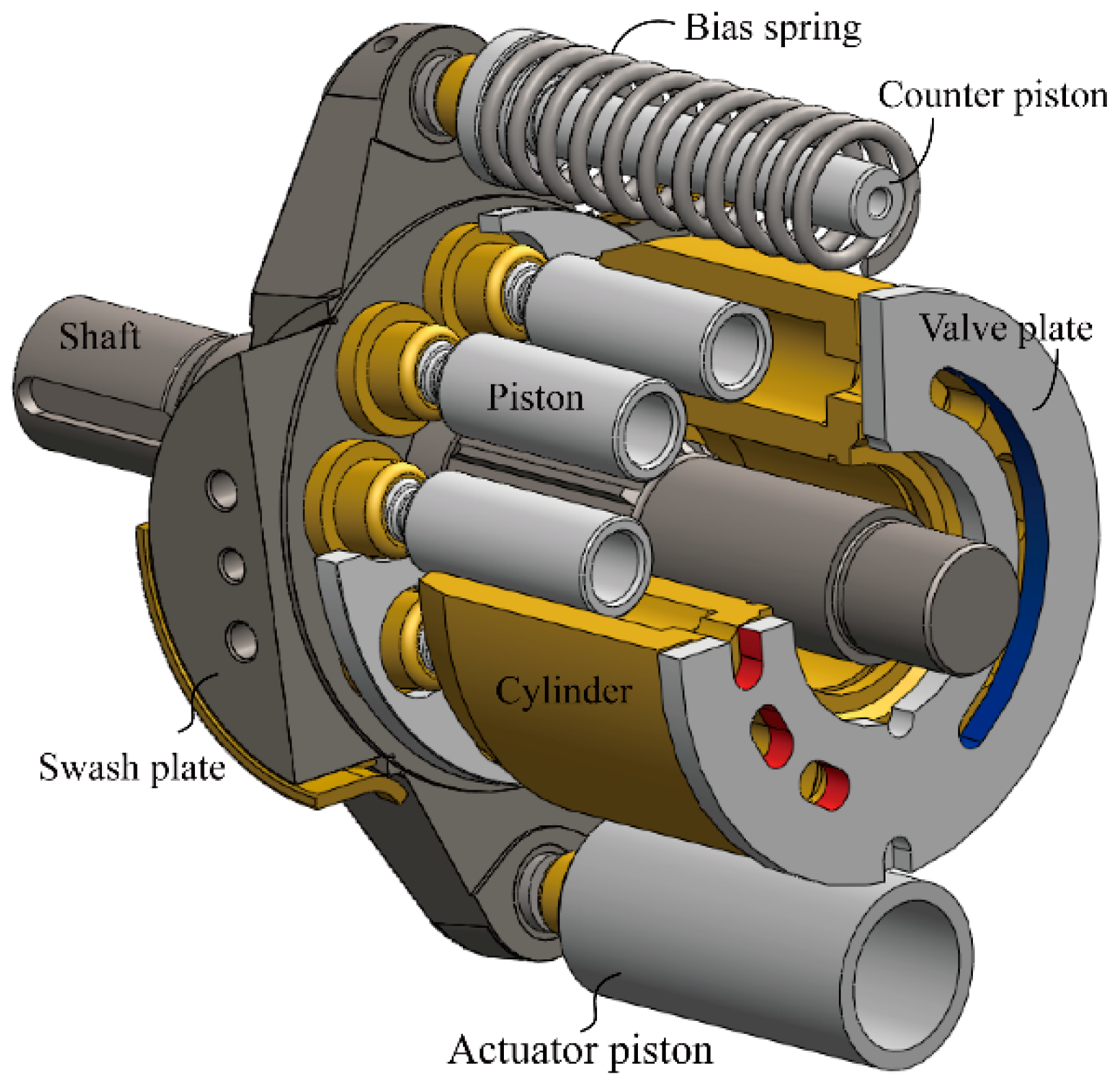
The plunger pump is a kind of hydraulic pump which relies on the reciprocating movement of the plunger in the special cylinder body to achieve oil suction or pressure. The shell only contains, connects and supports the working parts. It is a kind of non pressure bearing hydraulic element. There are two types of piston pumps, axial piston type and radial piston type, with different structures and processes. This section only introduces the material and technology of the key parts of axial piston pump.
(1) The technical requirements are shown in Figure K. the straight shaft axial piston pump is composed of key parts such as transmission shaft 1, swashplate 2, slipper 3, plunger 4, cylinder block 5, valve plate 6, return plate 8, etc. The straight axis axial piston pump can work under high pressure, high speed, high temperature and other harsh conditions for a long time, and has high volumetric efficiency and total efficiency. Therefore, all parts in the piston pump shell should have enough strength and stiffness, and also have high dimensional accuracy and shape accuracy. Therefore, it is necessary to reasonably select the material and heat treatment method of the key parts of the pump, and improve the processing quality, especially the reasonable friction pair material.
(2) Common materials and process requirements of different manufacturers, different specifications of products, the material selection and processing technology are not the same, with the continuous improvement and development of surface treatment technology, the material of hydraulic pump appears the trend of diversification. The combination of various traditional heat treatment technologies and modern surface treatment technologies, including ion implantation, thermal spraying, laser cladding, electrochemical plating, physical chemical vapor deposition and so on, has increasingly shown great technical and economic advantages. In addition, the application of other new engineering materials, such as engineering composite materials and ceramic materials, provides more and more extensive ways for pump material selection and manufacturing.
a. There are two schemes for material and heat treatment of plunger and cylinder: one is hard plunger and soft cylinder; the other is soft plunger and hard cylinder. The first scheme is often used in high pressure and large flow piston pump.
② The common material of slipper is wear-resistant copper alloy; several concentric ring grooves are made on the supporting plane of one end of the swash plate, and sometimes silver, indium and other metal antifriction layers are plated. The hydrostatic thrust bearing is formed on the working face of the swash plate by the pressure oil introduced from the center of the plunger; the other end is hinged with the plunger head by rolling ball wrapping process.
③ The working surface of swash plate and pressure plate (return plate) swash plate must be flat, smooth, wear-resistant and have enough compressive strength. Therefore, GCr15 is usually used for swash plate, the hardness after quenching is 58-62hrc, and ZQAl9-4 is usually used for its bearing bush.
④ The material of valve plate should be selected according to the cylinder block. The commonly used material pairs are shown in the table below. Among them, zqsn10-1 and Cr12MoV have the best anti bite ability.
After quenching (or nitriding steel nitriding) of valve plate, in order to stabilize the microstructure, cold treatment and aging treatment are usually carried out.
Some manufacturers spray or sinter engineering plastics such as nylon or peek on the surface of valve plate or cylinder block, and try their best to improve the hardness (50HRC or higher) of the dual surface, or use ceramic coating.
The surface roughness of the valve plate is 0.4 ~ 0.1 μ m, and the flatness tolerance of the valve plate is about 0.005mm, and only concave is allowed, not convex.
Designed for power and speed, the Oilgear PVV open-loop axial-piston hydraulic pumps can handle large, heavy-duty systems. Manufactured with advanced engineering and computer-optimized, the PVV pump range delivers up to 450 Bar / 560 horespower which equates to four times the horsepower at less than half the cost of other manufacturers pumps.
With it"s compact design available in several displacements (200-540cc/rev), the PVV pumps offer a large selection of readily interchangeable controls. With improved response controls and reduced noise levels, its rugged cylinder design enhances performance.
The patented, pressure lubricated swashblock design offers high performance for high-cycling operations. It also contributes to the pump’s ability to run on low-viscosity fluids, including high water content, fire-resistant and other special fluids.
Zeus Hydratech fully supports the PVV pump product line and is the only valid source for OEM parts. All Oilgear repairs are machined and tested per our original factory specifications.

Another option is to utilize a load sense compensator. With a load sense compensator, this compensator will include a lighter spring setting to control the swash plate. Upstream pressure is ported into a load sense port on the pump, as the pressure requirement increases, the pressure acts against the load sense piston. Once the pressure requirement is higher than the offset, the pump swash plate angle changes and the pump begins to increase flow, by increasing the swash plate angle, until we have enough pressure to balance the piston. Once balanced, the flow remains steady until the load changes.
The offset pressure is normally 200-300 PSI. With a load sense compensator, the pump produces what the load requires plus the spring offset, normally 200-300 PSI.
This system will also utilize a standard compensator so if the system pressure increases enough, the pressure compensator will take control and reduce the swash plate angle to reduce the pressure.
With a standard pressure compensator, you would have to set the pump at 2600 PSI to accomplish the work. When the work only requires 1500 PSI, the pump will be trying to produce 2600 PSI. Fifty percent of the time, your system will be operating at 1100 PSI of inefficiency, which means heat. With a load sense compensator, when the load requires 1500 PSI, the pump will actually produce about 17-1800 PSI. Yes, this is 300 PSI inefficient, but that is much better than 1100 PSI inefficient.
With a varying load, the load sense is a much better system. For additional control, you can utilize an electronic proportional flow control or throttle. You can use an electrical signal to vary the hydraulic signal which is received by the pump’s load sense line. This would give you full electronic control of the amount of flow the pump produces.
There are additional control options which allow you to remotely control the pressure compensator. With this remote compensator control, you can set 2 or more different system pressures. With the ability of a variable piston pump to build 5,000 or more PSI; the additional setting can be used when operating components with a much lower pressure requirement.
The next control is a torque limiting or HP limiting control. By adding an additional spring and piston, you can set a pump to always maximize its allowable input torque, therefore, maximizing output flow and pressure at a defined setting.
Our pump has an output of 15 CIR, a maximum flow of about 113 gallons at 1750 RPM. Our prime mover is an electric motor, 75HP with a 1.15 service factor. I want to keep my cylinder moving as fast as possible, but I also want to ensure that I never exceed a power demand 82 HP.
At 82 HP, the pump can produce 1254 PSI at full output, 113 GPM. As the load requires more pressure, the pump will begin to reduce flow and increase pressure. At 90 GPM flow, the system will produce about 1560 PSI; at 60 GPM we can get almost 2350 PSI. At 4500 PSI, the pump flow will be reduced to about 31 GPM. The advantage of this pump is that the internal controls of the pump are adjusting to maximize flow and pressure at all times without exceeding the available HP.
If I wanted to use a pump which could produce 113 gallons of flow at 4500 PSI, I would need 296 HP. If I choose a 75 HP motor with a pressure compensated variable piston pump, the motor would stall before the pressure compensator could kick in and reduce the pump flow. Depending on the load, a load sense pump could also stall the 75 HP motor if the load pressure is high enough to use up the HP before the pressure compensator kicks in. With a torque limiting (HP) control, we utilize the full limits of the prime mover and maximize power usage.

Piston pumps are typically much more complicated and are often available in wither fixed or, commonly, variable displacement configurations and with pressure compensation. These are big words that mean that piston pumps can usually adapt to the system pressure, providing maximum efficiency and flexibility. They are often used in “closed center” systems where the pump displacement varies to meet the needs of the work being done. Piston pumps use a “swashplate” to move the pistons and the angle of the swashplate & bore of the pistons determines the displacement. Pressure compensation regulates outputs in response to variations in the system. Piston pumps are typically the most efficient type of hydraulic pumps.




 8613371530291
8613371530291