wasteland 3 hydraulic pump in stock

You can find the Mustard in a Mound of Shit just to the east of the Hydraulics Control Room. You have to dig all the way through it in order to get the mustard. You will also find the R&D Meeting Tape #783 which will tell you that the Moose and Squirrel are the worst enemies (which you need to know if you want to keep Boris and Natasha alive).
Once you have collected all three components, craft the 1000 Island Dressing in the Miscellaneous section of your crafting menu. Then go to the Hydraulics Control Room, interact with the Hydraulics Pump, go through the dialogue, and sabotage it with the 1000 Island Dressing to get the achievement.
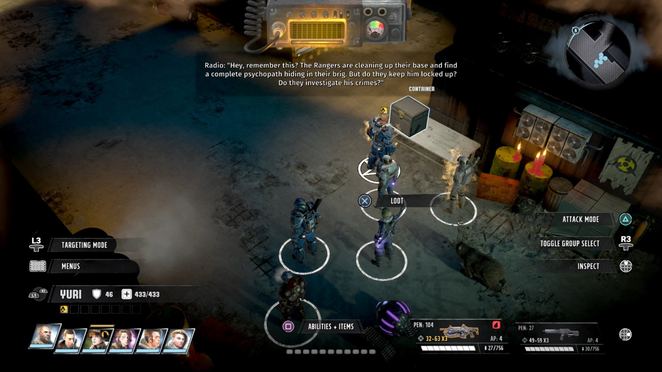
Most importantly, learning the secret of the Thousand island bottle from Boris and Natasha. Collect Mayo bottle from them, the Mustard bottle from the epic mound of shit, and Ketchup bottle from the Lockpick 7 locked chamber in the Genetic Research Lab on the research level to create the Thousand island bottle. Then you need to use Mechanics 7 on the hydraulics pump in the northern chamber of the storage corridor, dumping the dressing into the service hatch. This will prevent particle cannons from being lowered, once raised.
According to Brother Goiter, we must destroy at least three Particle Cannons to shut down the Nucleists" experiment and raise the Central Core. We can expose the cannons by using the switches in the side wings.\n\n\nCannons Destroyed: [Global: e4001_Cores_Destroyed]/3

Wasteland 3’s new DLC, the Cult of the Holy Detonation again features a new location and a new story. Similar to the Steeltown DLC, this new DLC also features a new ending that can affect the whole of Colorado. Depending on the player’s choices, these endings may greatly influence the overall story campaign. Read the following to know the Wasteland 3 Cult of the Holy Detonation Ending and their rewards
In this DLC, the Rangers must convince the 2 parties grappling for the control of the “Holy Detonation”. Regardless of the outcome of the power struggle, the final battle occurs inside the hall of the reactor. At the end of this battle, the player is given 3 choices:

This achievement guide is essentially complete. Two achievements were originally broken on launch (August 28th, 2020) but have been fixed as of patch 1.3.0 (January 26th, 2021). If you"re seeing this guide on a website, that means it was copied from the original guide on Steam. While I have no issues with it being copied, you might want to check Steam for the latest version of it. If you have something to contribute, feel free to leave a comment on the Steam guide and I"ll update it.. Thanks in advance.
Kill 4 enemies at once with a single shotgun attack. This one is fairly self-explanatory but triggering it early (pun intended) can be tricky. If you"re looking for a way to farm it up, I was able to by starting a new game on Easy difficulty using the preset characters, Punk Lovers, one of which has a pump shotgun. You"ll need some luck (and reloads) but after the first round of combat, you"ll hopefully get left with a pack of 4 enemies on your left. With the right positioning, you"ll have to get lucky with two 72% chance hits but it"s possible. If you use any difficulty above Easy, this won"t work, as the pump shotgun won"t be able to one-shot enemies. Groups of civilians in Downtown Colorado Springs near the Marshalls make great targets for this kind of an achievement on almost any kind of difficulty, so that"s a good option as well.
Liquefy an enemy with energy damage. Basically you need to defeat an enemy with an energy weapon. These aren"t incredibly easy to find early on but you"ll find some eventually. I was able to farm this out near the start of the game when I first arrived at the Ranger HQ by repairing the Rusted Slicer Dicer in the garage, which initiates a fight with it. It drops a Pulse Gun laser weapon (or at least it did for me the three times in a row I fought it) which you can then equip and use on the dogs near the Cyborg Chicken. If you don"t have a character with 3 skill points in Mechanics, save your game and drop a few spare skills points into Mechanics temporarily. If you don"t have any spare points, run through the Ambush Site again quickly on Easy difficulty while saving up your skill points before entering the Ranger HQ.
You collected all STDs in the Wasteland. This one is done fairly easily after you get access to Little Vegas nightclub in Downtown Colorado Springs. This will happen shortly after you finish up with the Garden of the Gods and get the quest "Big Trouble in Little Vegas". In the club, there are six named prostitutes upstairs in separate bedrooms. Pay them $10 each and you"ll catch a different STD from each one. Make sure you use the same party member for each of these encounters so that all the STDs get stacked on a single character. The 6 STDs are: Ace in the Hole (+25% Critical Chance), Dealer"s Choice (+5% Experience), Shuffled (+1 Action Points and +1 Maximum Action Points), Royal Flush (+25% Hit Chance), Bad Beat (+15% Evasion), and Kicker (+4 Penetration). There are two ways to the get final STD that pops the achievement. One way is to wait until you get to the Machine Commune in Denver. There you can speak to a robot called Little Sparrow and agree to have sex with it, which will give you the Denver Rot STD. If you want to get it sooner, you can, but it will take a bit more work. To get Denver Rot sooner, you can leave Little Vegas and find a pile of snowballs (there"s one near the dogs outside the club) and pee on them. Gather up about 20 Yellow Snowballs and have a party member start throwing them repeatedly on the character that has the stacked STDs from Little Vegas. The Yellow Snowballs have a %5 chance to apply a bunch of nasty stuff. Of all the effects that come from the Yellow Snowballs, one of them is Denver Rot. You also need to get Denver Rot first before any of the other snowball effects, so save your game before you start throwing snowballs because if you get any of the other effects from the snowballs, you need to reload and try again. Keep in mind that while the STDs from Little Vegas are good for you (but wear off), the Denver Rot doesn"t and requires a doctor NPC or Antidote to get rid of. You might want to do this one and then reload before you started stacking diseases.
3. Cyborg Chicken #3 (Animal Whisperer 3) - In Apartment 1 of the Sans Luxe Apartments, behind a locked door that requires Mechanics 5 in order to access.
Gold Insulated Power Cord - In a trap filled room at the back of the Wesson Estate in Broadmoor Heights. To get to the Toaster, you"ll need Perception 6 to see all 5 traps in the room, Explosives 3 to disarm the trap at the door, and Explosives 4 to disarm the Gas Mine in front of the toaster. The toaster itself requires Toaster Repair 4. Although there are 3 more traps, you don"t need to disable them to get to the toaster.
Cats - There are cats wandering around the streets of Downtown Colorado Springs (Animal Whisperer 2). Other cats include Bellameow in Garden of the Gods near the entrance although you"ll need Perception 3 to see the frag mines surrounding her locked cage, Explosives 2 to disarm the mines, Mechanics 2 to unlock the gate she"s behind, and then you"ll need Animal Whisperer 2 to tame her. Another would be Kathmandu (Animal Whisperer 2) in Rosie Wong"s Apartment in Sans Luxe Apartments. All of that said, I would tame every single one of the named cats in addition to the regular cat just to be safe. You must tame Major Tomcat and a separate cat for the achievement to work.
2. "Keen Karen" (+1 Perception to all party members) - Located in the Garden of the Gods in a snow pile just South of the mass grave where Waste Wolves are feasting. To access it, you"ll need a character with Perception 3 to be able to see a way through the large snow bank even further to the South. Once through that, the hidden snow pile is between the snow bank and the Waste Wolves. If you absolutely can"t muster 3 Perception, you can still get to the snow pile but you"ll have to fight the Dorseys and then go around the back way and fight through the Waste Wolves to get to it, although I"m not sure if you"ll be able to locate the hidden snow pile with less than 3 Perception.
3."Maneater Maury" (+15 CON to all party members) - Located in a Duffel Bag in the Parking Garage of the Bizarre Exterior. Specifically it"s at the top of the ramps before the path to the human smugglers that you visit as part of the "Unwelcome Guests" quest. These are the ramps with the Bomb Hoppers on them.
Find all the cassette tapes left around Colorado. This achievement was originally broken on launch (August 27th, 2020) but was fixed in patch 1.3.0 (January 26th, 2021). Sadly, if you had an endgame save from prior to patch 1.3.0 and you looted boxes throughout the game, you will not be able to go back and find the two cassettes that were restored (see numbers 24 and 34 below) as the containers they were in are open and already looted. The tapes for this achievement are found in the main game and requires no cassettes from any DLC expansions.
6. "New Tour Introduction, Version 1" - Found in a room in the Colorado Heritage Museum in Downtown Colorado Springs. You"ll need Lockpicking 3 to unlock the door into the museum and Mechanics 3 to start the generator that opens the door to the room where the cassette is located.
8. "Bellamy Test #110" - Found in a locker inside a cage near the entrance of Garden of the Gods, just after the fight at the entrance with the Dorseys attacking Bellamy Ward. You"ll need Perception 3 to see the frag mines surrounding locked cage, Explosives 2 to disarm the mines, and Mechanics 2 to unlock the cage the locker is in.
13. "The Gangster"s Guide to Diction" - In a locker in a locked room (requires Lockpicking 2) in the back room of Little Vegas. You"ll get into the back room of Little Vegas near the end of the quest "Big Trouble in Little Vegas".
30. "What Came Before?" - Found in the dirt pile under the billboard in the East Ruins of Denver Ruins. The dirt pile gets "revealed" if you have Perception 5 or higher but the dirt pile isn"t really hidden and can be looted either way. It"s probably a bug. The cassette is in the pile regardless of whether the pile was revealed or not.
31. "What Comes After?" - Found in the dirt pile in the West Ruins of Denver Ruins. The dirt pile gets "revealed" if you have Perception 5 or higher but the dirt pile isn"t really hidden and can be looted either way. It"s probably a bug. The cassette is in the pile regardless of whether the pile was revealed or not.
32. "Mourning the Music" - Found in a frozen Container in the Denver Blast Crater of Denver Ruins. You"ll need a flamethrower to freeze the ice around the Container before you can access it.
33. "Serious Argument with Satisfactory Resolution" - Found in a dirt pile behind the nose of the space shuttle at the entrance of the Machine Commune in Denver Ruins.
35. "Pico"s Playtesting" - Found in a frozen Container outside the door leading from the Pico"s place in the Machine Commune in Denver. Use a flamethrower to melt down the ice block.
36. "You Won"t Believe Your Eyes!!" - Found in the dirt pile next to the computer in the Radio Beacon in Union Station. If you can"t get in through the front entrance of the Radio Beacon room, there"s a huge hole in the back of the building you can just walk through.
43. "Marriage Counseling" - Found in a Container in the Guest Suites of Little Hell. Specifically it"s the first suite that the Reed sisters are being held prisoner in.
You found every lore book in the game. While the achievement exclusively states that you need to find "every lore book", it"s looking like that"s not actually the case. Right now, it looks like there are approximately 30 pieces or more of lore in the game but that you only need to acquire 26 specific pieces in order to qualify for the achievement. While this achievement was originally broken on launch (August 28th, 2020), it is now fixed as of patch 1.3.0 (January 26th, 2021). The lore for this achievement is found the main game and requires no lore books from any DLC expansions.
3. "Encyclopedia Robotica" - Found in a bookshelf in the War Room of Ranger HQ. That said, the bookshelf is not in the room at the start of the game. After first reaching Ranger HQ, eventually you"ll leave. The next time you come back, some things will have changed slightly in Ranger HQ regarding placement of NPCs and such. One of those changes will be the arrival of the bookshelf in the War Room. While this one doesn"t depend on choices you make in the game, it"s very easy to miss the arrival of a bookshelf that wasn"t there before.
8. "The Clown"s Guide to Paints, Makeup and Acid" - Found in a container in a Apartment 3 of the Sans Luxe Apartments. In order to access the room you"ll need Lockpicking 5. Just past the entrance is a trap that should probably be avoided that requires Sneaky ♥♥♥♥ 4 to pass but it"s not required that you defuse the trap to access the container.
1. "Survivalist"s Diary" - Found in a locked room past the Hoon household on the Hoon Homestead map. It will become reachable the first time you leave the Ranger HQ to head out on the world map in the Kodiak, during which you"ll be presented with the quest "Heads or Tails". You must make the choice to save Hoon Homestead in order to have access to the area where this lore is found. If you save Arapaho Caravan and then return to Hoon Homestead, the way past the Hoon household to the rooms at the back of the map will be blocked by fallen debris that cannot be passed. If you choose to save Hoon Homestead, there is an area past the Hoon household with a series of interconnected rooms. In order to open doors to the room where the diary is found, you need to have Lockpicking at 6 or higher but you can also use Mechanics 3 to get there through a separate door and then use a computer terminal.
3. "Time Capsule Letter" - This used to be found in a buried treasure on the battlefield of a secluded fight with a Golden Scorpitron. While the fight still exists, the letter is no longer lootable as of a patch that came out a few month into launch. The location of the fight is just slightly West of the entrance to Yuma County and directly South of the Massacre Site, in a tiny alcove. Drive your Kodiak in and you"ll immediately get ambushed by it. This was part of a contest in which Inxile was looking to award somebody that could find the letter first. A few months after they declared a winner, they removed the ability to loot the letter. The letter does still technically exist in game and if you looted it prior to the patch, you do get to keep it in your inventory.
Made 1000 Island Dressing and used it to sabotage the Particle Accelerator. This one takes place in both the Loading Dock and the Research Level but ideally you should start on the Loading Dock. First, you"ll need the Crane Operations Key from a container in a room to the NorthWest. This key will get you into the Crane Operations Room. There are three toilets in the room. In the leftmost toilet you"ll find a Cereal Box Decoder Ring. In the SouthEast corner of the room with the evangelist and his cronies, you"ll find a diggable loot pile that includes a Food Storage Door Code. This will get you access to the Vault Door in the NorthEast of the map. Inside, you"ll find Boris and Natasha, who will see your ring and tell you about their mission. After that, you"ll be asked who the enemy of the Soviets is - it is, of course, The United States of America. When Boris and Natasha commit suicide, you"ll be able to loot two things from them. The first is the Thousand Island Dressing Recipe and the second is a Mayo Bottle. The recipe also calls for Ketchup and Mustard, which can be found in the Research Level. The Mustard Bottle is in the South end of the map. Keep digging in the Mound of ♥♥♥♥ and you"ll eventually get the mustard. If you get to the end of the looting process and it looks like you didn"t find it in the pile, check your inventory, as it sometimes shows up there even though the game interface didn"t specifically tell you that it was looted. If you have the anti-radiation suit from the Research Level, looting the mound will be a lot easier. The Ketchup Bottle is in the SouthEast in a container along with a Special Sauce Recipe behind some locked doors (require Lockpicking 7). Do not craft the Special Sauce, as it will waste the ketchup and mustard you need for the Thousand Island Dressing. Craft the Thousand Island Bottle in your crafting menu, under Miscellaneous. In the middle of the map is a door (requires Lockpicking 8), behind which is the Hydraulics Pump. Use it to get a dialog option to sabotage the machine using the Thousand Island Dressing. This will unlock the achievement.
While I have spent a lot of time editing and compiling this guide, there is no question that I am doing so on the backs of many contributors who have hacked at game code and searched the game pixel by pixel looking for missing pieces. Without them, this guide just wouldn"t exist. So for that, I would like to thank the following contributors for their help in the comments section: 2 tay 3 súng, anja_nowa, Asher Mir"s Juicebox, BeardedS0ul, Big Boom Boom, BibbityBoppity, CaptHolt, cyan10101, DeusVult Joker, Ephenesien, fabula_rasa, felix_0911, Hayden, HELLFIRE, June Fox, Kuronan32, LArc7thHeaven, Lokiel, Morrinn, Mortismal Gaming, Naaza, nameless, negative, Queegon, Reiskorn, Risen_Grayswandir, robert.roding, Schadenfreudian Slip, Shinzou, SnapSlav, and Uncle Fester. I"m sure this is just a drop in the bucket and some of those people contributed more than others but all of it was appreciated. Some other contributions came from various websites, some of them anonymously, so I couldn"t credit everyone unfortunately.
FeatureThe entire Wasteland 3 experience in one colossal collection. In addition to the award-winning tactical RPG Wasteland 3, the Colorado Collection includes both The Battle of Steeltown and Cult of the Holy Detonation expansions, as well as the Colorado Survival Gear bonus items.
The award-winning sequel in the Wasteland franchise brings the Desert Rangers to the frozen wastes of Colorado to deal with gangs, cults, and psychopathic clowns in an effort to bring stability to one more frontier of the wastes.

Adding a player vehicle, environmental dangers, and a revamped, more fluid action system, we are evolving on Wasteland 2"s tactical turn-based combat and unique encounter design.

The Polluted Wasteland, often found in more realistic, dystopian or Sci-Fi settings, is an Aesop against abusing resources. Its inhabitants stripped the land of everything good, and polluted the air. This may justify the activities of Planet Looters who raid other worlds for the resources that they"ve squandered on their own.
A Polluted Wasteland will often stand in contrast to a pristine natural setting, such as the Ghibli Hills or an Enchanted Forest, which may exist as a separate area or be what the Wasteland used to be — or what it may become once again.
See Mordor for the Polluted Wasteland"s more traditionally fantasy counterpart, although it should be noted that the Polluted Wasteland can be caused by magic in fantasy settings too. For more information see Clarke"s Third Law.
Chester"s Mill briefly becomes this in the last few chapters, when Big Jim Rennie sends members of his new police force to the radio station to collect some of the propane he has been stealing from the town to run his meth lab. Chef panics and blows up the meth lab, releasing a wave of fire that sweeps down from the old radio station and torches half the town, obscuring the surface of the dome and turning the town into a darkened wasteland with a toxic atmosphere.
Mordor and a Polluted Wasteland at once. It started as a dark volcanic wasteland... and then the Chaos Dwarfs brought in thousands of slaves to start strip mining and heavy industry. It"s a wonder how they manage to feed their single giant city in such conditions.
Mordor and a Polluted Wasteland. It has Gangplank Galleon, an Amusement Park of Doom called Krazy Kremland, a forboding Evil Tower of Ominousness, is filled with dead trees, Zingers (wasps), Brambles and danger, and the whole place and ocean around it is dark murky green. It actually sinks into the ocean after the final boss is defeated.
Advance Wars: Dual Strike gives us what happens when a Black Crystal is allowed to run. First the land is turned into a desert. Let it keep running, and it transforms the entire landscape around it into a burned-out, blackened wasteland - the waters even turn blood red. Best part: the ending leaves it ambiguous as to whether or not breaking the things will turn everything back.
Reconstruction (literally) of this trope, the entire goal of the game is to depollute one of the bleakest wastelands ever seen into a beautiful healthy landscape.
Pick a hydraulic fracturingnotecommonly referred to as fracking site. Any hydraulic fracturing site. In case the chemicals in the sludge aren"t bad enough, the ones in Pennsylvania are radioactive.
The Ruhr Valley in Germany, throughout the late-19th and 20th centuries. The River Rhine was said to be polluted enough to be able to develop photographs in it. Add in the coal-mining, steel industry and chemical industry and the result was a Polluted Wasteland. The GDR had a few such places as well, and tales of former Soviet-personnel-occupied areas (specifically industrial and military) brimming with pollution, loaded with deadly chemicals in the soil and generally being almost impossible to enter are fairly widespread, since the Soviets didn"t bother to clean up anything when they left. After the reunion, one of the bigger issues was getting rid of all the pollution and making those places inhabitable again. Overall, it generally worked.
Petsamo qualifies as well. Like Norilsk, Petsamo has been centered around nickel production. The Petsamo ore deposit was discovered in the 1920s, when Petsamo belonged to Finland. Mining was begun in 1933, and continued there until 1944. After the WWII, USSR annexed Petsamo from Finland, and continued the mining and roasting operations. The process, plant and equipment were never renewed or developed, and USSR operated with the original Finnish 1930s" technology until 1991. After the collapse of the USSR, the mine was acquired by oligarchs, who saw no interest on investing on it any more, but who instead extracted everything what extractable was, with the 1930s technology and gross neglect on environmental protection. The nickel production ended in early 2021, leaving behind a polluted wasteland. To make things worse, Petsamo is located beyond the Arctic Circle, making the nature extremely vulnerable.

According to United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), over 250 million people are directly affected by land degradation. In addition, some one billion people in over one hundred countries are at risk. These people include many of the world’s poorest, the most marginalized, and politically weak citizens.As per United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD, 2019) report most of the poor live-in areas where the land has degraded. It has also been reported that 31 per cent of the Asian population that live on degraded land resides in rural areas
Among the major resources available in India, the most important is land comprising soil, water, associated flora and fauna involving the total eco-system (Suraj Bhan,2013).In the last few decades, there has been constant pressure on land because of increasing human population, diversion of land in fragile ecosystems, infrastructure development, indiscriminate felling of trees, expansion of irrigation without adequate concern have caused the serious level of degradation. Land degradation in India is steadily increasing due to the growing pressure on land and unsustainable land use (Venkateswarlu and Prasad, 2011). In Indialand degradation mapping has been carried out by the NRSC/ISRO using Indian Remote Sensing Satellite data and prepared a wasteland Atlas.
According to wasteland atlas 2019 the total wasteland in India was observed to be 5,57,665.51 sq. km. in 2015-16, while it was 5,66,070.36 sq. km. in 2008-09. This indicates a conversion of 8,404.86 sq. km. of different wastelands categories in the country to non-wastelands during 2008-09 to 2015-16. After the comparison of aforementioned period decrease in wastelands in 18 states and an increase in wastelands in 11 states of the country were reported (wasteland Atlas,2019). A major positive change is observed in the state of Rajasthan with a conversion of 4,803.56 sq. km. of sandy wastelands area to non-wastelands. This was followed by Uttar Pradesh and Bihar states where a respective change of 1,082.29sq. km. and 1,130.07 sq. km. wastelands area have been brought underutilization. However, increase in wastelands was observed in the states of Odisha (465.82sq. km.) followed by Assam (406.69sq. km.), Telangana (377.79 sq. km.) and Chhattisgarh states (373.54 sq. km.).
The eighteen states of India have been reported decrease in the wastelands area whereas, eleven states have been reported increase in the wastelands area. However, increasing population and mismanagement of land causes declined per capita of available land from 0. 89 ha in 1951 to 0. 37 ha in the mid-1990s and is estimated to reduce further to 0. 19 ha by 2035(Bhan,2013).
Land degradation can exacerbate climate change and threaten agricultural productivity, water quality, biodiversity, sustainable development, and the living conditions of humans and wildlife. Globally, one third of our land is degraded, affecting 3 billion people, and it is expected to worsen with rising demand for food. Therefore, it is need of the hour to focus on Land degradation issues which ultimately can help eradicate poverty and reduce inequality. Reclaiming also helps to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The status of land use land cover of Uttar Pradesh 2015-16 shows total seven types of Land Category and twenty-four types of Land classes have been identified (Table 1). The agriculture is the dominant class in which crop land is 182306.22 Sq. Km followed by fallow land which is 7285.57Sq. Km. The wasteland area is also the dominant class where scrub land, salt affected area and Gully/Ravinous land is the most dominant class coving the area of 3364.19Sq. Km, 2573.72Sq. Km and 1278.4Sq. Km respectively.
Types of degraded land in the year 2008-09 and 2015-16 and changes has been shown in Table 2. In Uttar Pradesh, degraded land has been decreased to 1082.29 Sq Km from year 2008-09 to 2015-16. The major change in different type of land degradation is Land affected by salinity/alkalinity (Medium), Land with Dense Scrub, Waterlogged and Marshy land (Seasonal), Land with Open Scrub and Land affected by salinity/alkalinity (Strong).The total decrease in land degradation categories is 328.78Sq Km, 190.19 Sq Km, 179.54 Sq Km, 161.01 Sq Km and 62.28 Sq Km respectively. However, Mining and Industrial wastelands have increased considerably. As per report of NRSC Atlas 2019 out of 1082.29SqKm of degraded area, 988.36 Sq Km is converted into cropland, contributed by land affected by salinity/alkalinity and land with open scrub whereas an area of 89.09SqKm is converted to water body.
As per the NRSC Atlas 2019, out of 23 wasteland classes 16 classes are present in the Uttar Pradesh state. The total 8537.06 SqKm of geographical area of the state comes under wasteland which is about 3.54 percentage of total geographical area of the state. The percentage of five major categories are 33.74%, 25.55%, 24.54% 12.48%and 2.5% respectively (Table 3).
Medium Saline/Alkali land: These are the areas located in the fluvial plains with the degree of salinity (ECe) ranging from 8 to 30 (dS/m), pH between 9.0 – 9.8, and the Exchangeable Sodium Percentage (ESP) values ranging between 15 – 40.
Degraded forest considered as one of the factors of land degradation. Forest of any area may degrade because of anthropogenic activities and climatic influences. As population size increases, the need for food also becomes high. India, where the population is mostly depended on agricultural activity, forced to cut the forest for cultivation that becomes the problem of land degradation. Deforestation occurred mostly due to increment in agricultural land in purpose of boosting agricultural productivity. At present, there are about 130 million ha of degraded land in India. In which approximately, 28% of belongs to the category of forest-degraded area.
Waterlogging and salinity is very serious problem of the Uttar Pradesh state. As per waste land Atlas of India 2019, the total water-logged area of the state is 750.86 Sq Km which is 8.8% of total wasteland of the state. Whereas the salinity of the area is about 2129.58 Sq Km which is 24.9 % of total wasteland. Both together consist of 33.7% of total wasteland area
Uttar Pradesh consists of gullied and/ or Ravinous land (Medium) and Gullied and/ or Ravinous land (Deep). Total area of Gullied and/ or Ravinous land of the state is 1065.48 sq.km which consist of 12.48% of total degraded land. In year 2008-09 Gullied and/ or Ravinous land (Medium) was found to be 843.60 Sq Km which became 804.51 in year 2015-2016. However, Gullied and/ or Ravinous land (Deep) became 260.90 Sq Km to 260.99 in period of 2008-09 to 2015-2016.
District Kanpur Dehat consist of maximum area of wasteland i. e 201.74 SqKm (18.9%) followed by Jalaun, Fatehpur, Banda, Agra, Jhansi, Hamirpur, Firozabad, Etawah, Auraiya, Mahoba and Prayagraj
Uttar Pradesh is facing problem of having underutilized/ Degraded Forest which cover around 2118.39 Sq Km. The percentage of underutilized/ Degraded Forest wasteland categories is found to be 25.55%. Under-utilized/degraded forest (Scrub dominated) and Under-utilized/degraded forest (Agriculture) are found to be 1993.06SqKm and 219.53SqKm in 2008-09 which became 1958.46SqKm and 222.90SqKm in year 2015-16. The decrease of Under-utilized/degraded forest (Scrub dominant) of the state during aforementioned year is 34.60SqKm whereas increase in Under-utilized/degraded forest (Agriculture) was found to be 3.37 Sq Km which is of serious concern (Table 2).
In wasteland categories, scrub land consists of 2095.31 sq. km of total degraded land. The percentage of this land category is about 24.5% of total degraded land of the state. The total land with dense scrub and land with open scrub of Uttar Pradesh state for the year 2008-09 were found to be 660.32SqKm and 470.12SqKm respectively. However, it became 1786.23SqKm and 1625.22SqKm in year 2015-16 (Table 2).
This wasteland category is a natural phenomenon, and can be defined as rock exposures of hillock, mountain slopes and plateau area, the class is devoid of vegetation and soils. The barren Rocky land cannot be brought under cultivation except at an exorbitant cost, and classified as unculturable, such land is in isolated blocks or may within cultivated holdings. The percentage of this land category is about 2.5% of total degraded land of the state. The 12 districts which cover the area of Barren/Rocky land are Agra, Lalitpur, Sonbhadra, Jhansi, Mirzapur, Mahobaand Chitrakoot which occupied 67.73Sq km, 41.33Sq km,32.46Sq km,18.9Sq km,13.28Sq km and 4.69Sq km respectively.
8,53,706 hectares area of the state comes under wasteland. The Uttar Pradesh wasteland categories majorly in four types i.e., Salinity & Waterlogged (33.74%), Degraded Forest (25.55%), Land with Scrub (24.54%), Gullied & Ravinous (12.48%). Wasteland of all districts of Uttar Pradesh is categorized into three groups based on percentage of land degraded. These categories are:
The status of wasteland of various districts of Uttar Pradesh is more than 5% is shown in the Table 9. Fourteen districts of the state have identified more than 5% area under wasteland. It has also been observed that district Etawah has maximum area of wasteland followed by Agra, Auraiya and Jhansi which consists of 13.0 %, 10.6%, 9.4% and 8.9% of total geographical area of the district. The District Etawah and Agra have more than 10% of area under wasteland.
14 districts having 48% Wastelands of the state. Geographically, these districts are distributed in southern part of the state along Madhya and Rajasthan border (as depicted in map). These 14 districts have category wise percentage of the state total wastelands:
829.38847.629241313.29159.174102.8555548Table 9: District having different categories of wasteland more than 5% Districts Having Wastelands > 5% of TGA (Area in SqKm)
Table 10 shows wasteland of various districts of Uttar Pradesh lies between 2-5% of total geographical area. Total 31 districts of the state come under this category. These 31 districts having 42% Wastelands of the state. The District Hamirpur, Kannauj, Sultanpur + Amethi and Jaunpur having wasteland 5%, 4.9%, 4.9 % and 4.8% respectively which is close to 5%.
30 districts having 10% Wastelands of the state. These 30 districts have category wise percentage of the state total wastelands: 15.4 % of Land with Scrub13.6 % of Salinity & Waterlogged 5.1 % of Degraded Forest0.6 % of Gullied & Ravinous 0.6 % of Barren Rocky/Stony waste
Table 11 shows wasteland of various districts of Uttar Pradesh which is less than 2% of total geographical area. Total 30 district of the state come under this category. These 31 districts having 10% Wastelands of the state.
97 % (1,03,685 Ha) Gullied & Ravinous land are available in 12 districts. Geographically these 12 districts are distributed in western part of the state along Madhya and Rajasthan border
82.3% (1,72,049 Ha) Land with Scrub Areas are available in 29 districts. Geographically these 29 districts are distributed in most part of the state, but eastern part has less numbers
90 % (2,59,290 Ha) of Salinity and Waterlogged Areas are available in 32 districts. Geographically these 32 districts are distributed in central part of the state east to west.
97 % (1,03,685 Ha) areas are available in only 12 districts, those have above 1% affected areas of the state. Geographically, these 12 districts are distributed in western part of the state along Madhya and Rajasthan border (as depicted in map 9).
The area covered by Land with Scrub is about 2,18,139 hectares areas in the state. 82.3 % (172049) areas are available in only 29 districts, those has above 1% affected areas of the state Geographically, these districts are distributed in most part of the state, but eastern part has less numbers (as depicted in map 10)
Salinity & Waterlogged areas both together consist of 2,88,044 Ha (33.7%) of total wasteland area. 90 % (2,59,290 Ha) areas are available in only 32 districts (above 1% affected areas) of the state. Geographically these districts are distributed in central part of the state east to west (as depicted in map)
The status of Under-utilised/degraded forest of various districts of Uttar Pradesh as represented. 2,18,139 (25.55%) hectares areas are degraded forest areas in the state. 94.4 % (2,05,588 Ha) areas are available in only 20 districts (above 1% affected areas) of the state. Geographically these 20 districts are distributed in north part of the state along Nepal border and southern part along MP border (as depicted in map 12)
India is the second largest populated country in the world showing rapid industrial developments, less-planed infrastructural development and continuous population growth have played a major role in promoting landscape fragmentation for last forty years. The overall population growth rate of India is as follows: 24.80%, 24.66%, 23.86%, 21.54% and 17.69 in the period of 1961–1971, 1971–1981, 1981–1991, 1991–2001 and 2001–2011, respectively (censusindia.gov.in). India is agriculture-based country where 70% population are based on agriculture activities. Continuous increase in population puts pressure on fixed available resources for instance decline in per capita soil and water resources, conversion of cropland into non-farm use, deforestation which promote land degradation.
As per planning commission report majority of population of Uttar Pradesh state relies on agriculture for livelihood. However, speed of agriculture growth of the state is slow. Fertiliser used in Uttar Pradesh is about 19% of country’s total fertilizer consumption. Average fertilizer consumption in the state is about 127kg/ha in 1997/98 which was about 30% more than the national average. The consumption of fertilizer in Western and Eastern regions of Uttar Pradesh is higher than the central and Bundelkhand regions. Waterlogging in canal irrigated area is a very serious threat to agriculture production in the state. Around one fourth waterlogged area of the country is confined in Uttar Pradesh. Most of the canal command area in the Eastern region are seriously affected. Use of excessive fertilizer and overirrigation in the area promote land degradation of the state.
Rainfall is the most important climatic factor in determining areas at risk of land degradation and potential desertification. Rainfall plays a key role in the development and distribution of plant life, as water is one of the primary inputs to photosynthesis. However, variability and extremes of rainfall can lead to soil erosion and land degradation. soil scientists consider rainfall the most important erosion factor among the many factors that cause soil erosion. Rainfall can erode soil by the force of raindrops, surface and subsurface runoff, and river flooding. The velocity of rain hitting the soil surface produces a large amount of kinetic energy, which can dislodge soil particles. Intensity and timing of rainfall play a crucial role in soil erosion leading to land degradation. As per report of IMD Pune Rainfall trend in last 30 years
There is overwhelming evidence which points the consequences of climate change in land degradation. There is a strong correlation between rainfall and biomass since water is one of primary inputs to photosynthesis. Rainfall plays a vital role in the development and distribution of plant life, but the variability and extremes of rainfall can lead to soil erosion and land degradation. If unchecked for longer period, this land degradation can lead to desertification. These vulnerabilities become more acute when the prospect of climate change is introduced. The districts with heavy precipitation can lead to excessive land degradation. The already heavy degraded districts like Chitrakoot, Praygraj, Raibareilly, Fatehpur, Mirzapur, Kanpur dehat and Pratapgarh will be most likely to face heavy land degradation due to heavy predicted precipitation during 2020-2100 (Map 13). Districts, like Jalaun, Kanpur Dehat, Fatehpur, banda, Agra and Jhansi, which covered a large gullied/ ravinous wastelands would likely to face heavy consequences in future.
Amongst natural disasters flood is one such calamity that is highly recurring event in the entire India especially in the state of Uttar Pradesh. The area of the state is 240.93 lac hectares land out of which 73.14 lac hectares is flood prone area. The estimated annual loss due to flood is about 432 crore rupees. Apart from these, loss of human life also occurs. The cause of flood and affected districts is shown in Table 17 and Table 18.
The 1987 and 2002 drought were by far the worst drought hi ts in the country with more than 50% reduction in crop area and nearly 30,000 crores of rupees in agricultural losses
The drought-prone areas of the country are confined to arid, semiarid and sub-humid parts of peninsular and western India. In last decade, the Bundelkhand region in central India have subjected to drought proneness with recurrent drought episodes. Frequency of drought in this region increased from one to three in last 16 years during 1968-1992 (Singh et al. 2003).
In last 25 years, 3 states/UTs have experienced more than 20 cold waves. Cold waves were reported more than 10 times in seven states. Highest number of cold-wave events was recorded in Uttar Pradesh (25), followed by Rajasthan and Bihar.
A survey of the effect of the cold wave on Rabi crops showed that the economic losses amounted to 6,230 million Indian rupees in the state of Rajasthan during the 2005–2006 Rabi season alone
About 8537.06 Sq Km area (853706ha) of land in Uttar Pradesh come under degraded land. Degraded land affected a significant portion of the arable lands, decreasing the wealth and economic of the state. The degraded land of Uttar Pradesh has been categorised in four classes 1. waterlogged/saline/alkaline land, 2. Gullied and /or ravenous land, 3. Scrub Land, 4. Under-utilized/ degraded forest which have different implications.
1,06,548 hectares area of the state are affected by Gullied and/ or Ravinous land. Gullies and ravine formation significantly increase soil loss from agricultural lands and severely impacts agricultural productivity. Although ravines and gullies occur all over India, the largest incidence is found in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan. Ravines are spread over an estimated area of 3.67 million hectares along the rivers and their tributaries. Gully erosion was reported to have a great impact on the faster depletion of soil moisture and ground water in arid and semiarid regions
2,09,531 hectares area come under scrub land in the state. Degradation of these land having severe impact on green cover and livelihood activities mainly livestock based. The scrublands are developed in areas where the scanty of rainfall experienced during monsoon season about less than 70 cm. To meat out the demand of development activities the deforestation is a major cause for increasing scrubland development. Lack of proper land use planning after deforestation remain the land exposed for withering by natural as well as anthropogenic processes. Unfortunately, after75 years of independency India still dependent on monsoon for our 60% agricultural land, due to inadequate facilities of irrigation and high cost of farming most of the marginal farmers remain farming land prone to develop scrublands. Rapid growth of development activities by human is the major cause to turn other landcover in to scrubland, after development process due to lack of proper management the remaining areas are turned into scrub lands is highly exposed to erosion, due to inadequate vegetation growth on topographically higher regions excluding hilly/mountainous terrain
2,18,139 hectares area are degraded forest areas in the state. Dense forest converted into degraded forest because of anthropogenic as well as natural activities. There are a few main drivers of forest degradation. higher temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns increase the risk and severity of forest fires, pest infestation, and disease. But the main cause of forest degradation is unsustainable and illegal logging.
Planning for land conservation should be prioritized based on the severity of the degradational problems arising owing to water and wind erosions and anthropogenic activities. Afforestation activities like agroforestry, silviculture and social forestry should be adopted to protect agricultural lands from further deterioration arising out of degradational processes. Afforestation of degraded and wastelands should be given priority.
Uttar Pradesh consists of four major types of wastelands which need to be mitigate and corrective actions for sustainable use of land. All the four land degradation categories can be mitigated through different approach. The planners, resource managers and developmental agencies in participation with stakeholders need to take some corrective actions to treat degraded land. The mitigative and corrective measures for the four major types of wastelands are discussed below:
Vegetation provides soil cover and protect the gully against scouring. It also reduces the flow velocity by increasing the hydraulic resistance of the channel section, thereby the scouring and ability of runoff is reduced to a great extent.
Scrub Land of the district is 2095.31Sq Km. The mitigative and corrective measure aims at improving the soil productivity and restoring fragile eco-system which is essentially the interplay between soil conservation and degradation processes of scrub lands. Vegetative cover improvements and grass lands creations help to improve soil moisture conditions in an area and thus maintain the ecosystem of scrub lands. Consistent initiates for land development, soil conservation measures and plantation, water conservation & harvesting and renovation of traditional water bodies. Some of the important activities can be
Underutilized/ degraded forest present in the districts is 2181.39 Sq. Km. At a local level, sustainable development requires effective natural resource management; the restoration of degraded and secondary forests is an integral part of this. If perceived in such a holistic manner, forest restoration and rehabilitation are likely to be effective and to lead to sustainable outcomes. The development and selection of site-specific integrative ecosystem designs is the most crucial stage in developing a suitable management approach.
Contribution to the five years plan of Ministry of Rural Development, GoI for the treatment of wastelands converging with Mahatma Gandhi NREGA. 93 million hectares wastelands are reported countrywide and 8.6 lakhs hectares in the state of Uttar Pradesh by Wastelands Atlas of NRSC.
Contribution for achieving the land degradation neutrality targets: Wasteland treatment will also directly contribute for Honorable Prime Minister of India announced target for restoring 26-million-hectare degraded land by 2030 at the 14th session of the Conference of Parties (COP) to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) on 2-13 September 2019 at New Delhi
Using Geo-informatic and Digital Tools for treatment of wastelands scientifically GIS based plans have been prepared for all 59156-gram panchayats of the state of Uttar Pradesh with technical support under Indo-German bilateral project ‘Water Security and Climate Adaptation in Rural Areas (WASCA)”. GIS based planning helps treatment of wastelands scientifically i.e.,
Department of Rural Development has directed mandatorily to include 9 Lakh Hectares of wastelands mapped under GIS enabled planning for Labour Budget 2022-23 under Mahatma Gandhi NREGS.
A typical exercise to identify all the works/ activities to be covered under Mahatma Gandhi NREGA and under watershed development programme / other similar programme (Available as annexure ‘Brief Description of Wasteland Category-wise works’).
Mahatma Gandhi NREGA has diverse nature of works and ample scope provided for reclamation of wastelands/degraded areas in the programme in convergence with number of Government schemes with the common objective of welfare of poor people in rural areas.
Bio-drainage is an agronomic solution providing natural means of drainage of excess water of the area through trees and plants, capable of transpiring more water like water pumps. In this the plants like eucalyptus, poplar etc having capability of withdrawing a large amount of water and salt serve to control water logging and salinity both. There are many plants like deodar cedar, merican cypress, silver oak, giant bamboo, oregon maple, birch, balsam poplar, black acacia, silverberry etc that can be planted suitable to terrain and agro-climatic zones.
Storm water drains is designed to drain excess rain in areas, which experience heavy rainfall, flooding and coastal area, which experience regular storms. Such works include storm water pipeline, box culverts, nullahs, river training works, polders and flood water pumping facilities.
The watercourse improvement / renovation consists of demolishing of community channel and its rebuilding/re-aligning according to the engineering design to increase conveyance and efficiency by reducing seepage, evaporation, and operational losses. Parts of channel are lined and necessary water control structures are installed to improve conveyance of the water course and canal. The standard “Pucca” lining carried out may be rectangular shaped channel using brick masonry walls (23 cm) and a brick masonry bed (7 cm) plastered inside and on top of the walls. Other types of lining e.g. cement concrete lining, pre-fabricated concrete (pre-cast parabolic lining), pipe, plastic etc. can also been considered keeping in view the farmers’ choice, field conditions, and cost effectiveness.
The process involves storing runoff rain water, filtering and injecting into suitable shallow sub aquifers and pumping out for critical irrigation in arid and semi-arid areas.
Approximately 120 m length of contour or field bunds per ha are required to be constructed. The cost will depend on local schedule of rates for earthwork. Total earth work will be 97.2 m3. In addition cost of outlets will be added to
m3. In addition cost of outlets will be added to Contour bunds effectively reduce runoff and soil loss and can potentially improve crop yields by about15-20%in addition to other ecological and environmental benefits.
Peripheral bund are constructed to protect agricultural land from ingress of ravine land, so as to prevent free fall of water in the fragile deep gullies that causes extension of ravines further into table land. Peripheral bunds are generally constructed at a distance of 2-3 times the vertical fall upstream from the edge of gully head to avoid over fall. Water is conveyed safely to a site, usually main gully section, which is well protected by energy dissipating structures. The recommended design specifications are given below:
These bunds are constructed in agricultural land at a distance about three time of the depth of ravine at gully head and accordingly marking has to be done on the field.Peripheral bund should have uniform grade level toward outlet for safe disposal of water from agricultural land in to ravine.Decide the location of the outlet at major drainage channel discharging into ravine to safely dispose runoff in ravines. A chute spillway may be the ideal outlet structure for disposal of runoff from table land to ravine beds. However, a masonry box inlet with pipe (PVC pipes of about 30 cm diameter) outlet and suitable apron in the bed portion is suggested for ease of construction. The outlets are to be located at major drainage channels; however, one outlet for 200 m length of peripheral bund is suggested for estimating the costs.
The size and number of trenches are worked out on the basis of the rainfall proposed to be retained in the trenches. Generally runoff generated by one day maximum rainfall of 2 year return period may be stored in trenches. Expected runoff in Mahi, Chambal and Yamuna ravine areas is about 50 mm from a 2 year return period rainfall. For one hectare area total volume of runoff will be 500 m3. To store this volume 1000 trenches of 2 m length, 0.5 m width and 0.5 m depth are to be made. Depending upon slope this number of trenches may be adjusted by spacing them at regular interval.
For successful field execution of the technology, contour lines are marked on the ravine slopes at the designed interval. The laborers are given 3 wooden sticks having dimensions of length, width and depth of trenches to be made. For staggered trenches lengths are marked on contour lines. Starting from lowest line trenches are made to the size of sticks given. The adjacent upper line trenches are then made by staggering.
Gully plugs can be defined as small earthen embankments constructed across the gullies to reduce the runoff velocity and stabilize the gullies (size and type of gully, catchment, runoff volume etc.). The size of the gully plug depends on width, length and bed slope of the gully, anticipated runoff and proposed plantations in the gully. The height of the gully plug is usually kept as 1 to 1.5 m, top width m for small and medium gullies, side slopes 1:1 (cross sections 1.5 and 3 m2), and length of the gully plug is kept as equal to the channel width. The spacing depends upon the gradient of the channel bed. Usually for 3% slope, at every 30 m distance a gully plug can be constructed. For uniform distribution of soil moisture to the plantations, minimum spacing and minimum height can be maintained.
Pipe outlets shall be made for higher flow rates where natural outlets cannot withstand the flow. In upstream a box inlet should be made. 30 cm diameter PVC pipe may be used to convey the runoff to downstream into a stilling basin.
The cost of this technology is Rs. 35,000/ha. Realized benefits are stabilization of gully beds and banks, deposition of sediments and nutrients and water storage thereby, enhancing soil moisture and plant growth and ground water recharge. It reduces the runoff and soil loss by 80 per cent.
Earthen check dams (ECDs) should be constructed at the upper reach of the 1st and 2nd order of streams in the continuous gully system of the ravine to retain runoffs and silt. The water retained behind the ECDs helps in artificial groundwater recharging and improving the groundwater level. It reduces slope length and slope gradient by deposition of silt which helps in stabilization of stream and stream bank protection. The maximum height for earthen CDs is 3 meters which limit the use of earthen check dams. The vegetative, loose boulder or masonry surplus weirs should be provided at one end of the earthen dam for safe disposal of excess runoff due the unexpected heavy rain storm. A trench filled with cohesive materials such as clay may be constructed to avoid the mining below the foundation. Earthen CDs can be adopted in shallow and medium gullies of the Chambal in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, Yamuna ravine system in Agra and Mahi ravines of Gujarat. The low earthen check dams are more desirable than high ones especially in upper reach of Yamuna and Mahi ravine system as the low dams silt up, gully bottom can be converted in agriculture and horticulture plantation.
The gully heads of the Chambal, Yamuna and Mahi River can be stabilized by the masonry spillways. This may be a straight drop, chute or drop inlet spillway depending upon the depth of the gully. Drop spillway can be used where drop is not more than 3 m and watershed area is relatively small. In case of high head of 3 to 6 m, chute spillway may be used for large drainage area. Drop inlet spillway is used for smaller watershed where some water storage is needed behind the structure and fall relatively less than 3 m. These structures should be built only after careful engineering studies.
Straight drop masonry spillway is the weir structure provided at the gully head for safe disposal of excess surface runoff from land above gully head to the gully bed. In straight drop spillway, water flow passes through weir, drops over the apron or stilling basin and then passes into downstream gully channel. These are constructed with concrete, stone or brick masonry. The straight drop masonry spillway is useful to the control of the gully head not higher than 3 m. The length and depth of weir is computed for incoming discharge and drop (height) of the spillway. Masonry straight drop spillways can be constructed at the gully head of gully systems in shallow, medium and deep ravines of the Chambal in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, Yamuna ravine system in Agra and Mahi ravines of Gujarat.
The masonry straight drop spillways are adapted to control the gully head not higher than 3 m. The low straight drop is also advisable for small gully head cuts (1.0-2.0 m). The gully where spillways are to be constructed should be demarcated by careful field survey by measuring the width and fall of the gully. Stability of gully head banks should be studied carefully for proper anchoring of the head wall extensions into banks. The spillway site should be surveyed for its watershed area including soil type, slope and land use and marked on the map on scale of 1:10,000 or 1:50, 000. The designed peak discharge should be estimated using rational formulae.
The masonry spillways should be designed as per engineering design. Table 3.3 can be used as guide for a given peak flow. Once the drop is fixed the table will give depth of weir and length of weir for a given peak flow. However, each structure has to be designed using software to get the best design with minimum cost.
The gully where spillways are to be constructed should be demarcated by careful field survey by measuring the width and fall of the gully. Stability of gully head banks should be studied carefully for proper anchoring of the head wall extensions into banks. The proposed spillway side should be surveyed or measured on topo sheet on scale of 1:10,000 maps or 1:50,000. The designed peak discharge should be estimated using the rational formulae. The masonry chute spillways should be designed as per engineering design. The cost of masonry chute spillway ranges from Rs 35, 000 to 50,000 depending upon the size of the chute spillways. The benefits of chute spillway are as in case of straight drop spillways.
The check dam should be located on a reasonable straight reach on gully with no curve at up or down stream within at least 30 m of the check dam. If needed, it shall be desirable to straighten the channel alignment up and down stream of the check dam. Poor alignment may result in excessive scoring of embankment and gully. The site selected should provide an adequate foundation for check dam. It should be constructed at least 10-20 m meter below the confluence points of the gullies to get more benefit in term of runoff storage and silt retention by a single CCD. If the gully crosses a farm/village road, masonry check dams may be built above the road at the junction points. The foundation material must have the required supporting strength, resistance to sliding and piping and should be reasonable homogenous to prevent uneven settlement of check dams. The loose bank sides must be avoided to prevent the side cutting in the check dams.
The spacing of check dam depends on the gradient of the gully and height of the proposed CDs. In medium gullies with no runoff from top and 1.2 m height masonry straight drop spillway the composite check dams constructed at 100 m interval at CSWCRTI, Research Centre Vasad are functioning very well. The one percent grade of the existing gully has reduced to less than 0.5 percent. Similarly in medium and deep ravines with runoff from upper catchments CCDs with about 1.5- 2.0 m height were spaced at about 200-300 m in gullies with 1% grade. These structures have reduced the grade to less than 0.5% and entrapped most of the silt behind them. The stored runoff water is recharged to ground water within 3-5 days as ravine bed soils are quite permeable. Similar spacing may be adopted for other areas.
The masonry spillways of composite check dams should be designed as per the engineering design. A 1.5 m deep foundation is generally sufficient. In general, a maximum of 2.0 m height may be kept. The earthen portion may be made with soil with 3:1 slope in upstream and 2:1 slope downstream. Top width may vary from 1 to 2 m depending upon height. The construction should be done in layers of 15 cm by compacting and watering. No trees should be allowed to grow on the earthen portion of CCD.
3.Marginal lands along ravinesLightSupplemental Irrigation availableAgri horticultureAmla, Guava, Lemon, Belpatra, Ber, Karonda, Lasoda, SharifaPits 1 x 1 x 1 m size
In medium rainfall areas with highly dissected topography, staggered contour trenches (SCT) are adopted. The staggered contour trenches are laid scattered with inter space between them. In staggered trenching, the trenches are located directly below one another in alternate rows and in a staggered fashion. Staggered trenches may be made to a length of 2-3 m and spacing between the rows may vary 3-5 m. The chances of breaches of SCT are less as compared to continuous contour trenches. The digging a trench on contour line and further work in similar fashion, then comes the next contour line. Begin digging in a stretch, which covers the gap left in the higher contour line. The gaps in this contour line should fall below the trenches in the higher contour line. in this way, we maximize the amount harvested runoff by the trenches. In other words, chains of staggered trenches should be made along successive contour lines so that water left by one line of trenches is captured by the immediately lower line.
Laying stone bunds in fields is a well-known technique to check runoff and to control erosion and is the most widely practiced technique by farmers. Contour stone bunds are built with quarry rock or stones along the natural contour of the land to a height of 20-30 cm from the ground and spaced 20 to 50 m apart depending on the inclination of the terrain. The stone bunds form a barrier that slows down water runoff, allowing rainwater to seep into the soil and spread more evenly over the land. This slowing down of water runoff helps with building-up a layer of fine soil and manure particles, rich in nutrients.
Bench terracing has been a widely-practiced measure to use the hill slopes for crop production on sustainable basis. It comprises, transforming original steep lands into a series of level or nearly level strips or steps across the slope supported by risers. It is and earthen embankment, constructed with an acceptable grade to an outlet or with a level channel and ridge. By adopting bench terracing, both degree and length of slope are reduced which help in soil moisture conservation for enhanced crop production. Bench terracing is recommended for slopes from 10 to 30%. They reduce runoff and soil losses, assist in reclaiming badly eroded gullied fields by intercepting runoff before it becomes concentrated and attains an eroding velocity. Terrace spacing is the vertical distance between two successive bench terraces, it is equal to the double the depth of cut, it depends on the soil depth and land slope. The width of terrace should be such that it enables convenient and economic agriculture operations.
Boulder checks or gully plugs are loos rock dams made on small drainage lines or seasonal streams which have a catchment area of less than 50 ha. The main aim of constructing loose boulders checks is to reduce the velocity of water flowing through a drainage line. By reducing the velocity of runoff helps in reducing soil erosion, trapping silt, creating hydraulic head locally to help infiltration of surface runoff and increasing the duration of low in the drainage line.
Afforestation and planation activities are relevant and important for reclamation of wastelands/degraded land and give several benefits by providing fruits, fodder, fuel wood, timber and enhance soil fertility by adding the bio mass to the fields. This strengthens agriculture, livestock systems, enhance green area, promote rural sustainable livelihoods, livestock support systems by p




 8613371530291
8613371530291